
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (10): 2192-2206.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0740
• Cultivation Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
PENG Ling1, FENG Lu1, SONG Aiyun1, DONG Linshui1, LI Qingjun2, LIU Jingtao1,*( )
)
Received:2023-04-17
Revised:2023-07-11
Online:2023-10-25
Published:2023-10-30
PENG Ling, FENG Lu, SONG Aiyun, DONG Linshui, LI Qingjun, LIU Jingtao. Interaction of Different Concentrations of Salt and Nitrogen Treatment on Fruit Quality Formation of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2192-2206.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0740
| NaCl/(g · L-1) | N/(g · L-1) | 叶绿素a/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll a | 叶绿素b/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll b | 叶绿素(a+b)/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll (a+b) | 叶绿素a/b Chlorophyll a/b | 相对电导率/% Relative electrolyte leakage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1.57 g | 0.59 h | 2.16 h | 2.64 d | 39.73 j |
| 2(低Low) | 1.65 e | 0.68 f | 2.33 f | 2.40 f | 37.50 k | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.04 a | 0.91 a | 2.95 a | 2.25 g | 33.30 l | |
| 8(高High) | 1.95 b | 0.84 c | 2.78 c | 2.33 g | 42.77 gh | |
| 1(低Low) | 0 | 1.53 h | 0.58 h | 2.11 i | 2.65 d | 41.71 hi |
| 2(低Low) | 1.63 e | 0.67 f | 2.31 f | 2.42 f | 40.70 ij | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.02 a | 0.89 b | 2.92 b | 2.26 g | 34.30 l | |
| 8(高High) | 1.91 c | 0.80 d | 2.71 d | 2.40 f | 45.11 f | |
| 3(中Middle) | 0 | 1.50 i | 0.56 i | 2.05 j | 2.69 d | 48.45 e |
| 2(低Low) | 1.61 f | 0.64 g | 2.24 g | 2.53 e | 44.65 f | |
| 4(中Middle) | 1.93 bc | 0.85 c | 2.77 c | 2.29 g | 43.37 g | |
| 8(高High) | 1.86 d | 0.77 e | 2.63 e | 2.41 f | 49.68 d | |
| 5(高High) | 0 | 1.24 l | 0.40 k | 1.70 m | 3.24 b | 62.43 a |
| 2(低Low) | 1.30 k | 0.47 j | 1.85 l | 2.94 c | 57.36 b | |
| 4(中Middle) | 1.34 j | 0.48 j | 1.91 k | 2.97 c | 55.83 c | |
| 8(高High) | 1.18 m | 0.32 l | 1.50 n | 3.64 a | 63.10 a |
Table 1 Pigment content and relative electrolyte leakage at different concentrations of salinity and nitrogen
| NaCl/(g · L-1) | N/(g · L-1) | 叶绿素a/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll a | 叶绿素b/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll b | 叶绿素(a+b)/ (mg · g-1 FW) Chlorophyll (a+b) | 叶绿素a/b Chlorophyll a/b | 相对电导率/% Relative electrolyte leakage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1.57 g | 0.59 h | 2.16 h | 2.64 d | 39.73 j |
| 2(低Low) | 1.65 e | 0.68 f | 2.33 f | 2.40 f | 37.50 k | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.04 a | 0.91 a | 2.95 a | 2.25 g | 33.30 l | |
| 8(高High) | 1.95 b | 0.84 c | 2.78 c | 2.33 g | 42.77 gh | |
| 1(低Low) | 0 | 1.53 h | 0.58 h | 2.11 i | 2.65 d | 41.71 hi |
| 2(低Low) | 1.63 e | 0.67 f | 2.31 f | 2.42 f | 40.70 ij | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.02 a | 0.89 b | 2.92 b | 2.26 g | 34.30 l | |
| 8(高High) | 1.91 c | 0.80 d | 2.71 d | 2.40 f | 45.11 f | |
| 3(中Middle) | 0 | 1.50 i | 0.56 i | 2.05 j | 2.69 d | 48.45 e |
| 2(低Low) | 1.61 f | 0.64 g | 2.24 g | 2.53 e | 44.65 f | |
| 4(中Middle) | 1.93 bc | 0.85 c | 2.77 c | 2.29 g | 43.37 g | |
| 8(高High) | 1.86 d | 0.77 e | 2.63 e | 2.41 f | 49.68 d | |
| 5(高High) | 0 | 1.24 l | 0.40 k | 1.70 m | 3.24 b | 62.43 a |
| 2(低Low) | 1.30 k | 0.47 j | 1.85 l | 2.94 c | 57.36 b | |
| 4(中Middle) | 1.34 j | 0.48 j | 1.91 k | 2.97 c | 55.83 c | |
| 8(高High) | 1.18 m | 0.32 l | 1.50 n | 3.64 a | 63.10 a |
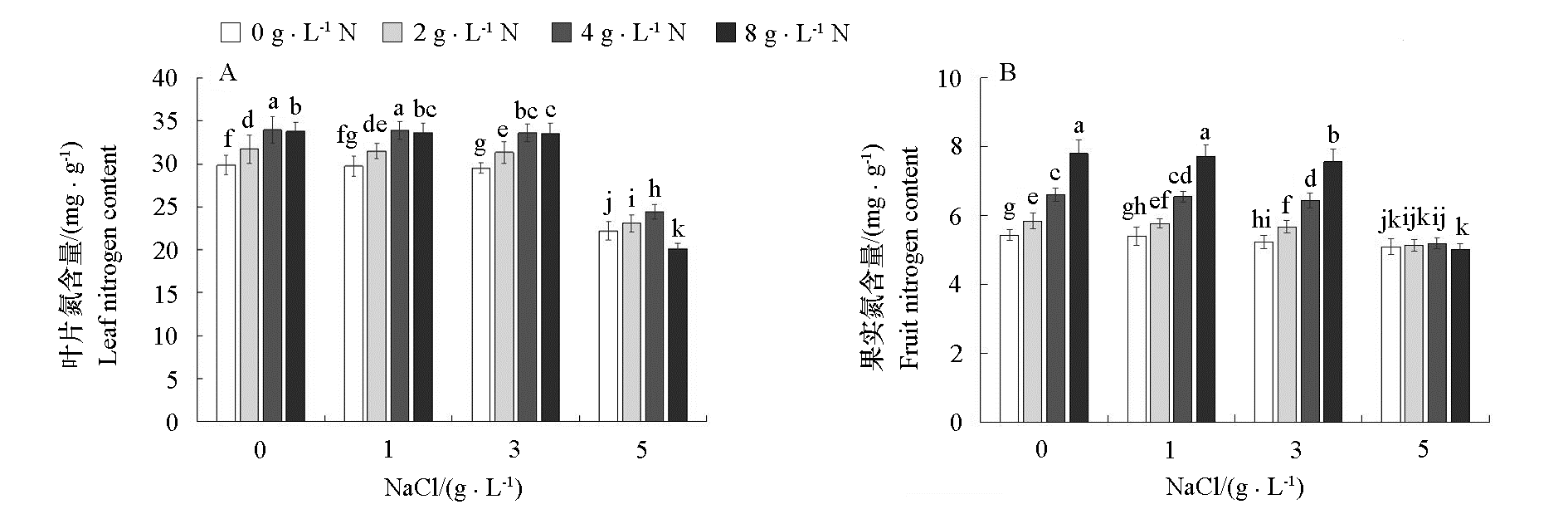
Fig. 1 Leaf nitrogen and fruit nitrogen content at different concentrations of salinity and nitrogen Different lowercase letters on the column chart indicate significant difference among treatments at 0.05 level(P < 0.05). The same below.
| NaCl/(g · L-1) | N/(g · L-1) | K+含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) K+ content | Na+含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) Na+ content | Cl-含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) Cl- content | K+/Na+ K+ /Na+ ratios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3.04 g | 0.15 i | 1.65 ij | 18.77 e |
| 2(低Low) | 3.39 d | 0.14 j | 1.75 hi | 22.21 c | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.89 a | 0.12 k | 1.63 j | 28.93 a | |
| 8(高High) | 3.58 b | 0.13 j | 1.80 gh | 24.16 b | |
| 1(低Low) | 0 | 2.82 i | 0.18 g | 1.90 fg | 15.48 f |
| 2(低Low) | 3.17 f | 0.17 gh | 1.92 ef | 18.21 e | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.57 b | 0.16 h | 1.86 fgh | 21.35 c | |
| 8(高High) | 3.49 c | 0.17 hi | 1.94 def | 21.05 d | |
| 3(中Middle) | 0 | 2.73 j | 0.25 d | 2.07 bc | 11.13 i |
| 2(低Low) | 2.90 h | 0.23 e | 2.07 bc | 12.43 h | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.28 e | 0.21 f | 2.03 cd | 15.37 f | |
| 8(高High) | 3.19 f | 0.23 e | 2.03 cde | 14.05 g | |
| 5(高High) | 0 | 2.34 l | 0.35 a | 2.25 a | 8.02 l |
| 2(低Low) | 2.45 l | 0.31 b | 2.07 bc | 8.99 jk | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.51 k | 0.29 c | 2.17 ab | 9.63 j | |
| 8(高High) | 2.31 l | 0.30 bc | 2.22 a | 8.30 kl |
Table 2 Ion accumulation in fruit at different concentrations of salinity and nitrogen
| NaCl/(g · L-1) | N/(g · L-1) | K+含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) K+ content | Na+含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) Na+ content | Cl-含量/ (mg · g-1 FW) Cl- content | K+/Na+ K+ /Na+ ratios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 3.04 g | 0.15 i | 1.65 ij | 18.77 e |
| 2(低Low) | 3.39 d | 0.14 j | 1.75 hi | 22.21 c | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.89 a | 0.12 k | 1.63 j | 28.93 a | |
| 8(高High) | 3.58 b | 0.13 j | 1.80 gh | 24.16 b | |
| 1(低Low) | 0 | 2.82 i | 0.18 g | 1.90 fg | 15.48 f |
| 2(低Low) | 3.17 f | 0.17 gh | 1.92 ef | 18.21 e | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.57 b | 0.16 h | 1.86 fgh | 21.35 c | |
| 8(高High) | 3.49 c | 0.17 hi | 1.94 def | 21.05 d | |
| 3(中Middle) | 0 | 2.73 j | 0.25 d | 2.07 bc | 11.13 i |
| 2(低Low) | 2.90 h | 0.23 e | 2.07 bc | 12.43 h | |
| 4(中Middle) | 3.28 e | 0.21 f | 2.03 cd | 15.37 f | |
| 8(高High) | 3.19 f | 0.23 e | 2.03 cde | 14.05 g | |
| 5(高High) | 0 | 2.34 l | 0.35 a | 2.25 a | 8.02 l |
| 2(低Low) | 2.45 l | 0.31 b | 2.07 bc | 8.99 jk | |
| 4(中Middle) | 2.51 k | 0.29 c | 2.17 ab | 9.63 j | |
| 8(高High) | 2.31 l | 0.30 bc | 2.22 a | 8.30 kl |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.08.006 pmid: 31303840 |
| [2] |
|
|
卞诗村, 陆雅妮, 许吴俊, 陈伯清, 王广龙, 熊爱生. 2021. 大蒜生物钟基因AsRVE1和AsRVE2及其在渗透胁迫下的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1706-1716.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0961 URL |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0139 URL |
|
陈皓炜, 陈梦娇, 王雅慧, 张榕蓉, 王欣蕊, 徐志胜, 谭国飞, 熊爱生. 2021. 盐胁迫下胡萝卜肉质根中木质素响应机理研究. 园艺学报, 48 (1):153-161.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0139 URL |
|
| [5] |
|
|
陈金陵, 杨启良, 刘小刚, 王卫华, 刘艳伟. 2016. 盐胁迫条件下施氮对小桐子光合特性的调控效应. 排灌机械工程学报, 34 (7):631-638.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00217 pmid: 29520289 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1021/jf051930a pmid: 16417302 |
| [9] |
pmid: 18409427 |
| [10] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.023 |
|
李红强, 姚荣江, 杨劲松, 王相平, 郑复乐, 陈强, 谢文萍, 张新. 2020. 盐渍化对农田氮素转化过程的影响机制和增效调控途径. 应用生态学报, 31 (11):3915-3924.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202011.023 |
|
| [11] |
|
|
李晓玲. 2012. NaCl诱导的葡萄果实品质变化及MYB转录因子的筛选[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0625-6 URL |
| [13] |
|
|
陆奇杰, 巢建国, 谷巍, 张文明. 2017. 不同氮素水平对茅苍术光合特性及生理指标的影响. 植物生理学报, 53 (9):1673-1679.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1080/03650340.2016.1276285 URL |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers354 pmid: 23307915 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0233-6 URL |
| [19] |
doi: 10.15835/nbha3925632 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2005.04.007 URL |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.01.010 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201904.011 |
|
沙建川, 贾志航, 徐新翔, 侯昕, 李秉毓, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2019. 氮水平对苹果叶片13C光合产物和15N向果实转移分配的影响. 应用生态学报, 30 (4):1373-1379.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201904.011 |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2008.133.issue-4 URL |
| [24] |
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas2020-0193 |
|
时丕彪, 蒋润枝, 沈明晨, 顾闽峰, 王春云, 李亚芳, 顾小兵. 2021. 盐胁迫对南瓜幼苗生长及光合特性的影响. 农学学报, 11 (12):74-79.
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas2020-0193 |
|
| [25] |
|
|
孙红, 孙田雨, 许丽丽, 杜远鹏, 姚玉新. 2017. 长期低盐处理对葡萄果实品质及转录组的影响. 植物生理学报, 53 (12):2197-2205.
|
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.1982.54.issue-1 URL |
|
孙红, 岳倩宇, 相广庆, 翟衡, 姚玉新. 2018. 不同浓度的NaCl处理对葡萄果实品质形成的影响. 植物生理学报, 54 (1):63-70.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120153 pmid: 23330792 |
| [29] |
|
|
王亚妮, 孙韬. 2022. 盐碱胁迫下小麦幼苗对施氮水平的生长、生理响应. 麦类作物学报, 42 (2):220-225.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
温志静, 郭延平, 张雯, 毛海燕, 梁俊. 2018. 叶喷不同水平氮肥对苹果果实淀粉和糖及代谢相关酶活性的影响. 西北农业学报, 27 (6):839-845.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
肖丹丹. 2020. 不同浓度盐水灌溉对水稻产量、叶片生理特性及品质的影响[硕士论文]. 扬州: 扬州大学.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
余天源, 何新林, 衡通. 2021. 盐氮效应对棉花氮素分配、转运和利用效率的影响. 水土保持学报, 35 (2):315-323.
|
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.52.6.569 URL |
|
岳利军, 崔彦农, 袁坤, 康建军, 王锁民. 2016. NaCl胁迫下沙芥的渗透调节作用. 植物生理学报, 52 (4):569-574.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
曾文治. 2015. 向日葵水、氮、盐耦合效应及其模拟[博士论文]. 武汉: 武汉大学.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00208 URL |
| [37] |
|
|
张强, 李兴亮, 李民吉, 周贝贝, 孙健, 魏钦平. 2016. ‘富士’苹果品质与果实矿质元素含量的关联性分析. 果树学报, 33 (11):1388-1395.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
赵世杰, 史国安, 董新纯. 2002. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社:1-4.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2013.05.010 URL |
| [40] |
|
|
朱占玲. 2019. 苹果生产系统养分投入特征和生命周期环境效益评价[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
| [1] | ZHANG Saihang, WEI Zhanlin, MA Ling. Pollen-pistil Interaction in Sexual Reproduction in Higher Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1813-1829. |
| [2] | XIAO Xiang, ZHOU Chujiang, JIN Shuwan, SHI Liyu, YANG Zhenfeng, CAO Shifeng, CHEN Wei. Mechanism of PpMADS2 and PpMADS3 Synergistically Regulating Carotenoids Accumulation in Peach Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1173-1186. |
| [3] | LI Yuting, REN Lihui, WANG Yuan, ZHOU Aiying, YANG Wei, HUANG Jian. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’Under Protected Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 647-656. |
| [4] | DING Lei, SUN Pingping, ZHANG Lei, and LI Zhengnan, . Screening Proteins of Nicotiana occidentalis That Interact with Coat Protein of Apple Stem Pitting Virus Using Yeast Two-hybrid System [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(11): 2509-2515. |
| [5] | YAN Wenyuan, QIN Junhong, DUAN Shaoguang, XU Jianfei, JIAN Yinqiao, JIN Liping, LI Guangcun. The Effect of Water-nitrogen Coupling on Potato Photosynthesis,Tuber Formation and Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1491-1504. |
| [6] | LIU Zhongjie, ZHENG Ting, ZHAO Fanggui, FU Weihong, ZHUGE Yaxian, ZHANG Zhichang, FANG Jinggui. Resistance Difference and Physiological Response Mechanism of Grape Rootstocks to Osmotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 984-994. |
| [7] | GAO Weilin, ZHANG Liman, XUE Chaoling, ZHANG Yao, LIU Mengjun, ZHAO Jin. Expression of E-type MADS-box Genes in Flower and Fruits and Protein Interaction Analysis in Chinese Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| [8] | LIU Xiaowei, XIA Bin, LI Ziwei, YANG Yujia, CHEN Bin, ZHOU Yunwei, HE Miao. Overexpression of Chrysanthemum indicum miR396a Gene in Arabidopsis Enhances Its Salt Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 816-826. |
| [9] | XIANG Li, ZHAO Lei, WANG Mei, LÜ Yi, WANG Yanfang, SHEN Xiang, CHEN Xuesen, YIN Chengmiao, MAO Zhiquan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of MdWRKY74 in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 482-492. |
| [10] | YANG Ni, WAN Qiwen, LI Yimin, HAN Miaohua, TENG Ruimin, LIU Jiexia, ZHUANG Jing. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expression of Key Enzymes Under Salt Stress in Tea Plant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 378-394. |
| [11] | MO Cuiping, WU Zilin, GUO Yongyi, ZHANG Shuguang, LI Pengfei, LI Huaping. The Neutral Interaction of Co-infection Papaya Between Papaya Ringspot Virus and Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2336-2346. |
| [12] | LI Ying, MENG Xianwei, MA Zhihang, LIU Mengjun, ZHAO Jin. Identification and Expression Analysis of MicroRNA Families Associated with Phase Transition in Chinese Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 23-40. |
| [13] | GUO Xuemin, WANG Xinrui, WANG Yingying, LI Zheng, MIAO Ningning, WANG Zhaojun. Anatomical Observation on the Tortuousness of Ziziphus jujuba var. tortuosa Branches [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1653-1664. |
| [14] | XIN Haiqing, ZHOU Junyong, SUN Yaoxing, MU Wenlei, YANG Jian, MA Fuli, SUN Jun, XUE Zhengrong, LU Lijuan, SUN Qibao. Differences in the Pericarp Structure and the Expression of Expansin Genes After Irrigation Between Easily Cracked and Resistant Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1785-1793. |
| [15] | LAN Liming, LUO Changguo, WANG Sanhong. Analysis of Resistance Mechanism to Powdery Mildew Based on Transcriptome Sequencing in Malus hupehensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 860-872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd