
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 41-61.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0726
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHEN Xu, CHEN Xiaohui, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Rongzhu, XU Xiaoping, LI Xiaofei, JIANG Mengqi, LIU Pudong, NI Shanshan, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong( )
)
Received:2021-09-15
Revised:2021-12-17
Online:2022-01-25
Published:2022-01-24
Contact:
LAI Zhongxiong
E-mail:laizx01@163.com
CLC Number:
SHEN Xu, CHEN Xiaohui, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Rongzhu, XU Xiaoping, LI Xiaofei, JIANG Mengqi, LIU Pudong, NI Shanshan, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong. Evolutionary Dynamics Investigation and the Expression Analysis of Chromatin Remodeling Factor Snf2 Gene Family During Early Somatic Embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 41-61.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0726
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| DlCHR2 | AACTTCTCAGCATCGGGTGG | CCTCAAGTGGTGGTGGAACA |
| DlCHR6 | CCGGAGGTCTGGGAATCAAC | GGTCTGCCCAAGTCGATGAG |
| DlCHR8 | TTACGGGACTTGATCATGCC | TCTTTGTTCTGCAGTGAGGC |
| DlCHR10 | AAGTCGAGGGAGTTGCTTGG | GTCACGCTCAGAGGACACAA |
| DlCHR11 | TAAGGTACTCCGGCCGTTTC | AGGCGTTTACGTTCTCCACC |
| DlCHR12 | ACACCGTCTCGTCCATCTAT | AACCTGACATGCATTTTGGC |
| DlCHR14 | AGCTTCTTCCATTCCAGCGG | AGCCCAATGCAAACGTAAGG |
| DlCHR16b | GACCCTGATGATGATGTCCG | ACTGGTGGATGGGCTTAGAT |
| DlCHR21 | ACATTCATCCCACGAGCCAG | GCAGTAGCCTCTTGACCCAG |
| DlCHR24 | GCTGCGAGAACGTATTCAACC | GTGGTGAGCCATCAAAAGCC |
| DlCHR28b | GCATCTGCAATGATCCCCCT | GTGTGGCCTTGGAAAACACC |
| DlCHR29 | TGATACGCAACAGTACTCGG | TTTCGCAGCTCCTCTACAAC |
| DlCHR31a | GCTTGATGTTGCATGGAACC | GTCCCGGATGTAATGAGACG |
| DlCHR35 | GCTTTCGGGAACCCTCTACC | CGGTTCACAATAGGCCGAGA |
| DlCHR36 | GCAGCAGGCACATCAACAAT | TGGGTGCGTTGTATGCTCTT |
| DlCHR42 | AGTGCTCCGTGAAAGTCCTG | ATGAACTTCGGTCGAGCCAG |
| DlEF-1a | GATGATTCCCACCAAGCCCAT | GGGTCCTTCT TCTCAACACT CT |
| DleIF-4a | TTGTGCTGGATGAAGCTGATG | GGAAGGAGCTGGAAGATATCATAGA |
| DlFe-SOD | GGTCAGATGGTGAAGCCGTAGAG | GTCTATGCCACCGATACAACAAACCC |
Table 1 The primer sequences in this study
| 基因 Gene | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| DlCHR2 | AACTTCTCAGCATCGGGTGG | CCTCAAGTGGTGGTGGAACA |
| DlCHR6 | CCGGAGGTCTGGGAATCAAC | GGTCTGCCCAAGTCGATGAG |
| DlCHR8 | TTACGGGACTTGATCATGCC | TCTTTGTTCTGCAGTGAGGC |
| DlCHR10 | AAGTCGAGGGAGTTGCTTGG | GTCACGCTCAGAGGACACAA |
| DlCHR11 | TAAGGTACTCCGGCCGTTTC | AGGCGTTTACGTTCTCCACC |
| DlCHR12 | ACACCGTCTCGTCCATCTAT | AACCTGACATGCATTTTGGC |
| DlCHR14 | AGCTTCTTCCATTCCAGCGG | AGCCCAATGCAAACGTAAGG |
| DlCHR16b | GACCCTGATGATGATGTCCG | ACTGGTGGATGGGCTTAGAT |
| DlCHR21 | ACATTCATCCCACGAGCCAG | GCAGTAGCCTCTTGACCCAG |
| DlCHR24 | GCTGCGAGAACGTATTCAACC | GTGGTGAGCCATCAAAAGCC |
| DlCHR28b | GCATCTGCAATGATCCCCCT | GTGTGGCCTTGGAAAACACC |
| DlCHR29 | TGATACGCAACAGTACTCGG | TTTCGCAGCTCCTCTACAAC |
| DlCHR31a | GCTTGATGTTGCATGGAACC | GTCCCGGATGTAATGAGACG |
| DlCHR35 | GCTTTCGGGAACCCTCTACC | CGGTTCACAATAGGCCGAGA |
| DlCHR36 | GCAGCAGGCACATCAACAAT | TGGGTGCGTTGTATGCTCTT |
| DlCHR42 | AGTGCTCCGTGAAAGTCCTG | ATGAACTTCGGTCGAGCCAG |
| DlEF-1a | GATGATTCCCACCAAGCCCAT | GGGTCCTTCT TCTCAACACT CT |
| DleIF-4a | TTGTGCTGGATGAAGCTGATG | GGAAGGAGCTGGAAGATATCATAGA |
| DlFe-SOD | GGTCAGATGGTGAAGCCGTAGAG | GTCTATGCCACCGATACAACAAACCC |
| 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼基因 Longan gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼基因 Longan gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtCHR33 | DlCHR28b | 0.40 | 1.36 | 0.30 | PNT24595 | DlCHR19 | 0.19 | 0.81 | 0.23 | |
| AtCHR30 | DlCHR28b | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.35 | PNS97818 | DlCHR21 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR15 | DlCHR15 | 0.73 | 1.85 | 0.39 | PNT29744 | DlCHR21 | 0.11 | 0.85 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR9 | DlCHR9 | 0.23 | 2.85 | 0.08 | PNT11818 | DlCHR28b | 0.32 | 0.85 | 0.37 | |
| AtCHR37 | DlCHR37 | 0.27 | 1.50 | 0.18 | PNT39429 | DlCHR28b | 0.25 | 0.87 | 0.28 | |
| AtCHR18 | DlCHR18 | 0.17 | 1.09 | 0.16 | PNT41192 | DlCHR25 | 0.13 | 0.80 | 0.16 | |
| AtCHR34 | DlCHR35 | 0.45 | — | — | PNT41496 | DlCHR35 | 0.20 | 1.51 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR35 | DlCHR35 | 0.31 | 2.02 | 0.15 | PNT20954 | DlCHR35 | 0.23 | 1.32 | 0.18 | |
| AtCHR6 | DlCHR6 | 0.21 | 1.82 | 0.12 | PNT56587 | DlCHR5 | 0.12 | 1.03 | 0.11 | |
| AtCHR36 | DlCHR36 | 0.27 | 1.38 | 0.19 | PNT42020 | DlCHR29 | 0.19 | 0.85 | 0.23 | |
| AtCHR10 | DlCHR10 | 0.20 | 1.34 | 0.15 | PNT42442 | DlCHR15 | 1.16 | 2.27 | 0.51 | |
| AtCHR2 | DlCHR2 | 0.20 | 1.31 | 0.15 | PNT19611 | DlCHR5 | 0.12 | 0.96 | 0.12 | |
| AtCHR25 | DlCHR25 | 0.19 | 1.18 | 0.16 | PNT05067 | DlCHR37 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.24 | |
| AtCHR12 | DlCHR12 | 0.18 | 1.70 | 0.10 | PNS94713 | DlCHR9 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.14 | |
| AtCHR11 | DlCHR11 | 0.06 | 1.67 | 0.03 | PNT09833 | DlCHR14 | 0.24 | 1.15 | 0.21 | |
| AtCHR7 | DlCHR6 | 0.32 | 2.14 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00002.143 | DlCHR6 | 1.12 | 2.87 | 0.39 | |
| AtCHR29 | DlCHR29 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 0.16 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR11 | 1.11 | — | — | |
| AtCHR17 | DlCHR11 | 0.06 | 1.57 | 0.04 | ar_scaffold00025.389 | DlCHR12 | 0.20 | 2.16 | 0.09 | |
| AtCHR23 | DlCHR12 | 0.20 | 1.60 | 0.12 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR18 | 0.24 | 1.80 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR22 | DlCHR36 | 0.95 | 2.20 | 0.43 | ar_scaffold00057.182 | DlCHR11 | 0.08 | 1.91 | 0.04 | |
| AtCHR24 | DlCHR24 | 0.32 | 1.78 | 0.18 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR11 | 1.04 | 3.04 | 0.34 | |
| AtCHR1 | DlCHR1a | 0.21 | 2.17 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR2 | 0.28 | 1.91 | 0.15 | |
| Os02t0762800-00 | DlCHR25 | 0.24 | 2.35 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR2 | 0.95 | 2.30 | 0.41 | |
| Os02t0527100-01 | DlCHR29 | 0.25 | 2.42 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR36 | 1.00 | 2.18 | 0.46 | |
| Os02t0650800-00 | DlCHR31a | 0.56 | — | — | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR8 | 0.26 | — | — | |
| Os03t0101700-01 | DlCHR10 | 0.52 | 2.15 | 0.24 | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR42 | 1.23 | 3.10 | 0.40 | |
| Os03t0722400-01 | DlCHR1a | 0.25 | — | — | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR36 | 0.35 | 1.67 | 0.21 | |
| Os05t0150300-01 | DlCHR11 | 0.10 | 3.63 | 0.03 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR8 | 1.02 | 3.20 | 0.32 | |
| Os06t0183800-01 | DlCHR6 | 0.67 | 2.42 | 0.28 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR2 | 1.15 | 3.54 | 0.32 | |
| Os07t0598300-01 | DlCHR14 | 0.40 | 2.10 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00111.13 | DlCHR10 | 0.68 | 3.82 | 0.18 | |
| Os07t0636200-01 | DlCHR18 | 0.23 | 1.93 | 0.12 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR1a | 0.72 | — | — | |
| PNT15539 | DlCHR12 | 0.13 | 0.83 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR1a | 0.78 | 4.74 | 0.16 | |
| PNT13987 | DlCHR18 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.16 | ar_scaffold00029.1 | DlCHR28a | 0.35 | 1.40 | 0.25 | |
| PNT14263 | DlCHR11 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.04 | ar_scaffold00053.139 | DlCHR21 | 0.22 | 2.15 | 0.10 | |
| PNS92200 | DlCHR6 | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.13 | ar_scaffold00003.327 | DlCHR28b | 0.25 | 1.56 | 0.16 | |
