
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 939-955.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0441
邓淑芳1, 刘倩1, 刘玲1, 陈鸥1, 王文军1,2, 曾凯芳1,2, 邓丽莉1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-26
修回日期:2024-03-11
出版日期:2024-05-25
发布日期:2024-05-29
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:denglili_361@163.com)
基金资助:
DENG Shufang1, LIU Qian1, LIU Ling1, CHEN Ou1, WANG Wenjun1,2, ZENG Kaifang1,2, DENG Lili1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-01-26
Revised:2024-03-11
Published:2024-05-25
Online:2024-05-29
Contact:
*(E-mail:denglili_361@163.com)
摘要:
蜜橘果实在25 ℃贮藏可加速转色,而在32 ℃则抑制转色。以这两个温度下贮藏的蜜橘果皮为材料,挖掘到对叶绿素代谢具有显著影响的关键转录因子CcHY5。对CcHY5的结构特征进行了分析,并利用农杆菌EHA105介导的瞬时过表达体系,分别在烟草叶片和蜜橘果实上对该转录因子基因功能进行了深入研究。结果显示,CcHY5全长为507 bp,编码168个氨基酸,与拟南芥AtHY5同源性较高,其启动子区域具有光响应元件、脱落酸响应元件及生长素响应元件等各类响应元件,亚细胞定位于细胞核,具有转录激活活性。烟草叶片瞬时过表达CcHY5后出现了明显黄化现象,且在25 ℃下黄化速度较32 ℃更快。蜜橘果皮瞬时过表达CcHY5后在注射孔附近发生了明显转色,而阴性对照依然保持绿色,与阴性对照相比,不同温度下果皮中CcHY5均显著上调表达,但32 ℃下表达量较25 ℃显著降低。瞬时过表达后的烟草叶片和蜜橘果皮中叶绿素及其代谢产物(叶绿素a、叶绿素b、脱镁叶绿酸甲酯a、脱镁叶绿酸甲酯b及脱镁叶绿素a)含量显著降低,而蜜橘果皮中类胡萝卜素及其代谢产物含量与阴性对照无显著差异。瞬时过表达后的蜜橘果皮中叶绿素循环基因CcCHL1、CcCHL2和CcCHL3的表达受到不同程度抑制,叶绿素降解代谢基因CcNYC和CcRCCR的表达显著上调。综上,适宜温度(25 ℃)下CcHY5可能通过促进蜜橘果皮中叶绿素降解,加速其转色进程。
邓淑芳, 刘倩, 刘玲, 陈鸥, 王文军, 曾凯芳, 邓丽莉. 蜜橘CcHY5的克隆及其对果实转色功能的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 939-955.
DENG Shufang, LIU Qian, LIU Ling, CHEN Ou, WANG Wenjun, ZENG Kaifang, DENG Lili. Cloning of Mandarin Fruit CcHY5 and Its Function in Fruit Coloration[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 939-955.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | TGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTG | TGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTG |
| CcHY5 | AAGGCGTACTTGAATGAGTT | AGGTAACTTTCAACCAGCAA |
| CcNYC | GGCACGGTTTTCCTTTACAGATG | TGTTGTAGTTCTGACGCTTTCTG |
| CcRCCR | CAAACGTTGCAGGTCTTCGG | CAAACGTTGCAGGTCTTCGG |
| CcCHL1 | CCCGTCTCCGTTGAAGCTAA | GCAGTGCCGTGGAAAAACAA |
| CcCHL2 | CGTTCTCGCGCGGAAAATAA | TTTGGAGGAGGTGGTGAGGA |
| CcCHL3 | CCTTGTGCTCCGAAAGGAGT | CCTTGTGCTCCGAAAGGAGT |
表1 qRT-PCR中所用的引物序列
Table 1 Primers used in qRT-PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | TGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTG | TGGATTCTGGTGATGGTGTG |
| CcHY5 | AAGGCGTACTTGAATGAGTT | AGGTAACTTTCAACCAGCAA |
| CcNYC | GGCACGGTTTTCCTTTACAGATG | TGTTGTAGTTCTGACGCTTTCTG |
| CcRCCR | CAAACGTTGCAGGTCTTCGG | CAAACGTTGCAGGTCTTCGG |
| CcCHL1 | CCCGTCTCCGTTGAAGCTAA | GCAGTGCCGTGGAAAAACAA |
| CcCHL2 | CGTTCTCGCGCGGAAAATAA | TTTGGAGGAGGTGGTGAGGA |
| CcCHL3 | CCTTGTGCTCCGAAAGGAGT | CCTTGTGCTCCGAAAGGAGT |

图1 不同贮藏温度对蜜橘果皮CcHY5表达量的影响 A:RNA-seq数据中的FPKM值,不同小写字母表示差异显著,P < 0.05;B:RT-qPCR测定的表达量。 * α = 0.05,** α = 0.01。
Fig. 1 Effect of different storage temperatures on the expression of CcHY5 in mandarin fruit peel A:FPKM values from RNAseq data,different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level;B:Gene quantification by RT-qPCR. * α = 0.05,** α = 0.01.
| 顺式作用元件 cis-Element | 序列 Sequence | 预测功能 Predictive function | 数量 Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件 Response element for abscisic acid | 2 |
| CACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件 Response element for abscisic acid | 1 | |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 4 |
| G-box | CACGTG | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 2 |
| TACGTG | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 1 | |
| ACE | CTAACGTATT | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 1 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 分生组织表达元件 Expression element of meristem tissue | 2 |
| AuxRR-core | GGTCCAT | 生长素响应元件 Response element for auxin | 1 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 Response element for methyl jasmonate | 1 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 Response element for methyl jasmonate | 1 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导响应元件 Anaerobic induced response element | 3 |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | MYB结合位点 MYB binding site | 1 |
表2 CcHY5启动子区域顺式作用元件分析
Table 2 Analysis of cis-elements in CcHY5 promoter region
| 顺式作用元件 cis-Element | 序列 Sequence | 预测功能 Predictive function | 数量 Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABRE | ACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件 Response element for abscisic acid | 2 |
| CACGTG | 脱落酸响应元件 Response element for abscisic acid | 1 | |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 4 |
| G-box | CACGTG | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 2 |
| TACGTG | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 1 | |
| ACE | CTAACGTATT | 光响应元件 Response element for light | 1 |
| CAT-box | GCCACT | 分生组织表达元件 Expression element of meristem tissue | 2 |
| AuxRR-core | GGTCCAT | 生长素响应元件 Response element for auxin | 1 |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 Response element for methyl jasmonate | 1 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 Response element for methyl jasmonate | 1 |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导响应元件 Anaerobic induced response element | 3 |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | MYB结合位点 MYB binding site | 1 |

图5 CcHY5在酵母中的转录激活活性分析 将pGBKT7-CcHY5转化酵母细胞,以pGBKT7-53 + pGADT7-T为阳性对照、pGBKT7为阴性对照,在单缺(SD/-Trp)及三缺(SD/-Trp-His-Ade)培养基上培养,根据酵母生长状态及滴加X-α-Gal后变蓝色表示具转录激活活性。
Fig. 5 Analysis of transcriptional activation activity of CcHY5 in yeast The pGBKT7-CcHY5 transformed yeast cells were cultured in single-deficient and triple-deficient medium with pGBKT7-53 + pGADT7-T as positive control and pGBKT7 as negative control. And transcriptional activation activity was analyzed based on yeast growth status and color change with addition of X-α-Gal.
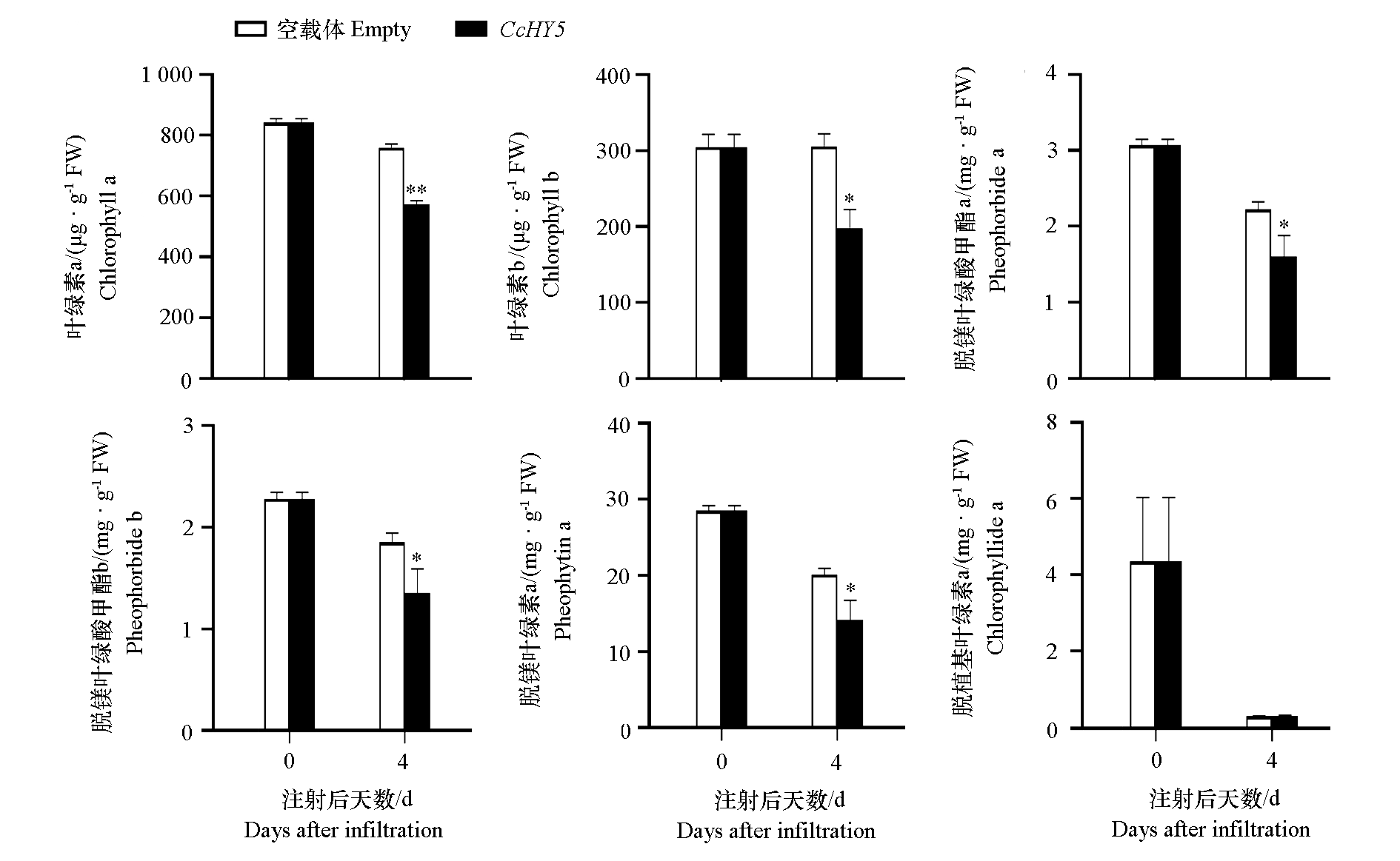
图7 烟草叶片CcHY5瞬时过表达后色素含量的变化(25 ℃)
Fig. 7 Changes in pigment content of tobacco leaves after transient overexpression of CcHY5(25 ℃) Student’s t-test,* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01.
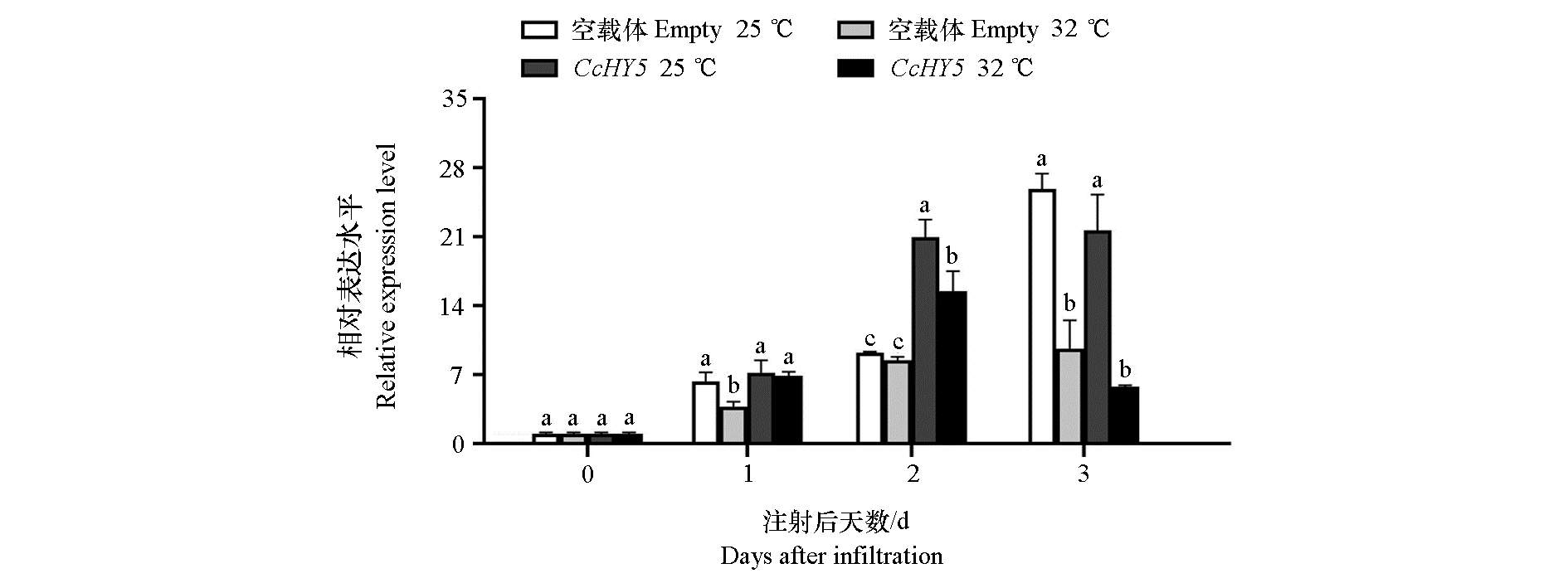
图8 不同贮藏温度对瞬时过表达后蜜橘果皮CcHY5表达量的影响 差异显著性分析采用Duncan’s检验,不同小写字母表示同一时间不同处理间差异显著,P < 0.05。
Fig. 8 Effect of different storage temperatures on the expression of CcHY5 in mandarin fruit peel after transient overexpression Significant difference analysis used Duncan’s test,different lowercase letters indicate significant difference between different treatments at the same time,P < 0.05.

图9 蜜橘果实CcHY5瞬时过表达后果皮外观及色差值的变化(25 ℃)
Fig. 9 Changes in appearance and color index of citrus peel after transient overexpression of CcHY5(25 ℃) Student’s t-test,* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01.
