
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 423-438.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Ao, ZHENG Xu, WU Chengxu, NIE Ruining, JI Xinying, TANG Jiali, ZHANG Junpei*( )
)
Received:2024-09-30
Revised:2024-11-22
Online:2025-02-25
Published:2025-02-23
Contact:
ZHANG Junpei
LI Ao, ZHENG Xu, WU Chengxu, NIE Ruining, JI Xinying, TANG Jiali, ZHANG Junpei. The Effect of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Walnut Seedlings Under Salt Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 423-438.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0348

Fig. 1 AMF inoculation in walnut seedlings(a,b)and their phenotypes under various NaCl concentrations(c) NM:Inoculation with inactivated AMF inoculants,the control;F.m:Inoculation with Funneliformis mosseae;R.i:Inoculation with Rhizophagus irregularis. ** Indicates extremely significant differences between treatments,t-test,α = 0.01
| NaCl/ (mmol · L-1) | AMF接种 AMF inoculation | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/mm Ground diameter | 比叶面积/(cm2 · g-1) Specific leaf area | 叶片含水量/% Leaf water content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | NM F.m | 14.33 ± 0.98 abc 16.13 ± 0.96 a | 5.97 ± 0.19 ab 6.40 ± 0.38 a | 329.94 ± 7.41 bc 355.16 ± 8.16 a | 73.12 ± 0.64 a 73.03 ± 0.80 a |
| R.i | 16.25 ± 1.25 a | 6.45 ± 0.61 a | 350.28 ± 1.68 a | 73.03 ± 0.34 a | |
| 100 | NM F.m R.i | 14.63 ± 1.29 abc 16.08 ± 1.10 a 14.10 ± 1.21 abc | 5.70 ± 0.54 ab 6.45 ± 0.27 a 6.03 ± 0.20 ab | 319.88 ± 5.52 cd 336.81 ± 4.05 b 319.96 ± 2.35 cd | 71.11 ± 0.56 bc 71.97 ± 0.51 ab 71.97 ± 0.47 ab |
| 200 | NM F.m R.i | 14.25 ± 1.60 abc 14.55 ± 1.43 abc 15.65 ± 0.93 ab | 5.16 ± 0.13 b 5.75 ± 0.84 ab 5.48 ± 0.22 ab | 289.68 ± 15.94 f 309.98 ± 2.23 de 303.88 ± 5.46 e | 70.03 ± 0.26 cd 70.84 ± 0.90 bcd 69.61 ± 1.30 d |
| 300 | NM F.m R.i | 13.63 ± 0.96 bc 15.13 ± 1.01 abc 13.25 ± 1.15 c | 5.84 ± 1.01 ab 5.57 ± 0.41 ab 5.56 ± 0.29 ab | 251.24 ± 8.10 h 299.84 ± 4.05 ef 266.31 ± 10.46 g | 68.02 ± 1.25 e 70.31 ± 0.49 cd 69.53 ± 0.41 d |
Table 1 Effect of AMF on the growth of walnut seedlings under NaCl stress
| NaCl/ (mmol · L-1) | AMF接种 AMF inoculation | 株高/cm Plant height | 地径/mm Ground diameter | 比叶面积/(cm2 · g-1) Specific leaf area | 叶片含水量/% Leaf water content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | NM F.m | 14.33 ± 0.98 abc 16.13 ± 0.96 a | 5.97 ± 0.19 ab 6.40 ± 0.38 a | 329.94 ± 7.41 bc 355.16 ± 8.16 a | 73.12 ± 0.64 a 73.03 ± 0.80 a |
| R.i | 16.25 ± 1.25 a | 6.45 ± 0.61 a | 350.28 ± 1.68 a | 73.03 ± 0.34 a | |
| 100 | NM F.m R.i | 14.63 ± 1.29 abc 16.08 ± 1.10 a 14.10 ± 1.21 abc | 5.70 ± 0.54 ab 6.45 ± 0.27 a 6.03 ± 0.20 ab | 319.88 ± 5.52 cd 336.81 ± 4.05 b 319.96 ± 2.35 cd | 71.11 ± 0.56 bc 71.97 ± 0.51 ab 71.97 ± 0.47 ab |
| 200 | NM F.m R.i | 14.25 ± 1.60 abc 14.55 ± 1.43 abc 15.65 ± 0.93 ab | 5.16 ± 0.13 b 5.75 ± 0.84 ab 5.48 ± 0.22 ab | 289.68 ± 15.94 f 309.98 ± 2.23 de 303.88 ± 5.46 e | 70.03 ± 0.26 cd 70.84 ± 0.90 bcd 69.61 ± 1.30 d |
| 300 | NM F.m R.i | 13.63 ± 0.96 bc 15.13 ± 1.01 abc 13.25 ± 1.15 c | 5.84 ± 1.01 ab 5.57 ± 0.41 ab 5.56 ± 0.29 ab | 251.24 ± 8.10 h 299.84 ± 4.05 ef 266.31 ± 10.46 g | 68.02 ± 1.25 e 70.31 ± 0.49 cd 69.53 ± 0.41 d |
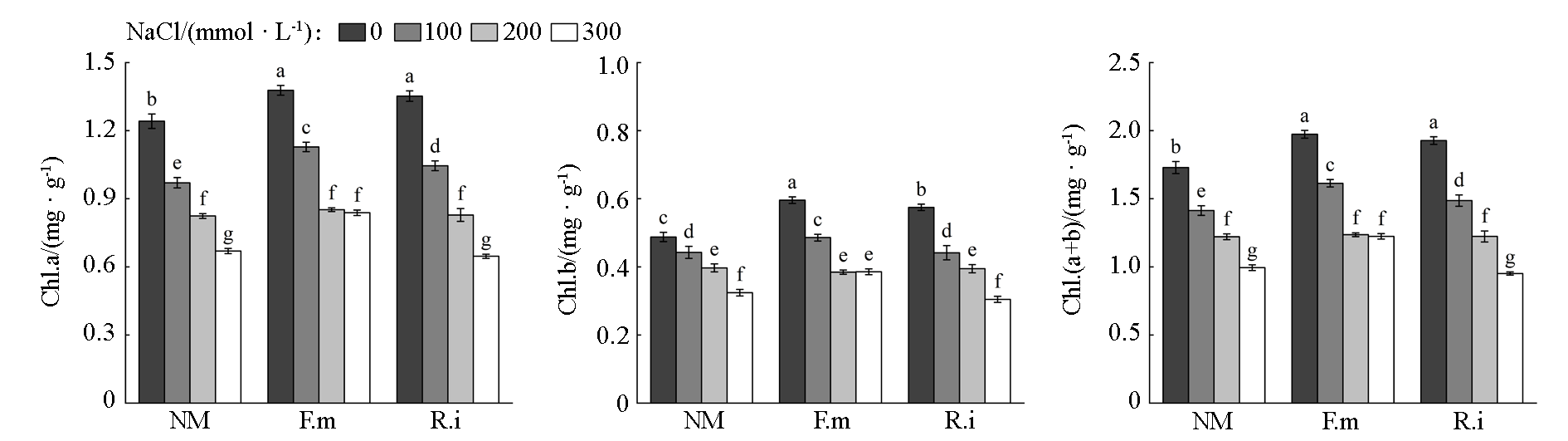
Fig. 2 Changes in chlorophyll content in leaves of walnut seedlings under AMF inoculation and NaCl stress NM:Inoculation with inactivated AMF inoculants,the control;F.m:Inoculation with Funneliformis mosseae;R.i:Inoculation with Rhizophagus irregularis. Different small letters indicate a significant difference between the treatments at the P < 0.05 level. The same below
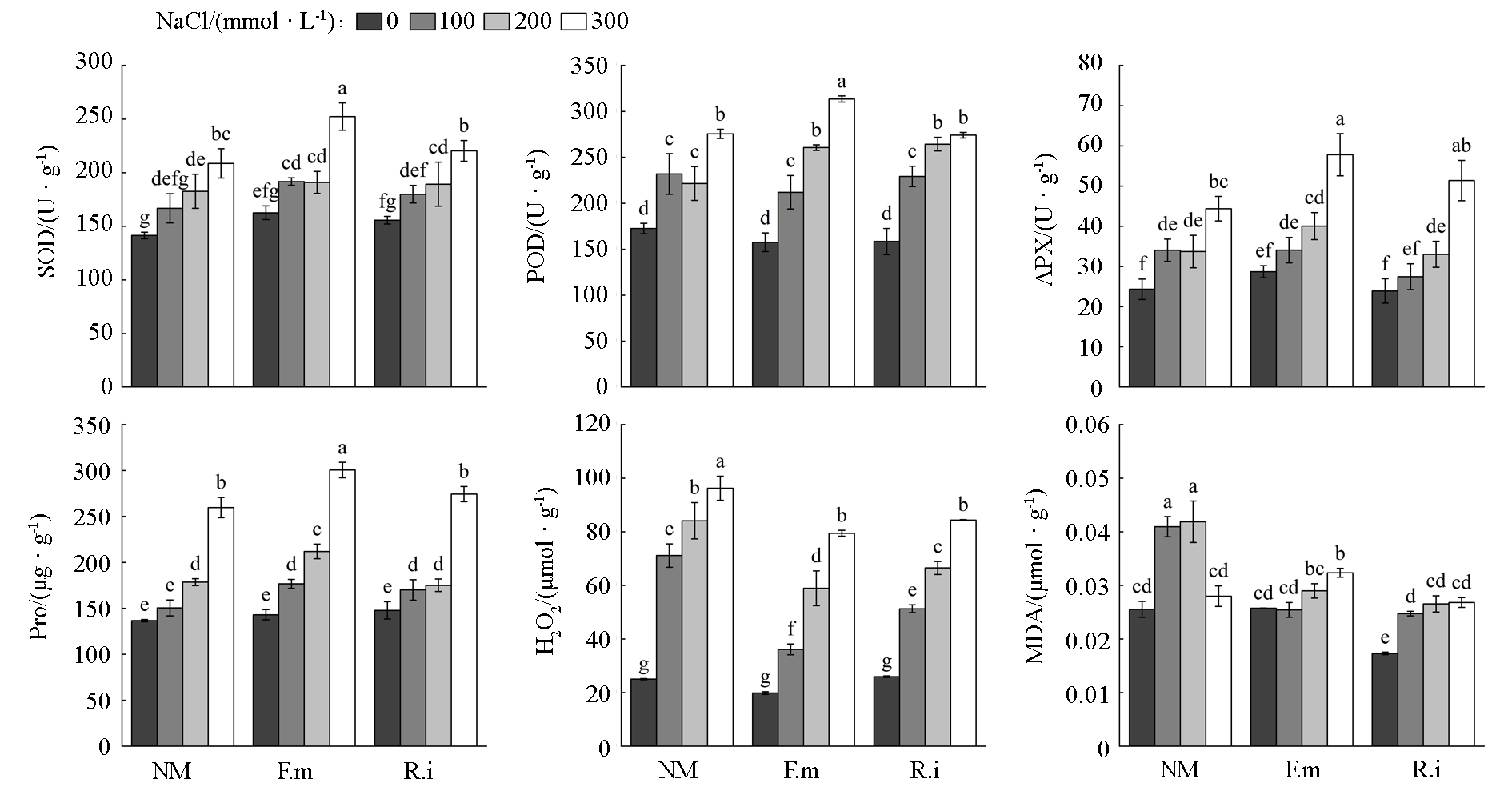
Fig. 8 Changes of antioxidant enzymes,proline,hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde contents in leaves of walnut seedlings under AMF inoculation and NaCl stress
| 指标Index | NaCl | AMF | NaCl × AMF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height | 2.798 | 2.023 | 1.68 |
| 地径Ground diameter | 4.606 | 0.632 | 0.641 |
| 比叶面积Specific leaf area | 143.643*** | 34.491*** | 3.846** |
| 叶片含水量Leaf water content | 51.562*** | 7.503** | 2.819* |
| Chl. a | 1129.989*** | 84.332*** | 12.145*** |
| Chl. b | 523.973*** | 53.622*** | 20.335*** |
| Chl.(a+b) | 988.983*** | 80.524*** | 14.573*** |
| Pn | 840.754*** | 73.736*** | 9.115*** |
| Gs | 1156.689*** | 109.228*** | 4.599** |
| Tr | 387.678*** | 28.262*** | 1.289 |
| Ci | 64.955*** | 1.246 | 1.799 |
| ABS/RC | 7.164*** | 1.565 | 0.965 |
| TRo/RC | 6.997** | 0.836 | 0.712 |
| ETo/RC | 3.296* | 4.882* | 0.855 |
| DIo/RC | 5.196** | 3.395* | 1.398 |
| Fv/Fm | 3.07* | 4.687* | 1.419 |
| PIABS | 4.531* | 12.736*** | 1.294 |
| 气孔长度Stomatal length | 4.083* | 7.873** | 5.275*** |
| 气孔宽度Stomatal width | 12.215*** | 6.167** | 1.657 |
| 气孔长宽比Stomatal length-width ratio | 10.935*** | 1.286 | 0.477 |
| 气孔密度Stomatal density | 7.546*** | 3.536* | 10.528*** |
| SOD | 43.455*** | 9.317*** | 1.033 |
| POD | 114.64*** | 1.555 | 5.271*** |
| APX | 58.359*** | 8.236** | 1.729 |
| Pro | 347.759*** | 23.912*** | 3.663** |
| H2O2 | 369.106*** | 72.425*** | 7.615*** |
| MDA | 39.018*** | 79.852*** | 19.385*** |
| IAA | 6.973** | 196.747*** | 5.551*** |
| ABA | 41.951*** | 960.551*** | 41.726*** |
| GA3 | 44.27*** | 585.264*** | 35.27*** |
| ZR | 12.673*** | 113.775*** | 0.956 |
Table 2 Two-way ANOVA F values with AMF for various physiological indicator under NaCl stress
| 指标Index | NaCl | AMF | NaCl × AMF |
|---|---|---|---|
| 株高Plant height | 2.798 | 2.023 | 1.68 |
| 地径Ground diameter | 4.606 | 0.632 | 0.641 |
| 比叶面积Specific leaf area | 143.643*** | 34.491*** | 3.846** |
| 叶片含水量Leaf water content | 51.562*** | 7.503** | 2.819* |
| Chl. a | 1129.989*** | 84.332*** | 12.145*** |
| Chl. b | 523.973*** | 53.622*** | 20.335*** |
| Chl.(a+b) | 988.983*** | 80.524*** | 14.573*** |
| Pn | 840.754*** | 73.736*** | 9.115*** |
| Gs | 1156.689*** | 109.228*** | 4.599** |
| Tr | 387.678*** | 28.262*** | 1.289 |
| Ci | 64.955*** | 1.246 | 1.799 |
| ABS/RC | 7.164*** | 1.565 | 0.965 |
| TRo/RC | 6.997** | 0.836 | 0.712 |
| ETo/RC | 3.296* | 4.882* | 0.855 |
| DIo/RC | 5.196** | 3.395* | 1.398 |
| Fv/Fm | 3.07* | 4.687* | 1.419 |
| PIABS | 4.531* | 12.736*** | 1.294 |
| 气孔长度Stomatal length | 4.083* | 7.873** | 5.275*** |
| 气孔宽度Stomatal width | 12.215*** | 6.167** | 1.657 |
| 气孔长宽比Stomatal length-width ratio | 10.935*** | 1.286 | 0.477 |
| 气孔密度Stomatal density | 7.546*** | 3.536* | 10.528*** |
| SOD | 43.455*** | 9.317*** | 1.033 |
| POD | 114.64*** | 1.555 | 5.271*** |
| APX | 58.359*** | 8.236** | 1.729 |
| Pro | 347.759*** | 23.912*** | 3.663** |
| H2O2 | 369.106*** | 72.425*** | 7.615*** |
| MDA | 39.018*** | 79.852*** | 19.385*** |
| IAA | 6.973** | 196.747*** | 5.551*** |
| ABA | 41.951*** | 960.551*** | 41.726*** |
| GA3 | 44.27*** | 585.264*** | 35.27*** |
| ZR | 12.673*** | 113.775*** | 0.956 |

Fig. 10 Principal component analysis(A,B) and cluster heatmap(C) of leaves of walnut seedlings under AMF inoculation and NaCl stress SL:Stomatal length;D:Ground diameter:SW:Stomatal width;SLA:Specific leaf area;LWC:Leaf water content;H:Plant height;SD:Stomatal density;SL/SW:Stomatal length-width ratio
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
曹明奡, 张菲, 黄光明, 刘瑞成, 刘利平, 吴强盛, 徐永杰. 2023. 丛枝菌根真菌对低磷胁迫下核桃幼苗根系磷吸收的影响及机制. 林业科学, 59 (12):117-124.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
陈晓楠, 伊力努尔 · 艾力, 高文礼, 马晓东. 2022. 盐胁迫下丛枝菌根真菌对疏叶骆驼刺幼苗生长和生理的影响. 草业科学, 39 (9):1763-1772.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
付海奇, 刘晓, 宋姝, 吕婉嘉, 杨永青. 2023. 次生代谢物调控植物抵抗盐碱胁迫的机制. 植物生理学报, 59 (4):727-740.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
葛诗蓓, 姜小春, 王羚羽, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 2020. 园艺植物丛枝菌根抗非生物胁迫的作用机制研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1752-1776.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
郝汉, 曹磊, 陈伟楠, 胡增辉, 冷平生. 2020. 盐胁迫对槲树(Quercus dentata)幼苗离子平衡及其生理生化特性的影响. 生态学报, 40 (19):6897-6904.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2010.05.1099 |
|
贺忠群, 李焕秀, 汤浩茹, 贺超兴, 张志斌, 王怀松. 2010. 丛枝菌根真菌对NaCl胁迫下番茄内源激素的影响. 核农学报, 24 (5):1099-1104.
doi: 10.11869/hnxb.2010.05.1099 |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04753-x pmid: 38262953 |
| [14] |
|
|
黄荣雁, 路程伟, 许嵘, 孙正轩, 房莉, 陈钦华, 马天意, 刘殿辉, 孟维珊, 王一顺, 饶欢, 刘俊辰. 2024. 盐碱胁迫对‘冬红’花楸生长、生理及光合特性的影响. 草地学报, 32 (2):480-488.
doi: 10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2024.02.015 |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 李敖, 郑旭, 王红霞, 张俊佩. 2024. 盐胁迫下不同基因型核桃实生幼苗生长及生理响应. 林业科学,(2):65-77.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
贾婷婷, 常伟, 范晓旭, 宋福强. 2018. 盐胁迫下AM真菌对沙枣苗木光合与叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 生态学报, 38 (4):1337-1347.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 16361781 |
|
李鹏民, 高辉远,
pmid: 16361781 |
|
| [20] |
|
|
李向彦. 2022. 三种水生植物对Na+盐和K+盐胁迫的生理生态响应研究[硕士论文]. 武汉: 武汉大学.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac239 pmid: 35604107 |
| [24] |
|
|
牛蛉磊. 2016. 核桃种子萌发及不同盐浓度对其生长特性的影响. 新疆农垦科技, 39 (12):19-24.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
商业绯, 李明, 丁博, 牛浩, 杨振宁, 陈小强, 曹高燚, 谢晓东. 2017. 生长素调控植物气孔发育的研究进展. 植物学报, 52 (2):235-240.
doi: 10.11983/CBB16099 |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.06.002 pmid: 16023886 |
| [28] |
|
|
王宝庆. 2021. 新疆早实核桃主要性状及分子基础研究[博士论文]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
王进. 2015. 丛枝菌根真菌对核桃幼苗接种效应研究[硕士论文]. 荆州: 长江大学.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
王炜, 母洪娜, 杨慧敏, 孙陶泽. 2024. 接种丛枝菌根真菌(AMF)对夏雪片莲生长状况和光合特性的影响. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), https://link.cnki.net/urlid/32.1161.S.20240408.0944.002.
|
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021410 |
|
吴雨涵, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 张永超. 2022. 干旱胁迫对燕麦幼苗叶片光合特性及活性氧清除系统的影响. 草业学报, 31 (10):75-86.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021410 |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
赵秀婷, 王延双, 段劼, 马履一, 何宝华, 贾忠奎, 桑子阳, 朱仲龙. 2021. 盐胁迫对红花玉兰嫁接苗生长和光合特性的影响. 林业科学, 57 (4):43-53.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [1] | LI Chaonan, LI Lu, GAO Danlei, QIAO Hongyong, YUAN Tao. Differences in Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Community in the Roots and Rhizosphere Soil of Paeonia ludlowii Between Original Site and Introduction Site [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 467-480. |
| [2] | ZHANG Songyan, DIE Pengxiang, SONG Mengting, LI Zhijian, ZHOU Jian. Effect of Overexpression of Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 Gene on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [3] | XIA Hongyi, LIU Qiao, PENG Jiaqing, WU Wei, GONG Linzhong. Effects of f-Shaped Tree Shape on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality in‘Shine Muscat’Grapevines with Rain-Shelter Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [4] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [5] | YANG Jiangshan, CHEN Yajuan, DAI Zibo, LI Dou, SHAO Zhang, JIN Xin, WANG Yuhang, WANG Chunheng. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality of‘Cabernet Gernischt’Grape [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2843-2856. |
| [6] | LU Jianzeng, ZHOU Liyan, HUANG Xinyi, WU Fengzhi, GAO Danmei. Effects of Carbon Pool Strength on Plant Growth and Potassium Uptake of Tomato Intercropped with Potato-Onion [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2620-2632. |
| [7] | CHEN Xin, WU Xiaolong, LIU Shengrui, HU Xianchun, LIU Chunyan. Effects of AMF on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expressions of Tea Plants Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2358-2370. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chen, LI Mengjie, YANG Xiaoxue, WANG Meiyun, XIAO Dong, WANG Jianjun, HOU Xilin, HU Jun, LIU Tongkun. The Creation and Study on Characteristics of New Material of Autotetraploid Purple Tsai-tai [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1419-1428. |
| [9] | LIU Hui, HUANG Ting, TAO Jianping, ZHANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Rongrong, SONG Liuxia, ZHAO Tongmin, YOU Xiong, XIONG Aisheng. Analysis of Circadian Clock Genes SlLNK1,SlEID1,and SlELF3 Response to Photoperiod in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2079-2090. |
| [10] | XING Wenxi, WANG Zeliang, WU Ningzi, LI Pijun, and WANG Jing. An Improved Walnut Cultivar‘Yanyuanzao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 33-34. |
| [11] | SONG Fang, LI Zixuan, WANG Ce, WANG Zhijing, HE Ligang, JIANG Yingchun, WU Liming, BAI Fuxi. Cloning and Function Analysis of Mycorrhizal Signaling Receptor Protein Lysin Motif Receptor-like Kinases 2 Gene(LYK2)in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 281-292. |
| [12] | YANG Ni, WAN Qiwen, LI Yimin, HAN Miaohua, TENG Ruimin, LIU Jiexia, ZHUANG Jing. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expression of Key Enzymes Under Salt Stress in Tea Plant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 378-394. |
| [13] | WANG Cuixiang, LIANG Yan, HAN Chuanming, SUN Chao, MENG Xiaoye, TAN Shuling, ZHANG Yanxing, CHEN Aichang, and CUI Peng. A New Juglans regia Cultivar‘Lumian 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(S2): 2801-2802. |
| [14] | YU Shangqi, ZHANG Rui, GUO Zhongzhong, SONG Yan, FU Jiazhi, WU Pengyu, MA Zhihao. Dynamic Changes of Auxin and Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes in Walnut Endocarp During Hardening [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(3): 487-504. |
| [15] | XU Haifeng, CHEN Xin, ZHANG Shigang, XIANG Kun, ZHANG Meiyong, XU Ying, WANG Guifang. Change of Fatty Acid During Storage Period of‘Qiuxiang’Walnut Based on Metabolomics Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(11): 2161-2170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd