
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (10): 2171-2182.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0506
文婷, 李婧, 张家琪, 魏仪, 祝文睿, 倪德江, 王明乐*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-21
修回日期:2023-07-14
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-10-30
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:wangmingle@mail.hzau.edu.cn)
基金资助:
WEN Ting, LI Jing, ZHANG Jiaqi, WEI Yi, ZHU Wenrui, NI Dejiang, WANG Mingle*( )
)
Received:2023-03-21
Revised:2023-07-14
Published:2023-10-25
Online:2023-10-30
Contact:
*(E-mail:wangmingle@mail.hzau.edu.cn)
摘要:
为探究镁转运子(Magnesium Transporters,MGT)参与调控茶树镁元素吸收、转运的机制,从茶树品种‘鄂茶10号’中克隆了1个镁转运子基因CsMGT6(GeneBank登录号:ON934629),并分析其功能。CsMGT6位于茶树第3号染色体上,开放阅读框为1 368 bp,编码455个氨基酸。多序列比对分析发现,CsMGT6含有2个跨膜结构域和1个保守的GMN基序。系统进化树显示,CsMGT6属于第5亚族,与山梨猕猴桃(Actinidia rufa)ArMGT6亲缘关系最近。亚细胞定位结果表明,CsMGT6定位在细胞质膜上。实时荧光定量 PCR分析发现,镁缺乏条件下CsMGT6在茶树根和叶部的响应不同,且在不同茶树品种中的响应存在差异。沙门氏杆菌功能互补试验表明,CsMGT6属于低亲和镁转运子,可能在较高浓度镁存在的条件下参与镁元素的吸收和转运。结果表明CsMGT6可被镁缺乏诱导表达,可能参与维持茶树细胞质膜内外的镁稳态。
文婷, 李婧, 张家琪, 魏仪, 祝文睿, 倪德江, 王明乐. 茶树镁转运子基因CsMGT6的表达和功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(10): 2171-2182.
WEN Ting, LI Jing, ZHANG Jiaqi, WEI Yi, ZHU Wenrui, NI Dejiang, WANG Mingle. Expression and Functional Identification of Magnesium Transporter Gene CsMGT6 in Camellia sinensis[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2171-2182.
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5ʹ-3ʹ) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆 Clone | CsMGT6 | F:ATGGGGAAGGGGCCATTCTC |
| R:CGATCCAATCAGTTTCTTCC | ||
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | CsMGT6-q | F:AGGTTGAGGTGGTGTCTCTG |
| R:GATTGCCCGAACTTGTCGAA | ||
| 内参基因 Reference gene | CsTBP-q | F:AAGGGATCCAAAGACGACAG |
| R:TGAAATCCTTGAATTTGGCA | ||
| CsTIP41-q | F:CGAAAGAGCCCATTCTCTTC | |
| R:ACGTGTGTCCCTCAATCTCA | ||
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | CsMGT6-pCAMBIA2300 | F:TTTGGAGAGGACAGGGTACCATGGGGAAGGGGCCATTCTC |
| R:CCTCCTCCTCTAGAGGATCCCGATCCAATCAGTTTCTTCC | ||
| 原核表达 Prokaryotic expression | CsMGT6-pTrc99A | F:AGACCATGGAATTCGAGCTCGGTACCATGGGGAAGGGGCCA |
| R:GCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGATCCTCACGATCCAATCAG |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Sequences of primers
| 用途 Usage | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5ʹ-3ʹ) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆 Clone | CsMGT6 | F:ATGGGGAAGGGGCCATTCTC |
| R:CGATCCAATCAGTTTCTTCC | ||
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | CsMGT6-q | F:AGGTTGAGGTGGTGTCTCTG |
| R:GATTGCCCGAACTTGTCGAA | ||
| 内参基因 Reference gene | CsTBP-q | F:AAGGGATCCAAAGACGACAG |
| R:TGAAATCCTTGAATTTGGCA | ||
| CsTIP41-q | F:CGAAAGAGCCCATTCTCTTC | |
| R:ACGTGTGTCCCTCAATCTCA | ||
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | CsMGT6-pCAMBIA2300 | F:TTTGGAGAGGACAGGGTACCATGGGGAAGGGGCCATTCTC |
| R:CCTCCTCCTCTAGAGGATCCCGATCCAATCAGTTTCTTCC | ||
| 原核表达 Prokaryotic expression | CsMGT6-pTrc99A | F:AGACCATGGAATTCGAGCTCGGTACCATGGGGAAGGGGCCA |
| R:GCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGATCCTCACGATCCAATCAG |
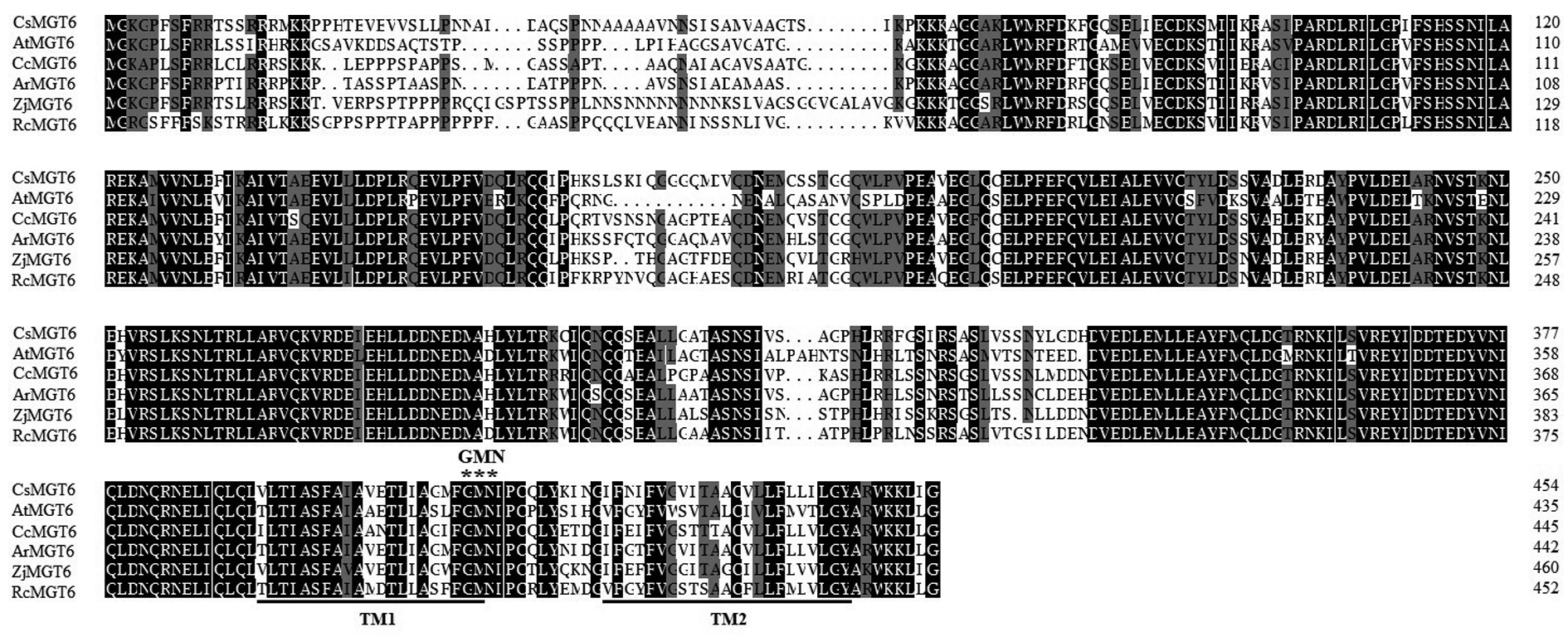
图2 茶树CsMGT6与其他植物MGTs蛋白的多序列比对 Cs:茶树;At:拟南芥;Cc:克莱门氏小柑橘;Ar:山梨猕猴桃;Zj:枣;Rc:蓖麻。
Fig. 2 The alignment of CsMGT6 protein sequences with MGTs from other plant species Cs:Camellia sinensis;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Cc:Citrus clementina;Ar:Actinidia rufa;Zj:Ziziphus jujuba;Rc:Ricinus communis.
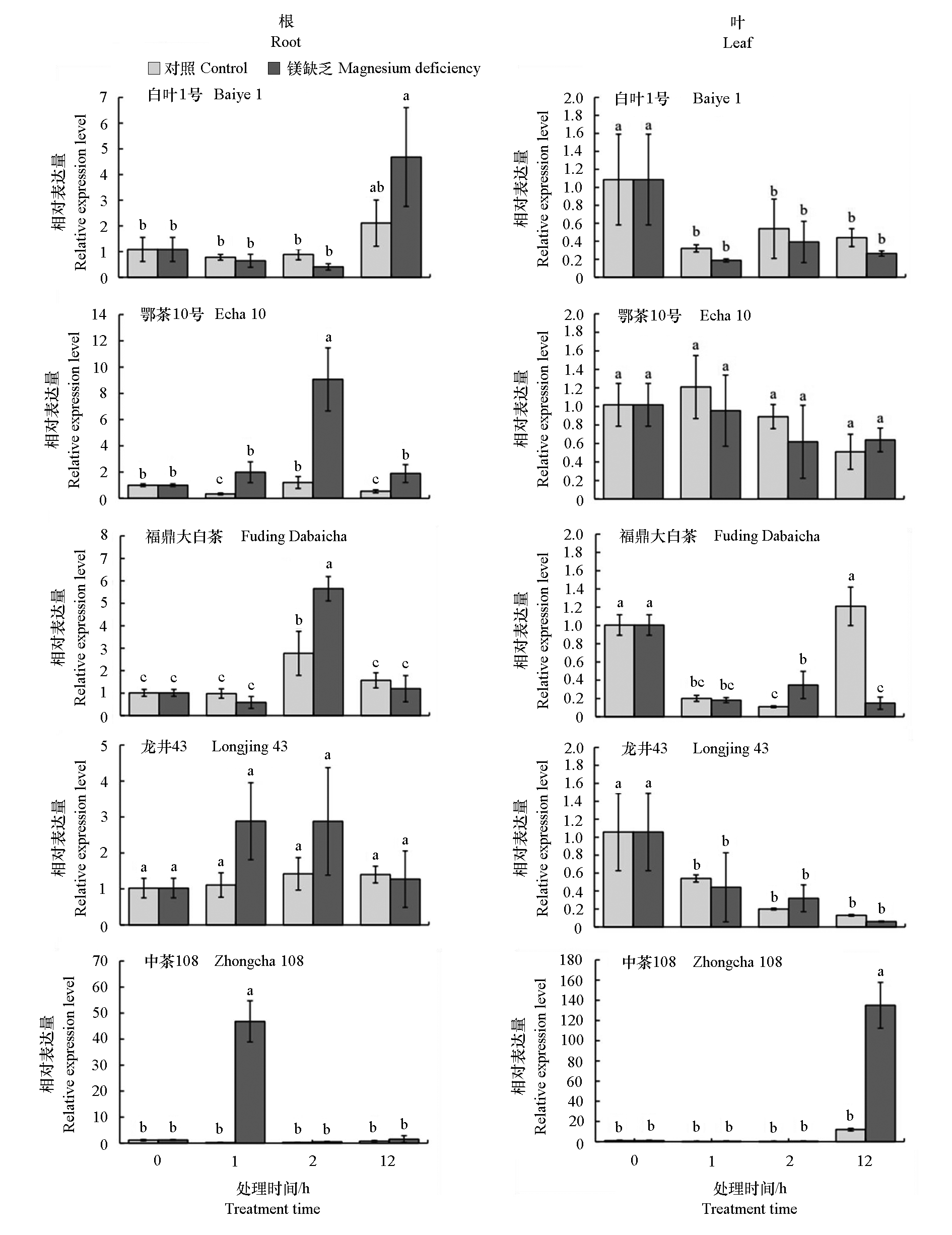
图5 不同茶树品种镁缺乏条件下根和叶中CsMGT6的表达水平 不同小写字母表示不同处理时间差异显著。Duncan’s多重比较法,P < 0.05。
Fig. 5 The expression level of CsMGT6 in response to low concentration of Mg2+ in roots and leaves of five tea plant cultivars Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different time. Duncan’s test for multiple comparison,P < 0.05.

图6 沙门氏杆菌镁转运缺失突变体MM281中CsMGT6的功能分析 A:平板试验;B:液体培养试验。Vector:转入pTrc99A空载的MM281;CsMGT6:转入pTrc99A-CsMGT6的MM281。 固体培养基上的菌液从左到右依次稀释10倍。
Fig. 6 Functional analysis of CsMGT6 in the magnesium transport mutant MM281 of Salmonella A:Functional complementary analysis of CsMGT6 in the spot assay;B:the growth curve of Salmonella MM281 in liquid medium. Vector:MM281 transformed with pTrc99A;CsMGT6:MM281 transformed with pTrc99A-CsMGT6. The strains was diluted 10 times from the left to the right in solid medium.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2008.133.issue-4 URL |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
陈良碧, 蔡丹, 张林安, 宋绍文, 罗璇, 陈依君, 李俊峰, 许涛, 毛丹丹. 2021. 植物镁离子转运及镁胁迫响应机制研究进展. 生命科学研究, 25 (5):442-447.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00532 URL |
| [8] |
|
|
邓沛怡, 田连福, 陈键, 栾升, 李东屏. 2007. 拟南芥AtMGT3基因转运功能研究. 生命科学研究, 11 (4):328-333.
|
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl201 pmid: 17101715 |
| [10] |
|
|
杜婧婧. 2021. 辣椒镁离子转运蛋白家族的分子鉴定和功能分析[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.3923/ajft.2010.31.39 URL |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
李洪有, 张素芝, 陈庆富. 2018. 玉米ZmMGT12基因的表达分析及拟南芥遗传转化. 分子植物育种, 16 (18):5940-5946.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05141 URL |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010352 URL |
| [17] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [18] |
|
|
栾雪, 张洋, 王瑞琪, 刘聪, 姜廷波, 魏志刚. 2021. 毛果杨MGT基因家族全基因组水平鉴定及表达分析. 分子植物育种, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20210802.1424.002.html.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
毛丹丹. 2011. 拟南芥AtMGT6的Mg2+转运功能研究[博士论文]. 长沙: 湖南师范大学.
|
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.124628 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/jipb.2008.50.issue-12 URL |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.05.010 pmid: 21640700 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4709 pmid: 22083631 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120 URL |
| [27] |
|
|
唐磊, 肖罗丹, 黄伊凡, 肖斌, 龚春梅. 2021. 茶树CsMGTs基因的克隆及其镁转运功能分析. 茶叶科学, 41 (6):761-776.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.17221/326/2012-PSE URL |
| [29] |
|
|
汪仁, 蔡黎丽, 徐晟, 李晓丹, 夏冰. 2014. 石蒜Mg2+转运体基因LrMGT的克隆与分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 23 (4):1-7.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
王勇军. 2019. 甘蔗MGT基因家族鉴定与缺镁胁迫的转录组动力学研究[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
阳江华, 秦云霞, 方永军, 唐朝荣. 2016. 巴西橡胶树镁离子转运蛋白基因HbMGT10的克隆及表达分析. 热带作物学报, 37 (12):2353-2358.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张露丹. 2019. OsMGT1响应水稻缺镁胁迫的功能分析[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
张群峰, 倪康, 伊晓云, 刘美雅, 阮建云. 2021. 中国茶树镁营养研究进展与展望. 茶叶科学, 41 (1):19-27.
|
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110904 URL |
| [35] |
|
|
赵智芳. 2016. 梨镁离子转运体家族分析及PbrMGT7的功能验证[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
| [1] | 彭 华, 王治会, 岳翠男, 杨普香 , 李文金 , 童忠飞, 郭 金. 茶树新品种‘赣茶 5 号’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 199-200. |
| [2] | 郑新强 , 李泽宇 , 李 凯 , 陆建良 , 赵 东 , 叶俭慧 , 叶晶晶 , 李寸羽 , 梁月荣 , . 早生优质茶树新品种‘浙农 301’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 201-202. |
| [3] | 王雷刚, 焦小雨, 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 黄化茶树新品种‘霍黄 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 203-204. |
| [4] | 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 焦小雨, 王雷刚, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 茶树新品种‘金鸡 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 205-206. |
| [5] | 李宇腾, 陈瑶, 任恒泽, 李聪聪, 王浩乾, 曹红利, 岳川, 郝心愿, 王新超. 茶树CsIDM的鉴定、表达分析及互作验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1696. |
| [6] | 侯炳豪, 高婷, 魏月德, 高水练, 蔡银笔, 陈志明, 金珊, 张兴坦, 王鹏杰, 叶乃兴. 基于高深度基因组重测序的‘铁观音’茶树无性繁殖后代遗传变异研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1505-1517. |
| [7] | 王泽涵, 于文涛, 王鹏杰, 刘财国, 樊晓静, 谷梦雅, 蔡春平, 王攀, 叶乃兴. 茶树秃房与茸房种质花器官差异表达基因的WGCNA分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 620-634. |
| [8] | 任菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [9] | 程庆华, 张志鹏, 吴艳萍, 万宇鹤, 陈应娟. 苦参碱对茶树炭疽菌的抑菌作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 432-440. |
| [10] | 崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [11] | 岳翠男, 王治会, 杨普香, 李文金, 彭 华, 陈罗军, 周汉中. 茶树新品种‘宁州早1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 281-282. |
| [12] | 李兰英, 胥亚琼, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 龚雪蛟, 罗 晟, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘金凤2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 283-284. |
| [13] | 李兰英, 王 强, 龚雪蛟, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 王迎春, 胥亚琼, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘甘露1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 285-286. |
| [14] | 任志红, 吴焕焕, 肖文敏, 张 虹, 杨圣祥, 孙海伟, 王 健, 高文星. 抗寒茶树新品种‘岱鼎御丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 287-288. |
| [15] | 王治会, 杨普香, 彭 华, 李文金, 王胜利, 鲍润元, 江新凤. 茶树新品种‘浮梁槠叶1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 191-192. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司