
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (7): 1282-1294.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0242
• Research Papars • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Yujing1, LU Yin1, FENG Daling1, LUO Lei1, WU Fang2, YANG Rui1, CHEN Yueqi1, SUN Xiaoxue1, WANG Yanhua1, CHEN Xueping1, SHEN Shuxing1,**( ), LUO Shuangxia1,**(
), LUO Shuangxia1,**( ), ZHAO Jianjun1,**(
), ZHAO Jianjun1,**( )
)
Received:2021-04-27
Revised:2021-05-21
Online:2021-07-25
Published:2021-08-10
Contact:
SHEN Shuxing,LUO Shuangxia,ZHAO Jianjun
E-mail:shensx@hebau.edu.cn;yylsx@hebau.edu.cn;jjz1971@aliyun.com
CLC Number:
ZHAO Yujing, LU Yin, FENG Daling, LUO Lei, WU Fang, YANG Rui, CHEN Yueqi, SUN Xiaoxue, WANG Yanhua, CHEN Xueping, SHEN Shuxing, LUO Shuangxia, ZHAO Jianjun. Association Analysis Between Background Selection InDel Markers and Important Agronomic Traits in Inbred Lines of Chinese Cabbage[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1282-1294.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0242
| 编号 No. | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 熟性 Maturity | 叶色 Leaf color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B14Q-101 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 2 | B17Q-432 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 晚熟Late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 3 | B14Q-109 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中熟Middle maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 4 | B14Q-113 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 5 | B17Q-433 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 6 | B14Q-124 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 7 | B17Q-435 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中熟Middle maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 8 | B17Q-436 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 9 | B17Q-437 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 10 | B17Q-442 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 11 | B17Q-441 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 12 | B17Q-443 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 晚熟Late maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 13 | B17Q-444 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 14 | B14Q-211 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 15 | B17Q-447 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中熟Middle maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 16 | B17Q-448 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中熟Middle maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 17 | B14Q-209 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 18 | B17Q-445 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 19 | B17Q-446 | 平头类型Flat head type | 中熟Middle maturity | 绿Green |
| 20 | B14Q-141 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 21 | B17Q-439 | 平头类型Flat head type | 极早熟Very early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 22 | B17Q-450 | 平头类型Flat head type | 极早熟Very early maturity | 绿Green |
| 23 | B17Q-452 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 24 | B17Q-453 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 25 | B14Q-260 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 极早熟Very early maturity | 绿Green |
| 26 | B17Q-440 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 极早熟Very early maturity | 黄绿Yellow green |
| 27 | B14Q-159 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 中熟Middle maturity | 绿Green |
| 28 | B17Q-449 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 晚熟Late maturity | 绿Green |
| 29 | B14Q-267 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 30 | B14Q-279 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 31 | B17Q-455 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 深绿Dark green |
Table 1 Information of Chinese cabbage inbred lines
| 编号 No. | 名称 Name | 类型 Type | 熟性 Maturity | 叶色 Leaf color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B14Q-101 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 2 | B17Q-432 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 晚熟Late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 3 | B14Q-109 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中熟Middle maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 4 | B14Q-113 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 5 | B17Q-433 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 6 | B14Q-124 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 7 | B17Q-435 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中熟Middle maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 8 | B17Q-436 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 9 | B17Q-437 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 10 | B17Q-442 | 卵圆类型Oval type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 11 | B17Q-441 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 12 | B17Q-443 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 晚熟Late maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 13 | B17Q-444 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 14 | B14Q-211 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中晚熟Middle late maturity | 绿Green |
| 15 | B17Q-447 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中熟Middle maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 16 | B17Q-448 | 直筒类型Straight tube type | 中熟Middle maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 17 | B14Q-209 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 18 | B17Q-445 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 19 | B17Q-446 | 平头类型Flat head type | 中熟Middle maturity | 绿Green |
| 20 | B14Q-141 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 21 | B17Q-439 | 平头类型Flat head type | 极早熟Very early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 22 | B17Q-450 | 平头类型Flat head type | 极早熟Very early maturity | 绿Green |
| 23 | B17Q-452 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 浅绿Light green |
| 24 | B17Q-453 | 平头类型Flat head type | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 25 | B14Q-260 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 极早熟Very early maturity | 绿Green |
| 26 | B17Q-440 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 极早熟Very early maturity | 黄绿Yellow green |
| 27 | B14Q-159 | 花心变种Flower heart variety | 中熟Middle maturity | 绿Green |
| 28 | B17Q-449 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 晚熟Late maturity | 绿Green |
| 29 | B14Q-267 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 30 | B14Q-279 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 绿Green |
| 31 | B17Q-455 | 散叶变种Loose leaf variety | 早熟Early maturity | 深绿Dark green |
| 染色体 Chromosome | InDel数 InDel number | 基因组物理位置/bp Genomic physical location | 扩增片段大小/bp Amplified fragment size |
|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 20 | 1 214 145 ~ 25 476 244 | 80 ~ 160 |
| A02 | 14 | 519 753 ~ 26 721 576 | 88 ~ 160 |
| A03 | 18 | 1 103 584 ~ 30 532 716 | 91 ~ 160 |
| A04 | 15 | 180 352 ~ 19 056 973 | 100 ~ 158 |
| A05 | 22 | 1 631 177 ~ 23 981 249 | 96 ~ 156 |
| A06 | 22 | 1 820 ~ 25 083 208 | 92 ~ 160 |
| A07 | 21 | 166 456 ~ 25 516 427 | 83 ~ 160 |
| A08 | 12 | 1 020 793 ~ 20 443 351 | 86 ~ 159 |
| A09 | 23 | 228 941 ~ 38 012 377 | 93 ~ 159 |
| A10 | 10 | 1 108 151 ~ 14 947 251 | 94 ~ 160 |
Table 2 Distribution of InDel molecular markers
| 染色体 Chromosome | InDel数 InDel number | 基因组物理位置/bp Genomic physical location | 扩增片段大小/bp Amplified fragment size |
|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | 20 | 1 214 145 ~ 25 476 244 | 80 ~ 160 |
| A02 | 14 | 519 753 ~ 26 721 576 | 88 ~ 160 |
| A03 | 18 | 1 103 584 ~ 30 532 716 | 91 ~ 160 |
| A04 | 15 | 180 352 ~ 19 056 973 | 100 ~ 158 |
| A05 | 22 | 1 631 177 ~ 23 981 249 | 96 ~ 156 |
| A06 | 22 | 1 820 ~ 25 083 208 | 92 ~ 160 |
| A07 | 21 | 166 456 ~ 25 516 427 | 83 ~ 160 |
| A08 | 12 | 1 020 793 ~ 20 443 351 | 86 ~ 159 |
| A09 | 23 | 228 941 ~ 38 012 377 | 93 ~ 159 |
| A10 | 10 | 1 108 151 ~ 14 947 251 | 94 ~ 160 |
| 性状类型 Character type | 性状 Trait | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Deviation | 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation | H’ | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连续性性状 Continuous traits | 株高Plant height | 17.33 | 56.50 | 39.17 | 37.88 | 10.77 | 28.44 | 1.961 | 0.943 |
| 开展度Expansion diameter | 41.50 | 83.67 | 42.17 | 62.47 | 12.14 | 19.44 | 2.038 | 0.927 | |
| 叶片长Leaf length | 24.00 | 58.00 | 34.00 | 40.03 | 9.19 | 22.95 | 2.156 | 0.937 | |
| 叶片宽Leaf width | 16.50 | 37.33 | 20.83 | 25.25 | 4.69 | 18.56 | 1.897 | 0.912 | |
| 中肋厚Middle rib thickness | 0.65 | 1.20 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 15.97 | 1.794 | 0.922 | |
| 中肋长Middle rib length | 10.00 | 36.33 | 26.33 | 21.98 | 7.12 | 32.40 | 2.238 | 0.972 | |
| 中肋宽Middle rib width | 4.00 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 5.94 | 0.98 | 16.57 | 1.965 | 0.895 | |
| 外叶数Outer leaf number | 6.00 | 17.50 | 11.50 | 10.72 | 3.30 | 30.74 | 1.634 | 0.912 | |
| 叶球高Height of leaf head | 13.00 | 53.00 | 40.00 | 32.96 | 10.67 | 32.38 | 1.965 | 0.945 | |
| 叶球宽Leaf head width | 12.00 | 31.50 | 19.50 | 20.57 | 5.22 | 25.38 | 2.035 | 0.926 | |
| 球叶数Heading leaf number | 21.50 | 56.00 | 34.50 | 37.81 | 8.56 | 22.65 | 2.093 | 0.909 | |
| 间断性性状 Discrete traits | 叶球质量Leaf head weight | 0.55 | 3.50 | 2.95 | 1.88 | 0.81 | 42.81 | 2.139 | 0.929 |
| 中心柱长Central column length | 1.50 | 6.50 | 5.00 | 4.01 | 1.36 | 33.97 | 2.173 | 0.906 | |
| 全株质量Whole plant weight | 0.60 | 4.25 | 3.65 | 2.52 | 1.10 | 43.57 | 2.044 | 0.983 | |
| 叶色Leaf color | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.77 | 1.04 | 37.59 | 1.111 | 0.801 | |
| 性状类型 Character type | 性状 Trait | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Deviation | 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation | H’ | J |
| 间断性性状 Discrete traits | 叶片光泽Leaf luster | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.13 | 0.35 | 30.51 | 0.393 | 0.567 |
| 叶缘波状Leaf margin undulate | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3.27 | 0.83 | 25.34 | 1.106 | 0.798 | |
| 叶缘锯齿Leaf margin serrate | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.53 | 1.14 | 44.87 | 1.134 | 0.818 | |
| 茸毛Pubescence | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.13 | 0.97 | 45.62 | 0.882 | 0.803 | |
| 叶脉鲜明度Vein freshness | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.90 | 0.31 | 16.06 | 0.325 | 0.469 | |
| 株形Plant shape | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.33 | 0.48 | 35.96 | 0.637 | 0.918 | |
| 叶形Leaf shape | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3.33 | 1.09 | 32.80 | 1.327 | 0.825 | |
| 中肋色Middle rib color | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.60 | 0.93 | 35.85 | 1.189 | 0.857 | |
| 中肋形状Middle rib shape | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.63 | 0.49 | 30.01 | 0.657 | 0.948 | |
| 叶球形状Leaf head shape | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.77 | 1.17 | 42.11 | 1.495 | 0.929 | |
| 抱合方式Embracing mode | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.80 | 1.27 | 45.37 | 1.089 | 0.991 | |
| 球顶部形状Top shape of leaf head | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.93 | 0.83 | 42.81 | 1.095 | 0.997 | |
| 叶球颜色Leaf head color | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3.07 | 0.74 | 24.12 | 0.904 | 0.652 | |
| 叶球内叶颜色 Inner leaf color of leaf head | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.53 | 0.73 | 47.63 | 0.912 | 0.830 | |
| 中心柱形状Center column shape | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.70 | 1.15 | 42.56 | 1.301 | 0.939 | |
| 熟性Maturity | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.73 | 1.23 | 45.00 | 1.486 | 0.923 |
Table 3 Statistical analysis of agronomic traits of Chinese cabbage
| 性状类型 Character type | 性状 Trait | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Deviation | 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation | H’ | J |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 连续性性状 Continuous traits | 株高Plant height | 17.33 | 56.50 | 39.17 | 37.88 | 10.77 | 28.44 | 1.961 | 0.943 |
| 开展度Expansion diameter | 41.50 | 83.67 | 42.17 | 62.47 | 12.14 | 19.44 | 2.038 | 0.927 | |
| 叶片长Leaf length | 24.00 | 58.00 | 34.00 | 40.03 | 9.19 | 22.95 | 2.156 | 0.937 | |
| 叶片宽Leaf width | 16.50 | 37.33 | 20.83 | 25.25 | 4.69 | 18.56 | 1.897 | 0.912 | |
| 中肋厚Middle rib thickness | 0.65 | 1.20 | 0.55 | 0.92 | 0.15 | 15.97 | 1.794 | 0.922 | |
| 中肋长Middle rib length | 10.00 | 36.33 | 26.33 | 21.98 | 7.12 | 32.40 | 2.238 | 0.972 | |
| 中肋宽Middle rib width | 4.00 | 8.00 | 4.00 | 5.94 | 0.98 | 16.57 | 1.965 | 0.895 | |
| 外叶数Outer leaf number | 6.00 | 17.50 | 11.50 | 10.72 | 3.30 | 30.74 | 1.634 | 0.912 | |
| 叶球高Height of leaf head | 13.00 | 53.00 | 40.00 | 32.96 | 10.67 | 32.38 | 1.965 | 0.945 | |
| 叶球宽Leaf head width | 12.00 | 31.50 | 19.50 | 20.57 | 5.22 | 25.38 | 2.035 | 0.926 | |
| 球叶数Heading leaf number | 21.50 | 56.00 | 34.50 | 37.81 | 8.56 | 22.65 | 2.093 | 0.909 | |
| 间断性性状 Discrete traits | 叶球质量Leaf head weight | 0.55 | 3.50 | 2.95 | 1.88 | 0.81 | 42.81 | 2.139 | 0.929 |
| 中心柱长Central column length | 1.50 | 6.50 | 5.00 | 4.01 | 1.36 | 33.97 | 2.173 | 0.906 | |
| 全株质量Whole plant weight | 0.60 | 4.25 | 3.65 | 2.52 | 1.10 | 43.57 | 2.044 | 0.983 | |
| 叶色Leaf color | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.77 | 1.04 | 37.59 | 1.111 | 0.801 | |
| 性状类型 Character type | 性状 Trait | 最小值Minimum | 最大值Maximum | 极差Range | 平均值Mean | 标准差Deviation | 变异系数/% Coefficient of variation | H’ | J |
| 间断性性状 Discrete traits | 叶片光泽Leaf luster | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.13 | 0.35 | 30.51 | 0.393 | 0.567 |
| 叶缘波状Leaf margin undulate | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3.27 | 0.83 | 25.34 | 1.106 | 0.798 | |
| 叶缘锯齿Leaf margin serrate | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.53 | 1.14 | 44.87 | 1.134 | 0.818 | |
| 茸毛Pubescence | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.13 | 0.97 | 45.62 | 0.882 | 0.803 | |
| 叶脉鲜明度Vein freshness | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.90 | 0.31 | 16.06 | 0.325 | 0.469 | |
| 株形Plant shape | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.33 | 0.48 | 35.96 | 0.637 | 0.918 | |
| 叶形Leaf shape | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3.33 | 1.09 | 32.80 | 1.327 | 0.825 | |
| 中肋色Middle rib color | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.60 | 0.93 | 35.85 | 1.189 | 0.857 | |
| 中肋形状Middle rib shape | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.63 | 0.49 | 30.01 | 0.657 | 0.948 | |
| 叶球形状Leaf head shape | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.77 | 1.17 | 42.11 | 1.495 | 0.929 | |
| 抱合方式Embracing mode | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.80 | 1.27 | 45.37 | 1.089 | 0.991 | |
| 球顶部形状Top shape of leaf head | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.93 | 0.83 | 42.81 | 1.095 | 0.997 | |
| 叶球颜色Leaf head color | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3.07 | 0.74 | 24.12 | 0.904 | 0.652 | |
| 叶球内叶颜色 Inner leaf color of leaf head | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1.53 | 0.73 | 47.63 | 0.912 | 0.830 | |
| 中心柱形状Center column shape | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2.70 | 1.15 | 42.56 | 1.301 | 0.939 | |
| 熟性Maturity | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2.73 | 1.23 | 45.00 | 1.486 | 0.923 |
| 自交系Inbred line | 特征引物Specific primer | 自交系Inbred line | 特征引物Specific primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| B14Q-101 | A10-3 | B17Q-442 | A01-5 |
| B14Q-109 | A10-3 | B17Q-444 | A10-8 |
| B14Q-209 | A09-14、09-15 | B17Q-446 | A01-17、A02-3、A02-14、A03-2、A04-8、A05-1、A05-17、A06-5、A06-7、A06-8、A06-9、A07-4、A07-5、A07-7、A07-11、A09-3、A09-6、A09-9 |
| B14Q-260 | A04-10、A05-7 | B17Q-448 | A01-10 |
| B14Q-279 | A02-11、A06-4、A06-6、A06-18、A07-13、A09-10 | B17Q-449 | A07-12 |
| B17Q-439 | A07-6 | B17Q-455 | A05-1、A05-10、A07-6、A09-3、A09-17 |
| B17Q-441 | A10-3 |
Table 4 Materials with specific primers
| 自交系Inbred line | 特征引物Specific primer | 自交系Inbred line | 特征引物Specific primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| B14Q-101 | A10-3 | B17Q-442 | A01-5 |
| B14Q-109 | A10-3 | B17Q-444 | A10-8 |
| B14Q-209 | A09-14、09-15 | B17Q-446 | A01-17、A02-3、A02-14、A03-2、A04-8、A05-1、A05-17、A06-5、A06-7、A06-8、A06-9、A07-4、A07-5、A07-7、A07-11、A09-3、A09-6、A09-9 |
| B14Q-260 | A04-10、A05-7 | B17Q-448 | A01-10 |
| B14Q-279 | A02-11、A06-4、A06-6、A06-18、A07-13、A09-10 | B17Q-449 | A07-12 |
| B17Q-439 | A07-6 | B17Q-455 | A05-1、A05-10、A07-6、A09-3、A09-17 |
| B17Q-441 | A10-3 |
| 序号 No. | 材料编号 Code | 遗传相似系数 GS coefficient | 序号 No. | 材料编号 Code | 遗传相似系数 GS coefficient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Average | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值 Average | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | ||||
| 1 | B14Q-101 | 0.688 | 0.750 (B17Q-440) | 0.609 (B14Q-279) | 17 | B17Q-444 | 0.709 | 0.765 (B17Q-447) | 0.656 (B17Q-432) |
| 2 | B17Q-432 | 0.712 | 0.781 (B17Q-442) | 0.634 (B17Q-446) | 18 | B14Q-209 | 0.663 | 0.854 (B14Q-113) | 0.575 (B17Q-446) |
| 3 | B14Q-109 | 0.682 | 0.785 (B14Q-113) | 0.616 (B17Q-455) | 19 | B14Q-211 | 0.718 | 0.859 (B17Q-441) | 0.647 (B17Q-435) |
| 4 | B14Q-113 | 0.699 | 0.854 (B14Q-209) | 0.598 (B17Q-446) | 20 | B17Q-445 | 0.713 | 0.796 (B14Q-211) | 0.620 (B14Q-267) |
| 5 | B17Q-433 | 0.693 | 0.738 (B17Q-442) | 0.619 (B17Q-446) | 21 | B17Q-446 | 0.671 | 0.760 (B14Q-141) | 0.575 (B14Q-209) |
| 6 | B14Q-124 | 0.708 | 0.792 (B17Q-450) | 0.625 (B14Q-209) | 22 | B17Q-447 | 0.716 | 0.844 (B17Q-442) | 0.620 (B17Q-453) |
| 7 | B17Q-435 | 0.680 | 0.752 (B17Q-432) | 0.630 (B14Q-260) | 23 | B17Q-448 | 0.721 | 0.775 (B17Q-442) | 0.656 (B17Q-446) |
| 8 | B17Q-436 | 0.707 | 0.768 (B14Q-141) | 0.661 (B17Q-455) | 24 | B17Q-449 | 0.681 | 0.740 (B17Q-452) | 0.597 (B14Q-209) |
| 9 | B17Q-437 | 0.686 | 0.804 (B14Q-141) | 0.615 (B14Q-209) | 25 | B17Q-450 | 0.732 | 0.910 (B17Q-439) | 0.606 (B14Q-209) |
| 10 | B14Q-141 | 0.740 | 0.872 (B17Q-439) | 0.621 (B14Q-209) | 26 | B14Q-260 | 0.701 | 0.779 (B17Q-450) | 0.590 (B14Q-209) |
| 11 | B17Q-439 | 0.735 | 0.910 (B17Q-450) | 0.605 (B14Q-209) | 27 | B17Q-452 | 0.681 | 0.740 (B17Q-449) | 0.614 (B14Q-209) |
| 12 | B17Q-440 | 0.703 | 0.778 (B14Q-159) | 0.624 (B14Q-279) | 28 | B14Q-267 | 0.661 | 0.715 (B17Q-432) | 0.608 (B17Q-446) |
| 13 | B14Q-159 | 0.702 | 0.778 (B17Q-440) | 0.650 (B17Q-435) | 29 | B17Q-453 | 0.685 | 0.729 (B14Q-159) | 0.620 (B17Q-447) |
| 14 | B17Q-441 | 0.717 | 0.859 (B14Q-211) | 0.638 (B17Q-452) | 30 | B14Q-279 | 0.672 | 0.739 (B17Q-455) | 0.609 (B14Q-101) |
| 15 | B17Q-442 | 0.742 | 0.844 (B17Q-447) | 0.676 (B14Q-209) | 31 | B17Q-455 | 0.688 | 0.758 (B17Q-444) | 0.616 (B14Q-109) |
| 16 | B17Q-443 | 0.704 | 0.760 (B17Q-445) | 0.640 (B14Q-267) | 平均 Mean | 0.700 | |||
Table 5 Genetic similarity coefficient of tested materials
| 序号 No. | 材料编号 Code | 遗传相似系数 GS coefficient | 序号 No. | 材料编号 Code | 遗传相似系数 GS coefficient | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均值 Average | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | 平均值 Average | 最大值 Max | 最小值 Min | ||||
| 1 | B14Q-101 | 0.688 | 0.750 (B17Q-440) | 0.609 (B14Q-279) | 17 | B17Q-444 | 0.709 | 0.765 (B17Q-447) | 0.656 (B17Q-432) |
| 2 | B17Q-432 | 0.712 | 0.781 (B17Q-442) | 0.634 (B17Q-446) | 18 | B14Q-209 | 0.663 | 0.854 (B14Q-113) | 0.575 (B17Q-446) |
| 3 | B14Q-109 | 0.682 | 0.785 (B14Q-113) | 0.616 (B17Q-455) | 19 | B14Q-211 | 0.718 | 0.859 (B17Q-441) | 0.647 (B17Q-435) |
| 4 | B14Q-113 | 0.699 | 0.854 (B14Q-209) | 0.598 (B17Q-446) | 20 | B17Q-445 | 0.713 | 0.796 (B14Q-211) | 0.620 (B14Q-267) |
| 5 | B17Q-433 | 0.693 | 0.738 (B17Q-442) | 0.619 (B17Q-446) | 21 | B17Q-446 | 0.671 | 0.760 (B14Q-141) | 0.575 (B14Q-209) |
| 6 | B14Q-124 | 0.708 | 0.792 (B17Q-450) | 0.625 (B14Q-209) | 22 | B17Q-447 | 0.716 | 0.844 (B17Q-442) | 0.620 (B17Q-453) |
| 7 | B17Q-435 | 0.680 | 0.752 (B17Q-432) | 0.630 (B14Q-260) | 23 | B17Q-448 | 0.721 | 0.775 (B17Q-442) | 0.656 (B17Q-446) |
| 8 | B17Q-436 | 0.707 | 0.768 (B14Q-141) | 0.661 (B17Q-455) | 24 | B17Q-449 | 0.681 | 0.740 (B17Q-452) | 0.597 (B14Q-209) |
| 9 | B17Q-437 | 0.686 | 0.804 (B14Q-141) | 0.615 (B14Q-209) | 25 | B17Q-450 | 0.732 | 0.910 (B17Q-439) | 0.606 (B14Q-209) |
| 10 | B14Q-141 | 0.740 | 0.872 (B17Q-439) | 0.621 (B14Q-209) | 26 | B14Q-260 | 0.701 | 0.779 (B17Q-450) | 0.590 (B14Q-209) |
| 11 | B17Q-439 | 0.735 | 0.910 (B17Q-450) | 0.605 (B14Q-209) | 27 | B17Q-452 | 0.681 | 0.740 (B17Q-449) | 0.614 (B14Q-209) |
| 12 | B17Q-440 | 0.703 | 0.778 (B14Q-159) | 0.624 (B14Q-279) | 28 | B14Q-267 | 0.661 | 0.715 (B17Q-432) | 0.608 (B17Q-446) |
| 13 | B14Q-159 | 0.702 | 0.778 (B17Q-440) | 0.650 (B17Q-435) | 29 | B17Q-453 | 0.685 | 0.729 (B14Q-159) | 0.620 (B17Q-447) |
| 14 | B17Q-441 | 0.717 | 0.859 (B14Q-211) | 0.638 (B17Q-452) | 30 | B14Q-279 | 0.672 | 0.739 (B17Q-455) | 0.609 (B14Q-101) |
| 15 | B17Q-442 | 0.742 | 0.844 (B17Q-447) | 0.676 (B14Q-209) | 31 | B17Q-455 | 0.688 | 0.758 (B17Q-444) | 0.616 (B14Q-109) |
| 16 | B17Q-443 | 0.704 | 0.760 (B17Q-445) | 0.640 (B14Q-267) | 平均 Mean | 0.700 | |||
| 变种 Variety | 生态型Ecological type | 自交系份数 No. of inbred lines | 平均遗传相似系数 Average of GS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 结球大白菜 Chinese cabbage | 卵圆类型Oval type | 10 | 0.700 |
| 平头类型Flat head | 8 | 0.703 | |
| 直筒类型Straight tube type | 6 | 0.714 | |
| 花心大白菜 Flower heart Chinese cabbage | 3 | 0.702 | |
| 散叶大白菜 Loose leaf Chinese cabbage | 4 | 0.676 | |
| 平均Average | 0.699 |
Table 6 Genetic diversity between Chinese cabbage varieties and ecotype inbred lines and other varieties or ecotypes
| 变种 Variety | 生态型Ecological type | 自交系份数 No. of inbred lines | 平均遗传相似系数 Average of GS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 结球大白菜 Chinese cabbage | 卵圆类型Oval type | 10 | 0.700 |
| 平头类型Flat head | 8 | 0.703 | |
| 直筒类型Straight tube type | 6 | 0.714 | |
| 花心大白菜 Flower heart Chinese cabbage | 3 | 0.702 | |
| 散叶大白菜 Loose leaf Chinese cabbage | 4 | 0.676 | |
| 平均Average | 0.699 |
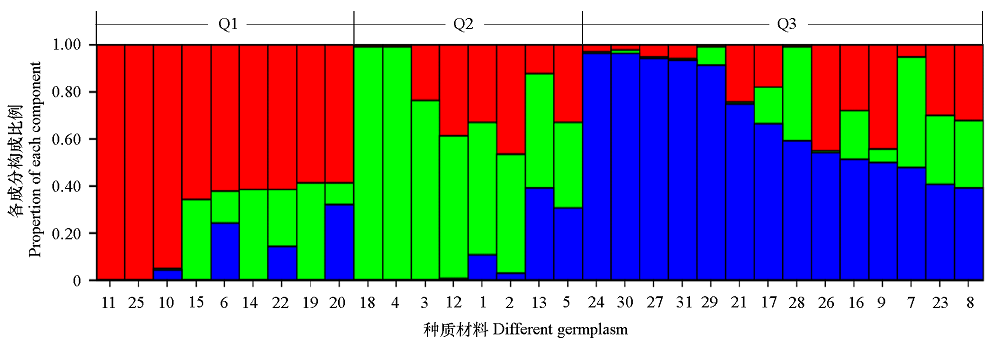
Fig. 2 Population structure of 31 Chinese cabbage inbred lines(1-31) The abscissa number is the same as the material number in Table 1,representing different germplasm. Different color blocks correspond to three different components.
| 引物编号 Primer ID | 位置 Position | 正向引物序列 Forward primer | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer | 产物大小/bp Product size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01-19 | 24837737 | AGAGAGAAGACCCATAAGCC | CACGAAGTCGAGAGGAAATA | 110 |
| A02-9 | 21774955 | CTCCAGAGACAACTTTCAGC | TCACTTGTAATCCTTGAGCA | 103 |
| A03-5 | 4727108 | ACCGTTTGCCATTATATACG | TCATTCTCTCCAATCACACA | 91 |
| A05-6 | 6340979 | ACGTCGTCGTATTGAACTCT | TGCTTCTTCTGGAGTGTCTT | 143 |
| A05-14 | 16436310 | CCTGCACATTATCCATCTTT | AATGACCCAGTAGATCAGGT | 156 |
| A05-16 | 18659064 | GGGACAACTCAATTACACCT | ACACCACCGTCTCAGAATAC | 126 |
| A06-12 | 16861849 | TCCTTTTCTTTGAAGTGTGG | GAACAATCACCACTAAACCC | 154 |
| A06-13 | 18292827 | GGACCAGTTATCGTTTTGTC | CATAAGAAAAACTATCCGGC | 92 |
| A06-15 | 19392228 | ACAAATCTGAACAACGAAGG | ACAAATAGATCGCGATAAGG | 105 |
| A07-5 | 4537468 | GCTAGTCCACAGCAAATGAT | TTGGCTTCTTCTTCACTGAT | 135 |
| A07-13 | 16364142 | GGGAAGCAATCTAACAGAAA | GGTGTAGACATGTTTCAAAGG | 148 |
| A07-14 | 17219194 | CCTGAAGCAAGAAGTGCTAT | TTTCTGCTACGGGTAAGTTG | 149 |
| A07-16 | 20894341 | CCACATGTAGTCACTGCAAC | AAGATGCTCAAGAAGTGCTC | 136 |
| A07-18 | 22027474 | GTGAATGTAGACGACACACG | AATCTTCAAGCTTTCACTCG | 149 |
| A09-3 | 1283777 | CTCCCACTTTTGAAGTTCTG | TGATATTTTCGATGACCTGG | 129 |
| A09-7 | 12459199 | CGTTCTTCAGTGTGATTCAA | TATGAGTTAACACCCCTTGG | 121 |
| A09-8 | 16434839 | TGTTAGATACTCCTCCACTCA | TGTCTCTCAACAACTTCGAG | 108 |
| A09-9 | 21909939 | CTATGAACCATCCCAAAGAA | CAGCTTAATTTGCAACATCC | 136 |
| A10-3 | 3030502 | AACATGATGCTGATAGGTCC | CTCTTTGATTTGAAGAGTGACC | 101 |
| A10-4 | 3775136 | CAGCTCTCTCTCTTCAGTGG | CTATTAACCGTGGATTGGTC | 145 |
| A10-7 | 11696916 | TTCTAATTTGTGCAGAGTCC | AACTTTGTCTGCGTGATGAT | 130 |
| A10-10 | 14947251 | AAACAAAACAGGAAGTGGTG | AGAGATATTGAGGCCCATTT | 133 |
Table 7 InDel primer sequence information
| 引物编号 Primer ID | 位置 Position | 正向引物序列 Forward primer | 反向引物序列 Reverse primer | 产物大小/bp Product size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01-19 | 24837737 | AGAGAGAAGACCCATAAGCC | CACGAAGTCGAGAGGAAATA | 110 |
| A02-9 | 21774955 | CTCCAGAGACAACTTTCAGC | TCACTTGTAATCCTTGAGCA | 103 |
| A03-5 | 4727108 | ACCGTTTGCCATTATATACG | TCATTCTCTCCAATCACACA | 91 |
| A05-6 | 6340979 | ACGTCGTCGTATTGAACTCT | TGCTTCTTCTGGAGTGTCTT | 143 |
| A05-14 | 16436310 | CCTGCACATTATCCATCTTT | AATGACCCAGTAGATCAGGT | 156 |
| A05-16 | 18659064 | GGGACAACTCAATTACACCT | ACACCACCGTCTCAGAATAC | 126 |
| A06-12 | 16861849 | TCCTTTTCTTTGAAGTGTGG | GAACAATCACCACTAAACCC | 154 |
| A06-13 | 18292827 | GGACCAGTTATCGTTTTGTC | CATAAGAAAAACTATCCGGC | 92 |
| A06-15 | 19392228 | ACAAATCTGAACAACGAAGG | ACAAATAGATCGCGATAAGG | 105 |
| A07-5 | 4537468 | GCTAGTCCACAGCAAATGAT | TTGGCTTCTTCTTCACTGAT | 135 |
| A07-13 | 16364142 | GGGAAGCAATCTAACAGAAA | GGTGTAGACATGTTTCAAAGG | 148 |
| A07-14 | 17219194 | CCTGAAGCAAGAAGTGCTAT | TTTCTGCTACGGGTAAGTTG | 149 |
| A07-16 | 20894341 | CCACATGTAGTCACTGCAAC | AAGATGCTCAAGAAGTGCTC | 136 |
| A07-18 | 22027474 | GTGAATGTAGACGACACACG | AATCTTCAAGCTTTCACTCG | 149 |
| A09-3 | 1283777 | CTCCCACTTTTGAAGTTCTG | TGATATTTTCGATGACCTGG | 129 |
| A09-7 | 12459199 | CGTTCTTCAGTGTGATTCAA | TATGAGTTAACACCCCTTGG | 121 |
| A09-8 | 16434839 | TGTTAGATACTCCTCCACTCA | TGTCTCTCAACAACTTCGAG | 108 |
| A09-9 | 21909939 | CTATGAACCATCCCAAAGAA | CAGCTTAATTTGCAACATCC | 136 |
| A10-3 | 3030502 | AACATGATGCTGATAGGTCC | CTCTTTGATTTGAAGAGTGACC | 101 |
| A10-4 | 3775136 | CAGCTCTCTCTCTTCAGTGG | CTATTAACCGTGGATTGGTC | 145 |
| A10-7 | 11696916 | TTCTAATTTGTGCAGAGTCC | AACTTTGTCTGCGTGATGAT | 130 |
| A10-10 | 14947251 | AAACAAAACAGGAAGTGGTG | AGAGATATTGAGGCCCATTT | 133 |
| 引物编号 Primer ID | 关联性状 associated traits | 引物编号 Primer ID | 关联性状 associated traits |
|---|---|---|---|
| A01-19 | 全株质量、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head weight | A07-14 | 叶片长、叶球高、中肋长、株高 Leaf length,leaf head height,middle rib length,plant height |
| A02-9 | 叶片宽Leaf width | A07-16 | 叶片宽Leaf width |
| A03-5 | 全株质量、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head weight | A07-18 | 叶片宽Leaf width |
| A05-6 | 叶片长Leaf length | A09-3 | 叶片长、叶球高、中肋长、株高 Leaf length,leaf head height,middle rib length,plant height |
| A05-14 | 中肋长、株高 Middle rib length,plant height | A09-7 | 叶片长Leaf length |
| A05-16 | 外叶数Outer leaf number | A09-8 | 球叶数Heading leaf number |
| A06-12 | 开展度、叶片宽 Expansion diameter,leaf width | A09-9 | 全株质量、叶球宽、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head width,leaf head weight |
| A06-13 | 叶球高、株高 Leaf head height,plant height | A10-3 | 全株质量Whole plant weight |
| A06-15 | 叶球高Leaf head height | A10-4 | 中心柱长Central column length |
| A07-5 | 叶球高Leaf head height | A10-7 | 全株质量、外叶数、叶球宽度、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,outer leaf number,leaf head width,leaf head weight |
| A07-13 | 叶球宽Leaf head width | A10-10 | 叶球宽Leaf head width |
Table 8 InDel Markers and associated traits
| 引物编号 Primer ID | 关联性状 associated traits | 引物编号 Primer ID | 关联性状 associated traits |
|---|---|---|---|
| A01-19 | 全株质量、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head weight | A07-14 | 叶片长、叶球高、中肋长、株高 Leaf length,leaf head height,middle rib length,plant height |
| A02-9 | 叶片宽Leaf width | A07-16 | 叶片宽Leaf width |
| A03-5 | 全株质量、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head weight | A07-18 | 叶片宽Leaf width |
| A05-6 | 叶片长Leaf length | A09-3 | 叶片长、叶球高、中肋长、株高 Leaf length,leaf head height,middle rib length,plant height |
| A05-14 | 中肋长、株高 Middle rib length,plant height | A09-7 | 叶片长Leaf length |
| A05-16 | 外叶数Outer leaf number | A09-8 | 球叶数Heading leaf number |
| A06-12 | 开展度、叶片宽 Expansion diameter,leaf width | A09-9 | 全株质量、叶球宽、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,leaf head width,leaf head weight |
| A06-13 | 叶球高、株高 Leaf head height,plant height | A10-3 | 全株质量Whole plant weight |
| A06-15 | 叶球高Leaf head height | A10-4 | 中心柱长Central column length |
| A07-5 | 叶球高Leaf head height | A10-7 | 全株质量、外叶数、叶球宽度、叶球质量 Whole plant weight,outer leaf number,leaf head width,leaf head weight |
| A07-13 | 叶球宽Leaf head width | A10-10 | 叶球宽Leaf head width |
| [1] |
Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, Davis R W. 1980. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. American Journal of Human Genetics, 32(3):314-331.
pmid: 6247908 |
| [2] | Cai Dong-fang. 2013. Association mapping of yield and quality-related traits in Brassica napus L.[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese). |
| 蔡东芳. 2013. 甘蓝型油菜产量和品质相关性状关联分析[博士论文]. 武汉:华中农业大学. | |
| [3] | Cao Jia-shu, Cao Shou-chun, Miao Ying, Lu Gang. 1997. Cladistic operational analysis and study on the evolution of Chinese cabbage groups(Brassica campestris L.). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 24(1):35-42. (in Chinese) |
| 曹家树, 曹寿椿, 缪颖, 卢刚. 1997. 中国白菜各类群的分支分析和演化关系研究. 园艺学报, 24(1):35-42. | |
| [4] | Chen Wen-hui, Fang Shu-gui, Zeng Xiao-ling, Zhong Kai-qin, Zhu Zhao-hui. 2011. Analysis of genetic diversity in Chinese cabbage with tolerance bolting based on ISSR and SRAP. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 32(10):1858-1863. (in Chinese) |
| 陈文辉, 方淑桂, 曾小玲, 钟开勤, 朱朝辉. 2011. 利用ISSR和SRAP标记分析耐抽薹大白菜的遗传多样性. 热带作物学报, 32(10):1858-1863. | |
| [5] | Chen Ya-nan. 2020. Identifying nitrogen-efficient Chinese cabbage varieties and genome-wide association analysis[M. D. Dissertation]. Jinan:Shandong Normal University. (in Chinese) |
| 陈亚男. 2020. 氮高效大白菜品种筛选及氮效率相关性状的全基因组关联分析[硕士论文]. 济南:山东师范大学. | |
| [6] |
Das A K, Chhabra R, Muthusamy V, Chauhan H S, Zunjare R U, Hossain F. 2019. Identification of SNP and InDel variations in the promoter and 5′ untranslated regions of γ-tocopherol methyl transferase(ZmVTE4)affecting higher accumulation of α-tocopherol in maize kernel. The Crop Journal, 7(4):469-479.
doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2019.01.004 URL |
| [7] | Duan Li-li, Zheng Yong-sheng, Li Hua, Sun Jia-mei, Wang Dong-jian, Wang Xue-mei, Xian Li-na, Wang Xiu-juan, Zhang Han. 2016. Genetic diversity analysis of 46 Chinese cabbage germplasm resources with SSR markers. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 48(5):5-8. (in Chinese) |
| 段丽丽, 郑永胜, 李华, 孙加梅, 王东建, 王雪梅, 仙丽娜, 王秀娟, 张晗. 2016. 46份大白菜种质资源SSR标记的遗传多样性分析. 山东农业科学, 48(5):5-8. | |
| [8] | Feng Fang-jun, Luo Li-jun, Li Ying, Zhou Li-guo, Xu Xiao-yan, Wu Jin-hong, Chen Hong-wei, Chen Liang, Mei Han-wei. 2005. Comparative analysis of polymorphism of InDel and SSR markers in rice. Molecular Plant Breeding, 3(5):725-730. (in Chinese) |
| 冯芳君, 罗利军, 李荧, 周立国, 徐小艳, 吴金红, 陈宏伟, 陈亮, 梅捍卫. 2005. 水稻InDel和SSR标记多态性的比较分析. 分子植物育种, 3(5):725-730. | |
| [9] | Gao Ying. 2012. Association analysis of bolting and flowering time with SSR and InDel markers in Chinese cabbage[M. D. Dissertation]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 高颖. 2012. 大白菜抽薹开花时间与SSR和InDel标记的关联分析[硕士论文]. 保定:河北农业大学. | |
| [10] | Gao Ying, Luo Shuang-xia, Wang Yan-hua, Gu Ai-xia, Zhao Jian-jun, Chen Xue-ping, Shen Shu-xing. 2012. Association analysis of bolting and flowering time with SSR and InDel markers in Chinese cabbage. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 39(6):1081-1089. (in Chinese) |
| 高颖, 罗双霞, 王彦华, 顾爱侠, 赵建军, 陈雪平, 申书兴. 2012. 大白菜抽薹开花时间与SSR和InDel标记的关联分析. 园艺学报, 39(6):1081-1089. | |
| [11] | Guan Xiao-yu. 2019. Genetic diversity analysis of Chinese cabbage inbred lines and division of heterotic groups[M. D. Dissertation]. Harbin: College of Horticulture and Landscape. (in Chinese) |
| 管晓雨. 2019. 大白菜自交系遗传多样性分析与杂种优势群的划分[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学. | |
| [12] |
Hospital F, Charcosset A. 1997. Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics, 147(3):1469-1485.
pmid: 9383086 |
| [13] | Institute of vegetables and flowers,Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. 2010. Chinese vegetable cultivation. Beijing:China Agriculture Press. |
| 中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所. 2010. 中国蔬菜栽培学. 北京:中国农业出版社. | |
| [14] |
Jander G, Norris S R, Rounsley S D, Bush D F, Levin I M, Last R L. 2002. Arabidopsis map-based cloning in the post-genome era. Plant Physiology, 129(2):440-450.
pmid: 12068090 |
| [15] |
Li X, Gao W, Guo H, Zhang X, Fang D D, Lin Z. 2014. Development of EST-based SNP and InDel markers and their utilization in tetraploid cotton genetic mapping. BMC Genomics, 15:1046-1056.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1046 URL |
| [16] | Liang Bao-ping. 2012. Genetic diversity study of DH lines in Chinese cabbage[M. D. Dissertation]. Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 梁宝萍. 2012. 大白菜DH系遗传多样性分析[硕士论文]. 郑州:河南农业大学. | |
| [17] | Liu Li-hua, Wang Li-xin, Zhao Chang-ping, Yao Ji, Zhang Feng-ting, Zhang Hua, Ye Zhi-jie, Qin Zhi-gang, Zheng Yong-lian. 2009. Genetic diversity and alterations of population structure in restorers of dual cross-line hybrid wheat with thermo-photoperiod sensitive male sterile. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 25(9):867-875. (in Chinese) |
| 刘丽华, 王立新, 赵昌平, 姚骥, 张风廷, 张华, 叶志杰, 秦志刚, 郑用琏. 2009. 光温敏二系杂交小麦恢复系遗传多样性和群体结构分析. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 25(9):867-875. | |
| [18] | Liu Shuan-tao, Zhang Zhi-gang, Si Li-ying, Wang Rong-hua, Li Qiao-yun, Wang Li-hua, Zhao Zhi-zhong, Liang Shui-mei, Zhang Quan-fang, Bu Xun. 2018. Identification of genetic relationships of Chinese cabbage inbred lines using InDels markers. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 19(4):657-667. (in Chinese) |
| 刘栓桃, 张志刚, 司立英, 王荣花, 李巧云, 王立华, 赵智中, 梁水美, 张全芳, 步迅. 2018. 基于InDels标记的大白菜育种材料的亲缘关系鉴定. 植物遗传资源学报, 19(4):657-667. | |
| [19] | Luo Shuang-xia. 2016. Mapping QTL for main agronomic traits and expression of genes related to head development in Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis)[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 罗双霞. 2016. 大白菜主要农艺性状QTL定位及叶球发育相关基因表达分析[博士论文]. 保定:河北农业大学. | |
| [20] | Meng Shu-chun. 2005. Studies on genetic relationships among Chinese cabbage(Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis)germplasm[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science. (in Chinese) |
| 孟淑春. 2005. 大白菜种质资源的亲缘关系研究[硕士论文]. 北京:中国农业科学院. | |
| [21] |
Murray M G, Thompson W F. 1980. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Research, 8(19):4321-4325.
pmid: 7433111 |
| [22] | Nei M, Li W H. 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 76(10):5269-5273. |
| [23] | Su Xiao-mei. 2014. The development and application of tomato foreground and background markers[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science. (in Chinese) |
| 苏晓梅. 2014. 番茄前景标记和背景标记的开发与应用研究[硕士论文]. 北京:中国农业科学院. | |
| [24] | Wang Lin-you, Zhang Li-xia, Gou Xiao-xia, Fan Hong-huan, Jin Qing-sheng, Wang Jian-jun. 2014. Identification of indica-japonica attribute and prediction of heterosis of Zheyou hybrids rice using InDel molecular markers. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 47(7):1243-1255. (in Chinese) |
| 王林友, 张礼霞, 勾晓霞, 范宏环, 金庆生, 王建军. 2014. 利用InDel标记鉴定浙优系列杂交稻籼粳属性和预测杂种优势. 中国农业科学, 47(7):1243-1255. | |
| [25] |
Wang X W, Wang H Z, Wang J, Sun R F, Wu J, Liu S Y, Bai Y Q, Mun J H, Bancroft I, Cheng F, Huang S W, Li X X, Hua W, Wang J Y, Wang X Y, Freeling M, Pires J C, Paterson A H, Chalhoub B, Wang B, Hayward A, Sharpe A G, Park B S, Weisshaar B, Liu B H, Li B, Liu B, Tong C B, Song C, Duran C, Peng C F, Geng C Y, Koh C, Lin CY, Edwards D, Mu D S, Shen D, Soumpourou E, Li F. 2011. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nature Genetic, 43(10):1035-1039.
doi: 10.1038/ng.919 URL |
| [26] | Wei Li-bin, Miao Hong-mei, Li Chun, Duan Ying-hui, Xu Fang-fang, Zhang Hai-yang. 2017. Genetic diversity,population structure and linkage disequilibrium analysis of sesame using SNP and InDel markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 15(8):3070-3079. (in Chinese) |
| 魏利斌, 苗红梅, 李春, 段迎辉, 徐芳芳, 张海洋. 2017. 芝麻SNP和InDel标记遗传多样性、群体结构及连锁不平衡分析. 分子植物育种, 15(8):3070-3079. | |
| [27] |
Wu Mi, Wang Nian, Shen Chao, Huang Cong, Wen Tian-wang, Lin Zhong-xu. 2019. Development and evaluation of InDel markers in cotton based on whole-genome re-sequencing data. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 45(2):196-203. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2019.84100 URL |
| 吴迷, 汪念, 沈超, 黄聪, 温天旺, 林忠旭. 2019. 基于重测序的陆地棉InDel标记开发与评价. 作物学报, 45(2):196-203. | |
| [28] | Xue Yin-ge, Yuan Yu-xiang, Zhang Xiao-wei, Dong Sen-sen, Yao Qiu-ju, Jiang Wu-sheng, Tian Bao-ming, Zhang Qiang, Zhao Yan-yan, Wei Xiao-chun. 2014. Purity identification of Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis)hybrid Yuxin No.4 by InDel markers. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 22(4):449-456. (in Chinese) |
| 薛银鸽, 原玉香, 张晓伟, 董森森, 姚秋菊, 蒋武生, 田保明, 张强, 赵艳艳, 魏小春. 2014. 利用InDel标记鉴定大白菜杂交种豫新四号种子纯度. 农业生物技术学报, 22(4):449-456. | |
| [29] | Yu X H, Peng J S, Feng X Z, Yang S X, Zheng Z R, Tang X G, Shen R J, Liu P L, He Y K. 2000. Cloning and structural and expressional characterization of BcpLH gene preferentially expressed in folding leaf of Chinese cabbage. Science in China Series C:Life Sciences, 43(3):321-329. |
| [30] | Zhang Hong-mei, Zhai Wen, Jin Hai-jun, Ding Xiao-tao, Yu Ji-zhu. 2019. Genetic diversity analysis of 23 cucumber germplasms and screening of core germplasm resources using InDel markers. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 35(4):28-33. (in Chinese) |
| 张红梅, 翟文, 金海军, 丁小涛, 余纪柱. 2019. 利用InDel标记分析23份黄瓜种质的遗传多样性及核心种质资源筛选. 上海农业学报, 35(4):28-33. | |
| [31] | Zhang Yan-fang. 2010. Establishing persimmon core germplasm using morphology and SSR molecular marker[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 张艳芳. 2010. 利用形态学和SSR标记建立柿核心种质[博士论文]. 武汉:华中农业大学. | |
| [32] |
Zhao J, Paulo M J, Jamar D, Lou P, van Eeuwijk F, Bonnema G, Vreugdenhil D, Koornneef M. 2007. Association mapping of leaf traits,flowering time,and phytate content in Brassica rapa. Genome, 50(10):963-973.
doi: 10.1139/G07-078 URL |
| [33] | Zhao Mei-hua, Lu Bao-de, Lan Chuang-ye, Zhao Jun-liang. 2011. Genetic diversity analysis of Chinese cabbage germplasms. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences, 39(1):12-16. (in Chinese) |
| 赵美华, 逯保德, 兰创业, 赵军良. 2011. 大白菜种质资源遗传多样性分析. 山西农业科学, 39(1):12-16. | |
| [34] | Zhu Dong-xu. 2014. Establishment and application of specific molecular markers on different linkage groups of cabbage compared with Chinese cabbage[M. D. Dissertation]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 朱东旭. 2014. 结球甘蓝相对于大白菜连锁群特异分子标记的建立及应用[硕士论文]. 保定:河北农业大学. |
| [1] | WANG Rui, HONG Wenjuan, LUO Hua, ZHAO Lina, CHEN Ying, and WANG Jun, . Construction of SSR Fingerprints of Pomegranate Cultivars and Male Parent Identification of Hybrids [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 265-278. |
| [2] | WANG Mengmeng, SUN Deling, CHEN Rui, YANG Yingxia, ZHANG Guan, LÜ Mingjie, WANG Qian, XIE Tianyu, NIU Guobao, SHAN Xiaozheng, TAN Jin, and YAO Xingwei, . Construction and Evaluation of Cauliflower Core Collection [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 421-431. |
| [3] | TANG Yuqing, YANG Huidong, YAN Chengpu, WANG Siyu, WANG Yuting, HU Zhongdong, ZHU Fanghong. Development and Application of Jinlan Pummelo(Citrus maxima)InDel Markers Based on Genome Re-sequencing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 15-26. |
| [4] | LIU Yiping, NI Menghui, WU Fangfang, LIU Hongli, HE Dan, KONG Dezheng. Association Analysis of Organ Traits with SSR Markers in Lotus(Nelumbo nucifera) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 103-115. |
| [5] | HAN Shuhui, HAN Caifeng, HAN Shurong, HAN Caimei, and HAN Xu. A New Autumn Chinese Cabbage Hybrid‘Jiaoyan Qiubao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 83-84. |
| [6] | WANG Weihong, ZHANG Fenglan, YU Yangjun, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, SU Tongbing, LI Peirong, and XIN Xiaoyun. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jingqiu 1518’for Autumn Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 85-86. |
| [7] | YU Yangjun, WANG Weihong, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Fenglan, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun, and WANG Jiao. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jingchun CR3’with Clubroot Resistance and Bolting Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [8] | WANG Lili, WANG Xin, WU Haidong, WEN Qiang, and Yang Xiaofei. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Liaobai 28’with Resistance to Clubroot Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [9] | YU Yangjun, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Fenglan, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, WANG Weihong, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun, WANG Jiao, and WU Changjian. A New Purple Seedling-Edible Chinese Cabbage F1 Hybrid‘Jingyan Zikuaicai’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 91-92. |
| [10] | HUANG Li, CHEN Caizhi, YU Xiaolin, YAO Xiangtan, and CAO Jiashu, . A New Early-mid Maturing Chinese Cabbage Pak-choi Cultivar‘Zhedaqing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 93-94. |
| [11] | XU Ligong, HAN Taili, SUN Jifeng, YANG Xiaodong, and TAN Jinxia. A New Seedling-edible Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jinlü 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 67-68. |
| [12] | WANG Yu, ZHANG Xue, ZHANG Xueying, ZHANG Siyu, WEN Tingting, WANG Yingjun, GAN Caixia, PANG Wenxing. The Effect of Camalexin on Chinese Cabbage Resistance to Clubroot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [13] | ZHANG Lugang, LU Qianqian, HE Qiong, XUE Yihua, MA Xiaomin, MA Shuai, NIE Shanshan, YANG Wenjing. Creation of Novel Germplasm of Purple-orange Heading Chinese Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [14] | LI Wenting, LI Cuixiao, LIN Xiaoqing, ZHENG Yongqin, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling. Population Genetic Structure of Xanthomonas citri pv. citri in Guangdong Province Based on the STR Locus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1233-1246. |
| [15] | ZHANG Meng, SHAN Yuying, YANG Yebo, ZHAI Feifei, WANG Zhaoshan, JU Guansheng, SUN Zhenyuan, LI Zhenjian. AFLP Analysis of Genetic Resources of Dendrobium from China [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1339-1350. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd