
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1575-1587.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0541
刘亚男1, 鲍丹丹1, 张四普2, 牛佳佳2, 许志飞3, 杨永锋3, 鲁云风1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-08
修回日期:2025-04-07
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-20
通讯作者:
基金资助:
LIU Yanan1, BAO Dandan1, ZHANG Sipu2, NIU Jiajia2, XU Zhifei3, YANG Yongfeng3, and LU Yunfeng1,*( )
)
Received:2024-08-08
Revised:2025-04-07
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-06-20
摘要: 为探讨纳米硒对猕猴桃氨基酸营养成分的影响及机制,以‘徐香’猕猴桃为试材,采用0、10、15、20和25 mg · L-1纳米硒进行叶面喷施,测定氨基酸含量的变化,并对猕猴桃果实进行代谢组测序。结果发现:15 mg · L-1纳米硒喷施后苏氨酸、缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸等氨基酸含量显著升高,鲜味氨基酸占比提升。非靶向代谢组学共鉴定出12 861种代谢物,通过KEGG、HMDB数据库,进一步分析了成熟猕猴桃果实中脂质和类脂质分子、苯丙烷和聚酮、有机氧化合物的生物合成和代谢,主要富集在氨基酸代谢、次生代谢产物、萜类化合物和聚酮代谢等代谢途径。纳米硒可能通过刺激次级代谢水平提高猕猴桃果实氨基酸含量。
刘亚男, 鲍丹丹, 张四普, 牛佳佳, 许志飞, 杨永锋, 鲁云风. 叶面喷施纳米硒对猕猴桃果实氨基酸含量及代谢组的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1575-1587.
LIU Yanan, BAO Dandan, ZHANG Sipu, NIU Jiajia, XU Zhifei, YANG Yongfeng, and LU Yunfeng. Effects of Foliar Spraying of Nano-selenium on Amino Acid Content and Metabolome of Kiwifruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(6): 1575-1587.
| 纳米硒/(mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 苏氨酸Thr | 缬氨酸Val | 蛋氨酸Met | 异亮氨酸Ile | 亮氨酸Leu | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 赖氨酸Lys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | 0.51 ± 0 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 0.47 ± 0.02 b | 0.54 ± 0.01 b | 0.42 ± 0 b | 0.61 ± 0.01 b |
| 10 | 0.48 ± 0.02 c | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 bc | 0.44 ± 0 c | 0.50 ± 0 d | 0.39 ± 0 c | 0.55 ± 0.01 d |
| 15 | 0.55 ± 0 a | 0.59 ± 0.03 a | 0.15 ± 0 a | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0 a | 0.67 ± 0.02 a |
| 20 | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 0.50 ± 0 b | 0.14 ± 0 ab | 0.46 ± 0 bc | 0.52 ± 0.01 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 b | 0.58 ± 0.01 c |
| 25 | 0.43 ± 0.01 d | 0.44 ± 0 c | 0.12 ± 0 c | 0.40 ± 0 d | 0.45 ± 0.01 e | 0.36 ± 0.01 d | 0.50 ± 0 e |
| 平均Average | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.58 |
表1 叶面喷施纳米硒猕猴桃果实中必需氨基酸含量
Table 1 The content of essential amino acid in fruits of kiwifruit sprayed with foliar nano-selenium mg · g-1
| 纳米硒/(mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 苏氨酸Thr | 缬氨酸Val | 蛋氨酸Met | 异亮氨酸Ile | 亮氨酸Leu | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 赖氨酸Lys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | 0.51 ± 0 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 ab | 0.47 ± 0.02 b | 0.54 ± 0.01 b | 0.42 ± 0 b | 0.61 ± 0.01 b |
| 10 | 0.48 ± 0.02 c | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 bc | 0.44 ± 0 c | 0.50 ± 0 d | 0.39 ± 0 c | 0.55 ± 0.01 d |
| 15 | 0.55 ± 0 a | 0.59 ± 0.03 a | 0.15 ± 0 a | 0.52 ± 0.02 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0 a | 0.67 ± 0.02 a |
| 20 | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 0.50 ± 0 b | 0.14 ± 0 ab | 0.46 ± 0 bc | 0.52 ± 0.01 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 b | 0.58 ± 0.01 c |
| 25 | 0.43 ± 0.01 d | 0.44 ± 0 c | 0.12 ± 0 c | 0.40 ± 0 d | 0.45 ± 0.01 e | 0.36 ± 0.01 d | 0.50 ± 0 e |
| 平均Average | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.58 |
| 纳米硒/ (mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 天冬氨酸 Asp | 丝氨酸 Ser | 谷氨酸 Glu | 甘氨酸 Gly | 丙氨酸 Ala | 酪氨酸 Tyr | 组氨酸 His | 精氨酸 Arg | 脯氨酸 Pro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 1.03 ± 0.02 b | 0.46 ± 0.01 ab | 1.70 ± 0.01 b | 0.53 ± 0 b | 0.46 ± 0 b | 0.36 ± 0 b | 0.23 ± 0 ab | 0.55 ± 0 b | 0.37 ± 0.01 b |
| 10 | 0.98 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.03 c | 1.63 ± 0.03 c | 0.48 ± 0.01 c | 0.41 ± 0.02 d | 0.33 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 bc | 0.62 ± 0.10 b | 0.33 ± 0.01 d |
| 15 | 1.12 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0 a | 1.94 ± 0.03 a | 0.56 ± 0.01 a | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 0.40 ± 0.01 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.85 ± 0.02 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| 20 | 1.02 ± 0.03 bc | 0.45 ± 0 bc | 1.63 ± 0 c | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 0.43 ± 0 c | 0.36 ± 0.01 b | 0.24 ± 0 ab | 0.54 ± 0 bc | 0.35 ± 0 c |
| 25 | 0.86 ± 0.01 d | 0.38 ± 0.03 d | 1.40 ± 0 d | 0.44 ± 0.04 d | 0.38 ± 0 e | 0.30 ± 0.02 d | 0.20 ± 0.03 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 0.30 ± 0 e |
| 平均Average | 1.00 | 0.44 | 1.66 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.60 | 0.35 |
表2 叶面喷施纳米硒猕猴桃果实中非必需氨基酸含量
Table 2 Non-essential amino acid content in kiwifruit fruits sprayed with foliar nano-selenium mg · g-1
| 纳米硒/ (mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 天冬氨酸 Asp | 丝氨酸 Ser | 谷氨酸 Glu | 甘氨酸 Gly | 丙氨酸 Ala | 酪氨酸 Tyr | 组氨酸 His | 精氨酸 Arg | 脯氨酸 Pro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 1.03 ± 0.02 b | 0.46 ± 0.01 ab | 1.70 ± 0.01 b | 0.53 ± 0 b | 0.46 ± 0 b | 0.36 ± 0 b | 0.23 ± 0 ab | 0.55 ± 0 b | 0.37 ± 0.01 b |
| 10 | 0.98 ± 0.02 c | 0.42 ± 0.03 c | 1.63 ± 0.03 c | 0.48 ± 0.01 c | 0.41 ± 0.02 d | 0.33 ± 0.01 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 bc | 0.62 ± 0.10 b | 0.33 ± 0.01 d |
| 15 | 1.12 ± 0.03 a | 0.49 ± 0 a | 1.94 ± 0.03 a | 0.56 ± 0.01 a | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 0.40 ± 0.01 a | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 0.85 ± 0.02 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| 20 | 1.02 ± 0.03 bc | 0.45 ± 0 bc | 1.63 ± 0 c | 0.52 ± 0.01 b | 0.43 ± 0 c | 0.36 ± 0.01 b | 0.24 ± 0 ab | 0.54 ± 0 bc | 0.35 ± 0 c |
| 25 | 0.86 ± 0.01 d | 0.38 ± 0.03 d | 1.40 ± 0 d | 0.44 ± 0.04 d | 0.38 ± 0 e | 0.30 ± 0.02 d | 0.20 ± 0.03 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 0.30 ± 0 e |
| 平均Average | 1.00 | 0.44 | 1.66 | 0.51 | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.60 | 0.35 |
| 纳米硒/(mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 氨基酸总量(T) Total amino acid | 必需氨基酸(E) Essential amino acid | 非必需氨基酸(N) Non-essential amino acid | E/N% | E/T% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 8.91 ± 0.02 b | 3.23 | 5.69 | 56.70 | 36.18 |
| 10 | 8.40 ± 0.08 d | 2.97 | 5.43 | 54.76 | 35.38 |
| 15 | 10.03 ± 0.07 a | 3.55 | 6.49 | 54.68 | 35.35 |
| 20 | 8.70 ± 0.01 c | 3.15 | 5.55 | 56.68 | 36.18 |
| 25 | 7.41 ± 0.04 e | 2.70 | 4.71 | 57.30 | 36.43 |
| 平均Average | 8.69 | 3.12 | 5.57 | 56.02 | 35.90 |
表3 叶面喷施纳米硒猕猴桃果实中氨基酸含量分析
Table 3 Analysis of amino acid content in fruits of kiwifruit sprayed with foliar nano-selenium mg · g-1
| 纳米硒/(mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 氨基酸总量(T) Total amino acid | 必需氨基酸(E) Essential amino acid | 非必需氨基酸(N) Non-essential amino acid | E/N% | E/T% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照Control) | 8.91 ± 0.02 b | 3.23 | 5.69 | 56.70 | 36.18 |
| 10 | 8.40 ± 0.08 d | 2.97 | 5.43 | 54.76 | 35.38 |
| 15 | 10.03 ± 0.07 a | 3.55 | 6.49 | 54.68 | 35.35 |
| 20 | 8.70 ± 0.01 c | 3.15 | 5.55 | 56.68 | 36.18 |
| 25 | 7.41 ± 0.04 e | 2.70 | 4.71 | 57.30 | 36.43 |
| 平均Average | 8.69 | 3.12 | 5.57 | 56.02 | 35.90 |
| 纳米硒/ (mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 苏氨酸 Thr | 缬氨酸Val | 蛋氨酸 Met | 异亮氨酸 Ile | 亮氨酸Leu | 苯丙氨酸 + 酪氨酸 Phe + Tyr | 赖氨酸Lys | 必需氨基酸比值系数分值SRC | 必需氨基酸指数 EAAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照 Control) | RAA | 1.47 | 1.14 | 0.45 | 1.33 | 0.87 | 1.35 | 1.25 | 47.70 | 1.27 |
| RC | 1.31 | 1.02 | 0.40 | 1.18 | 0.78 | 1.20 | 1.11 | |||
| 10 | RAA | 1.43 | 1.14 | 0.44 | 1.32 | 0.85 | 1.32 | 1.20 | 44.64 | 1.26 |
| RC | 1.30 | 1.04 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.77 | 1.20 | 1.09 | |||
| 15 | RAA | 1.38 | 1.17 | 0.42 | 1.30 | 0.85 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 53.60 | 1.29 |
| RC | 1.26 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 1.22 | 1.19 | |||
| 20 | RAA | 1.50 | 1.15 | 0.46 | 1.32 | 0.86 | 1.38 | 1.21 | 45.95 | 1.27 |
| RC | 1.33 | 1.02 | 0.41 | 1.18 | 0.76 | 1.23 | 1.08 | |||
| 25 | RAA | 1.45 | 1.18 | 0.47 | 1.35 | 0.87 | 1.37 | 1.22 | 38.48 | 1.24 |
| RC | 1.28 | 1.05 | 0.41 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 1.21 | 1.08 |
表4 叶面喷施纳米硒猕猴桃果实氨基酸比值系数和比值系数分
Table 4 The ratio coefficients and ratio coefficient scores of amino acids
| 纳米硒/ (mg · L-1) Nano-selenium | 评价指标 Evaluation index | 苏氨酸 Thr | 缬氨酸Val | 蛋氨酸 Met | 异亮氨酸 Ile | 亮氨酸Leu | 苯丙氨酸 + 酪氨酸 Phe + Tyr | 赖氨酸Lys | 必需氨基酸比值系数分值SRC | 必需氨基酸指数 EAAI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0(对照 Control) | RAA | 1.47 | 1.14 | 0.45 | 1.33 | 0.87 | 1.35 | 1.25 | 47.70 | 1.27 |
| RC | 1.31 | 1.02 | 0.40 | 1.18 | 0.78 | 1.20 | 1.11 | |||
| 10 | RAA | 1.43 | 1.14 | 0.44 | 1.32 | 0.85 | 1.32 | 1.20 | 44.64 | 1.26 |
| RC | 1.30 | 1.04 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.77 | 1.20 | 1.09 | |||
| 15 | RAA | 1.38 | 1.17 | 0.42 | 1.30 | 0.85 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 53.60 | 1.29 |
| RC | 1.26 | 1.06 | 0.39 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 1.22 | 1.19 | |||
| 20 | RAA | 1.50 | 1.15 | 0.46 | 1.32 | 0.86 | 1.38 | 1.21 | 45.95 | 1.27 |
| RC | 1.33 | 1.02 | 0.41 | 1.18 | 0.76 | 1.23 | 1.08 | |||
| 25 | RAA | 1.45 | 1.18 | 0.47 | 1.35 | 0.87 | 1.37 | 1.22 | 38.48 | 1.24 |
| RC | 1.28 | 1.05 | 0.41 | 1.19 | 0.77 | 1.21 | 1.08 |
| 类别 Classification | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 味觉阈值 Taste threshold | 不同浓度(mg · L-1)处理的RCT RCT of different treatments | 平均 Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | ||||
| 甜味氨基酸 Sweet amino acids | 甘氨酸Gly | 1.1 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.46 |
| 丙氨酸Ala | 6.0 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.72 | |
| 苏氨酸Asp | 2.6 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.19 | |
| 丝氨酸Ser | 1.5 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.29 | |
| 脯氨酸Pro | 3.0 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | |
| 组氨酸His | 2.0 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 1.20 | 0.98 | 1.14 | |
| 鲜味氨基酸 Delicate amino acids | 天冬氨酸Asp | 0.03 | 34.47 | 32.63 | 37.27 | 34.07 | 28.72 | 33.43 |
| 谷氨酸Glu | 0.05 | 34.01 | 32.69 | 38.76 | 32.67 | 27.97 | 33.22 | |
| 赖氨酸Lys | 0.5 | 1.23 | 1.11 | 1.34 | 1.16 | 1.00 | 1.17 | |
| 苦味氨基酸 Bitter amino acids | 缬氨酸Val | 1.5 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| 蛋氨酸Met | 3.0 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.45 | |
| 异亮氨酸lle | 0.9 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.51 | |
| 亮氨酸Leu | 3.8 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
| 精氨酸Arg | 0.1 | 0.55 | 6.19 | 8.52 | 5.41 | 4.54 | 6.03 | |
| 芳香族氨基酸 Aromatic amino acids | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 1.5 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.27 |
| 酪氨酸Tyr | 2.6 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
表5 叶面喷施纳米硒猕猴桃果实的含量阈值比(RCT)
Table 5 The content threshold ratios(RCT)of kiwifruit fruits
| 类别 Classification | 氨基酸 Amino acid | 味觉阈值 Taste threshold | 不同浓度(mg · L-1)处理的RCT RCT of different treatments | 平均 Average | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | ||||
| 甜味氨基酸 Sweet amino acids | 甘氨酸Gly | 1.1 | 0.48 | 0.44 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.46 |
| 丙氨酸Ala | 6.0 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.63 | 0.72 | |
| 苏氨酸Asp | 2.6 | 0.20 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.19 | |
| 丝氨酸Ser | 1.5 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.29 | |
| 脯氨酸Pro | 3.0 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | |
| 组氨酸His | 2.0 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 1.28 | 1.20 | 0.98 | 1.14 | |
| 鲜味氨基酸 Delicate amino acids | 天冬氨酸Asp | 0.03 | 34.47 | 32.63 | 37.27 | 34.07 | 28.72 | 33.43 |
| 谷氨酸Glu | 0.05 | 34.01 | 32.69 | 38.76 | 32.67 | 27.97 | 33.22 | |
| 赖氨酸Lys | 0.5 | 1.23 | 1.11 | 1.34 | 1.16 | 1.00 | 1.17 | |
| 苦味氨基酸 Bitter amino acids | 缬氨酸Val | 1.5 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.34 |
| 蛋氨酸Met | 3.0 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.45 | |
| 异亮氨酸lle | 0.9 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.51 | |
| 亮氨酸Leu | 3.8 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
| 精氨酸Arg | 0.1 | 0.55 | 6.19 | 8.52 | 5.41 | 4.54 | 6.03 | |
| 芳香族氨基酸 Aromatic amino acids | 苯丙氨酸Phe | 1.5 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.27 |
| 酪氨酸Tyr | 2.6 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.14 | |
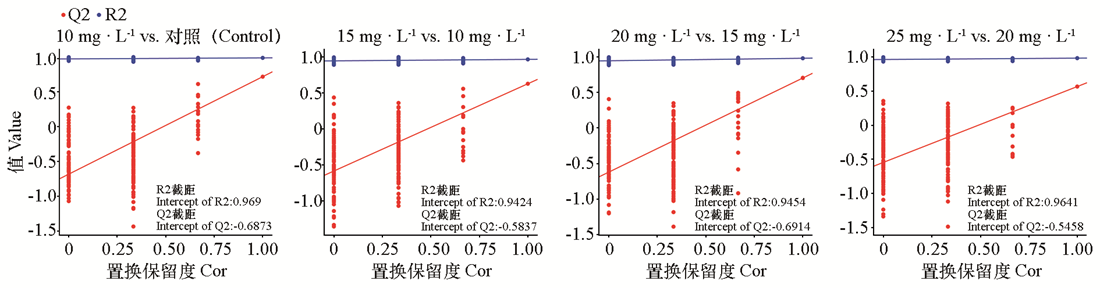
图4 PLS-DA置换检验图 R2代表模型的解释率;Q2代表模型的预测率
Fig. 4 PLS-DA replacement test chart R2 represents the explanation rate of the model;Q2 represents the prediction rate of the model
| [1] |
doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2020.06.018 pmid: 33413775 |
|
陈宏靖, 阳丽君, 宋涛. 2020. 闽产25种蔬菜氨基酸含量及营养评价. 卫生研究, 49 (6):978-983.
pmid: 33413775 |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
冯两蕊, 杜慧玲, 王曰鑫. 2007. 叶面喷施硒对生菜富硒量及产量与品质的影响. 山西农业大学学报,(3):291-294.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
GB/T 5009.124-2016. Determination of amino acids in food safety national standards. (in Chinese)
|
|
GB/T 5009.124-2016. 食品安全国家标准食品中氨基酸的测定.
|
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0784 |
|
郭丽娜, 王璐, 郝心愿, 祁蒙, 李晓嫚, 王新超, 曾建明. 2022. 茶树根系吸收硒的生理特性研究. 园艺学报, 49 (9):1967-1976.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0784 |
|
| [9] |
|
|
胡万行, 石玉, 程玉琦, 赵博思, 周云云, 张毅. 2020. 纳米硒对紫色马铃薯生长及其矿质元素含量和品质特性的影响. 西北植物学报, 40 (2):296-303.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
孔清华. 2020. 谷子施用生物纳米硒的生理生化效应及对产量的影响[硕士论文]. 济南: 山东师范大学.
|
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
李秀启, 尹国红, 郝浩浩, 贾宝华, 牛小沛. 2019. 植物对硒的吸收利用及主要农作物硒生物强化研究进展. 甘肃农业科技,(4):65-71.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
卢鹏飞, 高志强, 孙敏, 董石峰, 任爱霞, 候非凡, 尹雪斌. 2020. 外源硒肥对小麦籽粒产量及植株硒元素积累的影响. 河北农业大学学报, 43 (3):17-22.
doi: 10.13320/j.cnki.jauh.2020.0046 |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
pmid: 14831997 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.13.014 |
|
孙娟娟, 阿拉木斯, 赵金梅, 薛艳林, 于林清, 玉柱, 张英俊. 2019. 6个紫花苜蓿品种氨基酸组成分析及营养价值评价. 中国农业科学, 52 (13):2359-2367.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.13.014 |
|
| [23] |
|
|
孙鹏波, 王志军, 格根图, 袁宁, 孙林, 司强, 张佳伟, 刘逸超, 贾玉山. 2023. 喷施纳米硒对紫花苜蓿产量、营养品质和硒含量的影响. 中国草地学报, 45 (8):79-87.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
王清华, 井大炜, 杜振宇, 马海林, 马丙尧, 刘方春, 王静. 2020. 不同时期叶面喷硒对冬枣含硒量与品质的影响. 农业资源与环境学报, 37 (2):226-232.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
杨三东. 2005. 红三叶草中硒的生理生化及其富集规律研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | 戢小梅, 翟敬华, 陈志伟, 张 鸿, 乐有章, 赵志远, 杨静文, 黄 维, 寇小文, 曾云流, 蔡礼鸿, 刘 杰, 米绪凯, 李秀丽. 早熟黄肉猕猴桃新品种‘香秾’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 49-50. |
| [2] | 杨玉皎, 孙应康, 朱贞顺, 李义林, 李 坤, 岳学文, 陈大明, 方海东. 猕猴桃新品种‘宣猕1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 51-52. |
| [3] | 韩 飞, 李大卫, 田 华, 吕海燕, 张 琦, 钟彩虹. 猕猴桃中花雄性新品种‘磨山雄6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 53-54. |
| [4] | 韩 飞, 张 琼, 李大卫, 吕海燕, 刘小莉, 田 华, 钟彩虹. 软枣猕猴桃授粉专用新品种‘中科猕枣雄1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 55-56. |
| [5] | 许秀秀, 叶鑫雨, 师博, 张淑江, 章时蕃, 李菲, 李国亮, 孙日飞, 王顺利, 孙华刚, 张慧. 大白菜玉田包尖的风味品质分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1364-1374. |
| [6] | 苏燕珊, 杨艺婷, 杨晓雅, 唐溶霞, 席德慧. 猕猴桃AcRhoGAP在响应Psa侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 25-36. |
| [7] | 刘艳飞, 何昕, 田爱林, 刘占德. 优质耐贮猕猴桃新品种‘金福’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2219-2220. |
| [8] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [9] | 李文远, 林梦桦, 李亚辉, 于全琦, 梁颖, 张志勇. 梨果实代谢组学研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1595-1609. |
| [10] | 董晓珂, 陈元磊, 牛友怡, 刘占德, 王南南. 以高产优质稳产为目标的‘徐香’猕猴桃不同生长期叶片营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1345-1360. |
| [11] | 乔成奎, 庄明, 田发军, 王彩霞, 庞涛, 陈如霞, 李晓光, 成昕, 谢汉忠. 氟啶虫酰胺和螺虫乙酯在猕猴桃园中的降解及膳食风险评估[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1386-1402. |
| [12] | 王海珍, 应瑶琳, 王雨晴, 吕瑞恒, 韩路. 软枣猕猴桃品种耐热性差异分析与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2857-2870. |
| [13] | 刘艳飞, 何昕, 贺浩浩, 刘占德. 早熟黄肉中华猕猴桃新品种‘黑金’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2725-2726. |
| [14] | 田洁, 周倩怡, 铁原毓, 孙海宏, 黄思杰. 干旱胁迫下大蒜幼苗的代谢组学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 133-144. |
| [15] | 徐旭华, 黄文洁, 陈旭峰, 陈园园, 吴绍文, 李红建, 晏石娟. ‘丹霞2号’红茶加工过程中品质特征成分的动态变化研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 145-161. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司