
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2425-2438.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0831
唐嘉怡1,2, 缪绸雨1,2, 尹豪杰1,2, 吴明月1,2, 曹向敏1,2, 张惠敏1,2, 金燕1,2, 卢晓鹏1,2, 朱亦赤1,2, 李大志1,2, 盛玲1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-21
修回日期:2025-07-02
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-09-24
通讯作者:
基金资助:
TANG Jiayi1,2, MIAO Chouyu1,2, YIN Haojie1,2, WU Mingyue1,2, CAO Xiangmin1,2, ZHANG Huimin1,2, JIN Yan1,2, LU Xiaopeng1,2, ZHU Yichi1,2, LI Dazhi1,2, SHENG Ling1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-05-21
Revised:2025-07-02
Published:2025-09-25
Online:2025-09-24
摘要:
为探究草酸处理对采后血橙果实品质和花色苷代谢的影响,以成熟塔罗科血橙(Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck‘Tarocco’)果实为材料,用10 mmol · L-1草酸浸泡处理5 min,测定贮藏期间果皮色泽、果汁色泽、花色苷、有机酸、糖、总黄酮和总酚含量以及发病率和失水率等指标。同时,还对花色苷生物合成通路相关基因和已报道的参与花色苷代谢调控的重要转录因子进行qRT-PCR分析。结果表明,草酸处理抑制了采后血橙果实贮藏期间花色苷的积累,果皮色泽和果汁色泽较淡,花色苷含量较低;果实柠檬酸含量较对照降低,蔗糖含量明显高于对照。此外,草酸处理明显降低了贮藏后期果实的真菌病害发病率和失重率。草酸处理果实中大多数花色苷合成通路基因(PAL4、CHI和ANS)以及调控基因(NAC、CHR4和PH4)与对照相比在贮藏期间表达显著下调。相关性分析表明,转录因子NAC、WRKY40、Ruby1和PH4的表达趋势与花色苷含量变化趋势显著正相关。研究结果表明草酸处理可对血橙果实采后花色苷的积累产生抑制作用,该抑制作用与花色苷生物合成及调控基因的表达受抑制相关。
唐嘉怡, 缪绸雨, 尹豪杰, 吴明月, 曹向敏, 张惠敏, 金燕, 卢晓鹏, 朱亦赤, 李大志, 盛玲. 外源草酸对采后血橙果实品质和花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2425-2438.
TANG Jiayi, MIAO Chouyu, YIN Haojie, WU Mingyue, CAO Xiangmin, ZHANG Huimin, JIN Yan, LU Xiaopeng, ZHU Yichi, LI Dazhi, SHENG Ling. The Effect of Exogenous Oxalic Acid Treatment on the Fruit Quality and Anthocyanin Metabolism of Postharvest Blood Orange Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(9): 2425-2438.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| CsActin | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Cs_ont_8g005310 | GTCGTTGAATGCTGCTGAGG | ACGCAAGTCCCTCTTTAGGC |
| Cs_ont_6g020620 | TCTCAGGGAATGGAATGGCG | GTACCATTTAGTCACATCGGCA |
| Cs_ont_9g012610 | TCAAGCGCATGTGTGACAA | GCCATGTACGCACACACATT |
| Cs_ont_2g025700 | AGTTCAAGCGCATGTGTGAC | GCACTTCGACCACCACAATG |
| Cs_ont_7g003040 | GATGCTCTTGTCTCTGCTCCA | GTCCCTCACCGCACTTTCTA |
| Cs_ont_1g027890 | TGGGAGGCACCTTTAAGCTC | TAAGAGAGGCCAGGGGTTCA |
| Cs_ont_2g002950 | TCGAATGGAGGAACCCATCAC | CCATGGTTCACCAACTGAAAGA |
| Cs_ont_5g038970 | CACGTTCGCCAGGAAGAGAT | CAACGCACAAGTTCAACCGT |
| Cs_ont_3g003380 | TCAATGTGCCCACAGAGTTCG | TGGCTCTGCAAGTATCCACAG |
| Cs_ont_5g040910 | CTCCAAGCGACTATACAGAGG | AAGCCAAGTGACAACACTGC |
| Cs_ont_6g006980 | CTTCTTCGACAGCCGTTTGG | GTTTGGCCCTTGGTTTGCAT |
| Cs_ont_2g004470 | GTTTCAGGATCAGGCGGGAA | TTTTCTGGTGCCTGTGGTGT |
| Cs_ont_2g009870 | ATCTGCGACGGCTACAGATG | AGGCGAAAGCTCAGCAAGAT |
| Cs_ont_2g009920 | AAGGGCTGGGACAACTGAAC | TGCAACTGAGAGGGTCCAAC |
| Cs_ont_2g035300 | AACGTCATACCTCTGCTGGC | AAGCGTTCGGTGAATACCCA |
| Cs_ont_4g001580 | GGATTCAACGTGGGTGGACA | TCAGCTTCTTGTTCTCAGTGCT |
| Cs_ont_4g010710 | AACTATGTGGAAGGCCGCTC | ATCGGTGACTTTGAAGCCGT |
| Cs_ont_5g010100 | TTCACCCACCAAAACCAGCT | CTCTTCTCCTTGGTTGGCGT |
| Cs_ont_6g003620 | CCAGCTGTGTCAAGCAGAGA | AACAATGCCGCATGCCATTT |
| Cs_ont_6g005110 | AAGCAGCTGTTCTGTAGGCT | CTGTGGTGCAACCGATGATT |
| Cs_ont_6g020160 | TGCATTTGCCCATCGAGAGT | TTCTGTCGGGGTTTGACGAG |
表1 实时荧光定量分析引物
Table 1 Primers used for qRT-PCR analysis
| 引物名称 Primer name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| CsActin | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Cs_ont_8g005310 | GTCGTTGAATGCTGCTGAGG | ACGCAAGTCCCTCTTTAGGC |
| Cs_ont_6g020620 | TCTCAGGGAATGGAATGGCG | GTACCATTTAGTCACATCGGCA |
| Cs_ont_9g012610 | TCAAGCGCATGTGTGACAA | GCCATGTACGCACACACATT |
| Cs_ont_2g025700 | AGTTCAAGCGCATGTGTGAC | GCACTTCGACCACCACAATG |
| Cs_ont_7g003040 | GATGCTCTTGTCTCTGCTCCA | GTCCCTCACCGCACTTTCTA |
| Cs_ont_1g027890 | TGGGAGGCACCTTTAAGCTC | TAAGAGAGGCCAGGGGTTCA |
| Cs_ont_2g002950 | TCGAATGGAGGAACCCATCAC | CCATGGTTCACCAACTGAAAGA |
| Cs_ont_5g038970 | CACGTTCGCCAGGAAGAGAT | CAACGCACAAGTTCAACCGT |
| Cs_ont_3g003380 | TCAATGTGCCCACAGAGTTCG | TGGCTCTGCAAGTATCCACAG |
| Cs_ont_5g040910 | CTCCAAGCGACTATACAGAGG | AAGCCAAGTGACAACACTGC |
| Cs_ont_6g006980 | CTTCTTCGACAGCCGTTTGG | GTTTGGCCCTTGGTTTGCAT |
| Cs_ont_2g004470 | GTTTCAGGATCAGGCGGGAA | TTTTCTGGTGCCTGTGGTGT |
| Cs_ont_2g009870 | ATCTGCGACGGCTACAGATG | AGGCGAAAGCTCAGCAAGAT |
| Cs_ont_2g009920 | AAGGGCTGGGACAACTGAAC | TGCAACTGAGAGGGTCCAAC |
| Cs_ont_2g035300 | AACGTCATACCTCTGCTGGC | AAGCGTTCGGTGAATACCCA |
| Cs_ont_4g001580 | GGATTCAACGTGGGTGGACA | TCAGCTTCTTGTTCTCAGTGCT |
| Cs_ont_4g010710 | AACTATGTGGAAGGCCGCTC | ATCGGTGACTTTGAAGCCGT |
| Cs_ont_5g010100 | TTCACCCACCAAAACCAGCT | CTCTTCTCCTTGGTTGGCGT |
| Cs_ont_6g003620 | CCAGCTGTGTCAAGCAGAGA | AACAATGCCGCATGCCATTT |
| Cs_ont_6g005110 | AAGCAGCTGTTCTGTAGGCT | CTGTGGTGCAACCGATGATT |
| Cs_ont_6g020160 | TGCATTTGCCCATCGAGAGT | TTCTGTCGGGGTTTGACGAG |

图1 草酸处理对血橙果汁和果皮表型(A)、色差指数CI(B、C)、花色苷含量(D)的影响 * 表示在相同时期草酸与对照在P < 0.05水平的显著性差异,t-test. 下同
Fig. 1 Effects of oxalic acid treatment on the phenotype of juice and peel(A),color difference index CI(B,C)and anthocyanin content(D)of blood oranges * represent significant differences at P < 0.05 between OA and the control at each stage,t-test. The same below

图3 草酸处理对血橙果实贮藏期间总黄酮(A)和总酚含量(B)的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of OA treatment on total flavonoid content(A)and total phenol content(B)in blood orange fruit during postharvest storage period

图5 草酸处理对血橙果实贮藏期花色苷生物合成相关基因表达的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of OA treatment on expression of genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis of blood orange fruits during postharvest storage period

图6 草酸处理对血橙果实贮藏期花色苷生物合成调控相关转录因子基因表达的影响
Fig. 6 Effect of OA treatment on the expression of transcription factor genes regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in blood orange fruits during storage period
| 元数据ID Mata_ID | 基因ID Gene_ID | 相关系数 Cor | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | FAR1(Cs_ont_2g009920) | 0.402869 | 0.219257 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | HAC12(Cs_ont_6g003620) | 0.453251 | 0.161490 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | PH4(Cs_ont_2g035300) | 0.698900 | 0.016715 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | ATC3H64(Cs_ont_4g010710) | 0.346240 | 0.296919 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | CHR4(Cs_ont_2g009870) | 0.153589 | 0.652082 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | NAC(Cs_ont_2g004470) | 0.882306 | 0.000324 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | CH-ZF(Cs_ont_6g020160) | 0.340465 | 0.305587 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | WRKY40(Cs_ont_4g001580) | 0.664538 | 0.025710 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | AN1(Cs_ont_5g010100) | 0.011326 | 0.973634 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | Ruby1(Cs_ont_6g005110) | 0.823061 | 0.001857 |
表2 10个转录因子表达水平与花色苷含量的相关性
Table 2 Correlation analysis between anthocyanin content and ten transcription factors
| 元数据ID Mata_ID | 基因ID Gene_ID | 相关系数 Cor | P值 P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | FAR1(Cs_ont_2g009920) | 0.402869 | 0.219257 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | HAC12(Cs_ont_6g003620) | 0.453251 | 0.161490 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | PH4(Cs_ont_2g035300) | 0.698900 | 0.016715 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | ATC3H64(Cs_ont_4g010710) | 0.346240 | 0.296919 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | CHR4(Cs_ont_2g009870) | 0.153589 | 0.652082 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | NAC(Cs_ont_2g004470) | 0.882306 | 0.000324 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | CH-ZF(Cs_ont_6g020160) | 0.340465 | 0.305587 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | WRKY40(Cs_ont_4g001580) | 0.664538 | 0.025710 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | AN1(Cs_ont_5g010100) | 0.011326 | 0.973634 |
| 花色苷Anthocyanin | Ruby1(Cs_ont_6g005110) | 0.823061 | 0.001857 |
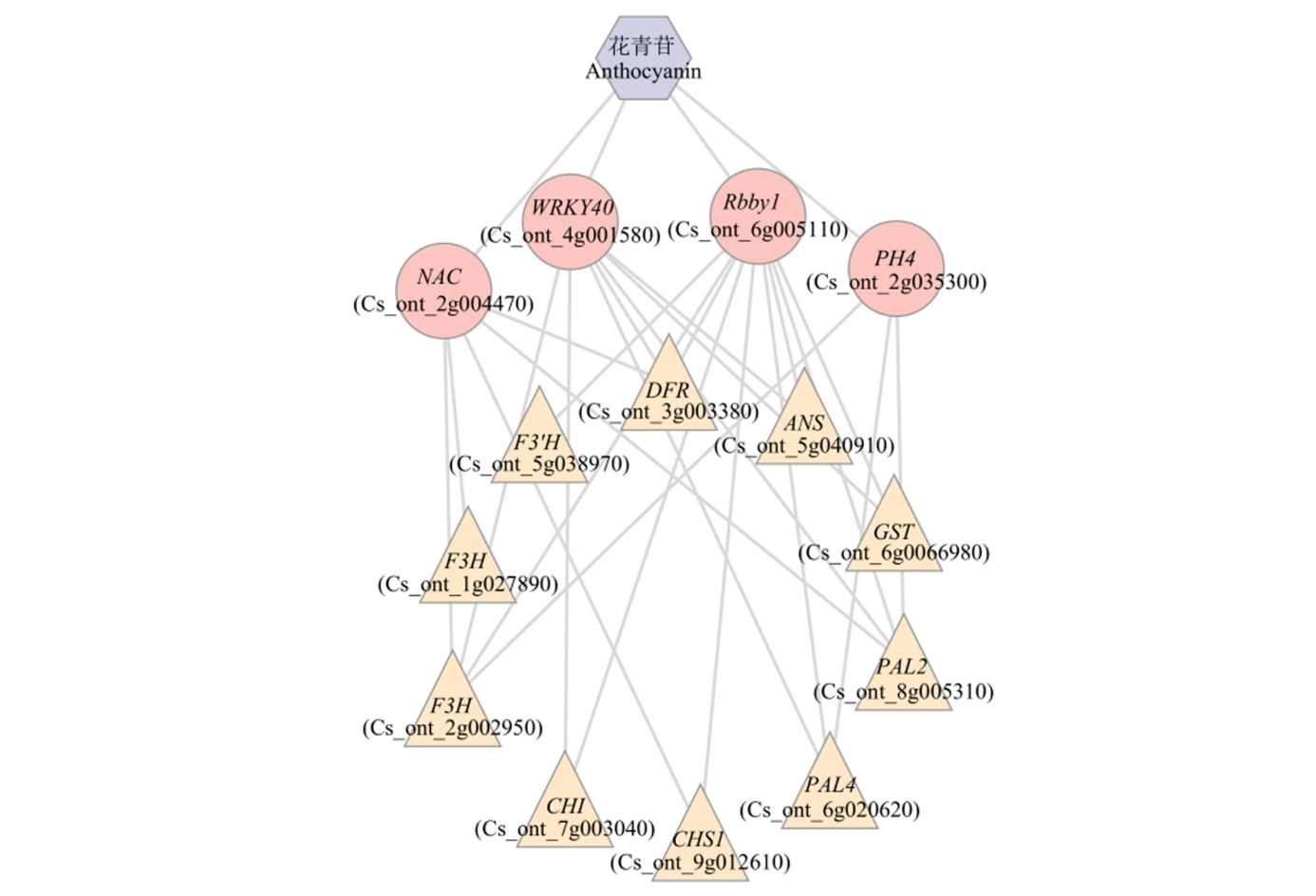
图7 与花色苷含量显著相关的转录因子和花色苷合成通路基因的相关网络示意图
Fig. 7 Correlation network diagram among anthocyanin content,transcription factor expression,and anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway gene expression
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
洪敏, 王晶, 王日葵, 冯雨, 周炼. 2023. 草酸处理对锦橙采后风味品质及乙醇代谢的影响. 食品与发酵工业, 49 (10):71-77.
doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.031836 |
|
| [16] |
|
|
黄玉咪, 徐超, 杨文慧, 吴晓露, 封碧红. 2021. 草酸—壳聚糖复合处理对采后芒果果实品质及保鲜效果的影响. 南方农业学报, 52 (7):1790-1797.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04309-5 pmid: 37268922 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0451 |
|
梁春强, 吕茳, 靳蜜静, 李桦, 饶景萍. 2017. 草酸处理对采后猕猴桃冷害、抗氧化能力及能荷的影响. 园艺学报, 44 (2):279-287
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0451 |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04868-1 pmid: 38429733 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9165 pmid: 29851071 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0329 |
|
王春伟, 王燕, 段天坤, 苏雅馨, 袁胜楠, 任璐, 赵晓军, 王美琴. 2025. 异辛醇对番茄灰霉病菌的抑菌机理研究. 园艺学报, 52 (3):761-772.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0329 |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
|
喻最新, 王日葵, 贺明阳, 洪敏, 袁小淞, 王晶, 冯雨, 吴志刚. 2020. ‘塔罗科’血橙成熟过程中花色苷积累及其与糖酸含量相关性. 食品科学, 41 (15):105-114.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张惠敏, 尹豪杰, 唐嘉怡, 吴明月, 金燕, 盛玲. 2024. 不同保鲜剂处理对血橙果实品质和贮藏性能的影响. 保鲜与加工, 24 (10):8-15.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
左龙亚, 滕左, 王孝仕, 江东, 于杰. 2017. 不同溶剂柠檬果皮提取物抗氧化、抑菌活性比较及其与多酚组成的关系. 园艺学报, 44 (4):743-754.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0715 |
| [1] | 任婷婷, 张廷秀, 战良, 张志昌, 任怡然, 季兴龙, 王培培, 刘源霞, 孟庆福, 刘更森, 房经贵, 冷翔鹏. 不同光质补光对设施栽培‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2464-2476. |
| [2] | 谭筱玉, 牛军鹏, 王全智, 张丽, 朱丽娟, 王国栋, 郑贺云, 郁志芳, 段玉权, 姜丽, 孙秀秀, 杨瑛, 罗伟奇, 李雪晖, 管乐, 赵艳岭, 李国晓, 殷从飞, 葛成, 马敏, 贾璐婷, 张旭, 赵垚垚, 耿新丽, 王利斌, 张绍铃. 茉莉酸及其衍生物提高园艺作物采后低温抗性的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 1987-2020. |
| [3] | 周天, 吕帅丽, 韩晗, 李雨佳, 刘海强, 刘永忠. 外源独脚金内酯对枳幼苗茎增粗生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1843-1854. |
| [4] | 王毅, 梁振昌. 基于群体转录组的葡萄远缘杂交遗传机制分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 835-845. |
| [5] | 唐伶俐, 贺玉花, 王庆涛, 安璐璐, 徐永阳, 张健, 孔维虎, 户克云, 赵光伟. 非呼吸跃变和呼吸跃变型甜瓜成熟果实的激素与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 883-896. |
| [6] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [7] | 许桐, 王越, 吴丽娜, 张航, 尹立来, 徐柯宇, 郑小林. 褪黑素处理对‘桃形李’采后果实品质及花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 395-405. |
| [8] | 史兴秀, 冯贝贝, 闫鹏, 耿文娟, 朱玛孜拉·沙尔山木汗. ‘王林’苹果早期水心病发生过程中的相关生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [9] | 任思源, 陈森, 龙治坚, 王博雅, 唐登国, 王正前, 杨斌, 胡尚连, 曹颖. 花魔芋球茎发育期氮分配变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [10] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [11] | 李雅晨, 郑艳梅, 宋雯佩, 李大卫, 梁红, 张宪智. 富氢水在植物生长发育及逆境胁迫响应中的作用研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1489-1500. |
| [12] | 黄彭, 丁捷, 刘春燕, 李红莹, 李昕渝, 刘耀文, 秦文. 可食性复合涂膜对蓝莓的保鲜效果综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1361-1376. |
| [13] | 周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 金光. 桃镁离子转运蛋白MGT基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 463-478. |
| [14] | 夏宏义, 刘巧, 彭家清, 吴伟, 龚林忠. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄避雨栽培f式树形对光合及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [15] | 孙权, 何政辰, 叶俊丽, 魏冉冉, 尹映紫, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 徐强, 徐娟, 郭文武, 程运江, 邓秀新. 与呼吸跃变型果实共贮藏改善柑橘果实色泽和品质[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司