
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1256-1272.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0336
收稿日期:2024-02-23
修回日期:2024-05-27
出版日期:2024-12-18
发布日期:2024-06-22
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LI Qinqin, DONG Shanrong, LUO Jianrang*( ), ZHANG Yanlong
), ZHANG Yanlong
Received:2024-02-23
Revised:2024-05-27
Published:2024-12-18
Online:2024-06-22
摘要:
为探究卵叶牡丹(Paeonia qiui)春色叶呈现紫红色的成因,从其叶片转录组数据中筛选出两个花青素合成关键基因PqDFR和PqANS进行克隆、表达模式分析、功能鉴定以及启动子活性分析。PqDFR开放阅读框为1 095 bp,编码364个氨基酸,含有NADPH保守结构域和1个substract-binding结合位点;PqANS开放阅读框为1 065 bp,编码354个氨基酸,含有2OG-FeⅡ_Oxy和结合亚铁离子的保守氨基酸。实时荧光定量PCR结果表明,PqDFR和PqANS在叶片发育过程中表达量先上升再下降,与花青素的积累趋势基本一致。在卵叶牡丹叶盘中分别沉默PqDFR和PqANS基因后,叶盘的花青素含量均明显下降。稳定过表达试验表明转基因拟南芥幼苗相比野生型花青素积累更明显。PqDFR和PqANS启动子序列含有MYB转录因子结合序列,也含有光响应元件(G-box)、脱落酸响应元件(ABRE)、生长素响应元件(TGA-element)等顺式作用元件,GUS染色和定量结果显示启动子均具有良好的活性。研究结果表明PqDFR和PqANS可以促进卵叶牡丹叶片花青素合成。
李琴琴, 董山榕, 罗建让, 张延龙. 卵叶牡丹PqDFR和PqANS及启动子克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1256-1272.
LI Qinqin, DONG Shanrong, LUO Jianrang, ZHANG Yanlong. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PqDFR and PqANS Genes and Its Promoters from Paeonia qiui[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1256-1272.
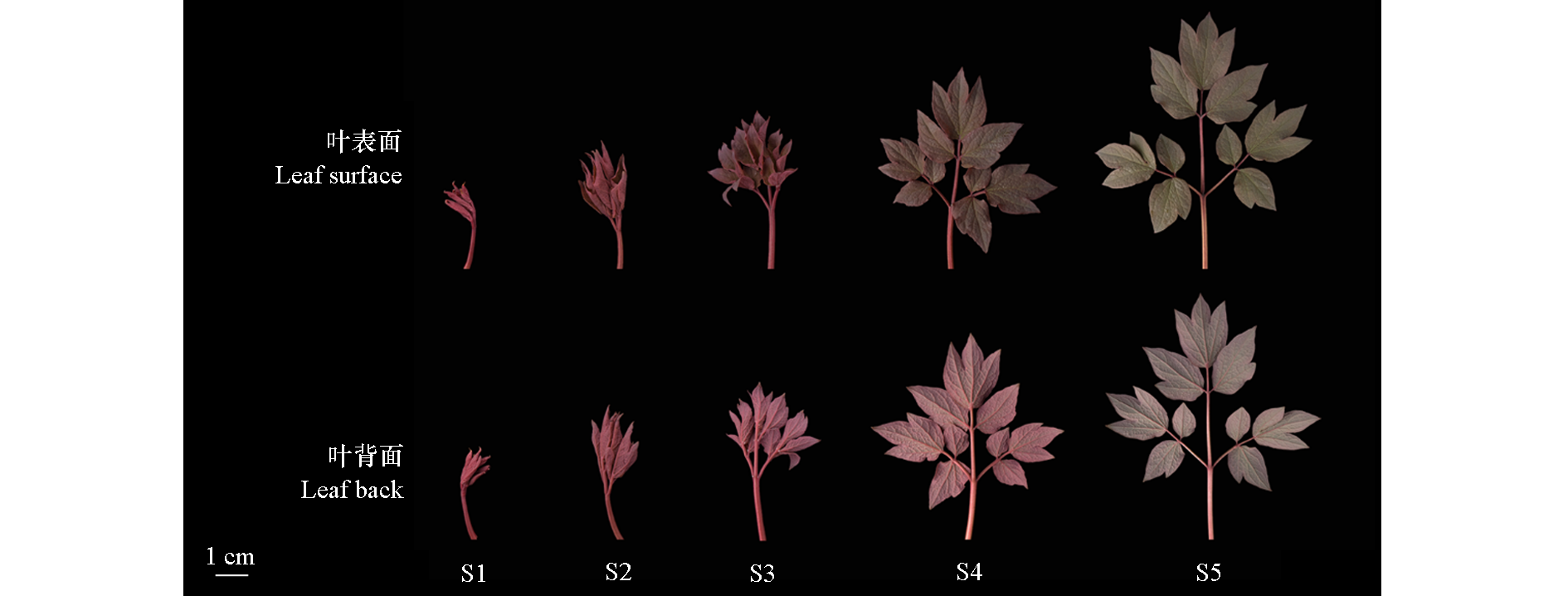

图1 卵叶牡丹不同时期叶片的表型 S1:显叶期;S2:张叶期;S3:展叶期;S4:大风铃期;S5:露色期。下同。
Fig. 1 Leaf phenotypes in different periods of Paeonia qiui S1:Petiole visibility;S2:Petiole spreading;S3:Leaves unfolding;S4:Wind bell bud;S5:Petal coloring. The same below.
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PqDFR | F:ATGGAAGCAGTGACCGAGTG;R:TTAGATTGTGTCATTAACAT |
| PqANS | F:ATGGTGAATTCAGTAGCTCC;R:TCAATTCTTAAACTCTTCTT |
| PqDFR(p1300) | F:GGGGTACCGCAAATGGAAGCAGTGACCGA;R:ACGCGTCGATGAAGTAGTGATCGACCCCTCT |
| PqANS(p1300) | F:ACGCGTCGACATGGTGAATTCAGTAGCTCCAAG;R:AACTGCAGCTGTATAAATCCATCACGGCCC |
| PqDFR(pTRV2) | F:TGCCAAAAGCGGATACCCAT;R:TCACTCCAGCAGGTTTCATC |
| PqANS(pTRV2) | F:CAACCAGCGAATACGCCAAG;R:GACACATTTTGCCGTCACCC |
| Actin | F:GGAACTGGAATGGTGAAGGCTG;R:CGATTGGATACTTCAGAGTGAGGA |
| PqDFR(qRT-PCR) | F:GCGGATACCCATTTGACCCT;R:TGAAAACGACTCTCCGCACA |
| PqANS(qRT-PCR) | F:TGAACTAGCTCTTGGCGTGG;R:CAGCACCGGCTTGAGTATGA |
表1 基因克隆及其载体构建的引物序列
Table 1 Sequence of primers used genes clone and vector construction
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PqDFR | F:ATGGAAGCAGTGACCGAGTG;R:TTAGATTGTGTCATTAACAT |
| PqANS | F:ATGGTGAATTCAGTAGCTCC;R:TCAATTCTTAAACTCTTCTT |
| PqDFR(p1300) | F:GGGGTACCGCAAATGGAAGCAGTGACCGA;R:ACGCGTCGATGAAGTAGTGATCGACCCCTCT |
| PqANS(p1300) | F:ACGCGTCGACATGGTGAATTCAGTAGCTCCAAG;R:AACTGCAGCTGTATAAATCCATCACGGCCC |
| PqDFR(pTRV2) | F:TGCCAAAAGCGGATACCCAT;R:TCACTCCAGCAGGTTTCATC |
| PqANS(pTRV2) | F:CAACCAGCGAATACGCCAAG;R:GACACATTTTGCCGTCACCC |
| Actin | F:GGAACTGGAATGGTGAAGGCTG;R:CGATTGGATACTTCAGAGTGAGGA |
| PqDFR(qRT-PCR) | F:GCGGATACCCATTTGACCCT;R:TGAAAACGACTCTCCGCACA |
| PqANS(qRT-PCR) | F:TGAACTAGCTCTTGGCGTGG;R:CAGCACCGGCTTGAGTATGA |
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PqDFR-SP1 | TCCACAAGGTCAAATGGGTATC |
| PqDFR-SP2 | AAAAATAAAACCACCCCCACAG |
| PqDFR-SP3 | GTCCCAGTAACAGGTGTAGATG |
| PqANS-SP1 | AAACCTCCCCTGCTTTCTTAACC |
| PqANS-SP2 | GTAAACGTTGCTGCAAAAATGG |
| PqANS-SP3 | GCCCTTCTTCTTTCTTCTCTTCCTC |
| PBI121 | F:TGGAAAGCGGGCAGTGAGCG;R:ATCCAGACTGAATGCCCACA |
| PqDFR(PBI121) | F:CCCAAGCTTAGGAGTAGCAAAGGCTGCACG;R:CGCGGATCCTTGTGTTTGGGTTCATGTTAGCTT |
| PqANS(PBI121) | F:CCCAAGCTTCATAGGCATTTATAATTAGTTAC;R:CGCGGATCCAGCAACGTTTACTCTCTGTTTTC |
表2 启动子克隆及其载体构建的引物序列
Table 2 Sequence of primers in gene promoter clone and vector construction
| 引物名称 Name of primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| PqDFR-SP1 | TCCACAAGGTCAAATGGGTATC |
| PqDFR-SP2 | AAAAATAAAACCACCCCCACAG |
| PqDFR-SP3 | GTCCCAGTAACAGGTGTAGATG |
| PqANS-SP1 | AAACCTCCCCTGCTTTCTTAACC |
| PqANS-SP2 | GTAAACGTTGCTGCAAAAATGG |
| PqANS-SP3 | GCCCTTCTTCTTTCTTCTCTTCCTC |
| PBI121 | F:TGGAAAGCGGGCAGTGAGCG;R:ATCCAGACTGAATGCCCACA |
| PqDFR(PBI121) | F:CCCAAGCTTAGGAGTAGCAAAGGCTGCACG;R:CGCGGATCCTTGTGTTTGGGTTCATGTTAGCTT |
| PqANS(PBI121) | F:CCCAAGCTTCATAGGCATTTATAATTAGTTAC;R:CGCGGATCCAGCAACGTTTACTCTCTGTTTTC |
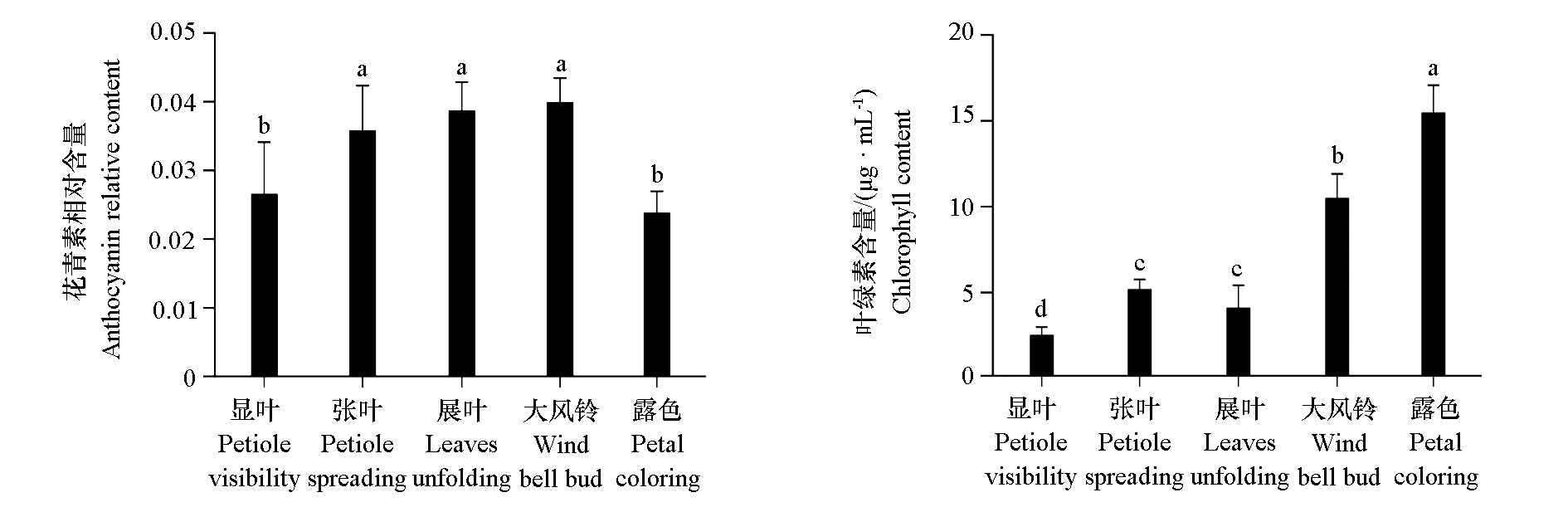
图3 卵叶牡丹不同时期叶片的花青素和叶绿素含量 不同小写字母表示经邓肯氏检验在P < 0.05的水平上差异显著。下同。
Fig. 3 Leaf anthocyanin and chlorophyll contents in different periods of Paeonia qiui Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the P < 0.05 level by Duncan’s test. The same below.

图6 卵叶牡丹沉默PqDFR和PqANS基因的叶盘表型和相对花青素含量
Fig. 6 Phenotype and anthocyanin content in leaf disks of Paeonia qiui with silenced PqDFR and PqANS genes ** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001.
| 调控序列 Regulatory sequence | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 特性 Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 对厌氧诱导至关重要 Essential for the anaerobic induction |
| O2-site | GATGATGTGG | 2 | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式作用调控因子cis-Acting regulatory factors irnvolved in regulation of zein metabolism |
| TATA-box | TATA | 4 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 2 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| G-Box | CACGTG | 2 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | 脱落酸反应顺式作用元件Abscisic acid reactive cis-acting element |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTCTCTAAC | 1 | 参与防御和胁迫反应 Involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| MYB | CAACCA | 2 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| STRE | AGGGG | 1 | 压力响应顺式调控元件Pressure responsive cis-control element |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1结合位点MYBHv1 binding site |
表3 proPqDFR顺式作用元件
Table 3 cis-Acting elements of proPqDFR
| 调控序列 Regulatory sequence | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 特性 Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 对厌氧诱导至关重要 Essential for the anaerobic induction |
| O2-site | GATGATGTGG | 2 | 参与玉米醇溶蛋白代谢调控的顺式作用调控因子cis-Acting regulatory factors irnvolved in regulation of zein metabolism |
| TATA-box | TATA | 4 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT | 2 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| G-Box | CACGTG | 2 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | 脱落酸反应顺式作用元件Abscisic acid reactive cis-acting element |
| TC-rich repeats | ATTCTCTAAC | 1 | 参与防御和胁迫反应 Involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| MYB | CAACCA | 2 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| STRE | AGGGG | 1 | 压力响应顺式调控元件Pressure responsive cis-control element |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1结合位点MYBHv1 binding site |
| 调控序列 Regulatory sequence | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 特性 Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 对厌氧诱导至关重要 Essential for the anaerobic induction |
| TATA-box | TATA | 10 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT/CAAT/ CCAAT | 17 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 1 | 参与部分光响应保守DNA组件 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 1 | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 1 | MYB结合位点参与光反应MYB binding sites are involved in photoreactions |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 脱落酸反应顺式作用元件Abscisic acid reactive cis-acting element |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件cis-Acting elements involved in the salicylic acid reaction |
| TCA | TCATCTTCAT | 1 | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件cis-Acting elements involved in the salicylic acid reaction |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 1 | 生长素反应顺式作用元件Auxin-reactive cis-acting element |
| MYB | TAACCA | 1 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| MYC | CATTTG | 2 | MYC结合位点MYC binding site |
| Myb | TAACTG | 1 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| W-box | TTGACC | 1 | 与WRKY 转录因子特异结合Specific binding to WRKY transcription factors |
表4 proPqANS顺式作用元件
Table 4 cis-Acting elements of proPqANS
| 调控序列 Regulatory sequence | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 特性 Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 对厌氧诱导至关重要 Essential for the anaerobic induction |
| TATA-box | TATA | 10 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site |
| CAAT-box | CAAAT/CAAT/ CCAAT | 17 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 1 | 参与部分光响应保守DNA组件 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| GA-motif | ATAGATAA | 1 | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 1 | MYB结合位点参与光反应MYB binding sites are involved in photoreactions |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 脱落酸反应顺式作用元件Abscisic acid reactive cis-acting element |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件cis-Acting elements involved in the salicylic acid reaction |
| TCA | TCATCTTCAT | 1 | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件cis-Acting elements involved in the salicylic acid reaction |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 1 | 生长素反应顺式作用元件Auxin-reactive cis-acting element |
| MYB | TAACCA | 1 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| MYC | CATTTG | 2 | MYC结合位点MYC binding site |
| Myb | TAACTG | 1 | 转录因子结合位点Transcription factor binding site |
| W-box | TTGACC | 1 | 与WRKY 转录因子特异结合Specific binding to WRKY transcription factors |
| [1] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0532 |
|
毕蒙蒙, 曹雨薇, 宋蒙, 唐玉超, 何国仁, 杨悦, 杨盼盼, 徐雷锋, 明军. 2021. 百合花色研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (10):2073-2086.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0532 |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.118919 pmid: 18539781 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
段晶晶, 罗建让, 李想, 张庆雨, 张延龙. 2018. 牡丹叶片红色消退过程中色素变化及相关基因表达分析. 西北植物学报, 38 (10):1885-1894.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
段晶晶. 2019. 卵叶牡丹叶片花青素合成相关MYB筛选、克隆与功能验证[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
甘林鑫. 2019. 三种色系牡丹花色素组成及相关基因表达分析[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
郭凤丹, 夏晗, 袁美, 王兴军. 2011. 花生二氢黄酮醇还原酶基因(DFR)的克隆及表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 19 (5):816-822.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
衡蒙, 孔祥莹, 赵海平, 方颖, 金雪花. 2023. 华丽龙胆花青素合成酶GsANS基因的克隆及其表达分析. 分子植物育种, 21 (11):3498-3504.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0497 |
|
洪艳, 武宇薇, 宋想, 李梦灵, 戴思兰. 2021. 光照调控园艺作物花青素苷生物合成的分子机制. 园艺学报, 48 (10):1983-2000.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0497 |
|
| [11] |
|
|
黄玲, 胡先梅, 梁泽慧, 王艳平, 产祝龙, 向林. 2022. 郁金香花青素合成酶基因TgANS的克隆与功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1935-1944.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0638 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
焦淑珍, 刘雅莉, 娄倩, 姜玲. 2014. 葡萄风信子二氢黄酮醇-4-还原酶基因(DFR)的克隆与表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 22 (5):529-540.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
蒋宝鑫, 汪庆昊, 杨国霞, 贾永红, 谢晓鸿, 吴月燕. 2023. 比利时杜鹃花RhDFR基因克隆及分析. 西北植物学报, 43 (1):10-20.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
李春雷, 崔国新, 许志茹, 李玉花. 2009. 植物二氢黄酮醇-4-还原酶基因的研究进展. 生物技术通讯, 20 (3):442-445.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
李果, 李厚华, 张延龙, 辛转霞, 魏新翠, 唐豆豆. 2016. 凤丹牡丹ANS(PoANS)基因克隆、特性及表达. 东北林业大学学报, 44 (7):64-69.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
李力. 2016. 北美红枫呈色生理机制及叶色调控[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
李云琴, 原晓龙, 陈中华, 王毅. 2020. 滇牡丹(Paeonia delavayi)二氢黄酮醇-4-还原酶基因的鉴定及表达. 分子植物育种, 18 (4):1083-1087.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
凌文华, 郭红辉. 2009. 植物花色苷. 北京:科学出版社:14-18.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
亓希武. 2014. 桑树花青素生物合成相关基因的鉴定及功能研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [29] |
pmid: 17157544 |
| [30] |
|
|
史倩倩. 2015. 基于转录组测序滇牡丹花色形成分子调控机理研究[博士论文]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0750 |
|
田密霞, 周福慧, 姜爱丽, 祝朋芳, 陈晨, 刘程惠, 原畅. 2023. 芸薹属植物呈色机理研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (9):1971-1986.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0750 |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
王海竹, 曲红云, 周婷婷, 徐启江. 2017. 茄萼花色苷合成相关基因DFR和MYB克隆及表达分析. 中国农业科学, 50 (14):2781-2792.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.14.014 |
|
| [35] |
|
|
王疆然, 王玉芬, 王舒婷, 张芳娟, 牛颜冰, 王德富. 2021. 不同花色黄芩中dfr基因的克隆及时空表达分析. 生物工程学报, 37 (4):1312-1323.
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
文樵夫, 沈红香, 姚允聪, 田佶, 宋婷婷. 2010. 苹果属观赏海棠McDFR的克隆及不同叶色品种间的表达差异. 林业科学, 46 (11):16-24.
|
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
|
杨晨. 2020. ‘凤丹’牡丹花色变化过程中花瓣色素组成及相关基因表达分析[硕士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
杨成龙, 张洁, 方少忠, 郑益平, 林智敏. 2021. 东方百合ANS基因的克隆与对拟南芥过表达的表型分析. 分子植物育种, 19 (20):6741-6746.
|
|
| [40] |
|
|
杨宁宁. 2021. 金线莲花青素DFR基因筛选与克隆及功能分析[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
原晓龙, 李子光, 陆刚, 李云琴, 王毅. 2020. 滇牡丹查尔酮异构酶基因的克隆及表达分析. 北方园艺, 469 (22):79-85.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
|
张龙, 李卫华, 姜淑梅, 朱根发, 王碧青, 李洪清. 2008. 花色素苷生物合成与分子调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 35 (6):909-916.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
|
周琳, 史倩倩, 齐宇, 缪崑, 王雁. 2019. 黄牡丹花瓣转录组分析及不同开放阶段差异基因筛选. 分子植物育种, 17 (15):4936-4943.
|
|
| [48] |
|
|
周琳, 王雁, 任磊, 彭镇华. 2011. 牡丹二氢黄酮醇4-还原酶基因PsDFR1的克隆及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 47 (9):885-892.
|
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
|
祝怛均, 石倩倩, 李希, 杜江涛, 李新岗. 2023. ‘胎里红’枣果皮花青素合成酶ZjANS基因克隆及表达分析. 分子植物育种, 21 (20):6613-6624.
|
|
| [51] |
|
| [1] | 董晓珂, 陈元磊, 牛友怡, 刘占德, 王南南. 以高产优质稳产为目标的‘徐香’猕猴桃不同生长期叶片营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1345-1360. |
| [2] | 冯志娟, 刘娜, 张古文, 卜远鹏, 王斌, 龚亚明. 菜用大豆GmDi19-3启动子对盐胁迫和外源ABA、MeJA的响应[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2791-2799. |
| [3] | 王雅楠, 刘绪涛, 景桐彤, 柴亚婷, 张晓伟, 艾希珍, 毕焕改. 褪黑素对番茄衰老叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606. |
| [4] | 叶玙璠, 王誉洁, 傅前媛, 王璐, 郝心愿, 丁长庆, 王新超, 曹红利, 李娜娜. 茶树镁离子螯合酶H亚基基因CsChlH的克隆及其表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 91-102. |
| [5] | 王宇航, 李斗, 王春恒, 金鑫, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹, 杨江山. 褪黑素对葡萄叶片发育衰老过程中亚细胞活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 103-120. |
| [6] | 田密霞, 周福慧, 姜爱丽, 祝朋芳, 陈晨, 刘程惠, 原畅. 芸薹属植物呈色机理研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1971-1986. |
| [7] | 李松琦, 李旭飞, 李敏, 刘海楠, 裴茂松, 韦同路, 郭大龙, 余义和. 葡萄细胞分裂素响应调节因子VlRRA1的克隆、表达及启动子活性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1609-1621. |
| [8] | 刘慧, 殷向静, 方景浩, 高敏, 李智, 王西平. 中国野生葡萄芪合成酶基因STS19及其启动子的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1389-1401. |
| [9] | 杨君, 孔羽, 刘群录, 叶康, 秦俊. 遮荫对‘花手鞠’绣球花色和花青素苷组成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1467-1481. |
| [10] | 周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 金光. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 959-971. |
| [11] | 高成昱, 王艺衡, 靳江周, 李涛, 李金斗, 周梦瑶, 张海霞, 马辉, 张玉星, 亓宝秀, 许建锋. 梨叶片原生质体制备方法的建立及其基因瞬时转化试验[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1141-1150. |
| [12] | 李玉梅, 娄玉穗, 王小龙, 马玉全, 王海波, 吕中伟. ‘夏黑’葡萄高品质果园植株叶片和土壤营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 864-874. |
| [13] | 蒋彧, 涂勋良, 何俊蓉. 国兰叶色突变体叶片差异表达基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [14] | 于婷婷, 李欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [15] | 孙玉帅, 王菲, 管雪强, 郗慧茹, 姚玉新. ABA和乙烯互作调控葡萄VlMybA1和VlMybA2表达并促进果皮着色[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(11): 2323-2336. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司