
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 25-36.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0179
收稿日期:2024-10-21
修回日期:2024-11-25
出版日期:2025-01-25
发布日期:2025-01-18
通讯作者:
基金资助:
SU Yanshan, YANG Yiting, YANG Xiaoya, TANG Rongxia, XI Dehui*( )
)
Received:2024-10-21
Revised:2024-11-25
Published:2025-01-25
Online:2025-01-18
Contact:
* E-mail:xidh@scu.edu.cn
摘要:
GTP酶激活蛋白(RhoGAP)作为小G蛋白的调控因子之一,在植物生长发育、细胞骨架调节和信号传导过程中发挥着重要作用,但其在植物抗病响应中的功能尚不清楚。以猕猴桃和本氏烟草为材料,利用农杆菌介导的瞬时过表达方法,对AcRhoGAP在植物响应猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病致病菌丁香假单胞菌猕猴桃致病变种(Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidiae,Psa)侵染过程中的作用进行了探究。结果显示,Psa的侵染会诱导猕猴桃叶片中AcRhoGAP表达量的上调,且瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP的叶片Psa侵染症状更严重,膜系统受到更大的损伤。在本氏烟草中,瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP叶片中Psa菌量更高,活性氧含量降低,膜系统受损更严重,防御相关激素途径标志基因的表达发生变化。综上,AcRhoGAP可能负调控猕猴桃对Psa的抗性。
苏燕珊, 杨艺婷, 杨晓雅, 唐溶霞, 席德慧. 猕猴桃AcRhoGAP在响应Psa侵染中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 25-36.
SU Yanshan, YANG Yiting, YANG Xiaoya, TANG Rongxia, XI Dehui. Functional Analysis of AcRhoGAP in Kiwifruit in Response to Psa Infection[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 25-36.
| 用途 Use | GI/基因ID号 GI/Gene ID | 片段大小/bp Product size | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆Gene cloning | 1371493451 | 1 410 | SalⅠ-1307AcGAP-F | GCGTCGACATGACAGAGGTCCTCCACTC |
| SpeⅠ-1307AcGAP-R | GGACTAGTTCACCGCCAGGCTTCA | |||
| 实时荧光定量 PCR Quantitative real-time PCR | 107826390 | 270 | EF1α-F | TGTTGTATGATTTTGGGGTAGAC |
| EF1α-R | GAATCATAAACAGATCATATATGCAC | |||
| 1371492652 | 270 | Ac-actinB-F | CAGCATAACGGTCAAGGTC | |
| Ac-actinB-R | GAAAACAAATCTAGAACGAAAA | |||
| 1371493451 | 185 | AcGAP-F | CGGGTGGCCGACTAATG | |
| AcGAP-R | GCACACTGTTCCCTCTAGG | |||
| 21552982 | 200 | NtEDS1-F | TCTTACCGATATTCCCTTGT | |
| NtEDS1-R | CTGCTTCTCCCATTCTCC | |||
| 19939 | 200 | NtPR1a-F | ATTGCCTTCATTTCTTCTTG | |
| NtPR1a-R | TTGGGACACCAGGAGCAT | |||
| 107807832 | 200 | NtPR1b-F | GTGGACACTATACTCAGGTG | |
| NtPR1b-R | TCCAACTTGGAATCAAAGGG | |||
| 107831756 | 200 | NtNPR1-F | ATGCGGATGACTTGTCTG | |
| NtNPR1-R | GGGCTTATCTACTCCCTTA | |||
| 107770253 | 200 | NtLOX-F | GGTCAAGAAGTTGTGAACATACA | |
| NtLOX-R | TTTGTCCAGCATCTCTGCA | |||
| 107783985 | 200 | NtAOS-F | TCCAGTCTTACCACTACATAAAA | |
| NtAOS-R | AAGAGAATGGAAAGGAAGTG | |||
| 109215681 | 200 | NtPDF1.2-F | AGATGGGACCAACGACAA | |
| NtPDF1.2-R | AAATCCTTCGGTCAAACA | |||
| 107819687 | 200 | NtCOI1-F | AGCAGCCCATTGTTTCTT | |
| NtCOI1-R | CACCTTGTTCATCCTCCA | |||
| 109235543 | 200 | NtEIN2-F | TCATCATCAATGTCGTCAAC | |
| NtEIN2-R | GCTAAGGTCGGTAATAGTGT | |||
| 半定量PCR Semi quantitative PCR | 107826390 | 270 | EF1α-F | TGTTGTATGATTTTGGGGTAGAC |
| EF1α-R | GAATCATAAACAGATCATATATGCAC | |||
| 1371492652 | 270 | Ac-actinB-F | CAGCATAACGGTCAAGGTC | |
| Ac-actinB-R | GAAAACAAATCTAGAACGAAAA | |||
| 39515390 | 280 | Psa-F1 | TTTTGCTTTGCACACCCGATTTT | |
| Psa-R2 | CACGCACCCTTCAATCAGGATG |
表1 本研究中使用的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| 用途 Use | GI/基因ID号 GI/Gene ID | 片段大小/bp Product size | 名称 Name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆Gene cloning | 1371493451 | 1 410 | SalⅠ-1307AcGAP-F | GCGTCGACATGACAGAGGTCCTCCACTC |
| SpeⅠ-1307AcGAP-R | GGACTAGTTCACCGCCAGGCTTCA | |||
| 实时荧光定量 PCR Quantitative real-time PCR | 107826390 | 270 | EF1α-F | TGTTGTATGATTTTGGGGTAGAC |
| EF1α-R | GAATCATAAACAGATCATATATGCAC | |||
| 1371492652 | 270 | Ac-actinB-F | CAGCATAACGGTCAAGGTC | |
| Ac-actinB-R | GAAAACAAATCTAGAACGAAAA | |||
| 1371493451 | 185 | AcGAP-F | CGGGTGGCCGACTAATG | |
| AcGAP-R | GCACACTGTTCCCTCTAGG | |||
| 21552982 | 200 | NtEDS1-F | TCTTACCGATATTCCCTTGT | |
| NtEDS1-R | CTGCTTCTCCCATTCTCC | |||
| 19939 | 200 | NtPR1a-F | ATTGCCTTCATTTCTTCTTG | |
| NtPR1a-R | TTGGGACACCAGGAGCAT | |||
| 107807832 | 200 | NtPR1b-F | GTGGACACTATACTCAGGTG | |
| NtPR1b-R | TCCAACTTGGAATCAAAGGG | |||
| 107831756 | 200 | NtNPR1-F | ATGCGGATGACTTGTCTG | |
| NtNPR1-R | GGGCTTATCTACTCCCTTA | |||
| 107770253 | 200 | NtLOX-F | GGTCAAGAAGTTGTGAACATACA | |
| NtLOX-R | TTTGTCCAGCATCTCTGCA | |||
| 107783985 | 200 | NtAOS-F | TCCAGTCTTACCACTACATAAAA | |
| NtAOS-R | AAGAGAATGGAAAGGAAGTG | |||
| 109215681 | 200 | NtPDF1.2-F | AGATGGGACCAACGACAA | |
| NtPDF1.2-R | AAATCCTTCGGTCAAACA | |||
| 107819687 | 200 | NtCOI1-F | AGCAGCCCATTGTTTCTT | |
| NtCOI1-R | CACCTTGTTCATCCTCCA | |||
| 109235543 | 200 | NtEIN2-F | TCATCATCAATGTCGTCAAC | |
| NtEIN2-R | GCTAAGGTCGGTAATAGTGT | |||
| 半定量PCR Semi quantitative PCR | 107826390 | 270 | EF1α-F | TGTTGTATGATTTTGGGGTAGAC |
| EF1α-R | GAATCATAAACAGATCATATATGCAC | |||
| 1371492652 | 270 | Ac-actinB-F | CAGCATAACGGTCAAGGTC | |
| Ac-actinB-R | GAAAACAAATCTAGAACGAAAA | |||
| 39515390 | 280 | Psa-F1 | TTTTGCTTTGCACACCCGATTTT | |
| Psa-R2 | CACGCACCCTTCAATCAGGATG |

图1 Psa侵染后‘红阳’(A ~ D)‘海沃德’(E ~ H)猕猴桃叶片中AcRhoGAP的时空表达 A、E:接种Psa后的表型;B、F:平板计数Psa菌量;C、G:半定量PCR检测Psa菌量;D、H:AcRhoGAP的相对表达量。** 表示两个材料间在P < 0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 1 Temporal and spatial expression of AcRhoGAP in Hongyang(A- D)and Hayward(E-H)kiwifruit leaves after Psa infection A,E:The phenotypes after inoculation of Psa;B,F:Psa CFU detected by tablet counting;C,G:Psa CFU detected by semi quantitative PCR;D,H:Relative expression level of AcRhoGAP. ** indicates the difference between two materials reaches a significant level when P < 0.01
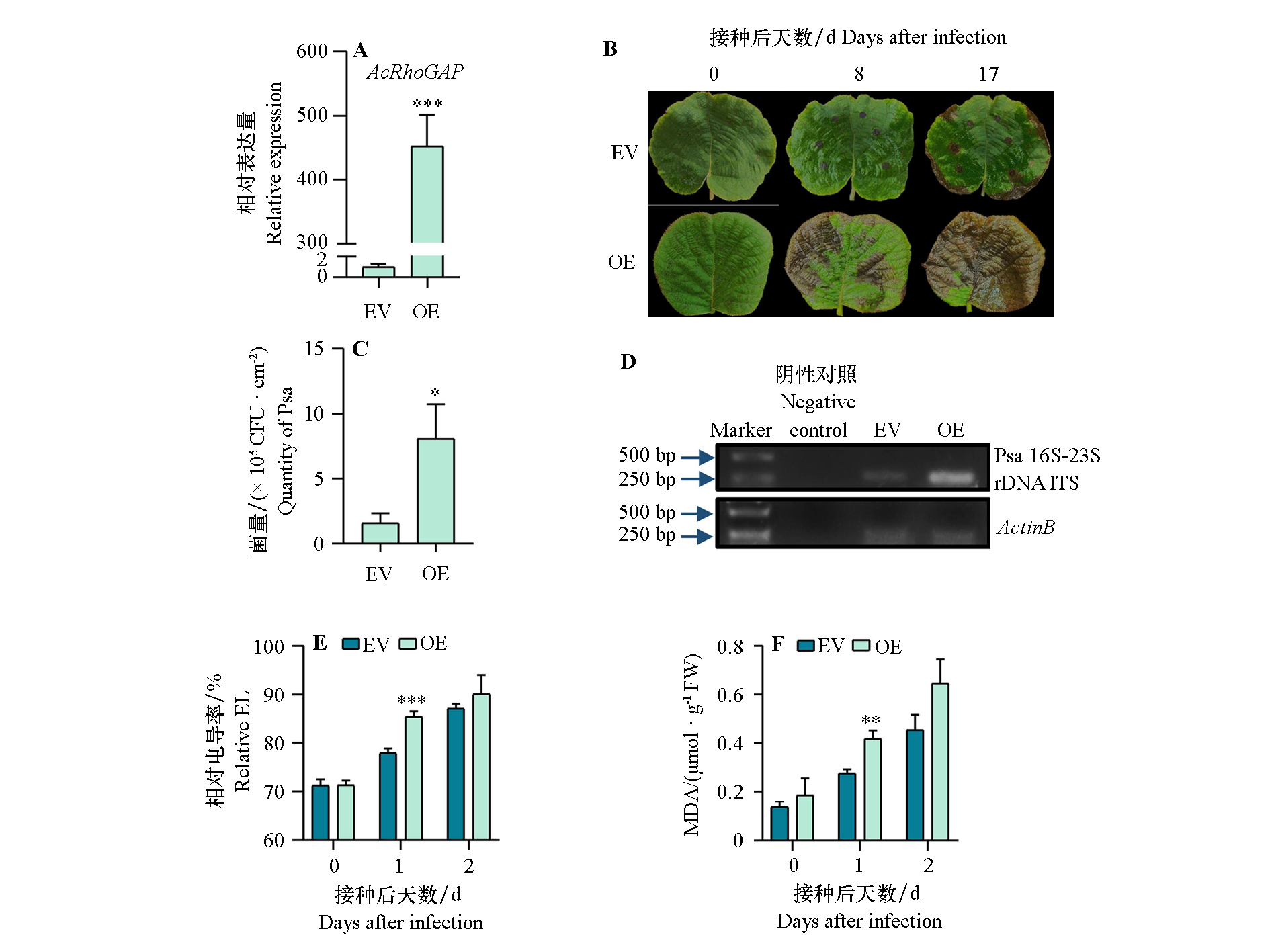
图2 ‘红阳’猕猴桃叶片中瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP(OE)及转入空载体(EV)对Psa侵染的影响 A:瞬时过表达效果;B:病程发展表型;C:平板计数Psa菌量;D:半定量PCR检测Psa菌量;E:相对电导率;F:MDA含量。 ***、**、*分别表示两个材料间在P < 0.001、P < 0.01、P < 0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 2 Effects of instantaneous overexpression of AcRhoGAP on Psa infection in Hongyang kiwifruit leaves A:The effect of transient overexpression;B:The phenotypes of disease progression;C:Psa CFU detected by tablet counting;D:Psa CFU detected by semi quantitative PCR;E:Relative EL;F:MDA content. ***,**,* respectively indicate the difference between two materials reaches a significant level when P < 0.001,P < 0.01,P < 0.05
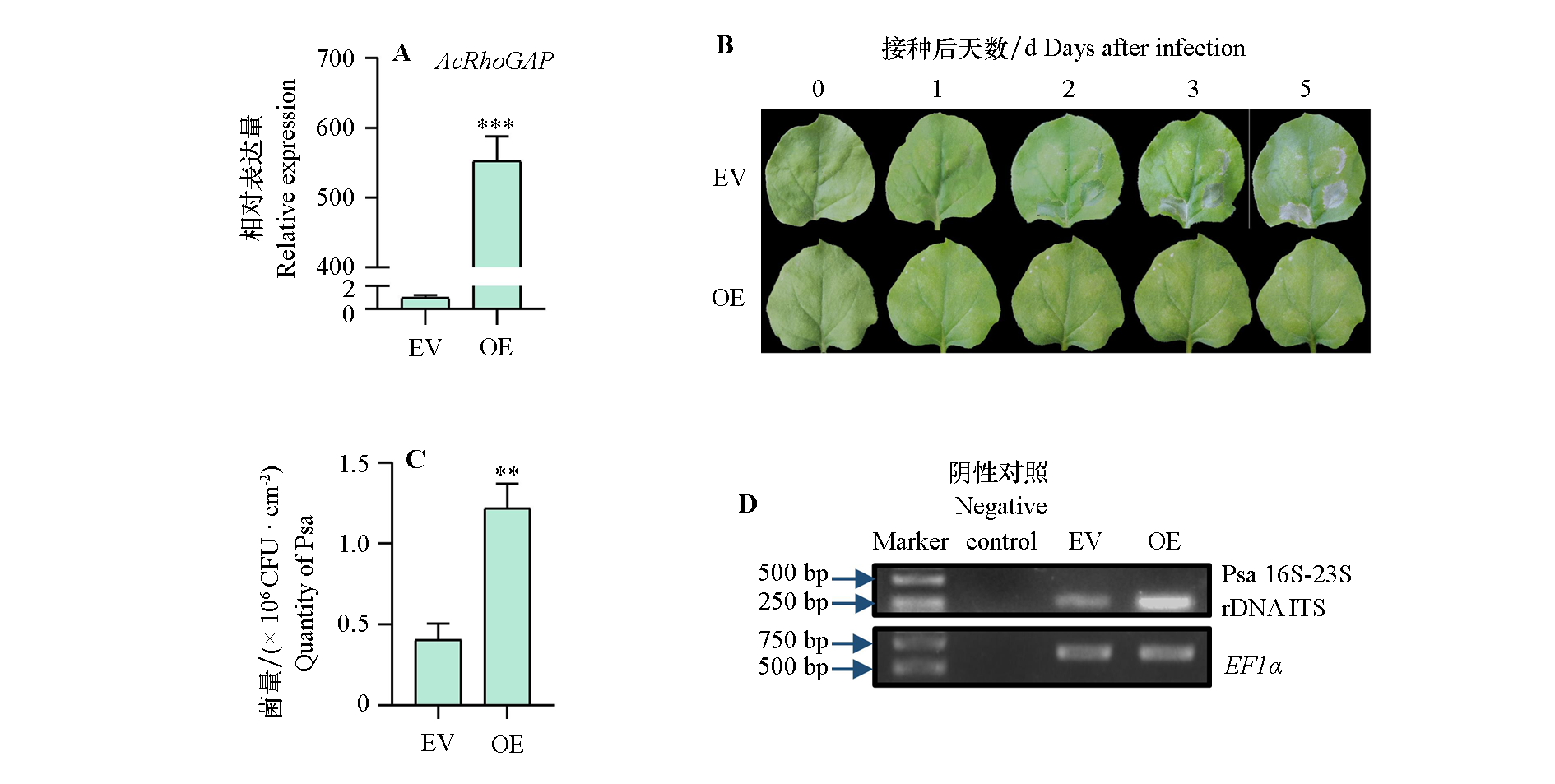
图3 本氏烟草叶片中瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP(OE)及转入空载体(EV)对Psa侵染的影响 A:瞬时过表达效果;B:病程发展表型;C:平板计数Psa菌量;D:半定量PCR检测Psa菌量。 ***、**分别表示两个材料间在P < 0.001、P < 0.01水平差异显著
Fig. 3 Effects of instantaneous overexpression of AcRhoGAP on Psa infection in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves A:The effect of transient overexpression;B:The phenotypes of disease progression;C:Psa CFU detected by tablet counting;D:Psa CFU detected by semi quantitative PCR. ***,** respectively indicate the difference between two materials reaches a significant level when P < 0.001,P < 0.01
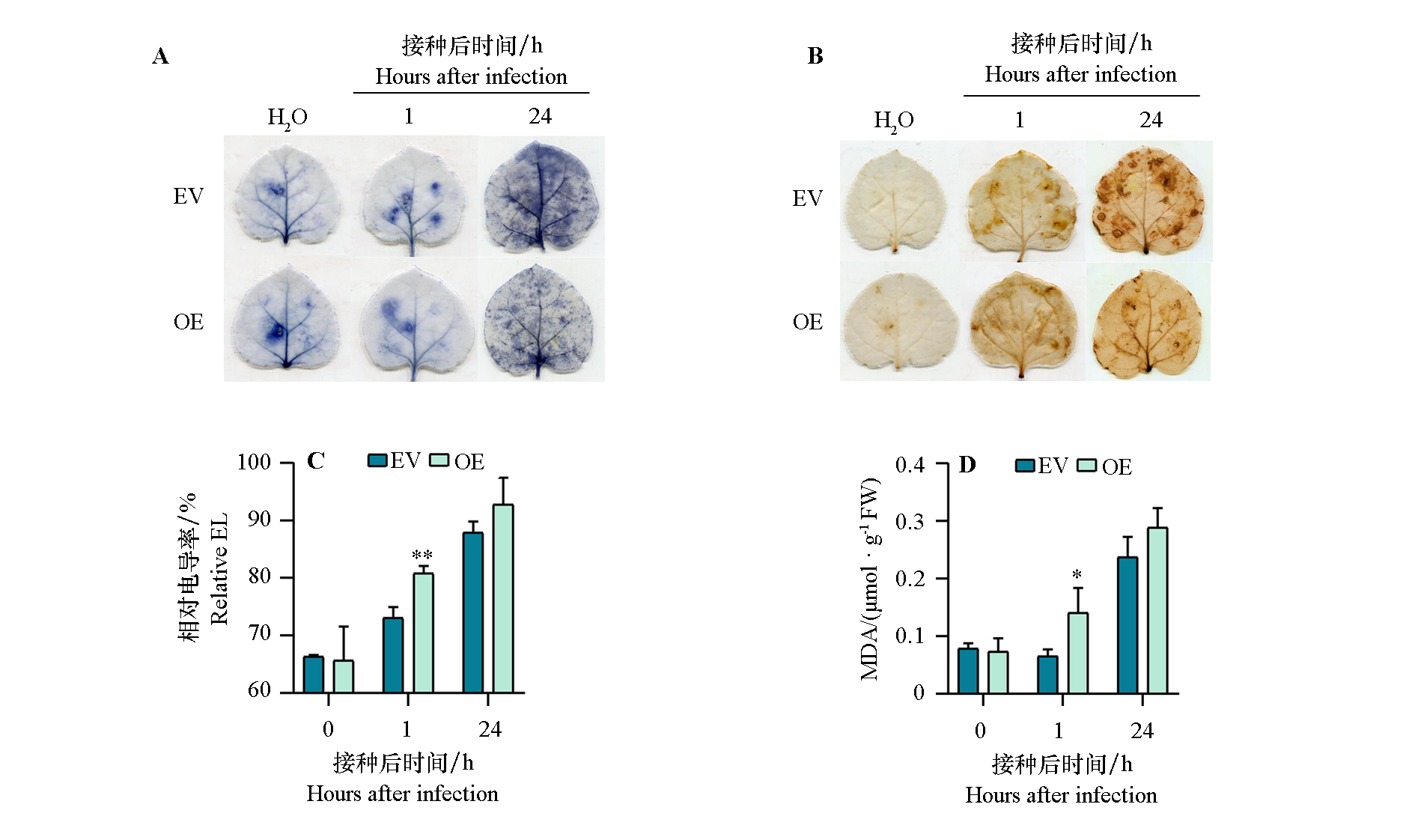
图4 本氏烟草叶片中瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP(OE)及转入空载体(EV)后Psa侵染对活性氧产生和膜系统受损的影响 A:NBT染色法检测超氧阴离子含量;B:DAB染色法检测H2O2含量;C:相对电导率;D:MDA含量。**、*分别表示两个材料间在P < 0.01、P < 0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 4 Effects of Psa infection on reactive oxygen species production and membrane system damage after transient overexpression of AcRhoGAP in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves A:Superoxide anion content detected by NBT staining method;B:H2O2 content detected by DAB staining method;C:Relative EL;D:MDA content. **,* respectively indicate the difference between two materials reaches a significant level when P < 0.01,P < 0.05
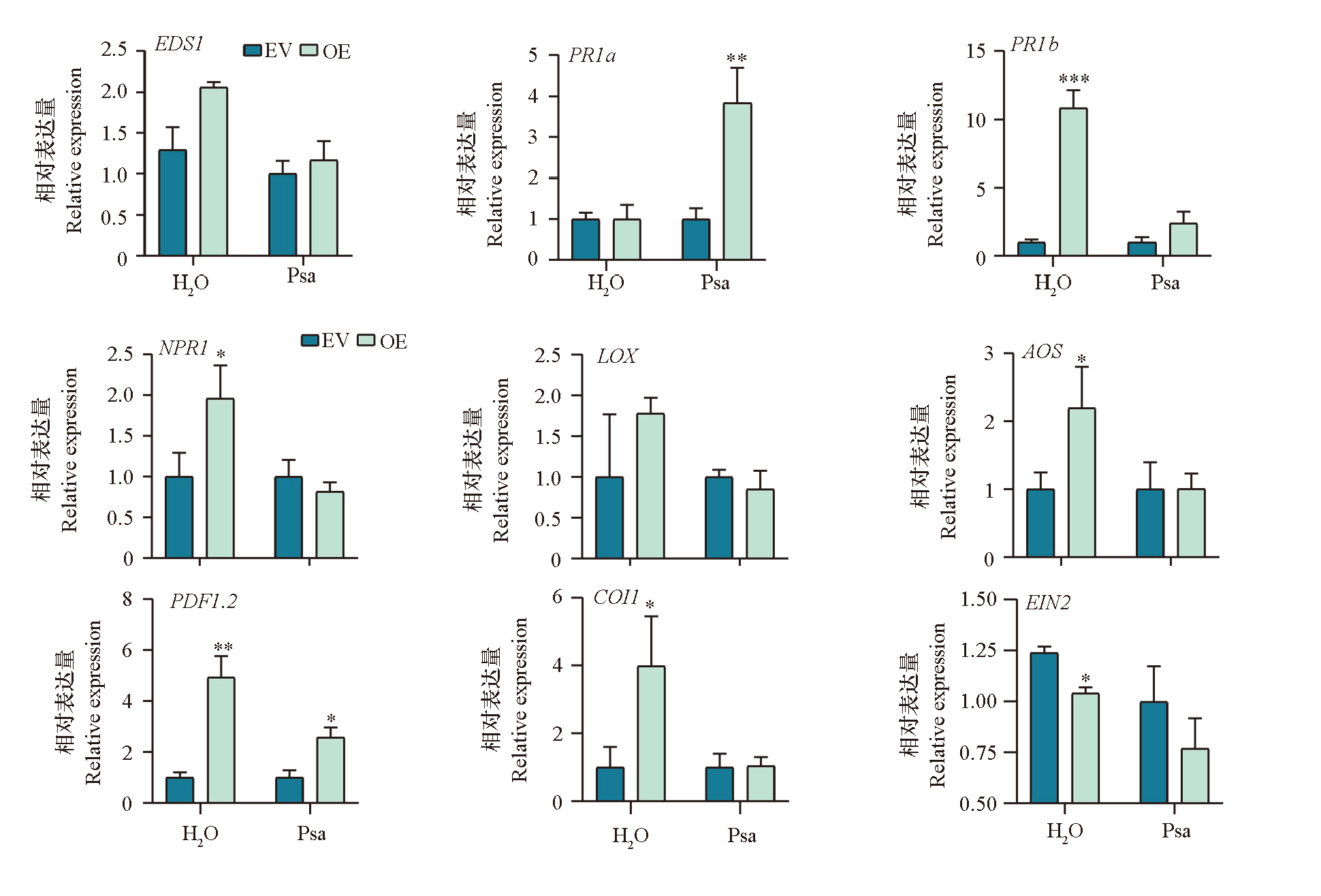
图5 本氏烟草叶片中瞬时过表达AcRhoGAP(OE)及转入空载体(EV)对抗病信号途径Marker基因表达的影响 ***、**、*分别表示两个材料间在P < 0.001、P < 0.01、P < 0.05水平差异显著
Fig. 5 Effects of instantaneous overexpression of AcRhoGAP on the expression of the marker gene in the anti disease signaling pathway in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves ***,**,* respectively indicate the difference between two materials reaches a significant level when P < 0.001,P < 0.01,P < 0.05 .
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-03-12-0064-R pmid: 22877312 |
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
高建有, 匡美美, 罗庆, 谭泽成, 崔丽红, 查满荣, 刘世彪. 2023. 不同猕猴桃品种溃疡病抗性及其与枝条含糖量的关系. 吉首大学学报(自然科学版), 44 (3):66-72.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13057 pmid: 26485342 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-21-0043-R pmid: 33834857 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv063 pmid: 25941234 |
| [16] |
|
|
匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 2024. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因. 园艺学报, 51 (8):1743-1757.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0488-x pmid: 32203420 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0166 URL |
|
彭期定, 吕蕊, 杨婷, 林宏辉, 席德慧. 2020. 四川地区猕猴桃病毒1的RT-PCR检测及外壳蛋白基因序列分析. 园艺学报, 47 (1):120-126.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0166 URL |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
王韵茹. 2022. 猕猴桃细菌性溃疡病的防治药剂筛选及其防治机理研究[硕士论文]. 成都: 四川大学.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055624 pmid: 18156215 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13388 pmid: 27701783 |
| [37] |
|
|
杨艺婷. 2024. NtRhoGAP1介导烟草免疫应答的机制研究[硕士论文]. 成都: 四川大学.
