
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1505-1517.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0521
侯炳豪1, 高婷1, 魏月德2, 高水练1, 蔡银笔3, 陈志明4, 金珊1, 张兴坦5, 王鹏杰1,5,*( ), 叶乃兴1,*(
), 叶乃兴1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-12-05
修回日期:2023-04-28
出版日期:2023-07-25
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
HOU Binghao1, GAO Ting1, WEI Yuede2, GAO Shuilian1, CAI Yinbi3, CHEN Zhiming4, JIN Shan1, ZHANG Xingtan5, WANG Pengjie1,5,*( ), YE Naixing1,*(
), YE Naixing1,*( )
)
Received:2022-12-05
Revised:2023-04-28
Published:2023-07-25
Online:2023-07-26
摘要:
对茶树[Camellia sinensis(L.)O. Kuntze]‘铁观音’母树及其连续3代无性繁殖后代和3个经多代无性繁殖的生产茶园叶片进行超过50× 的高深度基因组重测序。通过SNP和InDel检测与注释,发现大部分变异位于基因间区,只有1.09% ~ 1.13%的SNP和0.51% ~ 0.61%的InDel位于基因编码区。在全基因组和编码区范围内,连续3代无性繁殖后代的样本之间总变异位点数均差别不大,各样本中涉及突变的基因数基本一致,推测‘铁观音’品种的种性在无性繁殖过程中总体保持稳定。与母树间差异基因的KEGG(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)富集结果表明,生产茶园样本在嘌呤类和糖类代谢通路中显著富集,并在咖啡碱代谢通路中呈极显著富集,推测‘铁观音’品种在长时间无性繁殖过程中,部分与品质相关的代谢通路基因发生变化。与前3代样本相比,FAR1、WAT1和MYB等3个与生长发育相关,PP2A、BTB/POZ、BAT2、RPP13和Lr10等5个与逆境响应相关的基因序列在生产茶园样本中发生了变异。
侯炳豪, 高婷, 魏月德, 高水练, 蔡银笔, 陈志明, 金珊, 张兴坦, 王鹏杰, 叶乃兴. 基于高深度基因组重测序的‘铁观音’茶树无性繁殖后代遗传变异研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1505-1517.
HOU Binghao, GAO Ting, WEI Yuede, GAO Shuilian, CAI Yinbi, CHEN Zhiming, JIN Shan, ZHANG Xingtan, WANG Pengjie, YE Naixing. Studies on Genetic Variation of‘Tieguanyin’Tea Trees Asexual Reproduction Based on High-depth Genome Resequencing[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1505-1517.
| 样本 Sample | 过滤后读长 Clean data | 比对读长 Mapped read | 比对率/% Mapped rate | 平均深度 Average depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 1 661 654 911 | 1 654 322 653 | 99.56 | 58.62 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 942 084 886 | 1 926 646 985 | 99.21 | 62.38 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 554 521 258 | 1 545 693 484 | 99.43 | 55.77 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 609 686 577 | 1 600 019 432 | 99.40 | 57.34 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 1 788 588 003 | 1 782 581 945 | 99.66 | 60.24 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 1 596 305 309 | 1 592 821 732 | 99.78 | 54.76 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 1 606 148 602 | 1 599 373 019 | 99.58 | 56.50 |
表1 测序数据比对统计
Table 1 Summary of read mapping of sequencing data
| 样本 Sample | 过滤后读长 Clean data | 比对读长 Mapped read | 比对率/% Mapped rate | 平均深度 Average depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 1 661 654 911 | 1 654 322 653 | 99.56 | 58.62 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 942 084 886 | 1 926 646 985 | 99.21 | 62.38 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 554 521 258 | 1 545 693 484 | 99.43 | 55.77 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 609 686 577 | 1 600 019 432 | 99.40 | 57.34 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 1 788 588 003 | 1 782 581 945 | 99.66 | 60.24 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 1 596 305 309 | 1 592 821 732 | 99.78 | 54.76 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 1 606 148 602 | 1 599 373 019 | 99.58 | 56.50 |
| 样本 Sample | 剪切位点 Splicing | 基因间 Intergenic | 基因上游1K Upstream 1K | 基因下游1K Downstream 1K | 内含子 Intronic | 外显子 Exonic | UTR5 | UTR3 | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 1 806 | 30 475 411 | 529 507 | 478 199 | 1 933 210 | 375 582 | 35 833 | 57 981 | 33 887 529 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 806 | 30 121 975 | 518 716 | 471 653 | 1 918 601 | 374 478 | 35 554 | 57 545 | 33 500 328 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 798 | 29 750 290 | 488 872 | 456 722 | 1 880 822 | 374 563 | 35 280 | 57 208 | 33 045 555 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 816 | 29 734 927 | 489 997 | 456 220 | 1 881 652 | 374 475 | 35 343 | 57 130 | 33 031 560 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 1 821 | 30 932 819 | 580 244 | 497 384 | 1 984 508 | 377 436 | 36 279 | 58 231 | 34 468 722 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 1 834 | 31 031 666 | 580 974 | 498 669 | 1 986 676 | 376 733 | 36 398 | 58 390 | 34 571 340 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 1 809 | 29 719 349 | 493 033 | 457 181 | 1 881 683 | 373 905 | 35 303 | 57 218 | 33 019 481 |
表2 不同代数‘铁观音’全基因组SNP位点统计
Table 2 Summary of genome-wide SNP in different generations of‘Tieguanyin’tea tree
| 样本 Sample | 剪切位点 Splicing | 基因间 Intergenic | 基因上游1K Upstream 1K | 基因下游1K Downstream 1K | 内含子 Intronic | 外显子 Exonic | UTR5 | UTR3 | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 1 806 | 30 475 411 | 529 507 | 478 199 | 1 933 210 | 375 582 | 35 833 | 57 981 | 33 887 529 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 806 | 30 121 975 | 518 716 | 471 653 | 1 918 601 | 374 478 | 35 554 | 57 545 | 33 500 328 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 798 | 29 750 290 | 488 872 | 456 722 | 1 880 822 | 374 563 | 35 280 | 57 208 | 33 045 555 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 1 816 | 29 734 927 | 489 997 | 456 220 | 1 881 652 | 374 475 | 35 343 | 57 130 | 33 031 560 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 1 821 | 30 932 819 | 580 244 | 497 384 | 1 984 508 | 377 436 | 36 279 | 58 231 | 34 468 722 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 1 834 | 31 031 666 | 580 974 | 498 669 | 1 986 676 | 376 733 | 36 398 | 58 390 | 34 571 340 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 1 809 | 29 719 349 | 493 033 | 457 181 | 1 881 683 | 373 905 | 35 303 | 57 218 | 33 019 481 |
| 样本 Sample | 非同义突变 Non-synonymous | 同义突变 Synonymous | 终止密码子缺失 Stop loss | 提前终止 Stop gain | 未知 Unknown | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 214 220 | 147 538 | 1 002 | 6 746 | 5 611 | 375 117 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 626 | 147 006 | 999 | 6 769 | 5 617 | 374 017 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 677 | 147 053 | 992 | 6 767 | 5 651 | 374 140 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 497 | 147 210 | 998 | 6 753 | 5 562 | 374 020 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 215 605 | 147 805 | 1 003 | 6 875 | 5 688 | 376 976 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 215 234 | 147 446 | 1 016 | 6 857 | 5 747 | 376 300 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 213 272 | 146 862 | 1 008 | 6 752 | 5 550 | 373 444 |
表3 不同代数‘铁观音’编码区SNP位点统计
Table 3 Summary of coding regions SNP in different generations of ‘Tieguanyin’ tea tree
| 样本 Sample | 非同义突变 Non-synonymous | 同义突变 Synonymous | 终止密码子缺失 Stop loss | 提前终止 Stop gain | 未知 Unknown | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 214 220 | 147 538 | 1 002 | 6 746 | 5 611 | 375 117 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 626 | 147 006 | 999 | 6 769 | 5 617 | 374 017 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 677 | 147 053 | 992 | 6 767 | 5 651 | 374 140 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 213 497 | 147 210 | 998 | 6 753 | 5 562 | 374 020 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 215 605 | 147 805 | 1 003 | 6 875 | 5 688 | 376 976 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 215 234 | 147 446 | 1 016 | 6 857 | 5 747 | 376 300 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 213 272 | 146 862 | 1 008 | 6 752 | 5 550 | 373 444 |
| 样本 Sample | 剪切位点 Splicing | 基因间 Intergenic | 基因上游1K Upstream 1K | 基因下游1K Downstream 1K | 内含子 Intronic | 外显子 Exonic | UTR5 | UTR3 | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 763 | 3 284 018 | 118 826 | 104 746 | 378 518 | 22 430 | 16 414 | 14 256 | 3 939 971 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 757 | 3 224 454 | 115 638 | 102 999 | 374 098 | 22 433 | 16 405 | 14 166 | 3 870 950 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 751 | 3 016 071 | 103 982 | 95 662 | 354 251 | 22 263 | 16 097 | 13 910 | 3 622 987 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 770 | 3 025 491 | 105 106 | 95 894 | 355 677 | 22 179 | 16 123 | 13 938 | 3 635 178 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 776 | 3 658 809 | 144 595 | 11 7148 | 415 208 | 22 351 | 16 732 | 14 615 | 4 390 234 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 776 | 3 641 989 | 143 626 | 11 6725 | 413 129 | 22 376 | 16 688 | 14 583 | 4 369 892 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 751 | 3 030 584 | 105 222 | 96 204 | 355 957 | 22 190 | 16 161 | 13 902 | 3 640 971 |
表4 不同代数‘铁观音’全基因组InDel统计
Table 4 Summary of genome-wide InDel in different generations of ‘Tieguanyin’ tea tree
| 样本 Sample | 剪切位点 Splicing | 基因间 Intergenic | 基因上游1K Upstream 1K | 基因下游1K Downstream 1K | 内含子 Intronic | 外显子 Exonic | UTR5 | UTR3 | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 763 | 3 284 018 | 118 826 | 104 746 | 378 518 | 22 430 | 16 414 | 14 256 | 3 939 971 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 757 | 3 224 454 | 115 638 | 102 999 | 374 098 | 22 433 | 16 405 | 14 166 | 3 870 950 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 751 | 3 016 071 | 103 982 | 95 662 | 354 251 | 22 263 | 16 097 | 13 910 | 3 622 987 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 770 | 3 025 491 | 105 106 | 95 894 | 355 677 | 22 179 | 16 123 | 13 938 | 3 635 178 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 776 | 3 658 809 | 144 595 | 11 7148 | 415 208 | 22 351 | 16 732 | 14 615 | 4 390 234 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 776 | 3 641 989 | 143 626 | 11 6725 | 413 129 | 22 376 | 16 688 | 14 583 | 4 369 892 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 751 | 3 030 584 | 105 222 | 96 204 | 355 957 | 22 190 | 16 161 | 13 902 | 3 640 971 |
| 样本 Sample | 非移码突变 Non-frameshift | 移码突变 Frameshift | 终止密码子缺失 Stop loss | 提前终止 Stop gain | 未知 Unknown | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 8 036 | 13 152 | 76 | 514 | 518 | 22 296 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 8 013 | 13 150 | 84 | 513 | 524 | 22 284 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 8 016 | 12 991 | 78 | 505 | 530 | 22 120 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 7 957 | 13 018 | 81 | 485 | 504 | 22 045 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 7 971 | 13 043 | 81 | 569 | 539 | 22 203 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 7 915 | 13 149 | 85 | 557 | 532 | 22 238 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 7 913 | 13 052 | 80 | 496 | 513 | 22 054 |
表5 不同代数‘铁观音’编码区InDel统计
Table 5 Summary of coding regions InDel in different generations of ‘Tieguanyin’ tea tree
| 样本 Sample | 非移码突变 Non-frameshift | 移码突变 Frameshift | 终止密码子缺失 Stop loss | 提前终止 Stop gain | 未知 Unknown | 总计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 8 036 | 13 152 | 76 | 514 | 518 | 22 296 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 8 013 | 13 150 | 84 | 513 | 524 | 22 284 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 8 016 | 12 991 | 78 | 505 | 530 | 22 120 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 7 957 | 13 018 | 81 | 485 | 504 | 22 045 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 7 971 | 13 043 | 81 | 569 | 539 | 22 203 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 7 915 | 13 149 | 85 | 557 | 532 | 22 238 |
| 龙门铁观音 Longmen Tieguanyin | 7 913 | 13 052 | 80 | 496 | 513 | 22 054 |
| 样本 Sample | 基因组总突变 Genome mutation | 编码区总突变 Coding region mutation | 涉及基因总数 Genes involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 37 827 500 | 397 413 | 29 421 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 37 371 278 | 396 301 | 29 458 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 36 668 542 | 396 260 | 29 454 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 36 666 738 | 396 065 | 29 507 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 38 858 956 | 399 179 | 29 449 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 38 941 232 | 398 538 | 29 427 |
| 龙门铁观音Longmen Tieguanyin | 36 660 452 | 395 498 | 29 459 |
表6 ‘铁观音’无性繁殖不同代数间基因突变统计
Table 6 Summary of mutation in different generations of‘Tieguanyin’tea tree asexual reproduction
| 样本 Sample | 基因组总突变 Genome mutation | 编码区总突变 Coding region mutation | 涉及基因总数 Genes involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| 母树铁观音 Mother tree Tieguanyin | 37 827 500 | 397 413 | 29 421 |
| 第1代无性繁殖铁观音 First generation clonal Tieguanyin | 37 371 278 | 396 301 | 29 458 |
| 第2代无性繁殖铁观音 Second generation clonal Tieguanyin | 36 668 542 | 396 260 | 29 454 |
| 第3代无性繁殖铁观音 Third generation clonal Tieguanyin | 36 666 738 | 396 065 | 29 507 |
| 西坪铁观音 Xiping Tieguanyin | 38 858 956 | 399 179 | 29 449 |
| 参内铁观音 Cannei Tieguanyin | 38 941 232 | 398 538 | 29 427 |
| 龙门铁观音Longmen Tieguanyin | 36 660 452 | 395 498 | 29 459 |

图2 不同代数‘铁观音’与母树间差异基因GO功能富集分析
Fig. 2 GO functional enrichment analysis of differential genes between different generations of‘Tieguanyin’and mother tea tree

图3 不同代数‘铁观音’与母树间差异基因KEGG代谢通路富集分析
Fig. 3 KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of differential genes between different generations of‘Tieguanyin’and mother tea tree
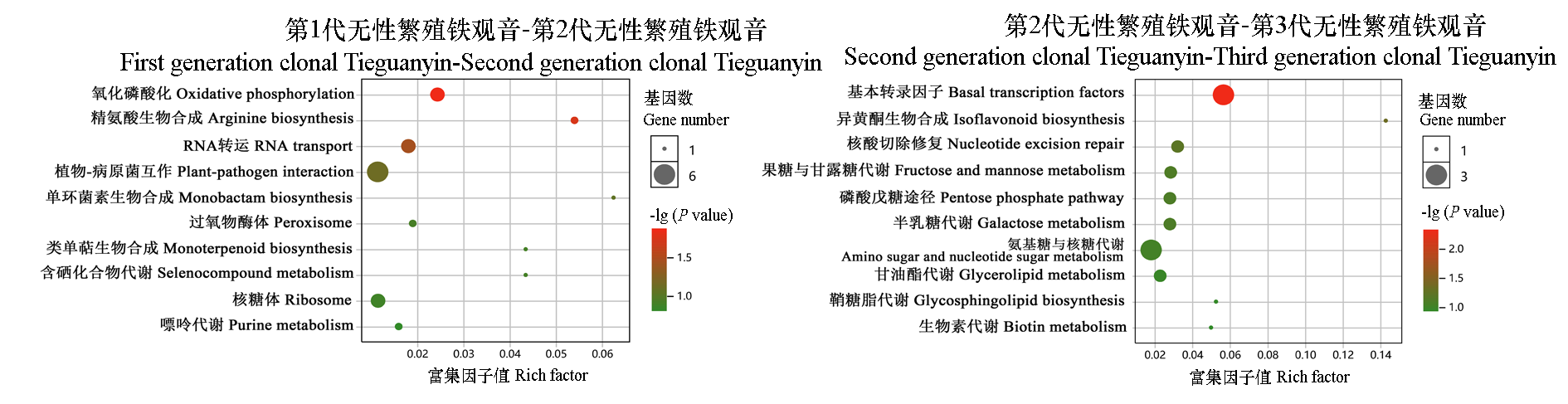
图4 前3代‘铁观音’间差异基因KEGG代谢通路富集分析
Fig. 4 KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis of differential genes between three consecutive asexual reproductions of‘Tieguanyin’tea tree
| 类型Type | ID | 注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| 逆境响应 Stress response | CsTGY02G0001488 | PP2A |
| CsTGY02G0002579 | BTB/POZ | |
| CsTGY03G0000235 | BAT2 domain protein | |
| CsTGY03G0001953 | RPP13 | |
| CsTGY06G0000804 | Lr10 | |
| 生长发育 Growth and development | CsTGY03G0002260 | FAR1 |
| CsTGY07G0002129 | WAT1 | |
| CsTGY12G0000888 | MYB | |
| 酶 Enzyme | CsTGY03G0001145 | 焦磷酸酶基因 PPase |
| CsTGY03G0002361 | 尿苷核苷酶基因 UPP | |
| CsTGY05G0000881 | DNA甲基转移酶基因 DNMT | |
| CsTGY05G0001818 | 醛酮还原酶基因 AKR | |
| CsTGY06G0000171 | 酸性磷酸酶基因 ACP | |
| CsTGY06G0000219 | 氧类固醇结合蛋白酶基因 OSBP | |
| CsTGY07G0001696 | 尿酸氧化酶基因 UO | |
| CsTGY10G0001326 | 锌指结构酶基因 ZFN | |
| CsTGY12G0001281 | 核酸外切酶基因 EXO | |
| CsTGY13G0000964 | 多萜醇激酶基因 DOLK | |
| CsTGY13G0001265 | 细胞色素P450酶基因 CYP450 | |
| CsTGY14G0001226 | 果胶酶抑制蛋白酶基因 PME | |
| 未知 Unknown | CsTGY01G0002129 | / |
| CsTGY01G0003692 | / | |
| CsTGY06G0002804 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0000579 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0001055 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0001417 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0002060 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0001756 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0001967 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0002508 | / | |
| CsTGY12G0000749 | / | |
| CsTGY13G0000037 | / | |
| CsTGY15G0001824 | / |
表7 ‘铁观音’3个生产茶园中均发生变异的基因
Table 7 Variation of genes in three‘Tieguanyin’tea trees used for actual production
| 类型Type | ID | 注释 Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| 逆境响应 Stress response | CsTGY02G0001488 | PP2A |
| CsTGY02G0002579 | BTB/POZ | |
| CsTGY03G0000235 | BAT2 domain protein | |
| CsTGY03G0001953 | RPP13 | |
| CsTGY06G0000804 | Lr10 | |
| 生长发育 Growth and development | CsTGY03G0002260 | FAR1 |
| CsTGY07G0002129 | WAT1 | |
| CsTGY12G0000888 | MYB | |
| 酶 Enzyme | CsTGY03G0001145 | 焦磷酸酶基因 PPase |
| CsTGY03G0002361 | 尿苷核苷酶基因 UPP | |
| CsTGY05G0000881 | DNA甲基转移酶基因 DNMT | |
| CsTGY05G0001818 | 醛酮还原酶基因 AKR | |
| CsTGY06G0000171 | 酸性磷酸酶基因 ACP | |
| CsTGY06G0000219 | 氧类固醇结合蛋白酶基因 OSBP | |
| CsTGY07G0001696 | 尿酸氧化酶基因 UO | |
| CsTGY10G0001326 | 锌指结构酶基因 ZFN | |
| CsTGY12G0001281 | 核酸外切酶基因 EXO | |
| CsTGY13G0000964 | 多萜醇激酶基因 DOLK | |
| CsTGY13G0001265 | 细胞色素P450酶基因 CYP450 | |
| CsTGY14G0001226 | 果胶酶抑制蛋白酶基因 PME | |
| 未知 Unknown | CsTGY01G0002129 | / |
| CsTGY01G0003692 | / | |
| CsTGY06G0002804 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0000579 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0001055 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0001417 | / | |
| CsTGY07G0002060 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0001756 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0001967 | / | |
| CsTGY08G0002508 | / | |
| CsTGY12G0000749 | / | |
| CsTGY13G0000037 | / | |
| CsTGY15G0001824 | / |
| [1] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.705285 URL |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1002/humu.23427 pmid: 29633501 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00531-0 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
陈渝, 邓洁, 陈君愉, 曾亭, 余婷婷, 黄千华, 陈培超, 刘庆, 简伟, 杨星勇. 2021. 番茄FAR1/FHY3转录因子家族的全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物生理学报, 57 (10):1983-1995.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
陈志丹, 林志坤, 林伟东, 孙威江. 2016. 基于表型性状的铁观音茶树种性变化分析. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 45 (6):631-635.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
陈宗懋. 2004. 科技创新和茶产业发展. 中国茶叶, 26 (2):4-7.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12027 URL |
| [11] |
|
|
管梦娇, 谢亚楠, 顾启玉, 孙秀东, 高荣广. 2021. 基于GBS技术的233份大蒜种质资源群体进化分析. 山东农业科学, 53 (4):12-18.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01758-0 |
| [13] |
|
|
李穆, 程志远, 何丽莲, 王先宏, 李富生. 2018. 甘蔗印度种响应干旱胁迫的数字基因表达谱. 分子植物育种, 16 (7):2099-2106.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v110.4 URL |
| [15] |
|
|
李旭娟, 李纯佳, 吴转娣, 田春艳, 胡鑫, 丘立杭, 吴建明, 刘新龙. 2021. 甘蔗HTD2基因的表达特征及基因多态性分析. 作物学报, 48 (7):1601-1613.
|
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.09.004 URL |
| [17] |
|
|
廖天悦. 2021. 基于转录组分析的福鼎大白茶叶片不同发育阶段差异研究[硕士论文]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
林荣溪. 2021. 安溪铁观音营销经验与优化建议. 中国茶叶, 43 (2):36-39.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02349-9 pmid: 32245415 |
| [20] |
|
|
刘玉良, 郑术芝. 2017. 水稻产量相关性状驯化研究进展. 植物学报, 52 (1):113-121.
doi: 10.11983/CBB16148 |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.2017.213.issue-4 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.03.001 URL |
| [23] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0092 |
|
潘鑫峰, 叶方婷, 毛志君, 李兆伟, 范凯. 2022. 睡莲WRKY家族的全基因组鉴定和分子进化分析. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1121-1135.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0092 |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0018 |
|
乔军, 刘婧, 李素文, 王利英. 2022. 基于极端混合池全基因组重测序的茄子萼下果色基因预测. 园艺学报, 49 (3):613-621.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0018 |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06485-7 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1071/CP16187 URL |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.07.007 URL |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00542-x pmid: 33931633 |
| [30] |
|
|
王鹏杰, 曹红利, 陈丹, 陈笛, 陈桂信, 杨江帆, 叶乃兴. 2020. 茶树脂肪酸去饱和酶家族基因的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (6):1141-1152.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0288 |
|
| [31] |
|
|
王鹏杰, 杨江帆, 张兴坦, 叶乃兴. 2021. 茶树基因组与测序技术的研究进展. 茶叶科学, 41 (6):743-752.
|
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1350 |
|
位欣欣, 兰海燕. 2022. 植物MYB转录因子调控次生代谢及逆境响应的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 38 (8):12-23.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1350 |
|
| [33] |
|
|
杨荧. 2019. 安吉白茶白化分子机制研究[硕士论文]. 贵阳: 贵州大学.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
袁金红, 李俊华, 黄小城, 李莎, 高武军. 2015. 基于全基因组重测序的SNP分析在作物基因定位中的研究进展. 植物生理学报, 51 (9):1400-1404.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
詹梓金. 1988. 铁观音原种母树及其品种复壮原理探讨. 福建茶叶,(4):14-16.
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
詹梓金, 巫仁高, 黄志军. 1992. 茶树多代次营养繁殖对遗传稳定性的影响——4个无性系品种的细胞学观察. 茶叶科学, 12 (1):21-26.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
张淑珍, 闫晓飞, 张传忠, 韩丹, 徐鹏飞. 2019. 植物BTB/POZ蛋白及其抗病性研究进展. 大豆科学, 38 (2):311-316.
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00895-y |
| [1] | 彭 华, 王治会, 岳翠男, 杨普香 , 李文金 , 童忠飞, 郭 金. 茶树新品种‘赣茶 5 号’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 199-200. |
| [2] | 郑新强 , 李泽宇 , 李 凯 , 陆建良 , 赵 东 , 叶俭慧 , 叶晶晶 , 李寸羽 , 梁月荣 , . 早生优质茶树新品种‘浙农 301’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 201-202. |
| [3] | 王雷刚, 焦小雨, 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 黄化茶树新品种‘霍黄 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 203-204. |
| [4] | 刘丹丹, 阮 旭, 焦小雨, 王雷刚, 吴 琼, 王文杰. 茶树新品种‘金鸡 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 205-206. |
| [5] | 聂兴华, 张 煜, 刘 松, 杨佳宾, 郝雅琼, 刘 阳, 秦 岭, 邢 宇. 基于基因组重测序的野生板栗遗传特征和分类地位研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1622-1636. |
| [6] | 李宇腾, 陈 瑶, 任恒泽, 李聪聪, 王浩乾, 曹红利, 岳 川, 郝心愿, 王新超. 茶树CsIDM的鉴定、表达分析及互作验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1698. |
| [7] | 王泽涵, 于文涛, 王鹏杰, 刘财国, 樊晓静, 谷梦雅, 蔡春平, 王攀, 叶乃兴. 茶树秃房与茸房种质花器官差异表达基因的WGCNA分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 620-634. |
| [8] | 程庆华, 张志鹏, 吴艳萍, 万宇鹤, 陈应娟. 苦参碱对茶树炭疽菌的抑菌作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 432-440. |
| [9] | 汤雨晴, 杨惠栋, 闫承璞, 王斯妤, 王雨亭, 胡钟东, 朱方红. 基于重测序的‘金兰柚’基因组InDel标记的开发及应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 15-26. |
| [10] | 岳翠男, 王治会, 杨普香, 李文金, 彭 华, 陈罗军, 周汉中. 茶树新品种‘宁州早1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 281-282. |
| [11] | 李兰英, 胥亚琼, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 龚雪蛟, 罗 晟, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘金凤2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 283-284. |
| [12] | 李兰英, 王 强, 龚雪蛟, 刘东娜, 尧 渝, 王迎春, 胥亚琼, 罗 凡, . 茶树新品种‘甘露1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 285-286. |
| [13] | 任志红, 吴焕焕, 肖文敏, 张 虹, 杨圣祥, 孙海伟, 王 健, 高文星. 抗寒茶树新品种‘岱鼎御丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 287-288. |
| [14] | 王治会, 杨普香, 彭 华, 李文金, 王胜利, 鲍润元, 江新凤. 茶树新品种‘浮梁槠叶1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 191-192. |
| [15] | 彭 华, 李文金, 杨普香, 王治会, 岳翠男, 李延升, 谢小群, 李 琛. 早生持嫩性强茶树新品种‘婺绿1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 193-194. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司