
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1505-1518.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0315
李姿燕1,2, 陈炜曦1,2, 李子涵1,2, 黎茵1,2, 梁峰铭5, 曾祥利5, 荐红举1,2,3,4,*( ), 吕典秋1,2,3,4,*(
), 吕典秋1,2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-20
修回日期:2025-03-06
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-20
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LI Ziyan1,2, CHEN Weixi1,2, LI Zihan1,2, LI Yin1,2, LIANG Fengming5, ZENG Xiangli5, JIAN Hongju1,2,3,4,*( ), and LÜ Dianqiu1,2,3,4,*(
), and LÜ Dianqiu1,2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2025-01-20
Revised:2025-03-06
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-06-20
摘要: 以早熟品种‘早大白’‘中薯5号’‘鄂马铃薯3号’与中晚熟品种‘大西洋’和‘青薯9号’为材料,分析了马铃薯顶端分生组织发育与结薯时间的关系,并利用RNA-Seq技术研究早大白与青薯9号差异表达基因的功能及可能参与的调控通路。结果表明,相比晚熟品种,早熟品种的顶端分生组织向生殖生长转变更早。转录组测序共鉴定出差异表达基因2 842个,其中与激素相关的基因85%集中在激素信号转导途径,特别是生长素(IAA)、脱落酸(ABA)和茉莉酸(JA)等通路;另外,筛选到127个差异表达基因编码转录因子,分布在35个转录因子家族。GO和KEGG富集分析发现差异表达基因主要富集在光合作用、对激素的响应、植物昼夜节律、淀粉和蔗糖代谢、植物激素信号转导等过程。挑选20个可能影响马铃薯结薯早晚的候选基因进行荧光定量PCR验证。其中参与昼夜节律通路的基因FT、HY5,参与淀粉和蔗糖代谢通路的基因BGLU17、CWIN2、GH9B13在早大白中高表达;参与植物激素信号转导或合成代谢的基因GH3、RD22、HB16、CYP74A在早大白中高表达,而IAA17、MES1、RCA在青薯9号中高表达。此外,在早大白中高表达的GRP3可能通过影响生长发育从而调控马铃薯结薯早晚。这些基因可能通过调控光周期响应、激素信号转导、蔗糖水平等在马铃薯中发挥作用,从而影响马铃薯熟性。
李姿燕, 陈炜曦, 李子涵, 黎茵, 梁峰铭, 曾祥利, 荐红举, 吕典秋. 基于RNA-Seq筛选调控马铃薯熟性的候选基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1505-1518.
LI Ziyan, CHEN Weixi, LI Zihan, LI Yin, LIANG Fengming, ZENG Xiangli, JIAN Hongju, and LÜ Dianqiu. Screening Candidate Genes Controlling Potato Maturation Time Based on RNA-Seq[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1505-1518.
| 名称Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(3′-5′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| GH3 | Soltu.DM.10G002010 | TGAAGCCATTCTCTGCCTAGACTC | AGCCAACACGAACGACTTCTCTG |
| SAUR79 | Soltu.DM.08G022860 | GGTAGCAATCTTGACAAGGCGATG | TTCCTTTCCCACCAGCACAGTTAC |
| IAA17 | Soltu.DM.03G035030 | GATGGAGACTGGATGCTTGTTGGA | CCTCCGTGCTCTTCATCAACCTAA |
| RD22 | Soltu.DM.08G017220 | GGTGTCTATGGTGGGTGCTGATG | ATAGGCTTGTCTCCAGGCTTAACG |
| HB16 | Soltu.DM.11G003380 | GGTTGGTTGTTCATCTCCGTTGA | TGTTGTTGTTGTTGTTGACGAAGG |
| CYP74A | Soltu.DM.10G003720 | TGGATTGGAACATCAGGACCTAGT | ACCACAGACTTAACAAGAGGCATT |
| MES1 | Soltu.DM.02G008550 | CCTGAAGAGCCTCGGACATCCA | GGTCTCACCAACGACGATGCTAAT |
| MES3 | Soltu.DM.01G048330 | TGCCAATCCTCCAACAACCTTCAT | GTAGTAGCCAGTGCCCAGTCCT |
| RCA | Soltu.DM.10G023180 | ACTCACCATCCTGTCTTGTCATCA | ATCCATCCAGCGTGTTGTCCAG |
| GIM2 | Soltu.DM.08G001760 | ACTTGGTATGCCACCTCATTCAGA | TCGAGATGGTCGCCGGTATTG |
| FT | Soltu.DM.05G026370 | CAAGCCCAAGCGACCCTAACTT | CGTAGGTGTTGGATTCTCGTAGCA |
| COP1 | Soltu.DM.11G001010 | AGGAGGAAGAGGAAGAGGAAGAGG | AACTATGTCCACACGCCGTTAGAA |
| HY5 | Soltu.DM.08G011730 | TGCCGCTAGTTCACTACCTTCAAG | ACATCGTTCCCGTCGCTTCTC |
| GRP3 | Soltu.DM.09G030440 | ATTATGGAGGCGGCTATGGTAAGG | AGTCTGGGCAGCCACATATTCTTC |
| RBCS3B | Soltu.DM.02G025840 | AGGTCTTGGCTGAGGTGGAGGA | AACTGATGCACTGCACTTGACGAA |
| GH9B13 | Soltu.DM.09G023670 | ACGAGCGATCAGATTACGAGCAAT | TGAGCAAGGTAAGTGAGTGTTCCA |
| BGLU45 | Soltu.DM.07G024580 | ACAAGGTGGAACGATAGGAATGGT | AGGATCAAGAAGCCAGGCAACAT |
| ADG2 | Soltu.DM.01G024440 | GCAGGTGAGGCTAAGTTGAAGGAT | CCCATTGGAACGGCAGGCTTA |
| BGLU17 | Soltu.DM.10G010830 | GTCGGCTCCCAAGATTCACAGTT | CAGCATGATTGTCAGTGGTGTAGC |
| CWIN2 | Soltu.DM.10G025030 | ATGTTGGTTGGGTCAGGATGGTT | CCGTCAACTGAATGAAGTGGATGT |
表1 候选基因qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 qRT-PCR primer sequences of candidate genes
| 名称Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 正向引物(5′-3′)Forward primer | 反向引物(3′-5′)Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| GH3 | Soltu.DM.10G002010 | TGAAGCCATTCTCTGCCTAGACTC | AGCCAACACGAACGACTTCTCTG |
| SAUR79 | Soltu.DM.08G022860 | GGTAGCAATCTTGACAAGGCGATG | TTCCTTTCCCACCAGCACAGTTAC |
| IAA17 | Soltu.DM.03G035030 | GATGGAGACTGGATGCTTGTTGGA | CCTCCGTGCTCTTCATCAACCTAA |
| RD22 | Soltu.DM.08G017220 | GGTGTCTATGGTGGGTGCTGATG | ATAGGCTTGTCTCCAGGCTTAACG |
| HB16 | Soltu.DM.11G003380 | GGTTGGTTGTTCATCTCCGTTGA | TGTTGTTGTTGTTGTTGACGAAGG |
| CYP74A | Soltu.DM.10G003720 | TGGATTGGAACATCAGGACCTAGT | ACCACAGACTTAACAAGAGGCATT |
| MES1 | Soltu.DM.02G008550 | CCTGAAGAGCCTCGGACATCCA | GGTCTCACCAACGACGATGCTAAT |
| MES3 | Soltu.DM.01G048330 | TGCCAATCCTCCAACAACCTTCAT | GTAGTAGCCAGTGCCCAGTCCT |
| RCA | Soltu.DM.10G023180 | ACTCACCATCCTGTCTTGTCATCA | ATCCATCCAGCGTGTTGTCCAG |
| GIM2 | Soltu.DM.08G001760 | ACTTGGTATGCCACCTCATTCAGA | TCGAGATGGTCGCCGGTATTG |
| FT | Soltu.DM.05G026370 | CAAGCCCAAGCGACCCTAACTT | CGTAGGTGTTGGATTCTCGTAGCA |
| COP1 | Soltu.DM.11G001010 | AGGAGGAAGAGGAAGAGGAAGAGG | AACTATGTCCACACGCCGTTAGAA |
| HY5 | Soltu.DM.08G011730 | TGCCGCTAGTTCACTACCTTCAAG | ACATCGTTCCCGTCGCTTCTC |
| GRP3 | Soltu.DM.09G030440 | ATTATGGAGGCGGCTATGGTAAGG | AGTCTGGGCAGCCACATATTCTTC |
| RBCS3B | Soltu.DM.02G025840 | AGGTCTTGGCTGAGGTGGAGGA | AACTGATGCACTGCACTTGACGAA |
| GH9B13 | Soltu.DM.09G023670 | ACGAGCGATCAGATTACGAGCAAT | TGAGCAAGGTAAGTGAGTGTTCCA |
| BGLU45 | Soltu.DM.07G024580 | ACAAGGTGGAACGATAGGAATGGT | AGGATCAAGAAGCCAGGCAACAT |
| ADG2 | Soltu.DM.01G024440 | GCAGGTGAGGCTAAGTTGAAGGAT | CCCATTGGAACGGCAGGCTTA |
| BGLU17 | Soltu.DM.10G010830 | GTCGGCTCCCAAGATTCACAGTT | CAGCATGATTGTCAGTGGTGTAGC |
| CWIN2 | Soltu.DM.10G025030 | ATGTTGGTTGGGTCAGGATGGTT | CCGTCAACTGAATGAAGTGGATGT |

图1 不同马铃薯品种在长日照(A、B)和短日照(C、D)条件下微型薯结薯时间和数量统计 早熟:早大白、中薯5号、鄂马铃薯3号;中晚熟:大西洋;晚熟:青薯9号。使用最小显著差异法对数据进行多重比较分析,不同小写字母表示差异显著,(P < 0.05)
Fig. 1 Statistics of tuberization time and number of microtuber in different potato cultivars under long day(A,B)and short day(C,D)condition Early maturing:Zaodabai,Zhongshu5,Eshu3;middle late maturing:Atlantic;late maturing:Qingshu9. The minimum significant difference method was used for multiple comparative analysis of the data. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level

图2 长日照条件下马铃薯不同品种组培苗茎顶端分生组织发育 绿色箭头代表顶端分生组织进行营养生长,红色箭头代表顶端分生组织已转向生殖生长
Fig. 2 Stem apical meristem development of plantlet of various potato cultivars under long day condition The green arrows indicates that the apical meristem has undergone vegetative growth,the red arrow indicates that the apical meristem has shifted to reproductive growth
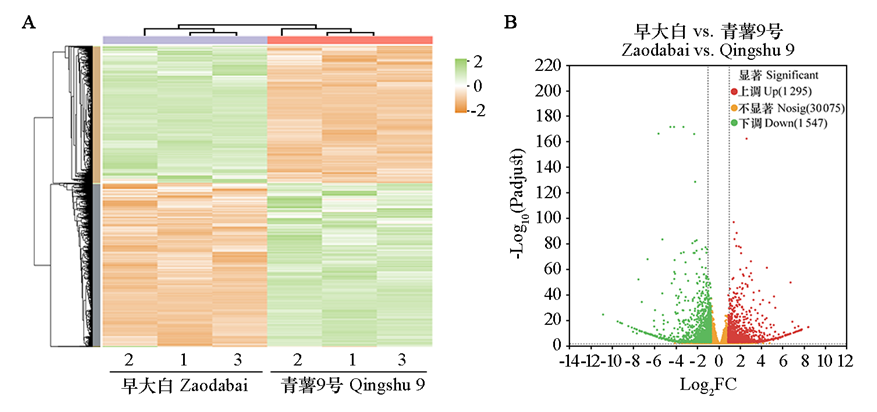
图3 马铃薯品种早大白与青薯9号差异基因表达模式聚类分析(A)和表达量差异统计(B)
Fig. 3 Cluster analysis of differential gene expression pattern(A)and statistical difference of expression level(B) between potato cultivars Zaodabai and Qingshu 9

图6 马铃薯品种早大白与青薯9号差异表达基因GO(A)和KEGG(B)富集分析
Fig. 6 GO(A)and KEGG(B)enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes of potato cultivars Zaodabai and Qingshu 9

图7 马铃薯熟性相关候选基因表达模式分析 使用t检验对数据进行分析,*代表显著性水平P ≤ 0.05;**代表显著性水平P ≤ 0.01;ns代表无显著性
Fig. 7 Analysis of candidate gene expression patterns related to potato maturation time t-Test was used to analyze the data,* represents a significance level of P ≤ 0.05,** represents a significance level of P ≤ 0.01,ns represents no significance
| [1] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.066 pmid: 26972319 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1996.9050745.x pmid: 8653120 |
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112334 pmid: 18083796 |
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
丛斌, 贾红武, 李严, 张丕方, 孙崇荣. 1999. 水稻幼穗形态发生与顶端分生组织的研究. 西北植物学报, 19 (3):415-421.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1327 |
|
冯建英, 李立芹, 鲁黎明. 2022. 马铃薯bHLH转录因子家族全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 生物技术通报, 38 (2):21-33.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2020-1327 |
|
| [11] |
pmid: 11402215 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
何蒲明, 狄书非. 2019. 生态安全与粮食安全并重导向下马铃薯主粮化发展路径研究. 农业经济,(6):12-14.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
胡月清. 2019. GA3和ABA对马铃薯薯形的影响. 江苏农业科学, 47 (18):125-128.
|
|
| [17] |
pmid: 19069877 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03245.x pmid: 17764503 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab409 pmid: 34734280 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-04032-9 pmid: 36374358 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
李晓梅. 2008. 大豆茎顶端分生组织石蜡切片的制备. 大豆科学, 27 (4):708-710.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
刘丹, 徐梦薇, 胡月清, 王若仲, 童建华, 肖浪涛. 2019. 马铃薯块茎发育期主要植物激素的动态变化. 分子植物育种, 17 (6):1998-2003.
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2013.07.001 pmid: 23856342 |
| [34] |
|
|
单建伟, 柳俊, 索海翠, 王丽, 安康, 刘计涛, 景晟林, 李成晨, 宋波涛, 李小波. 2021. 糖信号调控马铃薯块茎发育的研究进展. 华中农业大学学报, 40 (4):27-35.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
孙磊, 邰枫, 张亮, 于洪涛, 苏航, 毕诗婷. 2018. 不同氮肥配施对马铃薯块茎形成及发育的影响. 东北农业大学学报, 49 (6):32-39.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1007/s11306-022-01950-3 pmid: 36334159 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
|
王冬雪. 2013. 马铃薯早熟相关性状研究及多样性分析[硕士论文]. 黑龙江: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [40] |
|
|
谢婷婷, 柳俊. 2013. 光周期诱导马铃薯块茎形成的分子机理研究进展. 中国农业科学, 46 (22):4657-4664.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.22.003 |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
|
许庆芬. 2005. 马铃薯早熟组合重要农艺性状的评价及分离趋势的研究[硕士论文]. 黑龙江: 东北农业大学.
|
|
| [43] |
|
|
许真, 徐蝉, 郭得平. 2008. 光周期调节马铃薯块茎形成的分子机制. 细胞生物学杂志,3:731-736.
|
|
| [44] |
|
|
姚翔宇, 李广存, 徐建飞, 卞春松, 金黎平, 徐志刚. 2023. 光照对雾培马铃薯前期生长及块茎形成的影响. 南京农业大学学报, 46 (1):14-22.
|
|
| [45] |
|
|
张烁. 2021. 中国马铃薯种植区划研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
| [1] | 杨 利, 覃 亚, 边巴次仁, 珍 珍, 穷 吉, 白玛曲珍, 周 雅. 彩色马铃薯新品种‘喜格孜2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 145-146. |
| [2] | 杨春梅, 于洋, 丁雨格, 夏京, 周玲, 彭磊. 转录—代谢联合分析‘贵妃’杧果腋芽转化花芽中的淀粉与蔗糖代谢途径[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1412-1426. |
| [3] | 唐伶俐, 贺玉花, 王庆涛, 安璐璐, 徐永阳, 张健, 孔维虎, 户克云, 赵光伟. 非呼吸跃变和呼吸跃变型甜瓜成熟果实的激素与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 883-896. |
| [4] | 邵一帆, 朱宝庆, 王童欣, 廖建和, 吴繁花, 杨思怡, 冯建行, 于旭东. 基于激素、转录组和代谢组研究木棉皮刺的遗传调控[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 933-946. |
| [5] | 田玉凤, 马松亚, 杨安, 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞. 苹果砧木B9再生体系的建立与优化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 947-958. |
| [6] | 林茜, 邓振鹏, 阳新月, 周克友, 易小平, 王季春. 减施化肥配施有机肥对马铃薯产量及养分利用的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1007-1019. |
| [7] | 周进华, 白磊, 张锐, 郭华春. 秸秆覆盖降温栽培对马铃薯生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 453-466. |
| [8] | 杨艳, 刘军, 周晓慧, 刘松瑜, 庄勇. 茄子SmWRKY4的克隆及耐冷性功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 101-110. |
| [9] | 黄勋, 刘霞, 邓琳梅, 王兴国, 徐亚锦, 杨艳丽. 马铃薯疮痂病生防菌1X1Y的鉴定及其生防促生特性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 229-246. |
| [10] | 仲阳, 秦亚芝, 罗帅, 荆玉玲, 王万兴, 李广存, 胡新喜, 秦玉芝, 程旭, 熊兴耀. 泥炭和蘑菇渣改土对马铃薯根源微生物组及产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2143-2154. |
| [11] | 郭群艳, 刘彩贤, 余秋岫, 张画, 郑美婷. 紫花含笑花发育过程中生理和内源激素的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1881-1890. |
| [12] | 王建昭, 高园, 刀梅, 张洪烨, 杨自云, 陈龙清, 吴田. 山茶叶片的离体再生及内源激素与不定芽分化的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1891-1905. |
| [13] | 文宋琴, 李佳霖, 池卓恒, 夏燕, 王淑明, 吴頔, 郝雅雯, 郭启高, 梁国鲁, 景丹龙. 光和温度对开花时间基因可变剪接的影响研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1949-1963. |
| [14] | 王稳, 张鹏, 王志敏, 刘根忠, 包志龙, 马方放. 菊花脑管状花响应蔗糖饲喂的差异基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1297-1310. |
| [15] | 范国权, 喻江, 高艳玲, 李庆全, 张抒, 于镇华. 马铃薯种薯催芽、切块和包衣对其立枯丝核菌病的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1151-1161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司