
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1745-1757.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0723
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
DOU Xueting1, ZHU Xi2,3, ZHANG Ning1,*( ), and SI Huaijun1
), and SI Huaijun1
Received:2024-11-12
Revised:2025-04-22
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-23
Contact:
ZHANG Ning
DOU Xueting, ZHU Xi, ZHANG Ning, and SI Huaijun. Functional Analysis of StHY5 Associated with Low-Temperature Stress in Potato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1745-1757.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0723
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | StHY5-F | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCATGCAAGAGCAAGCGACAAGTTC |
| StHY5-R | TGCTCACCATGTCGACTTACTTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| pMD18-StHY5-F | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGGTCG | |
| pMD18-StHY5-R | CCATGTCGACTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCCATGGC | |
| StHY5-YF | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCATGCAAGAGCAAGCGACAAGTTC | |
| StHY5-YR | TGCTCACCATGTCGACCTTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| HYG-F | GCTTCTGCGGGCGATTTGTGT | |
| HYG-R | GGTCGCGGAGGCTATGGATGC | |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | StHY5-qF | CAGCAAGCAAGGGAGAGGAA |
| StHY5-qR | TTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| 内参基因 Reference gene | StEf1α-F | GATGGTCAGACCCGTGAACA |
| StEf1α-R | CCTTGGAGTACTTCGGGGTG |
Table 1 Specific primers for PCR and qRT-PCR in this study
| 用途Usage | 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列Primer sequence(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene cloning | StHY5-F | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCATGCAAGAGCAAGCGACAAGTTC |
| StHY5-R | TGCTCACCATGTCGACTTACTTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| pMD18-StHY5-F | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCGGGCCCCCCCTCGAGGTCG | |
| pMD18-StHY5-R | CCATGTCGACTCTAGAACTAGTGGATCCCCCCATGGC | |
| StHY5-YF | CGGGGGACGAGCTCGGTACCATGCAAGAGCAAGCGACAAGTTC | |
| StHY5-YR | TGCTCACCATGTCGACCTTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| HYG-F | GCTTCTGCGGGCGATTTGTGT | |
| HYG-R | GGTCGCGGAGGCTATGGATGC | |
| 实时荧光定量PCR qRT-PCR | StHY5-qF | CAGCAAGCAAGGGAGAGGAA |
| StHY5-qR | TTCCTCCCTTCCTTTGCACC | |
| 内参基因 Reference gene | StEf1α-F | GATGGTCAGACCCGTGAACA |
| StEf1α-R | CCTTGGAGTACTTCGGGGTG |
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| Ⅰ | gaTTTCAGTATATGTCTAAGCGTtctctcttttgtattcc |
| Ⅱ | gaACGCTTAGACATATACTGAAAtcaaagagaatcaatga |
| Ⅲ | gaACACTTAGACATAAACTGAATtcacaggtcgtgatatg |
| Ⅳ | gaATTCAGTTTATGTCTAAGTGTtctacatatatattcct |
| A | CTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTGGGTAAC |
| B | GCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAAACAG |
Table 2 Primers of amiR-StHY5 for PCR
| 引物名称Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′)Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| Ⅰ | gaTTTCAGTATATGTCTAAGCGTtctctcttttgtattcc |
| Ⅱ | gaACGCTTAGACATATACTGAAAtcaaagagaatcaatga |
| Ⅲ | gaACACTTAGACATAAACTGAATtcacaggtcgtgatatg |
| Ⅳ | gaATTCAGTTTATGTCTAAGTGTtctacatatatattcct |
| A | CTGCAAGGCGATTAAGTTGGGTAAC |
| B | GCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGGAAACAG |
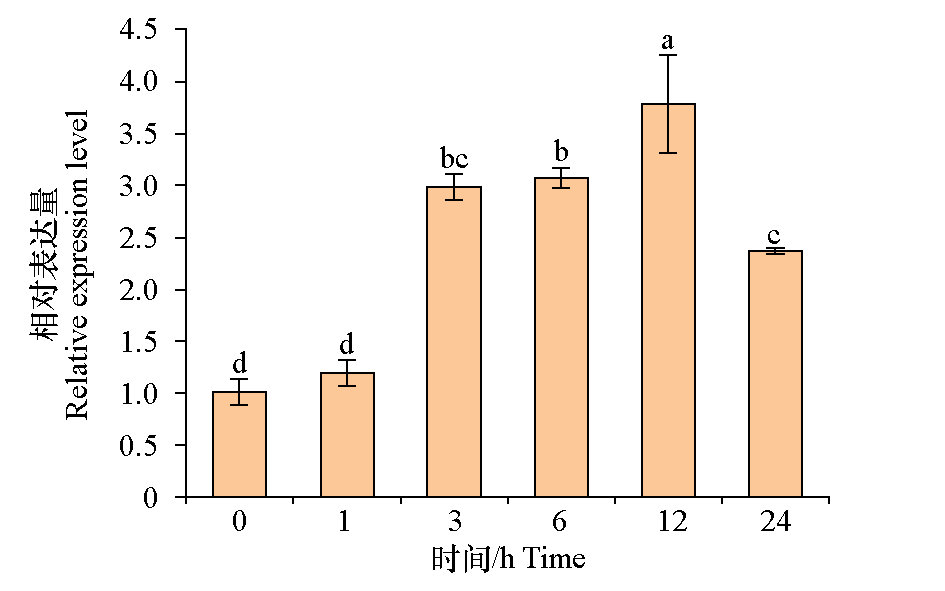
Fig. 6 Relative expression of StHY5 gene under low temperature treatment The error line indicates the standard error,different lowercase letters represent significant differences(P < 0.05)
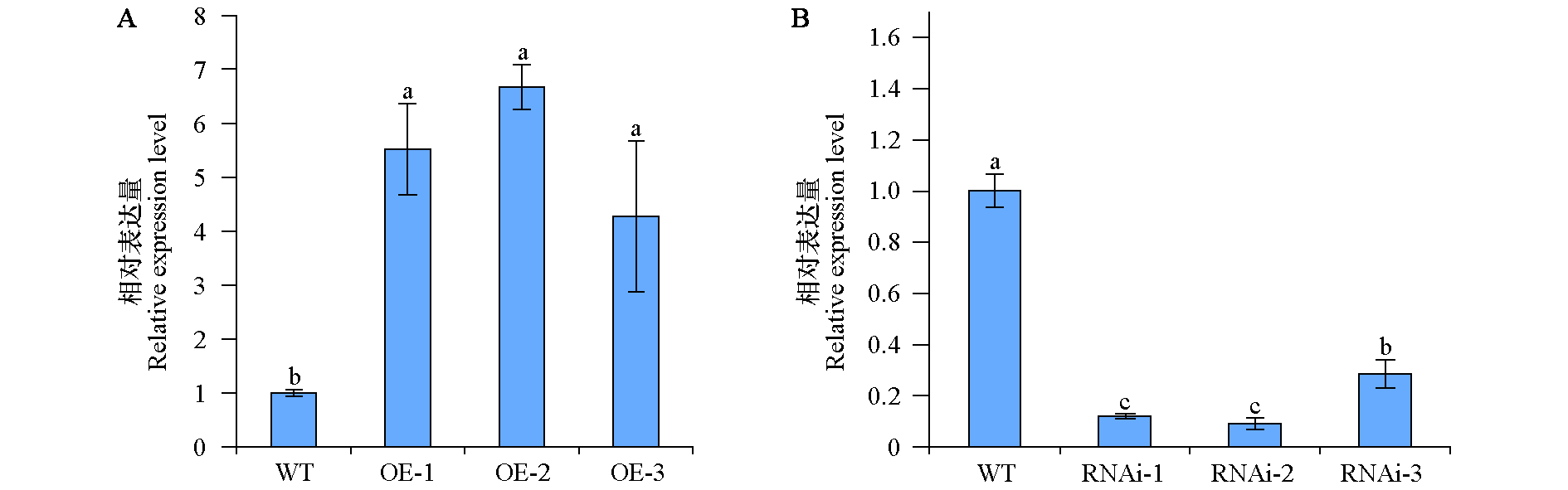
Fig. 8 Relative expression of the transgenic plants by qRT-PCR WT:Wild type. The error line indicates the standard error,different lowercase letters represent significant differences(P < 0.05),the same below
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80022-2 pmid: 9659918 |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1126/science.218.4571.443 pmid: 17808529 |
| [3] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00478 pmid: 28775143 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
邓涪元, 乔中全, 王晓明, 李春霞, 陆柳淑, 李雪露, 何钢. 2022. 紫薇LiHY5基因的克隆、亚细胞定位与不同光质下的表达分析. 江西农业大学学报, 44 (6):1546-1554.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
邓淑芳, 刘倩, 刘玲, 陈鸥, 王文军, 曾凯芳, 邓丽莉. 2024. 蜜橘CcHY5的克隆及其对果实转色功能的研究. 园艺学报, 51 (5):939-955.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
邓英毅, 郑虚, 熊军, 许娟, 覃维治. 2017. 马铃薯新品种桂农薯1号冬种田间耐寒性鉴定. 南方农业学报, 48 (1):66-71.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru059 pmid: 24569036 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112821 pmid: 18065552 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
司怀军, 谢从华, 柳俊. 2003. 农杆菌介导的马铃薯试管薯遗传转化体系的优化及反义class I patatin基因的导入. 作物学报, 29 (6):801-805.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
谭政委, 鲁丹丹, 李磊, 余永亮, 许兰杰, 杨红旗, 杨青, 董薇, 李春明, 安素妨, 芦海灵, 梁慧珍. 2022. 红花光调控信号途径关键基因CtHY5的克隆及表达分析. 中草药, 53 (18):5825-5833.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0556 |
|
王梦瑶, 王梦洁, 赖慧萍, 贺雅萍, 鄢璐, 黎鹏, 郭丽婷, 艾叶. 2024. 温度影响植物花青苷积累的研究进展. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1501-1515.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
|
杨颖, 高世庆, 唐益苗, 冶晓芳, 王永波, 刘美英, 赵昌平. 2009. 植物bZIP转录因子的研究进展. 麦类作物学报, 29 (4):730-737.
|
|
| [37] |
pmid: 19798935 |
|
张超, 张晖, 赵晓燕, 马越, 姚惠源. 2009. 使用圆二色性光谱和红外光谱研究冬小麦麸皮抗冻蛋白的二级结构. 光谱学与光谱分析, 29 (7):1764-1767.
pmid: 19798935 |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
|
张荔, 周波, 李玉花. 2010. 植物HY5蛋白结构与功能的研究进展. 植物生理学通讯, 46 (10):985-990.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [1] | YANG Li, QIN Ya, BIAN Baciren, ZHEN Zhen, QIONG Ji, BAI Maquzhen, ZHOU Ya. A New Cultivar of Colored Potato‘Xigezi 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 145-146. |
| [2] | TIAN Hongmei, WANG Yuanlong, WANG Fei, PAN Hong, TAO Zhen, ZHANG Jian, WANG Pengcheng. A New Muskmelon Cultivar‘Jinzhongyuan Jintian’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 153-154. |
| [3] | SONG Qianna, SONG Lushuai, DUAN Yonghong, BAI Xiaodong, and FENG Ruiyun. Establishment a System to Obtain CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Plants Based on Hairy Root Transformation in Potatoes [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1758-1768. |
| [4] | YE Yanran, LIU Jiangang, BIAN Chunsong, GUO Huachun, and JIN Liping. Quantitative Analysis of Potato Growth Under Different Nitrogen Management Practices Based on UAV-Acquired RGB Imagery [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1870-1882. |
| [5] | ZHU Xingzhe, SU Xianyue, SU Wang, ZHANG Honglin, PAN Zhechao, LIU Tao, and XU Xiaoyu. Understanding the Anabolic Differences of Steroidal Glycoalkaloids in Leaf Between Two Potato Varieties Grown at the Winter and Spring Cropping Patterns [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1883-1900. |
| [6] | LI Ziyan, CHEN Weixi, LI Zihan, LI Yin, LIANG Fengming, ZENG Xiangli, JIAN Hongju, and LÜ Dianqiu. Screening Candidate Genes Controlling Potato Maturation Time Based on RNA-Seq [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1505-1518. |
| [7] | YAN Lijuan, OU Chenggang, LIANG Chen, HU Tiankuo, LIU Xing, YANG Jing, LIN Guocang, and ZHUANG Feiyun. Response of Premature Bolting of Carrots Under Different Low Temperature and Day Length [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1588-1598. |
| [8] | XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, ZHANG Mannan, TANG Huaiqian, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, and YE Jie. Effects of Potassium on Growth and Development of Tomato Seedlings Under Abiotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1599-1618. |
| [9] | WANG Wenlong, LIU Zhaokun, LU Wenjun, WANG Yaolong, LI Xiaofeng, ZHU Hongfang, LIU Tongkun, LI Ying, HOU Xilin, ZHANG Changwei. Enhancing Ascorbic Acid Content in Non-heading Chinese Cabbage Using Gene Editing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1317-1325. |
| [10] | LIN Xi, DENG Zhenpeng, YANG Xinyue, ZHOU Keyou, YI Xiaoping, WANG Jichun. Effects of Reducing Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer on Potato Yield and Nutrient Utilization [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 1007-1019. |
| [11] | WANG Zhongyi, LIU Yi, HU Bowen, ZHU Fan, LIU Feng, YANG Sha, XIONG Cheng, OU Lijun, DAI Xiongze, ZOU Xuexiao. Construction of a High-Efficiency Genetic Transformation System in Pepper Leveraging RUBY and CaREF1 [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 1093-1104. |
| [12] | XING Zhigan, LEI Xiangzhao, WANG Haochen, FENG Mingxin, LI Jingwen, LIU Yujia, FANG Yulin, MENG Jiangfei. Physiological Response of Shine Muscat Grape Seedlings Grafted with Different Rootstocks to Combined Stress of Salt and Low Temperature [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 693-704. |
| [13] | ZHOU Jinhua, BAI Lei, ZHANG Rui, GUO Huachun. The Effect of Reducing Soil Temperature with Straw Mulching Cultivation on Potato Growth [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 453-466. |
| [14] | LI Min, LI Siyu, SHI Zihan, CHEN Shuang, XU Yan, LIU Guotian. Studies on the Efficiency of GRFs/GIFs for Genetic Transformation and Regeneration in Grapevine [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 51-65. |
| [15] | HE Dandan, HE Hongtai, WANG Wenting, ZHOU Wenmei, LIU Yanmin, LIU Sushuang. Identification of Melon GolS Genes Family and the Expression Analysis in Response to Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 136-148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd