
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 145-161.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0019
徐旭华1, 黄文洁1, 陈旭峰1, 陈园园1, 吴绍文1, 李红建2, 晏石娟1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-09
修回日期:2023-03-06
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-01-16
通讯作者:
基金资助:
XU Xuhua1, HUANG Wenjie1, CHEN Xufeng1, CHEN Yuanyuan1, WU Shaowen1, LI Hongjian2, YAN Shijuan1,*( )
)
Received:2023-01-09
Revised:2023-03-06
Published:2024-01-25
Online:2024-01-16
摘要:
为了探究‘丹霞2号’红茶在鲜叶采摘、萎凋、揉捻、发酵和干燥等5个加工阶段次生代谢产物动态变化特征及其对茶品质形成的影响,利用液相色谱串联四极杆—静电场轨道阱—线性离子阱质谱系统(LC-Q-LIT-OT-MS)对不同阶段茶叶进行了代谢组学分析。在‘丹霞2号’茶叶中共鉴定到124种代谢物,包括22种儿茶素类、19种儿茶素聚合物类和32种黄酮及黄酮糖苷等。多维统计数据分析显示,在由鲜叶采摘到萎凋、萎凋到揉捻、揉捻到发酵、发酵到干燥的转变中分别涉及162、412、308、126种代谢物的显著变化。其中红茶滋味品质特征成分种类和含量在揉捻和发酵两个阶段变化最为显著。儿茶素类物质的含量随着加工过程整体呈现下降趋势;儿茶素聚合物在揉捻期含量显著升高,随后在发酵和干燥过程中逐渐降低。黄酮类及黄酮糖苷类物质的含量整体呈现增加趋势,在揉捻或发酵阶段升高最为明显。儿茶素类、儿茶素聚合物、黄酮及其糖苷类的含量与天冬氨酸、谷氨酰胺、苯丙氨酸及可溶性糖的含量呈现正相关。
徐旭华, 黄文洁, 陈旭峰, 陈园园, 吴绍文, 李红建, 晏石娟. ‘丹霞2号’红茶加工过程中品质特征成分的动态变化研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 145-161.
XU Xuhua, HUANG Wenjie, CHEN Xufeng, CHEN Yuanyuan, WU Shaowen, LI Hongjian, YAN Shijuan. Research on the Dynamic Change of Tea Quality-related Chemical Compositions During‘Danxia 2’Black Tea Processing[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 145-161.
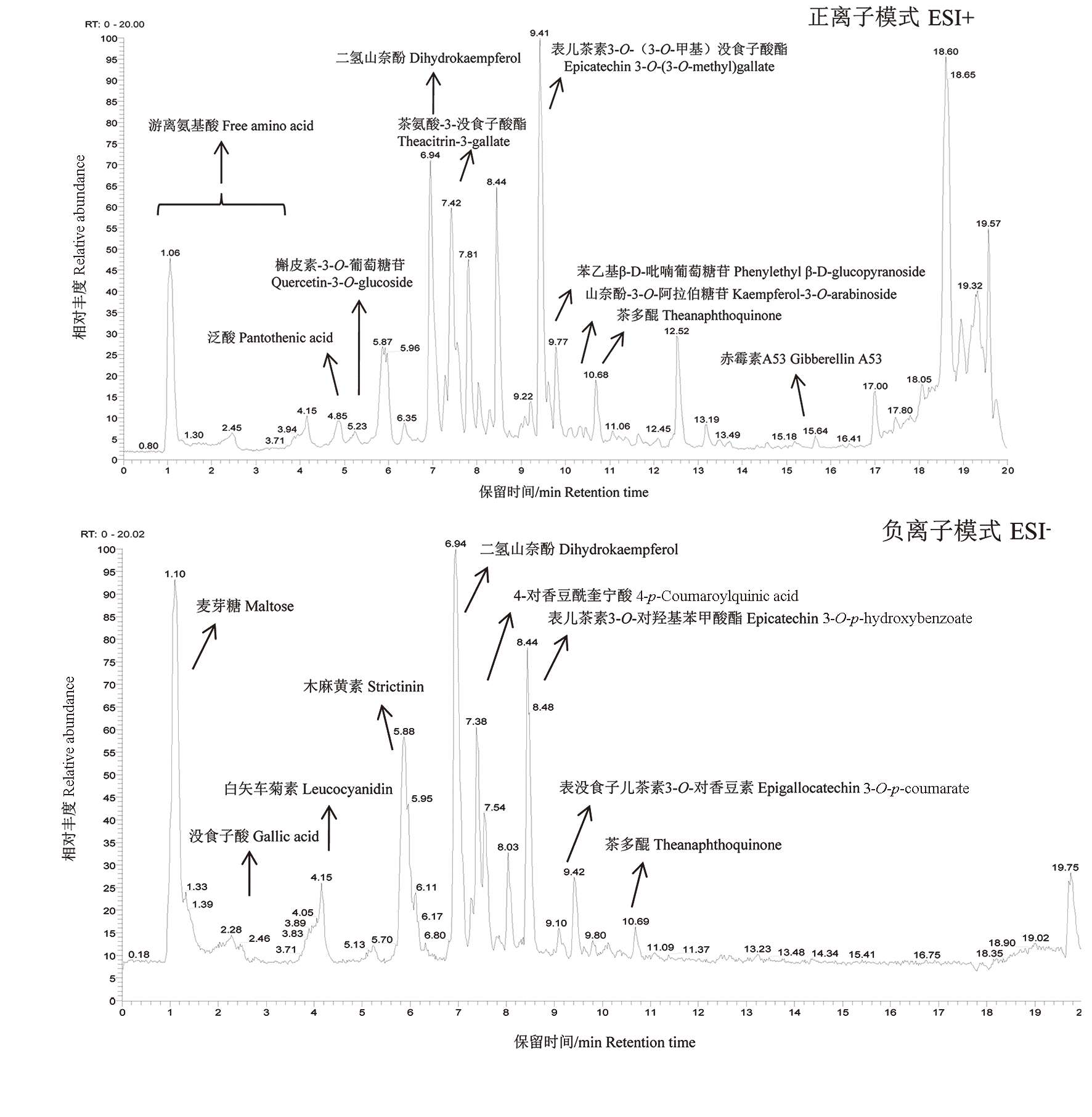
图1 LC-Q-LIT-OT-MS 在正离子(ESI+)、负离子(ESI-)扫描模式下分析‘丹霞2号’红茶代谢组的总离子流色谱图
Fig. 1 The total ion chromatograms of‘Danxia 2’black tea determined in the ESI+ and ESI- mode by LC-Q-LIT-OT-MS-based metabolomics
| 保留时间/ min Retention time | 代谢物 Metabolite | 实测质荷比/ (m/z) Accurate mass | 理论质荷比/(m/z) Theoretical mass | 分子式 Formula | 检测模式 Detection mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 儿茶素类 Catechins(22) | |||||
| 5.423 | 儿茶素 Catechin | 289.0717 | 289.0718 | C15H14O6 | ESI- |
| 6.050/6.050 | 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 291.0857/289.0719 | 291.0863/289.0718 | C15H14O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.605 | 没食子儿茶素 Gallocatechin | 305.0666 | 305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI- |
| 12.645 | 儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Catechin 3-O-gallate | 441.0828 | 441.0827 | C22H18O10 | ESI- |
| 5.265/5.265 | 表儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-gallate | 443.0966/441.0826 | 443.0973/441.0827 | C22H18O10 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 2.688 | 表没食子儿茶素 Epigallocatechin | 305.0666 | 305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI- |
| 4.289 | 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 Epigallocatechin gallate | 457.0776 | 457.0776 | C22H18O11 | ESI- |
| 7.640/7.640 | 没食子儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Gallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 459.0914/457.078 | 459.0922/457.0776 | C22H18O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.933/4.933 | 表阿福豆素3-O-没食子酸酯 Epiafzelechin 3-O-gallate | 427.1017/425.0878 | 427.1024/425.0878 | C22H18O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 6.278 | 表没食子儿茶素3,5-双没食子酸酯Epigallocatechin 3,5-digallate | 609.0885 | 609.0886 | C29H22O15 | ESI- |
| 8.47/8.48 | 表儿茶素3-O-对羟基苯甲酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-p-hydroxybenzoate | 411.1075/409.0931 | 411.1074/409.0929 | C22H18O8 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.380 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-对香豆素 Epigallocatechin 3-O-p-coumarate | 451.1034 | 451.1035 | C24H20O9 | ESI- |
| 9.500 | 表儿茶素3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-(3-O-methyl)gallate | 457.1129 | 457.1129 | C23H20O10 | ESI+ |
| 6.253/6.258 | 表阿福豆素 Epiafzelechin | 275.0896/273.0768 | 275.0914/273.0768 | C15H14O5 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.940 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-肉桂酸酯 Epigallocatechin 3-O-cinnamate | 437.1223 | 437.1231 | C24H20O8 | ESI+ |
| 12.590/12.590 | 3-O-没食子酰-表儿茶素-(4β->8)-儿茶素3-O-galloyl-epicatechin-(4β->8)-catechin | 731.1594/729.1473 | 731.1607/729.1461 | C37H30O16 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.177 | 表儿茶素3-葡萄糖苷 Epicatechin 3-glucoside | 451.1245 | 451.1246 | C21H24O11 | ESI- |
| 12.84 | 没食子儿茶素-(4α->8)-表儿茶素Gallocatechin-(4α->8)-epicatechin | 593.1301 | 593.1300 | C30H26O13 | ESI- |
| 8.120/8.120 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯Epigallocatechin 3-O- (3-O-methyl)gallate | 473.1069/471.093 | 473.1078/471.0933 | C23H20O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 5.520 | 8-C-抗坏血酸表没食子儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯8-C-Ascorbyl epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 631.0949 | 631.0941 | C28H24O17 | ESI- |
| 11.430/11.430 | 表茶黄棓灵3-O-没食子酸酯 Epitheaflagallin 3-O-gallate | 553.0969/551.0829 | 553.0977/551.0831 | C27H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 8.410 | 表没食子儿茶素-(4β->8)-表儿茶-3-O-没食子酸酯 Epigallocatechin-(4β->8)-epicatechin-3-O-gallate ester | 747.1553 | 747.1556 | C37H30O17 | ESI+ |
| 儿茶素聚合物 Dimeric,oligomeric and polymeric of catechins(19) | |||||
| 6.390/6.390 | 聚酯型儿茶素B Theasinensin B | 763.1491/761.1359 | 763.1505/761.1359 | C37H30O18 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.765 | 聚酯型儿茶素A Theasinensin A | 913.1468 | 913.1468 | C44H34O22 | ESI- |
| 0.807 | 聚酯型儿茶素C Theasinensin C | 609.1249 | 609.1249 | C30H26O14 | ESI- |
| 6.420/6.420 | 聚酯型儿茶素F Theasinensin F | 899.1665/897.1519 | 899.1665/897.1519 | C44H34O21 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 7.290 | 新唢呐草素I Tellimagrandin I | 785.0859 | 785.0843 | C34H26O22 | ESI- |
| 7.450 | 茶氨酸-3-没食子酸酯 Theacitrin-3-gallate | 761.1326 | 761.1348 | C37H28O18 | ESI+ |
| 7.670 | 乌龙茶素3′-O-没食子酸酯 Oolongtheanin 3′-O-gallate | 883.1357 | 883.1363 | C43H32O21 | ESI- |
| 9.040 | 茶氨酸C Theacitrin C | 911.1321 | 911.1312 | C44H32O22 | ESI+ |
| 9.040 | 茶氨酸A Theacitrin A | 759.1204 | 759.1203 | C37H28O18 | ESI- |
| 9.610 | 茶黄素 Theaflavin | 565.1344 | 565.1341 | C29H24O12 | ESI+ |
| 11.260 | 茶黄素3-O-没食子酸酯 Theaflavin 3-O-gallate | 715.1309 | 715.1305 | C36H28O16 | ESI- |
| 10.340 | 茶黄酸 Theaflavic acid | 427.0674 | 427.0671 | C21H16O10 | ESI- |
| 9.463 | 茶黄素3,3′-双没食子酸酯 Theaflavin 3,3′-digallate | 867.1414 | 867.1414 | C43H32O20 | ESI- |
| 12.190 | 乌龙茶素 Oolongtheanin | 731.1253 | 731.0124 | C36H28O17 | ESI- |
| 12.450/12.450 | 脱氢茶黄素 Dehydrotheaflavin | 579.1127/577.0984 | 579.1133/577.0977 | C29H22O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 12.650/12.650 | 茶黄酸盐B Theaflavate B | 717.144/699.137 | 701.1501/699.1355 | C36H28O15 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 7.210 | 原花青素B2 Procyanidin B2 | 865.1985 | 865.1985 | C45H38O18 | ESI- |
| 8.970 | 原花青素B4 Procyanidin B4 | 577.1354 | 577.1351 | C30H26O12 | ESI- |
| 10.610/10.610 | 茶多醌 Theanaphthoquinone | 535.1229/533.1094 | 535.1234/533.1089 | C28H22O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 黄酮和黄酮糖苷Flavone and flavone glycosides(32) | |||||
| 9.860 | 芦丁 Rutin | 611.1597 | 611.1607 | C27H30O16 | ESI+ |
| 1.490 | 圣草酚 Eriodictyol | 288.0633 | 288.0628 | C15H11O6 | ESI+ |
| 9.980/9.980 | 茶黄棓灵 Theaflagallin | 401.0855/399.0719 | 401.0867/399.0722 | C20H16O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.170/4.170 | 白矢车菊素 Leucocyanidin | 307.0807/305.0668 | 307.0812/305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.640 | 槲皮素 Quercetin | 301.0353 | 301.0354 | C15H10O7 | ESI- |
| 5.270/5.270 | 槲皮-3-O-葡萄糖苷 Quercetin-3-O-glucoside | 465.1027/463.0881 | 465.1027/463.0881 | C21H20O12 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 8.752/8.572 | 槲皮-3-O-半乳糖苷 Quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 465.1026/463.08842 | 465.1028/463.0881 | C21H20O12 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.080/11.150 | 槲皮素3-O-鼠李糖苷 Quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside | 449.1072/447.0932 | 449.1078/447.0933 | C21H20O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 5.920 | 飞燕草素3-O-β-D-(6-O-(E)-对香豆素基)吡喃半乳糖苷 Delphinidin 3-O-β-D-(6-O-(E)-p-coumaryl)galactopyranoside | 610.1332 | 610.1328 | C30H27O14 | ESI- |
| 5.970 | 花青素3-O-(2-O-β-吡喃木糖基)-β-吡吡喃半乳糖苷 Cyanidin 3-O-(2-O-β-xylopyranosyl)-β- galactopyranoside | 580.1428 | 580.1433 | C26H29O15 | ESI- |
| 7.030 | 二氢山奈酚 Dihydrokaempferol | 289.0707 | 289.0707 | C15H12O6 | ESI+ |
| 7.640 | Assamicain A | 915.1629 | 915.1625 | C44H36O22 | ESI- |
| 7.890 | 二氢槲皮素 Dihydroquercetin | 303.0511 | 303.0510 | C15H12O7 | ESI- |
| 8.950/8.950 | 杨梅素 Myricetin | 319.0443/317.0302 | 319.0448/317.0303 | C15H10O8 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.090/9.090 | 杨梅素3-O-葡萄糖苷 Myricetin 3-O-glucoside | 481.0976/479.0831 | 481.0976/479.0831 | C21H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.190/9.190 | 杨梅素3-O-半乳糖苷 Myricetin 3-O-galactoside | 481.0967/479.0829 | 481.0977/479.0831 | C21H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.190/9.190 | 山奈酚 Kaempferol | 287.0543/285.0404 | 287.0550/285.0404 | C15H10O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 10.450 | 山奈酚-3-O-阿拉伯糖苷Kaempferol-3-O-arabinoside | 419.0747 | 419.0972 | C20H18O10 | ESI+ |
| 6.483 | 山奈酚-3-芸香苷 Kaempferol-3-rutinoside | 595.1651 | 595.1657 | C27H30O15 | ESI+ |
| 6.517 | 山奈酚-3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | 447.0934 | 447.0932 | C21H20O11 | ESI+ |
| 6.846 | 山奈酚-3-O-半乳糖苷Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside | 447.0934 | 447.0932 | C21H20O11 | ESI+ |
| 9.780 | 槲皮素3-木糖-(1->2)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-葡萄糖苷 Quercetin 3-xylosyl-(1->2)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-glucoside | 741.1884 | 741.1883 | C32H38O20 | ESI- |
| 9.880 | 槲皮素3-葡萄糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-半乳糖苷 Quercetin 3-glucosyl-(1->3)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-galactoside | 771.1989 | 771.1989 | C33H40O21 | ESI- |
| 10.780 | 山奈酚3-葡萄糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-半乳糖苷 Kaempferol 3-glucosyl-(1->3)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-galactoside | 755.2041 | 755.204 | C33H40O20 | ESI- |
| 11.080 | 山奈酚3-鼠李糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖-(1->6)-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-rhamnosyl-(1->3)- rhamnosyl-(1->6)-glucoside | 739.2096 | 739.2091 | C33H40O19 | ESI- |
| 11.140 | 牡荆-2-O-葡萄糖苷 Vitexin-2-O-glucoside | 595.1649 | 595.1657 | C27H30O15 | ESI- |
| 11.450 | 茶花粉黄酮 Pollenitin | 315.0514 | 315.0510 | C16H12O7 | ESI- |
| 10.930 | 牡荆素 Vitexin | 433.1129 | 433.1129 | C21H20O10 | ESI+ |
| 13.740 | 芹菜素 Apigenin | 269.0457 | 269.0455 | C15H10O5 | ESI- |
| 8.741 | 芹菜素6-C-葡糖基-8-C-阿拉伯糖苷 Apigenin 6-C-glucosyl-8-C-arabinoside | 725.1934 | 725.1934 | C32H38O19 | ESI- |
| 7.293 | 槲皮素3-O-葡糖苷酸 Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide | 477.0674 | 477.0675 | C21H18O13 | ESI- |
| 5.078 | 槲皮素3-O-葡糖基-芸香糖苷 Quercetin 3-O-glucosyl-rutinoside | 771.1989 | 771.1989 | C33H40O21 | ESI- |
| 氨基酸Amino acids(19) | |||||
| 0.764/0.764 | 精氨酸 Arginine | 175.1189/173.1042 | 175.1190/173.1044 | C6H14N4O2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 0.762 | 谷氨酸 Glutamic acid | 148.0604 | 148.0604 | C5H9NO4 | ESI+ |
| 0.761 | 谷氨酰胺 Glutamine | 145.0618 | 145.0619 | C5H10N2O3 | ESI- |
| 1.023 | 亮氨酸 Leucine | 132.1019 | 132.1019 | C6H13NO2 | ESI+ |
| 0.742 | 赖氨酸 Lysine | 147.1128 | 147.1128 | C6H14N2O2 | ESI+ |
| 1.631 | 哌啶酸 Pipecolic acid | 130.0862 | 130.0863 | C6H11NO2 | ESI+ |
| 1.049 | 脯氨酸 Proline | 116.0706 | 116.0706 | C5H9NO2 | ESI+ |
| 0.761/0.761 | 焦谷氨酸 Pyroglutamic acid | 130.0498/128.0353 | 130.0499/128.0353 | C5H7NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.842 | 茶氨酸 Theanine | 175.1077 | 175.1077 | C7H14N2O3 | ESI+ |
| 5.691 | 色氨酸 Tryptophan | 203.0826 | 203.0826 | C11H12N2O2 | ESI- |
| 0.812/0.812 | 缬氨酸 Valine | 118.0862/116.0717 | 118.0862/116.0717 | C5H11NO2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.060/1.060 | 丝氨酸 Serine | 106.0497/104.0353 | 106.0499/104.0353 | C3H7NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.080 | 苏氨酸 Threonine | 120.0654 | 120.0655 | C4H9NO3 | ESI+ |
| 1.070 | 天冬酰胺 Asparagine | 133.0607 | 133.0608 | C4H8N2O3 | ESI+ |
| 1.070 | 天冬氨酸 Aspartic acid | 134.0447 | 134.0448 | C4H7NO4 | ESI+ |
| 1.220 | 蛋氨酸 Methionine | 150.0581 | 150.0583 | C5H11NO2S | ESI+ |
| 1.060 | 组氨酸 Histidine | 156.0766 | 156.0768 | C6H9N3O2 | ESI+ |
| 3.990 | 苯丙氨酸 Phenylalanine | 166.0861 | 166.0863 | C9H11NO2 | ESI+ |
| 1.420/1.420 | 酪氨酸 Tyrosine | 182.0809/180.0666 | 182.0812/180.0666 | C9H11NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 有机酸Organic acids(7) | |||||
| 5.950 | 香豆酸 Coumaric acid | 163.0401 | 163.0401 | C9H8O3 | ESI- |
| 2.320 | 没食子酸 Gallic acid | 169.0142 | 169.0142 | C7H6O5 | ESI- |
| 5.960 | 咖啡酸 Caffeic acid | 179.0349 | 179.0350 | C9H8O4 | ESI- |
| 12.110 | 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 209.1185 | 209.1183 | C12H18O3 | ESI- |
| 4.840 | 泛酸 Pantothenic acid | 218.1034 | 218.1034 | C9H17NO5 | ESI- |
| 1.130 | 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid | 175.0246 | 175.0248 | C6H8O6 | ESI- |
| 1.646 | 5-没食子酰奎宁酸 5-Galloylquinic acid | 345.0809 | 345.0816 | C14H16O10 | ESI+ |
| 糖类Sugars(8) | |||||
| 1.130 | 木酮糖 Xylulose | 149.0455 | 149.0455 | C5H10O5 | ESI- |
| 7.790 | 苄基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Benzyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 269.1031 | 269.1031 | C13H18O6 | ESI- |
| 1.110/1.110 | 麦芽糖 Maltose | 341.1089/343.1234 | 341.1089/343.1235 | C12H22O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.070 | 棉子糖 Raffinose | 503.1619 | 503.1618 | C18H32O16 | ESI- |
| 6.560 | 香豆酰β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Coumaroyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 325.0929 | 325.0929 | C15H18O8 | ESI- |
| 6.690/7.030 | 阿魏酰-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷Feruloyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | 357.1173/355.1034 | 357.1180/355.1035 | C16H20O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.170 | 6-O-没食子酰葡萄糖 6-O-galloylglucose | 331.0671 | 331.0671 | C13H16O10 | ESI- |
| 9.740 | 苯乙基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Phenylethyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 285.1324 | 285.1332 | C14H20O6 | ESI+ |
| 酚酸Phenolic acids(5) | |||||
| 5.810 | 木麻黄素 Strictinin | 633.0733 | 633.0733 | C27H22O18 | ESI- |
| 7.410 | 4-对香豆酰奎宁酸 4-p-Coumaroylquinic acid | 337.0931 | 337.0929 | C16H18O8 | ESI- |
| 2.192 | 1-咖啡酰奎宁酸 1-Caffeoylquinic acid | 353.0878 | 353.0878 | C16H18O9 | ESI- |
| 0.768/0.768 | 奎尼酸 Quinic acid | 193.0706/191.0561 | 193.0707/191.0561 | C7H12O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 3.304 | 原儿茶酸 Protocatechuic acid | 153.0193 | 153.0193 | C7H6O4 | ESI- |
| 生物碱Alkaloids(3) | |||||
| 4.990/4.990 | 茶碱 Theophylline | 181.0717/179.0574 | 181.0720/179.0574 | C7H8N4O2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.978/5.346 | 咖啡碱 Caffeine | 195.0876 | 195.0877 | C8H10N4O2 | ESI+ |
| 1.018 | 哌啶 Piperidine | 86.0964 | 86.0964 | C5H11N | ESI+ |
| 核苷和核苷酸Nucleosides and nucleotides(4) | |||||
| 0.848 | 腺苷酸 Adenosine monophosphate | 346.0558 | 346.0558 | C10H14N5O7P | ESI- |
| 1.595 | 鸟苷 Guanosine | 284.0989 | 284.0989 | C10H13N5O5 | ESI+ |
| 2.603 | 1-甲基黄嘌呤 1-Methylxanthine | 167.0563 | 167.0564 | C6H6N4O2 | ESI+ |
| 5.331 | 甲硫腺苷 Methylthioadenosine | 298.0968366 | 298.0968 | C11H15N5O3S | ESI+ |
| 激素Hormones(2) | |||||
| 9.100 | 茉莉酸甲酯 Methyl jasmonate | 225.1477 | 225.1485 | C13H20O3 | ESI+ |
| 15.380 | 赤霉素A53 Gibberellin A53 | 349.1979 | 349.2010 | C20H28O5 | ESI+ |
| 其他Others(3) | |||||
| 8.490 | 淫羊藿次苷B5 Icariside B5 | 389.2159 | 389.2170 | C19H32O8 | ESI+ |
| 0.769 | N-乳酰基乙醇胺 N-Lactoyl ethanolamine | 132.0666 | 132.0666 | C5H11NO3 | ESI- |
| 8.260 | 核黄素 Riboflavin | 377.1449 | 377.1456 | C17H20N4O6 | ESI+ |
表1 ‘丹霞2号’红茶中鉴定的124种代谢物
Table 1 124 metabolites identified in‘Danxia 2’black tea
| 保留时间/ min Retention time | 代谢物 Metabolite | 实测质荷比/ (m/z) Accurate mass | 理论质荷比/(m/z) Theoretical mass | 分子式 Formula | 检测模式 Detection mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 儿茶素类 Catechins(22) | |||||
| 5.423 | 儿茶素 Catechin | 289.0717 | 289.0718 | C15H14O6 | ESI- |
| 6.050/6.050 | 表儿茶素 Epicatechin | 291.0857/289.0719 | 291.0863/289.0718 | C15H14O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.605 | 没食子儿茶素 Gallocatechin | 305.0666 | 305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI- |
| 12.645 | 儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Catechin 3-O-gallate | 441.0828 | 441.0827 | C22H18O10 | ESI- |
| 5.265/5.265 | 表儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-gallate | 443.0966/441.0826 | 443.0973/441.0827 | C22H18O10 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 2.688 | 表没食子儿茶素 Epigallocatechin | 305.0666 | 305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI- |
| 4.289 | 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 Epigallocatechin gallate | 457.0776 | 457.0776 | C22H18O11 | ESI- |
| 7.640/7.640 | 没食子儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯 Gallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 459.0914/457.078 | 459.0922/457.0776 | C22H18O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.933/4.933 | 表阿福豆素3-O-没食子酸酯 Epiafzelechin 3-O-gallate | 427.1017/425.0878 | 427.1024/425.0878 | C22H18O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 6.278 | 表没食子儿茶素3,5-双没食子酸酯Epigallocatechin 3,5-digallate | 609.0885 | 609.0886 | C29H22O15 | ESI- |
| 8.47/8.48 | 表儿茶素3-O-对羟基苯甲酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-p-hydroxybenzoate | 411.1075/409.0931 | 411.1074/409.0929 | C22H18O8 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.380 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-对香豆素 Epigallocatechin 3-O-p-coumarate | 451.1034 | 451.1035 | C24H20O9 | ESI- |
| 9.500 | 表儿茶素3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯 Epicatechin 3-O-(3-O-methyl)gallate | 457.1129 | 457.1129 | C23H20O10 | ESI+ |
| 6.253/6.258 | 表阿福豆素 Epiafzelechin | 275.0896/273.0768 | 275.0914/273.0768 | C15H14O5 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.940 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-肉桂酸酯 Epigallocatechin 3-O-cinnamate | 437.1223 | 437.1231 | C24H20O8 | ESI+ |
| 12.590/12.590 | 3-O-没食子酰-表儿茶素-(4β->8)-儿茶素3-O-galloyl-epicatechin-(4β->8)-catechin | 731.1594/729.1473 | 731.1607/729.1461 | C37H30O16 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.177 | 表儿茶素3-葡萄糖苷 Epicatechin 3-glucoside | 451.1245 | 451.1246 | C21H24O11 | ESI- |
| 12.84 | 没食子儿茶素-(4α->8)-表儿茶素Gallocatechin-(4α->8)-epicatechin | 593.1301 | 593.1300 | C30H26O13 | ESI- |
| 8.120/8.120 | 表没食子儿茶素3-O-(3-O-甲基)没食子酸酯Epigallocatechin 3-O- (3-O-methyl)gallate | 473.1069/471.093 | 473.1078/471.0933 | C23H20O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 5.520 | 8-C-抗坏血酸表没食子儿茶素3-O-没食子酸酯8-C-Ascorbyl epigallocatechin 3-O-gallate | 631.0949 | 631.0941 | C28H24O17 | ESI- |
| 11.430/11.430 | 表茶黄棓灵3-O-没食子酸酯 Epitheaflagallin 3-O-gallate | 553.0969/551.0829 | 553.0977/551.0831 | C27H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 8.410 | 表没食子儿茶素-(4β->8)-表儿茶-3-O-没食子酸酯 Epigallocatechin-(4β->8)-epicatechin-3-O-gallate ester | 747.1553 | 747.1556 | C37H30O17 | ESI+ |
| 儿茶素聚合物 Dimeric,oligomeric and polymeric of catechins(19) | |||||
| 6.390/6.390 | 聚酯型儿茶素B Theasinensin B | 763.1491/761.1359 | 763.1505/761.1359 | C37H30O18 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.765 | 聚酯型儿茶素A Theasinensin A | 913.1468 | 913.1468 | C44H34O22 | ESI- |
| 0.807 | 聚酯型儿茶素C Theasinensin C | 609.1249 | 609.1249 | C30H26O14 | ESI- |
| 6.420/6.420 | 聚酯型儿茶素F Theasinensin F | 899.1665/897.1519 | 899.1665/897.1519 | C44H34O21 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 7.290 | 新唢呐草素I Tellimagrandin I | 785.0859 | 785.0843 | C34H26O22 | ESI- |
| 7.450 | 茶氨酸-3-没食子酸酯 Theacitrin-3-gallate | 761.1326 | 761.1348 | C37H28O18 | ESI+ |
| 7.670 | 乌龙茶素3′-O-没食子酸酯 Oolongtheanin 3′-O-gallate | 883.1357 | 883.1363 | C43H32O21 | ESI- |
| 9.040 | 茶氨酸C Theacitrin C | 911.1321 | 911.1312 | C44H32O22 | ESI+ |
| 9.040 | 茶氨酸A Theacitrin A | 759.1204 | 759.1203 | C37H28O18 | ESI- |
| 9.610 | 茶黄素 Theaflavin | 565.1344 | 565.1341 | C29H24O12 | ESI+ |
| 11.260 | 茶黄素3-O-没食子酸酯 Theaflavin 3-O-gallate | 715.1309 | 715.1305 | C36H28O16 | ESI- |
| 10.340 | 茶黄酸 Theaflavic acid | 427.0674 | 427.0671 | C21H16O10 | ESI- |
| 9.463 | 茶黄素3,3′-双没食子酸酯 Theaflavin 3,3′-digallate | 867.1414 | 867.1414 | C43H32O20 | ESI- |
| 12.190 | 乌龙茶素 Oolongtheanin | 731.1253 | 731.0124 | C36H28O17 | ESI- |
| 12.450/12.450 | 脱氢茶黄素 Dehydrotheaflavin | 579.1127/577.0984 | 579.1133/577.0977 | C29H22O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 12.650/12.650 | 茶黄酸盐B Theaflavate B | 717.144/699.137 | 701.1501/699.1355 | C36H28O15 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 7.210 | 原花青素B2 Procyanidin B2 | 865.1985 | 865.1985 | C45H38O18 | ESI- |
| 8.970 | 原花青素B4 Procyanidin B4 | 577.1354 | 577.1351 | C30H26O12 | ESI- |
| 10.610/10.610 | 茶多醌 Theanaphthoquinone | 535.1229/533.1094 | 535.1234/533.1089 | C28H22O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 黄酮和黄酮糖苷Flavone and flavone glycosides(32) | |||||
| 9.860 | 芦丁 Rutin | 611.1597 | 611.1607 | C27H30O16 | ESI+ |
| 1.490 | 圣草酚 Eriodictyol | 288.0633 | 288.0628 | C15H11O6 | ESI+ |
| 9.980/9.980 | 茶黄棓灵 Theaflagallin | 401.0855/399.0719 | 401.0867/399.0722 | C20H16O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.170/4.170 | 白矢车菊素 Leucocyanidin | 307.0807/305.0668 | 307.0812/305.0667 | C15H14O7 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.640 | 槲皮素 Quercetin | 301.0353 | 301.0354 | C15H10O7 | ESI- |
| 5.270/5.270 | 槲皮-3-O-葡萄糖苷 Quercetin-3-O-glucoside | 465.1027/463.0881 | 465.1027/463.0881 | C21H20O12 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 8.752/8.572 | 槲皮-3-O-半乳糖苷 Quercetin-3-O-galactoside | 465.1026/463.08842 | 465.1028/463.0881 | C21H20O12 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 11.080/11.150 | 槲皮素3-O-鼠李糖苷 Quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside | 449.1072/447.0932 | 449.1078/447.0933 | C21H20O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 5.920 | 飞燕草素3-O-β-D-(6-O-(E)-对香豆素基)吡喃半乳糖苷 Delphinidin 3-O-β-D-(6-O-(E)-p-coumaryl)galactopyranoside | 610.1332 | 610.1328 | C30H27O14 | ESI- |
| 5.970 | 花青素3-O-(2-O-β-吡喃木糖基)-β-吡吡喃半乳糖苷 Cyanidin 3-O-(2-O-β-xylopyranosyl)-β- galactopyranoside | 580.1428 | 580.1433 | C26H29O15 | ESI- |
| 7.030 | 二氢山奈酚 Dihydrokaempferol | 289.0707 | 289.0707 | C15H12O6 | ESI+ |
| 7.640 | Assamicain A | 915.1629 | 915.1625 | C44H36O22 | ESI- |
| 7.890 | 二氢槲皮素 Dihydroquercetin | 303.0511 | 303.0510 | C15H12O7 | ESI- |
| 8.950/8.950 | 杨梅素 Myricetin | 319.0443/317.0302 | 319.0448/317.0303 | C15H10O8 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.090/9.090 | 杨梅素3-O-葡萄糖苷 Myricetin 3-O-glucoside | 481.0976/479.0831 | 481.0976/479.0831 | C21H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.190/9.190 | 杨梅素3-O-半乳糖苷 Myricetin 3-O-galactoside | 481.0967/479.0829 | 481.0977/479.0831 | C21H20O13 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 9.190/9.190 | 山奈酚 Kaempferol | 287.0543/285.0404 | 287.0550/285.0404 | C15H10O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 10.450 | 山奈酚-3-O-阿拉伯糖苷Kaempferol-3-O-arabinoside | 419.0747 | 419.0972 | C20H18O10 | ESI+ |
| 6.483 | 山奈酚-3-芸香苷 Kaempferol-3-rutinoside | 595.1651 | 595.1657 | C27H30O15 | ESI+ |
| 6.517 | 山奈酚-3-O-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | 447.0934 | 447.0932 | C21H20O11 | ESI+ |
| 6.846 | 山奈酚-3-O-半乳糖苷Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside | 447.0934 | 447.0932 | C21H20O11 | ESI+ |
| 9.780 | 槲皮素3-木糖-(1->2)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-葡萄糖苷 Quercetin 3-xylosyl-(1->2)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-glucoside | 741.1884 | 741.1883 | C32H38O20 | ESI- |
| 9.880 | 槲皮素3-葡萄糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-半乳糖苷 Quercetin 3-glucosyl-(1->3)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-galactoside | 771.1989 | 771.1989 | C33H40O21 | ESI- |
| 10.780 | 山奈酚3-葡萄糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖基-(1->6)-半乳糖苷 Kaempferol 3-glucosyl-(1->3)-rhamnosyl- (1->6)-galactoside | 755.2041 | 755.204 | C33H40O20 | ESI- |
| 11.080 | 山奈酚3-鼠李糖基-(1->3)-鼠李糖-(1->6)-葡萄糖苷 Kaempferol 3-rhamnosyl-(1->3)- rhamnosyl-(1->6)-glucoside | 739.2096 | 739.2091 | C33H40O19 | ESI- |
| 11.140 | 牡荆-2-O-葡萄糖苷 Vitexin-2-O-glucoside | 595.1649 | 595.1657 | C27H30O15 | ESI- |
| 11.450 | 茶花粉黄酮 Pollenitin | 315.0514 | 315.0510 | C16H12O7 | ESI- |
| 10.930 | 牡荆素 Vitexin | 433.1129 | 433.1129 | C21H20O10 | ESI+ |
| 13.740 | 芹菜素 Apigenin | 269.0457 | 269.0455 | C15H10O5 | ESI- |
| 8.741 | 芹菜素6-C-葡糖基-8-C-阿拉伯糖苷 Apigenin 6-C-glucosyl-8-C-arabinoside | 725.1934 | 725.1934 | C32H38O19 | ESI- |
| 7.293 | 槲皮素3-O-葡糖苷酸 Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide | 477.0674 | 477.0675 | C21H18O13 | ESI- |
| 5.078 | 槲皮素3-O-葡糖基-芸香糖苷 Quercetin 3-O-glucosyl-rutinoside | 771.1989 | 771.1989 | C33H40O21 | ESI- |
| 氨基酸Amino acids(19) | |||||
| 0.764/0.764 | 精氨酸 Arginine | 175.1189/173.1042 | 175.1190/173.1044 | C6H14N4O2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 0.762 | 谷氨酸 Glutamic acid | 148.0604 | 148.0604 | C5H9NO4 | ESI+ |
| 0.761 | 谷氨酰胺 Glutamine | 145.0618 | 145.0619 | C5H10N2O3 | ESI- |
| 1.023 | 亮氨酸 Leucine | 132.1019 | 132.1019 | C6H13NO2 | ESI+ |
| 0.742 | 赖氨酸 Lysine | 147.1128 | 147.1128 | C6H14N2O2 | ESI+ |
| 1.631 | 哌啶酸 Pipecolic acid | 130.0862 | 130.0863 | C6H11NO2 | ESI+ |
| 1.049 | 脯氨酸 Proline | 116.0706 | 116.0706 | C5H9NO2 | ESI+ |
| 0.761/0.761 | 焦谷氨酸 Pyroglutamic acid | 130.0498/128.0353 | 130.0499/128.0353 | C5H7NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.842 | 茶氨酸 Theanine | 175.1077 | 175.1077 | C7H14N2O3 | ESI+ |
| 5.691 | 色氨酸 Tryptophan | 203.0826 | 203.0826 | C11H12N2O2 | ESI- |
| 0.812/0.812 | 缬氨酸 Valine | 118.0862/116.0717 | 118.0862/116.0717 | C5H11NO2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.060/1.060 | 丝氨酸 Serine | 106.0497/104.0353 | 106.0499/104.0353 | C3H7NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.080 | 苏氨酸 Threonine | 120.0654 | 120.0655 | C4H9NO3 | ESI+ |
| 1.070 | 天冬酰胺 Asparagine | 133.0607 | 133.0608 | C4H8N2O3 | ESI+ |
| 1.070 | 天冬氨酸 Aspartic acid | 134.0447 | 134.0448 | C4H7NO4 | ESI+ |
| 1.220 | 蛋氨酸 Methionine | 150.0581 | 150.0583 | C5H11NO2S | ESI+ |
| 1.060 | 组氨酸 Histidine | 156.0766 | 156.0768 | C6H9N3O2 | ESI+ |
| 3.990 | 苯丙氨酸 Phenylalanine | 166.0861 | 166.0863 | C9H11NO2 | ESI+ |
| 1.420/1.420 | 酪氨酸 Tyrosine | 182.0809/180.0666 | 182.0812/180.0666 | C9H11NO3 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 有机酸Organic acids(7) | |||||
| 5.950 | 香豆酸 Coumaric acid | 163.0401 | 163.0401 | C9H8O3 | ESI- |
| 2.320 | 没食子酸 Gallic acid | 169.0142 | 169.0142 | C7H6O5 | ESI- |
| 5.960 | 咖啡酸 Caffeic acid | 179.0349 | 179.0350 | C9H8O4 | ESI- |
| 12.110 | 茉莉酸 Jasmonic acid | 209.1185 | 209.1183 | C12H18O3 | ESI- |
| 4.840 | 泛酸 Pantothenic acid | 218.1034 | 218.1034 | C9H17NO5 | ESI- |
| 1.130 | 抗坏血酸 Ascorbic acid | 175.0246 | 175.0248 | C6H8O6 | ESI- |
| 1.646 | 5-没食子酰奎宁酸 5-Galloylquinic acid | 345.0809 | 345.0816 | C14H16O10 | ESI+ |
| 糖类Sugars(8) | |||||
| 1.130 | 木酮糖 Xylulose | 149.0455 | 149.0455 | C5H10O5 | ESI- |
| 7.790 | 苄基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Benzyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 269.1031 | 269.1031 | C13H18O6 | ESI- |
| 1.110/1.110 | 麦芽糖 Maltose | 341.1089/343.1234 | 341.1089/343.1235 | C12H22O11 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.070 | 棉子糖 Raffinose | 503.1619 | 503.1618 | C18H32O16 | ESI- |
| 6.560 | 香豆酰β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Coumaroyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 325.0929 | 325.0929 | C15H18O8 | ESI- |
| 6.690/7.030 | 阿魏酰-β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷Feruloyl-β-D-glucopyranoside | 357.1173/355.1034 | 357.1180/355.1035 | C16H20O9 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 1.170 | 6-O-没食子酰葡萄糖 6-O-galloylglucose | 331.0671 | 331.0671 | C13H16O10 | ESI- |
| 9.740 | 苯乙基β-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷 Phenylethyl β-D-glucopyranoside | 285.1324 | 285.1332 | C14H20O6 | ESI+ |
| 酚酸Phenolic acids(5) | |||||
| 5.810 | 木麻黄素 Strictinin | 633.0733 | 633.0733 | C27H22O18 | ESI- |
| 7.410 | 4-对香豆酰奎宁酸 4-p-Coumaroylquinic acid | 337.0931 | 337.0929 | C16H18O8 | ESI- |
| 2.192 | 1-咖啡酰奎宁酸 1-Caffeoylquinic acid | 353.0878 | 353.0878 | C16H18O9 | ESI- |
| 0.768/0.768 | 奎尼酸 Quinic acid | 193.0706/191.0561 | 193.0707/191.0561 | C7H12O6 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 3.304 | 原儿茶酸 Protocatechuic acid | 153.0193 | 153.0193 | C7H6O4 | ESI- |
| 生物碱Alkaloids(3) | |||||
| 4.990/4.990 | 茶碱 Theophylline | 181.0717/179.0574 | 181.0720/179.0574 | C7H8N4O2 | ESI+/ESI- |
| 4.978/5.346 | 咖啡碱 Caffeine | 195.0876 | 195.0877 | C8H10N4O2 | ESI+ |
| 1.018 | 哌啶 Piperidine | 86.0964 | 86.0964 | C5H11N | ESI+ |
| 核苷和核苷酸Nucleosides and nucleotides(4) | |||||
| 0.848 | 腺苷酸 Adenosine monophosphate | 346.0558 | 346.0558 | C10H14N5O7P | ESI- |
| 1.595 | 鸟苷 Guanosine | 284.0989 | 284.0989 | C10H13N5O5 | ESI+ |
| 2.603 | 1-甲基黄嘌呤 1-Methylxanthine | 167.0563 | 167.0564 | C6H6N4O2 | ESI+ |
| 5.331 | 甲硫腺苷 Methylthioadenosine | 298.0968366 | 298.0968 | C11H15N5O3S | ESI+ |
| 激素Hormones(2) | |||||
| 9.100 | 茉莉酸甲酯 Methyl jasmonate | 225.1477 | 225.1485 | C13H20O3 | ESI+ |
| 15.380 | 赤霉素A53 Gibberellin A53 | 349.1979 | 349.2010 | C20H28O5 | ESI+ |
| 其他Others(3) | |||||
| 8.490 | 淫羊藿次苷B5 Icariside B5 | 389.2159 | 389.2170 | C19H32O8 | ESI+ |
| 0.769 | N-乳酰基乙醇胺 N-Lactoyl ethanolamine | 132.0666 | 132.0666 | C5H11NO3 | ESI- |
| 8.260 | 核黄素 Riboflavin | 377.1449 | 377.1456 | C17H20N4O6 | ESI+ |
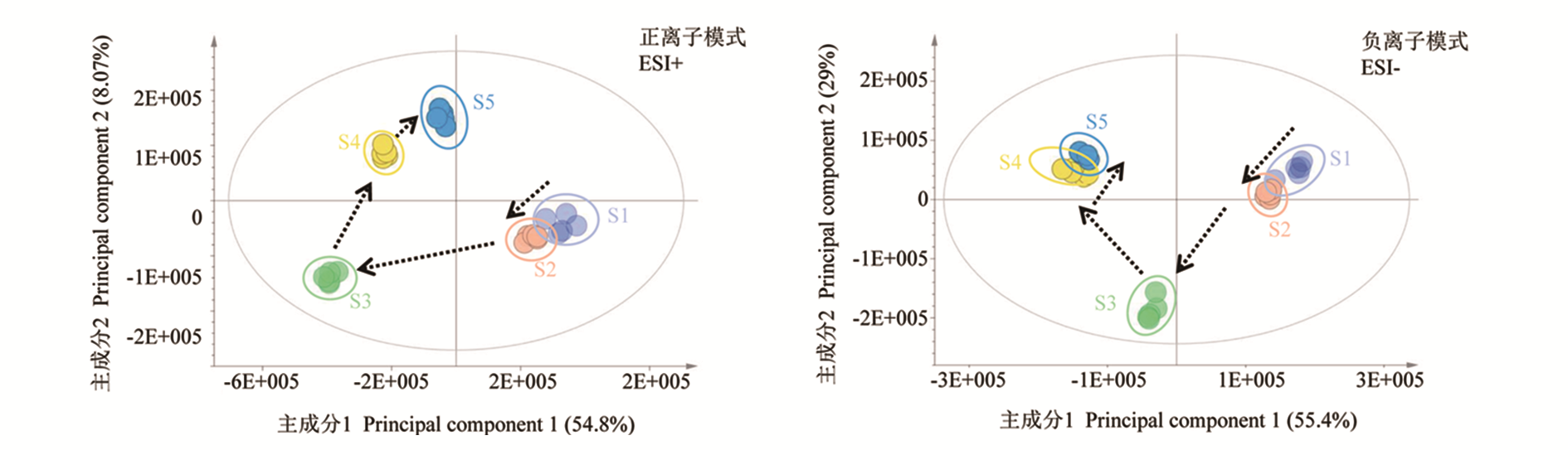
图2 ‘丹霞2号’红茶5个加工阶段的正(ESI+)、负(ESI-)离子模式OPLS-DA模型得分图 S1:鲜叶采摘;S2:萎凋;S3:揉捻;S4:发酵;S5:干燥。下同。
Fig. 2 The score plots of OPLS-DA model for‘Danxia 2’black tea from the five processing stages S1:Fresh leaves plucking;S2:Withering;S3:Rolling;S4:Fermentation;S5:Drying. The same below.

图3 ‘丹霞2号’相邻红茶加工阶段的差异代谢物分析 红色数字表示上调差异代谢物个数,绿色数字表示下调差异代谢物个数。
Fig. 3 Analysis of differential metabolites for‘Danxia 2’black tea in two adjacent processing stages Numbers marked with red color indicates the number of up-regulated differential metabolites,and those marked green indicates the number of down-regulated differential metabolites.
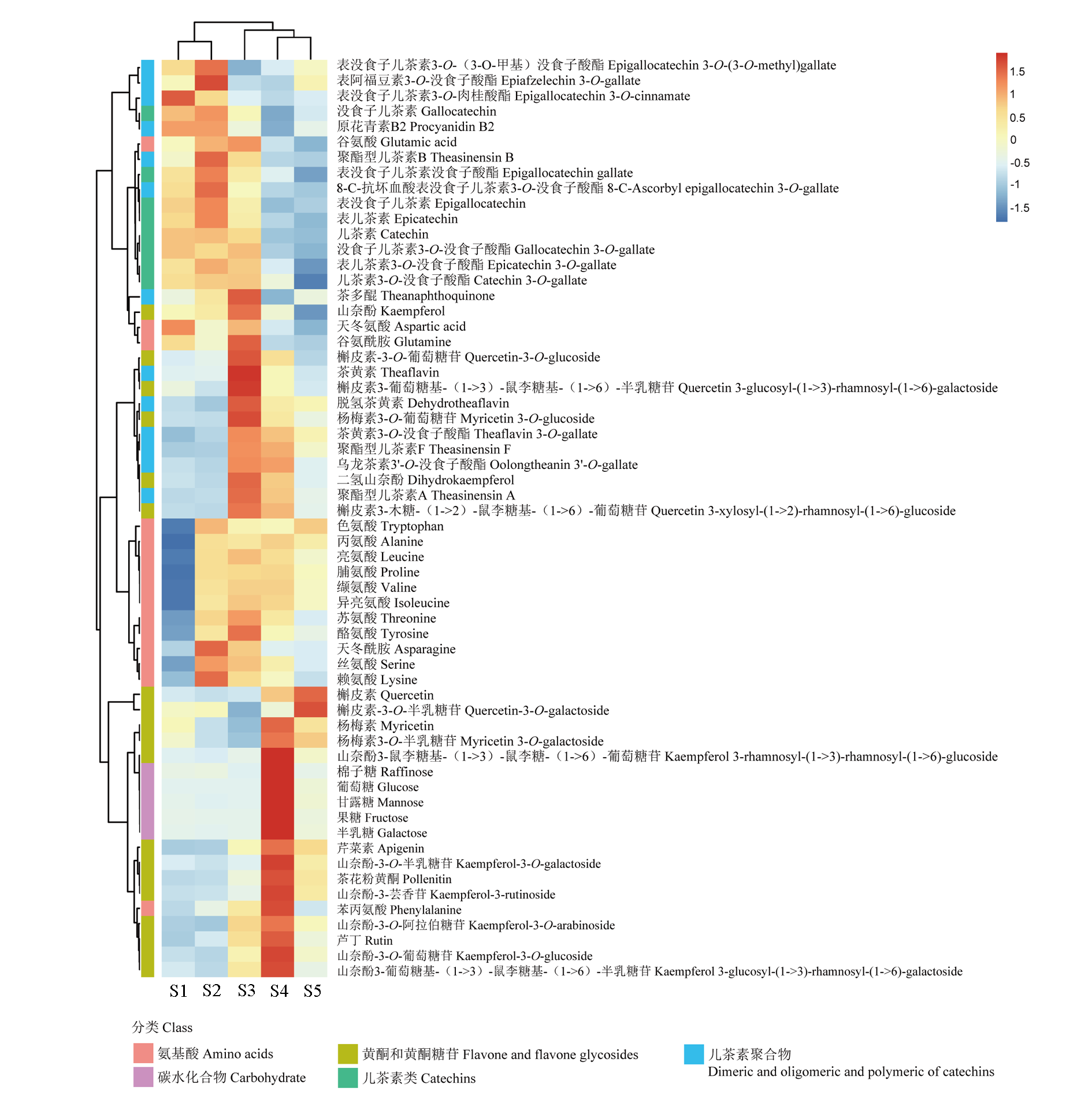
图6 ‘丹霞2号’红茶五个加工阶段的代谢产物的相关性分析 热图色块代表归一化后的代谢产物相对含量,蓝色代表代谢产物相对含量低,红色代表相对含量高。
Fig. 6 Correlation analysis of metabolites accumulated in‘Danxia 2’tea leaves during black tea processing The heatmap colour blocks represent the relativecontent of metabolite after normalization,blue color represents low level and red color represents high level of metabolite.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1080/10408399709527797 URL |
| [2] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131342 URL |
| [3] |
|
|
范捷, 王秋霜, 秦丹丹, 方开星, 朱海燕, 姜晓辉, 陈栋, 吴华玲. 2020. 红茶品质及其相关生化因子研究进展. 食品科学, 41 (3):246-253.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190217-077 |
|
| [4] |
|
|
宫连瑾, 薄佳慧, 杜哲儒, 李瑾, 孙红玉, 陈义琴, 裴若云, 肖力争. 2021. 基于代谢组学分析工夫红茶发酵过程中代谢物的变化. 食品工业科技, 42 (21):8-16.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
宫连瑾, 薄佳慧, 张天天, 孙红玉, 陈义琴, 裴若云, 肖力争. 2022. 黄金茶红茶加工过程中香气成分及其相关酶活性的动态变化. 食品与发酵工业, 48 (6):204-209.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
滑金杰, 袁海波, 江用文. 2022. 我国红茶产业现状、加工进展及前景展望. 华中农业大学学报, 41 (5):16-23.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
黄浩, 余鹏辉, 赵熙, 钟妮, 郑红发, 肖力争. 2022. 基于变温发酵技术的黄金茶工夫红茶品质分析. 现代食品科技, 38 (2):155-163
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
黄怀生, 黎娜, 钟兴刚, 粟本文. 2023. 自然发酵工夫红茶品质形成与儿茶素氧化动力学分析. 食品与发酵工业, 49 (8):164-169.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
赖宛仪. 2021. 红茶加工过程中化学物质转化及其对尼古丁诱导HOEC损伤的保护作用研究[硕士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132126 URL |
| [11] |
|
|
李鑫磊, 俞晓敏, 龚智宏, 林宏政, 郝志龙, 张妍, 金心怡. 2019. 绿茶、红茶、乌龙茶和白茶中主要代谢产物的差异. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 48 (5):559-566.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1976.41.issue-1 URL |
|
李鑫磊, 俞晓敏, 林军, 赵小嫚, 张妍, 林宏政, 郝志龙, 金心怡. 2020. 基于非靶向代谢组学的白茶与绿茶、乌龙茶和红茶代谢产物特征比较. 食品科学, 41 (12):197-203.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190128-358 |
|
| [13] |
|
|
林洁鑫, 颜廷宇, 邵淑贤, 王鹏杰, 叶乃兴, 金珊, 吴芹瑶, 郑德勇, 杨江帆. 2022. 基于UPLC-MS/MS的不同产地金观音红茶代谢组学分析. 江苏农业科学, 50 (15):162-168.
|
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1978.43.issue-1 URL |
|
刘飞, 叶阳, 李春华, 汪闵, 唐晓波, 张厅, 王小萍, 王云. 2022. 工夫红茶加工过程中类胡萝卜素成分的动态变化. 食品科学, 43 (4):231-240.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
刘亚芹, 周汉琛, 王辉, 胡善国, 黄建琴, 雷攀登, 李明智. 2020. 红茶加工过程中纤维素酶和主要品质成分的动态变化. 食品工业科技, 41 (6):66-70.
|
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.09.047 URL |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
潘宇. 2009. 红茶香气成分分析及茶红素类物质的初步研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
乔小燕, 吴华玲, 陈栋, 王秋霜, 李家贤, 黄华林, 何玉媚. 2013. 丹霞2号红茶加工关键技术参数研究. 广东农业科学, 40 (1):3-6,237.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1021/jf60188a007 URL |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1021/jf049802u URL |
| [23] |
|
|
舒心, 高彦祥. 2022. 茶叶挥发性成分提取及其香气特征分析研究进展. 食品工业科技, 43 (15):469-480.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
宋加艳. 2021. 不同产地英红9号红茶加工中香味物质代谢组学研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.11.018 URL |
| [26] |
|
|
檀业维, 温立香, 张芬, 彭靖茹, 黄寿辉. 2017. 广西金秀红茶加工过程中主要生化成分变化研究. 农业研究与应用,(4):30-33.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
王成燕, 崔宏春, 黄海涛, 赵芸, 肖元. 2022. 红茶色、香、味品质化学成分研究进展. 茶叶通讯, 49 (3):292-297,368.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
王辉, 刘亚芹, 周汉琛, 胡善国, 黄建琴, 雷攀登. 2018. 不同萎凋处理的红茶加工过程中氨基酸和儿茶素组分的动态变化研究. 中国茶叶加工,(4):29-34.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: S0963-9969(19)30124-3 pmid: 31000247 |
| [30] |
|
|
夏涛, 高丽萍, 刘亚军, 王云生, 刘莉, 赵磊, 蒋晓岚, 钱玉梅. 2013. 茶树酯型儿茶素生物合成及水解途径研究进展. 中国农业科学, 46 (11):2307-2320.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2013.11.015 |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2020.10.007 URL |
| [32] |
|
|
杨延, 陆多林, 查银娟. 2021. 红茶品质影响因素研究进展. 农业技术与装备,(2):12-13.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
余鹏辉, 陈盼, 黄浩, 赵熙, 钟妮, 刘姝娟, 郑红发, 龚雨顺. 2020. 保靖黄金茶1号工夫红茶加工工序对主要滋味物质形成的影响. 食品科学, 41 (10):185-191.
doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190612-130 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
曾议霆, 吴雪莉, 杨春梅, 刘高杰, 高丙德, 唐克纯. 2022. 基于非靶向代谢组学比较不同发酵方式红茶滋味物质差异. 食品安全质量检测学报, 13 (16):5288-5296.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
张娅楠. 2019. 黄金茶1号夏秋红茶加工技术及香味品质形成机理研究[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.12.016 URL |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112169 URL |
| [38] |
|
| [1] | 李怡斐, 杨小苗, 王春萍, 段敏杰, 黄启中, 黄任中, 张世才. 加工型辣椒新品种‘艳椒465’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2223-2224. |
| [2] | 李文远, 林梦桦, 李亚辉, 于全琦, 梁颖, 张志勇. 梨果实代谢组学研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1595-1609. |
| [3] | 田洁, 周倩怡, 铁原毓, 孙海宏, 黄思杰. 干旱胁迫下大蒜幼苗的代谢组学分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 133-144. |
| [4] | 沈进娟, 范永红, 管中荣 , 张召荣, 彭丽莎, 王 彬, 杨 平, 王 浩. 茎瘤芥新品种‘涪优 928’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(S1): 55-56. |
| [5] | 周成, 方怡, 周锦杨, 黄企浩, 盘永坚, 史千千, 倪慧娴, 杨震峰, 宋春波. 低温诱导的桃果实采后膜脂代谢变化与冷害的关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1305-1317. |
| [6] | 王晓玲, 仇晓靖, 李智慧, 刘淑怡, 李旭茂, 毛永民, 申连英. 酸枣新品种‘丽园珍珠10号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 63-64. |
| [7] | 樊丁宇, 靳 娟, 杨 磊, 郝 庆, 阿布都卡尤木 • 阿依麦提. 鲜食制干兼用枣新品种‘赛蜜酥1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(S2): 2807-2808. |
| [8] | 许海峰, 陈新, 张士刚, 相昆, 张美勇, 徐颖, 王贵芳. 基于代谢组学分析‘秋香’核桃贮藏期间脂肪酸的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2161-2170. |
| [9] | 陈倩如, 蔡文淇, 张霞, 张大毛, 李卫东, 许璐, 于晓英, 李炎林. 檵木不同叶色形成的化学成分比较研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(10): 1969-1982. |
| [10] | 刘嘉彬, 刘孟军, 刘 平, . 鲜食加工兼用枣新品种‘雨珠’[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(S2): 2931-2932. |
| [11] | 杨 涛, 唐亚萍, 张国儒, 帕提古丽, 王柏柯, 李 宁, 王 娟, 余庆辉, 杨生保. 加工型辣椒新品种‘园椒34号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(S2): 2977-2978. |
| [12] | 孙晓红1,2,柏素花1,2,侯鸿敏1,3,孙 欣1,3,祝 军1,3,戴洪义1,3,张玉刚1,3,*. 红肉苹果新品种‘黛红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(S2): 2729-2730. |
| [13] | 李燕山1,2,李小波3,姚春光1,2,普红梅1,2,梁淑敏1,2,隋启君1,2,白建明1,2,*. 薯片加工型马铃薯新品种‘云薯306’[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(S2): 2817-2818. |
| [14] | 李怡斐*,张世才*,杨小苗,蒋晓英,王春萍,林 清,黄启中**,黄任中**. 加工型辣椒新品种‘艳椒435’[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(S2): 2761-2762. |
| [15] | 崔霞霞1,2,*,王亚钦2,*,任 毅2,Alisdair R Fernie3,Saleh Alseekh4,何洪巨2,宫国义2,张海英2,郭绍贵2,张 洁. 低糖野生种与高糖栽培种西瓜果实代谢产物组分差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(4): 775-783. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司