
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (12): 2360-2374.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0911
侯黔东1, 沈天娇1, 余欢欢1, 仇志浪1, 文壮1, 张惠敏1,2, 吴亚维3, 文晓鹏1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-01-06
修回日期:2021-05-06
发布日期:2022-01-04
通讯作者:
文晓鹏
E-mail:xpwensc@hotmail.com
基金资助:
HOU Qiandong1, SHEN Tianjiao1, YU Huanhuan1, QIU Zhilang1, WEN Zhuang1, ZHANG Huimin1,2, WU Yawei3, WEN Xiaopeng1,*( )
)
Received:2021-01-06
Revised:2021-05-06
Published:2022-01-04
Contact:
WEN Xiaopeng
E-mail:xpwensc@hotmail.com
摘要:
以甜樱桃(Prunus avium L.)为材料,对IAA酰胺合成酶(Gretchen Hagen 3,GH3)基因家族全基因组进行鉴定及生物信息分析;同时,分析其在不同组织中的表达及对外源GA3、ABA、MeJA、IAA的响应。结果表明,甜樱桃基因组中共存在8个GH3基因,根据在染色体的位置依次命名为PavGH3.1 ~ PavGH3.8,编码区长度为1 683 ~ 1 851 bp,预测大多数基因定位在叶绿体中;PavGH3外显子数3 或 4,且有较多保守基序;除5号和7号染色体外,其他染色体均有分布;启动子存在ABA、MeJA等6种激素响应元件;PavGH3在进化上分为2组,且PavGH3.5和PavGH3.6与拟南芥GH3一些成员存在共线性。表达分析显示,PavGH3.2、PavGH3.6和PavGH3.7为3个主要表达基因。PavGH3.4和PavGH3.5在第2次生理落果中较第1次上调表达,与正常果实相比,第1次生理落果中PavGH3.5和PavGH3.7下调表达,PavGH3.4和PavGH3.6上调表达。PavGH3.2、PavGH3.3、PavGH3.6和PavGH3.7为主要响应激素的基因。推测PavGH3基因家族广泛参与甜樱桃的生长发育,且可能与落果关系密切。
中图分类号:
侯黔东, 沈天娇, 余欢欢, 仇志浪, 文壮, 张惠敏, 吴亚维, 文晓鹏. 甜樱桃GH3基因家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(12): 2360-2374.
HOU Qiandong, SHEN Tianjiao, YU Huanhuan, QIU Zhilang, WEN Zhuang, ZHANG Huimin, WU Yawei, WEN Xiaopeng. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Prunus avium Gretchen Hagen 3(GH3)Gene Family[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12): 2360-2374.
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 扩增产物/bp PCR product | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PavGH3.1 | CAGTTGCAGAAATGCTGTGTCC | TCATGTGGCTTGCTTAGTGGGT | 276 | 61 |
| PavGH3.2 | GGTCCTCAGCAGCCGAATCAC | CCACCCTTCAGAAGCGCCATA | 265 | 64 |
| PavGH3.3 | ACTTCTTTGGTGCCCCTTGCTTC | GTGGTCTGTGCGCTATGGTGTGT | 179 | 65 |
| PavGH3.4 | CTCTTACACCCTCATTCCCTCCAT | CGACTCTCAGCACATCTCCAACT | 224 | 59 |
| PavGH3.5 | CATAGAGGAGACGACCAGGAACA | GGAACTCAGAGATGGGATGAGAGCT | 239 | 62 |
| PavGH3.6 | CTCCCATCTTGTCAGCTCACCCA | GCTCACGAACAGAAAGTACAGGCCC | 197 | 62 |
| PavGH3.7 | CTGTTGAGGTTCTTGGTGGGC | AGTTTTCTCGGGGGGTTGCA | 263 | 60 |
| PavGH3.8 | CTCCCTTGCTTTCTCTGCCTAAT | GACCACAGCCTCAATGTACTTG | 125 | 60 |
| PavEF1-α2 | ATCCAGAGTAGCAGAACCAATCAC | GTTAGGCATCCAGTCCCAGAAT | 127 | 58 |
| PavRSP3 | TCAAGGTCAGGTAAGGGGGTC | GTGAGGTGATTGTTAGTGGAAAGC | 223 | 56.5 |
表1 甜樱桃GH3基因家族荧光定量引物
Table 1 Quantitative real-time PCR primer of Prunus avium GH3 gene family
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 扩增产物/bp PCR product | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PavGH3.1 | CAGTTGCAGAAATGCTGTGTCC | TCATGTGGCTTGCTTAGTGGGT | 276 | 61 |
| PavGH3.2 | GGTCCTCAGCAGCCGAATCAC | CCACCCTTCAGAAGCGCCATA | 265 | 64 |
| PavGH3.3 | ACTTCTTTGGTGCCCCTTGCTTC | GTGGTCTGTGCGCTATGGTGTGT | 179 | 65 |
| PavGH3.4 | CTCTTACACCCTCATTCCCTCCAT | CGACTCTCAGCACATCTCCAACT | 224 | 59 |
| PavGH3.5 | CATAGAGGAGACGACCAGGAACA | GGAACTCAGAGATGGGATGAGAGCT | 239 | 62 |
| PavGH3.6 | CTCCCATCTTGTCAGCTCACCCA | GCTCACGAACAGAAAGTACAGGCCC | 197 | 62 |
| PavGH3.7 | CTGTTGAGGTTCTTGGTGGGC | AGTTTTCTCGGGGGGTTGCA | 263 | 60 |
| PavGH3.8 | CTCCCTTGCTTTCTCTGCCTAAT | GACCACAGCCTCAATGTACTTG | 125 | 60 |
| PavEF1-α2 | ATCCAGAGTAGCAGAACCAATCAC | GTTAGGCATCCAGTCCCAGAAT | 127 | 58 |
| PavRSP3 | TCAAGGTCAGGTAAGGGGGTC | GTGAGGTGATTGTTAGTGGAAAGC | 223 | 56.5 |
| 基因 Gene | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体 chromosome | CDS/bp | 氨基酸 长度/aa Length | 蛋白 分子量 Molecular weight | 理论 等电点 Theoretical pI | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞 定位预测 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PavGH3.1 | Pav_sc0001540.1_g090.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr1 | 1 851 | 616 | 70 875.15 | 5.68 | -0.295 | 细胞质,细胞核 Cytoplasm,nucleus |
| PavGH3.2 | Pav_sc0000254.1_g140.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr2 | 1 683 | 560 | 62 622.79 | 5.80 | -0.136 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.3 | Pav_sc0002360.1_g300.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr3 | 1 794 | 597 | 67 453.09 | 6.45 | -0.212 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.4 | Pav_sc0000269.1_g440.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr4 | 1 845 | 614 | 69 182.12 | 5.91 | -0.272 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.5 | Pav_sc0000049.1_g070.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr6 | 1 800 | 599 | 67 477.05 | 5.81 | -0.265 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.6 | Pav_sc0001422.1_g120.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 803 | 600 | 67 636.32 | 5.56 | -0.258 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.7 | Pav_sc0003065.1_g090.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 725 | 574 | 64 563.26 | 5.92 | -0.096 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.8 | Pav_sc0000848.1_g820.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 806 | 601 | 68 250.59 | 5.87 | -0.196 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
表2 甜樱桃PavGH3基因家族成员信息
Table 2 Member information of PavGH3 gene family in Prunus avium
| 基因 Gene | 基因ID Gene ID | 染色体 chromosome | CDS/bp | 氨基酸 长度/aa Length | 蛋白 分子量 Molecular weight | 理论 等电点 Theoretical pI | 亲水性 GRAVY | 亚细胞 定位预测 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PavGH3.1 | Pav_sc0001540.1_g090.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr1 | 1 851 | 616 | 70 875.15 | 5.68 | -0.295 | 细胞质,细胞核 Cytoplasm,nucleus |
| PavGH3.2 | Pav_sc0000254.1_g140.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr2 | 1 683 | 560 | 62 622.79 | 5.80 | -0.136 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.3 | Pav_sc0002360.1_g300.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr3 | 1 794 | 597 | 67 453.09 | 6.45 | -0.212 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.4 | Pav_sc0000269.1_g440.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr4 | 1 845 | 614 | 69 182.12 | 5.91 | -0.272 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.5 | Pav_sc0000049.1_g070.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr6 | 1 800 | 599 | 67 477.05 | 5.81 | -0.265 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.6 | Pav_sc0001422.1_g120.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 803 | 600 | 67 636.32 | 5.56 | -0.258 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.7 | Pav_sc0003065.1_g090.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 725 | 574 | 64 563.26 | 5.92 | -0.096 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
| PavGH3.8 | Pav_sc0000848.1_g820.1.mk | PAV_r1.0chr8 | 1 806 | 601 | 68 250.59 | 5.87 | -0.196 | 叶绿体 Chloroplast |
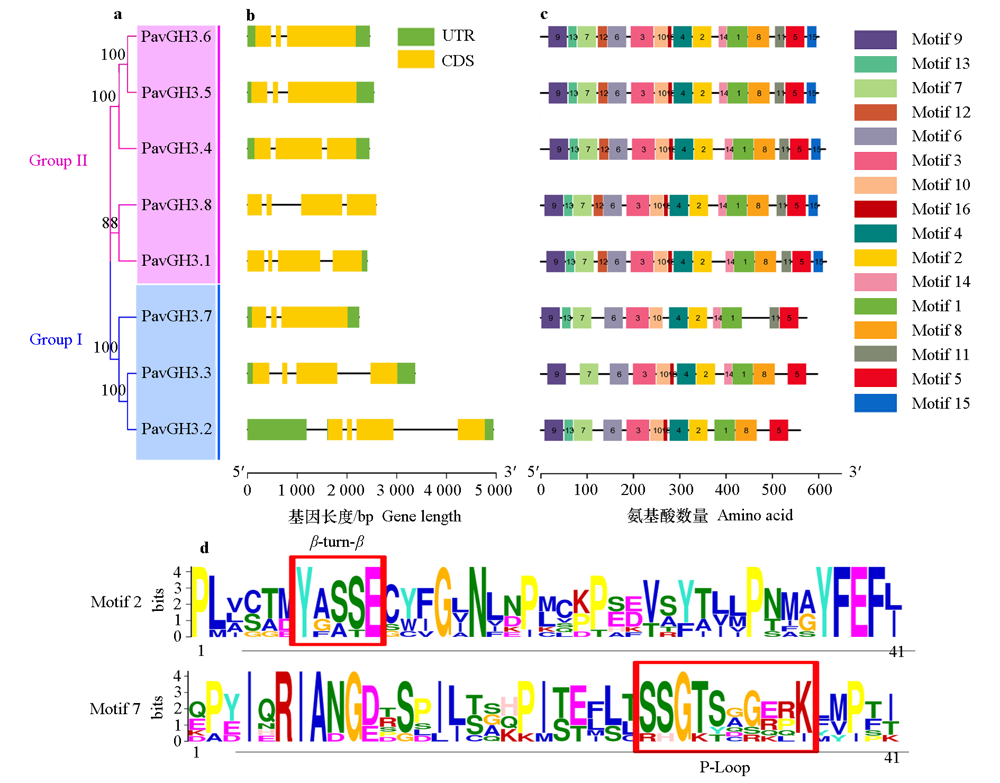
图1 甜樱桃PavGH3基因家族进化树(a)、基因结构(b)、保守结构域(c)及Motif(d)
Fig. 1 Phylogenetic tree(a),gene structure(b),conserved domain(c)and Motif Logo(d)of PavGH3 gene family in Prunus avium
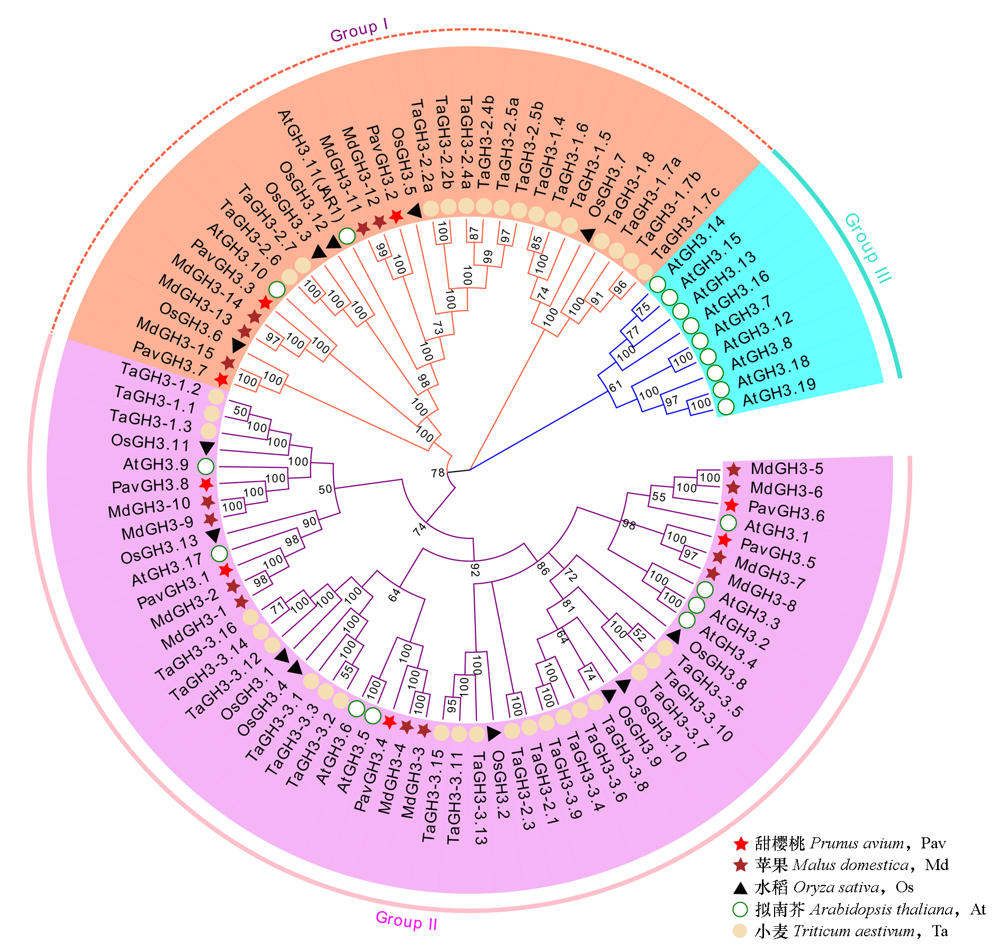
图2 甜樱桃、拟南芥、小麦、苹果及水稻GH3基因家族系统进化树
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of Prunus avium,Arabidopsis thaliana,Triticum aestivum,Malus domestica and Oryza sativa GH3 gene families
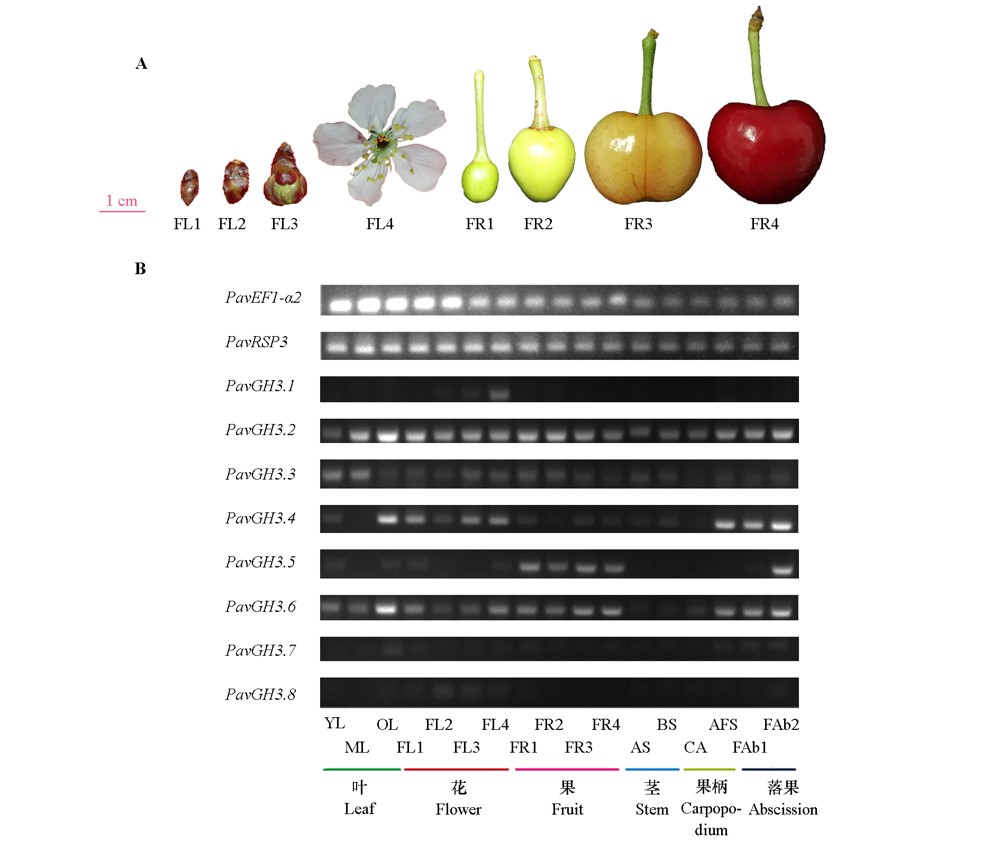
图5 甜樱桃不同组织中的PavGH3半定量 A:不同时期花和果实;B:PavGH3半定量。YL:幼叶;ML:成熟叶;OL:老叶;FL1:休眠花芽;FL2:小花蕾;FL3:开花前花蕾;FL4:盛开花朵;FR1:小果;FR2:中果;FR3:转色期果;FR4:成熟果;AS:一年生茎;BS:二年生茎;CA:果柄;AFS:脱落果柄;FAb1:小果落果;FAb2:中果落果。
Fig. 5 PavGH3 semi-quantitative in different tissue of sweet cherries A:Flowers and fruit;B:Semi-quantitative in sweet cherries. YL:Young leaf;ML:Mature leaf;OL:Old leaf;FL1:Dormant flower bud;FL2:Flower bud;FL3:Flower bud before flowering;FL4:Blooming flowers;FR1:Small fruit;FR2:Middle fruit;FR3:Fruit of red-fleshed;FR4:Ripe fruit;AS:Annual stem;BS:Biennial stem;CA:Carpopodium;AFS:Abscising fruit carpopodium;FAb1:Fruit abscising of small fruit;FAb2:Fruit abscising of middle fruit.
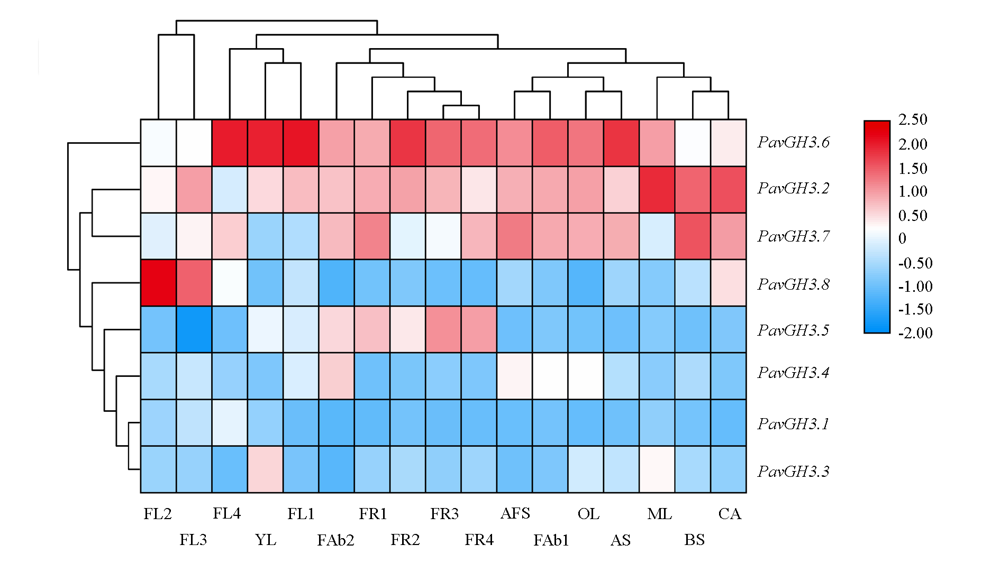
图6 甜樱桃PavGH3基因表达热图 YL:幼叶;ML:成熟叶;OL:老叶;FL1:休眠花芽;FL2:小花蕾;FL3:开花前花蕾;FL4:盛开花朵;FR1:小果;FR2:中果;FR3:转色期果;FR4:成熟果;AS:一年生茎;BS:二年生茎;CA:果柄;AFS:脱落果柄;FAb1:小果落果;FAb2:中果落果。
Fig. 6 PavGH3 gene expression heat map of sweet cherries YL:Young leaf;ML:Mature;OL:Old leaf;FL1:Dormant flower bud;FL2:Flower bud;FL3:Flower bud before flowering;FL4:Blooming flowers;FR1:Small fruit;FR2:Middle fruit;FR3:Fruit of red-fleshed;FR4:Ripe fruit;AS:Annual stem;BS:Biennial stem;CA:Carpopodium;AFS:Abscising fruit carpopodium;FAb1:Fruit abscising of small fruit;FAb2:Fruit abscising of middle fruit.
| [1] |
Abel S, Theologis A. 1996. Early genes and auxin action. Plant Physiology, 111 (1):9-17.
pmid: 8685277 |
| [2] | Bailey T L, Boden M, Buske F A, Frith M, Grant C E, Clementi L, Ren J, Li W W, Noble W S. 2009. MEME SUITE:tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Research, 37 (Web Server issue):W202-208. |
| [3] |
Berens M L, Berry H M, Mine A, Argueso C T, Tsuda K. 2017. Evolution of hormone signaling networks in plant defense. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 55:401-425.
doi: 10.1146/arplant.2004.55.issue-1 URL |
| [4] |
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden T L. 2009. BLAST+:architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics, 10:421.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 URL |
| [5] |
Casanova-Sáez R, Voß U. 2019. Auxin metabolism controls developmental decisions in land plants. Trends in Plant Science, 24 (8):741-754.
doi: S1360-1385(19)30124-4 pmid: 31230894 |
| [6] | Chao J T, Kong Y Z, Wang Q, Sun Y H, Gong D P, Lv J, Liu G S. 2015. MapGene2Chrom,a tool to draw gene physical map based on Perl and SVG languages. Yi Chuan, 37 (1):91-97. |
| [7] |
Chapman E J, Estelle M. 2009. Mechanism of auxin-regulated gene expression in plants. Annual Review of Genetics, 43:265-285.
doi: 10.1146/genet.2009.43.issue-1 URL |
| [8] |
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y, Xia R. 2020. TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [9] | Chen C Y, Ho S S, Kuo T Y, Hsieh H L, Cheng Y S. 2017. Structural basis of jasmonate-amido synthetase FIN219 in complex with glutathione S-transferase FIP 1 during the JA signal regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 114 (10):E1815-E1824. |
| [10] |
Chou K C, Shen H B. 2008. Cell-PLoc:a package of Web servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nature Protocols, 3 (2):153-162.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.494 URL |
| [11] |
Crooks G E, Hon G, Chandonia J M, Brenner S E. 2004. WebLogo:a sequence logo generator. Genome Research, 14 (6):1188-90.
pmid: 15173120 |
| [12] |
Denisov Y, Glick S, Zviran T, Ish-Shalom M, Levin A, Faigenboim A, Cohen Y, Irihimovitch V. 2017. Distinct organ-specific and temporal expression profiles of auxin-related genes during mango fruitlet drop. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 115:439-448.
doi: S0981-9428(17)30143-2 pmid: 28456120 |
| [13] | Du Yi. 2016. The Preliminary study on genes expression and and endogenous hormones quantitation analysis related to IAA and ABA during fruitlet abscission in litchi[M. D. Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 杜艺. 2016. 荔枝落果过程中IAA和ABA相关基因表达及其定量检测初探[硕士论文]. 广州: 华南农业大学. | |
| [14] |
Feng L, Li G R, He Z B, Han W Y, Sun J X, Huang F L, Di J J, Chen Y S. 2019. The ARF,GH3,and Aux/IAA gene families in castor bean(Ricinus communis L.):genome-wide identification and expression profiles in high-stalk and dwarf strains. Industrial Crops and Products, 141:111804.
doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111804 URL |
| [15] |
Feng S, Yue R, Tao S, Yang Y, Zhang L, Xu M, Wang H, Shen C. 2015. Genome-wide identification, expression analysis of auxin-responsive GH 3 family genes in maize(Zea mays L.)under abiotic stresses. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 57 (9):783-95.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12327 URL |
| [16] | Guo H, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Lin L, Cui M, Long Y, Xing Z. 2019. Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in the Asteranae. Plants (Basel), 8 (10):393. |
| [17] |
Gutierrez L, Mongelard G, Floková K, Pacurar D I, Novák O, Staswick P, Kowalczyk M, Pacurar M, Demailly H, Geiss G, Bellini C. 2012. Auxin controls Arabidopsis adventitious root initiation by regulating jasmonic acid homeostasis. Plant Cell, 24 (6):2515-2527.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.099119 URL |
| [18] |
Hagen G, Guilfoyle T. 2002. Auxin-responsive gene expression:genes,promoters and regulatory factors. Plant Molecular Biology, 49 (3-4):373-385.
doi: 10.1023/A:1015207114117 URL |
| [19] |
Hagen G, Kleinschmidt A, Guilfoyle T. 1984. Auxin-regulated gene expression in intact soybean hypocotyl and excised hypocotyl sections. Planta, 162 (2):147-153.
doi: 10.1007/BF00410211 pmid: 24254049 |
| [20] | Jain M, Kaur N, Tyagi A K, Khurana J P. 2006. The auxin-responsive GH 3 gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Functional & Integrative Genomics, 6 (1):36-46. |
| [21] | Khan S, Stone J M. 2007. Arabidopsis thaliana GH3.9 in auxin and jasmonate cross talk. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2 (6):483-485. |
| [22] |
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones S J, Marra M A. 2009. Circos:an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Research, 19 (9):1639-1645.
doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109 pmid: 19541911 |
| [23] |
Kuang J F, Wu J Y, Zhong H Y, Li C Q, Chen J Y, Lu W J, Li J G. 2012. Carbohydrate stress affecting fruitlet abscission and expression of genes related to auxin signal transduction pathway in litchi. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13 (12):16084-16103.
doi: 10.3390/ijms131216084 URL |
| [24] |
Kućko A, Wilmowicz E, Ostrowski M. 2019. Spatio-temporal IAA gradient is determined by interactions with ET and governs flower abscission. Journal of Plant Physiology, 236:51-60.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2019.02.014 URL |
| [25] |
Kumar R, Agarwal P, Tyagi A K, Sharma A K. 2012. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis suggest diverse roles of auxin-responsive GH 3 genes during development and response to different stimuli in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Mol Genet Genomics, 287 (3):221-235.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-011-0672-6 URL |
| [26] |
Kühn N, Serrano A, Abello C, Arce A, Espinoza C, Gouthu S, Deluc L, Arce-Johnson P. 2016. Regulation of polar auxin transport in grapevine fruitlets(Vitis vinifera L.)and the proposed role of auxin homeostasis during fruit abscission. BMC Plant Biology, 16 (1):234.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0914-1 URL |
| [27] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S. 2002. PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 30 (1):325-327. |
| [28] |
Ludwig-Müller J, Jülke S, Bierfreund N M, Decker E L, Reski R. 2009. Moss(Physcomitrella patens)GH 3 proteins act in auxin homeostasis. New Phytologist, 181 (2):323-338.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02677.x pmid: 19032442 |
| [29] | Madeira F, Park Y M, Lee J, Buso N, Gur T, Madhusoodanan N, Basutkar P, Tivey A R N, Potter S C, Finn R D, Lopez R. 2019. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Research, 47 (W1):W636-W641. |
| [30] |
Mockaitis K, Estelle M. 2008. Auxin receptors and plant development:a new signaling paradigm. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 24:55-80.
doi: 10.1146/cellbio.2008.24.issue-1 URL |
| [31] |
Okrent R A, Wildermuth M C. 2011. Evolutionary history of the GH 3 family of acyl adenylases in rosids. Plant Mol Biol, 76 (6):489-505.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9776-y URL |
| [32] |
Ostrowski M, Jakubowska A. 2013. GH 3 expression and IAA-amide synthetase activity in pea(Pisum sativum L.)seedlings are regulated by light,plant hormones and auxinic herbicides. Journal of Plant Physiology, 170 (4):361-368.
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.10.016 pmid: 23332498 |
| [33] |
Paponov I A, Teale W, Lang D, Paponov M, Reski R, Rensing S A, Palme K. 2009. The evolution of nuclear auxin signalling. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 9:126.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-126 pmid: 19493348 |
| [34] |
Pinto R T, Freitas N C, Máximo W P F, Cardoso T B, Prudente D O, Paiva L V. 2019. Genome-wide analysis,transcription factor network approach and gene expression profile of GH3 genes over early somatic embryogenesis in Coffea spp. BMC Genomics, 20 (1):812.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6176-1 URL |
| [35] | Prakash A, Jeffryes M, Bateman A, Finn R D. 2017. The HMMER Web server for protein sequence similarity search. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 60:3.15.1-3.15.23. |
| [36] | Qiu Zhilang, He Meiqian, Wen Zhuang, Yang Kun, Hong Yi, Wen Xiaopeng. 2020. Selection and validation of reference genes in sweet cherry flower bud at different development stages. Seed, 39 (2):37-43. (in Chinese) |
| 仇志浪, 何美乾, 文壮, 杨鵾, 洪怡, 文晓鹏. 2020. 甜樱桃花芽不同发育时期内参基因的筛选与验证. 种子, 39 (2):37-43. | |
| [37] | Robert X, Gouet P. 2014. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Research,42 (Web Server issue):W320-W324. |
| [38] |
Schmittgen T D, Livak K J. 2008. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nature Protocols, 3 (6):1101-1108.
pmid: 18546601 |
| [39] |
Sherp A M, Lee S G, Schraft E, Jez J M. 2018. Modification of auxinic phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides by the acyl acid amido synthetase GH3.15 from Arabidopsis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293 (46):17731-17738.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004975 URL |
| [40] |
Staswick P E, Serban B, Rowe M, Tiryaki I, Maldonado M T, Maldonado M C, Suza W. 2005. Characterization of an Arabidopsis enzyme family that conjugates amino acids to indole-3-acetic acid. Plant Cell, 17 (2):616-627.
pmid: 15659623 |
| [41] |
Staswick P E, Tiryaki I, Rowe M L. 2002. Jasmonate response locus JAR1 and several related Arabidopsis genes encode enzymes of the firefly luciferase superfamily that show activity on jasmonic,salicylic,and indole-3-acetic acids in an assay for adenylation. Plant Cell, 14 (6):1405-1415.
pmid: 12084835 |
| [42] |
Sun R, Wang S, Ma D, Li Y, Liu C. 2019. Genome-wide analysis of cotton auxin early response gene families and their roles in somatic embryogenesis. Genes (Basel), 10 (10):730.
doi: 10.3390/genes10100730 URL |
| [43] |
Terol J, Domingo C, Talón M. 2006. The GH 3 family in plants:genome wide analysis in rice and evolutionary history based on EST analysis. Gene, 371 (2):279-290.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.12.014 URL |
| [44] |
Wang C, Liu Y, Li S S, Han G Z. 2015. Insights into the origin and evolution of the plant hormone signaling machinery. Plant Physiology, 167 (3):872-886.
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.247403 URL |
| [45] |
Wei L, Yang B, Jian H, Zhang A, Liu R, Zhu Y, Ma J, Shi X, Wang R, Li J, Xu X. 2019. Genome-wide identification and characterization of Gretchen Hagen3(GH3)family genes in Brassica napus. Genome, 62 (9):597-608..
doi: 10.1139/gen-2018-0161 URL |
| [46] |
Westfall C S, Sherp A M, Zubieta C, Alvarez S, Schraft E, Marcellin R, Ramirez L, Jez JM. 2016. Arabidopsis thaliana GH3.5 acyl acid amido synthetase mediates metabolic crosstalk in auxin and salicylic acid homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 113(48):13917-13922.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1612635113 URL |
| [47] |
Westfall C S, Zubieta C, Herrmann J, Kapp U, Nanao M H, Jez JM. 2012. Structural basis for prereceptor modulation of plant hormones by GH3 proteins. Science, 336 (6089):1708-1711.
doi: 10.1126/science.1221863 pmid: 22628555 |
| [48] |
Wilkins M R, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez J C, Williams K L, Appel R D, Hochstrasser D F. 1999. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods in Molecular Biology, 112:531-552.
pmid: 10027275 |
| [49] |
Woodward A W, Bartel B. 2005. Auxin:regulation,action,and interaction. Annals of Botany, 95 (5):707-735.
pmid: 15749753 |
| [50] |
Xie R, Pang S, Ma Y, Deng L, He S, Yi S, Lv Q, Zheng Y. 2015. The ARF,AUX/IAA and GH 3 gene families in citrus:genome-wide identification and expression analysis during fruitlet drop from abscission zone A. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 290 (6):2089-105.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1063-1 URL |
| [51] |
Yang Y, Yue R, Sun T, Zhang L, Chen W, Zeng H, Wang H, Shen C. 2015. Genome-wide identification,expression analysis of GH3 family genes in Medicago truncatula under stress-related hormones and Sinorhizobium meliloti infection. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 99 (2):841-854.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6311-5 URL |
| [52] |
Yu D, Qanmber G, Lu L, Wang L, Li J, Yang Z, Liu Z, Li Y, Chen Q, Mendu V, Li F, Yang Z. 2018. Genome-wide analysis of cotton GH 3 subfamily II reveals functional divergence in fiber development,hormone response and plant architecture. BMC Plant Biology, 18 (1):350.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1545-5 URL |
| [53] |
Yuan H, Zhao K, Lei H, Shen X, Liu Y, Liao X, Li T. 2013. Genome-wide analysis of the GH3 family in apple (Malus × domestica). BMC Genomics, 14:297.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-297 URL |
| [54] | Zeng Wen-fang, Pan Lei, Niu Liang, Lu Zhen-hua, Cui Guo-chao, Wang Zhi-qiang. 2015. Bioinformatics analysis and expression of the nectarine indole-3-aceticacid-amido synthase(GH3)gene family during fruit development. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (5):833-842. (in Chinese) |
| 曾文芳, 潘磊, 牛良, 鲁振华, 崔国朝, 王志强. 2015. 桃GH3基因家族的生物信息学分析及其在果实发育中的表达. 园艺学报, 42 (5):833-842. | |
| [55] |
Zhang C, Zhang L, Wang D, Ma H, Liu B, Shi Z, Ma X, Chen Y, Chen Q. 2018. Evolutionary history of the glycoside hydrolase 3(GH3)family based on the sequenced genomes of 48 plants and identification of jasmonic acid-related GH3 proteins in Solanum tuberosum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19 (7):1850.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19071850 URL |
| [56] | Zhang He. 2013. Mechanism of dwarfing effect of M9 used as rootstock or interstem for apple[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 张鹤. 2013. 苹果砧木M9作自根砧或中间砧的致矮机理研究[博士论文]. 北京: 中国农业大学. | |
| [57] |
Zhao Y. 2018. Essential roles of local auxin biosynthesis in plant development and in adaptation to environmental changes. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 69:417-435.
doi: 10.1146/arplant.2018.69.issue-1 URL |
| [58] |
Zuo X H, Xu T, Qi M F, Lü S S, Li J H, Gao S, Li T L. 2012. Expression patterns of auxin-responsive genes during tomato flower pedicel abscission and potential effects of calcium. Australian Journal of Botany, 60 (1):68.
doi: 10.1071/BT10271 URL |
| [1] | 于婷婷, 李 欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [3] | 赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [4] | 吴延军, 刘庆忠, 陈鸿才, 戚行江, 朱东姿, 郑家祥, 曹学敏, 方丹燕. 甜樱桃新品种‘江南锦’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 29-30. |
| [5] | 张晓明, 闫国华, 周 宇, 王 晶, 段续伟, 吴传宝, 张开春. 甜樱桃砧木新品种‘京春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [6] | 高彦龙, 吴玉霞, 张仲兴, 王双成, 张瑞, 张德, 王延秀. 苹果ELO家族基因鉴定及其在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [7] | 刘金明, 郭彩华, 袁星, 亢超, 全绍文, 牛建新. 梨Dof家族基因鉴定及其在宿存与脱落萼片中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1637-1649. |
| [8] | 邱子文, 刘林敏, 林永盛, 林晓洁, 李永裕, 吴少华, 杨超. 千层金MbEGS基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [9] | 郑林, 王帅, 刘语诺, 杜美霞, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 柑橘响应黄龙病菌侵染的NAC基因的克隆及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [10] | 马维峰, 李艳梅, 马宗桓, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 苹果POD家族基因的鉴定与MdPOD15的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [11] | 张凯, 麻明英, 王萍, 李益, 金燕, 盛玲, 邓子牛, 马先锋. 柑橘HSP20家族基因鉴定及其响应溃疡病菌侵染表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [12] | 梁晨, 孙如意, 向锐, 孙艺萌, 师校欣, 杜国强, 王莉. 葡萄生长调控因子GRF家族基因的鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [13] | 李丽仙, 王烁, 陈莹, 邬滢涛, 王雅倩, 房月, 陈学森, 田长平, 冯守千. 甜樱桃PavMYB10.1促进PavRiant表达和花青苷积累[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1023-1030. |
| [14] | 肖学宸, 刘梦雨, 蒋梦琦, 陈燕, 薛晓东, 周承哲, 吴兴健, 吴君楠, 郭寅生, 叶开温, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 龙眼褪黑素合成途径SNAT、ASMT和COMT家族基因鉴定及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [15] | 高玮林, 张力曼, 薛超玲, 张垚, 刘孟军, 赵锦. 枣E类MADS基因在花和果中的表达及其蛋白互作研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司