
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 279-291.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0264
收稿日期:2024-11-13
修回日期:2024-12-16
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-23
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHAO Yulei, LI Shan, LI Chengnan, MA Jinlong, MA Hongyi, YIN Xiao*( )
)
Received:2024-11-13
Revised:2024-12-16
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-23
摘要:
利用非标记定量蛋白质组学技术,对易感灰霉病的欧洲葡萄(Vitis vinifera)品种‘黑比诺’和高抗灰霉病的野生山葡萄(V. amurensis)品种‘双优’的幼嫩叶片进行灰霉菌接种,以接种无菌水为对照,分析二者在灰霉菌侵染初期(接种后12 h)的差异表达蛋白。2个品种共鉴定出12 210个蛋白质,在‘黑比诺’中,检测出868个差异表达蛋白,‘双优’中检测出1 946个差异表达蛋白。通过GO和KEGG富集分析,发现差异表达蛋白主要集中于代谢通路、次生代谢物、氨基酸代谢等信号途径中。在2个品种中共筛选出10个关键差异表达蛋白,并且在高抗品种‘双优’中筛选出的过氧化物酶、谷胱甘肽转移酶、酯氧合酶、乙醛脱氢酶和二苯乙烯合酶的表达量发生上调,NADH脱氢酶和碳酸酐酶的表达量受到抑制,说明以上蛋白在‘双优’叶片受到灰霉菌侵染过程中起重要作用,其中过氧化物酶在易感品种‘黑比诺’中也有表达,表明过氧化物酶在葡萄叶片受灰霉菌侵染初期积极响应,是重要差异表达蛋白。
赵钰磊, 李珊, 李承男, 马金龙, 马红义, 尹晓. 灰霉菌侵染葡萄叶片初期的蛋白质组学研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 279-291.
ZHAO Yulei, LI Shan, LI Chengnan, MA Jinlong, MA Hongyi, YIN Xiao. Proteomics Studies on the Early Stages of Botrytis cinerea Infection in Grapevine Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 279-291.
| 蛋白 Protein | 基因ID Gene ID | 描述 Description | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0A438C3M1 | PNC1_16 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | F:GTTTGTGCCCTGGGGTTGTTTC |
| R:ACTCGCCGTGGTTGAATCTCTTC | |||
| A0A438C992 | GSTU10_1 | 谷胱甘肽转移酶Glutathione transferase | F:TGAGGTAGTTGGTGTGGTTGTCG |
| R:GTCTCCTTCATCAGTGGGCAGTC | |||
| D7TAQ3 | XM_002265469 | 脂氧合酶Lipoxygenase | F:TGAGGACAAGACTGTGGAAGGTG |
| R:AGAAGACGACGACGACGACAAC | |||
| D7SL57 | XM_002285430 | 乙醛脱氢酶Aldehyde dehydrogenase | F:TTCACACACGAGAAGGCGATCC |
| R:TCAAGCCCAAGAGGACAAGCAG | |||
| A5AEM3 | XM_003634025 | 二苯乙烯合酶Stilbene synthase 4 | F:AACGACGACAGGTGAAGGATTGG |
| R:TGGAGCACAACGGTCTCAATGG | |||
| D7TU30 | XM_010649825 | 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase | F:TGGCCTTCTCATCCTCCTCTCTC |
| R:TGGGTCTGCTCAATTACGCTCAG | |||
| A5C501 | XM_002265668 | NADH脱氢酶NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4,mitochondrial | F:AGTCACTGCAACGGCTATGGAG R:CGATCTCGCCCGGTTTGATTTC |
| A0A438JBL2 | POX2_1 | 脯氨酸脱氢酶Proline dehydrogenase | F:GCAGGATGTGGAGGAGGCTTG |
| R:AGGTGGCGTTATCGGTGGTATG | |||
| A0A438CM14 | POXN1_5 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | F:GAGGGCTGCGTGGATTGAATTTC |
| R:TCCCAGTCTTCACCCCAATGTTG | |||
| A0A438IMB3 | VvCHDp000857_1 | 葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶 Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase | F:TTCGTCTTTCTCGGCACCCTTC R:AATGGCGGCTGATGGTACTGAG |
表1 本研究中所用引物
Table 1 List of primers used in this study
| 蛋白 Protein | 基因ID Gene ID | 描述 Description | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| A0A438C3M1 | PNC1_16 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | F:GTTTGTGCCCTGGGGTTGTTTC |
| R:ACTCGCCGTGGTTGAATCTCTTC | |||
| A0A438C992 | GSTU10_1 | 谷胱甘肽转移酶Glutathione transferase | F:TGAGGTAGTTGGTGTGGTTGTCG |
| R:GTCTCCTTCATCAGTGGGCAGTC | |||
| D7TAQ3 | XM_002265469 | 脂氧合酶Lipoxygenase | F:TGAGGACAAGACTGTGGAAGGTG |
| R:AGAAGACGACGACGACGACAAC | |||
| D7SL57 | XM_002285430 | 乙醛脱氢酶Aldehyde dehydrogenase | F:TTCACACACGAGAAGGCGATCC |
| R:TCAAGCCCAAGAGGACAAGCAG | |||
| A5AEM3 | XM_003634025 | 二苯乙烯合酶Stilbene synthase 4 | F:AACGACGACAGGTGAAGGATTGG |
| R:TGGAGCACAACGGTCTCAATGG | |||
| D7TU30 | XM_010649825 | 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase | F:TGGCCTTCTCATCCTCCTCTCTC |
| R:TGGGTCTGCTCAATTACGCTCAG | |||
| A5C501 | XM_002265668 | NADH脱氢酶NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4,mitochondrial | F:AGTCACTGCAACGGCTATGGAG R:CGATCTCGCCCGGTTTGATTTC |
| A0A438JBL2 | POX2_1 | 脯氨酸脱氢酶Proline dehydrogenase | F:GCAGGATGTGGAGGAGGCTTG |
| R:AGGTGGCGTTATCGGTGGTATG | |||
| A0A438CM14 | POXN1_5 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | F:GAGGGCTGCGTGGATTGAATTTC |
| R:TCCCAGTCTTCACCCCAATGTTG | |||
| A0A438IMB3 | VvCHDp000857_1 | 葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶 Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase | F:TTCGTCTTTCTCGGCACCCTTC R:AATGGCGGCTGATGGTACTGAG |
| 品种 Cultivar | 显著差异蛋白 Significant difference protein | 上调 Up-regulation | 下调 Down-regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 黑比诺Pinot Noir | 868 | 543 | 325 |
| 双优Shuangyou | 1 946 | 969 | 977 |
表2 ‘黑比诺’和‘双优’葡萄接种灰霉菌后的差异表达蛋白数量
Table 2 Number of differential proteins in‘Pinot Noir’and‘Shuangyou’grapes inoculated with Botrytis cinerea
| 品种 Cultivar | 显著差异蛋白 Significant difference protein | 上调 Up-regulation | 下调 Down-regulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 黑比诺Pinot Noir | 868 | 543 | 325 |
| 双优Shuangyou | 1 946 | 969 | 977 |
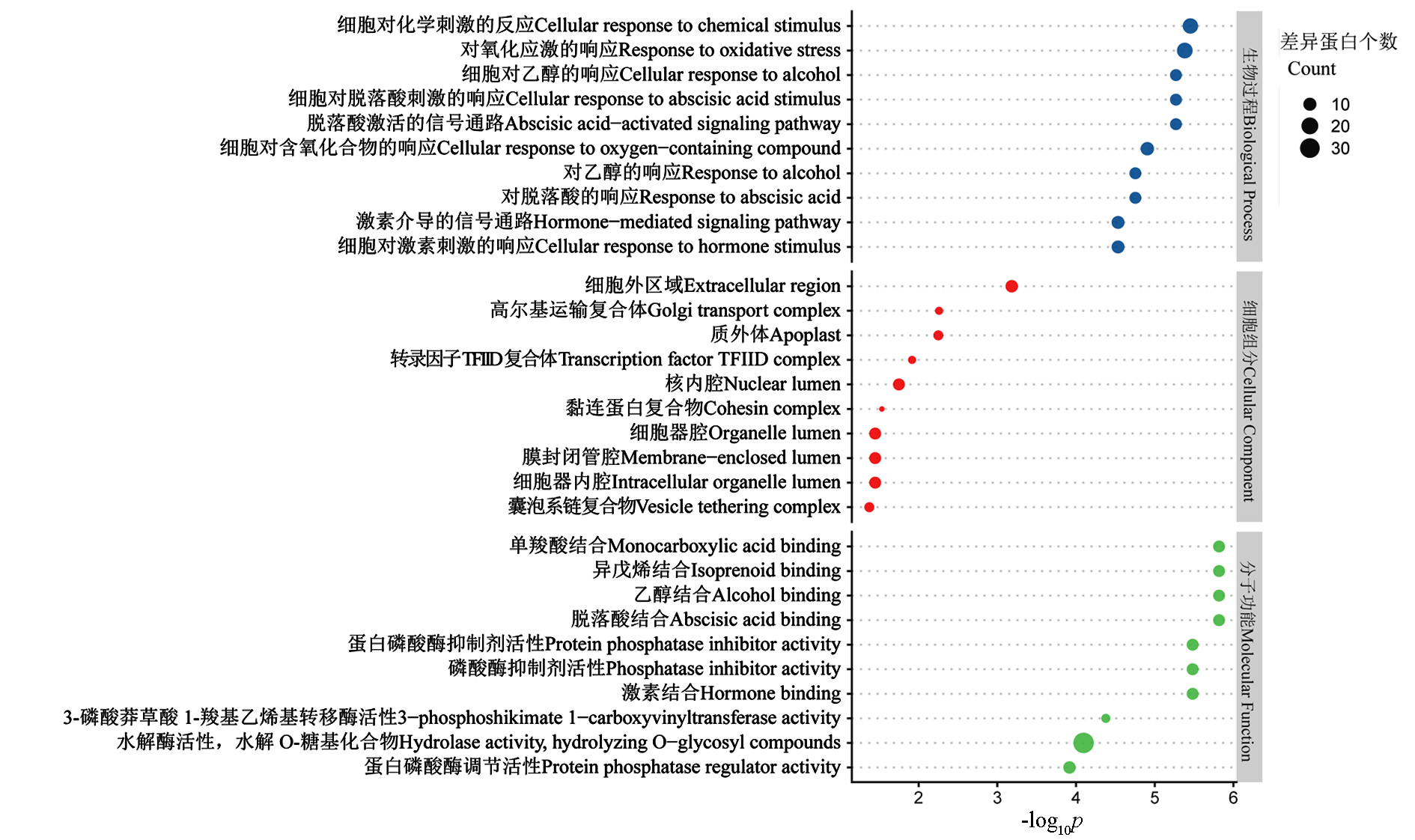
图1 ‘黑比诺’葡萄接种灰霉菌处理与对照差异蛋白的GO term注释(top 10)
Fig. 1 GO term annotation of‘Pinot Noir’grape inoculated with Botrytis cinerea treatment and control differential proteins(top 10)
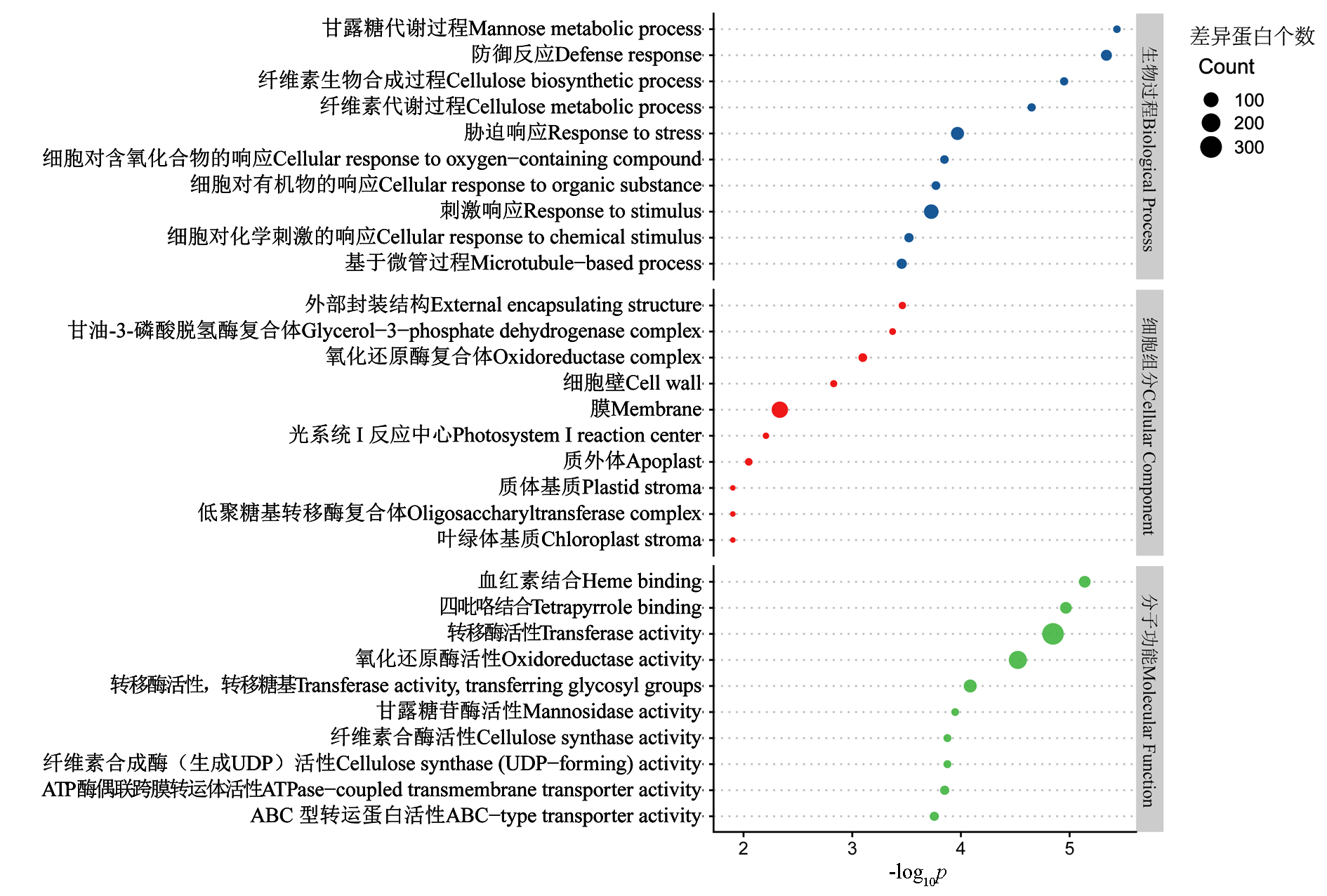
图2 ‘双优’葡萄接种灰霉菌处理与对照差异蛋白的GO term注释(top 10)
Fig. 2 GO term annotation of‘Shuangyou’grape inoculated with Botrytis cinerea treatment and control differential proteins(top 10)
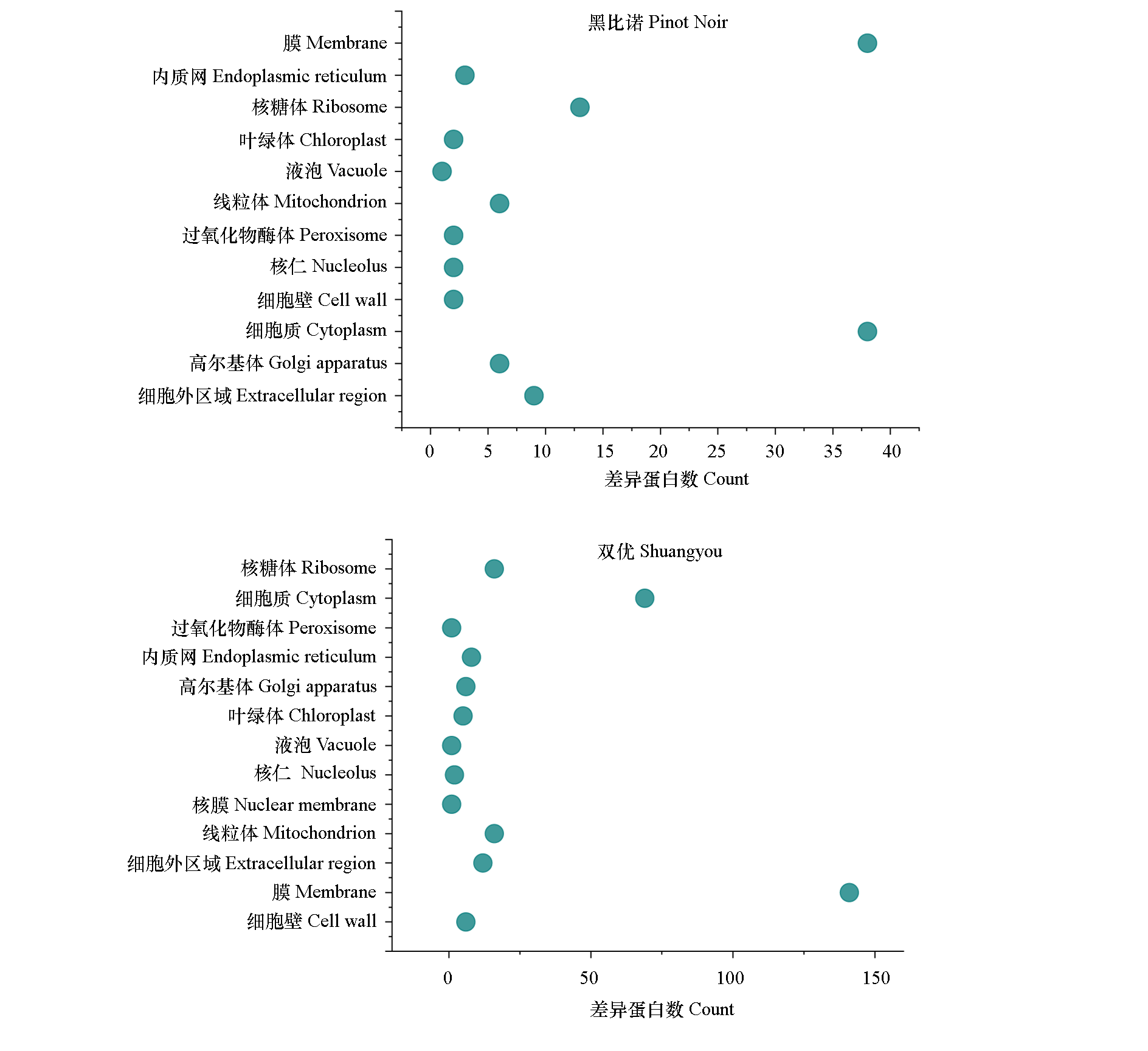
图3 ‘黑比诺’和‘双优’葡萄接种灰霉菌处理与对照差异蛋白的亚细胞定位
Fig. 3 Subcellular localization of differential proteins in‘Pinot Noir’and‘Shuangyou’grapes inoculated with Botrytis cinerea treatment and the control

图4 ‘黑比诺’和‘双优’葡萄接种灰霉菌处理与对照差异蛋白的KEGG富集与注释(top 30) C:细胞过程;G:遗传信息处理;M:代谢
Fig. 4 KEGG enrichment and annotation of‘Pinot Noir’and‘Shuangyou’ grapes inoculated with Botrytis cinerea treatment and the control differential proteins(top 30) C:Cellular processes;G:Genetic information processing;M:Metabolism
| 品种 Cultivar | 表达 Express | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 描述 Description | log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑比诺 Pinot Noir | 上调 Up-regulated | A0A438JBL2 | 脯氨酸脱氢酶Proline dehydrogenase | 3.71 |
| A0A438CM14 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 3.66 | ||
| A0A438IMB3 | 葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase | 2.15 | ||
| 双优 Shuangyou | 上调 Up-regulated | A0A438C3M1 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 3.56 |
| A0A438C992 | 谷胱甘肽转移酶Glutathione S-transferase | 3.31 | ||
| D7TAQ3 | 脂氧合酶Lipoxygenase | 2.11 | ||
| D7SL57 | 乙醛脱氢酶Aldehyde dehydrogenase | 2.09 | ||
| A5AEM3 | 二苯乙烯合酶Stilbene synthase 4 | 1.65 | ||
| 下调 Down-regulated | D7TU30 | 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase | -2.89 | |
| A5C501 | NADH脱氢酶NADH dehydrogenase[ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4,mitochondrial | -2.72 |
表3 ‘黑比诺’和‘双优’葡萄接种灰霉菌处理与对照主要差异表达蛋白
Table 3 The main difference in expression of protein between‘Pinot Noir’and‘Shuangyou’grape inoculated with Botrytis cinerea treatment and the control
| 品种 Cultivar | 表达 Express | 蛋白ID Protein ID | 描述 Description | log2FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑比诺 Pinot Noir | 上调 Up-regulated | A0A438JBL2 | 脯氨酸脱氢酶Proline dehydrogenase | 3.71 |
| A0A438CM14 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 3.66 | ||
| A0A438IMB3 | 葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase | 2.15 | ||
| 双优 Shuangyou | 上调 Up-regulated | A0A438C3M1 | 过氧化物酶Peroxidase | 3.56 |
| A0A438C992 | 谷胱甘肽转移酶Glutathione S-transferase | 3.31 | ||
| D7TAQ3 | 脂氧合酶Lipoxygenase | 2.11 | ||
| D7SL57 | 乙醛脱氢酶Aldehyde dehydrogenase | 2.09 | ||
| A5AEM3 | 二苯乙烯合酶Stilbene synthase 4 | 1.65 | ||
| 下调 Down-regulated | D7TU30 | 碳酸酐酶Carbonic anhydrase | -2.89 | |
| A5C501 | NADH脱氢酶NADH dehydrogenase[ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4,mitochondrial | -2.72 |

图5 ‘黑比诺’和‘双优’葡萄中响应灰霉菌的关键差异蛋白的相对表达量及蛋白质组学测序结果 Mock:无菌水对照;Bc:接种灰霉菌
Fig. 5 Relative expression and proteomic sequencing results of key differential proteins in response to Botrytis cinerea in ‘Pinot Noir’and‘Shuangyou’grapes Mock:Sterile water control;Bc:Inoculation of Botrytis cinerea
| [1] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru517 pmid: 25675955 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
柴生樾. 2021. 中国野生山葡萄抗灰霉病转录因子VaERF99功能及其作用机理[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-16-1227-RE pmid: 30677353 |
| [9] |
|
|
方献平, 和雅妮, 奚晓军, 查倩, 张丽勍, 蒋爱丽. 2019. 多组学技术揭示葡萄叶片响应灰葡萄孢菌侵染的抗性机制. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 45 (3):306-316.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0887-1 pmid: 12430017 |
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-91-4-0407 pmid: 30781182 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
|
童建华,
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
万然. 2016. 中国野生葡萄种质叶片抗灰霉病的机制研究[博士论文]: 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
王梦楠. 2018. 中国野生山葡萄转录因子VaERF20克隆与功能研究[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
pmid: 23167192 |
|
于定群, 汤浩茹, 张勇, 罗娅, 刘泽静. 2012. 高等植物葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶的研究进展. 生物工程学报, 28 (7):800-812.
pmid: 23167192 |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
|
朱彦勋. 2022. 葡萄抗灰霉病关键ERF基因筛选及VaERF16抗灰霉病调控机理[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
| [1] | 陈亚娟, 金鑫, 杨江山, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄果实糖酸代谢及香味物质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 406-422. |
| [2] | 李晓庆, 闫思远, 顾沛雯. 宁夏地区葡萄灰霉病菌的多样性及致病力分化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 481-490. |
| [3] | 李敏, 李思雨, 施紫涵, 陈爽, 徐炎, 刘国甜. 葡萄GRF/GIF家族基因对遗传转化再生效率的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 51-65. |
| [4] | 梁国平, 曾宝珍, 刘铭, 边志远, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 山葡萄VaSR基因家族的鉴定及VaSR1抗寒功能验证与互作蛋白筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 37-50. |
| [5] | 杨敬辉, 许媛, 肖婷, 褚姝频, 刘吉祥, 姚克兵. 葡萄胶孢炭疽病菌复合种(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complexes)对嘧菌酯的抗药性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1906-1912. |
| [6] | 韩斌, 刘长江, 尹勇刚, 孙艳, 贾楠, 赵胜建, 郭紫娟, 李敏敏. 中晚熟鲜食葡萄新品种‘金光’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1977-1978. |
| [7] | 刘苗苗, 姚锦, 包敏, 楚言言, 王西平. 赤霉素诱导葡萄无核形成机理研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(7): 1610-1622. |
| [8] | 张文静, 徐大勇, 吴倩琳, 杨佛, 信丙越, 曾昕, 李峰. 拮抗番茄灰霉病的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌XDY66基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [9] | 马宗桓, 李玉梅, 韦霞霞, 李文芳, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 河西走廊不同产地‘美乐’葡萄品质及香气物质的差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1083-1098. |
| [10] | 伍少福, 韩科峰, 吴良欢. 生物有机肥加专用肥对葡萄园土壤养分、微生物和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1099-1112. |
| [11] | 何长霞, 罗陈, 闫晋强, 刘文睿, 王敏, 谢大森, 吴智明, 江彪. 冬瓜实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的筛选与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 748-760. |
| [12] | 李斗, 王宇航, 王春恒, 金鑫, 杨江山, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 冯丽丹. GABA对葡萄叶片光合色素及糖含量和果实风味的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 815-831. |
| [13] | 杜易静, 刘文林, 乔月莲, 王莉, 安德志, 杜国强, 师校欣. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄试管苗热处理结合茎尖和腋芽培养脱毒技术研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 893-902. |
| [14] | 夏宏义, 刘巧, 彭家清, 吴伟, 龚林忠. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄避雨栽培f式树形对光合及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [15] | 王海霞, 蒋娅萍, 方艳, 杨学山, 祝霞. 外源水溶性β-葡聚糖对‘贵人香’葡萄果实糖苷酶及香气品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 571-586. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司