
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (8): 1697-1710.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0642
• Cultivation Physiology & Biochemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Zhijuan2, LIU Wenjie1, ZHENG Xiaodong1, XI Xiangli1, MA Changqing1, LIU Xiaoli1, WANG Caihong1, TIAN Yike1,**( )
)
Received:2023-05-29
Revised:2023-07-10
Online:2023-08-25
Published:2023-08-23
Contact:
TIAN Yike
SUN Zhijuan, LIU Wenjie, ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, MA Changqing, LIU Xiaoli, WANG Caihong, TIAN Yike. Effects and Functional Mechanism of Melatonin on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Seedlings Under Saline-Alkali Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1697-1710.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0642
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AATGCCATTTGCCAATAACCT |
| MhNHX1 | TTCTGCGTGAACTTTAGACCCT | AAGACTGAGATTTCCTTTCAAGC |
| MhNHX2 | CCACATTGATTCCAGTATTGCTT | CTCTTGAACTCTCCGTCACATTG |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhCHX15 | AGATTATCCGTATCCTCTAAGTCTGG | TGGTTCGGCCTATCGTGAAA |
| MhSOS1 | TACACTGTCGCTCTGCTCATCC | CCAGTCGTAAGGGAAAGTGAGC |
| MhGPX6 | TTCCGAGAGTAAATCAATCCACG | AGGCAAACTCTACAATCTCGTCA |
| MhpoxN1 | GCTCCTCCAAATCATTGTTACTG | AAGAAGGACAGAAGCATCACAA C |
| MhPER65 | GGCATTCTATTCCCATTCCCTT | GAGTTGGAAGCGATGAGGAGG |
| MhAHA1 | CCAGAGAAAACAAAAGAGAGTC | TTCACATTCACACCGAGATTG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| MhSKOR | CATCCTGACAACTGGTGGTATCG | AATGCCATTTGCCAATAACCT |
| MhNHX1 | TTCTGCGTGAACTTTAGACCCT | AAGACTGAGATTTCCTTTCAAGC |
| MhNHX2 | CCACATTGATTCCAGTATTGCTT | CTCTTGAACTCTCCGTCACATTG |
| MhNHX4 | ACGAAACTCCTTTACTATACAGCCT | TGATACCACAGATAAGTGAGCATAG |
| MhCHX15 | AGATTATCCGTATCCTCTAAGTCTGG | TGGTTCGGCCTATCGTGAAA |
| MhSOS1 | TACACTGTCGCTCTGCTCATCC | CCAGTCGTAAGGGAAAGTGAGC |
| MhGPX6 | TTCCGAGAGTAAATCAATCCACG | AGGCAAACTCTACAATCTCGTCA |
| MhpoxN1 | GCTCCTCCAAATCATTGTTACTG | AAGAAGGACAGAAGCATCACAA C |
| MhPER65 | GGCATTCTATTCCCATTCCCTT | GAGTTGGAAGCGATGAGGAGG |
| MhAHA1 | CCAGAGAAAACAAAAGAGAGTC | TTCACATTCACACCGAGATTG |
| MhAHA2 | AAAGTGTGAAGAAAGAGAAAATGC | AGTTCATTTGCTTGACATTCTTT |
| MhAHA8 | GGTCAAAAGTGTGTTGGTAAGCA | AAACCAAAATCCTCCAACAGC |
| MhActin | CTTCAATGTGCCTGCCATGTAT | AATTTCCCGTTCAGCAGTAGTG |
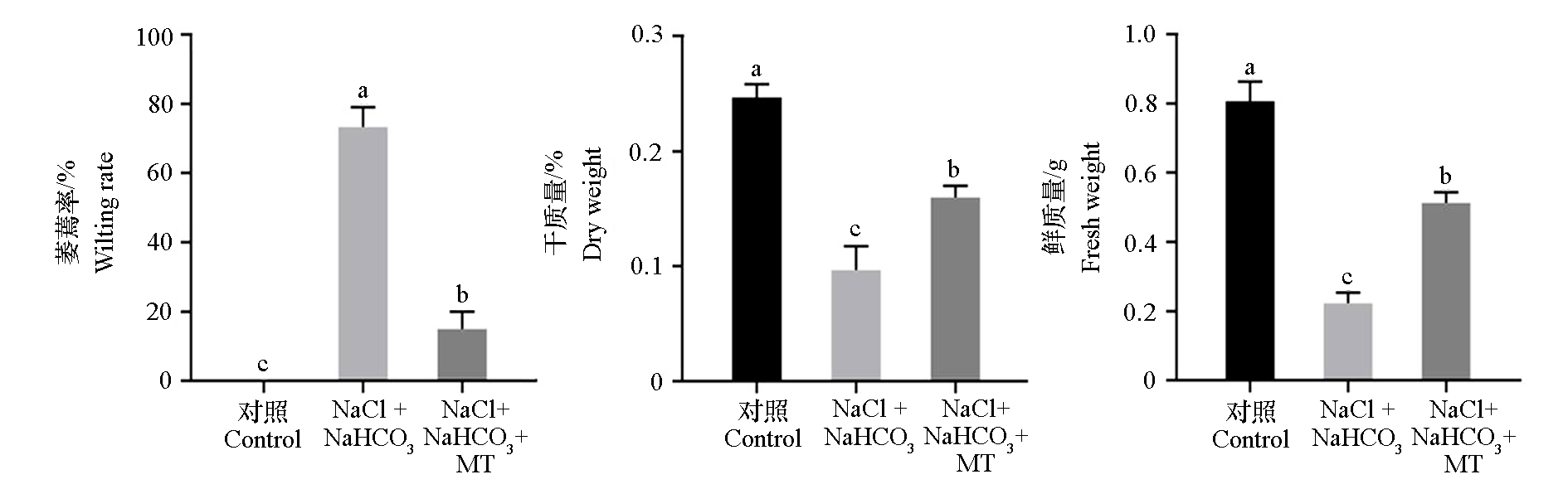
Fig. 2 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on wilting rate and biomass of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress Different lowercase letters represent significant differcences(P < 0.05). The same below.
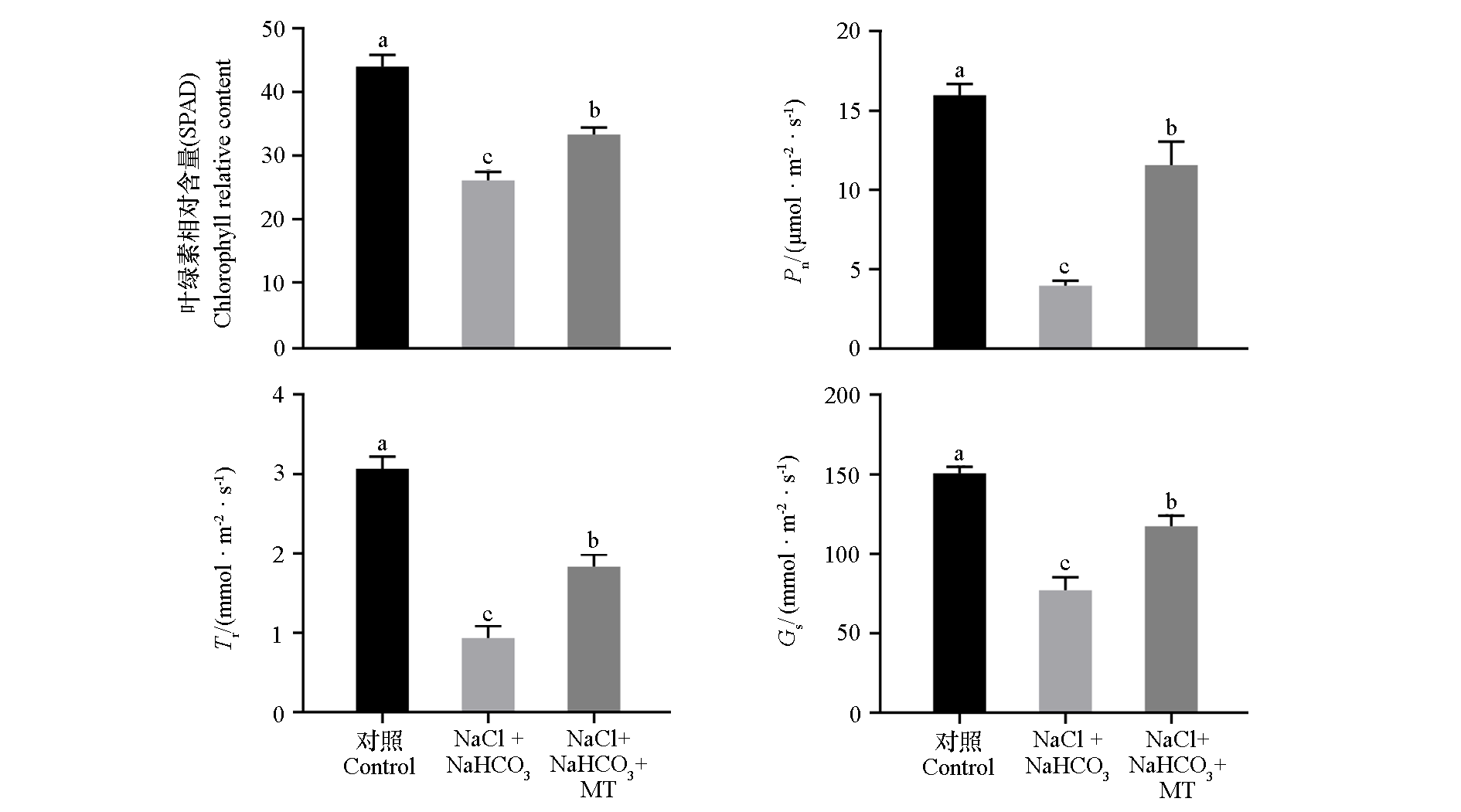
Fig. 3 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on chlorophyll content and photosynthetic indexes of Malus hupehensis leaves under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress

Fig. 5 Effects of exogenous melatonin(MT)on reactive oxygen content and antioxidant enzyme activities of Malus hupehensis plants under saline-alkali(NaCl + NaHCO3)stress
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈如男, 任春元, 李贺, 王华美, 张严文, 于高波. 2021. 外源褪黑素通过诱导SIRR基因表达调控番茄盐碱胁迫响应. 北方园艺,(10):7-14.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1111/ppl.2018.164.issue-3 URL |
| [4] |
|
|
段文静, 孟妍君, 江丹, 刘连涛, 张科, 张永江, 孙红春, 白志英, 李存东. 2022. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花幼苗形态及抗氧化系统的影响. 中国生态农业学报, 30 (1):92-104.
|
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.667458 URL |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.03.006 URL |
| [8] |
|
|
高倩, 卢楠. 2021. 盐碱地综合治理开发研究现状及展望. 南方农机, 52 (16):153-155.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
霍宏亮, 王超, 杨祥, 曹玉芬, 田路明, 董星光, 张莹, 齐丹, 徐家玉, 刘超. 2021. 杜梨对盐碱胁迫的生理响应及耐盐碱性评价. 植物遗传资源学报, 23 (2):480-492.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
焦德志, 赵泽龙. 2019. 盐碱胁迫对植物形态和生理生化影响及植物响应的研究进展. 江苏农业科学, 47 (20):1-4.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
康益晨. 2021. 马铃薯响应碱性盐胁迫的生理及分子机制研究[博士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.03.015 URL |
| [14] |
|
|
刘奕媺, 于洋, 方军. 2018. 盐碱胁迫及植物耐盐碱分子机制研究. 土壤与作物, 7 (2):201-211.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘玉莲, 车飞, 王海, 陈佰鸿, 陈年来. 2016. 苹果果实中糖、酸和花青苷的组分及含量特征分析. 西北林学院学报, 31 (6):236-242.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
毛恋, 芦建国, 江海燕. 2020. 植物响应盐碱迫的机制. 分子植物育种, 18 (10):3441-3448.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
毛庆莲, 王胜. 2020. 国内盐碱地治理趋势探究浅析. 湖北农业科学, 59 (S1):302-306.
|
|
| [18] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.10.23 |
|
毛爽, 周万里, 杨帆, 狄小琳, 蔺吉祥, 杨青杰. 2021. 植物根系应答盐碱胁迫机理研究进展. 浙江农业学报, 33 (10):1991-2000.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.10.23 |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
沙广利, 郝玉金, 万述伟, 束怀瑞. 2015. 苹果砧木种类及应用进展. 落叶果树, 47 (3):2-6.
|
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110026 URL |
| [23] |
|
|
王佺珍, 刘倩, 高娅妮, 柳旭. 2017. 植物对盐碱胁迫的响应机制研究进展. 生态学报, 37 (16):5565-5577.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
王晚霞, 高立杨, 张瑞, 赵婷, 张仲兴, 王双成, 王延秀. 2021. 2, 4-表油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下垂丝海棠光合及生理特性的影响. 果树学报, 38 (9):1479-1490.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
王娟, 黄荣峰. 2015. 乙烯调控植物耐盐性的研究进展. 植物生理学报, 51 (10):1567-1572.
|
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.12.006 URL |
| [27] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0159 |
|
向妙莲, 吴帆, 李树成, 马巧利, 王印宝, 肖刘华, 陈金印, 陈明. 2022. 外源褪黑素调控活性氧代谢诱导梨果实抗采后黑斑病. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1102-1110
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0159 |
|
| [28] |
|
|
许盼云, 李春兰, 宋金迪, 王鑫, 程嘉宝, 吴玉霞, 何天明. 2017. 不同苹果砧木实生苗对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应. 新疆农业科学, 58 (9):1694-1703.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.07.015 URL |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.04.003 URL |
| [31] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00568 URL |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
赵德英, 程存刚, 仇贵生, 董雅凤, 张彩霞, 李壮, 张怀江, 胡国君, 厉恩茂. 2021. 苹果高质量发展技术创新途径. 中国果树,(8):1-5.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
赵海亮, 左璐, 马长恩, 白龙强, 胡晓辉, 侯雷平. 2021. 果实膨大期叶面喷施褪黑素对番茄品质的影响. 北方园艺,(17):15-21.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
赵怀玉, 林鸿宣. 2020. 植物响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制. 土壤与作物, 9 (2):103-113.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0496 |
|
赵雨晴, 陈涛, 袁明. 2021. 褪黑素在果实发育和采后保鲜中的应用. 园艺学报, 48 (6):1233-1249.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0496 |
|
| [37] |
|
|
赵占周. 2020. 土壤盐碱化对植物的影响及改良预防措施. 西北园艺(果树),(6):40-42.
|
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03215-y |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.12.015 URL |
| [40] |
|
|
郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 2022. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1401-1414.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0499 |
|
| [41] |
|
|
朱建峰, 崔振荣, 吴春红, 邓丞, 陈军华, 张华新. 2018. 我国盐碱地绿化研究进展与展望. 世界林业研究, 31 (4):70-75.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [1] | LI Shaoxuan, WANG Zhiyun , HU Dagang , ZHU Bo , and HAN Mingsan, . A New Late Ripening Apple Cultivar‘Qinfu 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 1-2. |
| [2] | SUN Yanxia , TANG Yan , LIU Daliang , ZHAO Lingling , ZHANG Xueyong , LIU Xueqing , Dorota Ewa Kruczynska , CHENG Zhijuan , Sylwia Keller-Przybylkowicz , and SONG Laiqing, . A New Early-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Yanqingyu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 3-4. |
| [3] | ZHAO Guodong, JIA Linguang, CHEN Dongmei, ZHAO Tongsheng , ZHANG Xinsheng , ZHANG Chaohong, LI Chunmin, and FU You . A New Apple Cultivar‘Yinghong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 5-6. |
| [4] | YU Lu , NIU Zimian, GUO Wenlong , LIN Lu , LI Quan , LI Zhiqiang , WANG Hongning , and LI Hongyan. A New Early-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Xialu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 7-8. |
| [5] | LIU Chuanhe, HE Han, SHAO Xuehua, LAI Duo, KUANG Shizi, XIAO Weiqiang, LIU Yan. A New Pineapple Cultivar‘Yuetian’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 2059-2060. |
| [6] | WANG Xiaofang, XIA Qun, LUAN Risheng, XU Li, YIN Chengmiao, WANG Yanfang, CHEN Xuesen, MAO Zhiquan, XIANG Kun. Inhibition of Tagetes erecta Straw Powder on the Main Pathogens of Apple Continuous Cropping Obstacle and Its Field Application Effect [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1518-1534. |
| [7] | WANG Jinxin, HUANG Jingmiao, HAO Jie, LI Xueying, FENG Jianzhong, SUO Xiangmin, YAN Xinmin. A New Late Ripening Apple Cultivar‘Jiping 5’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1601-1602. |
| [8] | QIN Sijun, ZHANG Kuo, QI Bianbin, YU Bo, LÜ Deguo. Effects of Exogenous Glucose on Soil Active Organic Carbon Pool in Apple Root Zone and Plant Growth and Development [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1295-1304. |
| [9] | KAN Zhiyong, ZHANG Dehui, LI Zhongxing, YU Sisi, QIAN Qian, FAN Tianle, LI Xuewei, MA Fengwang, GUAN Qingmei. Evaluation of Cold Tolerance of 90 Apple Cultivars and Genome Wide Association Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 921-932. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kun, SI Binbin, ZHOU Jun, REN Yufeng, ZHANG Xin, XU Wendi, WANG Jiawei, QIAO Shuai, WANG Huiran. Construction of cDNA Library of Apple Rootstock‘Qingzhen 1’Leaf and Screen of MdMLO Genes’ Upstream Regulator [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 933-946. |
| [11] | GAO Meina, SUN Mingfei, ZHU Jie, JING Junli, LI Jia, ZHOU Shasha, LIANG Bowen, XU Jizhong, LI Zhongyong. The Rooting Effect and Changes of IAA Content in Constriction,Girdling Treatment During Shoot Layering of Apple Rootstock‘Jizhen 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1063-1072. |
| [12] | LIU Youxian, LI Guofang, TAN Ming, YANG Zhichang, ZHOU Shiwei, HUO Wenjing, ZHANG He, SUN Jianshe, SHAO Jianzhu. Expression Analysis of MdTOPP13/28 During Axillary Bud Outgrowth in Malus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 697-712. |
| [13] | NING Yuansheng, LI Huan, SONG Jianfei, YU Tingting, HAN Mengyuan, PENG Lulin, JIA Junqi, ZHANG Weiwei, YANG Hongqiang. Characterization of NCL Family Genes in Malus and Their Relationship with Cellular Calcium Concentration in Root [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 475-484. |
| [14] | YU Tingting, LI Huan, NING Yuansheng, SONG Jianfei, PENG Lulin, JIA Junqi, ZHANG Weiwei, YANG Hongqiang. Genome-wide Identification of GRAS Gene Family in Apple and Expression Analysis of Its Response to Auxin [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [15] | HAN Xiaolei, ZHANG Caixia, LIU Kai, YANG An, YAN Jiadi, LI Wuxing, KANG Liqun, and CONG Peihua. A New Mid-ripening Apple Cultivar‘Zhongping Youlei’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 1-2. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd