
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 705-713.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0273
胡亚伟1, 马金龙2, 钟八莲2, 姚锋先1,2, 刘桂东1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-19
修回日期:2025-01-13
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-25
通讯作者:
基金资助:
HU Yawei1, MA Jinlong2, ZHONG Balian2, YAO Fengxian1,2, LIU Guidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-12-19
Revised:2025-01-13
Published:2025-03-25
Online:2025-03-25
摘要:
通过测定脐橙幼树氮素的吸收利用及其在土壤中的残留与损失情况,为进一步优化幼树期脐橙生产体系氮素管理提供依据。以2年树龄的‘纽荷尔’脐橙/枳和‘赣南早’脐橙(纽荷尔脐橙的芽变早熟品种)/枳为试材,采用15N同位素示踪技术,于夏季分两次施入同位素标记氮肥,在当年秋梢老熟后采集植物和土壤样品,测定植物各器官和不同土层土壤15N丰度并计算氮素利用率及其残留和损失情况。结果显示,纽荷尔和赣南早脐橙的生物量存在明显差异,但各部位干物质量在整株中的占比一致,当年生叶片和枝条在整株干物质中的占比达40%以上,为脐橙幼树树体生长中心,15N均主要分配到其中;纽荷尔二年生叶片和粗根中的15N分配率显著高于赣南早,而在枝条和主干等非功能器官中显著低于赣南早。纽荷尔对15N标记尿素的当年利用率、土壤残留率和损失率分别为6.45%、75.72%和17.83%,赣南早则为3.36%、54.25%和42.39%。上述结果表明,脐橙幼树对夏施氮肥的当年利用率较低,两个品种幼龄脐橙园氮素去向存在明显差异,可能与不同品种生物量(包括根系分布)存在显著差异有关。
胡亚伟, 马金龙, 钟八莲, 姚锋先, 刘桂东. 脐橙幼树夏施15N-尿素的利用与土壤残留初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 705-713.
HU Yawei, MA Jinlong, ZHONG Balian, YAO Fengxian, LIU Guidong. Preliminary Study on Utilization of 15N-urea Applied to Young Navel Orange Trees in Summer and Its Residual in Soil[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 705-713.
| 器官 Organ | 干质量/(g · plant-1) Dry weight | 在整株中的占比/% Proportion in the whole plant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 795.9 ± 52.5 | 453.7 ± 34.1* | 27.58 ± 0.59 | 27.04 ± 2.17 | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 377.6 ± 15.3 | 227.7 ± 18.0* | 13.11 ± 0.48 | 13.54 ± 0.64 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 73.8 ± 15.7 | 54.7 ± 6.4* | 2.54 ± 0.46 | 3.26 ± 0.14 | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 312.4 ± 18.1 | 203.9 ± 24.6* | 10.83 ± 0.24 | 12.12 ± 1.26 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 380.8 ± 47.9 | 252.0 ± 16.2* | 13.15 ± 0.98 | 14.99 ± 0.58 | |
| 主根 Main root | 260.7 ± 21.1 | 138.5 ± 5.0* | 9.03 ± 0.34 | 8.26 ± 0.52 | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 481.5 ± 9.0 | 250.5 ± 30.9* | 16.76 ± 1.21 | 14.91 ± 1.69 | |
| 细根 Fine root | 201.7 ± 19.6 | 99.0 ± 12.2* | 7.00 ± 0.59 | 5.88 ± 0.55 | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 2 884.4 ± 157.7 | 1 680.1 ± 62.8* | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
表1 脐橙幼树各部位干质量及在整株中的占比
Table 1 Dry weight of various parts of young navel orange plants and their proportion in the whole plant
| 器官 Organ | 干质量/(g · plant-1) Dry weight | 在整株中的占比/% Proportion in the whole plant | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 795.9 ± 52.5 | 453.7 ± 34.1* | 27.58 ± 0.59 | 27.04 ± 2.17 | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 377.6 ± 15.3 | 227.7 ± 18.0* | 13.11 ± 0.48 | 13.54 ± 0.64 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 73.8 ± 15.7 | 54.7 ± 6.4* | 2.54 ± 0.46 | 3.26 ± 0.14 | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 312.4 ± 18.1 | 203.9 ± 24.6* | 10.83 ± 0.24 | 12.12 ± 1.26 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 380.8 ± 47.9 | 252.0 ± 16.2* | 13.15 ± 0.98 | 14.99 ± 0.58 | |
| 主根 Main root | 260.7 ± 21.1 | 138.5 ± 5.0* | 9.03 ± 0.34 | 8.26 ± 0.52 | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 481.5 ± 9.0 | 250.5 ± 30.9* | 16.76 ± 1.21 | 14.91 ± 1.69 | |
| 细根 Fine root | 201.7 ± 19.6 | 99.0 ± 12.2* | 7.00 ± 0.59 | 5.88 ± 0.55 | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 2 884.4 ± 157.7 | 1 680.1 ± 62.8* | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| 器官 Organ | 15N分配率/% 15N distribution ratio | 15N利用率/% 15N utilization rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 65.89 ± 2.42 | 60.06 ± 4.46 | 4.25 ± 0.61 | 2.03 ± 0.29* | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 8.35 ± 1.45 | 12.58 ± 2.35* | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 7.90 ± 0.47 | 3.72 ± 0.47* | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 5.02 ± 0.49 | 7.20 ± 0.48* | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 3.44 ± 0.66 | 5.45 ± 0.64* | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | |
| 主根 Main root | 3.58 ± 0.52 | 3.69 ± 0.54 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 6.29 ± 0.44 | 4.60 ± 0.58* | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.02* | |
| 细根 Fine root | 4.53 ± 1.39 | 2.69 ± 1.17 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.03* | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 100.00 | 100.00 | 6.45 ± 0.89 | 3.36 ± 0.28* | |
表2 脐橙幼树各器官的15N分配率和利用率
Table 2 15N distribution ratio and utilization of different parts in young naval orange plants
| 器官 Organ | 15N分配率/% 15N distribution ratio | 15N利用率/% 15N utilization rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早 Gannanzao | 纽荷尔 Newhall | 赣南早Gannanzao | ||
| 当年生叶片 1-Year leaf | 65.89 ± 2.42 | 60.06 ± 4.46 | 4.25 ± 0.61 | 2.03 ± 0.29* | |
| 当年生枝条 1-Year branch | 8.35 ± 1.45 | 12.58 ± 2.35* | 0.54 ± 0.13 | 0.42 ± 0.05 | |
| 二年生叶片 2-Year leaf | 7.90 ± 0.47 | 3.72 ± 0.47* | 0.19 ± 0.05 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 二年生枝条 2-Year branch | 5.02 ± 0.49 | 7.20 ± 0.48* | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | |
| 主干 Trunk | 3.44 ± 0.66 | 5.45 ± 0.64* | 0.23 ± 0.07 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | |
| 主根 Main root | 3.58 ± 0.52 | 3.69 ± 0.54 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.02* | |
| 粗根 Coarse root | 6.29 ± 0.44 | 4.60 ± 0.58* | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.02* | |
| 细根 Fine root | 4.53 ± 1.39 | 2.69 ± 1.17 | 0.28 ± 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.03* | |
| 整株 Whole plant | 100.00 | 100.00 | 6.45 ± 0.89 | 3.36 ± 0.28* | |

图2 不同土层土壤Ndff 不同字母表示同一品种不同土层之间存在显著差异
Fig. 2 Ndff of soil in different soil layers The different letters indicate that there are significant differences in different soil layers of the same variety
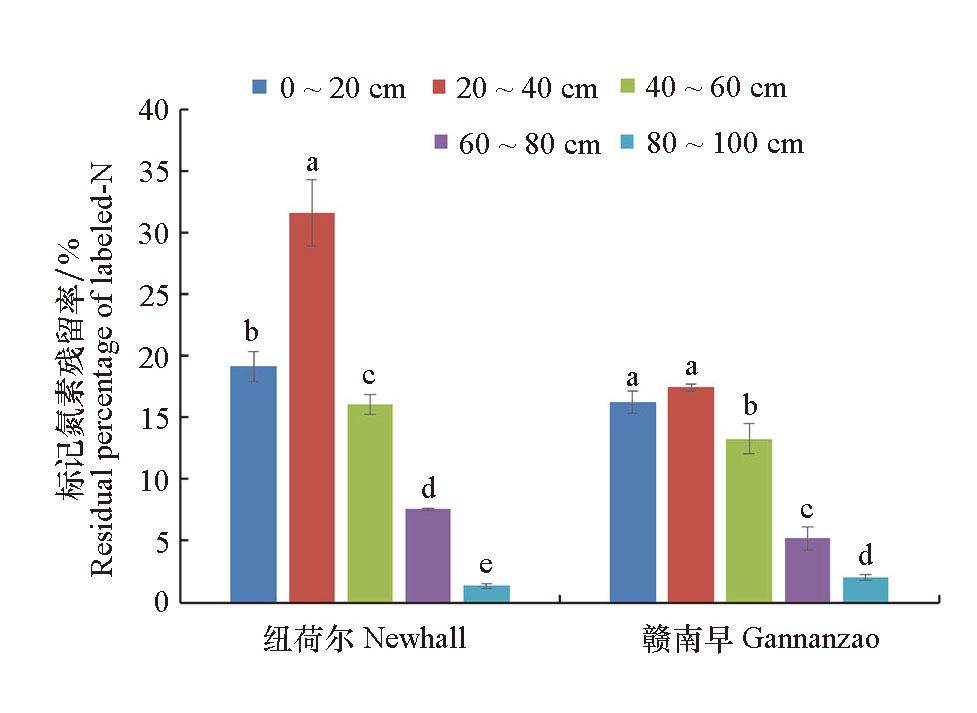
图3 不同土层15N残留率 不同字母表示同一品种不同土层之间存在显著差异
Fig. 3 Residual percentage of 15N in different soil layers The different letters indicate that there are significant differences in different soil layers of the same variety
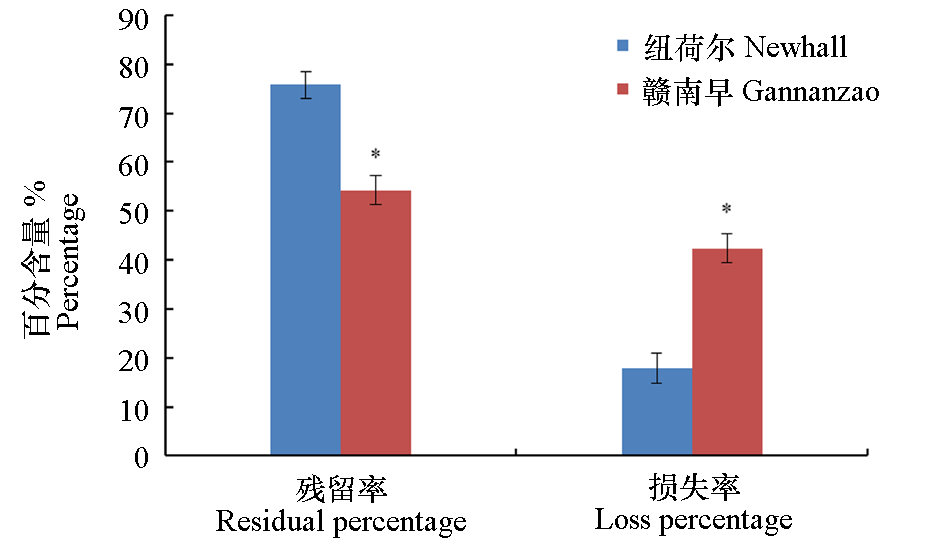
图4 土壤15N残留率和损失率 * 表示品种间存在显著性差异
Fig. 4 Residual and loss percentage of 15N in soil Asterisk above the same index indicate that there is a significant difference between the two cultivars
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
杜思婕, 张艺磊, 张志勇, 吉艳芝, 尹兴, 韩建, 张丽娟. 2021. 冬小麦-夏玉米轮作体系不同新型尿素的氮素利用率及去向. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27 (1):24-34.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
范玉兰, 薛珺, 梁梅青, 李勋, 彭良志, 淳长品. 2012. 赣南脐橙果园土壤有机质变化特征研究. 中国南方果树, 41 (4):18-20.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
葛顺峰, 姜远茂, 魏绍冲, 房祥吉. 2011. 不同供氮水平下幼龄苹果园氮素去向初探. 植物营养与肥料学报, 17 (4):949-955.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
黄成能, 卢晓鹏, 李静, 肖玉明, 孙敏红, 谢深喜. 2013. 柑橘氮素营养生理研究进展. 湖南农业科学, 15:76-79.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
柯健. 2017. 氮肥种类和施肥方式对水稻产量及氮素去向的影响[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
雷靖, 梁珊珊, 谭启玲, 胡承孝, 孙学成, 赵小虎. 2019. 我国柑橘氮磷钾肥用量及减施潜力. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (9):1504-1513.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李旭. 2020. 减氮施肥对柑橘树体氮素含量、果实品质产量和氮肥利用的影响[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0110 URL |
|
梁振旭, 孙明德, 武阳, 田海青, 杜瑞瑞, 赵艳艳, 刘松忠. 2021. 梨幼树到结果初期春施15N-尿素的利用及其在土壤的残留与损失. 园艺学报, 48 (1):137-145.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0110 URL |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘桂东, 姜存仓, 王运华, 彭抒昂, 鲁剑巍. 2010. 柑橘对不同矿质营养元素效应的研究进展. 土壤通报, 41 (6):1547-1552.
|
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0280 URL |
|
刘照霞, 张鑫, 王璐, 马玉婷, 陈倩, 朱占玲, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2022. 肥料穴施位点对苹果细根生长、15N吸收利用及产量品质的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1545-1556.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0280 URL |
|
| [16] |
pmid: 14717433 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
孙秋玲, 戴思兰, 张春英, 魏翔莺. 2012. 菌根真菌促进植物吸收利用氮素机制的研究进展. 生态学杂志, 31 (5):1302-1310.
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0126 URL |
|
王芬, 田歌, 于波, 何流, 刘晓霞, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂. 2017. 富士苹果果实膨大期肥料氮去向及土壤氮素平衡的研究. 园艺学报, 44 (8):1569-1578.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0126 URL |
|
| [20] |
|
|
王海宁, 葛顺峰, 姜远茂, 魏绍冲, 陈倩, 孙聪伟. 2013. 不同砧木嫁接的富士苹果幼树13C和15N分配利用特性比较. 园艺学报, 40 (4):733-738.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
王前登, 刘雪艳, 何雪菲, 王成, 柴仲平. 2019. 基于15N示踪的库尔勒香梨园氮素去向研究. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (9):1523-1531.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
王瑞东, 姜存仓, 刘桂东, 王运华, 彭抒昂, 钟八莲, 曾庆銮. 2011. 赣南脐橙园立地条件及种植现状调查与分析. 中国南方果树, 40 (1):1-3.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0350 |
|
王晓荣, 唐万鹏, 付甜, 黄志霖, 何伟, 刘常富. 2021. 不同管理措施对三峡库区柑橘园土壤养分和径流氮磷流失的影响. 中国农学通报, 37 (11):95-102.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0350 |
|
| [24] |
|
|
吴梦娜, 王少杰, 兰唱, 闫旭, 冯国忠, 高强. 2024. 不同秸秆还田方式下黑土玉米田肥料氮素去向. 土壤学报, 61 (2):506-514.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0063 |
|
武阳, 孙明德, 刘军, 田海青, 王文娟, 刘松忠. 2017. 施氮深度对‘黄金梨’树氮素吸收、分配及利用效率的影响. 园艺学报, 44 (11):2171-2178.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0063 |
|
| [26] |
|
|
徐明杰, 董娴娴, 刘会玲, 张丽娟, 巨晓棠. 2014. 不同管理方式对小麦氮素吸收、分配及去向的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 20 (5):1084-1093.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
徐明杰, 张琳, 汪新颖, 彭亚静, 张丽娟, 巨晓棠. 2015. 不同管理方式对夏玉米氮素吸收、分配及去向的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 21 (1):36-45.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
赵环宇. 2023. 我国柑橘生产的环境代价及氮素优化措施研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
钟八莲, 赖晓桦, 杨斌华, 米兰芳, 谢上海, 黄彩英, 杨文侠, 张湟. 2013. 纽荷尔脐橙芽变早熟品种—赣南早脐橙. 中国南方果树, 42 (2):48-51.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.08.010 |
|
周丽平, 杨俐苹, 白由路, 卢艳丽, 王磊. 2018. 夏玉米施用不同缓释化处理氮肥的效果及氮肥去向. 中国农业科学, 51 (8):1527-1536.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.08.010 |
| [1] | 张书凝, 郑舒琪, 王新胜, 柯甫志, 张岚岚, 孙学鹏, 宫金礼. 柑橘果皮生理性病害与细胞壁代谢的关系研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 513-525. |
| [2] | 杨金磊, 吕壁纹, 陈岳文, 金燕, 杨俊枫, 周铁, 唐俊, 常媛媛, 杨长耀, 卢晓鹏. 湖南柑橘产区镉污染状况及镉对柑橘发育影响分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 200-212. |
| [3] | 任思源, 陈森, 龙治坚, 王博雅, 唐登国, 王正前, 杨斌, 胡尚连, 曹颖. 花魔芋球茎发育期氮分配变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [4] | 董丽婷, 屈荣荣, 庞淑炜, 莫凯琴, 陈爽, 商兰月, 邹修平. 柑橘CsMEKK1-1响应黄龙病菌侵染的表达特征与功能探究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2168-2182. |
| [5] | 张文龙, 万润楚, 郑妮, 陈焱, 赖恒鑫, 余歆, 钱春, 曹立. 柑橘不育系新品种‘阳光1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2221-2222. |
| [6] | 李旭娇, 吕齐, 姚东东, 赵丰云, 王小非, 于坤. ‘烟富3’苹果不同砧木嫁接对其15N–尿素吸收利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1868-1880. |
| [7] | 杜美霞, 庞淑玮, 董丽婷, 莫凯琴, 候梦圆, 王帅, 邹修平. 柑橘黄龙病菌与寄主互作的分子机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1623-1638. |
| [8] | 曹惠祥, 罗鑫, 刘婉荣, 管书萍, 王婷婷, 伍小萌, 郭文武, 解凯东. 柑橘2个三倍体果实囊衣发育与化渣性评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1179-1188. |
| [9] | 周慧珍, 张嘉, 胡军华, 李白雪, 曹立, 余歆, 王福生, 邹修平, 周彦. 柑橘感染褐斑病过程中BAG1的作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 956-970. |
| [10] | 彭爱红, 张婧芸, 陈志毅, 苏娟, 何永睿, 姚利晓. CsEXPA8过表达对‘晚锦橙’生长及溃疡病抗性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 971-981. |
| [11] | 游平, 杨进, 周俊, 黄爱军, 鲍敏丽, 易龙. 柑橘黄龙病菌原噬菌体的遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 727-736. |
| [12] | 熊志伟, 李智龙, 尹晖, 高玉霞. 柑橘黄龙病菌亚洲种的泛基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 737-747. |
| [13] | 易倩, 张曼曼, 汪小利, 冯继鹏, 朱世平, 王福生, 赵晓春. CclSAUR49对柑橘生长及类柠檬苦素代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 479-494. |
| [14] | 孙权, 何政辰, 叶俊丽, 魏冉冉, 尹映紫, 柴利军, 谢宗周, 徐强, 徐娟, 郭文武, 程运江, 邓秀新. 与呼吸跃变型果实共贮藏改善柑橘果实色泽和品质[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 601-615. |
| [15] | 刘梦, 贾惠婷, 周新刚. 黄瓜枯萎病菌共生细菌的分离鉴定及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 643-655. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司