
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 597-612.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0942
• Research Notes • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Shuting, XUE Xiaodong, XIAO Xuechen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling*( )
)
Received:2021-05-31
Revised:2021-09-09
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-03-25
Contact:
LIN Yuling
E-mail:buliang84@163.com
CLC Number:
LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Shuting, XUE Xiaodong, XIAO Xuechen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of GDSL Esterase/Lipase Genes in Dimocarpus longan[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 597-612.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0942
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dlo000316 | DLGDSL1 | 1 167 | 388 | 42.94 | 5.42 | 28.17 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo001274 | DLGDSL2 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.98 | 7.52 | 33.37 | -0.16 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo001275 | DLGDSL3 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.82 | 6.93 | 32.28 | -0.15 | 有 Yes | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo003341 | DLGDSL4 | 1 023 | 340 | 37.70 | 6.33 | 34.55 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞骨架Cytoskleton |
| Dlo003368 | DLGDSL5 | 867 | 288 | 31.79 | 7.59 | 32.64 | -0.12 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo003369 | DLGDSL6 | 1 083 | 360 | 38.37 | 8.00 | 28.46 | 0.18 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo003726 | DLGDSL7 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.07 | 9.20 | 27.33 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo003857 | DLGDSL8 | 1 446 | 481 | 53.08 | 5.23 | 34.14 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo004146 | DLGDSL9 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.31 | 5.55 | 39.39 | 0.04 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo004148 | DLGDSL10 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.39 | 8.43 | 29.70 | -0.05 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo004149 | DLGDSL11 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.58 | 8.17 | 35.43 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004150 | DLGDSL12 | 1 107 | 368 | 40.63 | 8.99 | 35.60 | -0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004345 | DLGDSL13 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.72 | 5.62 | 37.99 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004346 | DLGDSL14 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.19 | 9.25 | 39.46 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004347 | DLGDSL15 | 1 110 | 369 | 40.53 | 8.78 | 30.98 | -0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004495 | DLGDSL16 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.69 | 6.10 | 37.58 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004496 | DLGDSL17 | 999 | 332 | 36.12 | 9.05 | 36.33 | 0 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004497 | DLGDSL18 | 999 | 332 | 36.12 | 9.05 | 36.33 | 0 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004498 | DLGDSL19 | 1 074 | 357 | 39.06 | 8.45 | 31.23 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo005884 | DLGDSL20 | 1 164 | 387 | 42.84 | 8.56 | 32.73 | 0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo006046 | DLGDSL21 | 996 | 331 | 37.43 | 9.52 | 28.81 | -0.27 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006047 | DLGDSL22 | 624 | 207 | 23.36 | 5.35 | 47.05 | -0.58 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006048 | DLGDSL23 | 1 131 | 376 | 41.79 | 6.20 | 22.52 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006049 | DLGDSL24 | 1 119 | 372 | 41.79 | 9.21 | 39.46 | -0.35 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo006050 | DLGDSL25 | 1 686 | 561 | 62.33 | 9.24 | 31.14 | -0.27 | 无 No | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo006051 | DLGDSL26 | 1 098 | 365 | 40.35 | 9.34 | 25.33 | -0.48 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006445 | DLGDSL27 | 1 146 | 381 | 41.12 | 8.94 | 27.42 | 0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo006446 | DLGDSL28 | 1 002 | 333 | 35.79 | 9.15 | 21.43 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo007129 | DLGDSL29 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.16 | 5.02 | 33.49 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo007130 | DLGDSL30 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.32 | 4.69 | 33.41 | -0.16 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo007131 | DLGDSL31 | 561 | 186 | 20.53 | 4.56 | 33.37 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo007132 | DLGDSL32 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.21 | 4.60 | 30.37 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo008436 | DLGDSL33 | 1 050 | 349 | 39.54 | 4.82 | 27.58 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞质/细胞外基质 Cytoplasm/Extracell |
| Dlo008488 | DLGDSL34 | 918 | 305 | 34.06 | 8.91 | 30.33 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo008489 | DLGDSL35 | 1 107 | 368 | 40.66 | 7.03 | 29.22 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/液泡 Nucleus/Vacuole |
| Dlo008490 | DLGDSL36 | 1 005 | 334 | 37.49 | 7.55 | 27.31 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo008545 | DLGDSL37 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.92 | 8.56 | 34.17 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo008546 | DLGDSL38 | 222 | 73 | 8.09 | 5.60 | 14.08 | -0.46 | 无 No | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo011392 | DLGDSL39 | 894 | 297 | 32.80 | 7.65 | 35.26 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011415 | DLGDSL40 | 894 | 297 | 32.75 | 7.65 | 33.93 | 0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011478 | DLGDSL41 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.15 | 7.11 | 34.06 | -0.17 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011955 | DLGDSL42 | 1 311 | 436 | 48.64 | 9.01 | 37.95 | -0.24 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/液泡 Chloroplast/Vacuole |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| Dlo011956 | DLGDSL43 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.77 | 6.44 | 30.29 | -0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo012251 | DLGDSL44 | 1 353 | 450 | 50.16 | 5.44 | 36.36 | -0.13 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo012654 | DLGDSL45 | 1 131 | 376 | 40.78 | 5.38 | 36.22 | 0.05 | 有 Yes | 线粒体/液泡 Mitochondrion/Vacuole |
| Dlo013347 | DLGDSL46 | 1 581 | 526 | 57.80 | 7.19 | 32.54 | -0.06 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo013348 | DLGDSL47 | 759 | 252 | 27.24 | 5.80 | 26.12 | 0.10 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo013350 | DLGDSL48 | 414 | 137 | 14.69 | 4.53 | 27.80 | 0.29 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo013351 | DLGDSL49 | 633 | 210 | 23.36 | 6.74 | 35.80 | -0.09 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo013352 | DLGDSL50 | 462 | 153 | 16.18 | 8.61 | 36.41 | 0.26 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo014916 | DLGDSL51 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.33 | 8.89 | 24.93 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo015050 | DLGDSL52 | 1 092 | 363 | 39.38 | 5.09 | 22.52 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo015051 | DLGDSL53 | 1 047 | 348 | 38.79 | 9.18 | 30.01 | -0.34 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo015279 | DLGDSL54 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.56 | 9.09 | 41.62 | 0.17 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo015440 | DLGDSL55 | 414 | 137 | 15.35 | 10.03 | 55.39 | 0.14 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo015441 | DLGDSL56 | 897 | 298 | 33.14 | 5.96 | 46.73 | 0.08 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo015778 | DLGDSL57 | 1 119 | 372 | 40.88 | 8.78 | 22.47 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/Nucleus |
| Dlo016597 | DLGDSL58 | 1 044 | 347 | 37.54 | 5.06 | 34.60 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018044 | DLGDSL59 | 489 | 162 | 17.84 | 9.51 | 58.45 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018809 | DLGDSL60 | 1 266 | 421 | 46.81 | 6.21 | 38.27 | -0.28 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018810 | DLGDSL61 | 2 301 | 766 | 85.50 | 5.89 | 37.09 | -0.40 | 无 No | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018811 | DLGDSL62 | 1 095 | 364 | 40.33 | 5.43 | 36.78 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018812 | DLGDSL63 | 1 155 | 384 | 41.98 | 8.63 | 39.42 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018813 | DLGDSL64 | 1 002 | 333 | 37.13 | 9.22 | 31.41 | -0.09 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo018821 | DLGDSL65 | 1 155 | 384 | 42.61 | 8.78 | 34.10 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo018822 | DLGDSL66 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.14 | 8.93 | 34.50 | -0.05 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo018823 | DLGDSL67 | 1 155 | 384 | 41.99 | 8.63 | 39.92 | -0.13 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018824 | DLGDSL68 | 1 200 | 399 | 44.02 | 5.70 | 35.37 | -0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018825 | DLGDSL69 | 1 236 | 411 | 45.68 | 6.07 | 41.05 | -0.29 | 无 No | 叶绿体/线粒体 Chloroplast/Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018826 | DLGDSL70 | 1 182 | 393 | 43.94 | 7.60 | 35.32 | -0.31 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018827 | DLGDSL71 | 711 | 236 | 26.64 | 7.03 | 37.54 | -0.31 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018828 | DLGDSL72 | 591 | 196 | 21.55 | 8.62 | 38.79 | -0.23 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/质膜 Nucleus/Plasma membrane |
| Dlo018829 | DLGDSL73 | 1 185 | 394 | 43.98 | 5.42 | 34.99 | -0.18 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018866 | DLGDSL74 | 2 490 | 829 | 87.76 | 8.83 | 45.02 | -0.72 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo018888 | DLGDSL75 | 1 413 | 470 | 50.96 | 8.88 | 41.37 | -0.26 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo020895 | DLGDSL76 | 1 071 | 356 | 39.13 | 7.53 | 28.29 | -0.09 | 无 No | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo020898 | DLGDSL77 | 858 | 285 | 31.37 | 5.33 | 32.75 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo021059 | DLGDSL78 | 858 | 285 | 31.36 | 5.33 | 32.18 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo021062 | DLGDSL79 | 1 071 | 356 | 39.17 | 6.88 | 29.62 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo021694 | DLGDSL80 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.98 | 5.69 | 22.79 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo021696 | DLGDSL81 | 1 095 | 364 | 40.80 | 9.08 | 31.63 | 0.05 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo021719 | DLGDSL82 | 1 140 | 379 | 41.98 | 8.65 | 42.73 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo021829 | DLGDSL83 | 2 457 | 818 | 91.37 | 8.14 | 46.45 | -0.34 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| Dlo021830 | DLGDSL84 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.06 | 5.54 | 30.40 | -0.27 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质/高尔基体 Extracell/Golgi apparatus |
| Dlo021839 | DLGDSL85 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.78 | 9.30 | 32.43 | -0.25 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo022859 | DLGDSL86 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.22 | 5.64 | 34.26 | 0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/液泡 Chloroplast/vacu |
| Dlo023097 | DLGDSL87 | 1 131 | 376 | 40.93 | 9.29 | 31.76 | 0.07 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo024293 | DLGDSL88 | 444 | 147 | 16.44 | 8.81 | 31.55 | -0.09 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024294 | DLGDSL89 | 567 | 188 | 21.66 | 6.73 | 24.42 | -0.33 | 无 No | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton |
| Dlo024299 | DLGDSL90 | 465 | 154 | 17.31 | 7.69 | 20.21 | -0.05 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024338 | DLGDSL91 | 1 284 | 427 | 47.21 | 8.25 | 38.18 | -0.26 | 无 No | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo024344 | DLGDSL92 | 972 | 323 | 36.11 | 6.55 | 31.35 | -0.17 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024345 | DLGDSL93 | 972 | 323 | 36.11 | 6.55 | 31.35 | -0.17 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024482 | DLGDSL94 | 1 023 | 340 | 37.62 | 8.80 | 37.81 | -0.19 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo025454 | DLGDSL95 | 1 110 | 369 | 41.35 | 5.63 | 36.29 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo026075 | DLGDSL96 | 1 062 | 353 | 38.56 | 8.47 | 33.85 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo027030 | DLGDSL97 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.93 | 8.65 | 33.01 | -0.21 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞质 Chloroplast/Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027031 | DLGDSL98 | 1 068 | 355 | 39.56 | 8.01 | 31.74 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo027690 | DLGDSL99 | 1 176 | 391 | 44.02 | 6.60 | 38.14 | -0.33 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/细胞质 Nucleus/Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027692 | DLGDSL100 | 810 | 269 | 30.17 | 6.44 | 40.11 | -0.19 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027693 | DLGDSL101 | 1 140 | 379 | 42.41 | 6.07 | 36.44 | -0.27 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo028167 | DLGDSL102 | 1 041 | 346 | 38.63 | 5.39 | 27.19 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo028168 | DLGDSL103 | 960 | 319 | 35.64 | 5.22 | 34.19 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo029634 | DLGDSL104 | 1 077 | 358 | 39.45 | 9.08 | 32.22 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo030986 | DLGDSL105 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.23 | 5.37 | 31.80 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo031180 | DLGDSL106 | 810 | 269 | 28.88 | 5.12 | 27.46 | 0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo031921 | DLGDSL107 | 1 170 | 389 | 43.18 | 8.78 | 36.17 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo032044 | DLGDSL108 | 804 | 267 | 29.89 | 7.09 | 50.80 | -0.26 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo032046 | DLGDSL109 | 798 | 265 | 29.70 | 5.63 | 47.67 | -0.03 | 无 No | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo032495 | DLGDSL110 | 1 263 | 420 | 47.18 | 4.82 | 49.24 | -0.06 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo032524 | DLGDSL111 | 1 149 | 382 | 42.75 | 6.01 | 33.02 | -0.02 | 无 No | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo033028 | DLGDSL112 | 2 433 | 810 | 92.63 | 7.25 | 43.64 | -0.36 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo033030 | DLGDSL113 | 369 | 122 | 13.62 | 8.16 | 27.10 | 0.06 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo033228 | DLGDSL114 | 1 146 | 381 | 41.12 | 8.94 | 27.42 | 0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo033229 | DLGDSL115 | 1 092 | 363 | 38.87 | 8.97 | 20.51 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo033340 | DLGDSL116 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.19 | 5.41 | 34.06 | 0.12 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo034402 | DLGDSL117 | 756 | 251 | 27.63 | 9.24 | 34.38 | -0.24 | 无 No | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo034801 | DLGDSL118 | 1 122 | 373 | 41.26 | 7.45 | 31.18 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
Table 1 The physicochemical properties of the proteins of DlGDSL family members
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dlo000316 | DLGDSL1 | 1 167 | 388 | 42.94 | 5.42 | 28.17 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo001274 | DLGDSL2 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.98 | 7.52 | 33.37 | -0.16 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo001275 | DLGDSL3 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.82 | 6.93 | 32.28 | -0.15 | 有 Yes | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo003341 | DLGDSL4 | 1 023 | 340 | 37.70 | 6.33 | 34.55 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞骨架Cytoskleton |
| Dlo003368 | DLGDSL5 | 867 | 288 | 31.79 | 7.59 | 32.64 | -0.12 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo003369 | DLGDSL6 | 1 083 | 360 | 38.37 | 8.00 | 28.46 | 0.18 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo003726 | DLGDSL7 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.07 | 9.20 | 27.33 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo003857 | DLGDSL8 | 1 446 | 481 | 53.08 | 5.23 | 34.14 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo004146 | DLGDSL9 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.31 | 5.55 | 39.39 | 0.04 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo004148 | DLGDSL10 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.39 | 8.43 | 29.70 | -0.05 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo004149 | DLGDSL11 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.58 | 8.17 | 35.43 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004150 | DLGDSL12 | 1 107 | 368 | 40.63 | 8.99 | 35.60 | -0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004345 | DLGDSL13 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.72 | 5.62 | 37.99 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004346 | DLGDSL14 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.19 | 9.25 | 39.46 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004347 | DLGDSL15 | 1 110 | 369 | 40.53 | 8.78 | 30.98 | -0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004495 | DLGDSL16 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.69 | 6.10 | 37.58 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004496 | DLGDSL17 | 999 | 332 | 36.12 | 9.05 | 36.33 | 0 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004497 | DLGDSL18 | 999 | 332 | 36.12 | 9.05 | 36.33 | 0 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo004498 | DLGDSL19 | 1 074 | 357 | 39.06 | 8.45 | 31.23 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo005884 | DLGDSL20 | 1 164 | 387 | 42.84 | 8.56 | 32.73 | 0.01 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo006046 | DLGDSL21 | 996 | 331 | 37.43 | 9.52 | 28.81 | -0.27 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006047 | DLGDSL22 | 624 | 207 | 23.36 | 5.35 | 47.05 | -0.58 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006048 | DLGDSL23 | 1 131 | 376 | 41.79 | 6.20 | 22.52 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo006049 | DLGDSL24 | 1 119 | 372 | 41.79 | 9.21 | 39.46 | -0.35 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo006050 | DLGDSL25 | 1 686 | 561 | 62.33 | 9.24 | 31.14 | -0.27 | 无 No | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo006051 | DLGDSL26 | 1 098 | 365 | 40.35 | 9.34 | 25.33 | -0.48 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo006445 | DLGDSL27 | 1 146 | 381 | 41.12 | 8.94 | 27.42 | 0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo006446 | DLGDSL28 | 1 002 | 333 | 35.79 | 9.15 | 21.43 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo007129 | DLGDSL29 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.16 | 5.02 | 33.49 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo007130 | DLGDSL30 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.32 | 4.69 | 33.41 | -0.16 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo007131 | DLGDSL31 | 561 | 186 | 20.53 | 4.56 | 33.37 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo007132 | DLGDSL32 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.21 | 4.60 | 30.37 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo008436 | DLGDSL33 | 1 050 | 349 | 39.54 | 4.82 | 27.58 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞质/细胞外基质 Cytoplasm/Extracell |
| Dlo008488 | DLGDSL34 | 918 | 305 | 34.06 | 8.91 | 30.33 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo008489 | DLGDSL35 | 1 107 | 368 | 40.66 | 7.03 | 29.22 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/液泡 Nucleus/Vacuole |
| Dlo008490 | DLGDSL36 | 1 005 | 334 | 37.49 | 7.55 | 27.31 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo008545 | DLGDSL37 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.92 | 8.56 | 34.17 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo008546 | DLGDSL38 | 222 | 73 | 8.09 | 5.60 | 14.08 | -0.46 | 无 No | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo011392 | DLGDSL39 | 894 | 297 | 32.80 | 7.65 | 35.26 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011415 | DLGDSL40 | 894 | 297 | 32.75 | 7.65 | 33.93 | 0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011478 | DLGDSL41 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.15 | 7.11 | 34.06 | -0.17 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo011955 | DLGDSL42 | 1 311 | 436 | 48.64 | 9.01 | 37.95 | -0.24 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/液泡 Chloroplast/Vacuole |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| Dlo011956 | DLGDSL43 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.77 | 6.44 | 30.29 | -0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo012251 | DLGDSL44 | 1 353 | 450 | 50.16 | 5.44 | 36.36 | -0.13 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo012654 | DLGDSL45 | 1 131 | 376 | 40.78 | 5.38 | 36.22 | 0.05 | 有 Yes | 线粒体/液泡 Mitochondrion/Vacuole |
| Dlo013347 | DLGDSL46 | 1 581 | 526 | 57.80 | 7.19 | 32.54 | -0.06 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo013348 | DLGDSL47 | 759 | 252 | 27.24 | 5.80 | 26.12 | 0.10 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo013350 | DLGDSL48 | 414 | 137 | 14.69 | 4.53 | 27.80 | 0.29 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo013351 | DLGDSL49 | 633 | 210 | 23.36 | 6.74 | 35.80 | -0.09 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo013352 | DLGDSL50 | 462 | 153 | 16.18 | 8.61 | 36.41 | 0.26 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo014916 | DLGDSL51 | 1 116 | 371 | 40.33 | 8.89 | 24.93 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo015050 | DLGDSL52 | 1 092 | 363 | 39.38 | 5.09 | 22.52 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo015051 | DLGDSL53 | 1 047 | 348 | 38.79 | 9.18 | 30.01 | -0.34 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo015279 | DLGDSL54 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.56 | 9.09 | 41.62 | 0.17 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo015440 | DLGDSL55 | 414 | 137 | 15.35 | 10.03 | 55.39 | 0.14 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo015441 | DLGDSL56 | 897 | 298 | 33.14 | 5.96 | 46.73 | 0.08 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo015778 | DLGDSL57 | 1 119 | 372 | 40.88 | 8.78 | 22.47 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞核 Chloroplast/Nucleus |
| Dlo016597 | DLGDSL58 | 1 044 | 347 | 37.54 | 5.06 | 34.60 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018044 | DLGDSL59 | 489 | 162 | 17.84 | 9.51 | 58.45 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018809 | DLGDSL60 | 1 266 | 421 | 46.81 | 6.21 | 38.27 | -0.28 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018810 | DLGDSL61 | 2 301 | 766 | 85.50 | 5.89 | 37.09 | -0.40 | 无 No | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018811 | DLGDSL62 | 1 095 | 364 | 40.33 | 5.43 | 36.78 | -0.07 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018812 | DLGDSL63 | 1 155 | 384 | 41.98 | 8.63 | 39.42 | -0.12 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018813 | DLGDSL64 | 1 002 | 333 | 37.13 | 9.22 | 31.41 | -0.09 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo018821 | DLGDSL65 | 1 155 | 384 | 42.61 | 8.78 | 34.10 | -0.08 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo018822 | DLGDSL66 | 1 167 | 388 | 43.14 | 8.93 | 34.50 | -0.05 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo018823 | DLGDSL67 | 1 155 | 384 | 41.99 | 8.63 | 39.92 | -0.13 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018824 | DLGDSL68 | 1 200 | 399 | 44.02 | 5.70 | 35.37 | -0.09 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018825 | DLGDSL69 | 1 236 | 411 | 45.68 | 6.07 | 41.05 | -0.29 | 无 No | 叶绿体/线粒体 Chloroplast/Mitochondrion |
| Dlo018826 | DLGDSL70 | 1 182 | 393 | 43.94 | 7.60 | 35.32 | -0.31 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo018827 | DLGDSL71 | 711 | 236 | 26.64 | 7.03 | 37.54 | -0.31 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018828 | DLGDSL72 | 591 | 196 | 21.55 | 8.62 | 38.79 | -0.23 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/质膜 Nucleus/Plasma membrane |
| Dlo018829 | DLGDSL73 | 1 185 | 394 | 43.98 | 5.42 | 34.99 | -0.18 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo018866 | DLGDSL74 | 2 490 | 829 | 87.76 | 8.83 | 45.02 | -0.72 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo018888 | DLGDSL75 | 1 413 | 470 | 50.96 | 8.88 | 41.37 | -0.26 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo020895 | DLGDSL76 | 1 071 | 356 | 39.13 | 7.53 | 28.29 | -0.09 | 无 No | 叶绿体/细胞外基质 Chloroplast/Extracell |
| Dlo020898 | DLGDSL77 | 858 | 285 | 31.37 | 5.33 | 32.75 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo021059 | DLGDSL78 | 858 | 285 | 31.36 | 5.33 | 32.18 | -0.19 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo021062 | DLGDSL79 | 1 071 | 356 | 39.17 | 6.88 | 29.62 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo021694 | DLGDSL80 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.98 | 5.69 | 22.79 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo021696 | DLGDSL81 | 1 095 | 364 | 40.80 | 9.08 | 31.63 | 0.05 | 有 Yes | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo021719 | DLGDSL82 | 1 140 | 379 | 41.98 | 8.65 | 42.73 | -0.13 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo021829 | DLGDSL83 | 2 457 | 818 | 91.37 | 8.14 | 46.45 | -0.34 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene name | 开放阅读框/bp ORF | 氨基酸数/aa Size | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数 The instabi- lity index | 亲水性 GRAVY | 信号肽 Signal peptide | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
| Dlo021830 | DLGDSL84 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.06 | 5.54 | 30.40 | -0.27 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质/高尔基体 Extracell/Golgi apparatus |
| Dlo021839 | DLGDSL85 | 1 101 | 366 | 40.78 | 9.30 | 32.43 | -0.25 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo022859 | DLGDSL86 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.22 | 5.64 | 34.26 | 0.12 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/液泡 Chloroplast/vacu |
| Dlo023097 | DLGDSL87 | 1 131 | 376 | 40.93 | 9.29 | 31.76 | 0.07 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo024293 | DLGDSL88 | 444 | 147 | 16.44 | 8.81 | 31.55 | -0.09 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024294 | DLGDSL89 | 567 | 188 | 21.66 | 6.73 | 24.42 | -0.33 | 无 No | 细胞骨架Cytoskeleton |
| Dlo024299 | DLGDSL90 | 465 | 154 | 17.31 | 7.69 | 20.21 | -0.05 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024338 | DLGDSL91 | 1 284 | 427 | 47.21 | 8.25 | 38.18 | -0.26 | 无 No | 过氧物酶体Peroxisome |
| Dlo024344 | DLGDSL92 | 972 | 323 | 36.11 | 6.55 | 31.35 | -0.17 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024345 | DLGDSL93 | 972 | 323 | 36.11 | 6.55 | 31.35 | -0.17 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo024482 | DLGDSL94 | 1 023 | 340 | 37.62 | 8.80 | 37.81 | -0.19 | 无 No | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo025454 | DLGDSL95 | 1 110 | 369 | 41.35 | 5.63 | 36.29 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo026075 | DLGDSL96 | 1 062 | 353 | 38.56 | 8.47 | 33.85 | 0.06 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo027030 | DLGDSL97 | 1 092 | 363 | 40.93 | 8.65 | 33.01 | -0.21 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体/细胞质 Chloroplast/Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027031 | DLGDSL98 | 1 068 | 355 | 39.56 | 8.01 | 31.74 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo027690 | DLGDSL99 | 1 176 | 391 | 44.02 | 6.60 | 38.14 | -0.33 | 有 Yes | 细胞核/细胞质 Nucleus/Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027692 | DLGDSL100 | 810 | 269 | 30.17 | 6.44 | 40.11 | -0.19 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo027693 | DLGDSL101 | 1 140 | 379 | 42.41 | 6.07 | 36.44 | -0.27 | 有 Yes | 内质网Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Dlo028167 | DLGDSL102 | 1 041 | 346 | 38.63 | 5.39 | 27.19 | -0.04 | 有 Yes | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo028168 | DLGDSL103 | 960 | 319 | 35.64 | 5.22 | 34.19 | -0.03 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo029634 | DLGDSL104 | 1 077 | 358 | 39.45 | 9.08 | 32.22 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo030986 | DLGDSL105 | 1 104 | 367 | 40.23 | 5.37 | 31.80 | -0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo031180 | DLGDSL106 | 810 | 269 | 28.88 | 5.12 | 27.46 | 0.14 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo031921 | DLGDSL107 | 1 170 | 389 | 43.18 | 8.78 | 36.17 | -0.11 | 有 Yes | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo032044 | DLGDSL108 | 804 | 267 | 29.89 | 7.09 | 50.80 | -0.26 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo032046 | DLGDSL109 | 798 | 265 | 29.70 | 5.63 | 47.67 | -0.03 | 无 No | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo032495 | DLGDSL110 | 1 263 | 420 | 47.18 | 4.82 | 49.24 | -0.06 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo032524 | DLGDSL111 | 1 149 | 382 | 42.75 | 6.01 | 33.02 | -0.02 | 无 No | 质膜Plasma membrane |
| Dlo033028 | DLGDSL112 | 2 433 | 810 | 92.63 | 7.25 | 43.64 | -0.36 | 无 No | 叶绿体Chloroplast |
| Dlo033030 | DLGDSL113 | 369 | 122 | 13.62 | 8.16 | 27.10 | 0.06 | 无 No | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| Dlo033228 | DLGDSL114 | 1 146 | 381 | 41.12 | 8.94 | 27.42 | 0.02 | 有 Yes | 细胞外基质Extracell |
| Dlo033229 | DLGDSL115 | 1 092 | 363 | 38.87 | 8.97 | 20.51 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
| Dlo033340 | DLGDSL116 | 1 113 | 370 | 40.19 | 5.41 | 34.06 | 0.12 | 有 Yes | 液泡Vacuole |
| Dlo034402 | DLGDSL117 | 756 | 251 | 27.63 | 9.24 | 34.38 | -0.24 | 无 No | 细胞核Nucleus |
| Dlo034801 | DLGDSL118 | 1 122 | 373 | 41.26 | 7.45 | 31.18 | -0.02 | 有 Yes | 线粒体Mitochondrion |
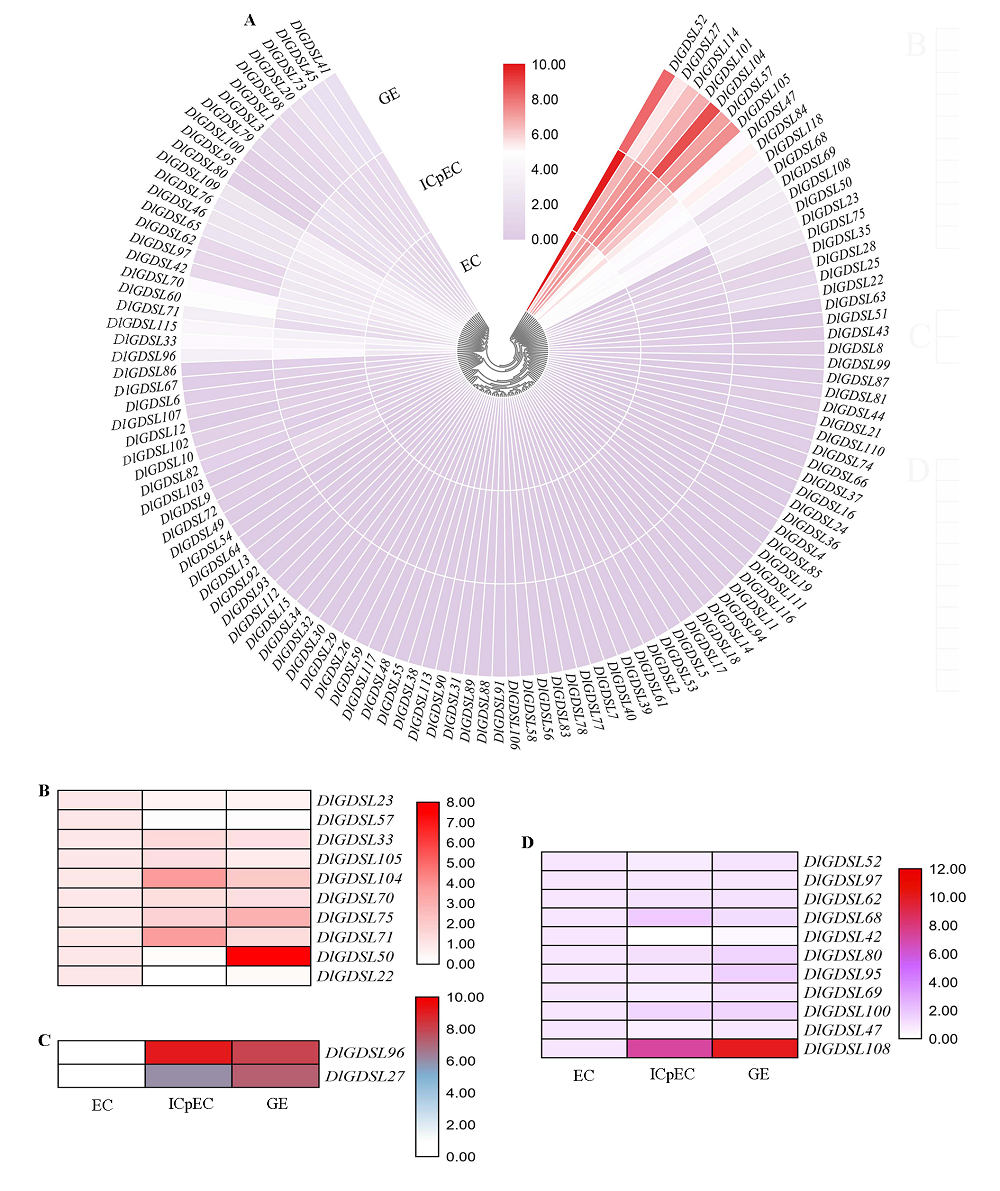
Fig. 3 FPKM values of members of DlGDSL family in the early somatic embryogenesis of longan(A)cluster and relative expression levels of some members of the DlGDSL family in the early somatic embryogenesis of longan(B-D) EC:Embryogenic callus;IcpEC:Incomplete embryogenic compact structure;GE:Globular embryo.
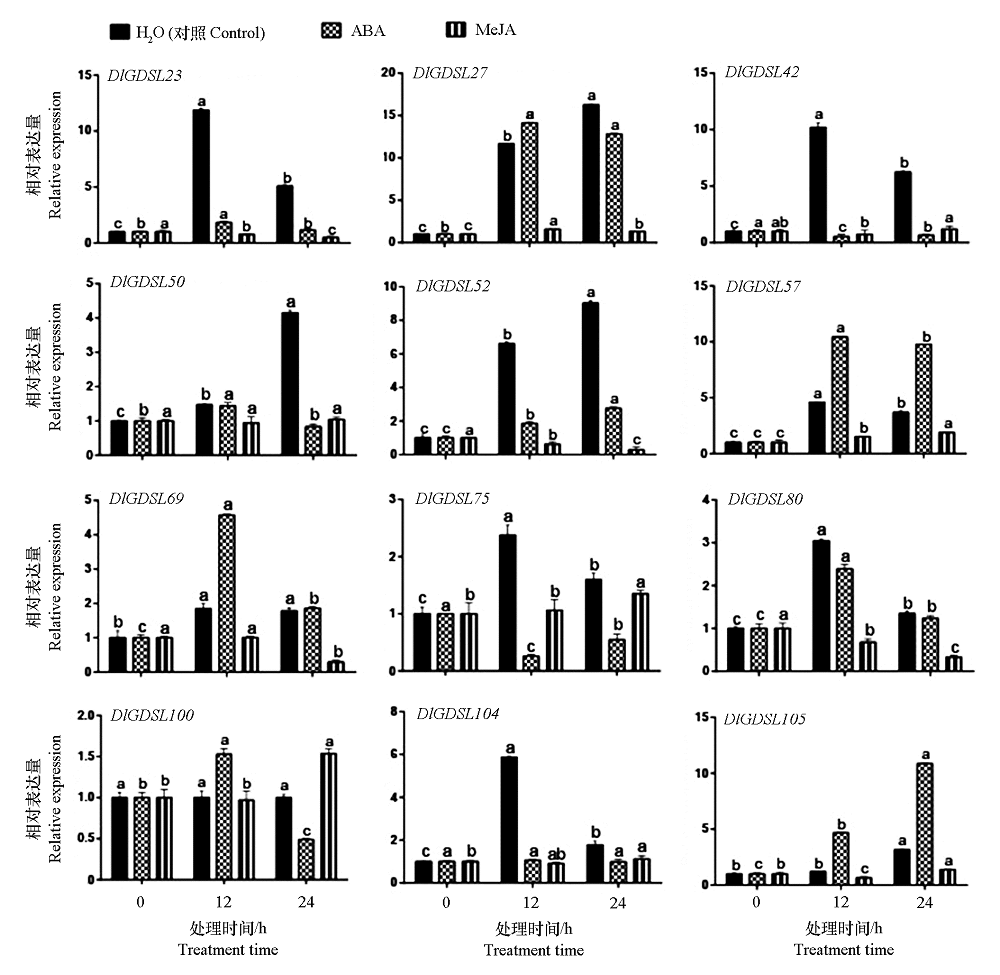
Fig. 4 The expression levels of some members of the DlGDSL family under the treatment of abscisic acid(ABA),methyl jasmonate(MeJA),and water control Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different time of the same treatment(P < 0.05).
| [1] |
Akoh C C, Lee G C, Liaw Y C, Huang T, Shaw J F. 2004. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Progress in Lipid Research, 43(6):534-552.
doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2004.09.002 URL |
| [2] |
Burg K, Helmersson A, Bozhkov P, Arnold S. 2007. Developmental and genetic variation in nuclear microsatellite stability during somatic embryogenesis in pine. Journal of Experimental Botany, 58(3):687-698.
pmid: 17237161 |
| [3] | Cao Y, Han Y, Meng D, Abdullah M, Yu J, Li D, Jin Y, Lin Y, Cai Y. 2018. Expansion and evolutionary patterns of GDSL-type esterases/lipases in Rosaceae genomes. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 18(6):673-684. |
| [4] |
Chen C J, Chen H, He Y H, Xia R. 2018. TBtools,a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various biological data handling tools with a user-friendly interface. bioRxiv,doi: org/10.1101/289660.
doi: org/10.1101/289660 URL |
| [5] | Chen Chunling, Lai Zhongxiong. 2002. Synchronous regulation and control of somatic embryogenesis of longan embryogenic callus and observation of histocytology. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), (2):192-194. (in Chinese) |
| 陈春玲, 赖钟雄. 2002. 龙眼胚性愈伤组织体胚发生同步化调控及组织细胞学观察. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), (2):192-194. | |
| [6] | Chen Jie, Wang Ying, Li Hui-liang, Peng Shi-qing. 2008. Research progress of gene expression in plant somatic embryogenesis. Letters in Biotechnology, (3):452-455. (in Chinese) |
| 陈洁, 王颖, 李辉亮, 彭世清. 2008. 植物体细胞胚发生过程中基因表达的研究进展. 生物技术通讯, (3):452-455. | |
| [7] | Chen Yu-kun. 2018. Transcriptome and proteomics analysis of early somatic embryogenesis in longan and analysis of gene expression and function related to flowering time[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University. (in Chinese) |
| 陈裕坤. 2018. 龙眼体胚发生早期转录组与蛋白质组学分析及开花时间相关基因表达与功能分析[博士论文]. 福建: 福建农林大学. | |
| [8] | Chen Yu-kun, Lin Xiao-yi, Lai Zhong-xiong. 2020. Research progress on somatic embryogenesis of longan. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 41(10):1990-2002. (in Chinese) |
| 陈裕坤, 林晓艺, 赖钟雄. 2020, 龙眼体细胞胚胎发生研究进展. 热带作物学报, 41(10):1990-2002. | |
| [9] |
Clauß K, RoepenackLahaye E, Böttcher C, Roth M, Welti R, Erban A, Kopka J, Scheel D, Milkowski C, Strack D. 2011. Overexpression of sinapine esterase BnSCE3 in oilseed rape seeds triggers global changes in seed metabolism. Plant Physiology, 155(3):1127-1145.
doi: 10.1104/pp.110.169821 URL |
| [10] |
Colorado P, Nicolás C, Nicolás G, Rodríguez D. 1995. Expression of three ABA-regulated clones and their relationship to maturation processes during the embryogenesis of chick-pea seeds. Physiologia Plantarum, 94(1):1-6.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.1995.94.issue-1 URL |
| [11] | Cui Ka-irong, Xing Geng-sheng, Zhou Gong-ke, Liu Xin-min, Wang Ya-fu. 2000. Induction and regulation of somatic embryogenesis by plant hormones. Genetics, (5):349-354. (in Chinese) |
| 崔凯荣, 邢更生, 周功克, 刘新民, 王亚馥. 2000. 植物激素对体细胞胚胎发生的诱导与调节. 遗传, (5):349-354. | |
| [12] |
Ding L, Guo X, Li M, Fu Z, Yan S, Zhu K, Wang Z, Tan X. 2019a. Improving seed germination and oil contents by regulating the GDSL transcriptional level in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Reports, 38(2):243-253.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2365-7 URL |
| [13] |
Ding L N, Li M, Wang W J, Cao J, Wang Z, Zhu K M, Yang Y Y, Li Y L, Tan X L. 2019b. Advances in plant GDSL lipases:from sequences to functional mechanisms. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 41(9):1-11.
doi: 10.1007/s11738-018-2785-6 URL |
| [14] | Dong J, Perras M R, Abrams S R, Dunstan D I. 1996. Induced gene exprssion following ABA uptake in embryogenic suspension cultures of Picea glauca. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 34(4):579-587. |
| [15] |
Dong X, Yi H, Han C, NouIll S, Hur Y. 2016. GDSL esterase/lipase genes in Brassica rapa L.:genome-wide identification and expression analysis. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 291(2):531-542.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1123-6 URL |
| [16] | Gao M, Yin X, Yang W, Lam S M, Tong X, Liu J, Wang X, Li Q, Shui G, He Z. 2017. GDSL lipases modulate immunity through lipid homeostasis in rice. PLoS Pathogens, 13(11):e1006724. |
| [17] |
Hammes G G. 2002. Multiple conformational changes in Enzyme Catalysis. Biochemistry, 41(26):8221-8228.
doi: 10.1021/bi0260839 URL |
| [18] |
Hanna C, Lai C, Huang L M, Liu J, Shaw J F. 2012. Multifunctionality and diversity of GDSL esterase/lipase gene family in rice(Oryza sativa L. japonica)genome:new insights from bioinformatics analysis. BMC Genomics, 13(1):309.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-309 URL |
| [19] |
Hong J K, Choi H W, Hwang I S, Kim D S, Kim N H, Choi D S, Kim Y J, Hwang B K. 2008. Function of a novel GDSL-type pepper lipase gene,CaGLIP1,in disease susceptibility and abiotic stress tolerance. Planta, 227(3):539-558.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0637-5 URL |
| [20] | Ji R, Wang H, Xin X, Peng S, Hur Y, Li Z, Feng H. 2017. BrEXL6,a GDSL lipase gene of Brassica rapa,functions in pollen development. Biologia Plantarum, 61(4):682-694. |
| [21] | Ken Y C, Ed B, Terry C, Charles C, Genevieve D, Paul D, Palitha D, Pankaj J, Paul K, Karthikeyan A S, Jerry L, McCouch S R, Ren L Y, William S, Stein J C, Jim T, Sharon W, Doreen W. 2011. Gramene database in 2010:updates and extensions. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(Database issue):1085-1094. |
| [22] |
Kim G K, Kwon S J, Jang Y J, Chung J H, Myung H N, Park O K. 2014. GDSL lipase 1 regulates ethylene signaling and ethylene-associated systemic immunity in Arabidopsis. FEBS Letters, 588(9):1652-1658.
doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.062 URL |
| [23] |
Kim K, Lim J, Kim M, Kim T, Chung H, Paek K. 2008. GDSL-lipase1(CaGL1)contributes to wound stress resistance by modulation of CaPR-4 expression in hot pepper. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 374(4):693-698.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.120 pmid: 18680725 |
| [24] |
Kwon S J, Jin H C, Lee S, Nam M H, Chung J H, Kwon S I, Ryu C, Park O K. 2009. GDSL lipase-like 1 regulates systemic resistance associated with ethylene signaling in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal:for Cell and Molecular Biology, 58(2):235-245.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2009.58.issue-2 URL |
| [25] |
Lai C P, Huang L M., Chen L F O, Chan M T, Shaw J F. 2017. Genome-wide analysis of GDSL-type esterases/lipases in Arabidopsis. Plant Molecular Biology, 95(1-2):181-197.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-017-0648-y URL |
| [26] | Lai Zhong-xiong, Chen Chun-ling. 2002. Endogenous hormone changes during somatic embryogenesis of longan. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, (2):41-47. (in Chinese) |
| 赖钟雄, 陈春玲. 2002. 龙眼体细胞胚胎发生过程中的内源激素变化. 热带作物学报, (2):41-47. | |
| [27] | Lai Zhong-xiong, Pan Liang-zhen, Chen Zhen-guang. 1997. Establishment and maintenance of longan embryogenic cell line. Journal of Fujian Agricultural University, (2):33-40. (in Chinese) |
| 赖钟雄, 潘良镇, 陈振光. 1997. 龙眼胚性细胞系的建立与保持. 福建农业大学学报, (2):33-40. | |
| [28] |
Langhansová L, Konrádová H, Vaněk T. 2004. Polyethylene glycol and abscisic acid improve maturation and regeneration of Panax ginseng somatic embryos. Plant Cell Reports, 22(10):725-730.
pmid: 14735313 |
| [29] |
Lee D S, Kim B K, Kwon S J, Jin H C, Park O K. 2009. Arabidopsis GDSL lipase 2 plays a role in pathogen defense via negative regulation of auxin signaling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 379(4):1038-1042.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.01.006 URL |
| [30] | Lee K A, Cho T J. 2003. Characterization of a salicylic acid- and pathogen-induced lipase-like gene in Chinese cabbage. Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 36(5):433-441. |
| [31] | Li X, Chen Y, Zhang S T, Su L Y, Xu X P, Chen X H, Lai Z X, Lin Y L. 2020. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of Sm genes reveal their involvement in early somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. PLoS ONE, 15(4):e0230795. |
| [32] | Lin Y J, Min J M, Lai R L, Wu Z Y, Chen Y K, Yu L L, Cheng C Z, Jin Y C, Tian Q L, Liu Q F, Liu W H, Zhang C G, Lin L X, Hu Y, Zhang D M, Thu M, Zhang Z, Liu S C, Fang X D, Wang J, Yang H M, Varshney R K, Yin Y, Lai Z X. 2017. Genome-wide sequencing of longan(Dimocarpus longan Lour.)provides insights into molecular basis of its polyphenol-rich characteristics. GigaScience, 6 (5):gix023 https://doi.org/010.1093/gigascience/gix1023. |
| [33] |
Ling H. 2008. Sequence analysis of GDSL lipase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 11(5):763-767.
doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2008.763.767 URL |
| [34] | Ma R D, Yuan H L, An J, Hao X Y, Li H B. 2018. A Gossypium hirsutum GDSL lipase/hydrolase gene(GhGLIP)appears to be involved in promoting seed growth in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE, 13(4):e0195556. |
| [35] | Naranjo M Á, Forment J, RoldÁN M, Serrano R, Vicente O. 2006. Overexpression of Arabidopsis thaliana LTL1,a salt-induced gene encoding a GDSL-motif lipase,increases salt tolerance in yeast and transgenic plants. Plant, Cell & Environment, 29(10):1890-1900. |
| [36] | Ni P Y, Ji X R, Guo D L. 2020. Genome-wide identification,characterization,and expression analysis of GDSL-type esterases/lipases gene family in relation to grape berry ripening. Scientia Horticulturae, 264:109162. |
| [37] |
Oh I S, Park A R, Bae M S, Kwon S J, Kim Y S, Lee J E, Kang N Y, Lee S, Cheong H, Park O K. 2005. Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. The Plant Cell, 17(10):2832-2847.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.034819 URL |
| [38] |
Park J J, Jin P, Yoon J, Yang J, Jeong H J, Ranathunge K, Schreiber L, Franke R, Lee I, An G. 2010. Mutation in Wilted Dwarf and Lethal 1 (WDL1)causes abnormal cuticle formation and rapid water loss in rice. Plant Mol Biol, 74(1-2):91-103.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9656-x URL |
| [39] |
Riemann M, Gutjahr C, Korte A, Riemann M, Danger B, Muramatsu T, Bayer U, Waller F, Furuya M, Nick P. 2007. GER1,a GDSL motif-encoding gene from rice is a novel early light- and jasmonate-induced gene. Plant Biology, 9(1):32-40.
pmid: 17048141 |
| [40] | Shen Xu, Chen Xiao-hui, Xu Xiao-ping, Huo Wen, Li Xiao-fei, Jiang Meng-qi, Zhang Jing, Lin Yu-ling, Lai Zhong-xiong. 2019. Genome identification and expression analysis of the SDG gene family in early somatic embryogenesis of longan. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 40(10):1889-1901. (in Chinese) |
| 申序, 陈晓慧, 徐小萍, 霍雯, 李晓斐, 蒋梦琦, 张婧, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 2019. 龙眼体细胞胚胎发生早期SDG基因家族的全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 热带作物学报, 40(10):1889-1901. | |
| [41] |
Takahashi K, Shimada T, Kondo M, Tamai A, Mori M, Nishimura M, Hara N I. 2009. Ectopic expression of an esterase,which is a candidate for the unidentified plant cutinase,causes cuticular defects in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology, 51(1):123-131.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp173 URL |
| [42] | Thomas T, Zhang Yu-xia. 2006. Effects of sugar,GA3 and ABA on somatic embryogenesis of Tylophora indica(Burm.f.)Merrill. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, (3):465-471. (in Chinese) |
| Thomas T, 张玉霞. 2006. 糖、GA3及ABA对印度娃儿藤[Tylophora indica(Burm.f.)Merrill.]体细胞胚发生的影响. 生物工程学报, (3):465-471. | |
| [43] |
Tyukhtenko S I, Litvinchuk A V, Chang C F, Leu R J, Shaw J F, Huang T H. 2002. NMR studies of the hydrogen bonds involving the catalytic triad of Escherichia coli thioesterase/protease I. FEBS Letters, 528(1-3):203-206.
pmid: 12297305 |
| [44] |
Upton C, Buckley J T. 1995. A new family of lipolytic enzymes? Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 20(5):178-179.
pmid: 7610479 |
| [45] |
Volokita M, Rosilio B T, Rivkin N, Zik M. 2010. Combining comparative sequence and genomic data to ascertain phylogenetic relationships and explore the evolution of the large GDSL-Lipase family in land plants. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28(1):551-565.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq226 URL |
| [46] | Wang Xiao-zhe, Chen Xiong, Wang Ya-fu. 1995. Some current researches on gene expression regulation in plant somatic embryogenesis. Genetics, (S1):34-38. (in Chinese) |
| 王晓哲, 陈雄, 王亚馥. 1995. 植物体细胞胚发生中基因表达调控研究的某些现状. 遗传, (S1):34-38. | |
| [47] |
Xie T, Chen C J, Li C H, Liu J R, Liu C Y, He Y H. 2018. Genome-wide investigation of WRKY gene family in pineapple:evolution and expression profiles during development and stress. BMC Genomics, 19(1):490.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4880-x URL |
| [48] |
Yao T H, Yen C L, Vitaliy Y G, Tai H H. 2001. Backbone dynamics of Escherichia coli thioesterase/protease I:evidence of a flexible active-site environment for a serine protease. Journal of Molecular Biology, 307(4):1075-1090.
doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4539 URL |
| [49] |
Youichi K, Miki N, Mika K, Takanari I, Takeshi Y, Kumiko S, Akie I, Tomoko K, Ryo M, Shu M, Minami M. 2008. RETARDED GROWTH OF EMBRYO1,a new basic Helix-Loop-Helix protein,expresses in endosperm to control embryo growth. Plant Physiology, 147(4):1924-1935.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.118364 pmid: 18567831 |
| [50] |
Yu C, Su C L, Jin F S, Yen C L. 2003. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli Thioesterase I/Protease I/Lysophospholipase L1:consensus sequence blocks constitute the catalytic center of SGNH-hydrolases through a conserved hydrogen bond network. Journal of Molecular Biology, 330(3):539-551.
pmid: 12842470 |
| [1] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [2] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [3] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [4] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [5] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [6] | ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. Identification of HSP20 Family Genes in Citrus and Their Expression in Pathogen Infection Responses Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [7] | LIANG Chen, SUN Ruyi, XIANG Rui, SUN Yimeng, SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, WANG Li. Genome-wide Identification of Grape GRF Family and Expression Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [8] | XIAO Xuechen, LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, XUE Xiaodong, ZHOU Chengzhe, WU Xingjian, WU Junnan, GUO Yinsheng, YEH Kaiwen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Whole-genome Identification and Expression Analysis of SNAT,ASMT and COMT Families of Melatonin Synthesis Pathway in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [9] | GAO Weilin, ZHANG Liman, XUE Chaoling, ZHANG Yao, LIU Mengjun, ZHAO Jin. Expression of E-type MADS-box Genes in Flower and Fruits and Protein Interaction Analysis in Chinese Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| [10] | JIANG Cuicui, FANG Zhizhen, ZHOU Danrong, LIN Yanjuan, YE Xinfu. Identification and Expression Analysis of Sugar Transporter Family Genes in‘Furongli’(Prunus salicina) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 252-264. |
| [11] | WANG Zhiyu, CHANG Beibei, LIU Qi, CHENG Xiaofan, DU Xiaoyun, YU Xiaoli, SONG Laiqing, ZHAO Lingling. Study on Expression and Anthocyanin Accumulation of Solute Carrier Gene MdSLC35F2-like in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2293-2303. |
| [12] | HUANG Renwei, REN Yinghong, QI Weiliang, ZENG Rui, LIU Xinyu, DENG Binyan. Cloning of Mulberry MaERF105-Like Gene and Its Expression Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2439-2448. |
| [13] | SHEN Xu, CHEN Xiaohui, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Rongzhu, XU Xiaoping, LI Xiaofei, JIANG Mengqi, LIU Pudong, NI Shanshan, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong. Evolutionary Dynamics Investigation and the Expression Analysis of Chromatin Remodeling Factor Snf2 Gene Family During Early Somatic Embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 41-61. |
| [14] | ZHANG Chunyu, XU Xiaoqiong, XU Xiaoping, ZHAO Pengcheng, SHEN Xu, Munir Nigarish, ZHANG Zihao, LIN Yuling, Chen Zhenguang, LAI Zhongxiong. Genome-wide Identification of the SKP1-like Family and Analysis of Their Expression During Early Somatic Embryogenesis in Longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1665-1679. |
| [15] | BIAN Shicun, LU Yani, XU Wujun, CHEN Boqing, WANG Guanglong, XIONG Aisheng. Garlic Circadian Clock Genes AsRVE1 and AsRVE2 and Their Expression Analysis Under Osmotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1706-1716. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd