
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 2800-2816.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0941
卜文轩1, 姚奕平1, 黄宇2, 杨星宇1, 罗小宁1, 张旻桓1,2,*( ), 雷维群2, 王政3, 田珈宁1, 陈露洁1, 秦莉萍2
), 雷维群2, 王政3, 田珈宁1, 陈露洁1, 秦莉萍2
收稿日期:2024-03-01
修回日期:2024-09-03
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2024-12-13
通讯作者:
基金资助:
BU Wenxuan1, YAO Yiping1, HUANG Yu2, YANG Xingyu1, LUO Xiaoning1, ZHANG Minhuan1,2( ), LEI Weiqun2, WANG Zheng3, TIAN Jianing1, CHEN Lujie1, QIN Liping2
), LEI Weiqun2, WANG Zheng3, TIAN Jianing1, CHEN Lujie1, QIN Liping2
Received:2024-03-01
Revised:2024-09-03
Published:2024-12-25
Online:2024-12-13
摘要:
为探究中国南方湿热地区本土牡丹(Paeonia suffruticosa)品种高温胁迫阶段的分子调控机制,以江南牡丹品种‘呼红’2 ~ 3年生植株为试材,采集20 ℃常温对照与40 ℃高温处理0、2、6、12和24 h的成熟叶片,采用生理指标和转录组分析方法探究高温胁迫下不同处理时间基因表达的差异。试验结果表明,随着高温胁迫时间的延长,叶片失水,生物膜受损,相对电导率和脯氨酸含量显著增加,明确了游离脯氨酸、相对电导率与可溶性蛋白为衡量牡丹高温胁迫响应中生理机制变化的重要指标。转录组测序总计产生492 693个unigene和840 509个转录本,36 174条差异表达基因在GO、KEGG等5个数据库得到注释。GO富集分析表明,高温处理对比组中热的反应途径、还原型戊糖磷酸循环途径等是主要的富集途径。KEGG富集分析表明,参与信号传导、光合作用、新陈代谢等相关的差异表达基因在响应高温胁迫中起主要作用。通过转录组分析,挖掘到多个参与耐热胁迫响应的转录因子和重要基因,包括热激转录因子PsHSFA2b、PsHSFA3、PsHSFB2b/2a、PsHSFB4、PsHSFC1和NAC、MYB、bHLH等家族基因。对选取的11个基因通过qRT-PCR检测在高温胁迫下的表达,其结果与RNA-seq结果相似。
卜文轩, 姚奕平, 黄宇, 杨星宇, 罗小宁, 张旻桓, 雷维群, 王政, 田珈宁, 陈露洁, 秦莉萍. ‘呼红’牡丹高温胁迫响应生理与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2800-2816.
BU Wenxuan, YAO Yiping, HUANG Yu, YANG Xingyu, LUO Xiaoning, ZHANG Minhuan, LEI Weiqun, WANG Zheng, TIAN Jianing, CHEN Lujie, QIN Liping. Transcriptome Analysis of the Response of Tree Peony‘Hu Hong’Under High Temperature Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2800-2816.
| 基因名称(编号) Gene name(number) | 底物名称 Substrate name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| HSP20(TRINITY_DN57811_c1_g1_i1) | S539-1 | F:TGCCCAAAGAGGAAGAGAA;R:CCCATGCCATCAGAAATTAA |
| WRKY20(TRINITY_DN58753_c6_g1_i1) | S539-4-2 | F:CTAATGGCATCACAACCGTC;R:ACTAGTTTTGACGCGTTTTGT |
| HSPA1s(TRINITY_DN58827_c1_g2_i1) | S539-3 | F:TTGTCAGCCGGAGAAAGC;R:GCAGGAGGCGGAGAAGTA |
| HSFC1(TRINITY_DN58986_c1_g1_i2) | S539-4 | F:AAGGCGGTGGTCTTGGTT;R:TGGGGGTGTTGAGTTGGA |
| HSFA3(TRINITY_DN61524_c1_g1_i2) | S539-5 | F:CATTTTGGTGGTGCTTGACA;R:AGACGGTTTCGTTCTTGGC |
| CRF4(TRINITY_DN63834_c0_g1_i1) | S539-6 | F:TTCAACAATCAACACTACGGG;R:AGAGTTAAGCACACGGGGTT |
| HSFB2b(TRINITY_DN64862_c0_g3_i2) | S539-7 | F:GACTACTTTCGCAAGGGGA;R:TTACCGTCGTTGAAGGAGC |
| NAC55(TRINITY_DN66043_c1_g1_i3) | S539-8 | F:ACAATACCAGTGCCGCTTC;R:CCCCTAATACCCCTAACGAC |
| MCU3(TRINITY_DN67541_c3_g1_i1) | S539-9 | F:ATTAGGGAATTATTTTGGGGG;R:TGGAAGGTGATTTTTTGTGAA |
| HSP90B(TRINITY_DN71090_c1_g1_i1) | S539-10 | F:AGGTCCTTGATTATGGGATGAT;R:TGGATGGTCTGCTAATATGGAA |
| HSP70(TRINITY_DN74057_c3_g1_i1) | S539-11-2 | F:CTGGGACTTGCCGATGAC;R:ACGACACTGAGAAGGCCCT |
| 内参 Reference | S539-DN59422 | F:CGAATCTTGTCTTGACCCCC;R:ATTGTCACCACCATCCCTACC |
表1 用于qRT-PCR的基因及其引物
Table 1 Genes and primers used for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称(编号) Gene name(number) | 底物名称 Substrate name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| HSP20(TRINITY_DN57811_c1_g1_i1) | S539-1 | F:TGCCCAAAGAGGAAGAGAA;R:CCCATGCCATCAGAAATTAA |
| WRKY20(TRINITY_DN58753_c6_g1_i1) | S539-4-2 | F:CTAATGGCATCACAACCGTC;R:ACTAGTTTTGACGCGTTTTGT |
| HSPA1s(TRINITY_DN58827_c1_g2_i1) | S539-3 | F:TTGTCAGCCGGAGAAAGC;R:GCAGGAGGCGGAGAAGTA |
| HSFC1(TRINITY_DN58986_c1_g1_i2) | S539-4 | F:AAGGCGGTGGTCTTGGTT;R:TGGGGGTGTTGAGTTGGA |
| HSFA3(TRINITY_DN61524_c1_g1_i2) | S539-5 | F:CATTTTGGTGGTGCTTGACA;R:AGACGGTTTCGTTCTTGGC |
| CRF4(TRINITY_DN63834_c0_g1_i1) | S539-6 | F:TTCAACAATCAACACTACGGG;R:AGAGTTAAGCACACGGGGTT |
| HSFB2b(TRINITY_DN64862_c0_g3_i2) | S539-7 | F:GACTACTTTCGCAAGGGGA;R:TTACCGTCGTTGAAGGAGC |
| NAC55(TRINITY_DN66043_c1_g1_i3) | S539-8 | F:ACAATACCAGTGCCGCTTC;R:CCCCTAATACCCCTAACGAC |
| MCU3(TRINITY_DN67541_c3_g1_i1) | S539-9 | F:ATTAGGGAATTATTTTGGGGG;R:TGGAAGGTGATTTTTTGTGAA |
| HSP90B(TRINITY_DN71090_c1_g1_i1) | S539-10 | F:AGGTCCTTGATTATGGGATGAT;R:TGGATGGTCTGCTAATATGGAA |
| HSP70(TRINITY_DN74057_c3_g1_i1) | S539-11-2 | F:CTGGGACTTGCCGATGAC;R:ACGACACTGAGAAGGCCCT |
| 内参 Reference | S539-DN59422 | F:CGAATCTTGTCTTGACCCCC;R:ATTGTCACCACCATCCCTACC |
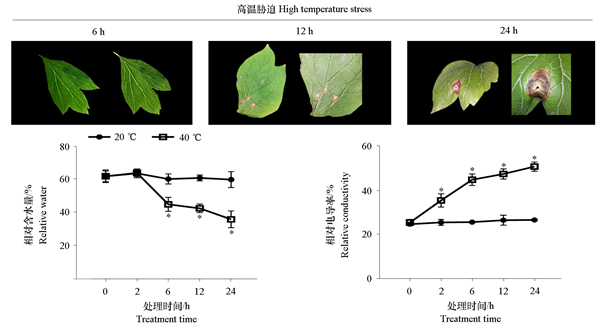
图1 高温(40 ℃)处理下‘呼红’牡丹叶片表型、相对含水量与相对电导率的变化
Fig. 1 Changes of leaf phenotype,relative water content and relative conductivity of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature(40 ℃)treatment t-test,* α = 0.05.

图2 高温(40 ℃)处理下‘呼红’牡丹叶片叶绿素a、叶绿素b含量、叶绿素a/b和丙二醛含量的变化
Fig. 2 Changes of chlorophyll a,chlorophyll b content,chlorophyll a/b and malondialdehyde content in leaves of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature(40 ℃)treatment t-test,* α = 0.05.

图3 高温(40 ℃)处理下‘呼红’牡丹叶片可溶性糖、可溶性蛋白和游离脯氨酸含量变化
Fig. 3 Changes of soluble sugar,soluble protein and free proline content in leaves of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature(40 ℃)treatment t-test,* α = 0.05.

图4 高温(40 ℃)处理下‘呼红’牡丹叶片超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性的变化
Fig. 4 Changes of superoxide dismutase(SOD),peroxidase(POD)and catalase(CAT)activities in leaves of Paeonia suffruticosa‘Hu Hong’under high temperature(40 ℃)treatment t-test,* α = 0.05.
| 指标 Index | RWC | Rec | Chl | SS | SP | MDA | Pro | SOD | POD | CAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RWC | 1 | |||||||||
| Rec | -0.916* | 1 | ||||||||
| Chl | 0.881* | -0.852 | 1 | |||||||
| SS | -0.924* | 0.922* | -0.857 | 1 | ||||||
| SP | -0.909* | 0.974** | -0.764 | 0.947* | 1 | |||||
| MDA | -0.871 | 0.788 | -0.943* | 0.917* | 0.763 | 1 | ||||
| Pro | -0.922* | 0.995** | -0.812 | 0.911* | 0.983** | 0.751 | 1 | |||
| SOD | 0.748 | -0.430 | 0.595 | -0.635 | -0.482 | -0.731 | -0.447 | 1 | ||
| POD | -0.817 | 0.892* | -0.557 | 0.771 | 0.929* | 0.504 | 0.931* | -0.359 | 1 | |
| CAT | -0.690 | 0.914* | -0.604 | 0.755 | 0.902* | 0.508 | 0.916* | -0.066 | 0.897* | 1 |
表2 ‘呼红’牡丹高温胁迫下生理指标相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of physiological indexes of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature stress
| 指标 Index | RWC | Rec | Chl | SS | SP | MDA | Pro | SOD | POD | CAT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RWC | 1 | |||||||||
| Rec | -0.916* | 1 | ||||||||
| Chl | 0.881* | -0.852 | 1 | |||||||
| SS | -0.924* | 0.922* | -0.857 | 1 | ||||||
| SP | -0.909* | 0.974** | -0.764 | 0.947* | 1 | |||||
| MDA | -0.871 | 0.788 | -0.943* | 0.917* | 0.763 | 1 | ||||
| Pro | -0.922* | 0.995** | -0.812 | 0.911* | 0.983** | 0.751 | 1 | |||
| SOD | 0.748 | -0.430 | 0.595 | -0.635 | -0.482 | -0.731 | -0.447 | 1 | ||
| POD | -0.817 | 0.892* | -0.557 | 0.771 | 0.929* | 0.504 | 0.931* | -0.359 | 1 | |
| CAT | -0.690 | 0.914* | -0.604 | 0.755 | 0.902* | 0.508 | 0.916* | -0.066 | 0.897* | 1 |
| 生理指标 Physiologic indexs | 特征向量 Eigenvector | |
|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | |
| RWC | -0.968 | 0.180 |
| Rec | 0.981 | 0.173 |
| Chl | -0.880 | 0.273 |
| SS | 0.968 | -0.108 |
| SP | 0.975 | 0.174 |
| MDA | 0.865 | -0.426 |
| Pro | 0.978 | 0.196 |
| SOD | -0.594 | 0.719 |
| POD | 0.866 | 0.378 |
| CAT | 0.830 | 0.550 |
| 特征值 Characteristic value | 8.058 | 1.361 |
| 方差贡献率/% Variance contribution rate | 80.578 | 13.612 |
| 累积贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 80.578 | 94.191 |
表3 ‘呼红’牡丹高温胁迫下生理指标主成分分析结果
Table 3 Principal component analysis results of physiological indexes of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature stress
| 生理指标 Physiologic indexs | 特征向量 Eigenvector | |
|---|---|---|
| 主成分1 Principal component 1 | 主成分2 Principal component 2 | |
| RWC | -0.968 | 0.180 |
| Rec | 0.981 | 0.173 |
| Chl | -0.880 | 0.273 |
| SS | 0.968 | -0.108 |
| SP | 0.975 | 0.174 |
| MDA | 0.865 | -0.426 |
| Pro | 0.978 | 0.196 |
| SOD | -0.594 | 0.719 |
| POD | 0.866 | 0.378 |
| CAT | 0.830 | 0.550 |
| 特征值 Characteristic value | 8.058 | 1.361 |
| 方差贡献率/% Variance contribution rate | 80.578 | 13.612 |
| 累积贡献率/% Cumulative contribution rate | 80.578 | 94.191 |

图5 ‘呼红’牡丹高温(40 ℃)与常温(20 ℃)处理下差异表达基因火山图
Fig. 5 Volcano map of differentially expressed genes of‘Hu Hong’peony under high temperature(40 ℃)and normal temperature(20 ℃)treatment

图6 高温胁迫处理的‘呼红’牡丹叶片差异表达基因表达谱 上方为趋势的ID,下方为趋势中的基因数量。
Fig. 6 Differentially expressed gene expression profiles of‘Hu Hong’peony leaves under high temperature stress Above is the ID of the trend,and below is the number of genes in the trend.

图7 ‘呼红’牡丹高温(40 ℃)处理与对照(20 ℃)同时间段差异表达基因GO富集分析气泡图
Fig. 7 GO enrichment analysis bubble diagram of differentially expressed genes between high temperature(40 ℃)treatment and control(20 ℃)at the same time period of‘Hu Hong’peony
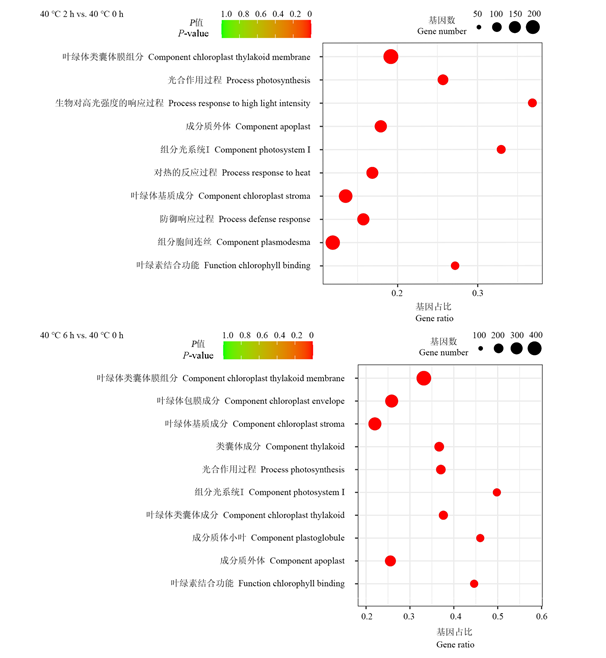
图8 ‘呼红’牡丹高温(40 ℃)处理与对照(20 ℃)不同时间段差异表达基因GO富集分析气泡图
Fig. 8 GO enrichment analysis bubble diagram of differentially expressed genes in different time periods of high temperature (40 ℃)treatment and control(20 ℃)of‘Hu Hong’peony

图9 ‘呼红’牡丹高温(40 ℃)处理与对照(20 ℃)同时间段差异表达转录因子数量热图
Fig. 9 Heat map of differentially expressed transcription factors between high temperature(40 ℃)treatment and control(20 ℃)at the same time period of‘Hu Hong’peony

图10 ‘呼红’牡丹不同温度下差异表达转录因子基因表达图谱
Fig. 10 Differentially expressed transcription factor gene expression profiles of‘Hu Hong’peony at different temperatures
| [1] |
|
|
艾千群, 杨慧琴, 杨思琦, 刘宪斌, 杨利云. 2023. 谷氨酸信号调控玉米幼苗耐热性的生理生化机制. 植物生理学报, 59 (10):1923-1932.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈嘉贝, 张芙蓉, 黄丹枫, 张利达, 张屹东. 2014. 盐胁迫下两个甜瓜品种转录因子的转录组分析. 植物生理学报, 50 (2):150-158.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
邓肖, 徐学欣, 孙芹, 张玉璐, 朱紫鑫, 郝天佳, 高国龙, 贺小彦, 王秀琳, 赵长星. 2023. 不同盐浓度胁迫下冬小麦幼苗光合特性及转录组分析. 植物生理学报, 59 (9):1819-1829.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
胡慧芳, 王子雨, 潘潇潇, 陈楠, 张华锋, 陈儒钢. 2023. 辣椒转录因子CaNAC083对高温胁迫的响应. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 51 (3):121-131.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.011 pmid: 17482504 |
| [7] |
|
|
刘路平, 刘高峰, 蒋程, 侯喜林. 2022. 不结球白菜耐热相关基因BcNAC036的克隆、亚细胞定位及功能分析. 南京农业大学学报, 45 (4):647-655.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
刘蕾, 杜海, 唐晓凤, 吴燕民, 黄玉碧, 唐益雄. 2008. MYB转录因子在植物抗逆胁迫中的作用及其分子机理. 遗传, 30 (10):1265-1271.
|
|
| [9] |
doi: S1360-1385(16)30126-1 pmid: 27666516 |
| [10] |
|
|
阮若昕, 骆慧枫, 张琛, 黄康康, 郗笃隽, 裴嘉博, 邢梦云, 刘辉. 2023. 杭州地区不同需冷量甜樱桃品种休眠阶段花芽转录组分析. 园艺学报, 50 (6):1187-1202.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0297 URL |
|
| [11] |
|
|
王灿. 2022. 黄瓜CsHSFA1功能鉴定及DREB家族生物信息学分析[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
王静, 谭放军, 梁成亮, 张西露, 欧立军,
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0470 URL |
|
| [13] |
|
|
徐艳. 2007. 几个牡丹品种的耐湿热生理生化特性研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0895 URL |
|
姚富文, 王枚阁, 宋春晖, 宋尚伟, 焦健, 王苗苗, 王昆, 白团辉, 郑先波. 2021. 苹果HSP90家族基因鉴定及高温胁迫下的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (5):849-859.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0895 URL |
|
| [15] |
|
|
姚奕平. 2022. 基于转录组测序技术挖掘牡丹响应高温胁迫基因研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
张旻桓. 2019. 湖南牡丹资源遗传多样性及耐热性研究[博士论文]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
尤倩, 刘晓, 刘梦梦, 刘丹, 伯晨, 朱艳芳, 段永波, 薛建平, 张爱民, 薛涛. 2024. 半夏热激因子HSF家族基因鉴定及生物信息学分析. 园艺学报, 51 (10):2371-2385.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 2022. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制. 园艺学报, 49 (2):237-251.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0077 URL |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
赵静珂. 2024. 辣椒对热胁迫的生理响应及耐热相关基因功能验证[硕士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
赵溪, 张婷婷, 邢文婷, 王健, 宋希强, 周扬. 2021. 铁皮石斛热激蛋白HSP70基因家族鉴定及温度胁迫下的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1743-1754.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0710 |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0822 URL |
|
赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 2023. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析. 园艺学报, 50 (1):177-187.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0822 URL |
| [1] | 李 芮, 王 稳, 杜明辉, 刘根忠, 马方放, 包志龙. SlBON1调控番茄植株营养生长机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 73-87. |
| [2] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [3] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [4] | 段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [5] | 李琴琴, 董山榕, 罗建让, 张延龙. 卵叶牡丹PqDFR和PqANS及启动子克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1256-1272. |
| [6] | 王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [7] | 张文昊, 张辉, 刘雨婷, 王艳, 张迎迎, 王馨曼, 王全华, 朱为民, 杨学东. 番茄含糖量不同的两个材料果实转录组初步分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 281-294. |
| [8] | 吕梦雯 , 杨 勇 , 王亮生 , 李珊珊 , . 牡丹新品种‘华玉脂凝’ [J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 145-146. |
| [9] | 康晓飞 , 刘玉梅 , 赵春雷 , 王 波 , 李 霞 , . 牡丹新品种‘蓝熙’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 147-148. |
| [10] | 代红军, 魏强, 贺琰, 汪月宁, 王振平. 油菜素内酯对高温胁迫下葡萄花色苷合成及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1711-1722. |
| [11] | 卢艳清, 林燕金, 卢新坤. 果皮细胞壁物质代谢及果皮对高温和水分亏缺逆境的响应与‘度尾文旦柚’裂果相关[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1747-1768. |
| [12] | 钟原, 杜明杰, 成仿云, 李坤彦, 季润泽, 崔珺. 牡丹异源四倍体核型和育性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1444-1454. |
| [13] | 刘春洋, 彭朝凤, 程世平, 姚鹏强, 耿喜宁, 谢丽华. 高温诱导‘凤丹’牡丹2n雌配子创制三倍体[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1455-1466. |
| [14] | 阮若昕, 骆慧枫, 张琛, 黄康康, 郗笃隽, 裴嘉博, 邢梦云, 刘辉. 杭州地区不同需冷量甜樱桃品种休眠阶段花芽转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1187-1202. |
| [15] | 徐悦, 李子雄, 陈婕, 孙亮. 2,4-D调控番茄果形的转录基础[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 802-814. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司