
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 1773-1791.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0374
段敏杰1, 李怡斐1, 王春萍2, 杨小苗1, 黄任中1, 黄启中1, 张世才1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-22
修回日期:2024-05-20
出版日期:2024-08-25
发布日期:2024-08-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
DUAN Minjie1, LI Yifei1, WANG Chunping2, YANG Xiaomiao1, HUANG Renzhong1, HUANG Qizhong1, ZHANG Shicai1,*( )
)
Received:2024-02-22
Revised:2024-05-20
Published:2024-08-25
Online:2024-08-21
摘要:
分析了辣椒自交系1189不同发育时期果实转录组和类胡萝卜素靶向代谢组,基于加权基因共表达网络分析(weight gene co-expression network analysis,WGCNA)鉴定了可能参与调控辣椒类胡萝卜素生物合成相关基因的转录因子。靶向代谢组共鉴定出60种类胡萝卜素代谢物,分析发现,幼果期和绿熟期果实类胡萝卜素主要组分均为叶黄素(73.4%和64.5%),转色期叶黄素含量急剧下降,红熟期主要为辣椒红素(32.5%),无法检测到叶黄素。转录组分析共鉴定出14 148个差异表达基因和15个类胡萝卜素代谢相关差异表达基因。通过WGCNA将筛选所得的12 286个差异表达基因划分至16个模块,发现MEdarkseagreen4、MElightcyan1和MEbrown2模块与11种主要类胡萝卜素组分显著相关。基于3个模块中类胡萝卜素相关差异表达基因构建代谢调控网络,并通过分析启动子结合基序,筛选出bHLH48、SEP3、CMB1、AGL27、YABBY2、GT-3B、NF-YA3、NAC2、HOX5和GATA26等10个转录因子可能在类胡萝卜素积累中发挥重要调控作用。
段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791.
DUAN Minjie, LI Yifei, WANG Chunping, YANG Xiaomiao, HUANG Renzhong, HUANG Qizhong, ZHANG Shicai. Integrated Transcriptomic and Targeted Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Regulation of Carotenoid Accumulation During Pepper Fruit Development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791.
| 基因 Gene | 引物(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|
| CCS | F:AGCACCCACATCAAAGCCAG R:GTGGTGAAGGGTCAACGCAA | 催化玉米黄质和紫黄质转化为辣椒红素和辣椒玉红素 Catalyzes the conversion of zeaxanthin and vioxanthin to capsanthin and capsorubin |
| PSY1 | F:ACAGGCAGGTCTATCCGACGAAG R:ACAACAGCAGAGATGCCAACACAG | 催化GGPP合成八氢番茄红素 Catalyzes the synthesis of phytoene by GGPP |
| CHYB | F:GCACGAGTCACACCATAGACCAAG R:CGTGAACGAACATGTAGGCCATCC | 催化β-胡萝卜素转化为玉米黄质 Catalyzes the conversion of β-carotene to zeaxanthin |
| NCED1 | F:GACATTCAGGGATAGCAAGGC R:TTGAAATAGACCAAACCAGCGT | 催化紫黄质和新黄质裂解成ABA前体 Catalytic cleavage of vioxanthin and neoxanthin into ABA precursors |
| LCYB | F:GTTGTTGGAATTGGTGGCACAGC R:ATGGCATTGGCAACGACAGGAG | 催化番茄红素生成β-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to β-carotene |
| ABA2 | F:CCCCTTGTTCAAATATCCTCG R:ACAGACCCTGCTATACTGCCTAA | 参与类胡萝卜素裂解及ABA的生物合成 Involved in carotenoid cleavage and ABA biosynthesis |
| PSY2 | F:AGACAGAGGTGGAATTTTGGGTCT R:CAAATTCCCCGGAAGCACA | 参与植物绿色器官色素积累 Involved in the accumulation of pigment in plant green organs |
| LCYE | F:ACCCTCGGTGTAAGAATTAAAG R:GAGTGATCTGACAACGGAATAA | 催化番茄红素转化为δ-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to δ-carotene |
| CRTISO | F:CACGGCAGGCGTTCATACA R:TCAGCCAGCAACACCCCAT | 催化八氢番茄红素转化为番茄红素 Catalyzes the conversion of phytoene to lycopene |
| CMB1 | F:CTCTAGTCGTGGCAAGCTTTAT R:CTGATGGTTGGGTTCCTTCA | 番茄:参与果实成熟及调控果实色素积累 Tomato:Involved in fruit ripening and regulating fruit pigment accumulation |
| SEP3 | F:ATCATGGCATTCTGGGGAGC R:TTTCGGTAGCACGGCATCG | 拟南芥:调控花器官发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates the development of floral organs |
| YABBY2 | F:GCGTGTTCCTTCTGCCTACA R:TTGCCCTCCAGCTTGAGTC | 番茄:调节果实心室数和内源赤霉素含量 Tomato:Regulates the number of ventricles and endogenous gibberellin content in the fruit |
| GT-3B | F:CGCAGATAGGTTCCCTCAATG R:TCAGGCTCCAGCGTTTCAC | 拟南芥:调控耐盐相关基因表达 Arabidopsis:Regulation of salt tolerance-related gene expression |
| NF-YA3 | F:AGAAGCCCCAAGAGTCCAAA R:CCGATGCACGATGAGAAGG | 拟南芥:调控早期胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates early embryonic development |
| NAC2 | F:TCACCCGACTGATGAAGAGC R:TCCCCATACAACGCCAAAT | 拟南芥:调控胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates embryonic development |
| AGL27 | F:AAACGAAGGAAAGGTCTGATGA R:TCTGCCACGATTGGAGATGAT | 拟南芥:增强植物对环境胁迫的耐受性 Arabidopsis:Enhancing plant tolerance to environmental stresses |
| HOX5 | F:AGGCAGGTGGCTGTATGGTT R:ATCGTTGTCTTTGCGAATGG | 拟南芥:ABA响应的正向调节因子 Arabidopsis:A positive regulator of ABA response |
| GATA26 | F:GCTGGATTCGTTGCGTTTT R:GCTGCTACTGGTGCTTGCTT | 拟南芥:参与光依赖调节 Arabidopsis:Involved in light-dependent regulation |
| bHLH48 | F:AATCCCTACAGCGACAAGTGG R:GTTTGTCCCTCGGTCCAGAT | 拟南芥:与光敏色素互作调控下胚轴伸长 Arabidopsis:Interacts with photosensitizer pigments to regulate hypocotyl elongation |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR
| 基因 Gene | 引物(5′-3′) Forward sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|
| CCS | F:AGCACCCACATCAAAGCCAG R:GTGGTGAAGGGTCAACGCAA | 催化玉米黄质和紫黄质转化为辣椒红素和辣椒玉红素 Catalyzes the conversion of zeaxanthin and vioxanthin to capsanthin and capsorubin |
| PSY1 | F:ACAGGCAGGTCTATCCGACGAAG R:ACAACAGCAGAGATGCCAACACAG | 催化GGPP合成八氢番茄红素 Catalyzes the synthesis of phytoene by GGPP |
| CHYB | F:GCACGAGTCACACCATAGACCAAG R:CGTGAACGAACATGTAGGCCATCC | 催化β-胡萝卜素转化为玉米黄质 Catalyzes the conversion of β-carotene to zeaxanthin |
| NCED1 | F:GACATTCAGGGATAGCAAGGC R:TTGAAATAGACCAAACCAGCGT | 催化紫黄质和新黄质裂解成ABA前体 Catalytic cleavage of vioxanthin and neoxanthin into ABA precursors |
| LCYB | F:GTTGTTGGAATTGGTGGCACAGC R:ATGGCATTGGCAACGACAGGAG | 催化番茄红素生成β-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to β-carotene |
| ABA2 | F:CCCCTTGTTCAAATATCCTCG R:ACAGACCCTGCTATACTGCCTAA | 参与类胡萝卜素裂解及ABA的生物合成 Involved in carotenoid cleavage and ABA biosynthesis |
| PSY2 | F:AGACAGAGGTGGAATTTTGGGTCT R:CAAATTCCCCGGAAGCACA | 参与植物绿色器官色素积累 Involved in the accumulation of pigment in plant green organs |
| LCYE | F:ACCCTCGGTGTAAGAATTAAAG R:GAGTGATCTGACAACGGAATAA | 催化番茄红素转化为δ-胡萝卜素 Catalyzes the conversion of lycopene to δ-carotene |
| CRTISO | F:CACGGCAGGCGTTCATACA R:TCAGCCAGCAACACCCCAT | 催化八氢番茄红素转化为番茄红素 Catalyzes the conversion of phytoene to lycopene |
| CMB1 | F:CTCTAGTCGTGGCAAGCTTTAT R:CTGATGGTTGGGTTCCTTCA | 番茄:参与果实成熟及调控果实色素积累 Tomato:Involved in fruit ripening and regulating fruit pigment accumulation |
| SEP3 | F:ATCATGGCATTCTGGGGAGC R:TTTCGGTAGCACGGCATCG | 拟南芥:调控花器官发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates the development of floral organs |
| YABBY2 | F:GCGTGTTCCTTCTGCCTACA R:TTGCCCTCCAGCTTGAGTC | 番茄:调节果实心室数和内源赤霉素含量 Tomato:Regulates the number of ventricles and endogenous gibberellin content in the fruit |
| GT-3B | F:CGCAGATAGGTTCCCTCAATG R:TCAGGCTCCAGCGTTTCAC | 拟南芥:调控耐盐相关基因表达 Arabidopsis:Regulation of salt tolerance-related gene expression |
| NF-YA3 | F:AGAAGCCCCAAGAGTCCAAA R:CCGATGCACGATGAGAAGG | 拟南芥:调控早期胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates early embryonic development |
| NAC2 | F:TCACCCGACTGATGAAGAGC R:TCCCCATACAACGCCAAAT | 拟南芥:调控胚胎发育 Arabidopsis:Regulates embryonic development |
| AGL27 | F:AAACGAAGGAAAGGTCTGATGA R:TCTGCCACGATTGGAGATGAT | 拟南芥:增强植物对环境胁迫的耐受性 Arabidopsis:Enhancing plant tolerance to environmental stresses |
| HOX5 | F:AGGCAGGTGGCTGTATGGTT R:ATCGTTGTCTTTGCGAATGG | 拟南芥:ABA响应的正向调节因子 Arabidopsis:A positive regulator of ABA response |
| GATA26 | F:GCTGGATTCGTTGCGTTTT R:GCTGCTACTGGTGCTTGCTT | 拟南芥:参与光依赖调节 Arabidopsis:Involved in light-dependent regulation |
| bHLH48 | F:AATCCCTACAGCGACAAGTGG R:GTTTGTCCCTCGGTCCAGAT | 拟南芥:与光敏色素互作调控下胚轴伸长 Arabidopsis:Interacts with photosensitizer pigments to regulate hypocotyl elongation |
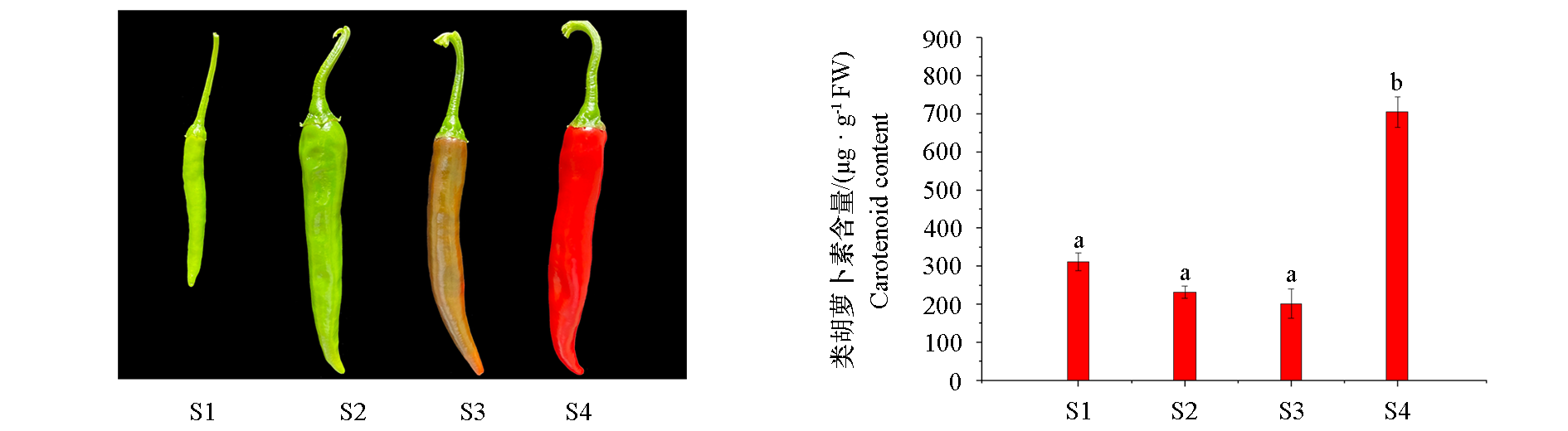
图1 辣椒果实4个发育时期表型和类胡萝卜素含量 S1:幼果期;S2:绿熟期;S3:转色期;S4:红熟期。不同小写字母表示在P < 0.05水平上差异显著。下同。
Fig. 1 Carotenoid accumulation(A)and phenotypes(B)of chili pepper fruits at the four ripening stages S1:Young fruit stage;S2:Mature green fruit stage;S3:Color-changed fruit stage;S4:Red ripe fruit stage. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at the 0.05 level. The same below.

图9 类胡萝卜素生物合成基因与转录因子的共表达网络 红色椭圆表示模块中差异表达的类胡萝卜素合成基因,其他方块表示与类胡萝卜素合成基因存在互作的差异表达转录因子。实线表示正调控,虚线表示负调控,线粗细表示权重大小。
Fig. 9 Coexpressionnetwork of carotenoid biosynthetic genes and transcription factors in chili pepper fruits Red ellipses indicate the differentially expressed carotenoid biosynthetic genes,and the other squares indicate differentially expressed transcription factors that interact with carotenoid biosynthetic genes. The soild line represents positive regulation,the dashed line represents negative regulation,and the thickness of line represents the weigth.
| 目标 基因 Target gene | 候选转录因子 Transcription factor candidate | 缩写 Abbreviation | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 启动子基序 结合位点 Promoter motif union sites | 拟南芥同源基因 Arabidopsis locus name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS | 预测:核转录因子Y亚基A-3-like亚型X1 Predicted:Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-3-like isoform X1 | NF-YA3 | XP_016562508.1 | 93 | AT1G72830 |
| 含NAC结构域的蛋白2 -like NAC domain-containing protein 2-like | NAC2 | XP_016569664.1 | 1 | AT3G15510 | |
| SEPALLATA-like MADS-box蛋白3 SEPALLATA-like MADS-box protein 3 | SEP3 | AYA60475.1 | 12 | AT1G24260 | |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 44 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY | 预测:MADS-box蛋白CMB -like Predicted:MADS-box protein CMB1-like | CMB1 | XP_016547230.1 | 1 | AT2G03710 |
| NCED1 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-3b Trihelix transcription factor GT-3b | GT-3B | XP_016542034.1 | 45 | AT5G01380 |
| CHYB | 预测:无性生殖类似MADS-box蛋白AGL27亚型X5 Predicted:Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL27 isoform X5 | AGL27 | XP_016551041.1 | 2 | AT1G77080 |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 78 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY2 | 预测:转录因子bHLH48亚型X2 Predicted:Transcription factor bHLH48 isoform X2 | bHLH48 | XP_016543852.1 | 16 | AT2G42300 |
| CRTISO | 假定的轴向调节YABBY 2亚型X1 Putative axial regulator YABBY 2 isoform X1 | YABBY2 | XP_016548878.1 | 2 | AT2G26580 |
| 同源框亮氨酸拉链蛋白HOX5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein HOX5 | HOX5 | KAF3660217.1 | 3 | AT5G65310 |
表2 目标基因启动子与候选转录因子结合位点分析
Table 2 Binding site analysis of the promoter of target genes and the candidate transcription
| 目标 基因 Target gene | 候选转录因子 Transcription factor candidate | 缩写 Abbreviation | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 启动子基序 结合位点 Promoter motif union sites | 拟南芥同源基因 Arabidopsis locus name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCS | 预测:核转录因子Y亚基A-3-like亚型X1 Predicted:Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit A-3-like isoform X1 | NF-YA3 | XP_016562508.1 | 93 | AT1G72830 |
| 含NAC结构域的蛋白2 -like NAC domain-containing protein 2-like | NAC2 | XP_016569664.1 | 1 | AT3G15510 | |
| SEPALLATA-like MADS-box蛋白3 SEPALLATA-like MADS-box protein 3 | SEP3 | AYA60475.1 | 12 | AT1G24260 | |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 44 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY | 预测:MADS-box蛋白CMB -like Predicted:MADS-box protein CMB1-like | CMB1 | XP_016547230.1 | 1 | AT2G03710 |
| NCED1 | 三螺旋转录因子GT-3b Trihelix transcription factor GT-3b | GT-3B | XP_016542034.1 | 45 | AT5G01380 |
| CHYB | 预测:无性生殖类似MADS-box蛋白AGL27亚型X5 Predicted:Agamous-like MADS-box protein AGL27 isoform X5 | AGL27 | XP_016551041.1 | 2 | AT1G77080 |
| 预测:GATA转录因子26亚型X1 Predicted:GATA transcription factor 26 isoform X1 | GATA26 | XP_016575075.1 | 78 | AT4G17570 | |
| PSY2 | 预测:转录因子bHLH48亚型X2 Predicted:Transcription factor bHLH48 isoform X2 | bHLH48 | XP_016543852.1 | 16 | AT2G42300 |
| CRTISO | 假定的轴向调节YABBY 2亚型X1 Putative axial regulator YABBY 2 isoform X1 | YABBY2 | XP_016548878.1 | 2 | AT2G26580 |
| 同源框亮氨酸拉链蛋白HOX5 Homeobox-leucine zipper protein HOX5 | HOX5 | KAF3660217.1 | 3 | AT5G65310 |

图10 辣椒果实4个发育时期19个基因的qRT-PCR和RNA-seq分析 *和**分别表示相对表达量在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Fig. 10 RT-qPCR and RNA-seq analysis of 19 genes at the four stages of chili pepper fruits * and ** mean significantly different in relative expression at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability level,respectively.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
pmid: 7259770 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3317 pmid: 25751142 |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/s0031-9422(01)00175-3 pmid: 11524116 |
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0410-2 pmid: 31086351 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.09.060 pmid: 23692768 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms140919025 pmid: 24065101 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.122127 pmid: 24858934 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
pmid: 9526511 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1187 |
|
雷建军, 朱张生, 陈长明, 陈国菊, 曹必好, 雷伶刚, 郑婕, 吴昊, 肖艳辉, 邱正坤, 颜爽爽. 2023. 辣椒红色素及其生物合成的分子机理研究进展. 园艺学报, 50 (3):669-684.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1187 |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04064.x pmid: 19891701 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1039/c0np00036a pmid: 21321752 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.1038/nbt.3122 pmid: 25690850 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04863.x pmid: 22111515 |
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.007 pmid: 25578273 |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
pmid: 16701678 |
| [54] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.09.001 pmid: 23043987 |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1068181 pmid: 11951045 |
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.03.016 pmid: 21514607 |
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [1] | 赵佳莹, 曾周婷, 岑欣颖, 施姣淇, 李效贤, 沈晓霞, 俞振明, . 铁皮石斛CCO基因家族鉴定及其在花发育中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [2] | 李怡斐, 杨小苗, 王春萍, 段敏杰, 黄启中, 黄任中, 张世才. 加工型辣椒新品种‘艳椒465’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2223-2224. |
| [3] | 李洁, 武超, 贾祥堑, 王娟. ‘壶瓶枣’果皮着色物质及其相关基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1728-1742. |
| [4] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [5] | 石凤岩, 王治丹, 张 曦, 王秀雪, 邹春蕾, . 辣椒疫病抗性机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1665-1682. |
| [6] | 赵泽阳, 周雨晴, 林德书, 任慧波, . 花瓣锥形表皮细胞形态建成研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1695-1706. |
| [7] | 张 茹, 陈灵芝, 王兰兰. 辣椒新品种‘陇椒13号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1709-1710. |
| [8] | 邓淑芳, 刘倩, 刘玲, 陈鸥, 王文军, 曾凯芳, 邓丽莉. 蜜橘CcHY5的克隆及其对果实转色功能的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 939-955. |
| [9] | 姚丰平, 王衍彬, 秦玉川, 王丽玲. 不同干燥处理的树参叶黄酮类成分的非靶向代谢组学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1069-1082. |
| [10] | 郭瑞, 陈高, 赵慧霞, 乾义柯, 兰红, 万何平, 陈禅友. 紫色辣椒新品种‘江大紫椒1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1175-1176. |
| [11] | 侯雪, 王姣姣, 张雯雯, 赵建龙, 茆振川. 辣椒乙烯反应抑制因子Cacl-6468的克隆及其抗根结线虫作用分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 761-772. |
| [12] | 刘艳艳, 丁颖, 刘兴华, 郑佳秋, 刘志钦. 辣椒CaSYT1的鉴定及其在疫霉侵染过程中的功能初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 533-544. |
| [13] | 付稳, 朱程红, 兰嘉仪, 李诗, 张正, 刘峰, 戴雄泽. 鲜食嫩果辣椒‘樟树港’果实品质特性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 616-630. |
| [14] | 张正海, 王永富, 吴华茂, 于海龙, 曹亚从, 冯锡刚, 王立浩. 辣椒重要性状遗传定位与候选基因研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 669-696. |
| [15] | 杨亮, 刘欢, 马燕勤, 李菊, 王海娥, 周玉洁, 龙海成, 苗明军, 李志, 常伟. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高番茄红素番茄新材料[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司