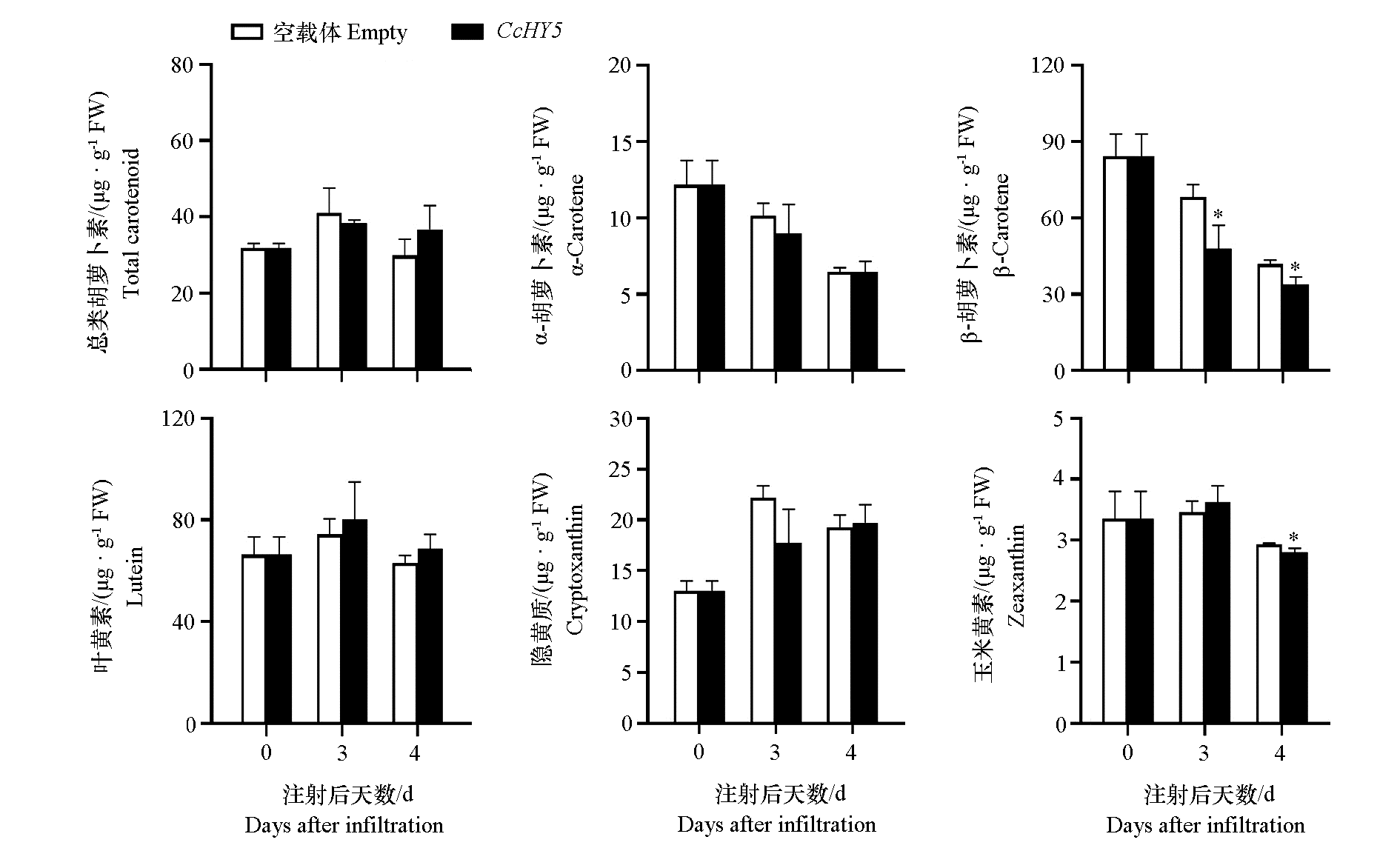
图10 瞬时过表达CcHY5蜜橘果实果皮类胡萝卜素及其代谢产物含量(25 ℃)
Fig. 10 Effects of transient overexpression of CcHY5 on the content of carotenoid and its metabolites in the peel of mandarin fruit(25 ℃) Student’s t-test,* α = 0.05.
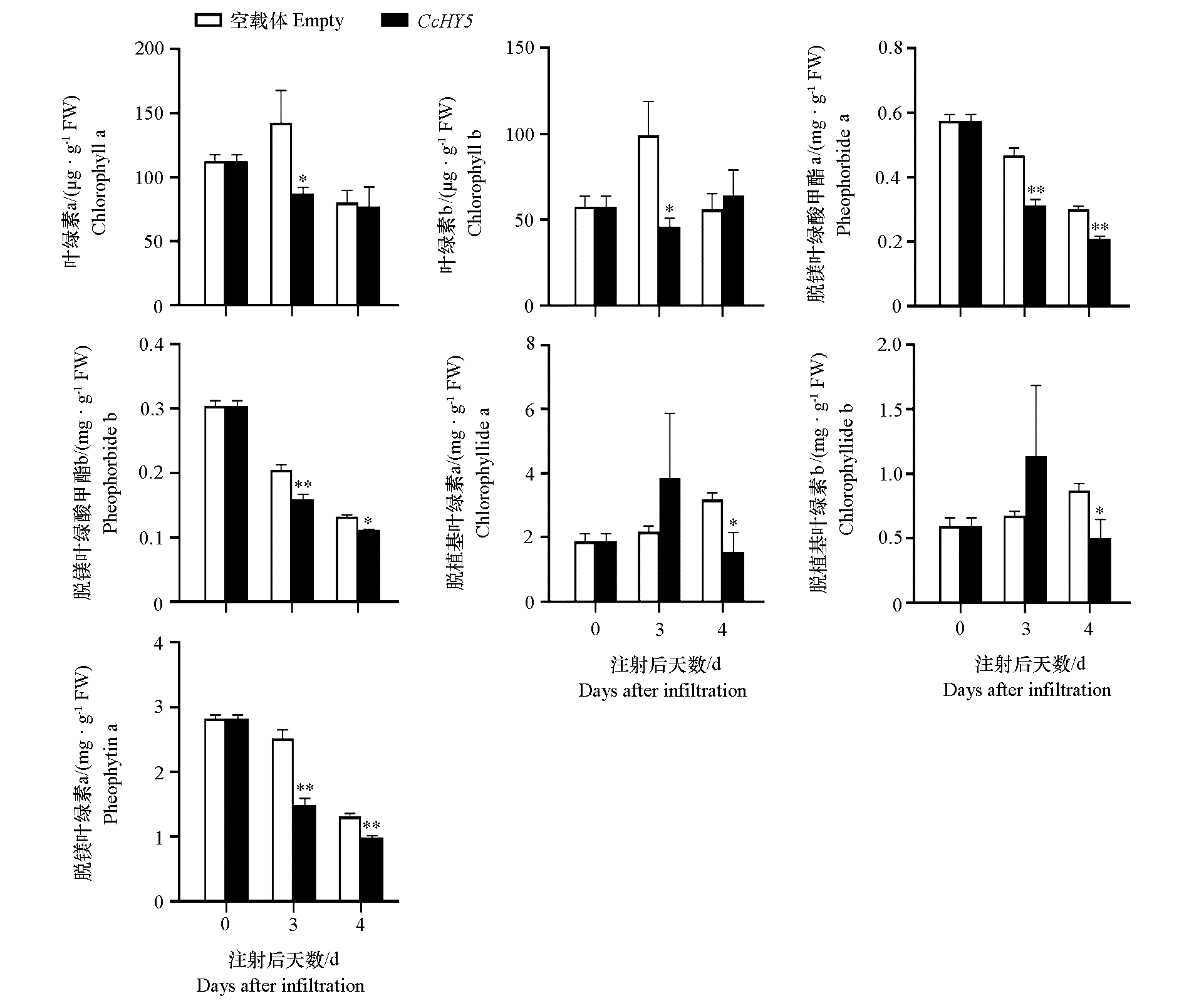
图11 CcHY5瞬时过表达对蜜橘果实果皮叶绿素及其代谢产物含量的影响(25 ℃)
Fig. 11 Effects of transient overexpression of CcHY5 on the content of chlorophyll and its metabolites in the peel of mandarin fruit(25 ℃) Student’s t-test,* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01.
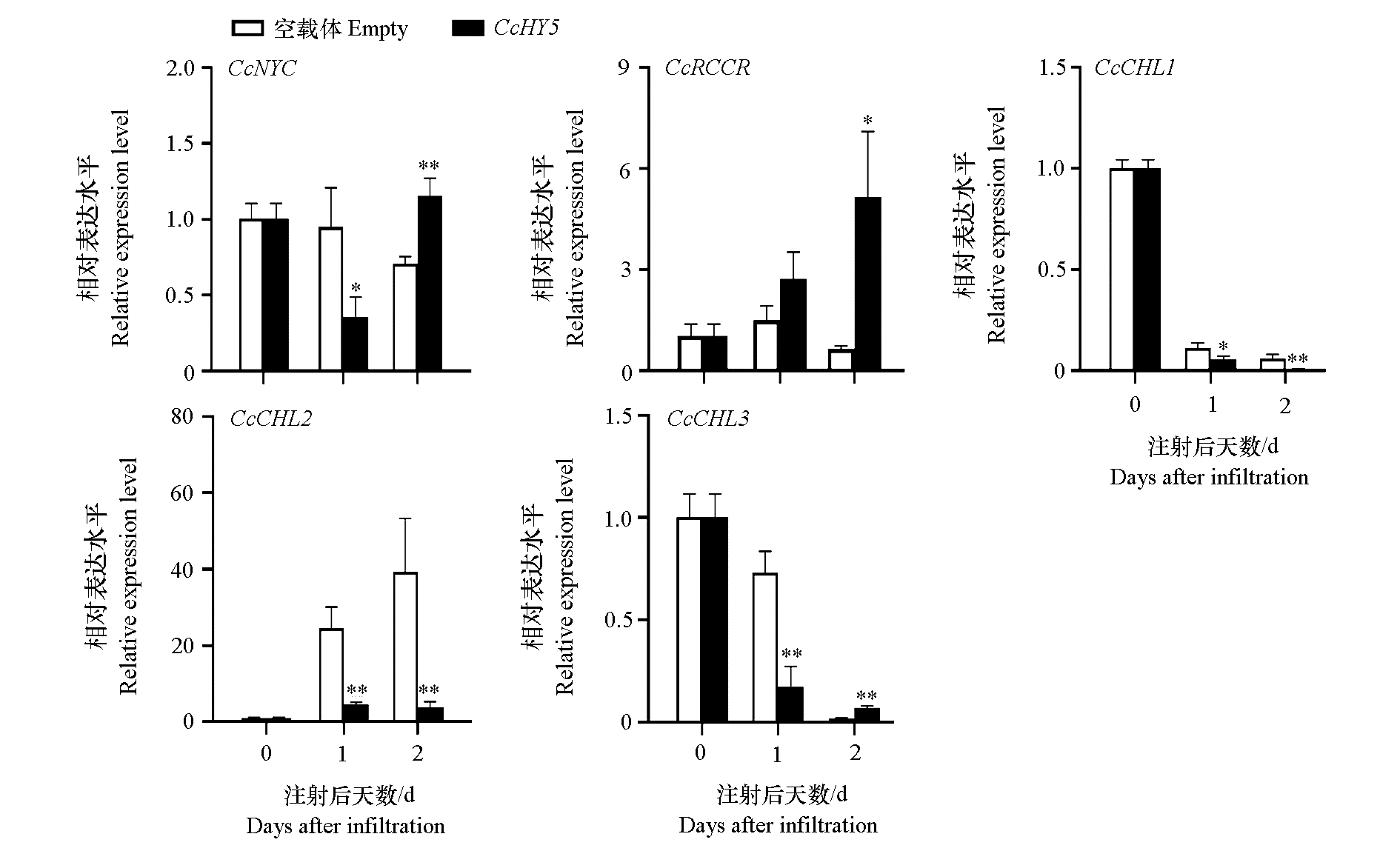
图12 CcHY5瞬时过表达对蜜橘果皮CcHY5及叶绿素代谢途径相关基因相对表达的影响(25 ℃)
Fig. 12 Effects of transient overexpression of CcHY5 on the relative expression of CcHY5 and chlorophyll metabolism pathway related genes in mandarin fruit peel(25 ℃) Student’s t-test,* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01.
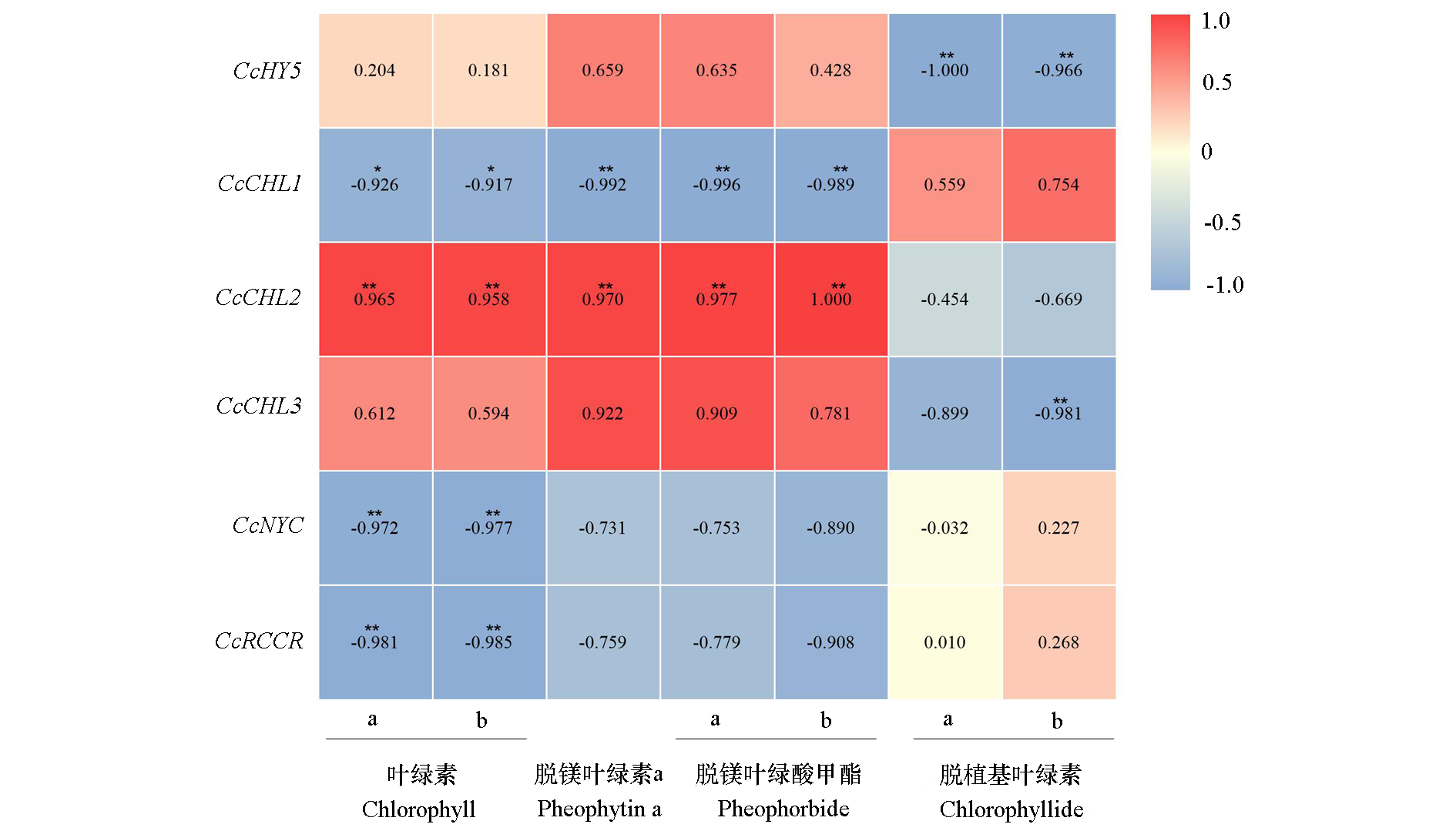
图13 CcHY5瞬时过表达后蜜橘果皮叶绿素及其代谢产物含量与叶绿素代谢基因表达量的皮尔逊相关性分析
Fig. 13 Pearson correlation analysis of chlorophyll and its metabolites and chlorophyll metabolism genes in mandarin fruit peel after transient overexpression of CcHY5 *P < 0.05,** P < 0.01.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.124933 pmid: 18633118 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0701 |
|
邓秀新. 2022. 中国柑橘育种60年回顾与展望. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2063-2074.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0701 |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8495 pmid: 28631804 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
李晓萌. 2020. HY5在番茄果实类胡萝卜素合成中的作用研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1021/jf9005998 pmid: 19441837 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0600 |
|
唐明佳, 徐进, 林锐, 宋珈凝, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 2022. 番茄响应光温逆境的生理分子机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (10):2174-2188.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0600 |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0913 |
|
王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕. 2022. 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控及其应用的研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2669-2682.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0913 |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
|
袁梓洢. 2017. 光照改善乙烯褪绿蜜橘果实着色效果的机理研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [49] |
|
| [1] | 刘宇香, 韩风庆, 赵鑫雨, 刘玉梅, 李占省, 方智远, . 青花菜侧枝调控基因BoBRC1的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 1997-2007. |
| [2] | 马 波, 李 雷, 胡增辉, 冷平生, 汪进萱, 冷 卓, 杨艺慧, 贾黎明, 吴 静, . 紫丁香SoF3′H对花瓣中花青苷合成的功能解析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1833-1843. |
| [3] | 任恒泽, 李丹莹, 余亚婷, 吕务云, 郝心愿, 王新超, 王玉春, . 植物VIGS载体构建策略研究与应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1455-1473. |
| [4] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李 营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [5] | 王佩云, 李子昂, 白 杨, 杨 萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华, . ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [6] | 杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明 凤, . 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [7] | 田 歌, 刘建廷, 高传彩, 赵雪惠, 樊永信, 李 森, 张寒啸, 陈修德, 李 玲, 李冬梅, . UV-B对设施油桃叶片叶绿素生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1332-1344. |
| [8] | 周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 金光. 桃镁离子转运蛋白MGT基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 463-478. |
| [9] | 罗健东, 邱梦青, 周慧敏, 解为玮, 黄海鑫, 刘洁琪, 张梓敏, 徐健, 陈程杰, 何业华, 刘朝阳. 菠萝AcZFP1的克隆及其在低温胁迫下的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 495-508. |
| [10] | 刘晋红, 王峥, 于昊, 辛依睿, 亓果宁, 柳参奎, 任慧敏. 毛竹SLAC家族基因鉴定及PheSLAC1功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 545-559. |
| [11] | 仲钊江, 吴 震, 周 蓉, 朱为民, 杨学东, 于筱薇, 徐 艳, 高扬杨, 蒋芳玲, . 番茄果胶裂解酶基因SlPL参与调控裂果机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 295-308. |
| [12] | 沈 衡, 王 琳, 李 骞, 袁守娟, 郑 伟, 王涛涛, 叶志彪, 杨长宪, . 番茄风味和功能性成分研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 423-438. |
| [13] | 杨娟博, 郭丽丽, 卢世雄, 苟惠敏, 王帅珽, 曾宝珍, 毛娟. 草莓FaGH3.17基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2483-2494. |
| [14] | 吴 丹, 柳佳欣, 卓林熙, 李 钰, 罗 英, 周 勇, 杨有新, 余 婷, . CaWRKY39在辣椒响应疫霉菌侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2297-2310. |
| [15] | 陆静, 韦素云, 尹佟明, 陈赢男. Type-A细胞分裂素响应调节因子基因家族研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1867-1888. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司