
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 463-478.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0056
• 遗传育种·种质资源·分子生物学 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-03-29
修回日期:2023-11-30
出版日期:2024-03-25
发布日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHOU Ping, YAN Shaobin, GUO Rui, JIN Guang*( )
)
Received:2023-03-29
Revised:2023-11-30
Published:2024-03-25
Online:2024-03-22
摘要:
为研究桃树镁离子转运蛋白(Magnesium Transporters,MGT)家族基因在镁离子运输中所起的作用,全基因组鉴定、分析了桃树MGT家族成员(PpMGT),并研究外源施镁对PpMGT基因表达的影响。通过同源比对、保守位点分析鉴定获得了8个PpMGT,在Chr1、Chr3、Chr6、Chr8染色体上不均匀分布。系统发育研究表明植物MGT家族可分为5个分支,各分支成员数存在差异。基因和蛋白结构分析发现PpMGT含有4 ~ 13个外显子,蛋白中存在10个保守基序,启动子上游分布有不同数量的胁迫响应、转录调控、节律调控、激素响应和发育调控元件。PpMGT在桃树花、果、叶、根器官均有表达且具有组织表达特异性。桃树外源喷施MgCl2 24 h后,检测到PpMGT转录表达变化。喷施镁使叶片、果皮出现不同的差异表达基因类群,均涉及光合途径。研究发现PpMGT4、PpMGT6、PpMGT8与喷镁后光系统Ⅱ捕光叶绿素a/b蛋白复合体基因表达变化正相关。异源表达PpMGT4、PpMGT6、PpMGT8可补偿Mg2+转运缺陷突变株MM281(鼠伤寒沙门氏菌突变株)生长缺陷,表明PpMGT4、PpMGT6、PpMGT8具有镁离子转运功能。根据序列特征、表达模式及外源镁喷施结果,推测PpMGT可能具有功能分化,通过协同作用调节桃树镁转运,PpMGT4、PpMGT6、PpMGT8的表达变化可能与外源镁摄入和利用相关。
周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 金光. 桃镁离子转运蛋白MGT基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 463-478.
ZHOU Ping, YAN Shaobin, GUO Rui, JIN Guang. Identification and Expressional Analysis of MGT Gene Family in Prunus persica[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 463-478.
| 基因 Gene | ID | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 跨膜域 Transmem- brane | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpMGT1 | Prupe.1G027800 | Chr1 | 393 | 43.71 | 4.64 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT2 | Prupe.1G287300 | Chr1 | 433 | 47.53 | 4.98 | 2 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT3 | Prupe.1G575700 | Chr1 | 455 | 50.79 | 5.14 | 2 | 叶绿体,线粒体 Chloroplast,mitochondrion |
| PpMGT4 | Prupe.3G100200 | Chr3 | 472 | 53.39 | 5.30 | 1 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT5 | Prupe.6G116100 | Chr6 | 452 | 50.71 | 6.21 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT6 | Prupe.8G147300 | Chr8 | 491 | 54.70 | 4.64 | 2 | 叶绿体,细胞质 Chloroplast,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT7 | Prupe.8G147400 | Chr8 | 460 | 51.20 | 4.84 | 2 | 叶绿体,液泡 Chloroplast,vacuole |
| PpMGT8 | Prupe.8G231400 | Chr8 | 435 | 48.81 | 4.54 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
表1 PpMGT蛋白特性
Table 1 The properties of PpMGTs
| 基因 Gene | ID | 染色体 Chromosome | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 跨膜域 Transmem- brane | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PpMGT1 | Prupe.1G027800 | Chr1 | 393 | 43.71 | 4.64 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT2 | Prupe.1G287300 | Chr1 | 433 | 47.53 | 4.98 | 2 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT3 | Prupe.1G575700 | Chr1 | 455 | 50.79 | 5.14 | 2 | 叶绿体,线粒体 Chloroplast,mitochondrion |
| PpMGT4 | Prupe.3G100200 | Chr3 | 472 | 53.39 | 5.30 | 1 | 高尔基体,细胞质 Golgi,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT5 | Prupe.6G116100 | Chr6 | 452 | 50.71 | 6.21 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |
| PpMGT6 | Prupe.8G147300 | Chr8 | 491 | 54.70 | 4.64 | 2 | 叶绿体,细胞质 Chloroplast,cytoplasm |
| PpMGT7 | Prupe.8G147400 | Chr8 | 460 | 51.20 | 4.84 | 2 | 叶绿体,液泡 Chloroplast,vacuole |
| PpMGT8 | Prupe.8G231400 | Chr8 | 435 | 48.81 | 4.54 | 2 | 质膜,叶绿体 Plasma membrane,chloroplast |

图1 桃MGT蛋白多序列比对 η代表蛋白质310螺旋;螺旋线代表α-螺旋;箭头代表β-折叠;TT代表β-转角。
Fig. 1 Multiple protein sequence alignment of the PpMGTs The η symbols refer to 310-helix,and squiggles and arrows indicate α-helices and β-strands. TT letters show β-turns.
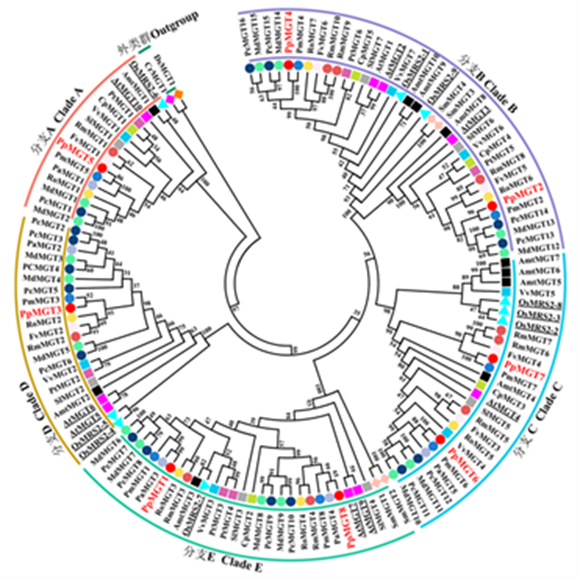

图2 MGT家族成员演化分析 物种为桃(Pp, )、拟南芥(At, )、水稻(Os, )、番木瓜(Cp, )、毛果杨(Pt, )、番茄(Sl, )、葡萄(Vv, )、无油樟(Amt, )、苹果(Md, )、梨(Pc, )、梅(Pm, )、喜阴悬钩子(Ro, )、草莓(Fv, )、樱桃(Pa, )、野蔷薇(Rm, )、江南卷柏(Sm, )、莱茵衣藻(Cr, )、盐生杜氏藻(Ds, )。
Fig. 2 Evolutionary analysis of MGT family members Prunus persica(Pp, ),Arabidopsis thaliana(At, ),Oryza sativa(Os, ),Carica papaya(Cp, ),Populus trichocarpa(Pt, ),Solanum lycopersicum(Sl, ),Vitis vinifera(Vv, ),Amborella trichopoda(Amt, ),Malus × domestica(Md, ),Pyrus communis(Pc, ),Prunus mume(Pm, ),Rubus occidentalis(Ro, ),Fragaria vesca(Fv, ),Prunus avium(Pa, ),Rosa multiflora (Rm, ),Selaginella moellendorffii(Sm, ),Chlamydomonas reinhardti(Cr, ),and Dunaliella salina(Ds, ).
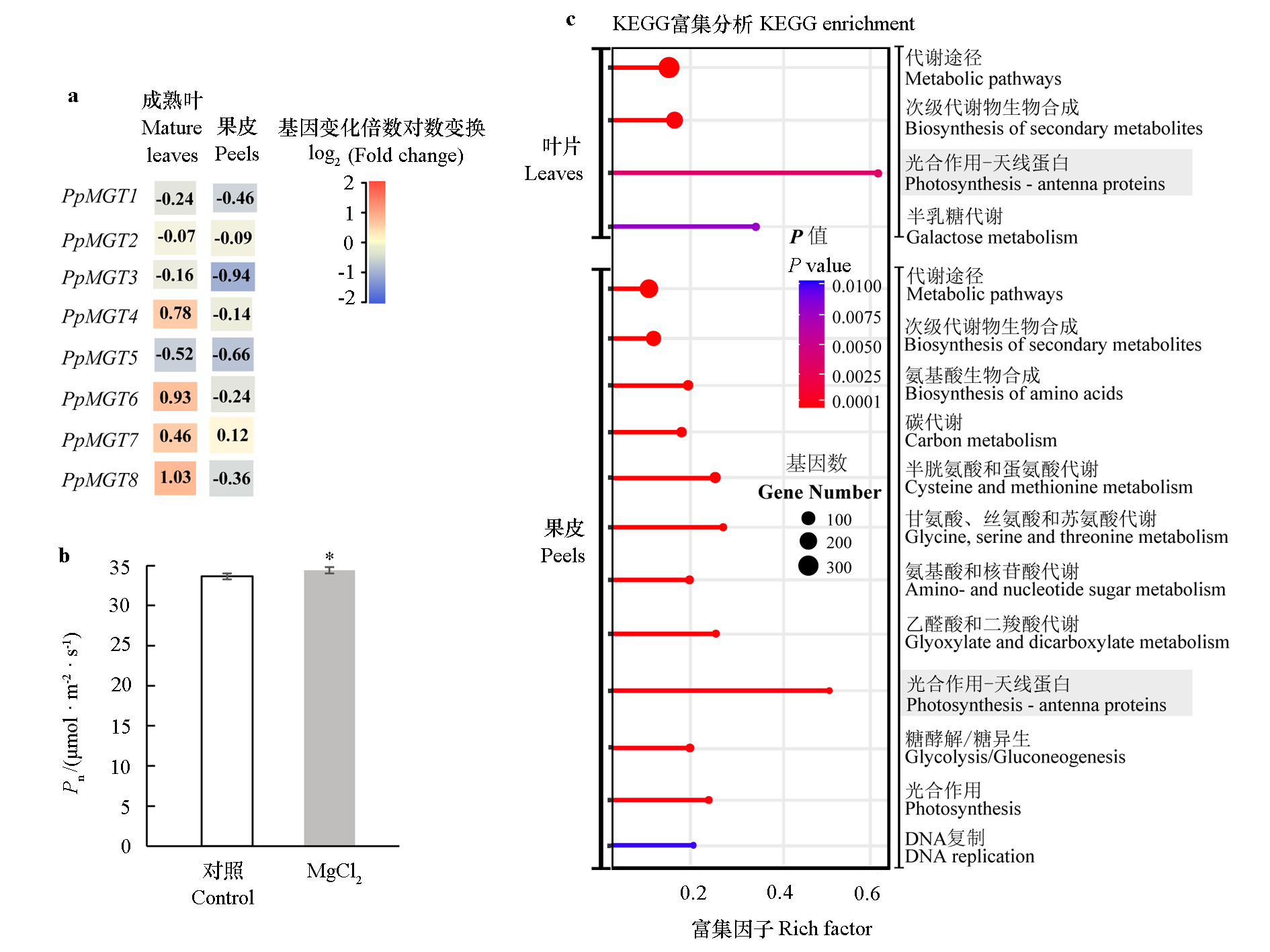
图7 桃树喷镁后叶片、果皮PpMGT表达变化(a)、光合速率(b)比较和代谢通路富集分析(c) * 代表处理与对照有统计学差异(Student t检验)。
Fig. 7 Gene expressional changes(a),photosynthetic rate comparison(b)and metabolic pathway enrichment analysis(c)after magnesium treatment * represents a significant difference between treatment and control group(Student t-test).

图8 镁处理桃叶片、果皮中光系统Ⅱ捕光叶绿素a/b蛋白复合体(LHC)基因表达变化(a)及其与MGT基因表达的皮尔逊相关性(b) *和**分别代表DEseq2分析结果中相应基因在对照—处理两组间表达差异处于P < 0.05和P < 0.01水平。
Fig. 8 Expressional changes of Light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex(LHC)genes(a)and their correlative relations to MGTs transcriptional changes(b) Symbols * or ** indicate that the corresponding genes were differentially expressed in control-treatment comparisons at P < 0.05 or P < 0.01 levels,analyzing by DEseq2.
| [27] |
doi: 10.1038/s41477-020-0686-3 pmid: 32541951 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30380-5 pmid: 29275166 |
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1021/bi4007397 pmid: 23781956 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: S1674-2052(17)30296-4 pmid: 28989088 |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [48] |
|
|
王勇军. 2019. 甘蔗MGT基因家族鉴定与缺镁胁迫的转录组动力学研究[硕士论文]. 福州: 福建农林大学.
|
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0506 |
|
文婷, 李婧, 张家琪, 魏仪, 祝文睿, 倪德江, 王明乐. 2023. 树镁转运子基因CsMGT6的表达和功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2171-2182.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0506 |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
|
许迎港, 邹智, 郭静远, 孔华, 朱国鹏, 郭安平. 2022. 番木瓜镁离子转运蛋白基因CpMGT1的克隆与功能分析. 热带作物学报, 43 (6):1114-1121.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.06.003 |
|
| [55] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
丛悦玺, 骆东峰, 陈坤明, 蒋立希, 郭万里. 2012. 生物镁离子转运体研究进展. 农业生物技术学报, 20 (7):837-848.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl201 pmid: 17101715 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
|
周平, 林志楷, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 张小丹, 马昕怡, 金光. 2021. 低温处理对桃树叶片基因表达及类黄酮合成代谢的影响. 农业生物技术学报, 29 (7):1283-1294.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcu245 pmid: 25550144 |
| [16] |
pmid: 12753976 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0197 |
|
贾亚敏, 徐浩, 胡文朗, 王玉雯, 叶欣, 陈立松, 李延, 郭九信. 2022. 缺镁对柑橘苗铁的吸收及亚细胞分布和化学形态的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (5):973-983.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0197 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] | 刘建豪, 荆彦付, 刘月芯, 徐摇光, 于 洋, 葛秀秀, 谢 华, . 桃NAC基因家族的鉴定及PpNAC050促进果实果糖积累研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 1983-1996. |
| [2] | 任思源, 陈 森, 龙治坚, 王博雅, 唐登国, 王正前, 杨 斌, 胡尚连, 曹 颖, . 花魔芋球茎发育期氮分配变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [3] | 张 帆, 杨 阳, 王 鸿, 张雪冰. 生物肥和有机肥对桃重茬土理化性状和细菌群落的改善作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2089-2104. |
| [4] | 刘艳飞, 何 昕, 田爱林, 刘占德 . 优质耐贮猕猴桃新品种‘金福’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2219-2220. |
| [5] | 匡美美, 李 黎, 马建伟, 刘 原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷 瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄 波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪, . 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [6] | 田 歌, 刘建廷, 高传彩, 赵雪惠, 樊永信, 李 森, 张寒啸, 陈修德, 李 玲, 李冬梅, . UV-B对设施油桃叶片叶绿素生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1332-1344. |
| [7] | 董晓珂, 陈元磊, 牛友怡, 刘占德, 王南南. 以高产优质稳产为目标的‘徐香’猕猴桃不同生长期叶片营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1345-1360. |
| [8] | 乔成奎, 庄 明, 田发军, 王彩霞, 庞 涛, 陈如霞, 李晓光, 成 昕, 谢汉忠, . 氟啶虫酰胺和螺虫乙酯在猕猴桃园中的降解及膳食风险评估[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1386-1402. |
| [9] | 曾 劲, 饶显龙, 胡晓敏, 叶小玲, 朱 军, 高 珊, 杨梓滨, 邱晓平. 樱花新品种‘天适’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1437-1438. |
| [10] | 于 静, 冯向君, 金英学, 丁国华, . 焦脱镁叶绿酸a对黄瓜枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 859-874. |
| [11] | 张 伟, 叶小玲, 胡晓敏, 朱 军, 熊育明, 陈端妮, 冯钦钊. 樱花新品种‘旺地’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 923-924. |
| [12] | 张伟, 朱军, 胡晓敏, 叶小玲, 高珊, 李园凤, 熊海坚. 樱花新品种‘宗儒樱’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 705-706. |
| [13] | 关思慧, 刘晨旭, 姚祝平, 万红建, 刁明, 程远. 腐植酸处理对樱桃番茄挥发性有机化合物成分和含量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 346-360. |
| [14] | 王海珍, 应瑶琳, 王雨晴, 吕瑞恒, 韩路. 软枣猕猴桃品种耐热性差异分析与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2857-2870. |
| [15] | 崔一琼, 李菊, 刘晓奇, 王俊文, 唐中祺, 武玥, 肖雪梅, 郁继华. 水分亏缺对设施基质栽培番茄果实蔗糖和淀粉代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2607-2619. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司