
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (9): 2155-2167.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0690
• Cultivation · Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Songyan1, DIE Pengxiang1, SONG Mengting1, LI Zhijian1, ZHOU Jian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-11-26
Revised:2024-04-01
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-09-19
Contact:
ZHOU Jian
ZHANG Songyan, DIE Pengxiang, SONG Mengting, LI Zhijian, ZHOU Jian. Effect of Overexpression of Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 Gene on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Nicotiana tabacum[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0690
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 转基因阳性苗鉴定Identification of transgenic positive seedlings | OE-RpACBP3 | F:GAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGGAGCTTGTAACTGCAAGTG R:CGATCGGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCATTTCTTTACATTGTTCTC |
| qRT-PCR | NtActin | F:ACCTCTATGGCAACATTGTGCTCAG R:CTGGGAGCCAAAGCGGTGATT |
| qRpACBP3 | F:ACCGGTACACGGTTCAAACA R:GACAATGTCTGGTTTCGCCG |
Table 1 The primers used in this experiment
| 用途 Function | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 转基因阳性苗鉴定Identification of transgenic positive seedlings | OE-RpACBP3 | F:GAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGGAGCTTGTAACTGCAAGTG R:CGATCGGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCATTTCTTTACATTGTTCTC |
| qRT-PCR | NtActin | F:ACCTCTATGGCAACATTGTGCTCAG R:CTGGGAGCCAAAGCGGTGATT |
| qRpACBP3 | F:ACCGGTACACGGTTCAAACA R:GACAATGTCTGGTTTCGCCG |
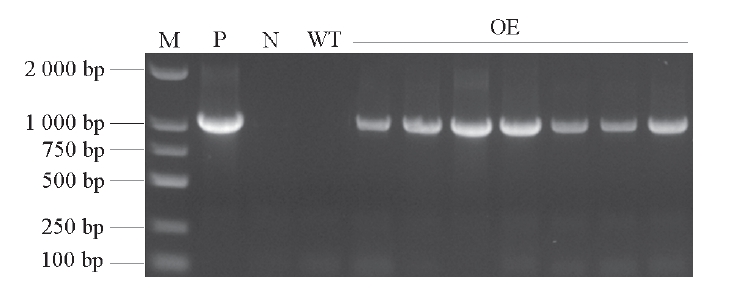
Fig. 1 PCR assay of Nicotiana tabacum-transformed Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 strains M:DNA marker DL2000;P:Positive plasmid control;N:Negative control;WT:Wild type plants;OE:Positive lines. The same below.

Fig. 2 qRT-PCR detection of Nicotiana tabacum trans-Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 strains(OE)and wild type(WT) Different lowercase letters represent the significant difference between the lines(P < 0.05). The same below.
| 株系 Lines | 长度/μm Length | 宽度/μm Width | 面积/μm2 Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 17.87 ± 1.10 b | 8.42 ± 0.65 bc | 92.18 ± 13.78 c |
| OE1 | 19.27 ± 1.15 ab | 8.29 ± 0.44 c | 129.73 ± 9.12 abc |
| OE3 | 19.36 ± 0.18 ab | 8.31 ± 0.22 c | 118.34 ± 6.46 bc |
| OE5 | 21.35 ± 0.44 a | 8.45 ± 0.20 bc | 144.81 ± 10.84 ab |
| OE6 | 19.76 ± 0.38 ab | 8.96 ± 0.55 abc | 143.18 ± 6.47 ab |
| OE9 | 21.29 ± 0.56 a | 9.79 ± 0.30 ab | 159.23 ± 15.25 ab |
| OE10 | 21.80 ± 1.27 a | 10.33 ± 0.63 a | 175.04 ± 29.95 a |
| OE12 | 20.30 ± 0.74 ab | 9.70 ± 0.19 abc | 143.35 ± 6.35 ab |
Table 2 The in stomatal morphology of Nicotiana tabacum turned Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 strain(OE)and wild type(WT)
| 株系 Lines | 长度/μm Length | 宽度/μm Width | 面积/μm2 Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 17.87 ± 1.10 b | 8.42 ± 0.65 bc | 92.18 ± 13.78 c |
| OE1 | 19.27 ± 1.15 ab | 8.29 ± 0.44 c | 129.73 ± 9.12 abc |
| OE3 | 19.36 ± 0.18 ab | 8.31 ± 0.22 c | 118.34 ± 6.46 bc |
| OE5 | 21.35 ± 0.44 a | 8.45 ± 0.20 bc | 144.81 ± 10.84 ab |
| OE6 | 19.76 ± 0.38 ab | 8.96 ± 0.55 abc | 143.18 ± 6.47 ab |
| OE9 | 21.29 ± 0.56 a | 9.79 ± 0.30 ab | 159.23 ± 15.25 ab |
| OE10 | 21.80 ± 1.27 a | 10.33 ± 0.63 a | 175.04 ± 29.95 a |
| OE12 | 20.30 ± 0.74 ab | 9.70 ± 0.19 abc | 143.35 ± 6.35 ab |
| 指标 Index | 第1主成分 Prin 1 | 第2主成分 Prin 2 | 第3主成分 Prin 3 | 第4主成分 Prin 4 | 第5主成分 Prin 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate | 43.56 | 24.27 | 10.72 | 6.88 | 4.48 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate | 43.56 | 67.83 | 78.55 | 85.43 | 89.91 |
Table 3 Principal component analysis of indicators in Nicotiana tabacum transgenic Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 strains %
| 指标 Index | 第1主成分 Prin 1 | 第2主成分 Prin 2 | 第3主成分 Prin 3 | 第4主成分 Prin 4 | 第5主成分 Prin 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方差贡献率Variance contribution rate | 43.56 | 24.27 | 10.72 | 6.88 | 4.48 |
| 累计贡献率Cumulative contribution rate | 43.56 | 67.83 | 78.55 | 85.43 | 89.91 |
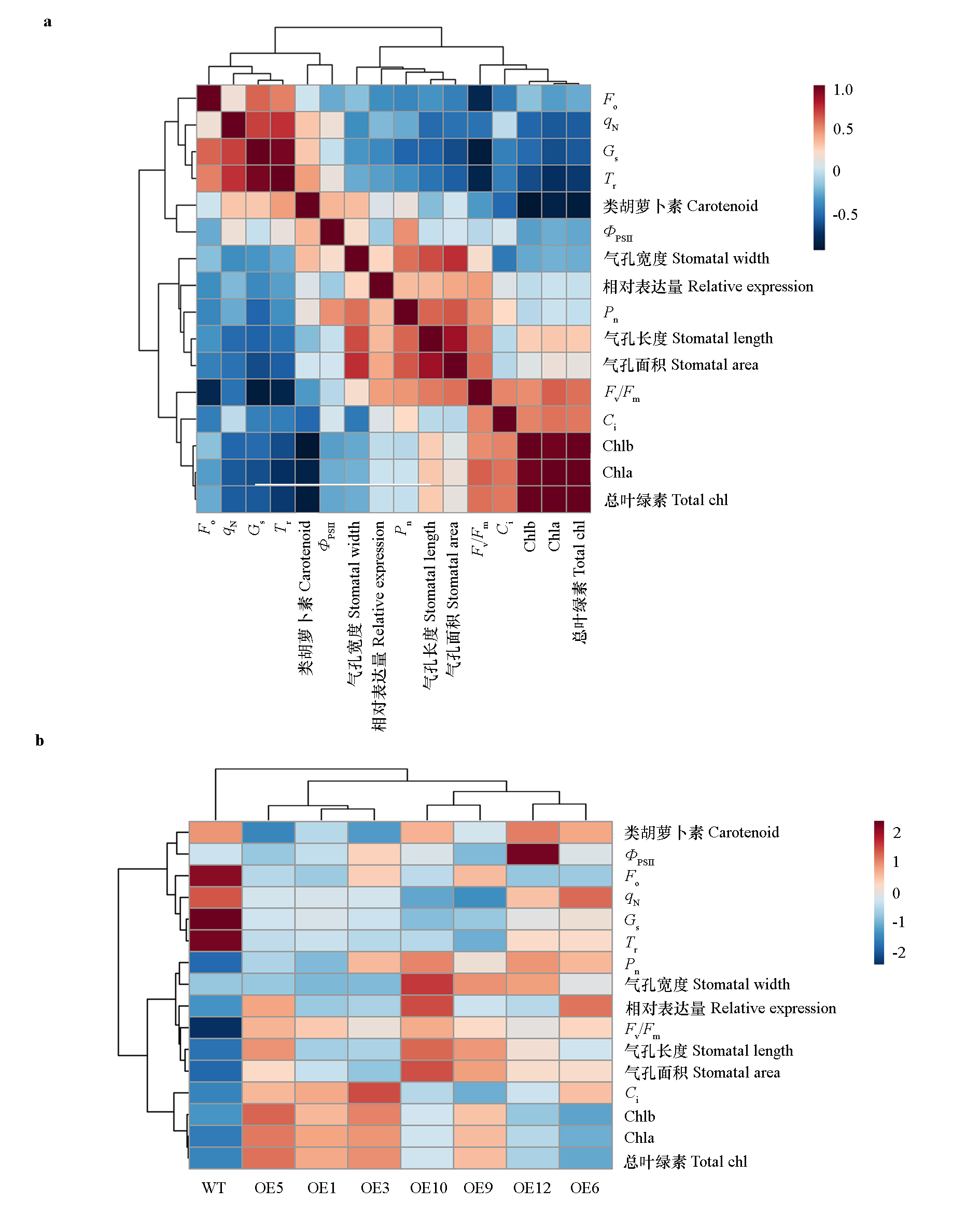
Fig. 7 Correlation(a)and cluster heat map(b)of indicators in Nicotiana tabacum transgenic Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 strains In figure a,red represents positively correlated,and blue represents negatively correlated. The darker the color,the larger the correlation.
| [41] |
|
|
余洪艳, 孙梅, 陈弘毅, 刘振亚, 杨航美. 2023. 滇西北湖滨带植物水葱的功能适应性. 东北林业大学学报, 51 (1):45-53,60.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
张晓静. 2022. 铅胁迫下刺槐组培苗生理特性及RpACBP3基因转化研究[硕士论文]. 新乡: 河南科技学院.
|
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
|
周建, 杨立峰, 郝峰鸽, 尤扬. 2009. 低温胁迫对广玉兰幼苗光合及叶绿素荧光特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 29 (1):136-142.
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
周远远. 2021. ZmACBPs家族的分子鉴定、表达及功能分析[硕士论文]. 济南: 济南大学.
|
|
| [1] |
|
|
柏素花, 祝军, 戴洪义. 2012. 苹果酰基辅酶A结合蛋白2编码基因MdACBP2的克隆和表达分析. 园艺学报, 39 (10):1893-1902.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
宝音满达, 李兆佳, 刘晓东, 王旭, 邓文剑, 周光益, 皮志豪. 2023. 不同种源光皮树叶绿素荧光特性及其光合响应能力. 经济林研究, 41 (2):205-213.
|
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
曹雄军, 韩佳宇, 成果, 王博, 马广仁, 林玲, 谭宗琨, 黄秋秘, 陈潇, 陈孚仪, 时晓芳, 盘丰平, 白先进. 2023. 光照时数及强度对‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄产量形成的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1739-1746.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
桂慧颖, 方发之, 麦有专, 吴二焕, 张晓凤. 2022. 修枝强度对坡垒幼树生长和生理特性的影响及综合评价. 西部林业科学, 51 (6):79-85,100.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
pmid: 8075407 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
胡选萍, 吉成均, 安丽华. 2015. 青藏高原草地双子叶植物叶片的气孔特征研究. 西北植物学报, 35 (7):1356-1366.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021154 |
|
金祎婷, 刘文辉, 刘凯强, 梁国玲, 贾志锋. 2022. 全生育期干旱胁迫‘青燕1号’燕麦叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 草业学报, 31 (6):112-126.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2021154 |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
李冬林, 王火, 江浩, 祝亚云, 金雅琴, 崔梦凡. 2019. 遮光对香果树幼苗光合特性及叶片解剖结构的影响. 生态学报, 39 (24):9089-9100.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
李亚亮, 刘玲, 李长爱, 王慧, 刘海涛, 缪国鹏. 2023. 10种蔷薇科绿化植物固碳释氧特性及叶片气孔微形态分析. 中南林业科技大学学报, 43 (8):102-112.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
|
刘宝, 陈存及, 林达定, 林思祖. 2014. 21个闽楠种源叶片光合色素含量及叶绿素荧光参数分析. 江西农业大学学报, 36 (1):115-121.
|
|
| [23] |
|
|
刘耀权, 张晓洋, 白斌. 2023. 不同生态型小麦品种叶片气孔密度及形态差异分析. 西北农业学报, 32 (5):677-684.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
倪鑫. 2021. 星星草PutACBP基因家族鉴定及功能分析[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
蒲璇, 王凌晖. 2023. 施氮水平对4个景观树种光合特性及抗旱性影响. 西部林业科学, 52 (5):146-154.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
乔建磊, 于海业, 宋述尧, 肖英奎, 张蕾, 张艳平. 2013. 氮素形态对马铃薯叶片光合色素及其荧光特性的影响. 中国农业大学学报, 18 (3):39-44.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01577 |
|
秦朋飞, 尚小光, 宋健, 郭旺珍. 2016. 棉花酰基辅酶A结合蛋白(ACBP)家族基因的发掘及在非生物胁迫抗性中的功能鉴定. 作物学报, 42 (11):1577-1591.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2016.01577 |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
|
孙娅楠, 赵杨, 赵渊祥, 曹海, 龙建磊. 2021. 棕榈幼苗光合和叶绿素荧光对干旱胁迫及复水的响应. 中南林业科技大学学报, 41 (9):45-52.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
文静, 胡红玲, 陈洪, 刘喜建, 代大川, 张如义. 2022. 巨桉幼树对镉胁迫的光合生理响应. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 50 (3):30-39.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
许珊珊, 唐银, 钟明慧, 李玲燕, 伍丽华, 林开敏, 曹光球, 叶义全. 2022. 遮阴对粗肋草生长、光合特性和养分含量的影响. 草业科学, 39 (10):2083-2094.
|
|
| [38] |
|
|
薛芳婷, 刘新亮, 刘玉华, 余鹏飞, 郁万文. 2023. 芽变黄叶银杏光合和叶绿素荧光特性. 西部林业科学, 52 (4):129-136.
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
姚新转, 吕立堂, 赵德刚. 2016. 转拟南芥BAS1基因提高烟草光合特性. 山地农业生物学报, 35 (3):30-34,62.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [1] | XIA Hongyi, LIU Qiao, PENG Jiaqing, WU Wei, GONG Linzhong. Effects of f-Shaped Tree Shape on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality in‘Shine Muscat’Grapevines with Rain-Shelter Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [2] | YANG Jiangshan, CHEN Yajuan, DAI Zibo, LI Dou, SHAO Zhang, JIN Xin, WANG Yuhang, WANG Chunheng. Effects of Potassium Fulvic Acid on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality of‘Cabernet Gernischt’Grape [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2843-2856. |
| [3] | CHEN Xin, WU Xiaolong, LIU Shengrui, HU Xianchun, LIU Chunyan. Effects of AMF on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expressions of Tea Plants Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(10): 2358-2370. |
| [4] | ZHANG Chen, LI Mengjie, YANG Xiaoxue, WANG Meiyun, XIAO Dong, WANG Jianjun, HOU Xilin, HU Jun, LIU Tongkun. The Creation and Study on Characteristics of New Material of Autotetraploid Purple Tsai-tai [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1419-1428. |
| [5] | LI Yuting, REN Lihui, WANG Yuan, ZHOU Aiying, YANG Wei, HUANG Jian. Photosynthetic Characteristics of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’Under Protected Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 647-656. |
| [6] | LIU Hui, HUANG Ting, TAO Jianping, ZHANG Jiaqi, ZHANG Rongrong, SONG Liuxia, ZHAO Tongmin, YOU Xiong, XIONG Aisheng. Analysis of Circadian Clock Genes SlLNK1,SlEID1,and SlELF3 Response to Photoperiod in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(10): 2079-2090. |
| [7] | PENG Yi, LI Yuanhui, YANG Rui, ZHANG Ziyi, LI Yanan, HAN Yunhao, ZHAO Wenchao, WANG Shaohui. The Jasmonic Acid Synthesis Gene LoxD Participates in the Regulation of Tomato Drought Resistance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 319-331. |
| [8] | YANG Ni, WAN Qiwen, LI Yimin, HAN Miaohua, TENG Ruimin, LIU Jiexia, ZHUANG Jing. Effects of Exogenous Spermidine on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Gene Expression of Key Enzymes Under Salt Stress in Tea Plant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 378-394. |
| [9] | ZHONG Zaofa, ZHANG Lijuan, GAO Sisi, PENG Ting. Leaf Cytological Characteristics and Resistance Comparison of Four Citrus Rootstocks Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1579-1588. |
| [10] | LIANG Qiaolan*,WEI Liexin,XU Bingliang,ZHANG Shuwu,and HAN Liang. Effect of the Trichoderma atroviride T2 Proteinaceous TraT2A Induction Treatment on Photoresponsive and Fluorescent Characteristics of Lily Leaves inoculated Botrytis cinerea [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(4): 769-778. |
| [11] | HU Shu,AN Yuyan,and WANG Liangju*. Ethylene is Involved in the Regulation of Stomatal Movement by ALA-ABA/dark in Apple Leaves [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(3): 409-420. |
| [12] | FANG Xia1,BAI Zhiliang1,ZHOU Shengcai2,ZHANG Lizhen2,WU Qiang 2,ZHANG Junhong1,and TONG Zaikang1,*. The Photosynthetic Characteristics of Phoebe zhennan f. elliptical and P. zhennan f. oblong [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(5): 964-974. |
| [13] | ZHOU Gaofeng,LI Bixian,FU Yanling,GUAN Guan,YAO Fengxian,and LIU Guidong*. Effects of Iron,Manganese and Zinc Deficiency on the Symptom,Photosynthetic Characteristics and Nutrient Status of‘Nanfeng’Tangerine [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(4): 691-700. |
| [14] | HU Jian,AN Yuyan,CAI Changyu,HE Shasha,and WANG Liangju*. Cytoplasmic pH is Involved in 5-aminolevulinic Acid(ALA)-induced Stomatal Opening in Apple Leaves [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(10): 1869-1881. |
| [15] | XIONG Lijun,AN Yuyan,and WANG Liangju*. The Role of Microtubule Skeleton and PP1/PP2A Protein Phosphatase in ALA-ABA Regulating Stomatal Movement in Apple Leaves [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(11): 2073-2088. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd