
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2625-2641.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0833
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
BIAN Shuanling1, DENG Changrong1, FAN Luze2, WU Yanxun1, REN Yanjing1,3,*( )
)
Received:2025-03-18
Revised:2025-06-16
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-10-28
Contact:
REN Yanjing
BIAN Shuanling, DENG Changrong, FAN Luze, WU Yanxun, REN Yanjing. Construction of Yeast Library and Identification of the BrrCDPK Gene Family of PSY Potential Interacting Proteins in Turnip[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2625-2641.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0833
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| CDPK8-F | ATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| CDPK8-R | TCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGBKT7-CDPK8-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| pGBKT7-CDPK8-R | CGCTGCAGGTCGACGGATCCTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGADT7-CDPK8-F | CCATGGAGGCCAGTGAATTCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| pGADT7-CDPK8-R | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGADT7-PSY-F | CCATGGAGGCCAGTGAATTCATGTCTTCTGTAGCAGTGTTA |
| pGADT7-PSY-R | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCTTAAGTTGTTCCTCTTGAACTT |
| G2-PSY-F | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| G2-PSY-R | CTACCCGGGAGCGGTACCCTCGAGTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| G4-CDPK8-F | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCATGTCTTCTGTAGCAGTGTTA |
| G4-CDPK8-R | GAGCTCCTACCCGGGAGCGGTACCTTAAGTTGTTCCTCTTGAACTT |
Table 1 Primer sequence of valivation PSY interacting proteins
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| CDPK8-F | ATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| CDPK8-R | TCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGBKT7-CDPK8-F | TGGCCATGGAGGCCGAATTCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| pGBKT7-CDPK8-R | CGCTGCAGGTCGACGGATCCTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGADT7-CDPK8-F | CCATGGAGGCCAGTGAATTCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| pGADT7-CDPK8-R | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| pGADT7-PSY-F | CCATGGAGGCCAGTGAATTCATGTCTTCTGTAGCAGTGTTA |
| pGADT7-PSY-R | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCTTAAGTTGTTCCTCTTGAACTT |
| G2-PSY-F | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCATGGGAGGTTGTACCTCCA |
| G2-PSY-R | CTACCCGGGAGCGGTACCCTCGAGTCACCGAGTTTTAGCTAAAGG |
| G4-CDPK8-F | AGCTCGAGCTCGATGGATCCATGTCTTCTGTAGCAGTGTTA |
| G4-CDPK8-R | GAGCTCCTACCCGGGAGCGGTACCTTAAGTTGTTCCTCTTGAACTT |
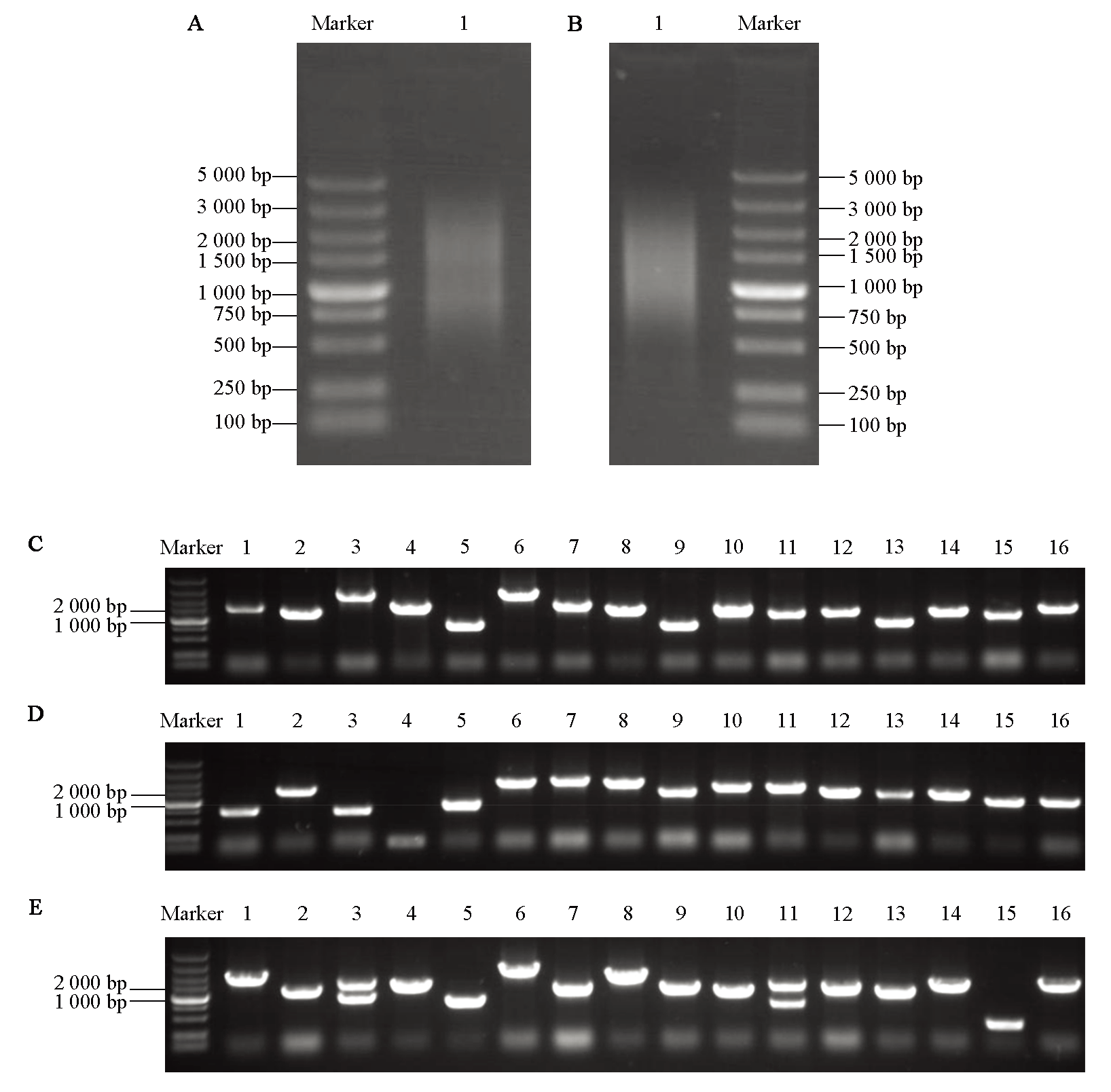
Fig. 1 Construction and identification of yeast cDNA library in turnip A:Electrophoresis detection map of cDNA synthesis;B:Electrophoresis detection map of cDNA homogenization;C:Identification of inserts in the primary library;D:Identification of inserts in the secondary library;E:Identification of inserts in the yeast two-hybrid library. 1-16:Electrophoretic detection results of colony PCR with different clones

Fig. 3 PSY interaction protein screening in turnip A:Covering effect of 1/100 dilution suspension on DDO plate;B:Covering effect of 1/1 000 dilution suspension on DDO plate;C,D:Front and back view of blue clonal plate screened by PSY on SD/-Ade/-His/-Leu/-Trp/X/A plates;E:Electrophoresis detection map of colonies that normally grow in QDO/X/A plates. 1-24:Electrophoretic detection results of colony PCR with different clones
| 序号No. | 样本名Sample name | 基因注释Gene annotation | 登录号GenBank | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1237-BD-1-1 1237-BD-4 1237-BD-10 | 白菜低分子量热休克蛋白(BcHSP17.6)mRNA,完整CDS Brassica rapa low molecular weight heat-shock protein(BcHSP17.6)mRNA,complete CDS | AF022217.1 | BraA06g020450.3C |
| C2 | 1237-BD-2 1237-BD-6 1237-BD-18 | 白菜核前体mRNA的调节域含蛋白1A(LOC103855848),转录本变体X2 Brassica rapa regulation of nuclear pre-mRNA domain-containing protein 1A(LOC103855848),transcript variant X2 | XM_009132891.3 | BraA03g004120.3C |
| C3 | 1237-BD-3-2 | 白菜嘌呤渗透酶1(LOC103838976),mRNA Brassica rapa purine permease 1(LOC103838976) | XM_009115443.3 | BraA09g036510.3C |
| C4 | 1237-BD-8-1 | 白菜Golgi SNAP受体复合体成员1-2(LOC103858165),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa Golgi SNAP receptor complex member 1-2(LOC103858165),transcript variant X2 | XM_018657146.2 | BraA03g023640.3C |
| C5 | 1237-BD-9 | 白菜translin(LOC103857651),转录变体X1 Brassica rapa translin(LOC103857651),transcript variant X1 | XM_009134861.3 | BraA03g019260.3C |
| C6 | 1237-BD-11 | 白菜17.6 kDⅠ类热休克蛋白2-like(LOC103843285) Brassica rapa 17.6 kD classⅠheat shock protein 2-like (LOC103843285) | XM_009119989.3 | BraA05g014680.3C |
| C7 | 1237-BD-12 | 甘蓝型油菜多细胞器RNA编辑因子1,mitochondrial(LOC106437506) Brassica napus multiple organellar RNA editing factor 1,mitochondrial(LOC106437506) | XM_013878402.3 | BraA03g049050.3C |
| C8 | 1237-BD-13 | 白菜RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基26的推定介质(LOC103833180) Brassica rapa putative mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranscription subunit 26(LOC103833180) | XM_033282535.1 | BraA10g022490.3C |
| C9 | 1237-BD-14-2 | 甘蓝型油菜CDPK相关激酶2(LOC106362920),转录变体X2 Brassica napus CDPK-related kinase 2(LOC106362920),transcript variant X2 | XM_022695160.2 | BraA01g033890.3C |
| C10 | 1237-BD-15-1 | 甘蓝型油菜formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase1,线粒体(LOC106402097),转录变体X4 Brassica napus formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase 1,mitochondrial(LOC106402097),transcript variant X4 | XM_048781377.1 | BraA06g041130.3C |
| C11 | 1237-BD-15-2 | 白菜 patellin-4(LOC103840314),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa patellin-4(LOC103840314),transcript variant X2 | XM_009116810.2 | BraA09g034310.3C |
| C12 | 1237-BD-17-1 | 甘蓝型油菜硫氧还蛋白O2,线粒体(LOC106352370),转录变体X1 Brassica napus thioredoxin O2,mitochondrial(LOC106352370),transcript variant X1 | XM_048739086.1 | BraA09g033920.3C |
| C13 | 1237-BD-17-2 | 白菜同源箱亮氨酸拉链蛋白ATHB-6(LOC103837893) Brassica rapa homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-6(LOC103837893) | XM_009114280.3 | BraA09g054870.3C |
| C14 | 1237-BD-20 | 白菜未鉴定的LOC103863008(LOC103863008),转录变体X3 Brassica rapa uncharacterized LOC103863008(LOC103863008),transcript variant X3 | XM_033289696.1 | BraA04g002940.3C |
| C15 | 1237-BD-21 | 白菜蛋白MET1,chloroplastic(LOC103829781) Brassica rapa protein MET1,chloroplastic(LOC103829781) | XM_009105478.3 | BraA05g016190.3C |
| C16 | 1237-BD-22 | 白菜转座酶蛋白At4g04430(LOC103847917),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa probable transposase-like protein At4g04430(LOC103847917),transcript variant X2 | XM_018655836.2 | 未检索到 Not retrieved |
| C17 | 1237-BD-23 | 甘蓝型油菜高迁移率B型蛋白2(LOC106416143),转录变体X2 Brassica napus high mobility group B protein 2(LOC106416143),transcript variant X2 | XM_048738078.1 | BraA08g027710.3C |
| C18 | 1237-BD-24 | 白菜E3泛素蛋白连接酶BRE1-like 1(LOC103866184) Brassica rapa E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1-like 1(LOC103866184) | XM_009144061.3 | BraA04g030860.3C |
Table 2 pGBKT7-PSY interaction protein annotation
| 序号No. | 样本名Sample name | 基因注释Gene annotation | 登录号GenBank | 基因ID Gene ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1237-BD-1-1 1237-BD-4 1237-BD-10 | 白菜低分子量热休克蛋白(BcHSP17.6)mRNA,完整CDS Brassica rapa low molecular weight heat-shock protein(BcHSP17.6)mRNA,complete CDS | AF022217.1 | BraA06g020450.3C |
| C2 | 1237-BD-2 1237-BD-6 1237-BD-18 | 白菜核前体mRNA的调节域含蛋白1A(LOC103855848),转录本变体X2 Brassica rapa regulation of nuclear pre-mRNA domain-containing protein 1A(LOC103855848),transcript variant X2 | XM_009132891.3 | BraA03g004120.3C |
| C3 | 1237-BD-3-2 | 白菜嘌呤渗透酶1(LOC103838976),mRNA Brassica rapa purine permease 1(LOC103838976) | XM_009115443.3 | BraA09g036510.3C |
| C4 | 1237-BD-8-1 | 白菜Golgi SNAP受体复合体成员1-2(LOC103858165),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa Golgi SNAP receptor complex member 1-2(LOC103858165),transcript variant X2 | XM_018657146.2 | BraA03g023640.3C |
| C5 | 1237-BD-9 | 白菜translin(LOC103857651),转录变体X1 Brassica rapa translin(LOC103857651),transcript variant X1 | XM_009134861.3 | BraA03g019260.3C |
| C6 | 1237-BD-11 | 白菜17.6 kDⅠ类热休克蛋白2-like(LOC103843285) Brassica rapa 17.6 kD classⅠheat shock protein 2-like (LOC103843285) | XM_009119989.3 | BraA05g014680.3C |
| C7 | 1237-BD-12 | 甘蓝型油菜多细胞器RNA编辑因子1,mitochondrial(LOC106437506) Brassica napus multiple organellar RNA editing factor 1,mitochondrial(LOC106437506) | XM_013878402.3 | BraA03g049050.3C |
| C8 | 1237-BD-13 | 白菜RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录亚基26的推定介质(LOC103833180) Brassica rapa putative mediator of RNA polymeraseⅡtranscription subunit 26(LOC103833180) | XM_033282535.1 | BraA10g022490.3C |
| C9 | 1237-BD-14-2 | 甘蓝型油菜CDPK相关激酶2(LOC106362920),转录变体X2 Brassica napus CDPK-related kinase 2(LOC106362920),transcript variant X2 | XM_022695160.2 | BraA01g033890.3C |
| C10 | 1237-BD-15-1 | 甘蓝型油菜formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase1,线粒体(LOC106402097),转录变体X4 Brassica napus formyltetrahydrofolate deformylase 1,mitochondrial(LOC106402097),transcript variant X4 | XM_048781377.1 | BraA06g041130.3C |
| C11 | 1237-BD-15-2 | 白菜 patellin-4(LOC103840314),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa patellin-4(LOC103840314),transcript variant X2 | XM_009116810.2 | BraA09g034310.3C |
| C12 | 1237-BD-17-1 | 甘蓝型油菜硫氧还蛋白O2,线粒体(LOC106352370),转录变体X1 Brassica napus thioredoxin O2,mitochondrial(LOC106352370),transcript variant X1 | XM_048739086.1 | BraA09g033920.3C |
| C13 | 1237-BD-17-2 | 白菜同源箱亮氨酸拉链蛋白ATHB-6(LOC103837893) Brassica rapa homeobox-leucine zipper protein ATHB-6(LOC103837893) | XM_009114280.3 | BraA09g054870.3C |
| C14 | 1237-BD-20 | 白菜未鉴定的LOC103863008(LOC103863008),转录变体X3 Brassica rapa uncharacterized LOC103863008(LOC103863008),transcript variant X3 | XM_033289696.1 | BraA04g002940.3C |
| C15 | 1237-BD-21 | 白菜蛋白MET1,chloroplastic(LOC103829781) Brassica rapa protein MET1,chloroplastic(LOC103829781) | XM_009105478.3 | BraA05g016190.3C |
| C16 | 1237-BD-22 | 白菜转座酶蛋白At4g04430(LOC103847917),转录变体X2 Brassica rapa probable transposase-like protein At4g04430(LOC103847917),transcript variant X2 | XM_018655836.2 | 未检索到 Not retrieved |
| C17 | 1237-BD-23 | 甘蓝型油菜高迁移率B型蛋白2(LOC106416143),转录变体X2 Brassica napus high mobility group B protein 2(LOC106416143),transcript variant X2 | XM_048738078.1 | BraA08g027710.3C |
| C18 | 1237-BD-24 | 白菜E3泛素蛋白连接酶BRE1-like 1(LOC103866184) Brassica rapa E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase BRE1-like 1(LOC103866184) | XM_009144061.3 | BraA04g030860.3C |
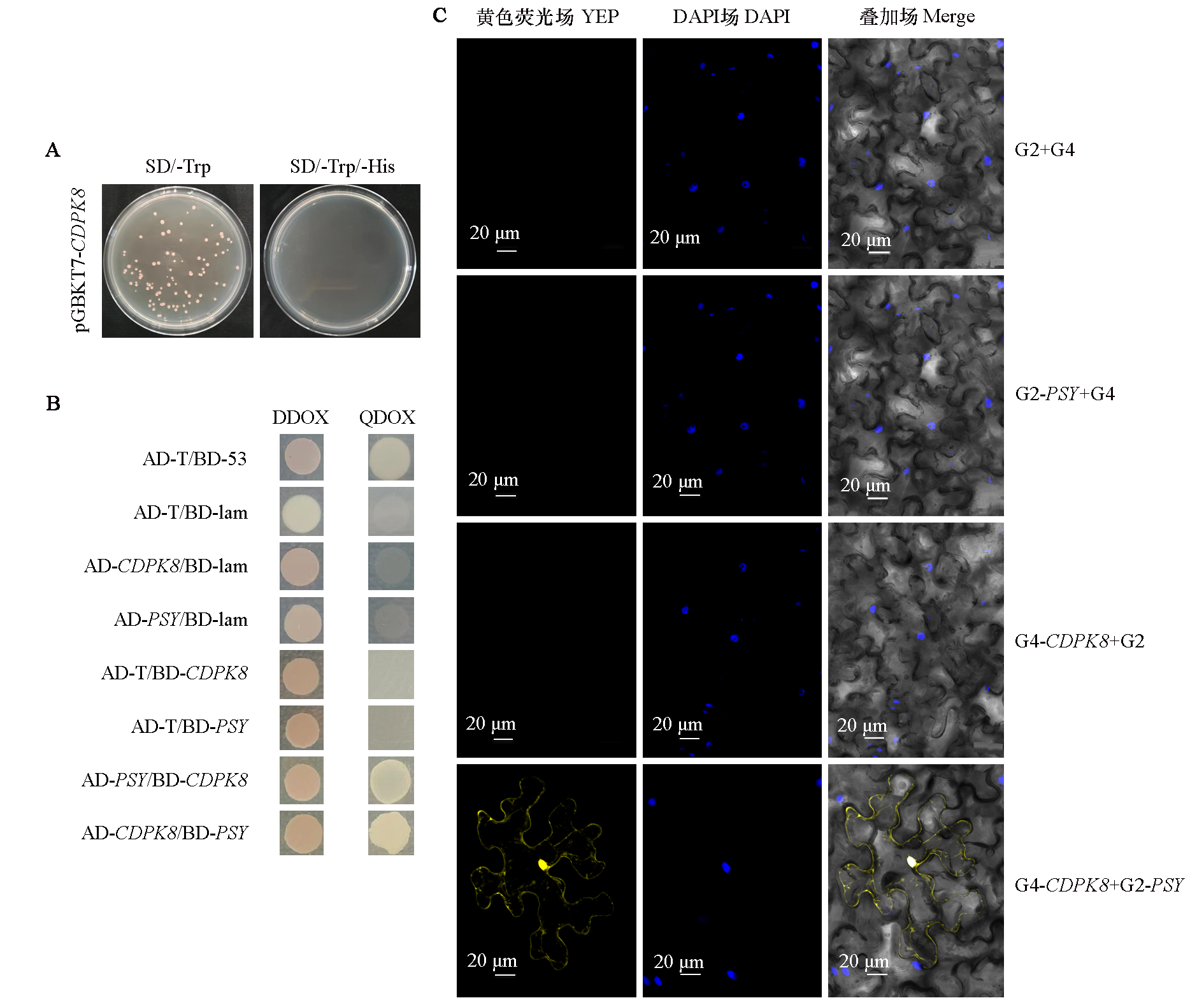
Fig. 4 Verification of interaction relationship between PSY and CDPK protein in turnips A:pGBKT7-CDPK Y2H Gold strain self-activation detection;B:Verification of interaction relationship between PSY and CDPK protein by yeast two-hybrid;C:Interaction between PSY and CDPK in BiFC experiment
| 基因名 Gene name | 基因编号 Gene ID | 登录号 Accession number | cDNA长度/bp cDNA length | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 Theoretical pI | 脂肪系数 Aliphatic index | 疏水性 GRAVY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrrCDPK1 | Cluster-30924.46777 | XM_009103718.3 | 1 737 | 578 | 64.58 | 8.95 | 83.39 | -0.317 | |
| BrrCDPK2 | Cluster-30924.137521 | XM_013807283.3 | 1 743 | 580 | 64.88 | 9.07 | 83.28 | -0.324 | |
| BrrCDPK3 | Cluster-30924.143914 | XM_013807283.3 | 1 731 | 576 | 64.47 | 9.01 | 83.68 | -0.318 | |
| BrrCDPK4 | Cluster-30924.13630 | XM_048738123.1 | 1 755 | 584 | 65.72 | 8.88 | 81.70 | -0.392 | |
| BrrCDPK5 | Cluster-30924.67984 | XM_010509132.2 | 1 806 | 601 | 67.46 | 8.99 | 88.80 | -0.318 | |
| BrrCDPK6 | Cluster-30924.158029 Cluster-30924.77034 Cluster-30924.77038 Cluster-30924.80376 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.74 | 9.06 | 83.43 | -0.374 | |
| BrrCDPK7 | Cluster-30924.58681 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.76 | 9.12 | 82.61 | -0.375 | |
| BrrCDPK8 | Cluster-30924.142390 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.77 | 9.06 | 83.60 | -0.373 | |
| BrrCDPK9 | Cluster-30924.157993 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.70 | 9.06 | 84.09 | -0.372 | |
| BrrCDPK10 | Cluster-30924.131630 | XM_013879035.3 | 1 704 | 567 | 63.43 | 8.84 | 86.84 | -0.218 | |
| BrrCDPK11 | Cluster-30924.136201 | XM_013792411.3 | 1 707 | 568 | 63.43 | 8.84 | 86.88 | -0.205 | |
| BrrCDPK12 | Cluster-30924.24510 | XM_013879035.3 | 1 704 | 567 | 63.59 | 8.67 | 85.47 | -0.219 | |
| BrrCDPK13 | Cluster-30924.57260 | XM_009140827.3 | 1 728 | 575 | 64.34 | 8.61 | 86.16 | -0.238 | |
| BrrCDPK14 | Cluster-30924.150034 | XM_013886734.3 | 1 713 | 570 | 63.80 | 8.85 | 86.74 | -0.251 | |
| BrrCDPK15 | Cluster-30924.150032 Cluster-30924.150033 | XM_009140827.3 | 1 728 | 575 | 64.38 | 8.70 | 86.16 | -0.243 | |
| BrrCDPK16 | Cluster-30924.14001 | XM_033289955.1 | 1 239 | 412 | 46.61 | 8.43 | 86.09 | -0.229 | |
| BrrCDPK17 | Cluster-30924.24231 | XM_013871943.3 | 1 236 | 411 | 46.25 | 8.00 | 88.42 | -0.203 | |
| BrrCDPK18 | Cluster-30924.82876 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.44 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.351 | |
| BrrCDPK19 | Cluster-30924.151434 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.45 | 8.88 | 84.80 | -0.343 | |
| BrrCDPK20 | Cluster-30924.142865 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.49 | 9.01 | 83.98 | -0.344 | |
| BrrCDPK21 | Cluster-30924.142866 | XM_009144190.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.45 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK22 | Cluster-30924.146395 Cluster-30924.169091 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.44 | 8.88 | 83.98 | -0.350 | |
| BrrCDPK23 | Cluster-30924.52514 | XM_018622041.2 | 1 809 | 602 | 67.28 | 9.16 | 82.66 | -0.366 | |
| BrrCDPK24 | Cluster-30924.140928 Cluster-30924.155408 | XM_009144190.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.46 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK25 | Cluster-30924.122791 | XM_013781701.1 | 1 734 | 577 | 64.40 | 8.52 | 84.85 | -0.260 | |
| BrrCDPK26 | Cluster-30924.24346 | XM_013892390.3 | 1 734 | 577 | 64.41 | 8.52 | 84.33 | -0.263 | |
| BrrCDPK27 | Cluster-30924.67985 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.20 | 9.02 | 85.41 | -0.248 | |
| BrrCDPK28 | Cluster-30924.67983 Cluster-30924.92828 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.31 | 9.07 | 86.15 | -0.246 | |
| BrrCDPK29 | Cluster-30924.11427 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.30 | 9.07 | 85.56 | -0.252 | |
| BrrCDPK30 | Cluster-30924.24345 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.33 | 9.07 | 84.97 | -0.254 | |
| BrrCDPK31 | Cluster-30924.77035 | XM_013732238.1 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 9.09 | 83.79 | -0.362 | |
| BrrCDPK32 | Cluster-30924.36432 | XM_013851068.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.95 | 9.13 | 83.79 | -0.355 | |
| BrrCDPK33 | Cluster-30924.77036 | XM_013893888.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.82 | 9.19 | 83.31 | -0.363 | |
| BrrCDPK34 | Cluster-30924.77037 | XM_013851068.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 9.13 | 83.79 | -0.362 | |
| BrrCDPK35 | Cluster-30924.114427 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.32 | 9.07 | 86.15 | -0.244 | |
| BrrCDPK36 | Cluster-69076.1 Cluster-69076.4 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.92 | 8.66 | 83.55 | -0.309 | |
| BrrCDPK37 | Cluster-69076.2 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.93 | 8.52 | 84.53 | -0.295 | |
| BrrCDPK38 | Cluster-69076.0 | XM_009151493.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.90 | 8.66 | 84.38 | -0.306 | |
| BrrCDPK39 | Cluster-30924.23018 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.95 | 8.77 | 83.89 | -0.314 | |
| BrrCDPK40 | Cluster-30924.12640 | XM_013787387.3 | 1 803 | 600 | 66.93 | 8.51 | 82.48 | -0.343 | |
| BrrCDPK41 | Cluster-30924.75342 | XM_048769751.1 | 1 242 | 413 | 47.04 | 6.68 | 93.27 | -0.195 | |
| BrrCDPK42 | Cluster-30924.119657 Cluster-30924.139625 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.84 | 8.98 | 81.88 | -0.355 | |
| BrrCDPK43 | Cluster-30924.119656 Cluster-30924.139627 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 8.98 | 81.39 | -0.360 | |
| BrrCDPK44 | Cluster-30924.139626 Cluster-30924.16433 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.87 | 8.98 | 81.22 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK45 | Cluster-30924.139628 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.87 | 8.91 | 81.71 | -0.360 | |
| BrrCDPK46 | Cluster-30924.74759 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.85 | 8.98 | 81.88 | -0.354 | |
| BrrCDPK47 | Cluster-30924.114809 Cluster-30924.114810 Cluster-30924.123336 Cluster-30924.127303 Cluster-30924.130998 Cluster-30924.49496 | XM_048739418.1 | 1 743 | 580 | 65.01 | 8.91 | 80.88 | -0.359 | |
| BrrCDPK48 | Cluster-30924.101435 Cluster-30924.124946 | XM_048739418.1 | 1 743 | 580 | 65.00 | 8.91 | 80.71 | -0.363 | |
| BrrCDPK49 | Cluster-30924.155459 | XM_048769751.1 | 1 242 | 413 | 47.04 | 6.44 | 93.51 | -0.188 | |
| BrrCDPK50 | Cluster-30924.148411 | XM_048741021.1 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.10 | 8.76 | 82.64 | -0.314 | |
Table 3 Analysis of protein physicochemical properties of CDPK gene family in turnip
| 基因名 Gene name | 基因编号 Gene ID | 登录号 Accession number | cDNA长度/bp cDNA length | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acids | 分子量/kD Molecular weight | 等电点 Theoretical pI | 脂肪系数 Aliphatic index | 疏水性 GRAVY | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BrrCDPK1 | Cluster-30924.46777 | XM_009103718.3 | 1 737 | 578 | 64.58 | 8.95 | 83.39 | -0.317 | |
| BrrCDPK2 | Cluster-30924.137521 | XM_013807283.3 | 1 743 | 580 | 64.88 | 9.07 | 83.28 | -0.324 | |
| BrrCDPK3 | Cluster-30924.143914 | XM_013807283.3 | 1 731 | 576 | 64.47 | 9.01 | 83.68 | -0.318 | |
| BrrCDPK4 | Cluster-30924.13630 | XM_048738123.1 | 1 755 | 584 | 65.72 | 8.88 | 81.70 | -0.392 | |
| BrrCDPK5 | Cluster-30924.67984 | XM_010509132.2 | 1 806 | 601 | 67.46 | 8.99 | 88.80 | -0.318 | |
| BrrCDPK6 | Cluster-30924.158029 Cluster-30924.77034 Cluster-30924.77038 Cluster-30924.80376 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.74 | 9.06 | 83.43 | -0.374 | |
| BrrCDPK7 | Cluster-30924.58681 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.76 | 9.12 | 82.61 | -0.375 | |
| BrrCDPK8 | Cluster-30924.142390 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.77 | 9.06 | 83.60 | -0.373 | |
| BrrCDPK9 | Cluster-30924.157993 | XM_009113894.3 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.70 | 9.06 | 84.09 | -0.372 | |
| BrrCDPK10 | Cluster-30924.131630 | XM_013879035.3 | 1 704 | 567 | 63.43 | 8.84 | 86.84 | -0.218 | |
| BrrCDPK11 | Cluster-30924.136201 | XM_013792411.3 | 1 707 | 568 | 63.43 | 8.84 | 86.88 | -0.205 | |
| BrrCDPK12 | Cluster-30924.24510 | XM_013879035.3 | 1 704 | 567 | 63.59 | 8.67 | 85.47 | -0.219 | |
| BrrCDPK13 | Cluster-30924.57260 | XM_009140827.3 | 1 728 | 575 | 64.34 | 8.61 | 86.16 | -0.238 | |
| BrrCDPK14 | Cluster-30924.150034 | XM_013886734.3 | 1 713 | 570 | 63.80 | 8.85 | 86.74 | -0.251 | |
| BrrCDPK15 | Cluster-30924.150032 Cluster-30924.150033 | XM_009140827.3 | 1 728 | 575 | 64.38 | 8.70 | 86.16 | -0.243 | |
| BrrCDPK16 | Cluster-30924.14001 | XM_033289955.1 | 1 239 | 412 | 46.61 | 8.43 | 86.09 | -0.229 | |
| BrrCDPK17 | Cluster-30924.24231 | XM_013871943.3 | 1 236 | 411 | 46.25 | 8.00 | 88.42 | -0.203 | |
| BrrCDPK18 | Cluster-30924.82876 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.44 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.351 | |
| BrrCDPK19 | Cluster-30924.151434 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.45 | 8.88 | 84.80 | -0.343 | |
| BrrCDPK20 | Cluster-30924.142865 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.49 | 9.01 | 83.98 | -0.344 | |
| BrrCDPK21 | Cluster-30924.142866 | XM_009144190.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.45 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK22 | Cluster-30924.146395 Cluster-30924.169091 | XM_013895504.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.44 | 8.88 | 83.98 | -0.350 | |
| BrrCDPK23 | Cluster-30924.52514 | XM_018622041.2 | 1 809 | 602 | 67.28 | 9.16 | 82.66 | -0.366 | |
| BrrCDPK24 | Cluster-30924.140928 Cluster-30924.155408 | XM_009144190.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.46 | 8.95 | 83.98 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK25 | Cluster-30924.122791 | XM_013781701.1 | 1 734 | 577 | 64.40 | 8.52 | 84.85 | -0.260 | |
| BrrCDPK26 | Cluster-30924.24346 | XM_013892390.3 | 1 734 | 577 | 64.41 | 8.52 | 84.33 | -0.263 | |
| BrrCDPK27 | Cluster-30924.67985 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.20 | 9.02 | 85.41 | -0.248 | |
| BrrCDPK28 | Cluster-30924.67983 Cluster-30924.92828 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.31 | 9.07 | 86.15 | -0.246 | |
| BrrCDPK29 | Cluster-30924.11427 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.30 | 9.07 | 85.56 | -0.252 | |
| BrrCDPK30 | Cluster-30924.24345 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.33 | 9.07 | 84.97 | -0.254 | |
| BrrCDPK31 | Cluster-30924.77035 | XM_013732238.1 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 9.09 | 83.79 | -0.362 | |
| BrrCDPK32 | Cluster-30924.36432 | XM_013851068.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.95 | 9.13 | 83.79 | -0.355 | |
| BrrCDPK33 | Cluster-30924.77036 | XM_013893888.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.82 | 9.19 | 83.31 | -0.363 | |
| BrrCDPK34 | Cluster-30924.77037 | XM_013851068.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 9.13 | 83.79 | -0.362 | |
| BrrCDPK35 | Cluster-30924.114427 | XM_009147578.3 | 1 983 | 660 | 74.32 | 9.07 | 86.15 | -0.244 | |
| BrrCDPK36 | Cluster-69076.1 Cluster-69076.4 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.92 | 8.66 | 83.55 | -0.309 | |
| BrrCDPK37 | Cluster-69076.2 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.93 | 8.52 | 84.53 | -0.295 | |
| BrrCDPK38 | Cluster-69076.0 | XM_009151493.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.90 | 8.66 | 84.38 | -0.306 | |
| BrrCDPK39 | Cluster-30924.23018 | XM_013786949.3 | 1 776 | 591 | 65.95 | 8.77 | 83.89 | -0.314 | |
| BrrCDPK40 | Cluster-30924.12640 | XM_013787387.3 | 1 803 | 600 | 66.93 | 8.51 | 82.48 | -0.343 | |
| BrrCDPK41 | Cluster-30924.75342 | XM_048769751.1 | 1 242 | 413 | 47.04 | 6.68 | 93.27 | -0.195 | |
| BrrCDPK42 | Cluster-30924.119657 Cluster-30924.139625 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.84 | 8.98 | 81.88 | -0.355 | |
| BrrCDPK43 | Cluster-30924.119656 Cluster-30924.139627 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.91 | 8.98 | 81.39 | -0.360 | |
| BrrCDPK44 | Cluster-30924.139626 Cluster-30924.16433 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.87 | 8.98 | 81.22 | -0.356 | |
| BrrCDPK45 | Cluster-30924.139628 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.87 | 8.91 | 81.71 | -0.360 | |
| BrrCDPK46 | Cluster-30924.74759 | XM_013880416.3 | 1 791 | 596 | 66.85 | 8.98 | 81.88 | -0.354 | |
| BrrCDPK47 | Cluster-30924.114809 Cluster-30924.114810 Cluster-30924.123336 Cluster-30924.127303 Cluster-30924.130998 Cluster-30924.49496 | XM_048739418.1 | 1 743 | 580 | 65.01 | 8.91 | 80.88 | -0.359 | |
| BrrCDPK48 | Cluster-30924.101435 Cluster-30924.124946 | XM_048739418.1 | 1 743 | 580 | 65.00 | 8.91 | 80.71 | -0.363 | |
| BrrCDPK49 | Cluster-30924.155459 | XM_048769751.1 | 1 242 | 413 | 47.04 | 6.44 | 93.51 | -0.188 | |
| BrrCDPK50 | Cluster-30924.148411 | XM_048741021.1 | 1 785 | 594 | 66.10 | 8.76 | 82.64 | -0.314 | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
陈湘宏, 刘燕, 翁裕馨, 康文娟, 杨仕兵. 2014. 芜菁挥发油对高脂高糖小鼠降血糖的作用机制. 山东大学学报(医学版),(12):20-23.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
费小钰, 李红丽, 王俊皓. 2017. 植物钙依赖蛋白激酶CDPK基因功能综述. 吉林农业,(9):104-105.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
龚丽莎, 向芷萱, 王照, 鲁敏, 安华明. 2023. 刺梨CDPK基因家族的鉴定及其对供钙水平的表达响应. 果树学报, 40 (4):639-652.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
靳燕, 王谢琴, 卿华, 马政, 姚慧鹏. 2021. 黄瓜CDPK基因家族的鉴定与进化特征分析. 四川农业大学学报, 39 (1):19-26.
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214808109 pmid: 23112190 |
| [14] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-433 pmid: 23815483 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2016.03.004 |
|
李可琪, 王莎莎, 曾新华, 闫晓红, 吴刚. 2016. 甘蓝型油菜温敏GMSTE5A幼蕾酵母双杂交cDNA文库的构建及筛选. 中国油料作物学报, 38 (3):292-299.
doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2016.03.004 |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01008.x pmid: 11359610 |
| [17] |
doi: S0024-3205(18)30591-5 pmid: 30248349 |
| [18] |
doi: S1569-9048(18)30243-X pmid: 30447305 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0719 |
|
李亚男, 张豪杰, 梁梦静, 罗涛, 李旺宁, 张春辉, 季春丽, 李润植, 薛金爱, 崔红利. 2024. 雨生红球藻钙依赖蛋白激酶(CDPK)家族鉴定与表达分析. 生物技术通报, 40 (2):300-312.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2023-0719 |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2022386 |
|
刘玉玲, 朱新霞, 吕新华, 孙辉. 2023. 雪莲SikCDPK1基因的表达特征和蛋白激酶活性分析. 草业学报, 32 (9):213-221.
doi: 10.11686/cyxb2022386 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.20.5556 pmid: 11597999 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.000869 pmid: 12011347 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.066936 pmid: 19880793 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
王文宁. 2018. 蔓菁营养成分分析及其改善小鼠肠道菌群的研究[硕士论文]. 郑州: 郑州大学.
|
|
| [31] |
pmid: 17873090 |
| [32] |
|
|
张海鑫. 2022. 多毛番茄CDPK基因家族分析及胁迫响应分析[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
张习敏. 2018. 高钙诱导天蓝苜蓿叶片草酸钙积累及其在环境适应中的作用研究[博士论文]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
庄丽丽, 宋林眉, 王芳, 李玉群, 张柱岐, 刘凯. 2023. 核桃CDPK基因家族鉴定与转录表达分析. 落叶果树, 55 (6):32-35.
|
| [1] | LIANG Jing, ZENG Baozhen, LIANG Guoping, MAO Juan, CHEN Baihong. Grapevine VvARF18 Regulates Fruit Expansion and Screening of its Interacting Proteins [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 821-834. |
| [2] | FU Qi, WANG Dan, JING Weikun, ZHANG Hao, WANG Huichun, JIAN Hongying, QIU Xianqin, WANG Qigang, TANG Kaixue, YAN Huijun. Functional Characterization of Carotenoid Cleavage Dioxygenases 4 Gene(RcCCD4)Involved in Biosynthetic Pathway of Floral Scent in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 623-634. |
| [3] | XIE Lihua, YAO Pengqiang, LIU Jiaxue, WANG Zhe, ZHU Nannan, CHENG Shiping, CHENG Zhanchao. Screening and Analysis of Phyllostachys edulis PheNAC4 Interacting Proteins by Yeast Two-Hybrid System [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2677-2690. |
| [4] | LIANG Guoping, ZENG Baozhen, LIU Ming, BIAN Zhiyuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of VaSR Gene Family in Vitis amurensis,Verification of Cold Resistance Function of VaSR1 and Screening of Interacting Proteins [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 37-50. |
| [5] | ZHAO Jiaying, ZENG Zhouting, CEN Xinying, SHI Jiaoqi, LI Xiaoxian, SHEN Xiaoxia, YU Zhenming. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CCO Gene Family in Dendrobium officinale During Flower Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [6] | QIU Hui, ZHU Dejuan, ZHANG Yongle, GAO Yujie, LI Liu, WANG Guoping, HONG Ni. Interaction Between the Coat Protein of Apple Chlorotic Leaf Spot Virus and Two E3 Ubiquitin Ligases of Pear and Their Subcellular Localization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1715-1727. |
| [7] | DUAN Minjie, LI Yifei, WANG Chunping, YANG Xiaomiao, HUANG Renzhong, HUANG Qizhong, ZHANG Shicai. Integrated Transcriptomic and Targeted Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Regulation of Carotenoid Accumulation During Pepper Fruit Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [8] | YANG Liang, LIU Huan, MA Yanqin, LI Ju, WANG Hai'e, ZHOU Yujie, LONG Haicheng, MIAO Mingjun, LI Zhi, CHANG Wei. Creating High Lycopene Fruit Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [9] | WANG Shujie, LUAN Yuting, XU Changjie. Research Progresses on Plant Xanthophyll Esterification [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1830-1840. |
| [10] | TIAN Mixia, ZHOU Fuhui, JIANG Aili, ZHU Pengfang, CHEN Chen, LIU Chenghui, YUAN Chang. Research Progress in Coloration Mechanism of Brassica Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1971-1986. |
| [11] | XIAO Xiang, ZHOU Chujiang, JIN Shuwan, SHI Liyu, YANG Zhenfeng, CAO Shifeng, CHEN Wei. Mechanism of PpMADS2 and PpMADS3 Synergistically Regulating Carotenoids Accumulation in Peach Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1173-1186. |
| [12] | DU Yanxia, WANG Yiguang, XIAO Zheng, DONG Bin, FANG Qiu, ZHONG Shiwei, YANG Liyuan, ZHAO Hongbo. Ectopic Overexpression of OfNCED3 Regulates the Synthesis of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls in Transgenic Tobacco Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1284-1294. |
| [13] | DING Lei, SUN Pingping, ZHANG Lei, LI Zhengnan. Screening Proteins of Nicotiana occidentalis That Interact with Coat Protein of Apple Stem Pitting Virus Using Yeast Two-hybrid System [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(11): 2509-2515. |
| [14] | ZHANG Lugang, LU Qianqian, HE Qiong, XUE Yihua, MA Xiaomin, MA Shuai, NIE Shanshan, YANG Wenjing. Creation of Novel Germplasm of Purple-orange Heading Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [15] | ZHOU Xuzixin, YANG Wei, MAO Meiqin, XUE Yanbin, MA Jun. Identification of Pigment Components and Key Genes in Carotenoid Pathway in Mutants of Chimeric Ananas comosus var. bracteatus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd