
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 921-932.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0532
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Yuwan, LIU Ao, LIU Xiangdong, ZHANG Yajing, DONG Xuanke, LI Yufan*( ), CHEN Jiren*(
), CHEN Jiren*( )
)
Received:2024-08-16
Revised:2024-12-09
Online:2025-05-08
Published:2025-04-25
Contact:
LI Yufan, CHEN Jiren
MA Yuwan, LIU Ao, LIU Xiangdong, ZHANG Yajing, DONG Xuanke, LI Yufan, CHEN Jiren. Cloning of the RcRAP2.7 Gene and its Expression Analysis Under Abiotic Stresses in Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 921-932.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0532
| 用途 Application | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆Gene clone | RcRAP2.7-F | GACGCAAATGGACGAGTCC |
| RcRAP2.7-R | TAATGGTTTTATTGAGACGTATGGT | |
| 启动子克隆Promoter clone | PRcRAP2.7-F | TTCTCTCTCCTCTTCCTGTCACCCA |
| PRcRAP2.7-R | ACTCGTCCATTTGCGTCGCG | |
| 亚细胞定位 | pBI121-RcRAP2.7-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACG |
| Subcellular localization | pBI121-RcRAP2.7-R | ACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCG |
| 转录激活活性分析 | BD-RcRAP2.7-N-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACGTC |
| Transcriptional activation | BD-RcRAP2.7-N-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCAGAACTCCGAGACCTGGGCC |
| activity analysis | BD-RcRAP2.7-AP2/ERF-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCCAGTACAGAGGGGTCACTTTC |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-AP2/ERF-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCCCCTTCGTAAGTACTTGCCTC | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-C-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCGAGATGATATCTGATGCTG | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-C-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCGG | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACGTC | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量 PCR | RT-RcRAP2.7-F | TATAGAAGAACTGGTAGA |
| Quantitative Real-time PCR | RT-RcRAP2.7-R | CATATCCTCCTCATAATC |
| RT-RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RT-RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 用途 Application | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆Gene clone | RcRAP2.7-F | GACGCAAATGGACGAGTCC |
| RcRAP2.7-R | TAATGGTTTTATTGAGACGTATGGT | |
| 启动子克隆Promoter clone | PRcRAP2.7-F | TTCTCTCTCCTCTTCCTGTCACCCA |
| PRcRAP2.7-R | ACTCGTCCATTTGCGTCGCG | |
| 亚细胞定位 | pBI121-RcRAP2.7-F | ACGGGGGACTCTAGAGGATCCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACG |
| Subcellular localization | pBI121-RcRAP2.7-R | ACTGACCACCCGGGGATCCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCG |
| 转录激活活性分析 | BD-RcRAP2.7-N-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACGTC |
| Transcriptional activation | BD-RcRAP2.7-N-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCAGAACTCCGAGACCTGGGCC |
| activity analysis | BD-RcRAP2.7-AP2/ERF-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCCAGTACAGAGGGGTCACTTTC |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-AP2/ERF-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCCCCTTCGTAAGTACTTGCCTC | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-C-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCGAGATGATATCTGATGCTG | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-C-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCGG | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGACGAGTCCGGGACGTC | |
| BD-RcRAP2.7-R | GACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCTTGAGACGTATGGTGGGCGG | |
| 实时荧光定量 PCR | RT-RcRAP2.7-F | TATAGAAGAACTGGTAGA |
| Quantitative Real-time PCR | RT-RcRAP2.7-R | CATATCCTCCTCATAATC |
| RT-RcCTP-F | GGGTGATGATGCAGCTTT | |
| RT-RcCTP-R | TTAGCACTTGACCTCCTTCA |
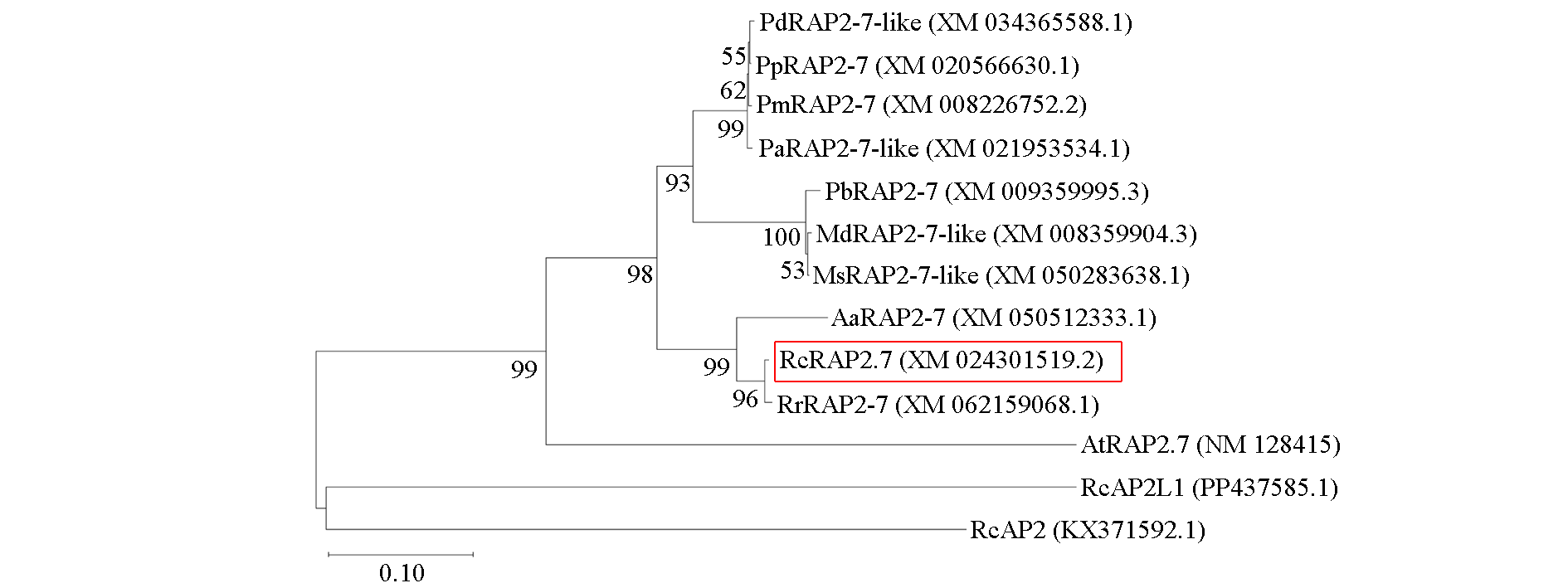
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic tree of RcRAP2.7 of Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’and homologous protein sequences from other species Pp:Prunus persica;Pa:Prunus avium;Pd:Prunus dulcis;Pm:Prunus mume;Pb:Pyrus bretschneideri;Ms:Malus sylvestris;Md:Malus × domestica;Rr:Rosa rugosa;Aa:Argentina anserina
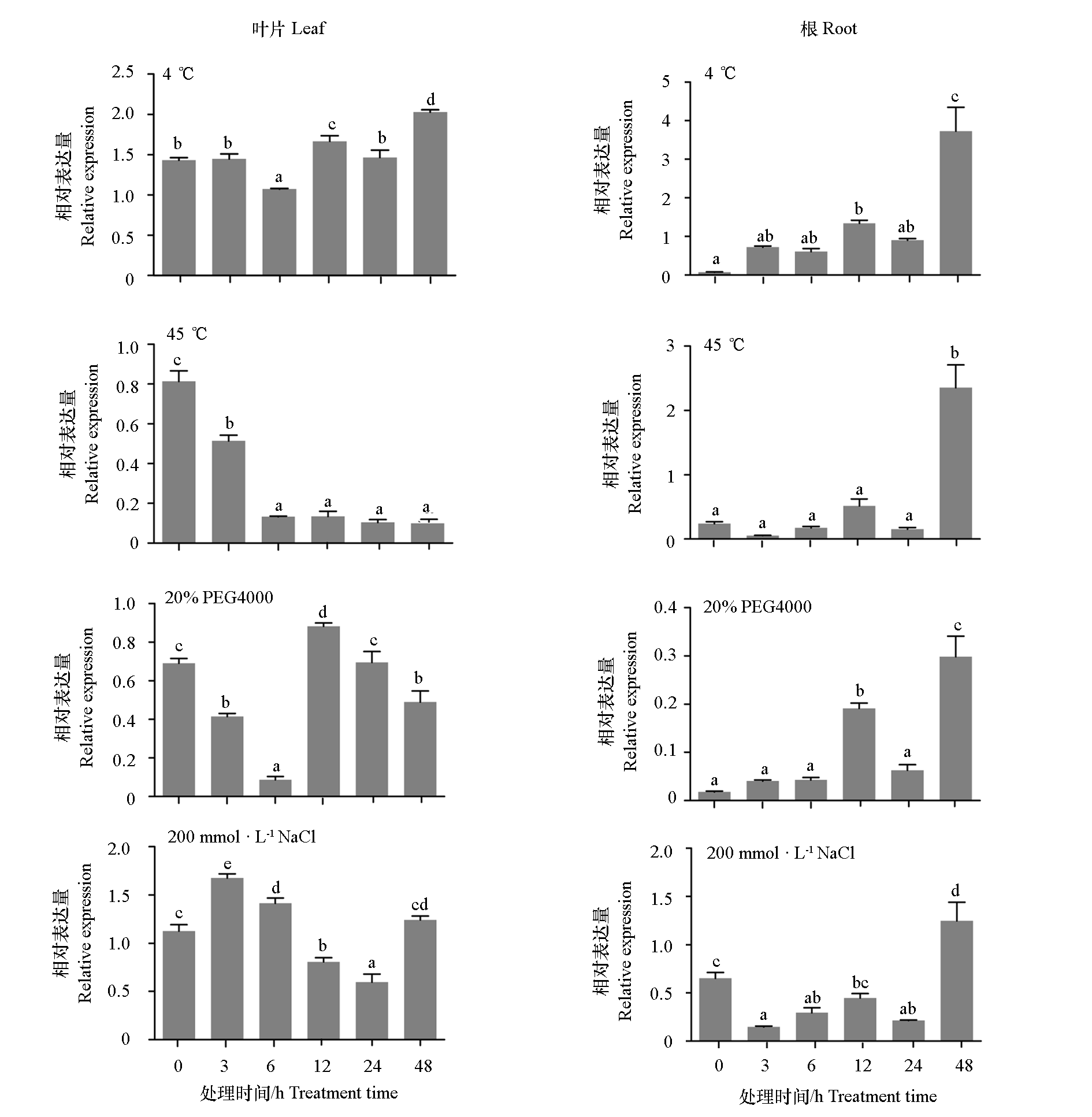
Fig. 7 Expression pattern of RcRAP2.7 of Rosa chinensis‘Yueyuehong’in different tissues under abiotic stresses Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatment time(P < 0.05)
| [1] |
|
|
艾蓉, 张春, 悦曼芳, 邹华文, 吴忠义. 2023. 玉米转录因子ZmEREB211对非生物逆境胁迫的应答. 作物学报, 49 (9):2433-2445.
|
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
崔波, 郝平安, 梁芳, 张燕, 王喜蒙, 李俊霖, 蒋素华, 许申平. 2020. 蝴蝶兰AP2/ERF 家族基因的克隆及在低温下表达特性分析. 园艺学报,2020, 47 (1):85-97.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
董翠翠, 马岩岩, 谢让金, 邓烈, 易时来, 吕强, 郑永强, 何绍兰. 2016. 柑橘CitERF9和CitAP2-7在不同逆境和外源激素处理下的表达. 园艺学报, 43 (2):239-248.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
贾鑫, 曾臻, 陈月, 冯慧, 吕英民, 赵世伟. 2022. 月季‘月月粉’RcDREB2A的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1945-1956.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
兰孟焦, 后猛, 肖满秋, 李臣, 潘皓, 张允刚, 卢凌志, 侯隆英, 葛瑞华, 吴问胜, 李强. 2023. AP2/ERF转录因子参与植物次生代谢和逆境胁迫响应的研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报, 24 (5):1223-1235.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘志薇, 熊洋洋, 李彤, 严雅君, 韩洪润, 吴致君, 庄静. 2014. 茶树中两个ERF类转录因子的分离及不同茶树中温度胁迫的响应分析. 植物生理学报, 50 (12):1821-1832.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
唐征, 陈思雀, 徐谦, 钟伟杰, 刘庆, 朱世杨. 2024. AP2/ERF在青花菜苗期响应黑腐病的功能研究. 园艺学报, 51 (11):2523-2539.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
王婉儿, 王炳臻, 周艳, 付佳宾, 陈玲玲, 牛一丁. 2023. 黄花苜蓿AP2/ERF家族MfERF028基因的表达特性与耐寒功能分析. 中国草地学报, 45 (6):15-22.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
悦曼芳, 张春, 吴忠义. 2022. 植物转录因子AP2/ERF家族蛋白结构和功能的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 38 (12):11-26.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
赵雅彬, 张博, 胡林, 袁浩, 朱俊勇, 孙丽芳, 张文慧. 2018. 白桦BpERF1和BpERF2基因的克隆与表达模式分析. 四川农业大学学报, 36 (3):329-336.
|
| [1] | WANG Yunyun, ZHOU Hui, QIU Keli, PAN Haifa, SHENG Yu, SHI Pei, XIE Qingmei, CHEN Hongli, ZHANG Jinyun, LI Dahui. Identification and Expression Analysis of Peach JMJ Histone Demethylase Gene Family [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 575-590. |
| [2] | DENG Shuqin, GAO Yingrui, LI Yutong, WANG Ying, GONG Chunmei, BAI Juan. Response of Ubiquitin-ligase Gene CsPUB21 to Different Abiotic Stress in Camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 655-670. |
| [3] | LI Yadi, WANG Hanxiang, HU Baigeng, YANG Hui, HU Xinxi, XIONG Xingyao, WANG Wanxing. Research Progress on Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria to Alleviate Abiotic Stress Tolerance of Horticultural Crops [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1964-1976. |
| [4] | LI Yachen, ZHENG Yanmei, SONG Wenpei, LI Dawei, LIANG Hong, ZHANG Xianzhi. Research Progress on the Role of Hydrogen-Rich Water in Plant Growth and Development and Stress Response [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1489-1500. |
| [5] | LUO Xinrui, ZHANG Xiaoxu, WANG Yuping, WANG Zhi, MA Yuanyuan, ZHOU Bingyue. Identification and Expression Analysis of Trihelix Gene Family in Common Bean [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2775-2790. |
| [6] | ZHANG Pan, YU Yongxu, CAO Linggai, ZHU Guangbing, WU Wei, GUO Yushuang, YIN Guoying, JIA Meng’ao. Research Progress of m6A Methylation Modification Response to Plant Biotic and Abiotic Stresses [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1841-1853. |
| [7] | WEI Jianming, LI Yunzhou, LIANG Yan. Advances in Research on Improving Tomato Disease Resistance and Stress Resistance by Grafting Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1997-2014. |
| [8] | SHEN Yuxiao, ZOU Jinyu, LUO Ping, SHANG Wenqian, LI Yonghua, HE Songlin, WANG Zheng, SHI Liyun. Genome-wide Identification and Abiotic Stress Response Analysis of PP2C Family Genes in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2139-2156. |
| [9] | XU Xiaoping, CAO Qingying, CAI Roudi, GUAN Qingxu, ZHANG Zihao, CHEN Yukun, XU HAN, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of miR408 and Its Target DlLAC12 in Globular Embryo Development and Abiotic Stress in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. |
| [10] | JIA Xin, ZENG Zhen, CHEN Yue, FENG Hui, LÜ Yingmin, ZHAO Shiwei. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RcDREB2A Gene in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1945-1956. |
| [11] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zhiming, YANG Jiabao, ZHANG Cheng, ZENG Linglu, MENG Wanqiu, SUN Li. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Long-chain Acyl-CoA Synthetases Under Abiotic Stresses in Helianthus annuus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 352-364. |
| [13] | XIE Siyi, ZHOU Chengzhe, ZHU Chen, ZHAN Dongmei, CHEN Lan, WU Zuchun, LAI Zhongxiong, GUO Yuqiong. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CsTIFY Transcription Factor Family Under Abiotic Stress and Hormone Treatments in Camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| [14] | LIANG Zhile, WANG Kuanhong, YANG Jing, ZHU Biao, ZHU Zhujun. The Importance of Glucosinolates on Plant Response to Abiotic Stress in Brassicaceae Family [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 200-220. |
| [15] | YANG Tianchen, CHEN Xiaotong, LÜ Ke, ZHANG Di. Expression Pattern and Regulation Mechanism of ApSK3 Dehydrin (Agapanthus praecox)Response to Abiotic Stress and Hormone Signals [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1565-1578. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd