
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (11): 2594-2606.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0964
王雅楠, 刘绪涛, 景桐彤, 柴亚婷, 张晓伟, 艾希珍, 毕焕改*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-31
修回日期:2024-07-02
出版日期:2024-12-12
发布日期:2024-11-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Yanan, LIU Xutao, JING Tongtong, CHAI Yating, ZHANG Xiaowei, AI Xizhen, BI Huangai*( )
)
Received:2024-05-31
Revised:2024-07-02
Published:2024-12-12
Online:2024-11-25
摘要:
为了探讨褪黑素(melatonin,MT)对番茄(Solanum lycopersicum L.)叶片衰老的调控机理,以‘金棚1号’番茄以及MT合成关键基因L–色氨酸脱羧酶编码基因SlTDC过量表达和敲除的番茄为试材,以黑暗模拟衰老,研究MT对番茄衰老相关基因Senescence-associated gene 12(SAG12)表达、活性氧(ROS)积累、抗氧化系统的影响。结果表明,随着黑暗处理时间的延长,番茄叶片的SAG12 mRNA表达量、过氧化氢(H2O2)和超氧阴离子积累量显著增加,超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化物酶(peroxidase,POD)和抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(ascorbate peroxidase,APX)活性及其基因表达量和氧化还原物质抗坏血酸(reduced ascorbic acid,AsA)、还原型谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)含量随着黑暗处理时间的延长亦趋于上升。与清水对照相比,外源MT处理的SAG12 mRNA表达量、H2O2和$\mathrm{O}_{2}^{\bar{·}}$含量显著下降,而SOD、POD和APX活性及其基因表达和氧化还原物质含量显著增加;SlTDC过量表达同样可以显著下调黑暗处理下番茄叶片的SAG12 mRNA表达量及H2O2和$\mathrm{O}_{2}^{\bar{·}}$含量,增强抗氧化能力,而抑制或敲除SlTDC则上调了黑暗下番茄叶片的衰老基因表达和活性氧(ROS)的积累,加速叶片衰老;田间应用研究发现,外源MT亦可以显著下调日光温室番茄衰老叶片(叶龄 > 35 d)衰老基因表达和ROS的积累,延缓叶龄增大导致的叶片衰老。综上说明,MT可通过下调衰老基因表达和上调抗氧化能力,加速ROS的清除,延缓黑暗或依赖于叶龄的番茄叶片衰老。
王雅楠, 刘绪涛, 景桐彤, 柴亚婷, 张晓伟, 艾希珍, 毕焕改. 褪黑素对番茄衰老叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606.
WANG Yanan, LIU Xutao, JING Tongtong, CHAI Yating, ZHANG Xiaowei, AI Xizhen, BI Huangai. Effect of Melatonin on Antioxidant System of Tomato Senescent Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606.
| 基因 Gene | 登录号 Accession number | Solyc基因号 Solyc gene number | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ß-Actin | XM_004243253.4 | Solyc07g054860.1.1 | F:TTTGCTGGTGATGATGCC |
| R:CCTTAGGGTTGAGAGGTGCTT | |||
| SAG12 | XM_004233006 | Solyc02g076910.3.1 | F:GGAGCTCTCAATTAGCTTCATC |
| R:GTACCCTTTATCTTCTCCTGCAT | |||
| SOD | NM_001347093 | Solyc08g079830.4.1 | F:CTTCTTCGCAGTTTGAACG R:AACACAGCCTTGACACGA |
| POD | NM_001247203 | Solyc01g006300.3.1 | F:GGTCCAACATGGCAAGTTCT R:ACATCTTGCCCTTCCAAATG |
| APX | NM_001306170 | Solyc06g060260.3.1 | F:AGCTTAAGATTCGAAATTG R:GATCTCCCCAAAGTGTGAGCC |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Table 1 The primer sequences of real-time qPCR
| 基因 Gene | 登录号 Accession number | Solyc基因号 Solyc gene number | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| ß-Actin | XM_004243253.4 | Solyc07g054860.1.1 | F:TTTGCTGGTGATGATGCC |
| R:CCTTAGGGTTGAGAGGTGCTT | |||
| SAG12 | XM_004233006 | Solyc02g076910.3.1 | F:GGAGCTCTCAATTAGCTTCATC |
| R:GTACCCTTTATCTTCTCCTGCAT | |||
| SOD | NM_001347093 | Solyc08g079830.4.1 | F:CTTCTTCGCAGTTTGAACG R:AACACAGCCTTGACACGA |
| POD | NM_001247203 | Solyc01g006300.3.1 | F:GGTCCAACATGGCAAGTTCT R:ACATCTTGCCCTTCCAAATG |
| APX | NM_001306170 | Solyc06g060260.3.1 | F:AGCTTAAGATTCGAAATTG R:GATCTCCCCAAAGTGTGAGCC |
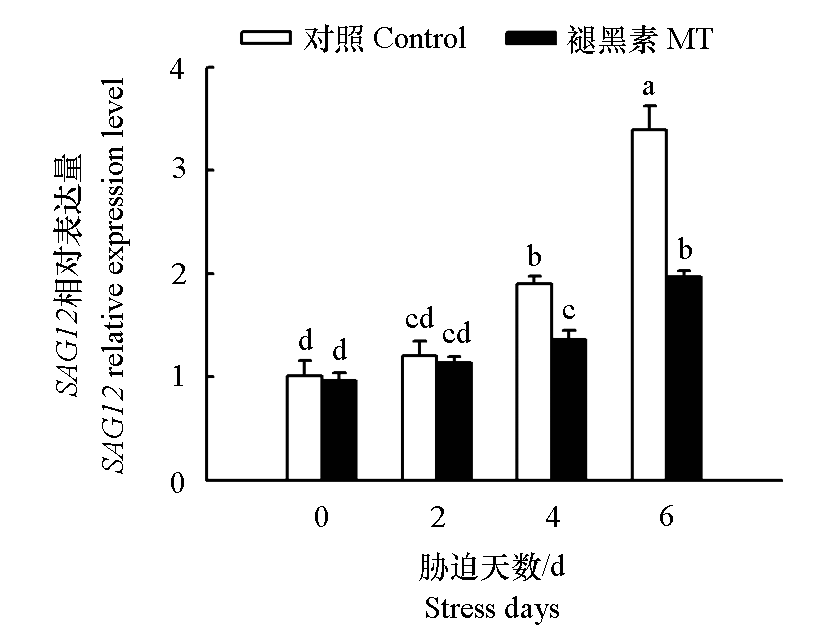
图1 外源褪黑素(MT)对黑暗条件下番茄叶片SAG12表达量的影响 不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Fig. 1 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on the expression of SAG12 in tomato leaves under dark condition Different letters after data indicate significant differences(P < 0.05). The same below.

图3 外源褪黑素(MT)对黑暗条件下番茄叶片抗氧化酶活性影响
Fig. 3 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on the activities and gene expression of antioxidant enzymes in tomato leaves in darkness

图5 SlTDC1对黑暗下番茄叶片SAG12表达量的影响 WT:野生型植株;OE14、OE10:过量表达植株;RNAi4、RNAi7:干扰植株;Crispr1:敲除植株。下同。
Fig. 5 Effect of SlTDC1 on the relative expression of SAG12 in tomato leaves under darkness WT:Wild-type plants;OE14,OE10:Overexpression plants;RNAi4,RNAi7:Interference plants;Crispr1:Knockout plants. The same below.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00625.x pmid: 18691358 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12120 pmid: 24433490 |
| [5] |
|
|
陈贤, 杨勇, 刘凤权. 2020. 植物褪黑素的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 48 (24):17-24.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1111/plb.12241 pmid: 25294336 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
巩彪, 史庆华. 2017. 园艺作物褪黑素的研究进展. 中国农业科学, 50 (12):2326-2337.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.12.013 |
|
| [10] |
|
|
郭明欣, 刘佳佳, 侯琳琳, 张笑天, 刘含笑. 2021. 植物体内活性氧的产生及清除机制研究进展. 科技视界,(8):104-106.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
|
何智冲. 2019. 银杏叶片衰老转色进程及调控研究[硕士论文]. 扬州: 扬州大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
贾乐, 韩延超, 房祥军, 陈杭君, 郜海燕. 2021. 褪黑素处理对香菇采后品质及活性氧代谢的影响. 食品科学, 42 (23):229-236.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.138552 pmid: 19439571 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0308-z pmid: 21805384 |
| [19] |
|
|
李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰, 章文华. 2000. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术. 北京:高等教育出版社:164-167.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
李君明, 项朝阳, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 黄泽军, 刘磊, 李鑫, 杜永臣. 2021. “十三五”我国番茄产业现状及展望. 中国蔬菜,(2):13-20.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
毛晶晶. 2020. 外源褪黑素延缓拟南芥叶片衰老的机制探讨[硕士论文]. 四川: 四川农业大学.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1994.tb04243.x pmid: 33874468 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
孙虎. 2016. 氮肥对番茄衰老调控及产量的影响. 北方园艺,(24):35-37.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.130013 pmid: 19074627 |
| [34] |
|
|
王爱国, 罗广华. 1990. 植物的超氧物自由基与羟胺反应的定量关系. 植物生理学通讯,(6):55-57.
|
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12017 pmid: 23106234 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
王荣, 成梦琳, 刘慧娜, 赵大球, 陶俊. 2018. 黑暗条件下褪黑素对栀子叶片类黄酮含量及相关基因表达水平的影响. 植物研究, 38 (4):559-567.
doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2018.04.010 |
|
| [38] |
|
|
王荣. 2019. 褪黑素对黑暗胁迫下栀子叶片衰老进程的影响[硕士论文]. 江苏: 扬州大学.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1214 |
|
王宇航, 李斗, 王春恒, 金鑫, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹, 杨江山. 2024. 褪黑素对葡萄叶片发育衰老过程中亚细胞活性氧代谢的影响. 园艺学报, 51 (1):103-120.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1214 |
|
| [40] |
pmid: 11706170 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
pmid: 4860954 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1111/jpi.12044 pmid: 23480341 |
| [47] |
|
|
郑莎, 朱映雪, 朱宝中, 张红, 向仲怀, 赵爱春. 2021. 过表达桑树色氨酸脱羧酶基因(MnTDC)转基因烟草提高其耐盐性. 蚕业科学, 47 (5):401-408.
|
| [1] | 韩荧, 段颖, 牛一杰, 李衍素, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 王君, 李强, 陈双臣, 闫妍. 腐殖酸生物降解地膜提高番茄品质的转录代谢机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | 龚小雅, 李贤, 周新刚, 吴凤芝. 分蘖洋葱伴生番茄诱导的根际微生物对根结线虫病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [3] | 孟思达, 韩磊磊, 相恒佐, 朱美玉, 冯 珍, 叶云珠, 孙美华, 李艳冰, 赵利萍, 谭昌华, 齐明芳, 李天来. 番茄心室数的调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [4] | 马星云, 范冰丽, 唐光彩, 贾芝琪, 李营, 薛东齐, 张世文. DXR调控番茄叶绿体发育、花色与果实着色机制初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [5] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [6] | 王永珍, 张剑国, 刘彩虹, 李思蓓, 吕甜甜. 番茄新品种‘圆红212’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [7] | 周慧珍, 张嘉, 胡军华, 李白雪, 曹立, 余歆, 王福生, 邹修平, 周彦. 柑橘感染褐斑病过程中BAG1的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 956-970. |
| [8] | 刘泽营, 孙帅, 刘志强, 崔霞, 李仁. 番茄尖果脐突变体的生理特性及其候选基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [9] | 李品, 甘宁, 陈家伟, 项思翔, 沈静漪, 欧阳波, 卢永恩. 番茄自然群体磷利用效率分析及耐低磷种质筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [10] | 杨婷, 席德慧, 夏明, 李佳楠. α-苦瓜素基因提高番茄对烟草花叶病毒抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [11] | 郝金倩, 王宝驹, 佟 静, 刘明池, 武占会, 王素娜, 刘 宁, . 外源褪黑素对水培韭菜生长和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 847-858. |
| [12] | 于 静, 冯向君, 金英学, 丁国华, . 焦脱镁叶绿酸a对黄瓜枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 859-874. |
| [13] | 胡志峰, 邵景成, 张 莉. 番茄新品种‘陇番15号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [14] | 刘根忠, 李方曼, 葛平飞, 陶金宝, 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋. 番茄抗坏血酸含量相关QTL定位及候选基因鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [15] | 董舒超, 洪骏, 凌嘉怡, 谢紫欣, 张胜军, 赵丽萍, 宋刘霞, 王银磊, 赵统敏. 番茄抗旱性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司