|
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
|
姚迎丽. 2021. 三种观枝干植物的抗寒性研究[硕士论文]. 保定: 河北农业大学.
|
|
| [40] |
|
|
叶文雨, 陈四妙, 陈晓, 林艺娟, 汪洋, 余文英, 鲁国东, 陈继圣, 王宗华. 2013. 稻瘟病菌中一个假定Rho GTP酶激活蛋白与Rho族蛋白的互作关系. 分子植物育种, 11 (6):719-724.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
叶文雨, 余文英, 鲁国东. 2017. RhoGAP结构域家族蛋白的研究进展. 基因组学与应用生物学, 36 (6):2573-2580.
|
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
|
张博宇, 葛玉珍, 韦宇静, 黎建杨, 黄仕训. 2018. 不同产地降香黄檀种子培育苗木叶片的抗寒性比较研究. 西南农业学报, 31 (10):2098-2103.
|
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssq035 pmid: 20713980 |
| [47] |
|
| [1] | 刘艳飞, 何昕, 田爱林, 刘占德. 优质耐贮猕猴桃新品种‘金福’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2219-2220. |
| [2] | 匡美美, 李黎, 马建伟, 刘原, 蒋鸿霏, 雷瑞, 满玉萍, 王一帆, 黄波, 王彦昌, 刘世彪. 利用中华猕猴桃杂交后代转录组测序筛选抗溃疡病相关基因[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1743-1757. |
| [3] | 董晓珂, 陈元磊, 牛友怡, 刘占德, 王南南. 以高产优质稳产为目标的‘徐香’猕猴桃不同生长期叶片营养诊断研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1345-1360. |
| [4] | 乔成奎, 庄明, 田发军, 王彩霞, 庞涛, 陈如霞, 李晓光, 成昕, 谢汉忠. 氟啶虫酰胺和螺虫乙酯在猕猴桃园中的降解及膳食风险评估[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1386-1402. |
| [5] | 王海珍, 应瑶琳, 王雨晴, 吕瑞恒, 韩路. 软枣猕猴桃品种耐热性差异分析与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2857-2870. |
| [6] | 刘艳飞, 何昕, 贺浩浩, 刘占德. 早熟黄肉中华猕猴桃新品种‘黑金’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2725-2726. |
| [7] | 罗 轩, 陈庆红 , 张 蕾, 高 磊, 白福玺, 汪 志, 叶丽霞, 彭 珏. 红肉软枣猕猴桃新品种‘金香红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 27-28. |
| [8] | 齐永杰 , 高正辉 , 马 娜 , 高 霞 , 柯凡君 , 徐义流 , . 优质抗旱猕猴桃新品种‘金山 1 号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 29-30. |
| [9] | 何斌, 徐勤超, 戢小梅, 王小玲, 张文东, 程运江, 曾云流. 气调保鲜技术在猕猴桃贮藏保鲜中的应用进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1916-1928. |
| [10] | 贾兵, 王克灿, 叶振风, 王谋才, 刘莉, 朱立武. 猕猴桃新品种‘皖黄’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1803-1804. |
| [11] | 刘南祥, 张慧琴, 谢鸣, 徐象华, 范芳娟. 猕猴桃新品种‘金丽’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1377-1378. |
| [12] | 毛可欣, 安淼, 王海荣, 王世金, 吕巍, 郭盈添, 李健, 李国田. 猕猴桃MYB家族成员鉴定及其低温表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 534-548. |
| [13] | 袁馨, 徐云鹤, 张雨培, 单楠, 陈楚英, 万春鹏, 开文斌, 翟夏琬, 陈金印, 甘增宇. 猕猴桃后熟过程中ABA响应结合因子AcAREB1调控AcGH3.1的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 53-64. |
| [14] | 宋 放, 陈 奇, 袁炎良, 陈 沙, 尹海军, 蒋迎春, . 黄肉猕猴桃新品种‘先沃1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 47-48. |
| [15] | 齐永杰, 高正辉, 马 娜, 王清明, 柯凡君, 陈 钱, 徐义流, . 黄肉抗溃疡病猕猴桃新品种‘皖农金果’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 49-50. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司