| PNT33877 | DlCHR6 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 0.13 | ar_scaffold00009.266 | DlCHR4 | 1.17 | 3.88 | 0.30 | |
| PNT25862 | DlCHR11 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.05 | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR4 | 0.87 | 3.48 | 0.25 | |
| PNT24755 | DlCHR12 | 0.13 | 0.90 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR28b | 1.09 | 2.01 | 0.54 | |
| PNT25862 | DlCHR12 | 0.64 | — | — | ar_scaffold00146.48 | DlCHR4 | 1.10 | 3.01 | 0.37 | |
| PNT06750 | DlCHR20a | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.20 | ar_scaffold00039.164 | DlCHR35 | 0.89 | — | — | |
| PNT07119 | DlCHR16a | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00126.55 | DlCHR25 | 0.22 | 2.06 | 0.11 | |
| PNT07119 | DlCHR16b | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00040.267 | DlCHR29 | 0.26 | 2.39 | 0.11 | |
| PNS90011 | DlCHR20a | 0.16 | 0.85 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00148.60 | DlCHR15 | 0.60 | 2.25 | 0.27 | |
| PNT17288 | DlCHR42 | 0.27 | 1.28 | 0.21 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR39 | 1.02 | 3.00 | 0.34 | |
| PNT03745 | DlCHR2 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR37 | 1.09 | 2.28 | 0.48 | |
| PNT03205 | DlCHR10 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.20 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR9 | 0.98 | — | — | |
| PNS90743 | DlCHR36 | 0.52 | — | — | ar_scaffold00002.143 | DlCHR13 | 1.21 | — | — | |
| PNT49991 | DlCHR2 | 0.11 | 0.81 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR13 | 0.93 | 2.75 | 0.34 | |
| PNT38168 | DlCHR8 | 0.15 | 0.78 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00032.254 | DlCHR13 | 0.82 | — | — | |
| PNT23278 | DlCHR42 | 0.24 | 1.04 | 0.23 | ar_scaffold00032.254 | DlCHR13 | 0.82 | — | — | |
| PNT35260 | DlCHR24 | 0.21 | 0.97 | 0.21 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR31a | 1.06 | — | — | |
| PNT28173 | DlCHR24 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 0.24 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR14 | 0.83 | — | — | |
| PNT15682 | DlCHR19 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00110.12 | DlCHR14 | 0.36 | 2.13 | 0.17 |
Table 2 Ka/Ks analysis of Snf2 collinear members in longan and Arabidopsis thaliana(At),Oryza sativa(Os),Populus trichocarpa(Pt),Amborella trichopoda(ar)
| 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼基因 Longan gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | 物种成员 Species member | 龙眼基因 Longan gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtCHR33 | DlCHR28b | 0.40 | 1.36 | 0.30 | PNT24595 | DlCHR19 | 0.19 | 0.81 | 0.23 | |
| AtCHR30 | DlCHR28b | 0.50 | 1.45 | 0.35 | PNS97818 | DlCHR21 | 0.11 | 0.87 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR15 | DlCHR15 | 0.73 | 1.85 | 0.39 | PNT29744 | DlCHR21 | 0.11 | 0.85 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR9 | DlCHR9 | 0.23 | 2.85 | 0.08 | PNT11818 | DlCHR28b | 0.32 | 0.85 | 0.37 | |
| AtCHR37 | DlCHR37 | 0.27 | 1.50 | 0.18 | PNT39429 | DlCHR28b | 0.25 | 0.87 | 0.28 | |
| AtCHR18 | DlCHR18 | 0.17 | 1.09 | 0.16 | PNT41192 | DlCHR25 | 0.13 | 0.80 | 0.16 | |
| AtCHR34 | DlCHR35 | 0.45 | — | — | PNT41496 | DlCHR35 | 0.20 | 1.51 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR35 | DlCHR35 | 0.31 | 2.02 | 0.15 | PNT20954 | DlCHR35 | 0.23 | 1.32 | 0.18 | |
| AtCHR6 | DlCHR6 | 0.21 | 1.82 | 0.12 | PNT56587 | DlCHR5 | 0.12 | 1.03 | 0.11 | |
| AtCHR36 | DlCHR36 | 0.27 | 1.38 | 0.19 | PNT42020 | DlCHR29 | 0.19 | 0.85 | 0.23 | |
| AtCHR10 | DlCHR10 | 0.20 | 1.34 | 0.15 | PNT42442 | DlCHR15 | 1.16 | 2.27 | 0.51 | |
| AtCHR2 | DlCHR2 | 0.20 | 1.31 | 0.15 | PNT19611 | DlCHR5 | 0.12 | 0.96 | 0.12 | |
| AtCHR25 | DlCHR25 | 0.19 | 1.18 | 0.16 | PNT05067 | DlCHR37 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.24 | |
| AtCHR12 | DlCHR12 | 0.18 | 1.70 | 0.10 | PNS94713 | DlCHR9 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.14 | |
| AtCHR11 | DlCHR11 | 0.06 | 1.67 | 0.03 | PNT09833 | DlCHR14 | 0.24 | 1.15 | 0.21 | |
| AtCHR7 | DlCHR6 | 0.32 | 2.14 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00002.143 | DlCHR6 | 1.12 | 2.87 | 0.39 | |
| AtCHR29 | DlCHR29 | 0.21 | 1.29 | 0.16 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR11 | 1.11 | — | — | |
| AtCHR17 | DlCHR11 | 0.06 | 1.57 | 0.04 | ar_scaffold00025.389 | DlCHR12 | 0.20 | 2.16 | 0.09 | |
| AtCHR23 | DlCHR12 | 0.20 | 1.60 | 0.12 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR18 | 0.24 | 1.80 | 0.13 | |
| AtCHR22 | DlCHR36 | 0.95 | 2.20 | 0.43 | ar_scaffold00057.182 | DlCHR11 | 0.08 | 1.91 | 0.04 | |
| AtCHR24 | DlCHR24 | 0.32 | 1.78 | 0.18 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR11 | 1.04 | 3.04 | 0.34 | |
| AtCHR1 | DlCHR1a | 0.21 | 2.17 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR2 | 0.28 | 1.91 | 0.15 | |
| Os02t0762800-00 | DlCHR25 | 0.24 | 2.35 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR2 | 0.95 | 2.30 | 0.41 | |
| Os02t0527100-01 | DlCHR29 | 0.25 | 2.42 | 0.10 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR36 | 1.00 | 2.18 | 0.46 | |
| Os02t0650800-00 | DlCHR31a | 0.56 | — | — | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR8 | 0.26 | — | — | |
| Os03t0101700-01 | DlCHR10 | 0.52 | 2.15 | 0.24 | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR42 | 1.23 | 3.10 | 0.40 | |
| Os03t0722400-01 | DlCHR1a | 0.25 | — | — | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR36 | 0.35 | 1.67 | 0.21 | |
| Os05t0150300-01 | DlCHR11 | 0.10 | 3.63 | 0.03 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR8 | 1.02 | 3.20 | 0.32 | |
| Os06t0183800-01 | DlCHR6 | 0.67 | 2.42 | 0.28 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR2 | 1.15 | 3.54 | 0.32 | |
| Os07t0598300-01 | DlCHR14 | 0.40 | 2.10 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00111.13 | DlCHR10 | 0.68 | 3.82 | 0.18 | |
| Os07t0636200-01 | DlCHR18 | 0.23 | 1.93 | 0.12 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR1a | 0.72 | — | — | |
| PNT15539 | DlCHR12 | 0.13 | 0.83 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR1a | 0.78 | 4.74 | 0.16 | |
| PNT13987 | DlCHR18 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.16 | ar_scaffold00029.1 | DlCHR28a | 0.35 | 1.40 | 0.25 | |
| PNT14263 | DlCHR11 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.04 | ar_scaffold00053.139 | DlCHR21 | 0.22 | 2.15 | 0.10 | |
| PNS92200 | DlCHR6 | 0.12 | 0.91 | 0.13 | ar_scaffold00003.327 | DlCHR28b | 0.25 | 1.56 | 0.16 | |
| PNT33877 | DlCHR6 | 0.12 | 0.95 | 0.13 | ar_scaffold00009.266 | DlCHR4 | 1.17 | 3.88 | 0.30 | |
| PNT25862 | DlCHR11 | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.05 | ar_scaffold00067.58 | DlCHR4 | 0.87 | 3.48 | 0.25 | |
| PNT24755 | DlCHR12 | 0.13 | 0.90 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR28b | 1.09 | 2.01 | 0.54 | |
| PNT25862 | DlCHR12 | 0.64 | — | — | ar_scaffold00146.48 | DlCHR4 | 1.10 | 3.01 | 0.37 | |
| PNT06750 | DlCHR20a | 0.16 | 0.79 | 0.20 | ar_scaffold00039.164 | DlCHR35 | 0.89 | — | — | |
| PNT07119 | DlCHR16a | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00126.55 | DlCHR25 | 0.22 | 2.06 | 0.11 | |
| PNT07119 | DlCHR16b | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00040.267 | DlCHR29 | 0.26 | 2.39 | 0.11 | |
| PNS90011 | DlCHR20a | 0.16 | 0.85 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00148.60 | DlCHR15 | 0.60 | 2.25 | 0.27 | |
| PNT17288 | DlCHR42 | 0.27 | 1.28 | 0.21 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR39 | 1.02 | 3.00 | 0.34 | |
| PNT03745 | DlCHR2 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 0.15 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR37 | 1.09 | 2.28 | 0.48 | |
| PNT03205 | DlCHR10 | 0.18 | 0.89 | 0.20 | ar_scaffold00077.105 | DlCHR9 | 0.98 | — | — | |
| PNS90743 | DlCHR36 | 0.52 | — | — | ar_scaffold00002.143 | DlCHR13 | 1.21 | — | — | |
| PNT49991 | DlCHR2 | 0.11 | 0.81 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00009.153 | DlCHR13 | 0.93 | 2.75 | 0.34 | |
| PNT38168 | DlCHR8 | 0.15 | 0.78 | 0.19 | ar_scaffold00032.254 | DlCHR13 | 0.82 | — | — | |
| PNT23278 | DlCHR42 | 0.24 | 1.04 | 0.23 | ar_scaffold00032.254 | DlCHR13 | 0.82 | — | — | |
| PNT35260 | DlCHR24 | 0.21 | 0.97 | 0.21 | ar_scaffold00009.110 | DlCHR31a | 1.06 | — | — | |
| PNT28173 | DlCHR24 | 0.21 | 0.89 | 0.24 | ar_scaffold00045.118 | DlCHR14 | 0.83 | — | — | |
| PNT15682 | DlCHR19 | 0.13 | 0.94 | 0.14 | ar_scaffold00110.12 | DlCHR14 | 0.36 | 2.13 | 0.17 |

Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree analysis of Snf2 proteins from longan and other seven plant species Dl:Dimocarpus longan;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Os:Oryza sativa;Pt:Populus trichocarpa;Ar:Amborella trichopoda;Pa:Picea abies;Pp:Physcomitrella patens;Sm:Selaginella moellendorffii.
| 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | ||
| DlCHR1a | miR5177 | 3 | Cleavage | DlCHR12 | miR1312 | 3 | Cleavage | miR1514b | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR166j | 4 | Cleavage | miR1428e | 4 | Translation | miR3452 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5079 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2868 | 4 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR2 | miR2657a | 3 | Cleavage | miR396a | 4 | Cleavage | miR415 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR420 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR13 | miR414 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5078 | 4 | Translation | ||||
| miR4415 | 4 | Cleavage | miR416 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR24 | miR778 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR845d | 4 | Translation | miR847 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR778 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR3 | miR5200 | 3 | Cleavage | miR850 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR414 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1881 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR860 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR25 | miR2936 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1027a | 4 | Cleavage | miR869 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR3631a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR1044 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1039 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR28a | miR1528 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1521 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1044 | 4 | Cleavage | miR4249 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR166c | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR14 | miR4400 | 2.5 | Cleavage | miR4366 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2089*-3 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1535 | 4 | Cleavage | miR857 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR3707 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR15 | miR1160 | 3 | Cleavage | miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR4 | miR1884b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1528 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR28b | miR172a | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||
| miR2595 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1884b | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863 | 3.5 | Translation | |||||
| miR2615a | 4 | Translation | miR2611 | 4 | Cleavage | miR419 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2616 | 4 | Translation | miR4223 | 4 | Cleavage | miR833 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR416 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR16a | miR1863 | 3 | Cleavage | DlCHR29 | miR3702 | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863b | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR31a | miR2673a | 2.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR5 | miR2673a | 2.5 | Cleavage | miR1510a | 4 | Cleavage | miR2118e | 3 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2673a | 4 | Translation | miR1871 | 4 | Cleavage | miR4249 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR6 | miR2677 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR2930 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1052 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR773b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Translation | miR2868 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR773b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5016 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR35 | miR870 | 3 | Translation | ||||
| miR1884b | 4 | Cleavage | miR820a | 4 | Cleavage | miR156e | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2105 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR16b | miR1863 | 3 | Cleavage | miR4391 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2642 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1525 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5072 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2928 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863b | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR36 | miR1028c | 3 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR870 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1510a | 4 | Cleavage | miR158b | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR8 | miR1863 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1871 | 4 | Cleavage | miR417 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2928 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2930 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1081 | 4 | Translation | |||||
| miR4393b | 4 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Translation | miR1217 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5021 | 4 | Cleavage | miR5016 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1919a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5200 | 4 | Cleavage | miR820a | 4 | Cleavage | miR5052 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR9 | miR1028c | 2.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR18 | miR390a.3 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5176 | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR3637 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR536 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR37 | miR1027a | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR393 | 3.5 | Translation | miR536 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1878 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR1320 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR19 | miR5025 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR39 | miR1169 | 3 | Cleavage | |||
| miR2604 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2097 | 4 | Translation | miR1888 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR20a | miR479 | 3 | Cleavage | miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR11 | miR5058 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1513 | 4 | Cleavage | miR3706 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1120 | 4 | Translation | miR2604 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR42 | miR1875 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2610a | 4 | Cleavage | miR413 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | miR811d | 4 | Cleavage | miR3437 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR3435 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR21 | miR5079 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR413 | 4 | Translation | ||||
| miR4246 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1044 | 4 | Translation | ||||||||
Table 3 Analysis of potential microRNA regulating longan DlSnf2 family genes
| 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | 基因 | 微小RNA | 期望值 | 抑制方式 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | Gene | MicroRNA | E-value | Inhibition | ||
| DlCHR1a | miR5177 | 3 | Cleavage | DlCHR12 | miR1312 | 3 | Cleavage | miR1514b | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR166j | 4 | Cleavage | miR1428e | 4 | Translation | miR3452 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5079 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2868 | 4 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR2 | miR2657a | 3 | Cleavage | miR396a | 4 | Cleavage | miR415 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR420 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR13 | miR414 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5078 | 4 | Translation | ||||
| miR4415 | 4 | Cleavage | miR416 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR24 | miR778 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR845d | 4 | Translation | miR847 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR778 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR3 | miR5200 | 3 | Cleavage | miR850 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR414 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1881 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR860 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR25 | miR2936 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1027a | 4 | Cleavage | miR869 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR3631a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR1044 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1039 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR28a | miR1528 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1521 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1044 | 4 | Cleavage | miR4249 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR166c | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR14 | miR4400 | 2.5 | Cleavage | miR4366 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2089*-3 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1535 | 4 | Cleavage | miR857 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR3707 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR15 | miR1160 | 3 | Cleavage | miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR4 | miR1884b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1528 | 4 | Translation | DlCHR28b | miR172a | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||
| miR2595 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1884b | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863 | 3.5 | Translation | |||||
| miR2615a | 4 | Translation | miR2611 | 4 | Cleavage | miR419 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2616 | 4 | Translation | miR4223 | 4 | Cleavage | miR833 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR416 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR16a | miR1863 | 3 | Cleavage | DlCHR29 | miR3702 | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863b | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR31a | miR2673a | 2.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR5 | miR2673a | 2.5 | Cleavage | miR1510a | 4 | Cleavage | miR2118e | 3 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2673a | 4 | Translation | miR1871 | 4 | Cleavage | miR4249 | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR6 | miR2677 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR2930 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1052 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR773b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Translation | miR2868 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR773b | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5016 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR35 | miR870 | 3 | Translation | ||||
| miR1884b | 4 | Cleavage | miR820a | 4 | Cleavage | miR156e | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2105 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR16b | miR1863 | 3 | Cleavage | miR4391 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2642 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1525 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5072 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2928 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1863b | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR36 | miR1028c | 3 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR870 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1510a | 4 | Cleavage | miR158b | 3.5 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR8 | miR1863 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1871 | 4 | Cleavage | miR417 | 3.5 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2928 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2930 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1081 | 4 | Translation | |||||
| miR4393b | 4 | Cleavage | miR3637 | 4 | Translation | miR1217 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5021 | 4 | Cleavage | miR5016 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1919a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR5200 | 4 | Cleavage | miR820a | 4 | Cleavage | miR5052 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| DlCHR9 | miR1028c | 2.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR18 | miR390a.3 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR5176 | 4 | Cleavage | |||
| miR3637 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR536 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR37 | miR1027a | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR393 | 3.5 | Translation | miR536 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1878 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR1320 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR19 | miR5025 | 3.5 | Cleavage | DlCHR39 | miR1169 | 3 | Cleavage | |||
| miR2604 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2097 | 4 | Translation | miR1888 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR860 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR20a | miR479 | 3 | Cleavage | miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| DlCHR11 | miR5058 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR1513 | 4 | Cleavage | miR3706 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR1120 | 4 | Translation | miR2604 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR42 | miR1875 | 4 | Cleavage | ||||
| miR2610a | 4 | Cleavage | miR413 | 4 | Cleavage | miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR2673a | 4 | Cleavage | miR811d | 4 | Cleavage | miR3437 | 4 | Cleavage | |||||
| miR3435 | 4 | Cleavage | DlCHR21 | miR5079 | 3.5 | Cleavage | miR413 | 4 | Translation | ||||
| miR4246 | 4 | Cleavage | miR1044 | 4 | Translation | ||||||||
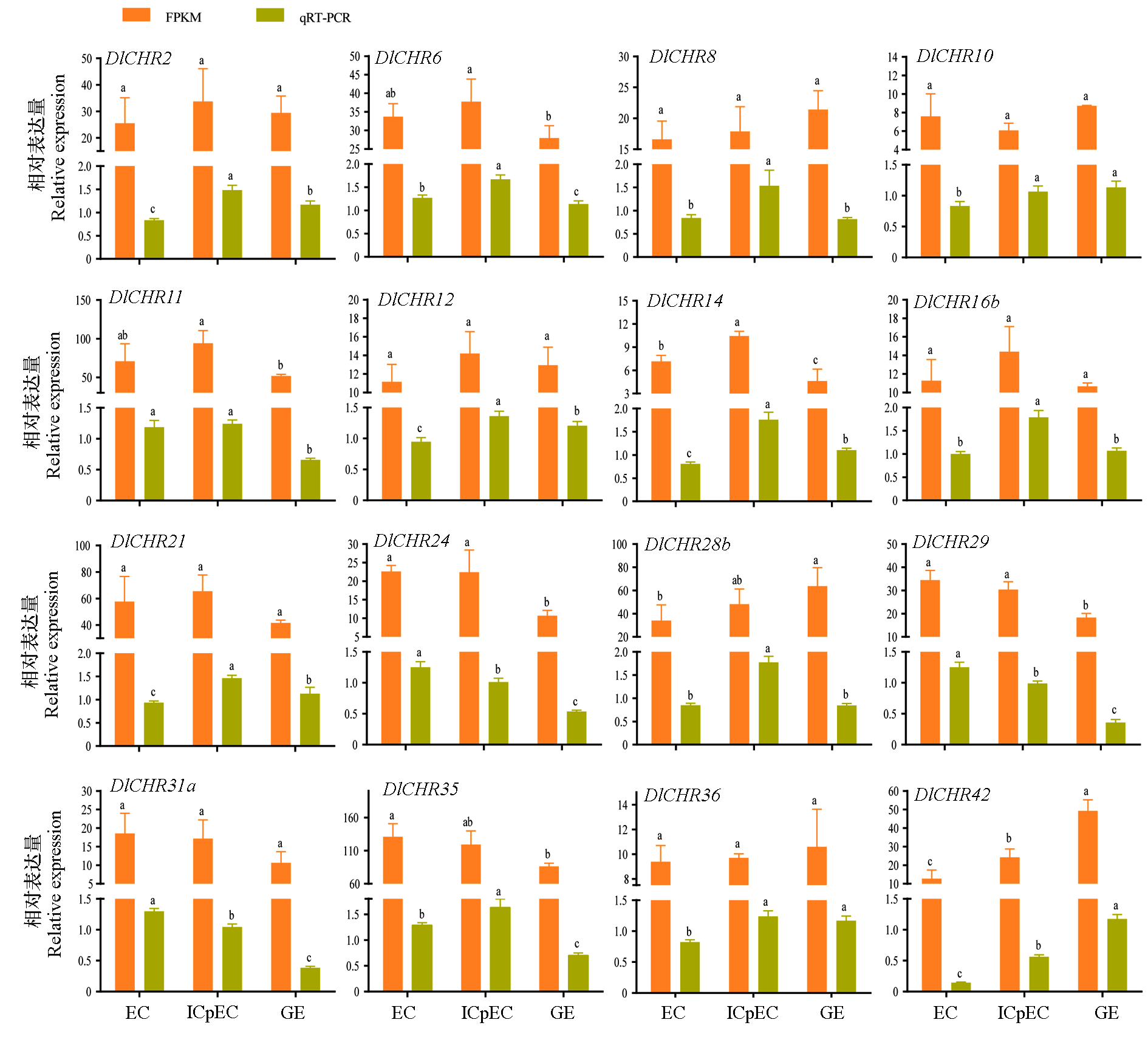
Fig. 6 A comparative analysis of DlSnf2 members by FPKM and qRT-PCR in longan early somatic embryogenesis Data were normalized by DlEF-1a,DlFe-SOD and DleIF-4a.Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference(P < 0.05,n = 3).
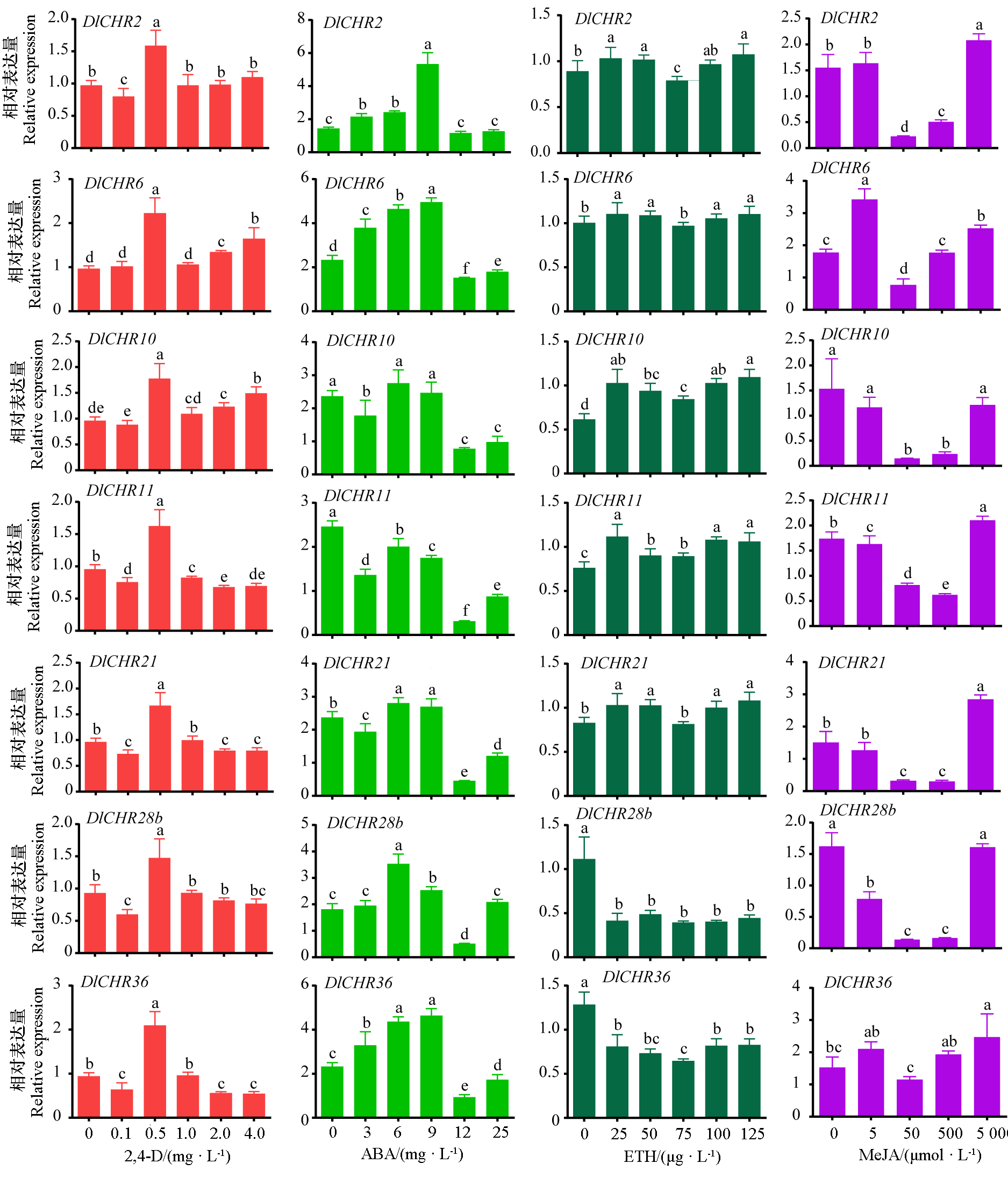
Fig. 7 Expression analysis of DlSnf2 members in EC under different plant growth regulator treatments The 2,4-D group was normalized by DlEF-1a and DleIF-4a,other groups were normalized by DlEF-1a,DlFe-SOD and DleIF-4a. Samples without plant growth regulators were used as controls,and different lowercase letters indicate significant difference(P < 0.05,n = 3).
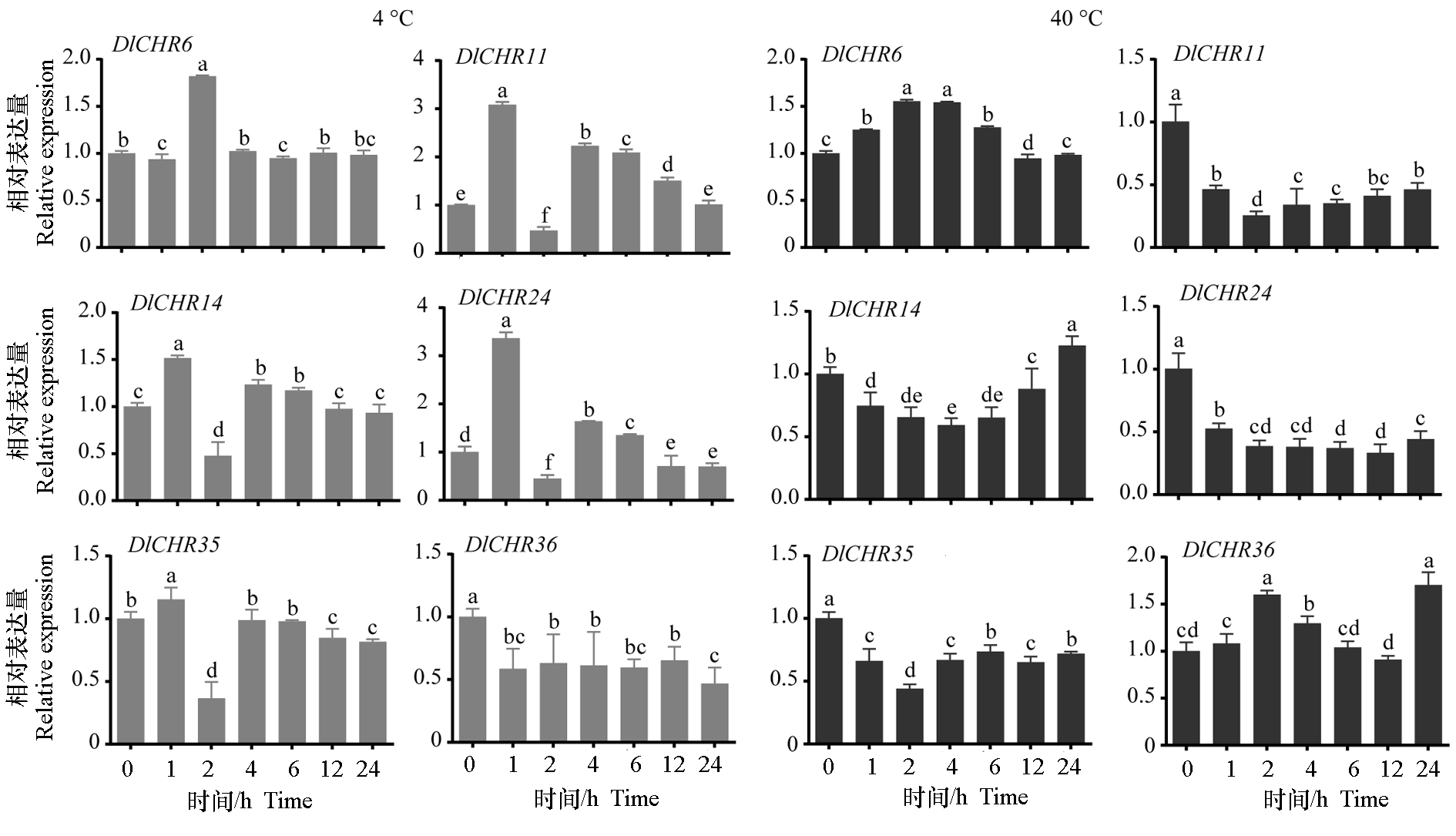
Fig. 8 Expression analysis of DlSnf2 members in EC under different temperature treatments Data were normalized by DleIF-4a. Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference(P < 0.05,n = 3).
| [1] |
Bargsten J W, Folta A, Mlynárová L, Nap J P. 2013. Snf 2 family gene distribution in higher plant genomes reveals DRD1 expansion and diversification in the tomato genome. PLoS ONE, 8 (11):e81147.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081147 URL |
| [2] |
Bouazoune K, Mitterweger A, Langst G, Imhof A, Akhtar A, Becker P B, Brehm A. 2002. The dMi-2 chromodomains are DNA binding modules important for ATP-dependent nucleosome mobilization. The EMBO Journal, 21 (10):2430-2440.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.10.2430 URL |
| [3] |
Busnelli S, Tripodi F, Nicastro R, Cirulli C, Tedeschi G, Pagliarin R, Alberghina L, Coccetti P. 2013. Snf1/AMPK promotes SBF and MBF-dependent transcription in budding yeast. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1833 (12):3254-3264.
doi: S0167-4889(13)00336-4 pmid: 24084603 |
| [4] |
Buszewicz D, Archacki R, Palusiński A, Kotliński M, Fogtman A, Iwanickanowicka R, Sosnowska K, Kuciński J, Pupel P, Olędzki J, Dadlez M, Misicka A, Jerzmanowski A, Koblowska M. 2016. HD2C histone deacetylase and a SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex interact and both are involved in mediating the heat stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ, 39 (10):2108-2122.
doi: 10.1111/pce.v39.10 URL |
| [5] |
Chanvivattana Y, Bishopp A, Schubert D, Stock C, Moon Y, Sung Z R, Goodrich J. 2004. Interaction of polycomb-group proteins controlling flowering in Arabidopsis. Development, 131 (21):5263-5276.
pmid: 15456723 |
| [6] |
Chen C J, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas H R, Frank M H, He Y H, Xia R. 2020a. TBtools:an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13 (8):1194-1202.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 URL |
| [7] |
Chen W, Zhu Q L, Liu Y G, Zhang Q Y. 2017. Chromatin remodeling and plant immunity. Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 106:243-260.
doi: S1876-1623(16)30050-5 pmid: 28057214 |
| [8] | Chen X H, Xu X P, Shen X, Li H S, Zhu C, Chen R Z, Nigarish Munir, Zhang Z H, Chen Y K, Xuhan X, Lin Y L, Lai Z X. 2020b. Genome-wide investigation of DNA methylation dynamics reveals a critical role of DNA demethylation during the early somatic embryogenesis of Dimocarpus longan Lour. Tree Physiology,(12):12. |
| [9] |
Deng W K, Wang Y B, Liu Z X, Cheng H, Xue Y. 2014. HemI:a toolkit for illustrating heatmaps. PLoS ONE, 9 (11):e111988.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111988 URL |
| [10] |
Erdel F, Rippe K. 2011. Chromatin remodelling in mammalian cells by ISWI-type complexes-where,when and why? Febs Journal, 278 (19):3608-3618.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08282.x URL |
| [11] |
Farrona S, Hurtado L, Bowman J L, Reyes J C. 2004. The Arabidopsis thaliana SNF 2 homolog AtBRM controls shoot development and flowering. Development, 131 (20):4965-4975.
pmid: 15371304 |
| [12] |
Flaus A, Martin D M, Barton G J, Owenhughes T. 2006. Identification of multiple distinct Snf 2 subfamilies with conserved structural motifs. Nucleic Acids Research, 34 (10):2887-2905.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl295 URL |
| [13] |
Folta A, Severing E I, Krauskopf J, van de Geest H, Verver J, Nap J P, Mlynarova L. 2014. Over-expression of Arabidopsis AtCHR23 chromatin remodeling ATPase results in increased variability of growth and gene expression. BMC Plant Biology, 14 (1):76.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-76 URL |
| [14] |
Fukaki H, Taniguchi N, Tasaka M. 2006. PICKLE is required for SOLITARY-ROOT/IAA14-mediated repression of ARF7 and ARF19 activity during Arabidopsis lateral root initiation. Plant Journal, 48 (3):380-389.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2006.48.issue-3 URL |
| [15] |
Gerhold C B, Gasser S M. 2014. INO80 and SWR complexes:relating structure to function in chromatin remodeling. Trends in Cell Biology, 24 (11):619-631.
doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.06.004 URL |
| [16] |
Guo F, Liu C L, Xia H, Bi Y P, Zhao C Z, Zhao S Z, Hou L, Li F G, Wang X J. 2013. Induced expression of AtLEC1 and AtLEC2 differentially promotes somatic embryogenesis in transgenic tobacco plants. PLoS ONE, 8 (8):e71714.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071714 URL |
| [17] |
Hahn J, Thiele D J. 2004. Activation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae heat shock transcription factor under glucose starvation conditions by Snf 1 protein kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279 (7):5169-5176.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311005200 URL |
| [18] |
Han S K, Sang Y, Rodrigues A, F B, Wu M, Rodriguez P L, Wagner D. 2012. The SWI2/SNF 2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA represses abscisic acid responses in the absence of the stress stimulus in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 24 (12):4892-4906.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105114 URL |
| [19] |
Han S K, Wu M, Cui S J, Wagner D. 2015. Roles and activities of chromatin remodeling ATPases in plants. Plant Journal, 83 (1):62-77.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2015.83.issue-1 URL |
| [20] |
Hara T, Katoh H, Ogawa D, Kagaya Y, Sato Y, Kitano H, Nagato Y, Ishikawa R, Ono A, Kinoshita T, Takeda S, Hattori T. 2015. Rice SNF 2 family helicase ENL1 is essential for syncytial endosperm development. Plant Journal, 81 (1):1-12.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12705 URL |
| [21] |
Holub E B. 2001. The arms race is ancient history in Arabidopsis,the wildflower. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2 (7):516-527.
pmid: 11433358 |
| [22] | Hu Y F, Liu D N, Zhong X C, Zhang C J, Zhang Q F, Zhou D X. 2012. CHD 3 protein recognizes and regulates methylated histone H3 lysines 4 and 27 over a subset of targets in the rice genome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109 (15):5773-5778. |
| [23] |
Hu Y F, Zhu N, Wang X M, Yi Q P, Zhu D Y, Lai Y, Zhao Y. 2013. Analysis of rice Snf2 family proteins and their potential roles in epigenetic regulation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 70:33-42.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.001 URL |
| [24] | Huancamamani W, Garciaaguilar M, Leonmartinez G, Grossniklaus U, Viellecalzada J. 2005. CHR11,a chromatin-remodeling factor essential for nuclear proliferation during female gametogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102 (47):17231-17236. |
| [25] |
Hurtado L, Farrona S, Reyes J C. 2006. The putative SWI/SNF complex subunit BRAHMA activates flower homeotic genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology, 62 (1):291-304.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9021-2 URL |
| [26] | Jerzmanowski A. 2007. SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling and linker histones in plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1769 (5):330-345. |
| [27] |
Knizewski L, Ginalski K, Jerzmanowski A. 2008. Snf 2 proteins in plants:gene silencing and beyond. Trends in Plant Science, 13 (10):557-565.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.08.004 pmid: 18786849 |
| [28] |
Kwon C S, Hibara K, Pfluger J, Bezhani S, Metha H, Aida M, Tasaka M, Wagner D. 2006. A role for chromatin remodeling in regulation of CUC gene expression in the Arabidopsis cotyledon boundary. Development, 133 (16):3223-3230.
doi: 10.1242/dev.02508 URL |
| [29] | Lai Zhong-xiong. 2003. Study of longan biotechnology. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese) |
| 赖钟雄. 2003. 龙眼生物技术研究. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社. | |
| [30] |
Li C L, Chen C, Gao L, Yang S G, Nguyen V, Shi X J, Siminovitch K A, Kohalmi S E, Huang S Z, Wu K Q, Chen X M, Cui Y H. 2015. The Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeler BRAHMA regulates polycomb function during vegetative development and directly activates the flowering repressor gene SVP. PLoS Genetics, 11 (1):e1004944.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004944 URL |
| [31] |
Li G, Zhang J W, Li J Q, Yang Z N, Huang H, Xu L. 2012. Imitation Switch chromatin remodeling factors and their interacting RINGLET proteins act together in controlling the plant vegetative phase in Arabidopsis. Plant Journal, 72 (2):261-270.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.05074.x URL |
| [32] |
Li Z X, Zhang L F, Li W F, Qi L W, Han S Y. 2017. MIR166a affects the germination of somatic embryos in Larix leptolepis by modulating IAA biosynthesis and signaling genes. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 36 (4):889-896.
doi: 10.1007/s00344-017-9693-7 URL |
| [33] |
Lin Y L, Lai Z X. 2010. Reference gene selection for qPCR analysis during somatic embryogenesis in longan tree. Plant Science, 178 (4):359-365.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.02.005 URL |
| [34] | Lin Y L, Min J M, Lai R L, Wu Z Y, Chen Y K, Yu L L, Cheng C Z, Jin Y C, Tian Q L, Liu Q F, Liu W H, Zhang C G, Lin L X, Hu Y, Zhang D M, Thu M, Zhang Z H, Liu S C, Zhong C S, Fang X D, Wang J, Yang H M, Varshney R K, Yin Y, Lai Z X. 2017. Genome-wide sequencing of longan(Dimocarpus longan Lour.)provides insights into molecular basis of its polyphenol-rich characteristics. GigaScience, 6 (5):1-14. |
| [35] |
Lotan T, Ohto M, Yee K M, West M A L, Lo R, Kwong R W, Yamagishi K, Fischer R L, Goldberg R B, Harada J J. 1998. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell, 93 (7):1195-1205.
pmid: 9657152 |
| [36] |
Makarevich G, Leroy O, Akinci U, Schubert D, Clarenz O, Goodrich J, Grossniklaus U, Kohler C. 2006. Different polycomb group complexes regulate common target genes in Arabidopsis. EMBO Reports, 7 (9):947-952.
pmid: 16878125 |
| [37] | Mccartney R R, Garnarwortzel L, Chandrashekarappa D G, Schmidt M C. 2016. Activation and inhibition of Snf 1 kinase activity by phosphorylation within the activation loop. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1864 (11):1518-1528. |
| [38] |
Mlynarova L, Nap J P, Bisseling T. 2007. The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling gene AtCHR12 mediates temporary growth arrest in Arabidopsis thaliana upon perceiving environmental stress. Plant Journal, 51 (5):874-885.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03185.x URL |
| [39] |
Mu J Y, Tan H L, Zheng Q, Fu F Y, Liang Y, Zhang J, Yang X H, Wang T, Chong K, Wang X J, Zuo J R. 2008. LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is a key regulator of fatty acid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 148 (2):1042-1054.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.126342 URL |
| [40] |
Noh Y, Amasino R M. 2003. PIE1,an ISWI family gene,is required for FLC activation and floral repression in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 15 (7):1671-1682.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.012161 URL |
| [41] |
Ogas J, Cheng J, Sung Z R, Somerville C. 1997. Cellular differentiation regulated by gibberellin in the Arabidopsis thaliana pickle mutant. Science, 277 (5322):91-94.
pmid: 9204906 |
| [42] | Ogas J, Kaufmann S H, Henderson J T, Somerville C. 1999. PICKLE is a CHD3 chromatin-remodeling factor that regulates the transition from embryonic to vegetative development in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96 (24):13839-13844. |
| [43] |
Pessina S, Tsiarentsyeva V, Busnelli S, Vanoni M, Alberghina L, Coccetti P. 2010. Snf1/AMPK promotes S-phase entrance by controlling CLB5 transcription in budding yeast. Cell Cycle, 9 (11):2189-2200.
doi: 10.4161/cc.9.11.11847 URL |
| [44] |
Reyes J C. 2014. The many faces of plant SWI/SNF complex. Molecular Plant, 7 (3):454-458.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sst147 pmid: 24177686 |
| [45] | Riemann M, Dhakarey R, Hazman M, Miro B, Kohli A, Nick P. 2015. Exploring jasmonates in the hormonal network of drought and salinity responses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6:1077. |
| [46] |
Rizhsky L, Liang H, Shuman J L, Shulaev V, Davletova S, Mittler R. 2004. When defense pathways collide. The response of Arabidopsis to a combination of drought and heat stress. Plant Physiology, 134 (4):1683-1696.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.033431 URL |
| [47] | Sanchez R, Zhou M M. 2009. The role of human bromodomains in chromatin biology and gene transcription. Current Opinion in Drug Discovery & Development, 12 (5):659-665. |
| [48] |
Sang Y, Silvaortega C O, Wu S, Yamaguchi N, Wu M, Pfluger J. 2012. Mutations in two non-canonical Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF 2 chromatin remodeling ATPases cause embryogenesis and stem cell maintenance defects. Plant Journal, 72 (6):1000-1014.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2012.72.issue-6 URL |
| [49] |
Sarnowski T J, Rios G, Jasik J, Świezewski S, Kaczanowski S, Li Y, Kwiatkowska A, Pawlikowska K, Koźbial M, Koźbial P, Koncz C, Jerzmanowski A. 2005. SWI 3 subunits of putative SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complexes play distinct roles during Arabidopsis development. The Plant Cell, 17 (9):2454-2472.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.031203 URL |
| [50] |
Schmutz J, Cannon S B, Schlueter J, Ma J X, Mitros T, Nelson W, Hyten D L, Song Q J, Thelen J J, Cheng J L, Xu D, Hellsten U, May G D, Yu Y, Sakurai T, Umezawa T, Bhattacharyya M K, Sandhu D, Valliyodan B, Lindquist E, Peto M, Grant D, Shu S Q, Goodstein D, Barry K, Futrell-Griggs M, Abernathy B, Du J C, Tian Z X, Zhu L C, Gill N, Joshi T, Libault M, Sethuraman A, Zhang X C, Shinozaki K, Nguyen H T, Wing R A, Cregan P, Specht J, Grimwood J, Rokhsar, Stacey G, Shoemaker R C, Jackson S A. 2010. Genome sequence of the palaeopolyploid soybean. Nature, 463 (7278):178-183.
doi: 10.1038/nature08670 URL |
| [51] |
Shaked H, Aviviragolsky N, Levy A A. 2006. Involvement of the Arabidopsis SWI2/SNF 2 chromatin remodeling gene family in DNA damage response and recombination. Genetics, 173 (2):985-994.
pmid: 16547115 |
| [52] | Shen Xu, Chen Xiao-hui, Xu Xiao-ping, Huo Wen, Li Xiao-fei, Jiang Meng-qi, Zhang Jing, Lin Yu-lin, Lai Zhong-xiong. 2019. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SDG gene family during early somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 40 (10):1889-1901. (in Chinese) |
| 申序, 陈晓慧, 徐小萍, 霍雯, 李晓斐, 蒋梦琦, 张婧, 林玉玲, 赖钟雄. 2019. 龙眼体细胞胚胎发生早期SDG基因家族的全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 热带作物学报, 40 (10):1889-1901. | |
| [53] |
Shibukawa T, Yazawa K, Kikuchi A, Kamada H. 2009. Possible involvement of DNA methylation on expression regulation of carrot LEC1 gene in its 5′-upstream region. Gene, 437 (1-2):22-31.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.02.011 pmid: 19264116 |
| [54] | Simpsonlavy K J, Johnston M. 2013. SUMOylation regulates the SNF1 protein kinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110 (43):17432-17437. |
| [55] | Smaczniak C, Immink R G, Muino J M, Blanvillain R, Busscher M, Busscherlange J, Dung-Dinh Q, Liu S J, Westphal A H, Boeren S, Parcy F, Xu L, Carles C C, Angenent G C, Kaufmann K. 2012. Characterization of MADS-domain transcription factor complexes in Arabidopsis flower development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109 (5):1560-1565. |
| [56] | Stone S L, Braybrook S A, Paula S L, Kwong L W, Meuser J E, Pelletier J M, Hsieh T, Fischer R L, Goldberg R B, Harada J J. 2008. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON2 induces maturation traits and auxin activity:implications for somatic embryogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105 (8):3151-3156. |
| [57] |
Wagner D, Meyerowitz E M. 2002. SPLAYED,a novel SWI/SNF ATPase homolog,controls reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Current Biology, 12 (2):85-94.
pmid: 11818058 |
| [58] |
Walley J W, Rowe H C, Xiao Y M, Chehab E W, Kliebenstein D J, Wagner D, Dehesh K. 2008. The chromatin remodeler SPLAYED regulates specific stress signaling pathways. PLoS Pathogens, 4 (12):e1000237.
doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000237 URL |
| [59] |
Wang Y P, Tang H B, Debarry J D, Tan X F, Li J P, Wang X Y, Lee T, Jin H Z, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger J C, Paterson A H. 2012. MCScanX:a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Research, 40 (7):e49.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293 URL |
| [60] |
Wilson M A, Koutelou E, Hirsch C L, Akdemir K C, Schibler A C, Barton M C, Dent S Y. 2011. Ubp8 and SAGA regulate Snf 1 AMP kinase activity. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 31 (15):3126-3135.
doi: 10.1128/MCB.01350-10 URL |
| [61] |
Wójcik A M, Nodine M D, Gaj M D. 2017. miR160 and miR166/ 165 contribute to the LEC2-mediated auxin response involved in the somatic embryogenesis induction in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:2024.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02024 pmid: 29321785 |
| [62] |
Wójcikowska B, Jaskóła K, Gąsiorek P, Meus M, Nowak K, Gaj M D. 2013. LEAFY COTYLEDON2(LEC2)promotes embryogenic induction in somatic tissues of Arabidopsis,via YUCCA-mediated auxin biosynthesis. Planta, 238 (3):425-440.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1892-2 pmid: 23722561 |
| [63] |
Yang D L, Zhang G P, Wang L L, Li J W, Xu D C, Di C R, Tang K, Yang L, Zeng L, Miki D, Duan C G, Zhang H M, Zhu J K. 2018. Four putative SWI2/SNF 2 chromatin remodelers have dual roles in regulating DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Cell Discovery, 4 (1):55.
doi: 10.1038/s41421-018-0056-8 URL |
| [64] |
Yang X Y, Wang L C, Yuan D J, Lindsey K, Zhang X L. 2013. Small RNA and degradome sequencing reveal complex miRNA regulation during cotton somatic embryogenesis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64 (6):1521-1536.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert013 URL |
| [65] |
Zhang D D, Gao S J, Yang P, Yang J, Yang S G, Wu K Q. 2019. Identification and expression analysis of Snf 2 family proteins in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Comparative and Functional Genomics,doi: 10.1155/2019/5080935.
doi: 10.1155/2019/5080935 |
| [66] | Zhang Qinglin, Su Liyao, Li Xue, Zhang Shuting, Xu Xiaoping, Chen Xiaohui, Wang Peiyu, Li Rong, Zhang Zihao, Chen Yukun, Lai Zhongxiong, Lin Yuling. 2018. Cloning and expression analysis of miR166 primary gene during the early stage of somatic embryogenesis of longan. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (8):1501-1512. (in Chinese) |
| 张清林, 苏立遥, 厉雪, 张舒婷, 徐小萍, 陈晓慧, 王培育, 李蓉, 张梓浩, 陈裕坤, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲. 2018. 龙眼体胚发生miR166初级体的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 45 (8):1501-1512. | |
| [67] |
Zhang S Z, Liu X G, Lin Y A, Xie G N, Fu F L, Liu H L, Wang J, Gao S B, Lan H, Rong T Z. 2011. Characterization of a ZmSERK gene and its relationship to somatic embryogenesis in a maize culture. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture, 105 (1):29-37.
doi: 10.1007/s11240-010-9834-1 URL |
| [68] |
Zhao M L, Yang S G, Chen C, Li C L, Shan W, Lu W J, Cui Y H. 2015. Arabidopsis BREVIPEDICELLUS interacts with the SWI2/SNF 2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA to regulate KNAT2 and KNAT6 expression in control of inflorescence architecture. PLoS Genetics, 11 (3):e1005125.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005125 URL |
| [69] |
Zhu J K, Hasegawa P M, Bressan R A. 1997. Molecular aspects of osmotic stress in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 16 (3):253-277.
doi: 10.1080/07352689709701950 URL |
| [1] | SHAO Fengqing, LUO Xiurong, WANG Qi, ZHANG Xianzhi, WANG Wencai. Advances in Research of DNA Methylation Regulation During Fruit Ripening [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 197-208. |
| [2] | XU Xiaoping, CAO Qingying, CAI Roudi, GUAN Qingxu, ZHANG Zihao, CHEN Yukun, XU HAN, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of miR408 and Its Target DlLAC12 in Globular Embryo Development and Abiotic Stress in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. |
| [3] | ZOU Xuexiao, ZHU Fan. Origin,Evolution and Cultivation History of the Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1371-1381. |
| [4] | LIANG Qin, ZHANG Yanhui, KANG Kaiquan, LIU Jinhang, LI Liang, FENG Yu, WANG Chao, YANG Chao, LI Yongyu. Molecular Evolution of MiR168 Family and Their Expression Profiling During Dormancy of Pyrus pyrifolia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 958-972. |
| [5] | LIANG Chen, SUN Ruyi, XIANG Rui, SUN Yimeng, SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, WANG Li. Genome-wide Identification of Grape GRF Family and Expression Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [6] | PAN Xinfeng, YE Fangting, MAO Zhijun, LI Zhaowei, FAN Kai. Genomic Identification and Molecular Evolution of the WRKY Family in Nymphaea colorata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1121-1135. |
| [7] | LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Shuting, XUE Xiaodong, XIAO Xuechen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of GDSL Esterase/Lipase Genes in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 597-612. |
| [8] | WU Xiaoxiao, CHEN Chuanwu, LIU Ping, TANG Yan, DENG Chongling. Genetic Evolution and Taxonomic Status Analysis of Wild Citrus Resources Based on Resequencing in Guposhan Mountain in Guangxi Province [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 407-415. |
| [9] | FENG Lixiao, HU Rong, BU Shan, ZHANG Deyong, LUO Xiangwen, LI Fan, DING Ming, ZHANG Zhuo, ZHANG Songbai, LIU Yong. Molecular Detection and Genetic Evolution Analysis of Yunnan Isolates of Lettuce Chlorosis Virus in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 141-147. |
| [10] | ZHANG Chunyu, XU Xiaoqiong, XU Xiaoping, ZHAO Pengcheng, SHEN Xu, Munir Nigarish, ZHANG Zihao, LIN Yuling, Chen Zhenguang, LAI Zhongxiong. Genome-wide Identification of the SKP1-like Family and Analysis of Their Expression During Early Somatic Embryogenesis in Longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1665-1679. |
| [11] | SU Liyao, WANG Peiyu, JIANG Mengqi, HUANG Shuqi, XUE Xiaodong, LIU Mengyu, XIAO Xuechen, LAI Chunwang, ZHANG Zihao, CHEN Yukun, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. The Activity Verification of pri-miR319a Encode Regulatory Peptide of Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 908-920. |
| [12] | CAI Roudi, LI Xue, CHEN Yan, XU Xiaoping, CHEN Xiaohui, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of DRB Gene Family in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 921-933. |
| [13] | JIANG Mengqi, XUE Xiaodong, SU Liyao, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Shuting, LI Xiaofei, WANG Peiyu, ZHANG Zihao, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of TCP Family in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12): 2481-2496. |
| [14] | YA Rong1,XU Weirong2,3,4,5,*,ZHANG Ying1,XIA Siqi2,and ZHANG Ningbo2,3,5. Investigation of Melatonin on Somatic Embryo Induction for‘Thompson Seedless’Grapevine [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(5): 953-962. |
| [15] | HUANG Zhinan, DUAN Weike, BAI Xueying, ZHOU Yi, ZHU Mengquan, LIU Siqin, JU Jia, and PAN Guoqing. Identification,Phylogenetic Evolution and Expression Analysis of NAT Gene Family in Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(11): 2132-2144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd