
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1789-1802.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0791
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
DONG Xuanke1,2, LI Yingyang1,2, MA Yuwan1,2, CAI Yanfang1, DING Qihan1,2, CHEN Haixia1,2, LI Yufan1,2,*( ), and CHEN Jiren1,2,*(
), and CHEN Jiren1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-20
Revised:2025-05-07
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-23
Contact:
LI Yufan, and CHEN Jiren
DONG Xuanke, LI Yingyang, MA Yuwan, CAI Yanfang, DING Qihan, CHEN Haixia, LI Yufan, and CHEN Jiren. The Functional Analysis of RcTCP9 Gene in Response to Salt and Drought Stress in Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1789-1802.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0791
| 用途 Purpose | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆RcTCP9基因CDS全长 Clone the full-length CDS of the RcTCP9 gene | KL-RcTCP9-F | ATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCAAG |
| KL-RcTCP9-R | TCACTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Construction of subcellular localization vector | pBI121-RcTCP9-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGA |
| pBI121-RcTCP9-R | GGACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGG | |
| 瞬时过表达载体构建 Construction of transient overexpression vector | 1305-RcTCP9-F | GGAGAGAACACGGGGGACATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCA |
| 1305-RcTCP9-R | CATCATGGTCTTTGTAGTCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGGG | |
| VIGS基因沉默载体构建 Construction of VIGS gene silencing vector | TRV2-RcTCP9-F | CTGTGAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGTTCGTGGGGAACGGCGGAG |
| TRV2-RcTCP9-R | CGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCGGATCCCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量表达 (qRT-PCR) | RcTCP9-F | TGGTAGTGGTAACAGTAACA |
| RcTCP9-R | CTCCTGCTTATCGTAAATCTC | |
| RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA | |
| RcPR4/1-F | ATGGCCGGAAAACAATGC | |
| RcPR4/1-R | GGGCTTGTCGGCATCC | |
| RcNAC091-F | TGTCTTCCTCGGAGTTACAGTTACC | |
| RcNAC091-R | CCCAGGGGTCGTATTTGTACAG |
Table 1 The sequences of primers used for experiment
| 用途 Purpose | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆RcTCP9基因CDS全长 Clone the full-length CDS of the RcTCP9 gene | KL-RcTCP9-F | ATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCAAG |
| KL-RcTCP9-R | TCACTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTG | |
| 亚细胞定位载体构建 Construction of subcellular localization vector | pBI121-RcTCP9-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGA |
| pBI121-RcTCP9-R | GGACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGG | |
| 瞬时过表达载体构建 Construction of transient overexpression vector | 1305-RcTCP9-F | GGAGAGAACACGGGGGACATGACGTCGTATTTTGAGGATCA |
| 1305-RcTCP9-R | CATCATGGTCTTTGTAGTCCTGGCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGGG | |
| VIGS基因沉默载体构建 Construction of VIGS gene silencing vector | TRV2-RcTCP9-F | CTGTGAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCGTTCGTGGGGAACGGCGGAG |
| TRV2-RcTCP9-R | CGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCGGATCCCTTCCTGGGCCTGCGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量表达 (qRT-PCR) | RcTCP9-F | TGGTAGTGGTAACAGTAACA |
| RcTCP9-R | CTCCTGCTTATCGTAAATCTC | |
| RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA | |
| RcPR4/1-F | ATGGCCGGAAAACAATGC | |
| RcPR4/1-R | GGGCTTGTCGGCATCC | |
| RcNAC091-F | TGTCTTCCTCGGAGTTACAGTTACC | |
| RcNAC091-R | CCCAGGGGTCGTATTTGTACAG |

Fig. 2 Construction of the TRV2-RcTCP9 silencing vector A:Comparison results between the effective fragment of RcTCP9 and TRV2-RcTCP9;B:Gel electrophoresis image of colony PCR
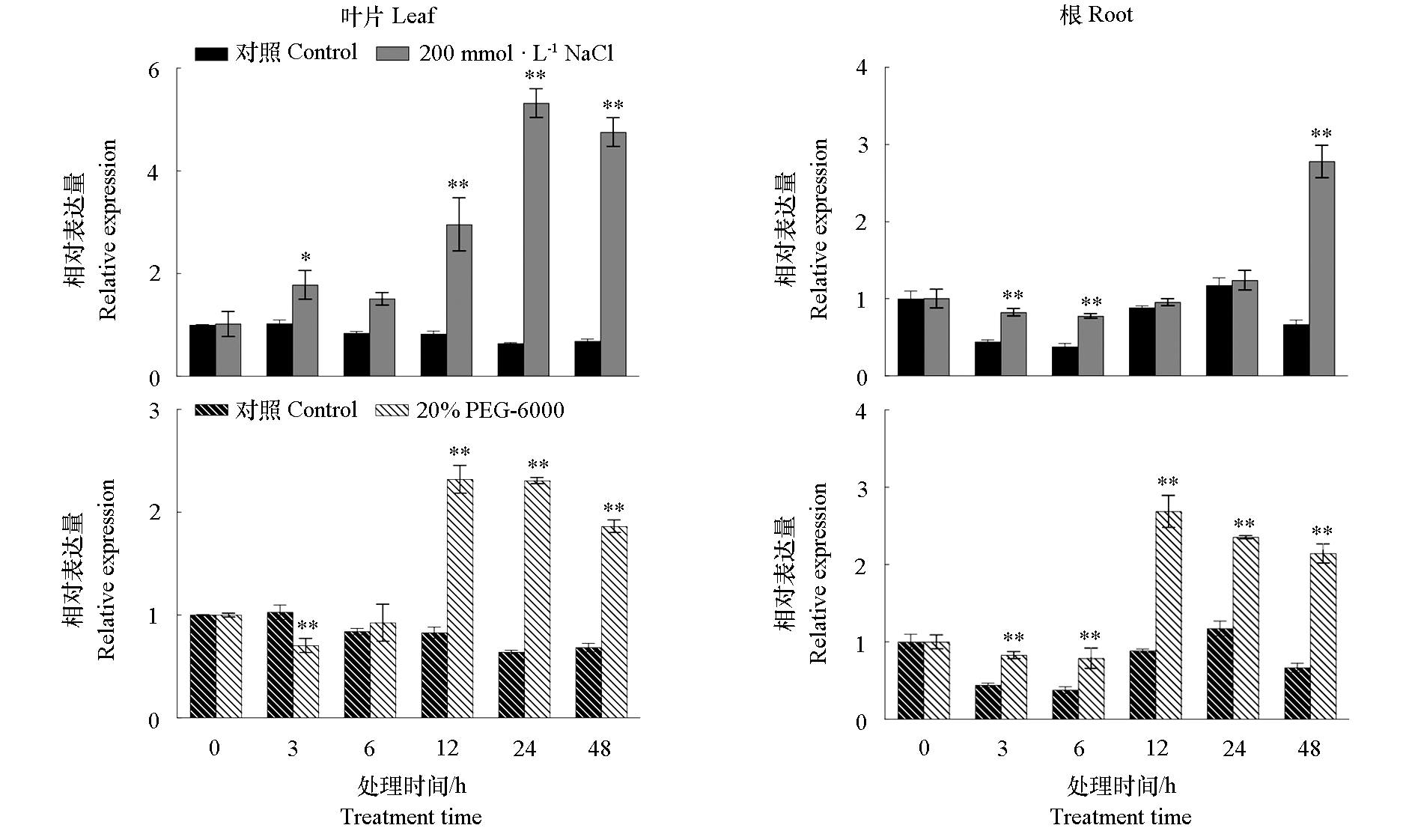
Fig. 5 Tissue-specific expression analysis of RcTCP9 in cuttings of Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’under salt and drought stress *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01. The same below
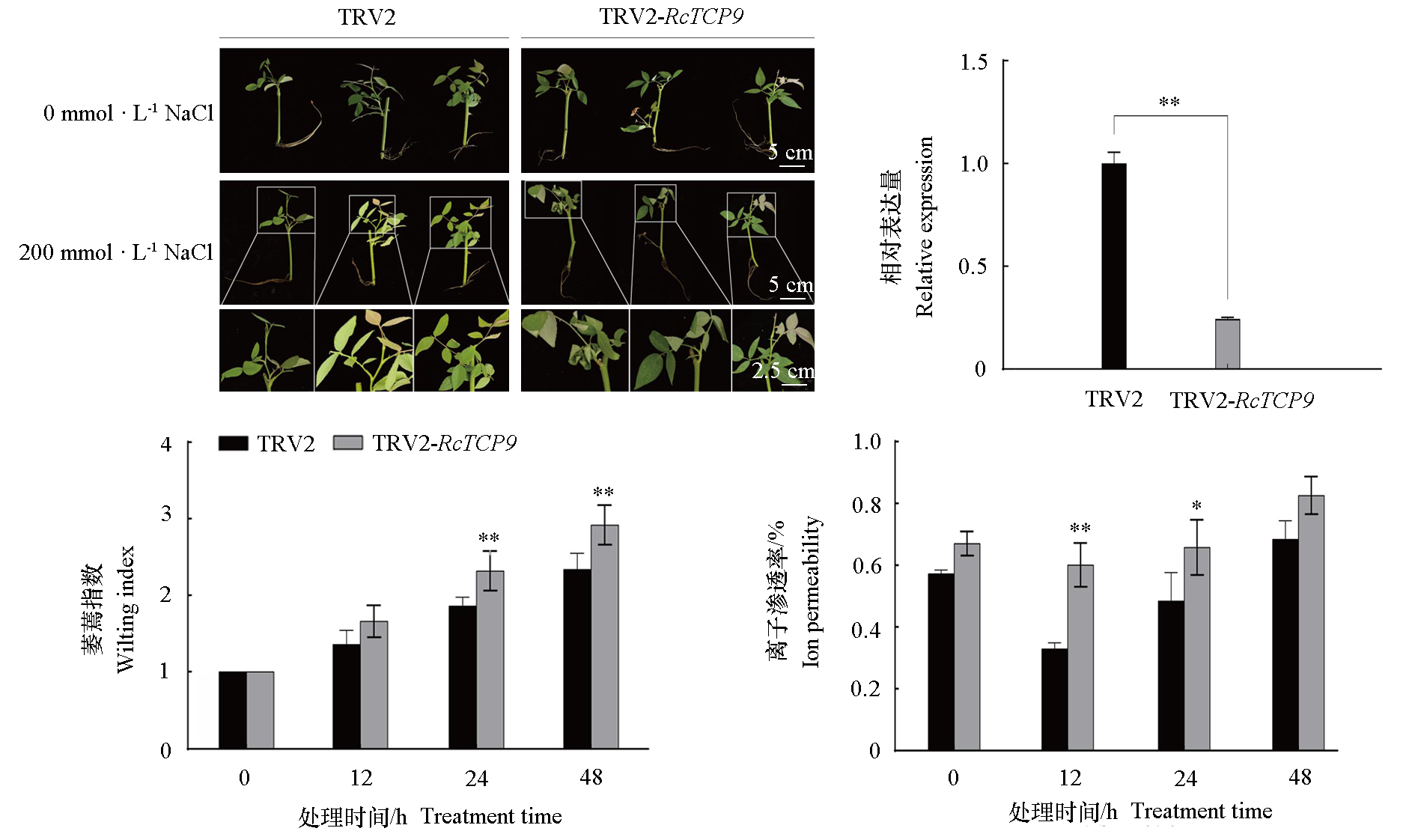
Fig. 6 The changes of phenotype phenotype,RcTCP9 expression and physiological indexes of roses cutting seedlings in VIGS silencing RcTCP9 group and control group under salt stress
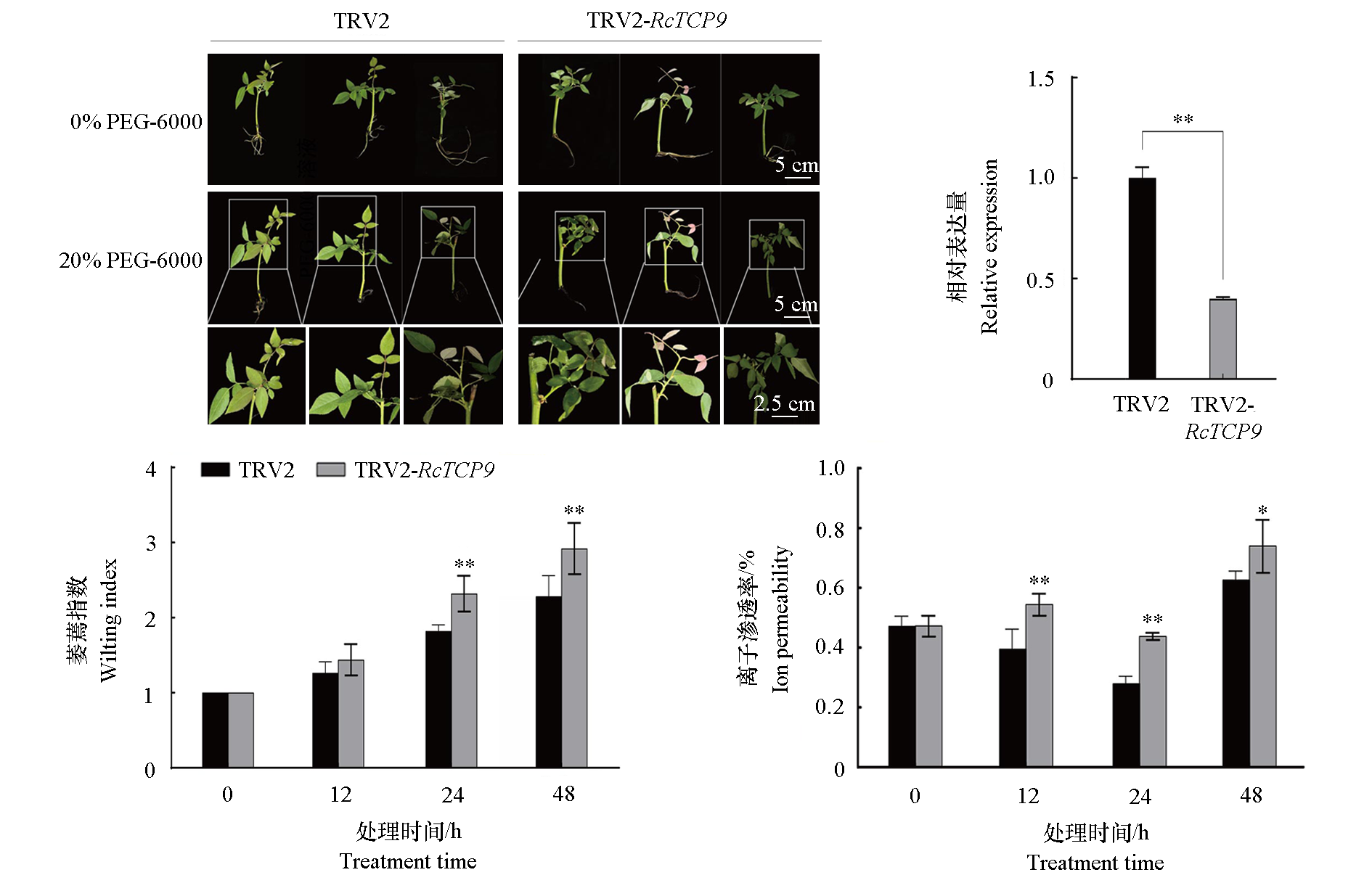
Fig. 9 The changes of phenotype,RcTCP9 expression and physiological indexes of roses cuttings in VIGS silencing RcTCP9 group and control group under drought stress
| [1] |
|
|
陈爱葵, 韩瑞宏, 李东洋, 凌连莲, 罗惠霞, 唐上剑. 2010. 植物叶片相对电导率测定方法比较研究. 广东教育学院学报, 30 (5):88-91.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0794 |
|
贾鑫, 曾臻, 陈月, 冯慧, 吕英民, 赵世伟. 2022. 月季‘月月粉’RcDREB2A的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1945-1956.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0794 |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-1045 |
|
李慧, 文钰芳, 王悦, 纪超, 石国优, 罗英, 周勇, 李志敏, 吴晓玉, 杨有新, 刘建萍. 2024. 盐胁迫下辣椒CaPIF4的表达特性与功能分析. 生物技术通报, 40 (4):148-158.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-1045 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
刘飞, 杨亲康, 何德钏, 邢宝龙, 李梦蛟. 2024. 豌豆NAC基因家族鉴定及其在干旱胁迫下的响应分析. 农业生物技术学报, 32 (7):504-1517.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
倪芮, 罗悠悠, 黄渺, 蔡骏一, 何奕含, 刘文霖, 姚依妮, 肇瑾. 2024. 火龙果HpTCP9基因克隆及其在干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 农业生物技术学报, 32 (7):1533-1542.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
[ 汪桂凤. 2019. PEG模拟耐干旱大豆种质资源的筛选及苗期生理生化特性研究[硕士论文]. 杭州:浙江大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
谢磊, 王姗珊, 胡博文, 熊兴耀, 陈己任. 2017. 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的月季TCP9基因转化拟南芥. 分子植物育种, 15 (3):928-933.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
杨碧楠, 李博文, 杨振宇, 徐奕芃, 阎韵清, 娄玉霞, 奉树成, 明凤. 2024. 月季‘安吉拉’热胁迫反应机制及功能基因的挖掘. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1284-1296.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.14920 pmid: 29205383 |
| [30] |
|
|
姚莹, 王伟, 孙永媛, 曹金锋, 魏建荣, 刘建凤. 2021. 沙棘HrTCP转录因子家族鉴定及其干旱胁迫下的表达分析. 西北植物学报, 41 (4):576-584.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
岳玲, 迟东明, 宋伟, 果鹏忠. 2010. 月季抗性研究进展. 北方园艺,(9):225-227.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
[ 张伟杰. 2023. 野生玫瑰耐盐生理机制研究与耐盐调控因子挖掘[硕士论文]. 扬州:扬州大学
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
[ 张欣. 2020. PdbTCP9基因调控山新杨干旱应答和次生壁合成的功能研究[博士论文]. 哈尔滨:东北林业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
周欢欢, 傅卢成, 马玲, 赵亚红, 张汝民, 高岩. 2019. 干旱胁迫及复水对‘波叶金桂’生理特性的影响. 浙江农林大学学报, 36 (4):687-696.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
周迎雪, 李沛曈, 苏江硕, 王海滨, 房伟民, 陈发棣, 张飞. 2023. 37份菊花近缘种的抗旱性评价. 南京农业大学学报, 46 (6):1060-1068.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
卓露, 林晓华, 薛山, 梁玉青, 张卓文, 李鸿彬,
|
| [1] | HU Aishuang, GUO Wenjing, XING Chunqiang, MENG Jie, SONG Shuang, YAO Yutao, LI Xiaoxue, SUN Yu, WANG Wencheng. A New Salt-Tolerant Malus Crabapple Cultivar‘Yanxing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 11-12. |
| [2] | KONG Danrui, ZHANG Wei, ZHENG Xiaoyue, WANG Meixian, ZHAO Huien. A New Ground-Cover Chrysanthemum Cultivar‘Damo Qiuxue’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 169-170. |
| [3] | SUN Dongyu, WEI Dong, YANG Yinyan, HU Caizhu, HU Zhiqun, ZHOU Donghui, and ZHOU Biyan. Physiological Response and Transcriptome Analysis of Wax Apple Flowering to Foliar Application of Chlorpyrifos [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1718-1732. |
| [4] | MO Jinxia, LI Fang, XIONG Xinting, ZHONG Zaofa, PENG Ting. Characterization of PtSARD1 and Its Preliminary Role in Drought Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1399-1411. |
| [5] | SUN Pei, ZHANG Hong, YANG Yuan, WANG Hua, LI Maofu, KANG Yanhui, SUN Xiangyi, JIN Wanmei. Genetic Diversity Analysis and Fingerprint Construction of Rosa Germplasm Resources Based on SSR Marker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1539-1552. |
| [6] | LI Wen, LI Shaopeng, LI Donghai, WU Fuchuan, and TIAN Bo. Changes in Onamental Quality and Physiological Substances of Cut Etlingera elatior Flwoers During the Vase Period [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1633-1643. |
| [7] | MA Yuwan, LIU Ao, LIU Xiangdong, ZHANG Yajing, DONG Xuanke, LI Yufan, CHEN Jiren. Cloning of the RcRAP2.7 Gene and its Expression Analysis Under Abiotic Stresses in Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 921-932. |
| [8] | LI Ao, ZHENG Xu, WU Chengxu, NIE Ruining, JI Xinying, TANG Jiali, ZHANG Junpei. The Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Walnut Seedlings Under Salt Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [9] | XIAO Wenfang, LI Zuo, CHEN Heming, LÜ Fubing. Development and Application of Universal SSR Molecular Marker Primers in Phalaenopsis and Rhynchostylis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1056-1068. |
| [10] | DONG Shuchao, HONG Jun, LING Jiayi, XIE Zixin, ZHANG Shengjun, ZHAO Liping, SONG Liuxia, WANG Yinlei, ZHAO Tongmin. Genome-wide Association Studies of Drought Tolerance in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [11] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [12] | WANG Yanan, LIU Xutao, JING Tongtong, CHAI Yating, ZHANG Xiaowei, AI Xizhen, BI Huangai. Effect of Melatonin on Antioxidant System of Tomato Senescent Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606. |
| [13] | WANG Yuhang, LI Dou, WANG Chunheng, JIN Xin, CHENG Yajuan, DAI Zibo, FENG Lidan, YANG Jiangshan. The Effect of Melatonin on the Subcellular Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism During Development and Senescence in Grape Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 103-120. |
| [14] | ZHOU Jie, LI Tianzhu, LIU Ruyi, LI Chenhao, YUAN Zenan, LI Jianming. Effects of Air Humidity and Soil Water Content Coupling on Tomato Gray Mold [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1779-1792. |
| [15] | SHEN Xinyan, HOU Xiaolei, SUN Peinan, LIU Minmin, TANG Yaping, LI Ning, LU Yong’en, YE Zhibiao, OUYANG Bo. Drought Tolerance Improvement of Processing Tomato by Molecular Marker Assisted Selection [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1429-1443. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd