
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 3031-3043.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0925
韩志磊, 阴筱, 洪浩, 许帅, 李丽莉*( ), 姜珊珊*(
), 姜珊珊*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-09
修回日期:2025-08-27
出版日期:2025-11-26
发布日期:2025-11-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
HAN Zhilei, YIN Xiao, HONG Hao, XU Shuai, LI Lili*( ), and JIANG Shanshan*(
), and JIANG Shanshan*( )
)
Received:2025-01-09
Revised:2025-08-27
Published:2025-11-26
Online:2025-11-26
摘要: 为了解山东省沿海苹果主产区苹果病毒病的发生现状及遗传多样性,利用高通量测序技术结合RT-PCR技术检测威海和烟台57份‘红富士’苹果样品中的病毒种类,随后对检测到的各病毒分离物的衣壳蛋白(coat protein,CP)或运动蛋白(movement protein,MP)进行了基因克隆、序列相似性分析及系统发育分析。结果表明,共检测到苹果茎痘病毒(apple stem pitting virus,ASPV)、苹果茎沟病毒(apple stem grooving virus,ASGV)、苹果褪绿叶斑病毒(apple chlorotic leaf spot virus,ACLSV)和柑橘叶斑病毒(citrus leaf blotch virus,CLBV)4种植物病毒,检出率分别为63.16%、87.72%、78.95%和1.75%。其中81.48%的样品为复合感染,ASPV、ASGV和ACLSV的复合感染样品占比61.11%。从感病样品中分别克隆了9个ASGV、2个ASPV、9个ACLSV的CP基因和1个CLBV的MP基因序列,ASGV和ACLSV的山东分离物与国内已报道的分离物具有较近的亲缘关系。9个ACLSV分离物分别聚集在P205、SHZ和B6组;9个ASGV分离物聚在4个分支上;2个ASPV分离物聚集在同一组的两个分支;1个CLBV分离物与其他物种的分离物聚在一起。
韩志磊, 阴筱, 洪浩, 许帅, 李丽莉, 姜珊珊. 山东沿海苹果产区病毒鉴定及遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(11): 3031-3043.
HAN Zhilei, YIN Xiao, HONG Hao, XU Shuai, LI Lili, and JIANG Shanshan. Identification and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Common Viruses of Apple in Shandong Coastal Areas[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(11): 3031-3043.
| 采集地点Collection site | 采集数量No. of samples |
|---|---|
| 山东省威海市临港经济技术开发区汪疃镇王家产村 Wangjiachan Village,Wangtuan Town,Lingang Economic and Technological Development Zone,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 6 |
| 山东省威海市环翠区凤凰山路 Fenghuangshan Road,Huancui District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 6 |
| 山东省威海市临港区汪疃镇后白鹿村 Houbailu Village,Wangtuan Town,Lingang District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 5 |
| 山东省威海市文登区米山镇西古场村 Xiguchang Village,Mishan Town,Wendeng District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 4 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区莒格庄镇桑园村 Sangyuan Village,Jugezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 8 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区武宁街道张家村 Zhangjia Village,Wuning Street,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 11 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区观水镇沟北村 Goubei Village,Guanshui Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 9 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区宁海街道城北村 Chengbei Village,Ninghai Street,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 2 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区王格庄镇清泉埠村 Qingquanbu Village,Wanggezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 3 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区王格庄镇小寨村 Xiaozhai Village,Wanggezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 3 |
表1 山东沿海‘红富士’苹果果实样本采集信息表
Table 1 Collection information of‘Fuji’apple samples from Shandong coastal areas
| 采集地点Collection site | 采集数量No. of samples |
|---|---|
| 山东省威海市临港经济技术开发区汪疃镇王家产村 Wangjiachan Village,Wangtuan Town,Lingang Economic and Technological Development Zone,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 6 |
| 山东省威海市环翠区凤凰山路 Fenghuangshan Road,Huancui District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 6 |
| 山东省威海市临港区汪疃镇后白鹿村 Houbailu Village,Wangtuan Town,Lingang District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 5 |
| 山东省威海市文登区米山镇西古场村 Xiguchang Village,Mishan Town,Wendeng District,Weihai City,Shandong Province | 4 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区莒格庄镇桑园村 Sangyuan Village,Jugezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 8 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区武宁街道张家村 Zhangjia Village,Wuning Street,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 11 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区观水镇沟北村 Goubei Village,Guanshui Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 9 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区宁海街道城北村 Chengbei Village,Ninghai Street,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 2 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区王格庄镇清泉埠村 Qingquanbu Village,Wanggezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 3 |
| 山东省烟台市牟平区王格庄镇小寨村 Xiaozhai Village,Wanggezhuang Town,Muping District,Yantai City,Shandong Province | 3 |
| 病毒名称Virus name | 引物名称Primer | 序列(5′-3′)Sequence | 扩增产物/bp Fragment size |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASPV | ASPV-det-F | CGAAGCATGTCTGGAACCT | 240 |
| ASPV-det-R | ACAGCTTGAGTACCTTCCAT | ||
| ASGV | ASGV-det-F | GCTGATTTGGCTCGTGAATTT | 257 |
| ASGV-det-R | TCCTAACCCT CCAGTTCCAG | ||
| ACLSV | ACLAV-det-F | TACAATCTGAAGGAGGTGGTC | 255 |
| ACLSV-det-R | AAGACGCCGGTTCATATTAGT | ||
| CLBV | CLBV-det-F | AGCCATAGTTGAACCATTCCT | 207 |
| CLBV-det-R | GCAGCTTTAAGTGACTCATTC | ||
| ASGV | ASGV-CP-F | CAGRMGAAGGAGRATGGCG | 721 |
| ASGV-CP-R | CGACTYCTAACCCTCCAGTTC | ||
| ASPV | ASPV-CP-F | ATGGCTTCMA ATGGHTCCCA | 1 191 |
| ASPV-CP-R | TTACTTCCTAATGGATAACACAG | ||
| ACLSV | ACLSV-CP-F | CAGRMGAAGGAGRATGGCG | 752 |
| ACLSV-CP-R | CCATGACTCTTTATACTCTYTC | ||
| CLBV | CLBV-MP-F | AGATATGAGTGGAGGAGAGG | 2 612 |
| CLBV-MP-R | GACTTGATGTTACATGCCCAG |
表2 苹果病毒检测和基因扩增引物信息
Table 2 Information on primers for detection and gene amplification of apple viruses
| 病毒名称Virus name | 引物名称Primer | 序列(5′-3′)Sequence | 扩增产物/bp Fragment size |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASPV | ASPV-det-F | CGAAGCATGTCTGGAACCT | 240 |
| ASPV-det-R | ACAGCTTGAGTACCTTCCAT | ||
| ASGV | ASGV-det-F | GCTGATTTGGCTCGTGAATTT | 257 |
| ASGV-det-R | TCCTAACCCT CCAGTTCCAG | ||
| ACLSV | ACLAV-det-F | TACAATCTGAAGGAGGTGGTC | 255 |
| ACLSV-det-R | AAGACGCCGGTTCATATTAGT | ||
| CLBV | CLBV-det-F | AGCCATAGTTGAACCATTCCT | 207 |
| CLBV-det-R | GCAGCTTTAAGTGACTCATTC | ||
| ASGV | ASGV-CP-F | CAGRMGAAGGAGRATGGCG | 721 |
| ASGV-CP-R | CGACTYCTAACCCTCCAGTTC | ||
| ASPV | ASPV-CP-F | ATGGCTTCMA ATGGHTCCCA | 1 191 |
| ASPV-CP-R | TTACTTCCTAATGGATAACACAG | ||
| ACLSV | ACLSV-CP-F | CAGRMGAAGGAGRATGGCG | 752 |
| ACLSV-CP-R | CCATGACTCTTTATACTCTYTC | ||
| CLBV | CLBV-MP-F | AGATATGAGTGGAGGAGAGG | 2 612 |
| CLBV-MP-R | GACTTGATGTTACATGCCCAG |
| 样品 Sample | 原始序列 Raw_reads | 纯净序列 Clean_reads | 质量值≥20碱基占比/% Q20 | 质量值≥30碱基占比/% Q30 | 聚集 Cluster | 病毒种类 Virus species | 核苷酸一致性/% Identity | 重叠群数量/个 No. contigs | 覆盖度/% Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP-1 | 23 736 150 | 22 922 314 | 97.92 | 94.08 | 23 925 | ASPV | 90.6 ~ 98.8 | 7 | 83.14 |
| ACLSV | 84.1 ~ 97.7 | 16 | 74.10 | ||||||
| ASGV | 87.1 ~ 99.8 | 7 | 87.47 | ||||||
| CTLV | 90.4 ~ 93.6 | 2 | 97.69 | ||||||
| AP-2 | 23 299 576 | 22 478 148 | 97.87 | 93.98 | 23 226 | ACLSV | 82.4 ~ 98.3 | 21 | 89.04 |
| ASGV | 91.6 ~ 99.4 | 9 | 94.75 | ||||||
| ASPV | 96.0 ~ 98.4 | 3 | 57.53 | ||||||
| AP-3 | 22 739 857 | 21 998 049 | 97.59 | 93.3 | 24 873 | ACLSV | 83.0 ~ 98.8 | 20 | 87.43 |
| ASGV | 87.7 ~ 98.1 | 6 | 94.69 | ||||||
| ASPV | 96.0 ~ 96.4 | 3 | 77.10 | ||||||
| CTLV | 85.1 | 1 | 76.91 | ||||||
| AP-4 | 23 812 838 | 22 901 748 | 97.96 | 94.17 | 24 619 | ACLSV | 83.4 ~ 99.2 | 19 | 75.98 |
| ASGV | 90.1 ~ 98.5 | 7 | 99.68 | ||||||
| CLBV | 89.5 | 1 | 99.67 | ||||||
| CTLV | 82.5 | 1 | 30.62 |
表3 转录组测序获取的病毒数据统计
Table 3 Statistical analysis of virus data obtained from transcriptome sequencing
| 样品 Sample | 原始序列 Raw_reads | 纯净序列 Clean_reads | 质量值≥20碱基占比/% Q20 | 质量值≥30碱基占比/% Q30 | 聚集 Cluster | 病毒种类 Virus species | 核苷酸一致性/% Identity | 重叠群数量/个 No. contigs | 覆盖度/% Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP-1 | 23 736 150 | 22 922 314 | 97.92 | 94.08 | 23 925 | ASPV | 90.6 ~ 98.8 | 7 | 83.14 |
| ACLSV | 84.1 ~ 97.7 | 16 | 74.10 | ||||||
| ASGV | 87.1 ~ 99.8 | 7 | 87.47 | ||||||
| CTLV | 90.4 ~ 93.6 | 2 | 97.69 | ||||||
| AP-2 | 23 299 576 | 22 478 148 | 97.87 | 93.98 | 23 226 | ACLSV | 82.4 ~ 98.3 | 21 | 89.04 |
| ASGV | 91.6 ~ 99.4 | 9 | 94.75 | ||||||
| ASPV | 96.0 ~ 98.4 | 3 | 57.53 | ||||||
| AP-3 | 22 739 857 | 21 998 049 | 97.59 | 93.3 | 24 873 | ACLSV | 83.0 ~ 98.8 | 20 | 87.43 |
| ASGV | 87.7 ~ 98.1 | 6 | 94.69 | ||||||
| ASPV | 96.0 ~ 96.4 | 3 | 77.10 | ||||||
| CTLV | 85.1 | 1 | 76.91 | ||||||
| AP-4 | 23 812 838 | 22 901 748 | 97.96 | 94.17 | 24 619 | ACLSV | 83.4 ~ 99.2 | 19 | 75.98 |
| ASGV | 90.1 ~ 98.5 | 7 | 99.68 | ||||||
| CLBV | 89.5 | 1 | 99.67 | ||||||
| CTLV | 82.5 | 1 | 30.62 |
| 地点(样本量) Locality(Samples) | 无毒样品 Virus-free samples | 带毒样品Virus-infected samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASGV(CTLV) | ASPV | ACLSV | CLBV | ||
| 威海(21)Weihai | 14.29 | 80.95 | 47.62 | 61.90 | 0 |
| 烟台(36)Yantai | 0 | 91.67 | 72.22 | 88.89 | 2.78 |
| 总样品(57)Total | 5.26 | 87.72 | 63.16 | 78.95 | 1.75 |
表4 各苹果病毒在不同区域的检出率
Table 4 Detection rates of different apple viruses in various regions %
| 地点(样本量) Locality(Samples) | 无毒样品 Virus-free samples | 带毒样品Virus-infected samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASGV(CTLV) | ASPV | ACLSV | CLBV | ||
| 威海(21)Weihai | 14.29 | 80.95 | 47.62 | 61.90 | 0 |
| 烟台(36)Yantai | 0 | 91.67 | 72.22 | 88.89 | 2.78 |
| 总样品(57)Total | 5.26 | 87.72 | 63.16 | 78.95 | 1.75 |
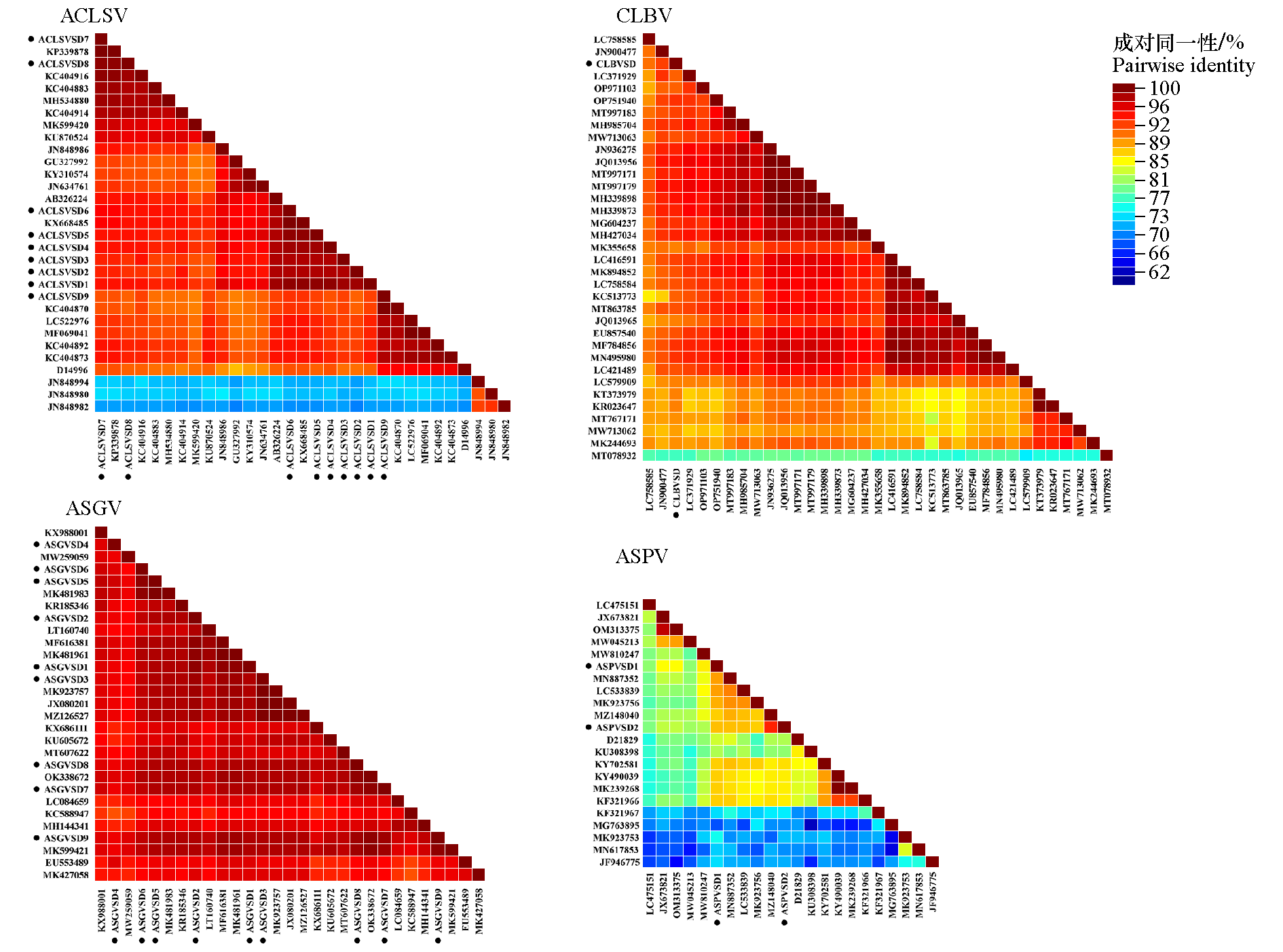
图4 山东沿海地区‘红富士’苹果病毒二维彩色编码矩阵 ·:山东沿海地区分离物
Fig. 4 Two-dimensional color-coded matrix of‘Fuji’apple virus isolates from Shandong coastal areas •:Isolates of Shandong coastal areas
| [1] |
|
|
陈玲, 郭铖, 贾安宁, 邓丛良, 种焱, 史喜菊, 李永强. 2023. 侵染牡丹的苹果茎沟病毒分离物基因组测序及分析. 园艺学报, 50 (12):2735-2747.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈荣鑫, 钟远闻, 孙鲁龙, 王辉, 王伯臣, 贾荣俭, 赵政阳. 2023. 3个苹果新品种病毒病的发生状况及ASSVd序列分析. 果树学报, 40 (6):1215-1225.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
陈雅寒, 孙平平, 马强, 赵明敏, 武占敏, 李正男. 2019. 东北冷寒产区苹果褪绿叶斑病毒检测及其分子多样性分析. 园艺学报, 46 (12):2397-2405.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
丁磊, 崔正秀, 陈伟, 吴云锋. 2022. 山西苹果茎痘病毒遗传多样性分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 36 (2):141-146.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
丁敏, 王莹, 钟家美, 黄爱军. 2021. 柑桔叶斑驳病毒江西分离物全基因组序列测定与分析. 中国南方果树, 50 (3):13-16,22.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
Fidanci Avci B Önelge N,
|
| [8] |
|
|
韩志磊, 李光艳, 孙晓辉, 吴斌, 洪浩, 庞宗洋, 王树森, 辛志梅, 竺晓平, 姜珊珊. 2024. 甘薯褪绿斑病毒山东分离物全基因组扩增及遗传进化分析. 植物病理学报, 54 (2):279-290.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
胡国君, 董雅凤, 张尊平, 范旭东, 任芳. 2022. 用于苹果树病毒鉴定的small RNA深度测序数据集. 农业大数据学报, 4 (2):25-29.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
贾晓君, 胡国君, 张尊平, 范旭东, 任芳, 董雅凤. 2023. 苹果茎沟病毒侵染对嘎拉苹果果实品质的影响. 中国果树,(3):18-22.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
李丽丽,杨洪一来永才. 2014. 苹果茎痘病毒基因变异及重组分析. 河南农业科学, 43 (5):102-105.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
李丽丽, 杨洪一. 2014. 苹果茎痘病毒种群遗传多样性分析. 广东农业科学, 41 (6):93-95.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
|
刘欢, 吕兆瑞, 吴薇, 吴云锋. 2023. 柑橘叶斑驳病毒研究进展. 植物病理学报, 53 (2):155-163.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
刘成龙, 范旭东, 任芳, 张尊平, 胡国君, 董雅凤. 2024. 苹果病毒检测技术. 园艺学报, 51 (7):1580-1594.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
马将令, 王田利. 2021. 中国苹果产业规模化生产存在的突出问题及发展思考. 果树资源学报, 2 (3):69-73.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
夏炎, 黄松, 武雪莉, 刘一琪, 王苗苗, 宋春晖, 白团辉, 宋尚伟, 庞宏光, 焦健, 郑先波. 2022. 基于宏病毒组测序技术的苹果病毒病鉴定与分析. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1415-1428.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
续海红, 王燕飞, 窦彦鑫, 陈伟, 杨凯. 2021. 山西苹果褪绿叶斑病毒的分布及遗传多样性分析. 植物保护, 47 (6):75-82,92.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
袁彧伟, 张磊, 付崇毅, 孙平平, 武占敏, 马强, 李正男. 2021. 苹果3种潜隐病毒研究进展. 北方农业学报, 49 (4):83-97.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
张力支, 魏亚楠, 王宏新, 王磊. 2019. 我国苹果病毒病的现状及其检测技术的研究进展. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版), 35 (2):116-121,128.
|
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
|
赵玲玲, 宋来庆, 刘美英,
|
| [1] | 杜宜南, 冀志蕊, 丛佳林, 周宗山. 早熟苹果新品种‘华御1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 1-2. |
| [2] | 杜宜南, 丛佳林, 冀志蕊, 周宗山. 中熟苹果新品种‘华阳’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 3-4. |
| [3] | 朱钰, 刘肖烽, 周佳, 李静, 王强. 苹果新品种‘华优贝红’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 5-6. |
| [4] | 韩晓蕾, 马松亚, 康立群, 张彩霞. 苹果新品种‘中苹早红4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 7-8. |
| [5] | 马松亚, 张彩霞, 韩晓蕾, 田玉凤, 康立群. 优质小果型苹果‘苹优3号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 9-10. |
| [6] | 马松亚, 张彩霞, 韩晓蕾, 杨安, 康立群. 小果型苹果新品种‘苹优4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 11-12. |
| [7] | 张宗营, 王 平, 王 楠, 马明德, 刘文军, 邹 琦, 徐月华, 陈晓流, 毛志泉, 陈学森. 苹果紫红色芽变新品种‘八仙新富’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 1-2. |
| [8] | 朱 钰, 刘肖烽, 周 佳, 李 静, 王 强. 苹果新品种‘华优宝丰’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 3-4. |
| [9] | 杜丽君, 刘英材, 史妍妍, 汪洋, 李春晖, 何银涛, 王旭, 边传杰, 张满让. 丛枝菌根真菌对苹果品种耐盐碱的影响及缓解机理[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2410-2424. |
| [10] | 徐功勋, 闫帅, 何美琦, 马怀宇, 吕德国, 秦嗣军, 程存刚, 赵德英. 苹果抗寒性研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2021-2045. |
| [11] | 钟声远, 罗宇婷, 陈剑锋, 钟海丰, 陈宇华, 刘中华. 蝴蝶兰品种DUS测试数量性状分级及遗传多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1817-1827. |
| [12] | 李佐, 肖文芳, 陈和明, 吕复兵. 蝴蝶兰种质资源遗传多样性及核心种质构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1519-1529. |
| [13] | 孙佩, 张宏, 杨媛, 王华, 李茂福, 康岩慧, 孙向一, 金万梅. 基于SSR标记的蔷薇属种质资源遗传多样性分析及指纹图谱构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1539-1552. |
| [14] | 陈学森, 王楠, 张宗营, 张淑辉, 刘文军, 邹琦, 于蕾, 张静, 姜远茂, 胡大刚, 李媛媛, 毛志泉. 富营养强风味轻简化宜机化苹果育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1661-1676. |
| [15] | 田玉凤, 马松亚, 杨安, 韩晓蕾, 张彩霞. 苹果砧木B9再生体系的建立与优化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 947-958. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司