
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 1913-1926.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0306
收稿日期:2024-01-15
修回日期:2024-04-29
出版日期:2024-08-25
发布日期:2024-08-22
通讯作者:
基金资助:
GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang*( ), WU Fengzhi*(
), WU Fengzhi*( )
)
Received:2024-01-15
Revised:2024-04-29
Published:2024-08-25
Online:2024-08-22
摘要:
采用16S rRNA高通量测序技术以及植物—土壤反馈方法,探究了分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对其根结线虫病发生、土壤微生物群落结构以及诱导抗性的影响。结果表明,分蘖洋葱伴生的番茄根际微生物显著降低了番茄根结线虫的病情指数、根结数和根结指数,显著提高了对根结线虫卵孵化的抑制率和二龄幼虫的致死率。在根结线虫胁迫下,伴生增加了番茄根际潜在有益菌群芽孢杆菌属和假单胞菌属的相对丰度。同时,伴生改变的番茄根际微生物通过提高抗性相关基因表达、防御酶活性和茉莉酸类物质含量增强了番茄的系统抗性。因此,分蘖洋葱伴生改变的番茄根际微生物组除对根结线虫具有直接抑杀作用外,还通过对番茄产生诱导抗性提高其对根结线虫的抗病能力。
龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926.
GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926.
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Upstream primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Downstream primer |
|---|---|---|
| MPK1 | GCTGACAGATTGTTGCAGGT | TCCACCCCATAAAGATACATCA |
| MPK2 | TACTCGCTCGTTTGCTGTTG | TTGGAGTACAGGAAAACAATGG |
| LOX | TGTGCCACTGGTAACTGGAT | TCCAAGCTTGCATGTGTACG |
表1 qRT-PCR分析的基因及引物序列
Table 1 Genes and primers sequence used in qRT-PCR analysis
| 基因 Gene | 上游引物(5′-3′) Upstream primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Downstream primer |
|---|---|---|
| MPK1 | GCTGACAGATTGTTGCAGGT | TCCACCCCATAAAGATACATCA |
| MPK2 | TACTCGCTCGTTTGCTGTTG | TTGGAGTACAGGAAAACAATGG |
| LOX | TGTGCCACTGGTAACTGGAT | TCCAAGCTTGCATGTGTACG |

图1 分蘖洋葱伴生诱导的番茄根际土壤微生物对番茄根结线虫病的影响 不同小写字母表示表示处理间的统计学差异,P < 0.05。下同。
Fig. 1 The schematic diagram of rhizosphere microflora transplantation experiment and the occurrence of tomato root-knot nematode disease Different letters are significantly different at 0.05 level. The same below.

图2 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄根际土壤悬浮液对番茄根结线虫卵孵化抑制率和二龄幼虫致死率的影响
Fig. 2 The effect of suspension of rhizosphere soil of tomato companion cropping with potato-onion on the hatching rate of RKN eggs and toxicity of RKNs
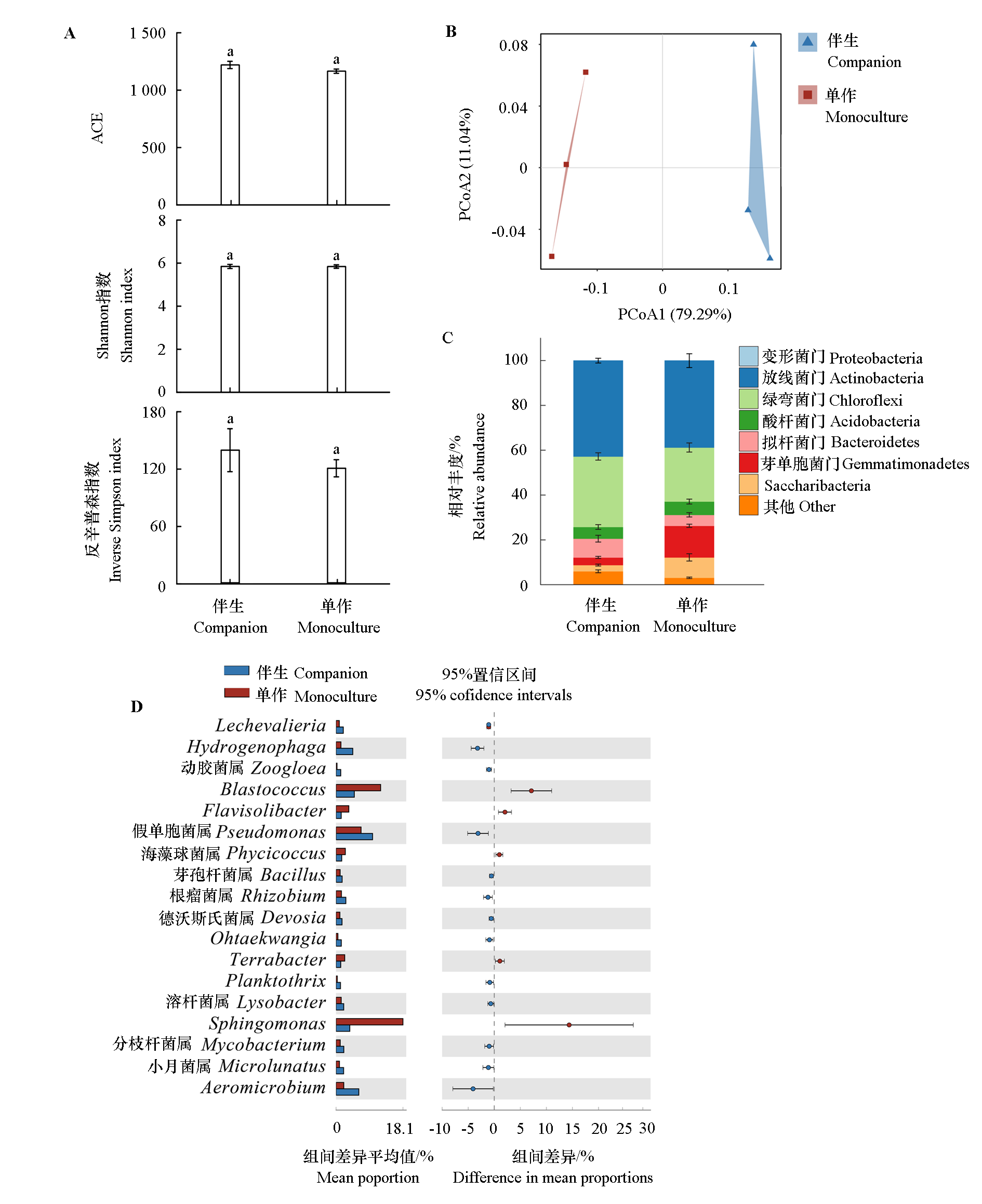
图3 接种根结线虫的单作和分蘖洋葱伴生的番茄根际土壤中的细菌群落 A:α多样性;B:β多样性的PCoA分析;C:细菌门柱状堆积图;D:丰度前30中有显著差异的菌属。
Fig. 3 Bacterial communities in monoculture and potato-onion companion with tomato rhizosphere soils inoculated root-knot nematode A:The α-diversity;B:PCoA analysis of β-diversity;C:The histogram of bacterial phylum;D:The top 30 bacterial showed significant differences.
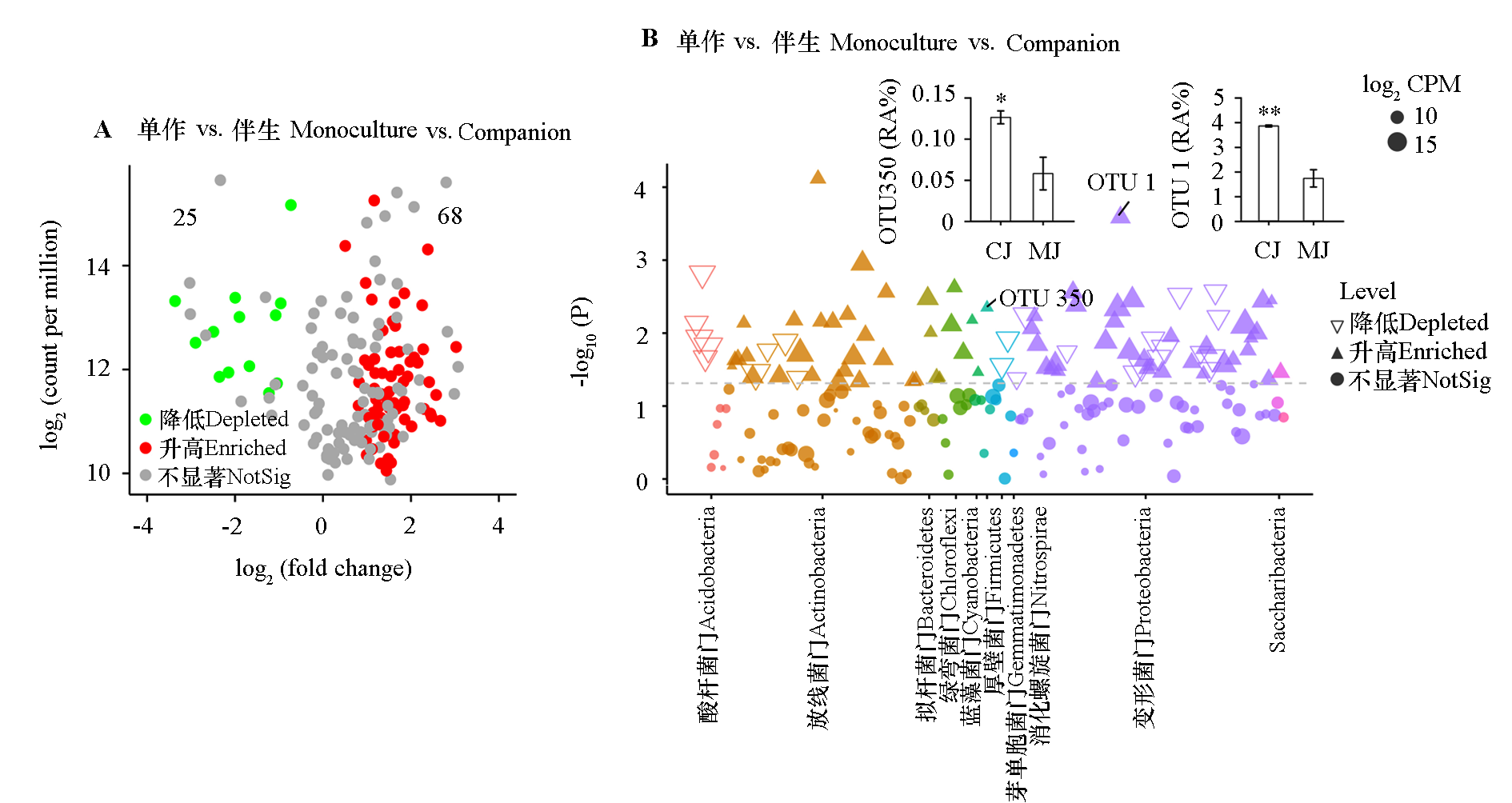
图4 接种根结线虫的单作分蘖洋葱伴生的番茄根际土壤细菌OUT丰度 A:火山图显示了富集和降低的OTU;B:曼哈顿图显示了富集的OTU的分类学信息。 *代表在P < 0.05水平有显著差异,**代表在P < 0.01水平有显著差异。
Fig. 4 Difference of bacterial community composition in rhizosphere of tomato inoculated with root-knot nematodes A:Volcano plot showing OTUs enriched or depleted in the companion tomato was inoculated with root-knot nematode. B:The Manhattan plot shows the taxonomic information of OTUs enriched in the companion tomato was inoculated with root-knot nematode. * represents a significant difference at the P < 0.05 level,** represents a significant difference at the P < 0.01 level.
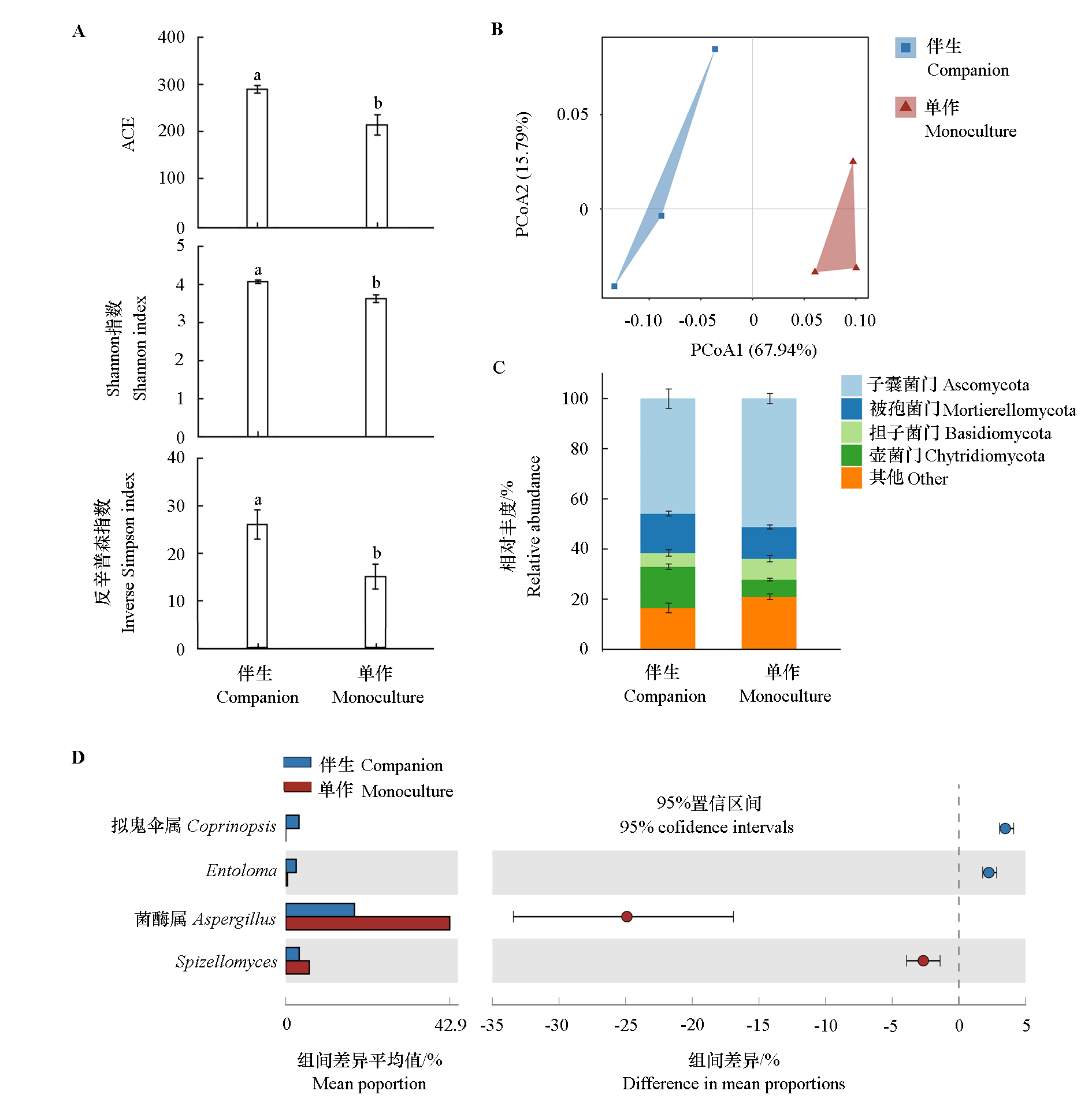
图5 接种根结线虫的单作和分蘖洋葱伴生的番茄根际土壤中的真菌群落 A:α多样性;B:β多样性;C:真菌门柱状堆积图;D:丰度前30中有显著差异的菌属。
Fig. 5 Fungal communities in monoculture and potato-onion companion with tomato rhizosphere soils inoculated root-knot nematode A:The α-diversity;B:The β-diversity;C:Histogram of phylum fungi;D:The top 30 fungi showed significant differences.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
白晶芝, 高欢, 杨帆, 周新刚, 刘守伟, 吴凤芝. 2021. 分蘖洋葱与番茄伴生根系分泌物对根结线虫的影响. 植物保护, 47 (3):22-28.
|
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.04.001 pmid: 22564542 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp144 pmid: 19429838 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1259 pmid: 18944464 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1002/jssc.201501239 pmid: 26990813 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
聂文锋. 2015. 番茄MPK1/2和H2O2在BR信号转导、诱导抗逆性中的作用和拟南芥H2A.Z参与DNA去甲基化的研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-95-0076 pmid: 18943839 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5646-5649.2005 pmid: 16151170 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.06.009 pmid: 19712950 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
|
王郭婷. 2020. 电信号和活性氧信号在茉莉酸调控番茄南方根结线虫抗性中的机制研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/s42832-020-0057-z |
| [41] |
|
|
吴凤芝. 2023. 多样性种植是设施蔬菜土壤健康保持及障碍消减的重要途径. 中国农村科技,(9):38-41.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
吴凤芝, 潘凯, 刘守伟. 2013. 设施土壤修复及连作障碍克服技术. 中国蔬菜,(13):39.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
吴加香, 刘涛, 寸梦壵, 徐志勇, 罗曌, 字淑慧. 2023. 黄草乌间作玉米对其根际微生物群落多样性的影响. 分子植物育种, 11 (16):1-15.
|
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
|
杨瑞娟, 王腾飞, 周希, 刘爱荣, 陈双臣, 杨英军. 2017. 禾本科作物伴生对番茄根区土壤酶活性、微生物及根结线虫的影响. 中国蔬菜,(3):38-42.
|
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5513-8 pmid: 30777003 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
|
张铁耀, 李衍素, 郭允娜, 闫妍, 贺超兴, 于贤昌. 2014. 万寿菊间作密度对黄瓜南方根结线虫防效和黄瓜生长与产量的影响. 中国生物防治学报, 30 (3):348-354.
|
|
| [50] |
|
|
张宗锦, 闫芳芳, 孔垂旭, 张映杰, 杨鹏, 倪荣清, 王蓉, 张海华. 2019. 烤烟菽麻间作对烟草根结线虫防效及烟叶产质量的影响. 中国烟草科学, 40 (2):52-56.
|
|
| [51] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01319-5 pmid: 30666369 |
| [52] |
|
| [1] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯 珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [3] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [4] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [5] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [6] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [7] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [8] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [9] | 侯雪, 王姣姣, 张雯雯, 赵建龙, 茆振川. 辣椒乙烯反应抑制因子Cacl-6468的克隆及其抗根结线虫作用分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 761-772. |
| [10] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [11] | 刘根忠, 李方曼, 葛平飞, 陶金宝, 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 番茄抗坏血酸含量相关QTL定位及候选基因鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [12] | 董舒超, 洪骏, 凌嘉怡, 谢紫欣, 张胜军, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 番茄抗旱性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | 徐琴, 王嘉颖, 张曼楠, 萧志浩, 郑涵楷, 卢永恩, 王涛涛, 张余洋, 张俊红, 叶志彪, 叶杰. 番茄苗期耐盐相关遗传位点鉴定及分子标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [14] | 杨亮, 刘欢, 马燕勤, 李菊, 王海娥, 周玉洁, 龙海成, 苗明军, 李志, 常伟. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高番茄红素番茄新材料[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [15] | 闫超凡, 孙雪梅, 钟启文, 邵登魁, 邓昌蓉, 文军琴. 番茄20S蛋白酶体基因家族鉴定及生物信息学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 266-280. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司