
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 1007-1019.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-1022
• Cultivation·Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Xi1, DENG Zhenpeng1, YANG Xinyue1, ZHOU Keyou2, YI Xiaoping1, WANG Jichun1,*( )
)
Received:2024-11-19
Revised:2025-01-17
Online:2025-05-08
Published:2025-04-25
Contact:
WANG Jichun
LIN Xi, DENG Zhenpeng, YANG Xinyue, ZHOU Keyou, YI Xiaoping, WANG Jichun. Effects of Reducing Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Organic Fertilizer on Potato Yield and Nutrient Utilization[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 1007-1019.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-1022
| 年份 Year | mg · kg-1 | g · kg-1 | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮Alkaline nitrogen | 速效钾Available Potassium | 速效磷Available phosphorus | 有机质Organic matter | 全氮Total nitrogen | 全磷Total phosphorus | 全钾Total potassium | ||
| 2020 | 64.79 | 40.25 | 32.88 | 12.18 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 12.37 | 7.20 |
| 2021 | 60.20 | 44.04 | 30.01 | 12.02 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 11.00 | 6.99 |
Table 1 Soil basic fertility status in experimental area
| 年份 Year | mg · kg-1 | g · kg-1 | pH | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碱解氮Alkaline nitrogen | 速效钾Available Potassium | 速效磷Available phosphorus | 有机质Organic matter | 全氮Total nitrogen | 全磷Total phosphorus | 全钾Total potassium | ||
| 2020 | 64.79 | 40.25 | 32.88 | 12.18 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 12.37 | 7.20 |
| 2021 | 60.20 | 44.04 | 30.01 | 12.02 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 11.00 | 6.99 |
| 处理 Treatment | 复合化肥 Compound fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 有效氮磷钾总养分 Available nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照No fertilization control(CK) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 高量化肥High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 1 125 | 0 | 506.25 |
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 750 | 3 375 | 506.25 |
| 中量化肥Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 750 | 0 | 337.50 |
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 375 | 3 375 | 337.50 |
| 低量化肥Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 375 | 0 | 168.75 |
| 单施有机肥Organic fertilizer(T6) | 0 | 3 375 | 168.75 |
Table 2 Fertilization status of each treatment kg · hm-2
| 处理 Treatment | 复合化肥 Compound fertilizer | 有机肥 Organic fertilizer | 有效氮磷钾总养分 Available nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照No fertilization control(CK) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 高量化肥High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 1 125 | 0 | 506.25 |
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 750 | 3 375 | 506.25 |
| 中量化肥Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 750 | 0 | 337.50 |
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 375 | 3 375 | 337.50 |
| 低量化肥Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 375 | 0 | 168.75 |
| 单施有机肥Organic fertilizer(T6) | 0 | 3 375 | 168.75 |
| 处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 产量/(kg . hm-2) Total yield | 商品薯率/% Commodity rate | 单株结薯数 Tuber number per plant | 单薯质量/g Single potato weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 12 814.29 ± 642.86 e | 67.58 ± 1.31 c | 4.01 ± 0.03 d | 53.19 ± 2.29 e | |
| 2021 | 6 370.00 ± 517.95 d | 59.00 ± 2.73 e | 3.40 ± 0.15 e | 31.34 ± 3.93 e | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 20 528.57 ± 42.86 bc | 76.58 ± 0.38 b | 5.14 ± 0.04 a | 66.53 ± 0.69 d | |
| 2021 | 11 235.00 ± 301.12 b | 78.86 ± 2.68 c | 4.52 ± 0.08 b | 41.47 ± 1.67 c | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 23 485.71 ± 214.29 a | 81.23 ± 0.77 a | 5.19 ± 0.07 a | 75.49 ± 0.35 b | |
| 2021 | 16 135.00 ± 1 199.47a | 89.75 ± 3.77 a | 5.30 ± 0.09 a | 50.71 ± 2.92 a | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 21 642.86 ± 385.71 b | 69.62 ± 0.70 c | 4.49 ± 0.09 b | 80.42 ± 0.10 a | |
| 2021 | 11 575.00 ± 338.19 b | 64.73 ± 3.52 d | 4.30 ± 0.10 c | 44.87 ± 1.25 bc | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 21 685.71 ± 257.14 b | 79.78 ± 1.60 a | 5.11 ± 0.03 a | 70.67 ± 0.44 c | |
| 2021 | 12 100.00 ± 153.95 b | 84.54 ± 1.16 b | 4.33 ± 0.10 c | 46.56 ± 1.65 ab | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 19 414.29 ± 557.14 d | 70.10 ± 0.15 c | 4.44 ± 0.07 b | 72.82 ± 0.92 bc | |
| 2021 | 8 390.00 ± 279.15 c | 66.48 ± 0.32 d | 3.88 ± 0.03 d | 36.02 ± 1.45 d | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 18 685.71 ± 1200.00d | 76.30 ± 3.35 b | 4.30 ± 0.09 c | 72.38 ± 3.21 c | |
| 2021 | 7 635.00 ± 286.18 c | 66.37 ± 2.00 d | 3.80 ± 0.09 d | 33.50 ± 1.40 de | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 2 787.28** | 6.21* | 319.30** | 2 458.88** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 197.59** | 91.06** | 246.66** | 81.26** | ||
| Y × T | 14.44** | 16.06** | 21.38** | 20.59** | ||
Table 3 Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer on potato yield and its composition
| 处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 产量/(kg . hm-2) Total yield | 商品薯率/% Commodity rate | 单株结薯数 Tuber number per plant | 单薯质量/g Single potato weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 12 814.29 ± 642.86 e | 67.58 ± 1.31 c | 4.01 ± 0.03 d | 53.19 ± 2.29 e | |
| 2021 | 6 370.00 ± 517.95 d | 59.00 ± 2.73 e | 3.40 ± 0.15 e | 31.34 ± 3.93 e | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 20 528.57 ± 42.86 bc | 76.58 ± 0.38 b | 5.14 ± 0.04 a | 66.53 ± 0.69 d | |
| 2021 | 11 235.00 ± 301.12 b | 78.86 ± 2.68 c | 4.52 ± 0.08 b | 41.47 ± 1.67 c | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 23 485.71 ± 214.29 a | 81.23 ± 0.77 a | 5.19 ± 0.07 a | 75.49 ± 0.35 b | |
| 2021 | 16 135.00 ± 1 199.47a | 89.75 ± 3.77 a | 5.30 ± 0.09 a | 50.71 ± 2.92 a | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 21 642.86 ± 385.71 b | 69.62 ± 0.70 c | 4.49 ± 0.09 b | 80.42 ± 0.10 a | |
| 2021 | 11 575.00 ± 338.19 b | 64.73 ± 3.52 d | 4.30 ± 0.10 c | 44.87 ± 1.25 bc | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 21 685.71 ± 257.14 b | 79.78 ± 1.60 a | 5.11 ± 0.03 a | 70.67 ± 0.44 c | |
| 2021 | 12 100.00 ± 153.95 b | 84.54 ± 1.16 b | 4.33 ± 0.10 c | 46.56 ± 1.65 ab | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 19 414.29 ± 557.14 d | 70.10 ± 0.15 c | 4.44 ± 0.07 b | 72.82 ± 0.92 bc | |
| 2021 | 8 390.00 ± 279.15 c | 66.48 ± 0.32 d | 3.88 ± 0.03 d | 36.02 ± 1.45 d | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 18 685.71 ± 1200.00d | 76.30 ± 3.35 b | 4.30 ± 0.09 c | 72.38 ± 3.21 c | |
| 2021 | 7 635.00 ± 286.18 c | 66.37 ± 2.00 d | 3.80 ± 0.09 d | 33.50 ± 1.40 de | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 2 787.28** | 6.21* | 319.30** | 2 458.88** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 197.59** | 91.06** | 246.66** | 81.26** | ||
| Y × T | 14.44** | 16.06** | 21.38** | 20.59** | ||
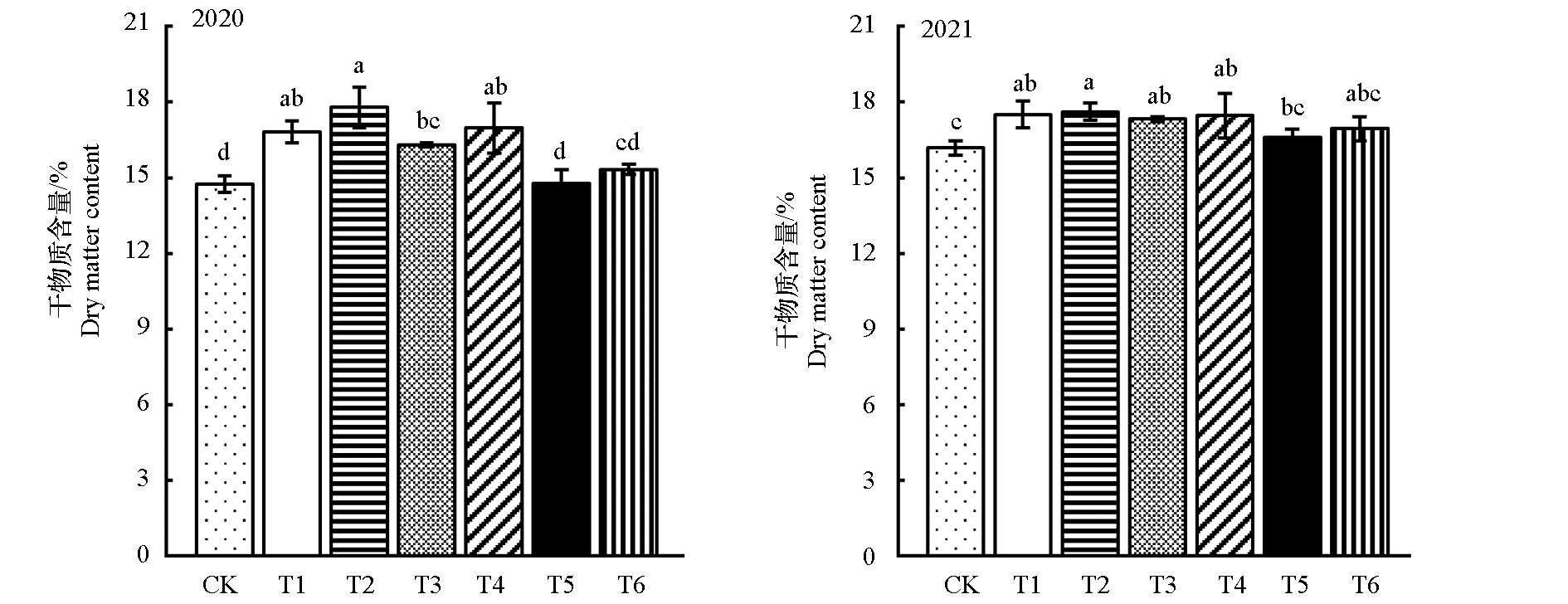
Fig. 1 Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer on dry matter content of potato tuber CK:no fertilization control;T1:high amount of chemical fertilizer;T2:medium chemical fertilizer+organic fertilizer,which is consistent with the total nutrients of high chemical fertilizer;T3:moderate fertilizer application(conventional fertilization by local farmers);T4:Low-amount chemical fertilizer + organic fertilizer consistent with the total nutrients of medium-amount chemical fertilizer;T5:low amount of chemical fertilizer;T6:Single application of organic fertilizer is consistent with the total nutrients of low amount of chemical fertilizer. Different lowercase letters indicate that there is a significant difference at 0.05 level between different treatments in the same year. The same below
| 处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 有机质/(g · kg-1) Organic matter | 碱解氮/(mg · kg-1) Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available phosphorus | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available potassium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 12.91 ± 0.17 b | 58.33 ± 2.38 d | 23.36 ± 0.39 e | 35.80 ± 3.95 e | |
| 2021 | 13.08 ± 0.51 b | 52.27 ± 2.91 d | 26.52 ± 1.54 d | 37.46 ± 2.86 e | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 12.91 ± 0.18 b | 110.13 ± 6.99 a | 59.80 ± 0.30 a | 118.69 ± 3.27 a | |
| 2021 | 11.83 ± 0.23 c | 107.33 ± 7.37 a | 49.08 ± 0.45 a | 154.13 ± 2.46 a | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 16.07 ± 0.85 a | 75.13 ± 1.47 c | 27.91 ± 0.60 d | 60.86 ± 6.88 c | |
| 2021 | 15.98 ± 0.38 a | 66.50 ± 3.50 c | 44.87 ± 2.07 b | 73.25 ± 3.23 c | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 12.44 ± 0.57 b | 84.70 ± 4.56 b | 36.21 ± 0.01 b | 95.15 ± 4.87 b | |
| 2021 | 12.53 ± 0.25 bc | 92.17 ± 5.06 b | 43.36 ± 2.06 b | 92.78 ± 3.23 b | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 15.67 ± 0.56 a | 70.70 ± 4.26 c | 27.77 ± 1.00 d | 58.93 ± 5.74 c | |
| 2021 | 16.12 ± 0.82 a | 63.70 ± 4.85 c | 32.46 ± 0.96 c | 48.19 ± 2.65 d | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 12.89 ± 0.40 b | 70.47 ± 2.72 c | 30.20 ± 0.57 c | 62.60 ± 5.38 c | |
| 2021 | 12.89 ± 0.38 b | 52.97 ± 5.70 d | 44.88 ± 2.49 b | 75.01 ± 3.34 c | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 15.93 ± 0.59 a | 67.33 ± 3.51 c | 24.08 ± 0.30 e | 46.00 ± 2.61 d | |
| 2021 | 15.28 ± 0.70 a | 52.50 ± 3.50 d | 28.61 ± 2.61 d | 42.24 ± 8.39 de | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 0.99 | 25.73** | 181.73** | 21.00** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 664.67** | 106.65** | 314.03** | 339.98** | ||
| Y × T | 1.54 | 4.95** | 63.24** | 17.06** | ||
Table 4 Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer on soil nutrients
| 处理 Treatment | 年份 Year | 有机质/(g · kg-1) Organic matter | 碱解氮/(mg · kg-1) Alkaline nitrogen | 速效磷/(mg · kg-1) Available phosphorus | 速效钾/(mg · kg-1) Available potassium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 12.91 ± 0.17 b | 58.33 ± 2.38 d | 23.36 ± 0.39 e | 35.80 ± 3.95 e | |
| 2021 | 13.08 ± 0.51 b | 52.27 ± 2.91 d | 26.52 ± 1.54 d | 37.46 ± 2.86 e | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 12.91 ± 0.18 b | 110.13 ± 6.99 a | 59.80 ± 0.30 a | 118.69 ± 3.27 a | |
| 2021 | 11.83 ± 0.23 c | 107.33 ± 7.37 a | 49.08 ± 0.45 a | 154.13 ± 2.46 a | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 16.07 ± 0.85 a | 75.13 ± 1.47 c | 27.91 ± 0.60 d | 60.86 ± 6.88 c | |
| 2021 | 15.98 ± 0.38 a | 66.50 ± 3.50 c | 44.87 ± 2.07 b | 73.25 ± 3.23 c | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 12.44 ± 0.57 b | 84.70 ± 4.56 b | 36.21 ± 0.01 b | 95.15 ± 4.87 b | |
| 2021 | 12.53 ± 0.25 bc | 92.17 ± 5.06 b | 43.36 ± 2.06 b | 92.78 ± 3.23 b | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 15.67 ± 0.56 a | 70.70 ± 4.26 c | 27.77 ± 1.00 d | 58.93 ± 5.74 c | |
| 2021 | 16.12 ± 0.82 a | 63.70 ± 4.85 c | 32.46 ± 0.96 c | 48.19 ± 2.65 d | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 12.89 ± 0.40 b | 70.47 ± 2.72 c | 30.20 ± 0.57 c | 62.60 ± 5.38 c | |
| 2021 | 12.89 ± 0.38 b | 52.97 ± 5.70 d | 44.88 ± 2.49 b | 75.01 ± 3.34 c | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 15.93 ± 0.59 a | 67.33 ± 3.51 c | 24.08 ± 0.30 e | 46.00 ± 2.61 d | |
| 2021 | 15.28 ± 0.70 a | 52.50 ± 3.50 d | 28.61 ± 2.61 d | 42.24 ± 8.39 de | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 0.99 | 25.73** | 181.73** | 21.00** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 664.67** | 106.65** | 314.03** | 339.98** | ||
| Y × T | 1.54 | 4.95** | 63.24** | 17.06** | ||
| 处理Treatment | 年份Year | N/(kg · kg-1) | P/(kg · kg-1) | K/(kg · kg-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 289.42 ± 0.52 a | 2 895.30 ± 92.08 a | 176.09 ± 2.63 c | |
| 2021 | 159.81 ± 1.01 a | 1 793.37 ± 328.40 a | 83.92 ± 0.98 c | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 210.33 ± 2.18 e | 1 162.09 ± 37.19 d | 185.16 ± 7.13 b | |
| 2021 | 108.60 ± 0.44 f | 922.94 ± 135.89 e | 85.65 ± 1.41 bc | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 219.46 ± 0.95 d | 1 493.40 ± 89.71 c | 190.69 ± 0.00 b | |
| 2021 | 110.20 ± 0.88 f | 1 059.81 ± 39.30 de | 87.92 ± 1.21 b | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 282.88 ± 1.78 b | 1 580.16 ± 19.48 c | 186.81 ± 5.65 b | |
| 2021 | 133.53 ± 1.47 d | 1 337.83 ± 50.82 bcd | 87.25 ± 0.76 b | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 285.43 ± 2.63 ab | 1 900.21 ± 280.52 b | 202.29 ± 3.07 a | |
| 2021 | 141.23 ± 2.56 c | 1 571.22 ± 66.77 ab | 98.94 ± 2.12 a | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 243.32 ± 2.06 c | 1 502.89 ± 51.79 c | 159.77 ± 2.02 d | |
| 2021 | 125.91 ± 0.16 e | 1 220.02 ± 75.23 cd | 64.83 ± 1.49 e | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 287.87 ± 4.72 a | 1 798.45 ± 82.05 b | 173.41 ± 3.05 c | |
| 2021 | 146.79 ± 0.49 b | 1 462.56 ± 71.16 bc | 81.13 ± 0.34 d | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 44 731.57** | 104.63** | 11 320.08** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 1 089.48** | 58.22** | 94.90** | ||
| Y × T | 133.89** | 7.83** | 3.72** | ||
Table 5 Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with organic fertilizer on utilization efficiency of nitrogen,phosphorus and potassium in potato
| 处理Treatment | 年份Year | N/(kg · kg-1) | P/(kg · kg-1) | K/(kg · kg-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不施肥对照 No fertilization control(CK) | 2020 | 289.42 ± 0.52 a | 2 895.30 ± 92.08 a | 176.09 ± 2.63 c | |
| 2021 | 159.81 ± 1.01 a | 1 793.37 ± 328.40 a | 83.92 ± 0.98 c | ||
| 高量化肥 High chemical fertilizer(T1) | 2020 | 210.33 ± 2.18 e | 1 162.09 ± 37.19 d | 185.16 ± 7.13 b | |
| 2021 | 108.60 ± 0.44 f | 922.94 ± 135.89 e | 85.65 ± 1.41 bc | ||
| 中量化肥 + 有机肥 Medium chemical + organic fertilizer(T2) | 2020 | 219.46 ± 0.95 d | 1 493.40 ± 89.71 c | 190.69 ± 0.00 b | |
| 2021 | 110.20 ± 0.88 f | 1 059.81 ± 39.30 de | 87.92 ± 1.21 b | ||
| 中量化肥 Medium chemical fertilizer(T3) | 2020 | 282.88 ± 1.78 b | 1 580.16 ± 19.48 c | 186.81 ± 5.65 b | |
| 2021 | 133.53 ± 1.47 d | 1 337.83 ± 50.82 bcd | 87.25 ± 0.76 b | ||
| 低量化肥 + 有机肥 Low chemical + organic fertilizer(T4) | 2020 | 285.43 ± 2.63 ab | 1 900.21 ± 280.52 b | 202.29 ± 3.07 a | |
| 2021 | 141.23 ± 2.56 c | 1 571.22 ± 66.77 ab | 98.94 ± 2.12 a | ||
| 低量化肥 Low chemical fertilizer(T5) | 2020 | 243.32 ± 2.06 c | 1 502.89 ± 51.79 c | 159.77 ± 2.02 d | |
| 2021 | 125.91 ± 0.16 e | 1 220.02 ± 75.23 cd | 64.83 ± 1.49 e | ||
| 单施有机肥 Organic fertilizer(T6) | 2020 | 287.87 ± 4.72 a | 1 798.45 ± 82.05 b | 173.41 ± 3.05 c | |
| 2021 | 146.79 ± 0.49 b | 1 462.56 ± 71.16 bc | 81.13 ± 0.34 d | ||
| 方差分析 ANOVA | 年度Year(Y) | 44 731.57** | 104.63** | 11 320.08** | |
| 处理Treat(T) | 1 089.48** | 58.22** | 94.90** | ||
| Y × T | 133.89** | 7.83** | 3.72** | ||
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2000. 土壤农化分析. 北京: 中国农业出版社.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
郭斌煜, 刘坤雨. 2019. 喷施有机水溶肥对马铃薯生长过程中干物质积累的影响研究. 吉林农业,(8):50.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
韩羽, 杨亚亚, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 满本菊, 杨永森. 2023. 施钾量对宁夏旱区马铃薯干物质积累及养分利用特性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 51 (9):119-124.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
侯红乾, 林洪鑫, 刘秀梅, 冀建华, 刘益仁, 蓝贤瑾, 吕真真, 周卫军. 2020. 长期施肥处理对双季晚稻叶绿素荧光特征及籽粒产量的影响. 作物学报, 46 (2):280-289.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
黄伟, 王西和, 贾宏涛, 杨金钰, 屈小慧, 刘盈锐, 刘晓菊. 2024. 磷肥有机替代、秸秆还田对棉花养分吸收和磷肥利用效率的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 41 (2):333-343.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
李成晨, 安康, 索海翠, 刘晓津, 李小波. 2019. 广东省冬种马铃薯施肥现状调查与施肥对策. 热带作物学报, 40 (10):2054-2060.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
柳燕兰, 郭贤仕, 张绪成, 马明生, 王宏康. 2021. 密度和施肥对旱地马铃薯干物质积累、产量和水肥利用的影响. 作物学报, 47 (2):320-331.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
娄菲, 左怿平, 李萌, 代鑫萌, 王健, 韩金玲, 吴舒, 李向岭, 段会军. 2024. 有机肥替代部分化肥氮对糯玉米产量、品质及氮素利用的影响. 作物学报, 50 (4):1053-1064.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
吕真真, 吴向东, 侯红乾, 冀建华, 刘秀梅, 刘益仁. 2017. 有机-无机肥配施比例对双季稻田土壤质量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23 (4):904-913.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
钱晨诚, 陈立, 马泉, 李春燕, 朱敏, 朱新开, 丁锦峰, 郭文善. 2023. 磷钾肥施用量和方法对弱筋小麦籽粒产量和蛋白质含量及养分吸收利用的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 29 (2):287-299.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
任科宇, 段英华, 徐明岗, 张旭博. 2019. 施用有机肥对我国作物氮肥利用率影响的整合分析. 中国农业科学, 52 (17):2983-2996.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
Shahinur, Amin, Biswas, Afrose, Hossain. 2019. Feasibility of replacing chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer in maize(Zea mays L.) Production in dhaka,bangladesh. International Journal of Plant & Soil Science:1-5.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
疏再发, 吉庆勇, 邵静娜, 郑生宏, 周慧娟, 何卫中. 2023. 茶园有机肥替代化肥对土壤养分和茶叶产量与品质的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2207-2219.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
唐继伟, 徐久凯, 温延臣, 田昌玉, 林治安, 赵秉强. 2019. 长期单施有机肥和化肥对土壤养分和小麦产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (11):1827-1834.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王三根. 2017. 植物生理学实验教程. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
王文赞, 韩建, 倪玉雪, 李记园, 尹兴, 王琛, 张丽娟. 2023. 有机肥替代化肥氮对苹果产量、品质及温室气体排放的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 29 (3):437-448.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
王小英, 同延安, 刘芬, 赵佐平. 2013. 陕西省马铃薯施肥现状评价. 植物营养与肥料学报, 19 (2):471-479.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
伍晓轩, 杨洪坤, 朱杰, 柳伟伟, 普琼达瓦, 樊高琼. 2019. 不同有机肥种类配施化学氮肥对丘陵旱地小麦产量和籽粒蛋白质品质的影响. 四川农业大学学报, 37 (3):283-287.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
谢勇, 赵易艺, 张玉平, 唐丽, 何石福, 石敦杰, 刘强, 荣湘民. 2018. 南方丘陵地区生物黑炭和有机肥配施化肥的应用研究. 水土保持学报, 32 (4):197-203.
|
|
| [29] |
|
|
杨浩瑜, 刘惠见, 张乃明, 贺婷, 邓洪, 包立. 2020. 化肥减施处理对茶园土壤养分及茶叶品质的影响. 南方农业学报, 51 (4):887-896.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
杨毅, 何志强, 林佳慧, 李洋, 陈飞, 吕长文, 唐道彬, 周全卢, 王季春. 2023. 椰糠施用量对土壤理化性状和甘薯产量的影响. 作物学报, 49 (9):2517-2527.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
于跃跃, 郭宁, 闫实, 姜言娇, 韩宝, 吴万军, 贾小红. 2021. 有机肥替代化肥对土壤肥力和玉米产量的影响. 中国土壤与肥料,(3):148-154.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张恩平, 谭福雷, 王月, 张淑红, 段瑜, 周芳. 2015. 氮磷钾与有机肥配施对番茄产量品质及土壤酶活性的影响. 园艺学报, 42 (10):2059-2067.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
张奇茹, 谢英荷, 李廷亮, 刘凯, 姜丽伟, 曹静, 邵靖琳. 2020. 有机肥替代化肥对旱地小麦产量和养分利用效率的影响及其经济环境效应. 中国农业科学, 53 (23):4866-4878.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
张然, 史雷, 马龙, 王楷, 翟丙年, 李紫燕, 王朝辉. 2020. 有机无机肥配施对旱地冬小麦产量及土壤物理性质的影响. 水土保持学报, 34 (6):325-330.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
张伟彬. 2022. 有机肥和化肥配施对小麦甘薯轮作土壤腐殖质结合形态及微生物群落结构的影响. 江苏农业科学, 50 (17):247-252.
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
张绪成, 于显枫, 王红丽, 侯慧芝, 方彦杰, 马一凡. 2016. 半干旱区减氮增钾、有机肥替代对全膜覆盖垄沟种植马铃薯水肥利用和生物量积累的调控. 中国农业科学, 49 (5):852-864.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
赵志伟, 高飞雁, 罗军, 盛阳阳, 韩丽, 张永平. 2022. 氮磷肥不同配比对河套地区春小麦产量、品质及养分利用的影响. 中国土壤与肥料,(11):1-9.
|
| [1] | JI Xiaomei, ZHAI Jinghua, CHEN Zhiwei, ZHANG Hong, YUE Youzhang, ZHAO Zhiyuan, Yang Jingwen, HUANG Wei, KOU Xiaowen, ZENG Yunliu, CAI Lihong, LIU Jie, MI Xukai, LI Xiuli. A New Early-Maturing Yellow-Fleshed Kiwifruit Cultivar‘Xiangnong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 49-50. |
| [2] | CHEN Li, LI Yadong, YANG Lei, LIU Jiaxin, ZHAO Dongshuang, SUN Haiyue. A New Cranberry Cultivar‘Heyunhong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 59-60. |
| [3] | CHENG Lili, HU Guanglong, CHENG Yunhe, LAN Yanping. A New Cultivar of Chinese Chestnut‘Jingnongza 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 63-64. |
| [4] | PATIGULI Maimaitituerxun, ZHOU Bin, LUO Qinghong, SHENG Wei, JIANG Teng. A New Cultivar of Elaeagnus moorcroftii‘Jinsha’in Xinjiang [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 71-72. |
| [5] | CHENG Shimin, HUANG Lina, WEI Junya, ZHAO Zengxian, LIU Jincheng, WEI Shouxing. A New Banana Cultivar‘Repin 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 73-74. |
| [6] | LIU Chong, YI Dandan, ZOU Danrong, ZHOU Lixue, WANG Hui, SHENG Lili, CHEN Xiaofeng, ZHANG Yaming, GUI Hang. A New Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Qingmei 1’of High-Yield and High-Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 87-88. |
| [7] | YU Xiaolin, PING Fan, HUANG Li, CAO Jiashu, SONG Jianwei, LU Gang. A New Early-Mid Maturing Non-Heading Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Qiantangqing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 91-92. |
| [8] | ZHANG Guwen, SHEN Li, LIU Na, FENG Zhijuan, BU Yuanpeng, WANG Bin, GONG Yaming. A New Vegetable Soybean Cultivar‘Zhenong 15’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 129-130. |
| [9] | YANG Li, QIN Ya, BIAN Baciren, ZHEN Zhen, QIONG Ji, BAI Maquzhen, ZHOU Ya. A New Cultivar of Colored Potato‘Xigezi 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 145-146. |
| [10] | CHU Zhuannan, LI Weiwen, WU Jiqiu, PENG Xingxing, TANG Maogui, DONG Ling, CUI Guangsheng, XIONG Rui, LIANG Hua, HAN Piao. A New Chrysanthemum morifolium Cultivar‘Gongju 3’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(S1): 177-178. |
| [11] | DU Hao, ZHAO Shilong, XIAO Yuansong, LUO Jingjing, PENG Futian. The Effect of Methionine on the Growth of Peach Tree Shoots and Fruit Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 973-983. |
| [12] | CHENG Xiaogai, WAN Yuan, LIN Lu, XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, LI Mi, WANG Pengpeng, NIU Zimian. Influences of Trunk Heights on Leaf Photosynthesis and Fruit Qualities at Different Canopy Locations in Open-Central Canopy of Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [13] | CONG Xin, HU Qianyuan, PANG Guibin, XU Lirong, XU Zhenghe, LIU Hongfei, PEI Xiangli. Effect of the Salinity of Irrigation Water on Growth,Yield,and Quality of Ziziphus jujuba‘Dongzao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 714-726. |
| [14] | REN Yi, ZHANG Yixing, HOU Saisai, NIE Lanchun, LI Qingyun, WANG Xinxin. Research Progress on the Preparation Method of Biochar and Its Application Effect on Returning to Field in Facility Vegetable Fields [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 792-812. |
| [15] | XU Tong, WANG Yue, WU Lina, ZHANG Hang, YIN Lilai, XU Keyu, ZHENG Xiaolin. Effects of Melatonin Treatment on Fruit Quality and Anthocyanin Metabolism of Postharvest‘Taoxingli’Plum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 395-405. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd