
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 623-634.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0382
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Qi1,2, WANG Dan1,2, JING Weikun1, ZHANG Hao1, WANG Huichun1, JIAN Hongying1, QIU Xianqin1, WANG Qigang1, TANG Kaixue1, YAN Huijun1,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-02
Revised:2025-02-20
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-25
Contact:
YAN Huijun
FU Qi, WANG Dan, JING Weikun, ZHANG Hao, WANG Huichun, JIAN Hongying, QIU Xianqin, WANG Qigang, TANG Kaixue, YAN Huijun. Functional Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases 4 Gene(RcCCD4)Involved in Biosynthetic Pathway of Floral Scent in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 623-634.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0382
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆基因 | RcCCD4-F | ATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Gene clone | RcCCD4-R | CAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默 | pTRV1-F | TTACAGGTTATTTGGGCTAG |
| Virus induced gene | pTRV1-R | CCGGGTTCAATTCCTTATC |
| silencing | pTRV2-F | TGGGAGATGATACGCTGTT |
| pTRV2-R | CCTAAAACTTCAGACACG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-F | GAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCAGCTCGACGTGTCGG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-R | CTCGAGACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCATACAACAGTCACAACGTTTGTG | |
| 原核表达 | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-F | CGCGGCAGCCATATGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCTT |
| Prokaryotic expression | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 过表达 | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-F | AAGCTTCTGCAGGGGCCCGGGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Overexpression | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-R | TCCTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGTACCCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | qRT-RcCCD4-F | AGCTCGACGTGTCGGG |
| qRT-RcCCD4-R | CCTCCGGATTCTCCGGATCC | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-F | GTTGATGTACGACAGTTCTCAGCCT | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-R | ACAAACTCTCCATTCAAGCAATCAGG | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-F | AGTGGAACAAGTCATCAGATTTTCCAGT | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-R | TAGTTGAAGCATTCAGCTTCACCAC | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-F | TGTTTTAATGACATGCCGCCTTGAG | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-R | ATAATTTCTTCTGTGTTGCTAAACCGGT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-F | GAGGGTGAAGCGATTGCAAAAATT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-R | TGACACGGAGAAAATTCATGGTTACAG | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-F | TGCCAACCTCATCGAACACCTAA | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-R | ATGGTCAACTACACACTTGTATACGACT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-F | CAATCTCACTGAACCCACTTGCTT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-R | CACTACTACTTTAACTCAAAGCCTGCTCC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-F | AGAAGACGTGGAAGTCGGAGC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-R | AGCTACTGCTATGCCTGGTTTTTCA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆基因 | RcCCD4-F | ATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Gene clone | RcCCD4-R | CAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 病毒诱导的基因沉默 | pTRV1-F | TTACAGGTTATTTGGGCTAG |
| Virus induced gene | pTRV1-R | CCGGGTTCAATTCCTTATC |
| silencing | pTRV2-F | TGGGAGATGATACGCTGTT |
| pTRV2-R | CCTAAAACTTCAGACACG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-F | GAGTAAGGTTACCGAATTCAGCTCGACGTGTCGG | |
| pTRV2-RcCCD4-R | CTCGAGACGCGTGAGCTCGGTACCATACAACAGTCACAACGTTTGTG | |
| 原核表达 | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-F | CGCGGCAGCCATATGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCTT |
| Prokaryotic expression | Pet28a(+)-RcCCD4-R | GTGGTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 过表达 | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-F | AAGCTTCTGCAGGGGCCCGGGATGGATGCCTTGTCTTCTTCT |
| Overexpression | pSurper-1300-RcCCD4-R | TCCTCGCCCTTGCTCACCATGGTACCCAACTTCTTCAGGTCACTCTCC |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | qRT-RcCCD4-F | AGCTCGACGTGTCGGG |
| qRT-RcCCD4-R | CCTCCGGATTCTCCGGATCC | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-F | GTTGATGTACGACAGTTCTCAGCCT | |
| qRT-RcCCD1-R | ACAAACTCTCCATTCAAGCAATCAGG | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-F | AGTGGAACAAGTCATCAGATTTTCCAGT | |
| qRT-RcCCD7-R | TAGTTGAAGCATTCAGCTTCACCAC | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-F | TGTTTTAATGACATGCCGCCTTGAG | |
| qRT-RcCCD8-R | ATAATTTCTTCTGTGTTGCTAAACCGGT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-F | GAGGGTGAAGCGATTGCAAAAATT | |
| qRT-RcZAS-R | TGACACGGAGAAAATTCATGGTTACAG | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-F | TGCCAACCTCATCGAACACCTAA | |
| qRT-RcZAS-like-R | ATGGTCAACTACACACTTGTATACGACT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-F | CAATCTCACTGAACCCACTTGCTT | |
| qRT-RcNCED1-R | CACTACTACTTTAACTCAAAGCCTGCTCC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-F | AGAAGACGTGGAAGTCGGAGC | |
| qRT-RcNCED6-R | AGCTACTGCTATGCCTGGTTTTTCA |
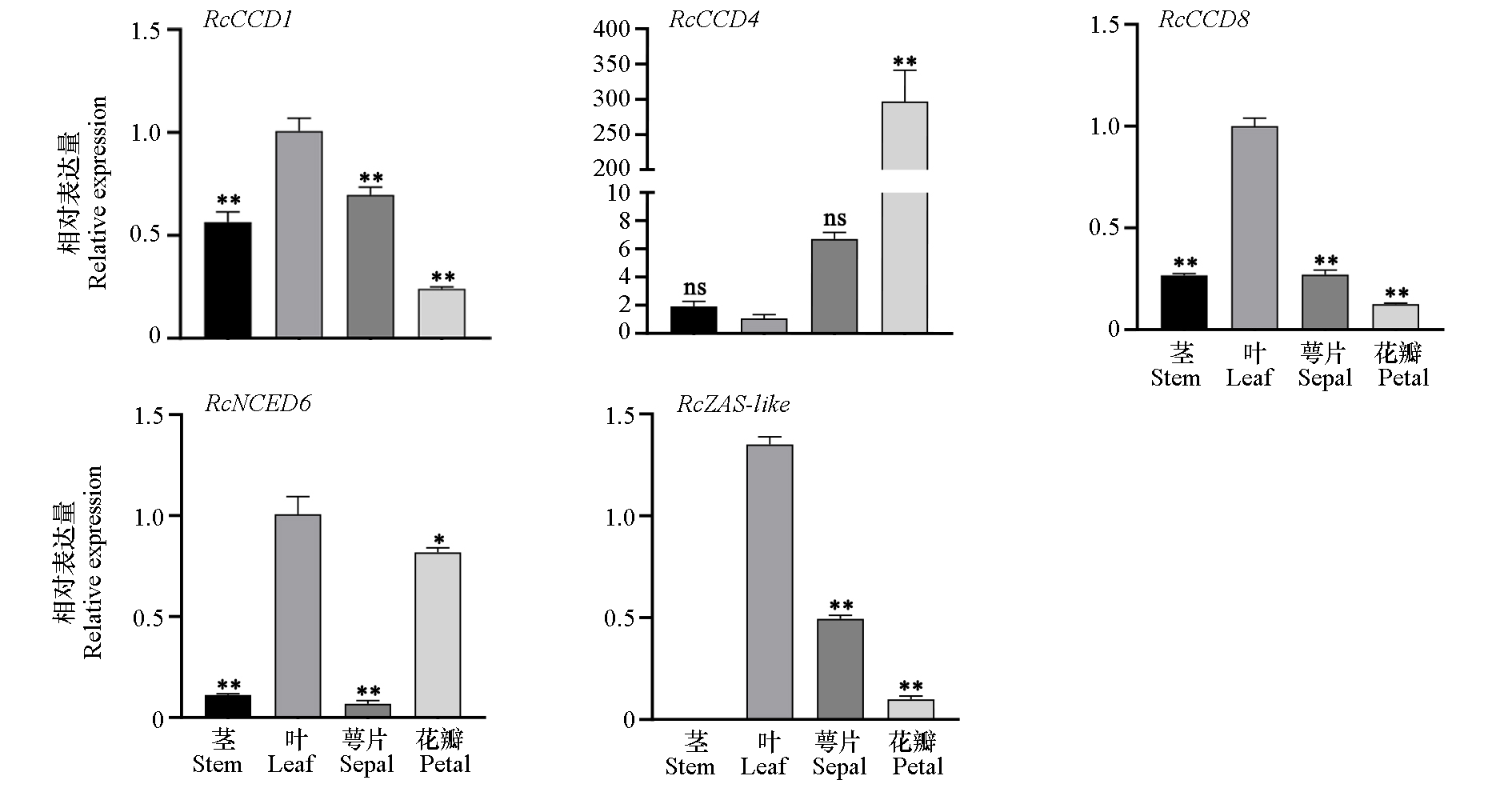
Fig. 3 Expression of CCD family genes in different organs of Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ Compared with leaf as a control,t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant
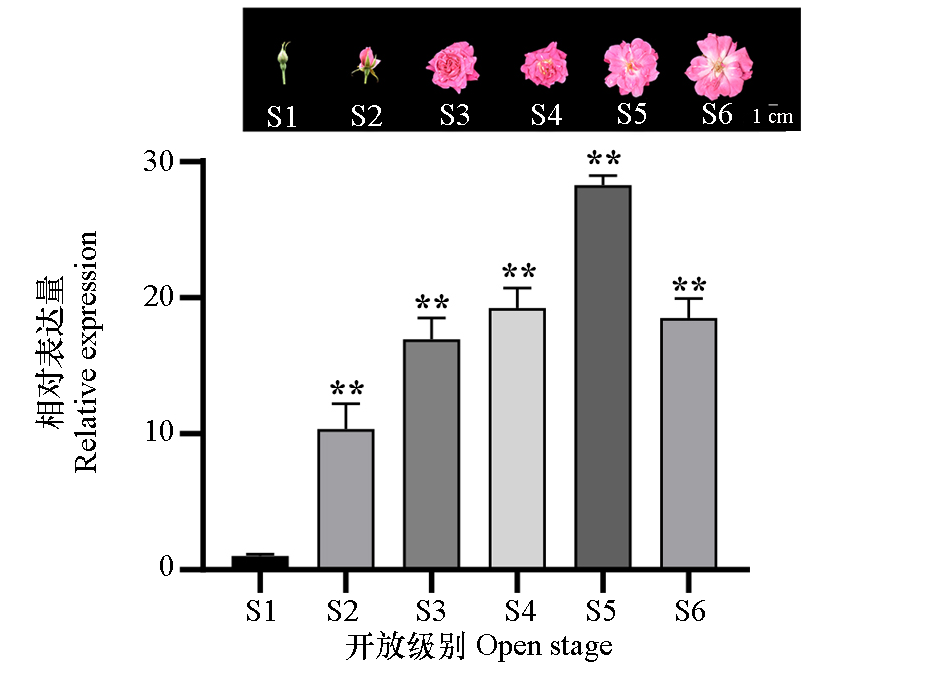
Fig. 4 Expression of RcCCD4 in the petals during different developmental stages of Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ Compared with S1 stage in the bud stage as a control,t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant
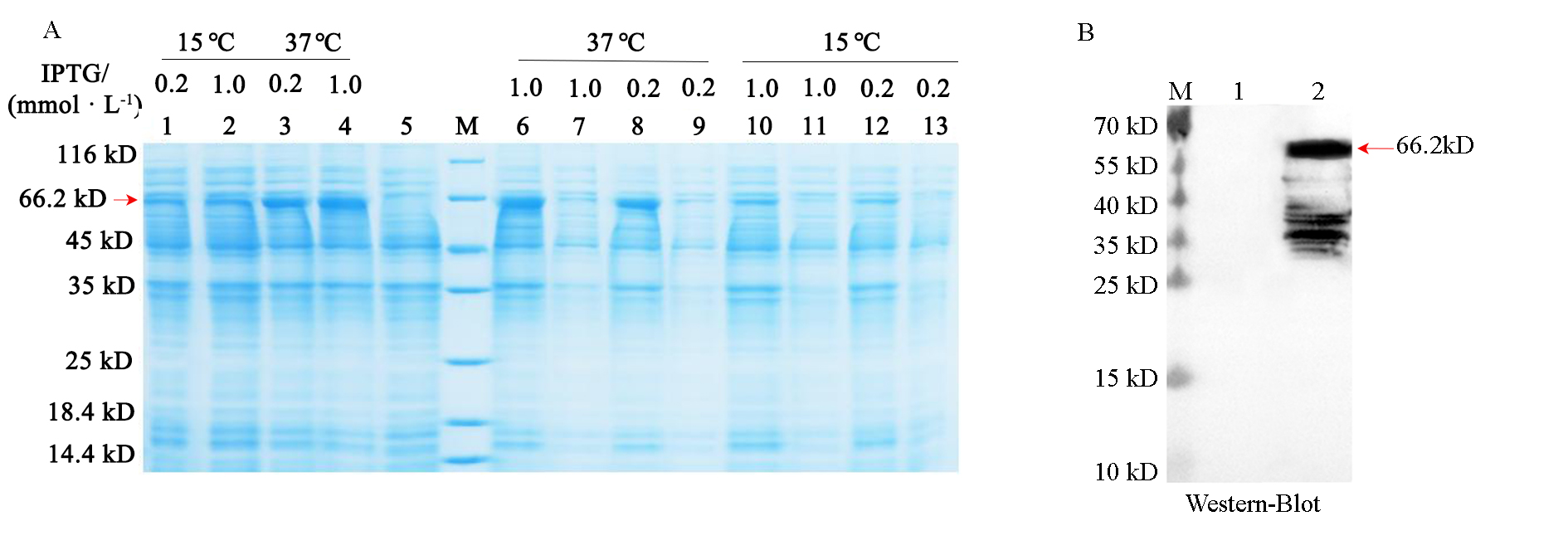
Fig. 5 Conditions optimization(A)and Western-Blot analysis(B)of RcCCD4 recombination protein M:Marker. The arrows indicate the protein of interest;1-4:IPTG-induced samples at different temperatures and concentrations;5:Uninduced sample;6,8,10,12:Precipitated sample;7,9,11,13:Supernatant samples

Fig. 7 Expression of RcCCD4 in infected plants by qRT-PCR and relative contents of dihydro-β-ionone in Rosa hybrida‘Luoshen’ t-test,* represents a significance level of α = 0.05;** represents a significance level of α = 0.01;ns:No significant;NT:No-treatment sample;Mock:TRV empty sample. The same below
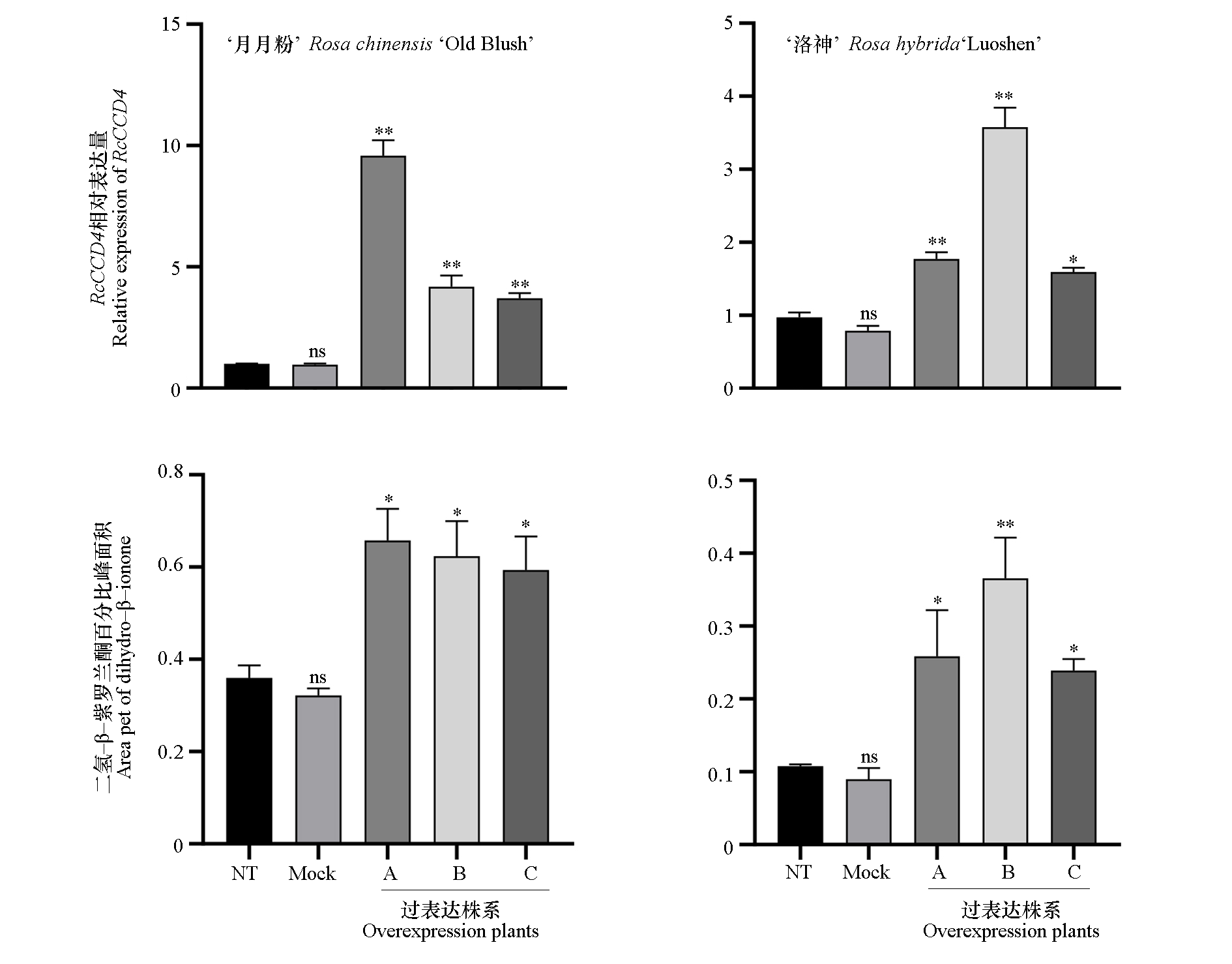
Fig. 8 Expression of RcCCD4 in overexpression plants by qRT-PCR and relative contents of dihydro-β-ionone in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’and Rosa hybrida‘Luoshen’
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.005 pmid: 16616608 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq123 pmid: 20478967 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: S0003-9861(15)00073-9 pmid: 25703194 |
| [5] |
|
|
房强. 2020. 香雪兰类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶(FhCCDs)基因克隆与功能鉴定[博士论文]. 长春: 东北师范大学.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1007/s11130-015-0482-9 pmid: 25861766 |
| [7] |
pmid: 12368489 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221 URL |
|
侯异璇, 张玲, 吕梦雯, 武耀星, 王亮生, 张秀卿, 李珊珊. 2023. 芍药属组间杂种花香成分分析. 园艺学报, 50 (4):842-852.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1221 URL |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘家仁, 杨艳梅, 董宏伟, 孙向荣, 于佳, 赵淑媛, 陈炳卿. 2005. β-紫罗兰酮对人乳腺癌细胞(Er-)MAPK途径的影响. 卫生研究, 34 (6):4.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0962-8 pmid: 23100158 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 16980560 |
| [20] |
Pino, Jorge, Antonio, Quijano, Clara, Elizabeth. 2012. Study of the volatile compounds from plum(Prunus domestica L. cv. Horvin)and estimation of their contribution to the fruit aroma. Ciência E Tecnologia De Alimentos, 32 (1):76-83
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0208 |
|
叶云芳, 田清尹, 施婷婷, 王亮, 岳远征, 杨秀莲, 王良桂. 2023. 植物中β-紫罗兰酮生物合成及调控研究进展. 生物技术通报, 39 (8):91-105.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0208 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
易星. 2014. ‘月月红’月季胚性愈伤组织诱导及遗传转化基础研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.13335 pmid: 25690717 |
| [36] |
|
|
赵静, 胡增辉, 冷平生, 杨晓红. 2013. 两个金鱼草品种香气成分分析. 北京农学院学报, 28 (3):5.
|
| [1] | YAN Xu, LI Yue, FU Xiaopeng, NING Guogui, LIANG Mei. Allele-specific Imbalance Analysis and Related Molecular Marker Development in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 365-379. |
| [2] | YANG Binan, LI Bowen, YANG Zhenyu, XU Yipeng, YAN Yunqing, LOU Yuxia, FENG Shucheng, MING Feng. The Mechanism of Heat Stress Response and the Exploration of Functional Genes in Rosa chinensis‘Angela’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1284-1296. |
| [3] | WANG Wen, ZHANG Peng, WANG Zhimin, LIU Genzhong, BAO Zhilong, MA Fangfang. Analysis of Differential Genes in Response to Sucrose Feeding in Disc Florets of Chrysanthemum nankingense [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1297-1310. |
| [4] | WANG Wenyu, WANG Jiayin, DU Tingting, ZHANG Jingjing, ZHANG Chao, XIN Cuihua, GUO Jiangbo, PEI Haixia. Cloning of RhRNF185-like Gene from Rose and Its Effect on Petal Senescence [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1047-1055. |
| [5] | LAN Wei, MENG Yanqiong, XUAN Yun, ZHU Kangning, DING Xiaohao, FAN Dexin, KANG Liyun. A New Rose Cultivar‘Yinghe’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 925-926. |
| [6] | LIANG Yuqing, SUN Chunhui, DENG Congliang, SHI Xiju, ZHONG Yan, LI Yongqiang. Identification and Analysis of Complete Genomic Sequence of Broad Bean Wilt Virus 2 Beijing Rose Isolate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2320-2328. |
| [7] | ZHANG Lilan, YANG Jun, WANG Rangjian. Mining of Genetic Locus of Phenylethyl Alcohol Primrose Glycoside Abundance in Tea Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 77-90. |
| [8] | LÜ Mengwen, YANG Yong, WANG Liangsheng, and LI Shanshan, . A New Tree Peony Cultivar‘Huayu Zhining’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 145-146. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yan, GAO Shumin , CUI Rongfeng , SUN Liping , and FU Zihao, . Breeding of New Rose Cultivar of‘Yanjinghuang’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 149-150. |
| [10] | GAO Junping, MA Nan, ZHOU Hougao, WANG Jiaxi, ZHANG Changqing, LI Yonghong, ZHOU Xiaofeng, SUN Xiaoming. A New Cut Rose Cultivar‘Feiyun’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 915-916. |
| [11] | REN Fei, LU Miaomiao, LIU Jixiang, CHEN Xinli, LIU Daofeng, SUI Shunzhao, MA Jing. Expression and Adversity Resistance Analysis of a Late Embryogenesis Abundant Protein Gene CpLEA from Chimonanthus praecox [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [12] | OUYANG Liying, HUANG Yanfei, CHEN Junmei, YANG Shu, and LIAN Huashan. A New Miniature Rose Cultivar‘Jiuer’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 223-224. |
| [13] | LIAN Huashan, OUYANG Liying, WU Shan, Chen Junmei, and SHU Bin. A New Miniature Rose Cultivar‘Yehua’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 225-226. |
| [14] | CHEN Junmei, LIAN Huashan, HUANG Yanfei, YU Ting, and JIANG Tianyi. A New Miniature Rose Cultivar‘Liuxing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 227-228. |
| [15] | JIA Xin, ZENG Zhen, CHEN Yue, FENG Hui, LÜ Yingmin, ZHAO Shiwei. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RcDREB2A Gene in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1945-1956. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd