
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 533-544.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0113
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yanyan1, DING Ying1, LIU Xinghua1, ZHENG Jiaqiu1, LIU Zhiqin2,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-30
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-03-25
Published:2024-03-22
Contact:
LIU Zhiqin
LIU Yanyan, DING Ying, LIU Xinghua, ZHENG Jiaqiu, LIU Zhiqin. Identification of Pepper CaSYT1 and Its Function in Phytophthora capsici Infection[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 533-544.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0113
| 用途 Usage | 基因 Gene | 正向序列(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 反向序列(5′-3′) Reverse sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实时荧光定量 qRT-PCR | CaSYT1 | ATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AATTGGTGCCGCAATATCTT |
| CaPR1(Rezaul et al., | CAGGATGCAACACTCTGGTGG | ATCAAAGGCCGGTTGGTC | |
| CaHIR1(Choi et al., | GACATGGTCCTGGTAACCCA | CCCAACAGAAGCCTGAAGAA | |
| CaNPR1(Dong, | ACTTCTTCGCCGACGCCAAG | GCCAACACATTCACCAGAGCATC | |
| CaDEF1(Do et al., | GAGGAAGAAGTTTGAAAG | GAAATACACCACATGAAG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建Construction of subcellular localization vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCGCTGCAATGGCGAACTGCATCT |
| 瞬时表达载体构建Construction of transient overexpression vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCTCAAGATGCAGTTCGCCATT |
| 沉默载体构建 Construction of silent vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCAATTGGTGCCGCAATATCTT |
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| 用途 Usage | 基因 Gene | 正向序列(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 反向序列(5′-3′) Reverse sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 实时荧光定量 qRT-PCR | CaSYT1 | ATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AATTGGTGCCGCAATATCTT |
| CaPR1(Rezaul et al., | CAGGATGCAACACTCTGGTGG | ATCAAAGGCCGGTTGGTC | |
| CaHIR1(Choi et al., | GACATGGTCCTGGTAACCCA | CCCAACAGAAGCCTGAAGAA | |
| CaNPR1(Dong, | ACTTCTTCGCCGACGCCAAG | GCCAACACATTCACCAGAGCATC | |
| CaDEF1(Do et al., | GAGGAAGAAGTTTGAAAG | GAAATACACCACATGAAG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建Construction of subcellular localization vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCGCTGCAATGGCGAACTGCATCT |
| 瞬时表达载体构建Construction of transient overexpression vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCTCAAGATGCAGTTCGCCATT |
| 沉默载体构建 Construction of silent vectors | CaSYT1 | AAAAAGCAGGCTACATGGGTTTTGTGAGTACGAT | AGAAAGCTGGGTCAATTGGTGCCGCAATATCTT |
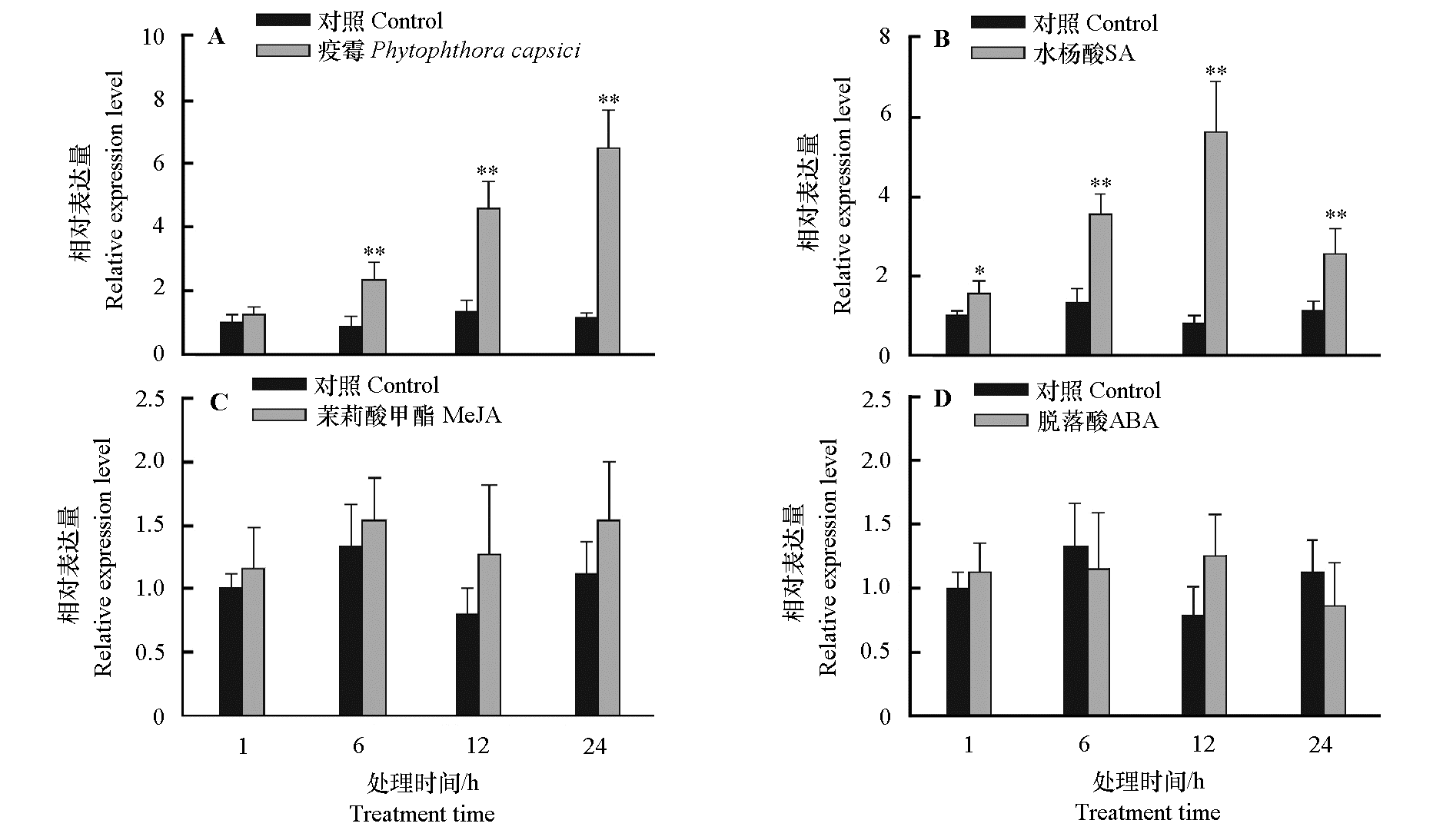
Fig. 3 The transcriptional expression levels of CaSYT1 in pepper plant leaves inoculated with Phytophthora capsica and treated with different exogenous phytohormones * and ** indicate that there are significant difference at the levels of P < 0.05 and P < 0.01. The same below.

Fig. 8 CaSYT1-silencing enhances pepper’s resistance to Phytophthora capsici inoculation A:The phenotype of CaPDS-silenced pepper plant three weeks post agro-infiltration. B:The relative expression of CaSYT1 was detected by real-time RT-PCR 24h after inoculation with Phytophthora capsici. C:Phenotype of pepper seedlings after inoculation with Phytophthora capsici. D:Diseased spots on isolated leaves of pepper after inoculation of Phytophthora capsici. E:Real-time RT-PCR detection of transcriptional levels of related resistance genes in pepper leaves.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2006.12.001 pmid: 17174083 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.11.007 pmid: 16356717 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.12.039 pmid: 18201575 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-10-0030 pmid: 20635864 |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1016/s1369-5266(02)00275-3 pmid: 12179966 |
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.06.015 pmid: 26166780 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006339200 pmid: 11073945 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00260 pmid: 25792253 |
| [23] |
pmid: 1985919 |
| [24] |
pmid: 8771209 |
| [25] |
|
|
钱田田. 2021. Tcb3和SYT1在内质网—细胞膜互作中的功能与机制研究[硕士论文]. 南京: 南京师范大学.
|
|
| [26] |
pmid: 15911881 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.12759 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
张丽. 2018. 辣椒疫霉菌(Phytophthora capsici)RxLR效应因子的克隆与功能分析[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0103 |
|
邹学校, 马艳青, 戴雄泽, 李雪峰, 杨莎. 2020. 辣椒在中国的传播与产业发展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1715-1726.
|
| [1] | GUO Changquan, LI Danqi, HUI Xinran, ZHENG Jingya, HOU Menglu, and ZHU Yongxing, . Identification and Expression Pattern Analysis of DUF966 Gene Family Members in Ginger [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2031-2047. |
| [2] | ZHAO Jiaying, ZENG Zhouting, CEN Xinying, SHI Jiaoqi, LI Xiaoxian, SHEN Xiaoxia, and YU Zhenming, . Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CCO Gene Family in Dendrobium officinale During Flower Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [3] | LI Yuteng, CHEN Yao, REN Hengze, LI Congcong, WANG Haoqian, CAO Hongli, YUE Chuan, HAO Xinyuan, WANG Xinchao. Identification,Expression Analysis and Interaction Validation of CsIDM in Tea Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1679-1696. |
| [4] | XUE Zhenzhen, GUAN Hongfa, LI Na, LI Lingfei, ZHONG Chunmei. Genome-wide Identification of GASA Family and Preliminary Exploration of Leaf Variegation Formation in Begonia masoniana [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1482-1494. |
| [5] | WANG Tonghuan, WU Yuxin, WU Yiyuan, LI Xinxin, LIU Mengyang, YANG Lianlian, LI Jiapeng, ZHANG Zhongshan, CAO Fang, ZHONG Xueting, WANG Zhanqi. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the GRAS Gene Family in Response to Cold Stress in Chrysanthemum nankingense [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 815-830. |
| [6] | LIU Hui, HUANG Ting, TAO Jianping, ZHANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Rongrong, SONG Liuxia, ZHAO Tongmin, YOU Xiong, XIONG Aisheng. Analysis of Circadian Clock Genes SlLNK1,SlEID1,and SlELF3 Response to Photoperiod in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2079-2090. |
| [7] | WANG Yixi, YAN Shuangshuang, YU Bingwei, GAN Yuwei, QIU Zhengkun, ZHU Zhangsheng, CHEN Changming, CAO Bihao. Screening and Identification of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Genes Relate to Bacterial Wilt Resistance in Eggplant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2271-2287. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [9] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [10] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [11] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [12] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [13] | ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. Identification of HSP20 Family Genes in Citrus and Their Expression in Pathogen Infection Responses Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [14] | LIANG Chen, SUN Ruyi, XIANG Rui, SUN Yimeng, SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, WANG Li. Genome-wide Identification of Grape GRF Family and Expression Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [15] | XIAO Xuechen, LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, XUE Xiaodong, ZHOU Chengzhe, WU Xingjian, WU Junnan, GUO Yinsheng, YEH Kaiwen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Whole-genome Identification and Expression Analysis of SNAT,ASMT and COMT Families of Melatonin Synthesis Pathway in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd