
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 959-971.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0190
收稿日期:2022-11-03
修回日期:2023-04-27
出版日期:2023-05-25
发布日期:2023-05-31
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:jinguang0591@163.com)基金资助:
ZHOU Ping, GUO Rui, YAN Shaobin, JIN Guang( )
)
Received:2022-11-03
Revised:2023-04-27
Published:2023-05-25
Online:2023-05-31
摘要:
为研究桃树(Prunus persica)外源喷施山梨醇(1 mmol · L-1)对其糖代谢的影响,整合代谢组与转录组数据,分析叶片和果肉中蔗糖、果糖、葡萄糖、山梨醇的含量和特定糖代谢、糖转运基因表达的变化,以期明确受影响的代谢通路。测定结果表明,山梨醇处理叶片葡萄糖、果糖、蔗糖含量提升,山梨醇含量变化不明显;处理果肉山梨醇含量下降,其他糖含量变化不明显;处理叶片和果肉蔗糖/果糖、蔗糖/葡萄糖、山梨醇/果糖、山梨醇/葡萄糖和山梨醇/蔗糖比值均显著下降。山梨醇处理后,叶片和果肉糖代谢、糖转运基因表达谱变化不相同,糖代谢酶(PpSDHb、PpPFKa/b/e、PpHXKa、PpSUSb/c、PpINVe)和糖转运子(PpSOTa/i、PpSWEET10/13)基因参与调控叶片和果肉中的蔗糖、果糖、葡萄糖和山梨醇积累。转录组分析证实山梨醇处理造成的差异表达基因富集于糖代谢相关途径(叶片蔗糖、淀粉代谢途径和果肉碳代谢途径)及其他次级代谢途径。这些结果说明外源山梨醇对桃叶片和果实果肉可溶性糖含量和糖组分平衡的影响不同。山梨醇处理造成桃叶片、果实糖代谢酶和糖转运子基因表达变化,影响了糖代谢。
中图分类号:
周平, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 金光. 外源山梨醇影响桃叶片和果实糖代谢的分子机制研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 959-971.
ZHOU Ping, GUO Rui, YAN Shaobin, JIN Guang. Molecular Mechanism Study of Exogenous Sorbitol Effects on Sugar Metabolism in Peach Leaves and Fruits[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 959-971.
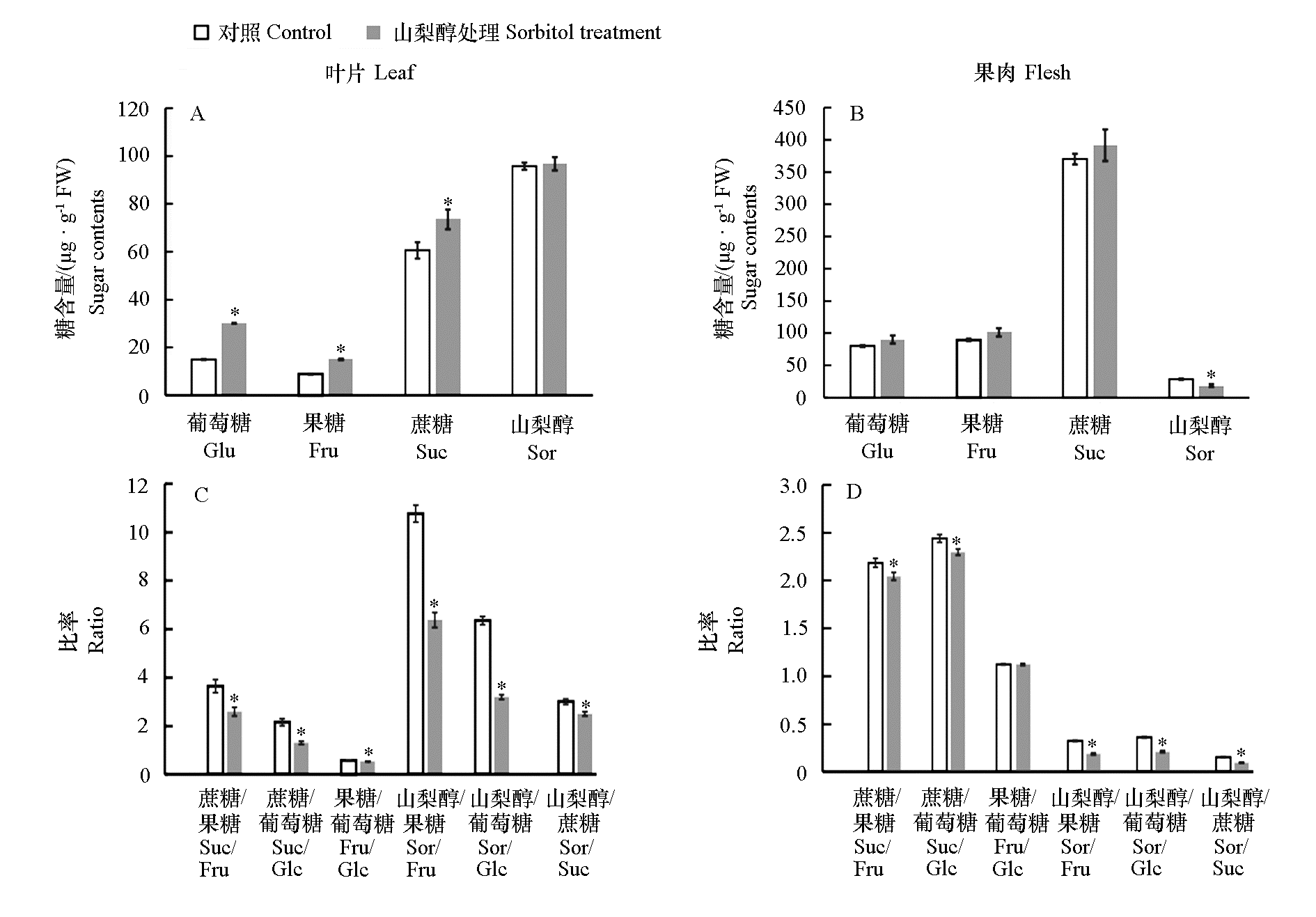
图1 山梨醇处理后桃叶片和果肉糖含量和糖组分比率的变化 * 代表处理组与对照组有统计学差异(Student t检验,α = 0.05)。
Fig. 1 Changes of sugar contents and sugar composition ratios in peach leaves and fruits with sorbitol treatments * represents a significant difference between treatment and control group(Student t-test,α = 0.05).
| 糖代谢酶 Sugar-metabolizing enzymes | 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 相似度/% Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山梨醇脱氢酶(SDH) | PpSDHa | Prupe.1G057900 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 60 |
| Sorbitol dehydrogenase | PpSDHb | Prupe.2G288800 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 81 |
| PpSDHc | Prupe.4G240300 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| PpSDHd | Prupe.8G142900 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| PpSDHe | Prupe.8G143000 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| 6-磷酸山梨醇脱氢酶(S6PDH) | PpS6PDHa | Prupe.8G083400 | AAV54113 | MdS6PDH | 76 |
| Sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase | PpS6PDHb | Prupe.2G061100 | AAV54113 | MdS6PDH | 69 |
| 蔗糖合酶(SUS) | PpSUSa | Prupe.1G131700 | AT5G49190 | AtSUS2 | 82 |
| Sucrose Synthase | PpSUSb | Prupe.8G264300 | AT4G02280 | AtSUS3 | 84 |
| PpSUSc | Prupe.7G192300 | AT3G43190 | AtSUS4 | 82 | |
| PpSUSd | Prupe.3G014100 | AT5G37180 | AtSUS5 | 73 | |
| PpSUSe | Prupe.5G241700 | AT1G73370 | AtSUS6 | 75 | |
| 蔗糖磷酸合成酶(SPS) | PpSPSa | Prupe.1G159700 | AT1G04920 | AtSPS3F | 77 |
| Sucrose phosphate synthase | PpSPSb | Prupe.1G483200 | AT5G11110 | AtSPS2F | 72 |
| PpSPSc | Prupe.7G249900 | AT5G20280 | AtSPS1F | 78 | |
| PpSPSd | Prupe.8G003700 | AT4G10120 | AtSPS4F | 70 | |
| 蔗糖磷酸酯酶(SPP) | PpSPPa | Prupe.5G001900 | AT1G51420 | AtSPP1 | 60 |
| Sucrose phosphate phosphatase | PpSPPb | Prupe.7G089300 | AT3G52340 | AtSPP2 | 62 |
| 转化酶(INV) | PpINVa | Prupe.6G309800 | AT1G56560 | A/N-InvA | 74 |
| Invertase | PpINVb | Prupe.1G365400 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 78 |
| PpINVc | Prupe.6G229900 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 58 | |
| PpINVd | Prupe.2G075000 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 84 | |
| PpINVe | Prupe.1G111800 | AT3G06500 | A/N-InvC | 67 | |
| PpINVf | Prupe.8G159800 | AT1G22650 | A/N-InvD | 78 | |
| PpINVg | Prupe.2G083900 | AT5G22510 | A/N-InvE | 70 | |
| PpINVh | Prupe.6G122600 | AT5G22510 | A/N-InvE | 71 | |
| 磷酸果糖激酶(PFK) | PpPFKa | Prupe.1G444000 | AT4G32840 | AtPFK6 | 82 |
| Phosphofructokinase | PpPFKb | Prupe.3G056600 | AT4G26270 | AtPFK3 | 83 |
| PpPFKc | Prupe.7G216700 | AT4G29220 | AtPFK1 | 82 | |
| PpPFKd | Prupe.2G272600 | AT5G61580 | AtPFK4 | 79 | |
| PpPFKe | Prupe.6G196200 | AT2G22480 | AtPFK5 | 83 | |
| PpPFKf | Prupe.4G002000 | AT5G47810 | AtPFK2 | 78 | |
| 己糖激酶(HXK) | PpHXKa | Prupe.3G057800 | AT4G29130 | AtHXK1 | 73 |
| Hexokinase | PpHXKb | Prupe.7G218800 | AT2G19860 | AtHXK2 | 78 |
| PpHXKc | Prupe.1G366000 | AT1G47840 | AtHXK3 | 68 | |
| PpHKLa | Prupe.4G256200 | AT1G50460 | AtHKL1 | 68 | |
| PpHKLb | Prupe.6G212100 | AT4G37840 | AtHKL3 | 60 | |
| 磷酸葡萄糖异构酶(PGI) | PpPGI | Prupe.1G528400 | AT4G24620 | AtPGI1 | 81 |
| Phosphoglucose isomerase |
表1 桃38个糖代谢酶基因
Table 1 Thirty-eight peach sugar-metabolizing enzyme genes
| 糖代谢酶 Sugar-metabolizing enzymes | 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 相似度/% Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山梨醇脱氢酶(SDH) | PpSDHa | Prupe.1G057900 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 60 |
| Sorbitol dehydrogenase | PpSDHb | Prupe.2G288800 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 81 |
| PpSDHc | Prupe.4G240300 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| PpSDHd | Prupe.8G142900 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| PpSDHe | Prupe.8G143000 | AT5G51970 | AtSDH | 78 | |
| 6-磷酸山梨醇脱氢酶(S6PDH) | PpS6PDHa | Prupe.8G083400 | AAV54113 | MdS6PDH | 76 |
| Sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase | PpS6PDHb | Prupe.2G061100 | AAV54113 | MdS6PDH | 69 |
| 蔗糖合酶(SUS) | PpSUSa | Prupe.1G131700 | AT5G49190 | AtSUS2 | 82 |
| Sucrose Synthase | PpSUSb | Prupe.8G264300 | AT4G02280 | AtSUS3 | 84 |
| PpSUSc | Prupe.7G192300 | AT3G43190 | AtSUS4 | 82 | |
| PpSUSd | Prupe.3G014100 | AT5G37180 | AtSUS5 | 73 | |
| PpSUSe | Prupe.5G241700 | AT1G73370 | AtSUS6 | 75 | |
| 蔗糖磷酸合成酶(SPS) | PpSPSa | Prupe.1G159700 | AT1G04920 | AtSPS3F | 77 |
| Sucrose phosphate synthase | PpSPSb | Prupe.1G483200 | AT5G11110 | AtSPS2F | 72 |
| PpSPSc | Prupe.7G249900 | AT5G20280 | AtSPS1F | 78 | |
| PpSPSd | Prupe.8G003700 | AT4G10120 | AtSPS4F | 70 | |
| 蔗糖磷酸酯酶(SPP) | PpSPPa | Prupe.5G001900 | AT1G51420 | AtSPP1 | 60 |
| Sucrose phosphate phosphatase | PpSPPb | Prupe.7G089300 | AT3G52340 | AtSPP2 | 62 |
| 转化酶(INV) | PpINVa | Prupe.6G309800 | AT1G56560 | A/N-InvA | 74 |
| Invertase | PpINVb | Prupe.1G365400 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 78 |
| PpINVc | Prupe.6G229900 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 58 | |
| PpINVd | Prupe.2G075000 | AT4G34860 | A/N-InvB | 84 | |
| PpINVe | Prupe.1G111800 | AT3G06500 | A/N-InvC | 67 | |
| PpINVf | Prupe.8G159800 | AT1G22650 | A/N-InvD | 78 | |
| PpINVg | Prupe.2G083900 | AT5G22510 | A/N-InvE | 70 | |
| PpINVh | Prupe.6G122600 | AT5G22510 | A/N-InvE | 71 | |
| 磷酸果糖激酶(PFK) | PpPFKa | Prupe.1G444000 | AT4G32840 | AtPFK6 | 82 |
| Phosphofructokinase | PpPFKb | Prupe.3G056600 | AT4G26270 | AtPFK3 | 83 |
| PpPFKc | Prupe.7G216700 | AT4G29220 | AtPFK1 | 82 | |
| PpPFKd | Prupe.2G272600 | AT5G61580 | AtPFK4 | 79 | |
| PpPFKe | Prupe.6G196200 | AT2G22480 | AtPFK5 | 83 | |
| PpPFKf | Prupe.4G002000 | AT5G47810 | AtPFK2 | 78 | |
| 己糖激酶(HXK) | PpHXKa | Prupe.3G057800 | AT4G29130 | AtHXK1 | 73 |
| Hexokinase | PpHXKb | Prupe.7G218800 | AT2G19860 | AtHXK2 | 78 |
| PpHXKc | Prupe.1G366000 | AT1G47840 | AtHXK3 | 68 | |
| PpHKLa | Prupe.4G256200 | AT1G50460 | AtHKL1 | 68 | |
| PpHKLb | Prupe.6G212100 | AT4G37840 | AtHKL3 | 60 | |
| 磷酸葡萄糖异构酶(PGI) | PpPGI | Prupe.1G528400 | AT4G24620 | AtPGI1 | 81 |
| Phosphoglucose isomerase |
| 糖转运子 Sugar transporter | 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 相似度/% Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山梨醇转运蛋白(SOT) | PpSOTa | Prupe.8G100700 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 |
| Sorbitol transporter | PpSOTb | Prupe.8G100900 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 |
| PpSOTc | Prupe.8G101000 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 | |
| PpSOTd | Prupe.8G101200 | AAO088964 | MdSOT1 | 78 | |
| PpSOTe | Prupe.8G105300 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTf | Prupe.8G105400 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTg | Prupe.8G105500 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTh | Prupe.8G105600 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTi | Prupe.8G101500 | BAD42343 | MdSOT3 | 72 | |
| 蔗糖转运蛋白(SUT) | PpSUTa | Prupe.1G271500 | AT2G02860 | AtSUT2 | 72 |
| Sucrose transporter | PpSUTb | Prupe.1G542000 | AT1G09960 | AtSUT4 | 73 |
| PpSUTc | Prupe.8G052700 | AT1G22710 | AtSUT1 | 68 | |
| 液泡膜单糖转运蛋白(TMT) | PpTMTa | Prupe.5G006300 | AT4G35300 | AtTMT2 | 70 |
| Tonoplast monosaccharide transporter | PpTMTb | Prupe.7G186000 | AT3G51490 | AtTMT3 | 64 |
| 多元醇/单糖转运蛋白(PMT) | PpPMTa | Prupe.8G105300 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 |
| Polyol/Monosaccharide transporter | PpPMTb | Prupe.8G105400 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 |
| PpPMTc | Prupe.8G105500 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| PpPMTd | Prupe.8G105600 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| PpPMTe | Prupe.8G101200 | AT4G36670 | AtPMT6 | 71 | |
| PpPMTf | Prupe.7G152100 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| 糖转运蛋白(STP) | PpSTPa | Prupe.4G037800 | AT1G11260 | AtSTP1 | 83 |
| Sugar transporter protein | PpSTPb | Prupe.1G070800 | AT3G19940 | AtSTP10 | 69 |
| PpSTPc | Prupe.1G070900 | AT1G50310 | AtSTP9 | 69 | |
| PpSTPd | Prupe.1G156300 | AT5G26340 | AtSTP13 | 84 | |
| SWEET蛋白(SWEET) | PpSWEET1 | Prupe.6G355900 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 62 |
| Sugar will eventually be | PpSWEET2 | Prupe.1G220700 | AT5G13170 | AtSWEET15 | 63 |
| exported transporter | PpSWEET3 | Prupe.8G253500 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 55 |
| (余彩云 等, | PpSWEET4 | Prupe.1G133300 | AT4G15920 | AtSWEET17 | 62 |
| PpSWEET5 | Prupe.5G146500 | AT5G50790 | AtSWEET10 | 55 | |
| PpSWEET6 | Prupe.3G283400 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 56 | |
| PpSWEET7 | Prupe.8G076100 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 69 | |
| PpSWEET8 | Prupe.3G034900 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 68 | |
| PpSWEET9 | Prupe.5G125100 | AT4G10850 | AtSWEET7 | 54 | |
| PpSWEET10 | Prupe.8G017400 | AT1G21460 | AtSWEET1 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET11 | Prupe.5G146400 | AT5G23660 | AtSWEET12 | 56 | |
| PpSWEET12 | Prupe.4G155700 | AT3G14770 | AtSWEET2 | 66 | |
| PpSWEET13 | Prupe.4G072300 | AT3G14770 | AtSWEET2 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET14 | Prupe.2G118600 | AT4G15920 | AtSWEET17 | 50 | |
| PpSWEET15 | Prupe.5G175500 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET16 | Prupe.2G245600 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 55 | |
| PpSWEET17 | Prupe.2G307800 | AT5G53190 | AtSWEET3 | 50 |
表2 桃41个糖转运子基因
Table 2 Forty-one peach sugar transporter genes
| 糖转运子 Sugar transporter | 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 同源基因编号 Homologous gene ID | 同源基因 Homologous gene | 相似度/% Similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 山梨醇转运蛋白(SOT) | PpSOTa | Prupe.8G100700 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 |
| Sorbitol transporter | PpSOTb | Prupe.8G100900 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 |
| PpSOTc | Prupe.8G101000 | AAO088965 | MdSOT2 | 80 | |
| PpSOTd | Prupe.8G101200 | AAO088964 | MdSOT1 | 78 | |
| PpSOTe | Prupe.8G105300 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTf | Prupe.8G105400 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTg | Prupe.8G105500 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTh | Prupe.8G105600 | BAD42344 | MdSOT4 | 70 | |
| PpSOTi | Prupe.8G101500 | BAD42343 | MdSOT3 | 72 | |
| 蔗糖转运蛋白(SUT) | PpSUTa | Prupe.1G271500 | AT2G02860 | AtSUT2 | 72 |
| Sucrose transporter | PpSUTb | Prupe.1G542000 | AT1G09960 | AtSUT4 | 73 |
| PpSUTc | Prupe.8G052700 | AT1G22710 | AtSUT1 | 68 | |
| 液泡膜单糖转运蛋白(TMT) | PpTMTa | Prupe.5G006300 | AT4G35300 | AtTMT2 | 70 |
| Tonoplast monosaccharide transporter | PpTMTb | Prupe.7G186000 | AT3G51490 | AtTMT3 | 64 |
| 多元醇/单糖转运蛋白(PMT) | PpPMTa | Prupe.8G105300 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 |
| Polyol/Monosaccharide transporter | PpPMTb | Prupe.8G105400 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 |
| PpPMTc | Prupe.8G105500 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| PpPMTd | Prupe.8G105600 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| PpPMTe | Prupe.8G101200 | AT4G36670 | AtPMT6 | 71 | |
| PpPMTf | Prupe.7G152100 | AT3G18830 | AtPMT5 | 69 | |
| 糖转运蛋白(STP) | PpSTPa | Prupe.4G037800 | AT1G11260 | AtSTP1 | 83 |
| Sugar transporter protein | PpSTPb | Prupe.1G070800 | AT3G19940 | AtSTP10 | 69 |
| PpSTPc | Prupe.1G070900 | AT1G50310 | AtSTP9 | 69 | |
| PpSTPd | Prupe.1G156300 | AT5G26340 | AtSTP13 | 84 | |
| SWEET蛋白(SWEET) | PpSWEET1 | Prupe.6G355900 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 62 |
| Sugar will eventually be | PpSWEET2 | Prupe.1G220700 | AT5G13170 | AtSWEET15 | 63 |
| exported transporter | PpSWEET3 | Prupe.8G253500 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 55 |
| (余彩云 等, | PpSWEET4 | Prupe.1G133300 | AT4G15920 | AtSWEET17 | 62 |
| PpSWEET5 | Prupe.5G146500 | AT5G50790 | AtSWEET10 | 55 | |
| PpSWEET6 | Prupe.3G283400 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 56 | |
| PpSWEET7 | Prupe.8G076100 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 69 | |
| PpSWEET8 | Prupe.3G034900 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 68 | |
| PpSWEET9 | Prupe.5G125100 | AT4G10850 | AtSWEET7 | 54 | |
| PpSWEET10 | Prupe.8G017400 | AT1G21460 | AtSWEET1 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET11 | Prupe.5G146400 | AT5G23660 | AtSWEET12 | 56 | |
| PpSWEET12 | Prupe.4G155700 | AT3G14770 | AtSWEET2 | 66 | |
| PpSWEET13 | Prupe.4G072300 | AT3G14770 | AtSWEET2 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET14 | Prupe.2G118600 | AT4G15920 | AtSWEET17 | 50 | |
| PpSWEET15 | Prupe.5G175500 | AT5G62850 | AtSWEET5 | 64 | |
| PpSWEET16 | Prupe.2G245600 | AT2G39060 | AtSWEET9 | 55 | |
| PpSWEET17 | Prupe.2G307800 | AT5G53190 | AtSWEET3 | 50 |
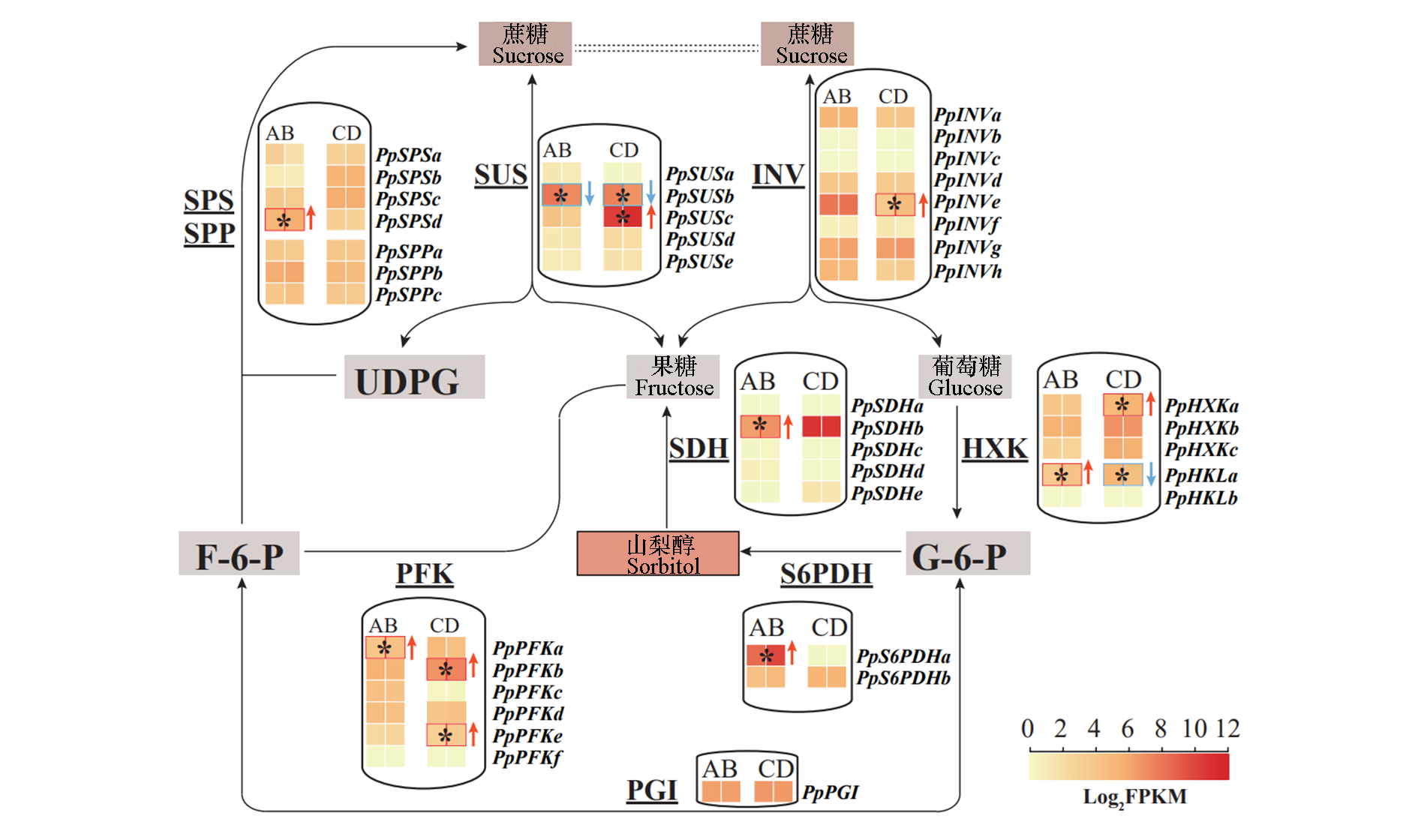
图2 桃外源山梨醇处理相关糖代谢基因表达变化 A:对照叶片;B:处理叶片;C:对照果肉;D:处理果肉。UDPG:尿苷二磷酸葡萄糖;G-6-P:葡萄糖-6-磷酸;F-6-P:果糖-6-磷酸。糖代谢酶及基因缩写同表1。*代表处理基因表达与对照有显著差异。上下箭头表示基因表达上调或下调。下同。
Fig. 2 Sugar-metabolizing genes expression changes caused by exogenous sorbitol treatments A:Leaves of control group;B:Leaves of sorbitol treatment group;C:Fruit flesh of control group;D:Fruit flesh of sorbitol treatment group. UDPG:Uridine-5'-diphosphoglucose;G-6-P:Glucose-6-phosphate;F-6-P:Fructose -6-phosphate. Sugar-metabolizing enzymes and their genes abbreviated as Table 1 showed. * represent the significant differences between treatment and control groups. Arrow-up or arrow-down tags indicate that corresponding genes were significantly upregulated or downregulated. The same below.
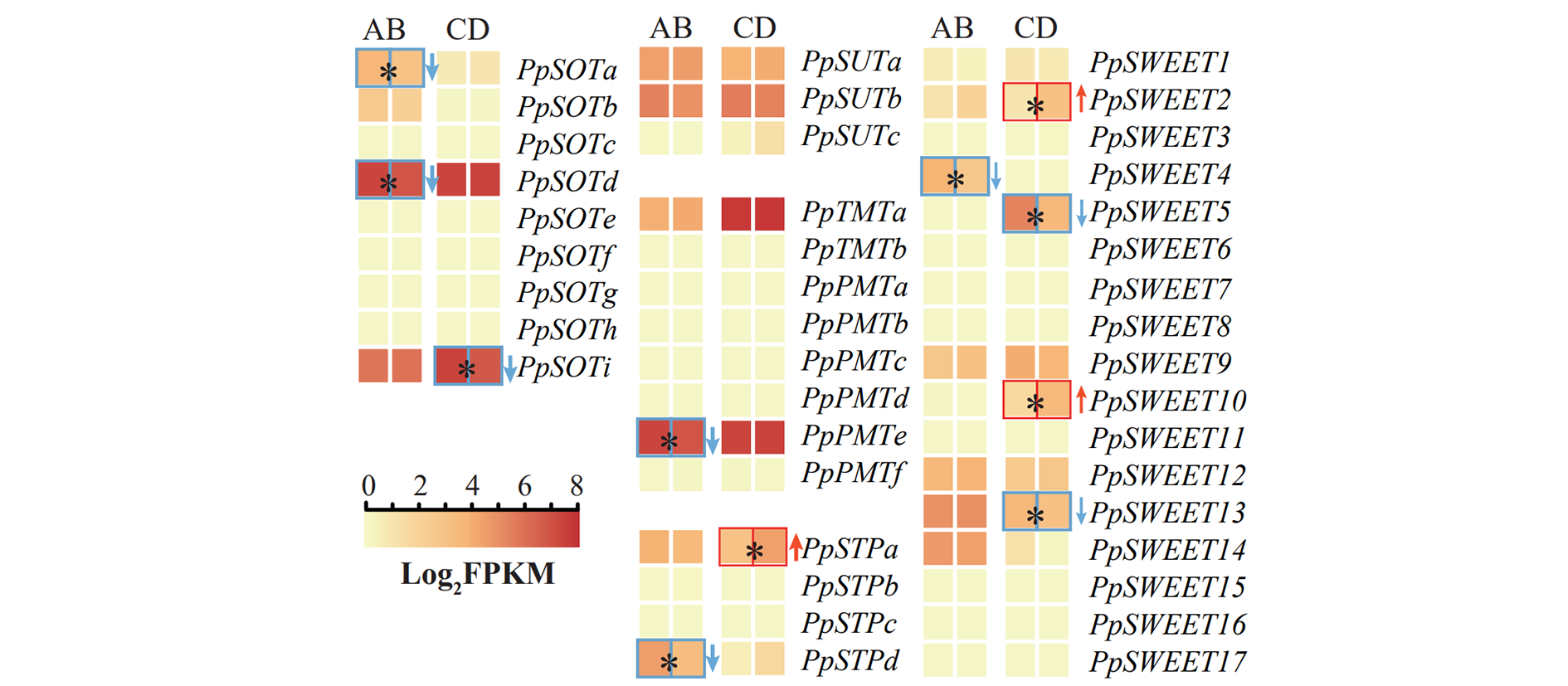
图3 桃外源山梨醇处理相关糖转运子基因表达变化 糖转运子基因缩写同表2。
Fig. 3 Sugar-transporting genes expression changes caused by exogenous sorbitol treatments Sugar transporter genes abbreviated as Table 2 showed.
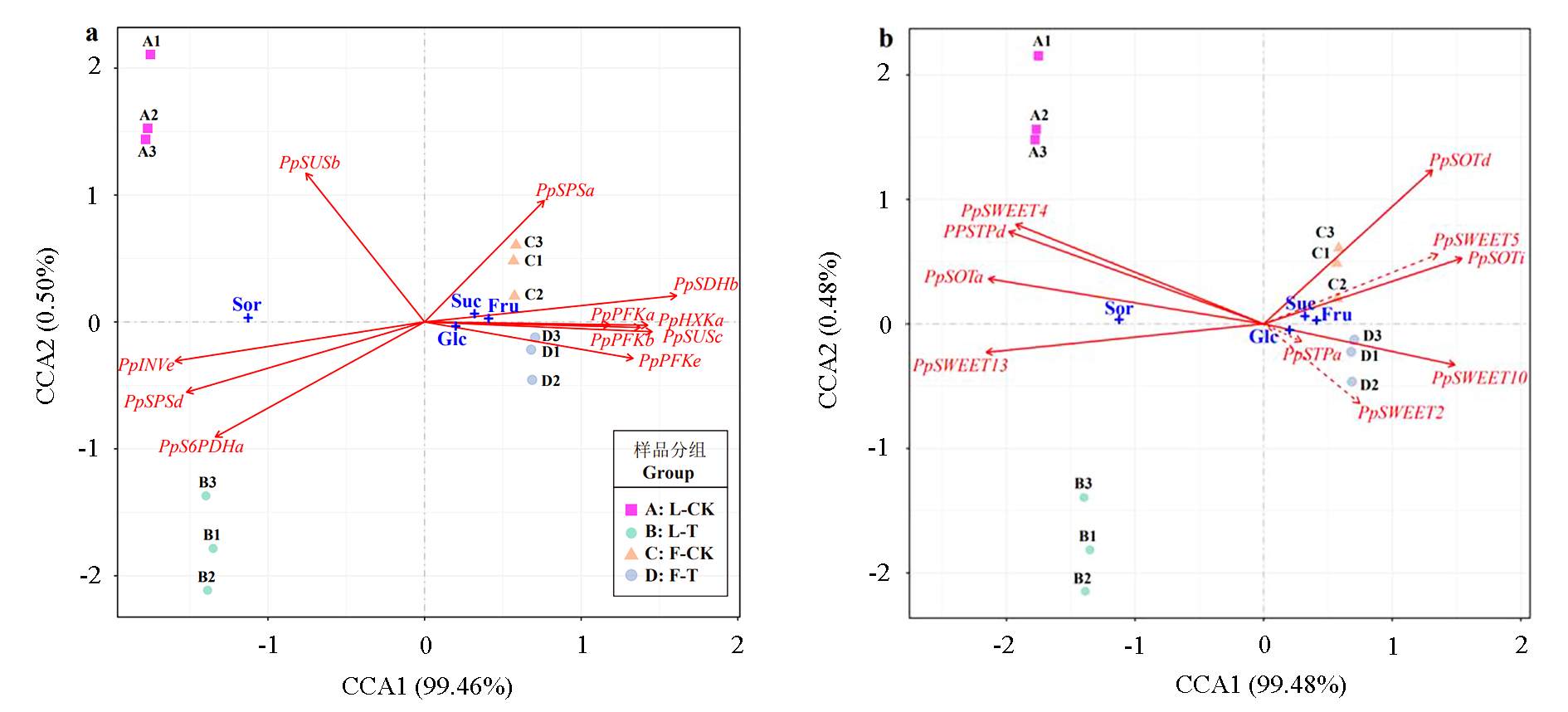
图4 糖含量与糖代谢基因(a)和糖转运基因(b)表达量典型关联分析 虚线箭符表示置换检验检测约束性排序模型的显著性P > 0.05,其他实线箭头代表P < 0.05。A:对照叶片;B:处理叶片;C:对照果肉;D:处理果肉。
Fig. 4 Canonical correlation analyses of datas between sugar contents and gene expression in sugar-metabolism(a)and sugar-transport(b)processes In this diagram,dashed-line arrows designate the significance of permutation tests for constrained ordination model P > 0.05,while other line arrows indicate the significance P < 0.05. A:Leaves of control group;B:Leaves of sorbitol treatment group;C:Fruit flesh of control group;D:Fruit flesh of sorbitol treatment group.

图5 山梨醇处理桃叶片和果肉差异表达基因KEGG代谢途径富集分析
Fig. 5 KEGG-based metabolic pathway enrichment analyses of differentially expressed genes in leaves and fruit flesh after sorbitol treatment
| [1] |
Almaghamsi A, Nosarzewski M, Kanayama Y, Archbold D D. 2021. Effects of abiotic stresses on sorbitol biosynthesis and metabolism in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum). Functional Plant Biology, 48 (3):286-297.
doi: 10.1071/FP20065 pmid: 33099326 |
| [2] |
Bu D, Luo H, Huo P, Wang Z, Zhang S, He Z, Wu Y, Zhao L, Liu J, Guo J, Fang S, Cao W, Yi L, Zhao Y, Kong L. 2021. KOBAS-i:intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Research, 49 (W1):W317-W325.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab447 URL |
| [3] |
Cao K, Li Y, Deng C H, Gardiner S E, Zhu G, Fang W, Chen C, Wang X, Wang L. 2019. Comparative population genomics identified genomic regions and candidate genes associated with fruit domestication traits in peach. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17 (10):1954-1970.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13112 pmid: 30950186 |
| [4] |
Cao K, Yang X, Li Y, Zhu G, Fang W, Chen C, Wang X, Wu J, Wang L. 2021. New high-quality peach(Prunus persica L. Batsch)genome assembly to analyze the molecular evolutionary mechanism of volatile compounds in peach fruits. The Plant Journal, 108 (1):281-295.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.15439 pmid: 34309935 |
| [5] |
Cao K, Zhou Z, Wang Q, Guo J, Zhao P, Zhu G, Fang W, Chen C, Wang X, Wang X, Tian Z, Wang L. 2016. Genome-wide association study of 12 agronomic traits in peach. Nature Communications, 7:13246.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms13246 pmid: 27824331 |
| [6] | Deguchi M, Bennett A B, Yamaki S, Yamada K, Kanahama K, Kanayama Y. 2010. An engineered sorbitol cycle alters sugar composition,not growth,in transformed tobacco. Plant Cell & Environment, 29 (10):1980-1988. |
| [7] | Jin Guang, Yan Shaobin, Guo Rui, Zhang Xiaodan, Yang Ling, Liao Ruyu, Zhou Ping. 2018. Effects of exogenous sorbitol spray on gene expression networks of peach leave. Journal of Fruit Science, 35 (9):1033-1042. (in Chinese) |
| 金光, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 张小丹, 杨凌, 廖汝玉, 周平. 2018. 外源山梨醇对桃苗叶片基因表达网络的影响. 果树学报, 35 (9):1033-1042. | |
| [8] |
Josef B, Monika E S F. 1995. Comparison of sorbitol transport in excised tissue discs and cortex tissue of intact apple fruit. Journal of Plant Physiology, 146 (1-2):95-102.
doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81973-5 URL |
| [9] |
Kou Dandan, Zhang Ye, Wang Pengfei, Li Dongdong, Zhang Xueying, Chen Haijiang. 2019. Differences in sucrose and malic acid accumulation and the related gene expression in‘Kurakato Wase’peach and its early-ripening mutant. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (12):2286-2298. (in Chinse)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0187 |
|
寇单单, 张叶, 王朋飞, 李东东, 张学英, 陈海江. 2019. ‘仓方早生’桃及其早熟芽变果实蔗糖和苹果酸积累与相关基因表达. 园艺学报, 46 (12):2286-2298.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0187 |
|
| [10] |
Li C, Meng D, Piñeros MA, Mao Y, Dandekar AM, Cheng L. 2020. A sugar transporter takes up both hexose and sucrose for sorbitol-modulated in vitro pollen tube growth in apple. Plant Cell, 32 (2):449-469.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00638 URL |
| [11] | Li Qiuli, Yang Wenjia, Gao Dengtao, Wei Zhifeng, Yu Huili, Liu Junwei. 2019. Effects of sorbitol and sucrose on soluble sugar content of peach fruits and leaves and fruits quality. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 48 (8):110-116. (in Chinese) |
| 李秋利, 杨文佳, 高登涛, 魏志峰, 于会丽, 刘军伟. 2019. 山梨醇和蔗糖对桃果实、叶片可溶性糖含量及果实品质的影响. 河南农业科学, 48 (8):110-116. | |
| [12] |
Li Y, Cao K, Zhu G, Fang W, Chen C, Wang X, Zhao P, Guo J, Ding T, Guan L, Zhang Q, Guo W, Fei Z, Wang L. 2019. Genomic analyses of an extensive collection of wild and cultivated accessions provide new insights into peach breeding history. Genome Biology, 20 (1):36.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1648-9 pmid: 30791928 |
| [13] |
Liang D, Cui M, Wu S, Ma F. 2012. Genomic Structure,Sub-cellular localization,and promoter analysis of the gene encoding Sorbitol-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase from Apple. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 30 (4):904-914.
doi: 10.1007/s11105-011-0409-z URL |
| [14] | Liu Huimin, Yu Huili, Shao Wei, Xu Bianbian, Zhang Zihua, Shi Zhaoyang, Zhao Xianfei, Xu Gguoyi, Yang Jinghui, Si Peng. 2021. Effects of sorbitol and mannitol combined with NPK on the growth,fruit quality and nutrient absorption of peach. Journal of Fruit Science, 38 (6):911-921. (in Chinese) |
| 刘慧敏, 于会丽, 邵微, 徐变变, 张子华, 史兆阳, 赵先飞, 徐国益, 杨静慧, 司鹏. 2021. 山梨醇和甘露醇与氮磷钾配施对桃生长、果实品质及养分吸收的影响. 果树学报, 38 (6):911-921. | |
| [15] |
Meng D, He M, Bai Y, Xu H, Dandekar A M, Fei Z, Cheng L. 2018. Decreased sorbitol synthesis leads to abnormal stamen development and reduced pollen tube growth via an MYB transcription factor,MdMYB39L,in apple(Malus domestica). New Phytologist, 217:641-656.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14824 URL |
| [16] | Moing A. 2000. Sugar alcohols as carbohydrate reserves in some higher plants. Developments in Crop Science, 26:337-358. |
| [17] |
Naoaki K, Yuji I, Sadao K, Michiko S, Hidenori K, Sae T, Mitsuo O, Junichi S, Katsuhiro S, Kunio Y, Shohei Y. 2004. Transgenic apple transformed by sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNA:switch between sorbitol and sucrose supply due to its gene expression. Plant Science, 167 (1):55-61.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.02.024 URL |
| [18] |
Nosarzewski M, Downie A B, Wu B, Archbold D D. 2012. The role of SORBITOL DEHYDROGENASE in Arabidopsis thaliana. Functional Plant Biology, 39 (6):462-470.
doi: 10.1071/FP12008 pmid: 32480797 |
| [19] |
Ryutaro T, Sandra L, Abhaya M. 1995. Sorbitol synthesis in transgenic tobacco with apple cdna encoding nadp-dependent sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Plant and Cell Physiology, 36 (3):525-532.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078789 pmid: 7757342 |
| [20] |
Shen Zhijun, Ma Ruijuan, Yu Mingliang, Cai Zhixiang, Song Hongfeng, Li Xiao. 2007. Regularity analysis of main sugar and acid in fruit development of peach. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 22 (6):130-134. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2007.06.027 |
|
沈志军, 马瑞娟, 俞明亮, 蔡志翔, 宋宏峰, 李晓. 2007. 桃果实发育过程中主要糖及有机酸含量的变化分析. 华北农学报, 22 (6):130-134.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2007.06.027 |
|
| [21] |
Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Garcia-Hernandez M, Foerster H, Li D, Meyer T, Muller R, Ploetz L, Radenbaugh A, Singh S, Swing V, Tissier C, Zhang P, Huala E. 2008. The Arabidopsis Information Resource(TAIR):gene structure and function annotation, Nucleic Acids Research, 36(suppl_1):D1009-D1014.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm965 URL |
| [22] | Wang Guifang, Yao Yuantao, Li Suhong, Dong Yaru, Gao Xiaolan, Wang Hong, Gao Huaifeng, Liang Jiahui, Zhang Yong, Wei Shuwei. 2021. Effects of nitrogen,phosphorous and potassium foliar fertilizer combined with different carbon sources on new shoot growth and fruit quality of peach trees. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 53 (1):69-76. (in Chinese) |
| 王贵芳, 姚元涛, 李素红, 董亚茹, 高晓兰, 王红, 郜怀峰, 梁家慧, 张勇, 魏树伟. 2021. 氮磷钾叶面肥配施不同碳源对桃树新梢生长及果实品质的影响. 山东农业科学, 53 (1):69-76. | |
| [23] | Yang Guang, Li Lingyu, Huang Mingli, Yang Fanchang, Zhang Fengkui, Xu Rongchen, Yan Dongyun. 2018. Progresses in study on sorbitol effect on plants resistance. Soils, 50 (3):446-454. (in Chinese) |
| 杨光, 李玲玉, 黄明丽, 杨凡昌, 张凤魁, 徐荣臣, 颜冬云. 2018. 山梨醇对植株抗逆性作用的研究进展. 土壤, 50 (3):446-454. | |
| [24] |
Yasuo S, Abhaya M D. 2013. Sucrose induces expression of the sorbitol-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene in source leaves of loquat. Physiologia Plantarum, 150 (3):355-362.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2014.150.issue-3 URL |
| [25] | Ye Chengrong. 2011. Studies on sorbitol metabolism and enzymological regulating mechanism in developing apple fruit[M. D. Dissertation]. Qingdao: Qingdao Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 叶成荣. 2011. 苹果果实发育过程中山梨醇代谢及酶学调控机理研究[硕士论文]. 青岛: 青岛农业大学. | |
| [26] |
Yu Caiyun, Gu Cao, Zhang Shaoling. 2018. Analysis of tissue specific expression of SOT gene family in white pear. Botanical Research, 7 (5):496-506. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.12677/BR.2018.75060 URL |
| 余彩云, 谷超, 张绍铃. 2018. 白梨SOT基因家族成员组织表达特性的分析. 植物学研究, 7 (5):496-506. | |
| [27] |
Yu Y, Guan J, Xu Y, Ren F, Zhang Z, Yan J, Fu J, Guo J, Shen Z, Zhao J, Jiang Q, Wei J, Xie H. 2021. Population-scale peach genome analyses unravel selection patterns and biochemical basis underlying fruit flavor. Nature Communications, 12:3604.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23879-2 pmid: 34127667 |
| [28] | Zhao Ruifen, Jiao Xiaoyan, Yang Zhiping. 2020. Effect of foliar application of sorbitol on boron transportation in boron deficiency Phaseolus aureus. Tianjin Agricultural Sciences, 26 (6):7-11. (in Chinese) |
| 赵瑞芬, 焦晓燕, 杨治平. 2020. 叶面施用山梨糖醇对缺硼绿豆体内硼运输的影响. 天津农业科学, 26 (6):7-11. | |
| [29] | Zhou Ping, Guo Rui, Liao Ruyu, Yan Shaobin, Jin Gunag, Yang Ling, Yao Qiyin. 2016. Effect of exogenous sorbitol on the soluble sugar content in peach fruit. South China Fruits, 45 (2):119-121. (in Chinese) |
| 周平, 郭瑞, 廖汝玉, 颜少宾, 金光, 杨凌, 姚启英. 2016. 喷施外源山梨醇对桃果实可溶性糖含量的影响. 中国南方果树, 45 (2):119-121. | |
| [30] | Zhou Ping, Lin Zhikai, Guo Rui, Yan Shaobin, Zhang Xiaodan, Ma Xinyi, Jin Guang. 2021. Effects of low temperature treatment on gene expression and flavonoids biosynthesis metabolism in peach(Prunus persica)leaves. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 29 (7):1283-1294. (in Chinese) |
| 周平, 林志楷, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 张小丹, 马昕怡, 金光. 2021. 低温处理对桃树叶片基因表达及类黄酮合成代谢的影响. 农业生物技术学报, 29 (7):1283-1294. | |
| [31] | Zhou Ping, Ma Xinyi, Guo Rui, Yan Shaobin, Zhang Xiaodan, Lin Zhicong, Jin Guang. 2020a. Effects of exogenous sorbitol and its analogs on iron transport and phytohormone contents in peach leaves and fruit. Journal of Fruit Science, 37 (4):502-510. (in Chinese) |
| 周平, 马昕怡, 郭瑞, 颜少宾, 张小丹, 林志聪, 金光. 2020a. 喷施外源山梨醇及其类似物对桃叶片和果实离子转运及激素含量的影响. 果树学报, 37 (4):502-510. | |
| [32] | Zhou Ping, Yan Shaobin, Guo Rui, Zhang Xiaodan, Liao Ruyu, Jin Guang, Wu Rui-dong. 2020b. Effects of sorbitol spraying on flavonoid and carotenoids content of bag-releasing peach. Southeast Horticulture, 8 (4):5-9. (in Chinese) |
| 周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 张小丹, 廖汝玉, 金光, 吴瑞东. 2020b. 喷施山梨醇对解袋后桃果肉类黄酮类胡萝卜素含量的影响. 东南园艺, 8 (4):5-9. | |
| [33] |
Zhu Lingcheng, Su Jing, Peng Yunjing, Cao Wenjing, Ma Fengwang, Ma Baiquan, Li Mingjun. 2022. Research progress on the relationship between sugar transporters and fruits sugar accumulation. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 49 (12):2529-2542. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0488 |
|
祝令成, 苏静, 彭云静, 曹文静, 马锋旺, 马百全, 李明军. 2022. 糖转运蛋白与果实糖积累的关系研究进展. 园艺学报, 49 (12):2529-2542.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0488 |
| [1] | 时 梦, 刘凤之, 王海波, 王莹莹, 史祥宾, 王志强, 李 鹏, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中寒翠霞’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 15-16. |
| [2] | 杨兴旺, 王莹莹, 王海波, 王小龙, 王志强, 史祥宾, 冀晓昊, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中寒红琼’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 17-18. |
| [3] | 王富荣, 艾小艳, 王会良, 刘 勇, 朱 炜, 张 杨, 顾 霞, 刘模发, 诸小敏, 甘志猛, 何华平 , 龚林忠. 特早熟红肉油桃新品种‘楚红 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 19-20. |
| [4] | 王富荣, 艾小艳, 王会良, 刘 勇, 朱 炜, 张 杨, 顾 霞, 刘模发, 诸小敏, 甘志猛, 何华平 , 龚林忠. 早熟离核高甜油桃新品种‘楚甜 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 21-22. |
| [5] | 段文宜, 牛 良, 崔国朝, 曾文芳, 潘 磊, 孙世航, 王志强. 晚熟黄桃新品种‘中桃黄金蜜 5 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 23-24. |
| [6] | 罗 轩, 陈庆红 , 张 蕾, 高 磊, 白福玺, 汪 志, 叶丽霞, 彭 珏. 红肉软枣猕猴桃新品种‘金香红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 27-28. |
| [7] | 齐永杰 , 高正辉 , 马 娜 , 高 霞 , 柯凡君 , 徐义流 , . 优质抗旱猕猴桃新品种‘金山 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 29-30. |
| [8] | 马小民 , 陈媛媛 , 张 荣 , 黄 铖 , 黄东晨 , 任晓亮 , 叶新忠 , 傅松玲 , . 樱花新品种‘漫天红’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 169-170. |
| [9] | 肖翔, 周储江, 金舒婉, 施丽愉, 杨震峰, 曹士锋, 陈伟. PpMADS2与PpMADS3协同调控黄肉桃果实类胡萝卜素积累机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1173-1186. |
| [10] | 阮若昕, 骆慧枫, 张琛, 黄康康, 郗笃隽, 裴嘉博, 邢梦云, 刘辉. 杭州地区不同需冷量甜樱桃品种休眠阶段花芽转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1187-1202. |
| [11] | 杨孟霞, 刘晓林, 曹雪, 魏凯, 宁宇, 杨沛, 李珊珊, 陈紫月, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 杜永臣, 李君明, 刘磊, 李鑫, 黄泽军. 番茄CRISPR/Cas9介导的多基因编辑技术体系构建与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1215-1229. |
| [12] | 周成, 方怡, 周锦杨, 黄企浩, 盘永坚, 史千千, 倪慧娴, 杨震峰, 宋春波. 低温诱导的桃果实采后膜脂代谢变化与冷害的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1305-1317. |
| [13] | 刘南祥, 张慧琴, 谢鸣, 徐象华, 范芳娟. 猕猴桃新品种‘金丽’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1377-1378. |
| [14] | 李中瀚, 唐美玲, 郑秋玲, 刘明慧, 康慧, 高振, 杜远鹏. 聚乙烯编织物Coverlys TF150®覆盖对‘蜜光’葡萄果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1073-1084. |
| [15] | 吕若亚, 李云, 郑永钦, 邓晓玲, 郑正. 黄龙病菌在柑橘果实橘络中的分布[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(5): 1110-1117. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司