
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 1402-1418.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0745
梅煜琳1,2, 徐劲剑1, 蒋梦玥1, 尉俊海1, 宗宇1, 陈文荣1, 廖芳蕾1,2,*( ), 郭卫东1,2,*(
), 郭卫东1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-11-21
修回日期:2023-01-18
发布日期:2023-07-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
MEI Yulin1,2, XU Jinjian1, JIANG Mengyue1, YU Junhai1, ZONG Yu1, CHEN Wenrong1, LIAO Fanglei1,2,*( ), GUO Weidong1,2,*(
), GUO Weidong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-11-21
Revised:2023-01-18
Online:2023-07-26
Contact:
摘要:
以香橼(Citrus medica L.)为母本,佛手(C. medica var. L. sarcodactylis Swingle)为父本进行授粉杂交,将得到的种子进行培育获得19份材料。从佛手和香橼转录组数据筛选出SSR位点设计TP-M13-SSR分子标记引物,对19份材料进行基因分型。每对核心引物获得17 ~ 32个等位基因,平均等位基因数为24.188个。观测杂合度变化为0.188 ~ 1.000,多态性指数为0.944。19个F1代株系中17个确定为真杂种,杂交率为89.47%。通过影像分析F1代果形,指状果与柑果果形分离比为2︰3。佛手和香橼花芽石蜡切片观察发现,形成指状或柑果果形差异起始于现蕾期至现瓣期的心皮隆起。对现蕾期至花后3 d的佛手、香橼花芽转录组信息与心皮特征进行相关性分析,分离得到一批雌蕊形成相关基因;在即将开花的佛手、香橼及F1代雌蕊中进行qRT-PCR验证,分析这些基因与果形差异的关联性,WOX1基因在现蕾期和现瓣期的表达与指状特征相关。YABBY家族基因可与花发育C类和E类基因及WOX家族协同作用调控佛手指状果形建成。
梅煜琳, 徐劲剑, 蒋梦玥, 尉俊海, 宗宇, 陈文荣, 廖芳蕾, 郭卫东. 香橼与佛手F1杂种鉴定及果形差异分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(7): 1402-1418.
MEI Yulin, XU Jinjian, JIANG Mengyue, YU Junhai, ZONG Yu, CHEN Wenrong, LIAO Fanglei, GUO Weidong. Identification of F1 Hybrids and Analysis of Fruit Shape Difference Between Fingered Citron and Citron[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1402-1418.
| 引物序号 Primer code | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | (AT)*8 | F:<M13>-TAACCTAGCATCCTCCAC | R:TATGCGGGTAAATCTCGT | 184 |
| Z5 | (TC)*10 | F:<M13>-CATTGATTCTTTCCTTCG | R:AAAATTAGCCAGAAACGT | 247 |
| Z7 | (TA)*9 | F:<M13>-TGATCTCCTCTGGCGAATG | R:CCTCCTCGTCACCATCCA | 277 |
| Z15 | (TC)*6 | F:<M13>-TCCCCTTCATTTATCCTT | R:TTTTGTTGATGGCGTTGG | 172 |
| Z17 | (CT)*8 | F:<M13>-ATGCAAGCCGCTTTTCTC | R:ACCCAAGATTCTGGTCAGG | 203 |
| Z24 | (AT)*18 | F:<M13>-ACCAGTCCTACGCATCAC | R:CCCGATACCCTGGATTTT | 260 |
| Z52 | (TA)*12 | F:<M13>-CTCCCACTGTCCCTTCGT | R:GCTTGCTGAGCGGATTTA | 186 |
| Z54 | (AT)*14 | F:<M13>-CATTAGAGTTCATTGGGAATA | R:TACCTTACGTTTTGTCGC | 254 |
| Z92 | (CT)*12 | F:<M13>-TACGGTATCAATTCCTTC | R:GGCATTATCAGACCCAAA | 312 |
| Z124 | (AG)*23 | F:<M13>-CCGATCATCAGGGACTACTA | R:CATCTCCAGCACCATTCTT | 316 |
| Z131 | (CT)*9 | F:<M13>-TATAAGGCAAGTGGGGTGA | R:GTGGCAACAAGAATACAAGAT | 161 |
| Z171 | (TA)*17 | F:<M13>-CTAAAGCGATCTTGACATA | R:GGACGGGACTTACTACCAG | 252 |
| Z178 | (AT)*11 | F:<M13>-GAGAACTTTTGTTTATTGGAG | R:TTCTTTCATGCTTCCGTTC | 165 |
| Z198 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 201 |
| Z199 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 220 |
| Z204 | (TG)*9 | F:<M13>-TGCTGGAAAGGAACGAAAC | R:CATTGCATGGCTGCTCATA | 244 |
| M13通用引物 <FAM>或<HEX>-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT | ||||
| M13 universal primer | ||||
表1 16对SSR核心引物信息
Table 1 Information of 16 core SSR primers
| 引物序号 Primer code | 重复单元 Repeat motif | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | (AT)*8 | F:<M13>-TAACCTAGCATCCTCCAC | R:TATGCGGGTAAATCTCGT | 184 |
| Z5 | (TC)*10 | F:<M13>-CATTGATTCTTTCCTTCG | R:AAAATTAGCCAGAAACGT | 247 |
| Z7 | (TA)*9 | F:<M13>-TGATCTCCTCTGGCGAATG | R:CCTCCTCGTCACCATCCA | 277 |
| Z15 | (TC)*6 | F:<M13>-TCCCCTTCATTTATCCTT | R:TTTTGTTGATGGCGTTGG | 172 |
| Z17 | (CT)*8 | F:<M13>-ATGCAAGCCGCTTTTCTC | R:ACCCAAGATTCTGGTCAGG | 203 |
| Z24 | (AT)*18 | F:<M13>-ACCAGTCCTACGCATCAC | R:CCCGATACCCTGGATTTT | 260 |
| Z52 | (TA)*12 | F:<M13>-CTCCCACTGTCCCTTCGT | R:GCTTGCTGAGCGGATTTA | 186 |
| Z54 | (AT)*14 | F:<M13>-CATTAGAGTTCATTGGGAATA | R:TACCTTACGTTTTGTCGC | 254 |
| Z92 | (CT)*12 | F:<M13>-TACGGTATCAATTCCTTC | R:GGCATTATCAGACCCAAA | 312 |
| Z124 | (AG)*23 | F:<M13>-CCGATCATCAGGGACTACTA | R:CATCTCCAGCACCATTCTT | 316 |
| Z131 | (CT)*9 | F:<M13>-TATAAGGCAAGTGGGGTGA | R:GTGGCAACAAGAATACAAGAT | 161 |
| Z171 | (TA)*17 | F:<M13>-CTAAAGCGATCTTGACATA | R:GGACGGGACTTACTACCAG | 252 |
| Z178 | (AT)*11 | F:<M13>-GAGAACTTTTGTTTATTGGAG | R:TTCTTTCATGCTTCCGTTC | 165 |
| Z198 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 201 |
| Z199 | (TAA)*13 | F:<M13>-GTAACTGGTGGATTTGTCG | R:CCATAGTCGGACCCTCTTT | 220 |
| Z204 | (TG)*9 | F:<M13>-TGCTGGAAAGGAACGAAAC | R:CATTGCATGGCTGCTCATA | 244 |
| M13通用引物 <FAM>或<HEX>-TGTAAAACGACGGCCAGT | ||||
| M13 universal primer | ||||
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEP1 | Cm158770.1 | F:GCTTAGGCTTAGAGGAGTTG | R:GAATGAGCAGGTTGGTTG | 244 |
| SEP2 | Cm240370.1 | F:AGCGAACTCAGAGGAATC | R:ACCTAGTTGCTGCTCACC | 263 |
| SEP4 | Cm146780.1 | F:CCTGAGGAAGAAGTTGGAC | R:CGATAGAGGCTGAAAGAACC | 142 |
| SHP1 | Cm078390.1 | F:GGAATCGGCAGAGTCAGA | R:GCGTACTGGTGATTGGGT | 260 |
| SHP2 | Cm164940.1 | F:AATACTGGGTCTATCTGTGAA | R:TCTCGGCTATCTTTGCTC | 289 |
| SPL6 | Cm158790.1 | F:GACTCATCTGTTGACCCTT | R:CACTACCGACTTCACCATTA | 211 |
| SPL8 | Cm162720.1 | F:AGATGAAGCGACTCAAGAAT | R:GTGGGTGGGAGCGTAAGA | 286 |
| SPL9 | Cm119150.1 | F:TCTGATCGACTTCAGTGCATATC | R:AATTCCAGGACCAGAGAAACC | 208 |
| YABBY1A | Cm015380.1 | F:ATCCCAAATCCATCTCCGAAC | R:TGAATCGGTTGTACGCAGAG | 157 |
| YABBY1B | Cm112520.1 | F:ACTTCCCTCACATCCATTTCG | R:ACTACAACGAAACCCCAGC | 192 |
| YABBY4 | Cm075530.1 | F:CAAACATGGCTCACAAGGAAG | R:CTTCAAAGTTCCAAGCTCGC | 132 |
| YABBY5A | Cm147040.1 | F:TGCGAACACCCACTAACAAG | R:AATGGATGTGAGGGAAGTGTG | 198 |
| CRC | Cm158810.1 | F:CTCTCACCACTTCTCTCTTCTTC | R:AGAAGTTGCAGCGGACATAG | 204 |
| WOX1 | Cm275910.1 | F:ATTCTACTACGACTGCTATT | R:TCTCTCTTGTTTTGTTCACC | 190 |
| PRS | Cm223590.1 | F:CCATAAAGCAAGAGAGAGGC | R:AGCTGGGTTAGAAAAGGAAC | 190 |
| LUG | Cm111030.1 | F:CCCACCTCCTAAATGGCAATA | R:TAGCCGCATCATCCAAAGAA | 150 |
| AGL66 | Cm105600.1 | F:ATGTGAAGGAGAAATGCTGG | R:AATCTTTGGGTTGAGACTGG | 388 |
| AP2 | Cm077350.1 | F:AATCTAAAATAATTGCCCAA | R:AATAACTCAACTCACTCTGC | 324 |
| TIR1 | Cm233920.1 | F:GACGCAGCTCTACTCTCAGG | R:CTTTCTTGGTCCAGCAACAG | 204 |
| CsActin | Cs1g05000.1 | F:CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | R:ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG | 101 |
表2 qRT-PCR 引物
Table 2 Information of qRT-PCR primers
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 ID | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 产物大小/bp Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEP1 | Cm158770.1 | F:GCTTAGGCTTAGAGGAGTTG | R:GAATGAGCAGGTTGGTTG | 244 |
| SEP2 | Cm240370.1 | F:AGCGAACTCAGAGGAATC | R:ACCTAGTTGCTGCTCACC | 263 |
| SEP4 | Cm146780.1 | F:CCTGAGGAAGAAGTTGGAC | R:CGATAGAGGCTGAAAGAACC | 142 |
| SHP1 | Cm078390.1 | F:GGAATCGGCAGAGTCAGA | R:GCGTACTGGTGATTGGGT | 260 |
| SHP2 | Cm164940.1 | F:AATACTGGGTCTATCTGTGAA | R:TCTCGGCTATCTTTGCTC | 289 |
| SPL6 | Cm158790.1 | F:GACTCATCTGTTGACCCTT | R:CACTACCGACTTCACCATTA | 211 |
| SPL8 | Cm162720.1 | F:AGATGAAGCGACTCAAGAAT | R:GTGGGTGGGAGCGTAAGA | 286 |
| SPL9 | Cm119150.1 | F:TCTGATCGACTTCAGTGCATATC | R:AATTCCAGGACCAGAGAAACC | 208 |
| YABBY1A | Cm015380.1 | F:ATCCCAAATCCATCTCCGAAC | R:TGAATCGGTTGTACGCAGAG | 157 |
| YABBY1B | Cm112520.1 | F:ACTTCCCTCACATCCATTTCG | R:ACTACAACGAAACCCCAGC | 192 |
| YABBY4 | Cm075530.1 | F:CAAACATGGCTCACAAGGAAG | R:CTTCAAAGTTCCAAGCTCGC | 132 |
| YABBY5A | Cm147040.1 | F:TGCGAACACCCACTAACAAG | R:AATGGATGTGAGGGAAGTGTG | 198 |
| CRC | Cm158810.1 | F:CTCTCACCACTTCTCTCTTCTTC | R:AGAAGTTGCAGCGGACATAG | 204 |
| WOX1 | Cm275910.1 | F:ATTCTACTACGACTGCTATT | R:TCTCTCTTGTTTTGTTCACC | 190 |
| PRS | Cm223590.1 | F:CCATAAAGCAAGAGAGAGGC | R:AGCTGGGTTAGAAAAGGAAC | 190 |
| LUG | Cm111030.1 | F:CCCACCTCCTAAATGGCAATA | R:TAGCCGCATCATCCAAAGAA | 150 |
| AGL66 | Cm105600.1 | F:ATGTGAAGGAGAAATGCTGG | R:AATCTTTGGGTTGAGACTGG | 388 |
| AP2 | Cm077350.1 | F:AATCTAAAATAATTGCCCAA | R:AATAACTCAACTCACTCTGC | 324 |
| TIR1 | Cm233920.1 | F:GACGCAGCTCTACTCTCAGG | R:CTTTCTTGGTCCAGCAACAG | 204 |
| CsActin | Cs1g05000.1 | F:CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA | R:ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG | 101 |
| 重复类型 | 重复次数 Number of repeat | 总数 | 比例/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | >12 | Total | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸Dinucleotide | — | 712 | 415 | 283 | 243 | 166 | 101 | 59 | 150 | 2 129 | 43.37 |
| 三核苷酸Trinucleotide | 1 322 | 605 | 311 | 131 | 49 | 35 | 18 | 8 | 22 | 2 501 | 50.95 |
| 四核苷酸Tetranucleotide | 115 | 36 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 166 | 3.38 |
| 五核苷酸Pentanucleotide | 20 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0.63 |
| 六核苷酸Hexanucleotide | 59 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 1.67 |
| 总数Total | 1 516 | 1 374 | 743 | 420 | 295 | 203 | 119 | 67 | 172 | 4 909 | |
| 比例/% Percentage | 30.88 | 27.99 | 15.14 | 8.56 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 2.42 | 1.36 | 3.50 | 100.00 | |
表3 佛手转录组中的SSR类型及重复次数分布
Table 3 Distribution of SSRs with different repeat types and repeat numbers in transcriptomic sequence of fingered citron
| 重复类型 | 重复次数 Number of repeat | 总数 | 比例/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | >12 | Total | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸Dinucleotide | — | 712 | 415 | 283 | 243 | 166 | 101 | 59 | 150 | 2 129 | 43.37 |
| 三核苷酸Trinucleotide | 1 322 | 605 | 311 | 131 | 49 | 35 | 18 | 8 | 22 | 2 501 | 50.95 |
| 四核苷酸Tetranucleotide | 115 | 36 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 166 | 3.38 |
| 五核苷酸Pentanucleotide | 20 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 0.63 |
| 六核苷酸Hexanucleotide | 59 | 13 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 1.67 |
| 总数Total | 1 516 | 1 374 | 743 | 420 | 295 | 203 | 119 | 67 | 172 | 4 909 | |
| 比例/% Percentage | 30.88 | 27.99 | 15.14 | 8.56 | 6.01 | 4.14 | 2.42 | 1.36 | 3.50 | 100.00 | |
| 重复类型 | 重复基序 | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | Repeat motif | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸 | AG/CT | 55.61 |
| Dinucleotide | AC/GT | 15.45 |
| AT/AT | 21.18 | |
| CG/CG | 0.75 | |
| 三核苷酸 | AAG/CTT | 24.32 |
| Trinucleotide | AGG/CCT | 4.37 |
| ACC/GGT | 5.19 | |
| AGC/CTG | 11.69 | |
| ATC/ATG | 16.06 | |
| CCG/CGG | 3.30 | |
| ACG/CGT | 2.48 | |
| AAC/GTT | 7.20 | |
| AAT/ATT | 24.20 | |
| ACT/AGT | 1.18 |
表4 佛手转录组中二核苷酸和三核苷酸不同重复基序分布比例
Table 4 Percentages of different repeat motifs among dinucleotide and trinucleotide repeats in transcriptomic sequence of fingered citron
| 重复类型 | 重复基序 | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|
| Repeat type | Repeat motif | Percentage |
| 二核苷酸 | AG/CT | 55.61 |
| Dinucleotide | AC/GT | 15.45 |
| AT/AT | 21.18 | |
| CG/CG | 0.75 | |
| 三核苷酸 | AAG/CTT | 24.32 |
| Trinucleotide | AGG/CCT | 4.37 |
| ACC/GGT | 5.19 | |
| AGC/CTG | 11.69 | |
| ATC/ATG | 16.06 | |
| CCG/CGG | 3.30 | |
| ACG/CGT | 2.48 | |
| AAC/GTT | 7.20 | |
| AAT/ATT | 24.20 | |
| ACT/AGT | 1.18 |
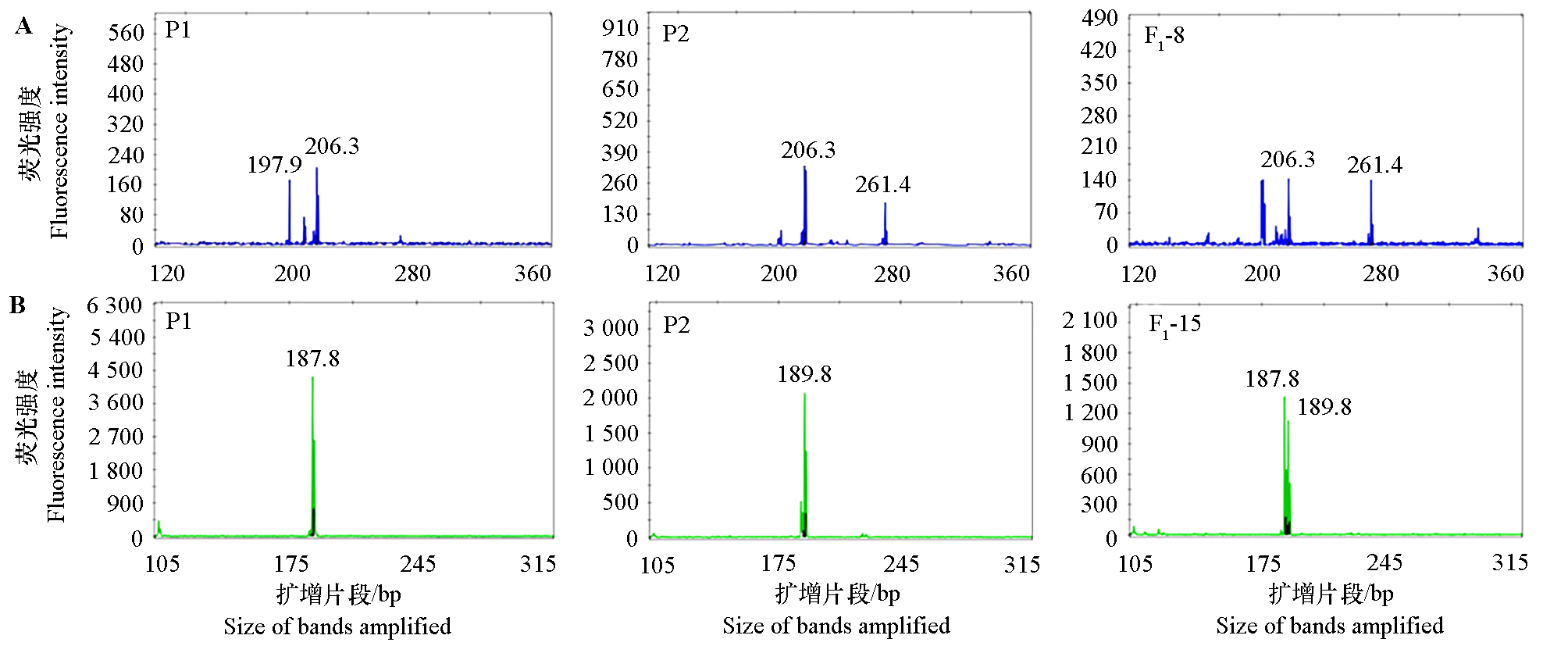
图1 部分佛手(P1)、香橼(P2)及其杂交F1代SSR位点的电泳图谱 A:Z5引物在亲本及F1-8中的扩增产物;B:Z15引物在亲本及F1-15中的扩增产物。
Fig. 1 Electropherogram of SSR locus and amplified allele sizes in base pairs of fingered citron(P1),citron(P2)and hybrid F1 lines A:The amplified products obtained in parents and F1-8 with the primer Z5;B:The amplified products obtained in parents and F1-15 with the primer Z15.
| 引物序号 Primer code | Na观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles | Ne有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles | Ho观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity | He期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity | Pi多态性信息量 Polymorphism information content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.981 | 0.956 |
| Z5 | 18 | 16 | 0.188 | 0.966 | 0.932 |
| Z7 | 17 | 14 | 0.429 | 0.963 | 0.924 |
| Z15 | 20 | 21 | 0.667 | 0.958 | 0.932 |
| Z17 | 28 | 17 | 0.941 | 0.988 | 0.957 |
| Z24 | 25 | 18 | 0.611 | 0.968 | 0.938 |
| Z52 | 19 | 14 | 0.929 | 0.968 | 0.930 |
| Z54 | 27 | 20 | 0.750 | 0.981 | 0.954 |
| Z92 | 25 | 19 | 0.526 | 0.977 | 0.949 |
| Z124 | 17 | 16 | 0.438 | 0.948 | 0.912 |
| Z131 | 32 | 21 | 0.952 | 0.986 | 0.961 |
| Z171 | 25 | 19 | 0.579 | 0.974 | 0.946 |
| Z178 | 26 | 19 | 0.474 | 0.982 | 0.954 |
| Z198 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.953 |
| Z199 | 30 | 21 | 0.762 | 0.985 | 0.960 |
| Z204 | 22 | 20 | 0.550 | 0.967 | 0.940 |
| 均值 Mean | 24.188 | 18.563 | 0.675 | 0.973 | 0.944 |
表5 SSR核心引物在F1代中的遗传多样性
Table 5 Genetic diversity of F1 hybrids as revealed by core SSR primers
| 引物序号 Primer code | Na观测等位基因数 Observed number of alleles | Ne有效等位基因数 Effective number of alleles | Ho观测杂合度 Observed heterozygosity | He期望杂合度 Expected heterozygosity | Pi多态性信息量 Polymorphism information content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.981 | 0.956 |
| Z5 | 18 | 16 | 0.188 | 0.966 | 0.932 |
| Z7 | 17 | 14 | 0.429 | 0.963 | 0.924 |
| Z15 | 20 | 21 | 0.667 | 0.958 | 0.932 |
| Z17 | 28 | 17 | 0.941 | 0.988 | 0.957 |
| Z24 | 25 | 18 | 0.611 | 0.968 | 0.938 |
| Z52 | 19 | 14 | 0.929 | 0.968 | 0.930 |
| Z54 | 27 | 20 | 0.750 | 0.981 | 0.954 |
| Z92 | 25 | 19 | 0.526 | 0.977 | 0.949 |
| Z124 | 17 | 16 | 0.438 | 0.948 | 0.912 |
| Z131 | 32 | 21 | 0.952 | 0.986 | 0.961 |
| Z171 | 25 | 19 | 0.579 | 0.974 | 0.946 |
| Z178 | 26 | 19 | 0.474 | 0.982 | 0.954 |
| Z198 | 28 | 21 | 1.000 | 0.978 | 0.953 |
| Z199 | 30 | 21 | 0.762 | 0.985 | 0.960 |
| Z204 | 22 | 20 | 0.550 | 0.967 | 0.940 |
| 均值 Mean | 24.188 | 18.563 | 0.675 | 0.973 | 0.944 |

图2 佛手与香橼及其部分杂交F1代果形 P1:母本香橼;P2:父本佛手; F1-4为F1代柑果形;F1-7为双亲中间形;F1-2,F1-6,F1-10为F1代指状形。
Fig. 2 The phenotype of fruit from fingered citron, citron and some F1 hybrids P1:Maternal citron;P2:Paternal fingered citron;F1-4 is hesperidium type;F1-7 is parents intermediate type;F1-2,F1-6 and F1-10 show finger fruit type.

图4 佛手与香橼现蕾期、现瓣期及半白期花芽石蜡切片 A(a) ~ C(c):现蕾期1 ~ 3 mm花芽;D(d) ~ E(e):现瓣期4 mm及5 mm花芽;F(f):灯笼期7 mm花芽出现胚珠分化;St:雄蕊原基;Pe:花瓣原基;Pi:雌蕊原基;Ca:心皮;方框内是胚珠。
Fig. 4 Paraffin sections of the visible bud stage,the petals emerging stage and the petals turning white stage of fingered citron and citron A(a)-C(c):1-3 mm flower buds in the visible bud stage;D(d)-E(e):4 mm and 5 mm flower buds in petals emerging stage;F(f):Ovule differentiation occurred in 7 mm flower buds at lantern petal stage;St:The stamen primordium;Pe:The petal primordium;Pi:The pistil primordium;Ca:The carpel;Ovules are in the black block.

图5 佛手与香橼转录组差异基因的热图分析 S1:现蕾期;S2:现瓣期;S3:即将开放期;S4:开花后3 d。
Fig. 5 Heat map analysis of differential genes from the transcriptome data of fingered citron and citron S1:Visible bud stage;S2:Petals emerging stage;S3:Pre-anthesis stage;S4:The 3 days after anthesis.
| 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | |||
| SEP1 | -0.358 | 0.086 | YABBY4 | 0.501 | 0.258 | |
| SEP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | YABBY5A | 0.645 | 0.430 | |
| SEP4 | 0.788* | -0.430 | CRC | 0.358 | 0.775 | |
| SHP1 | -0.072 | -0.775* | WOX1 | 0.788* | -0.775* | |
| SHP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | PRS | 0.620 | 0.430 | |
| SPL6 | -0.358 | 0.775* | LUG | -0.072 | -0.775* | |
| SPL8 | -0.501 | -0.430 | AGL66 | -0.358 | 0.086 | |
| SPL9 | 0.501 | 0.258 | AP2 | -0.501 | -0.602 | |
| YABBY1A | 0.358 | 0.258 | TIR1 | 0.501 | 0.775* | |
| YABBY1B | 0.501 | 0.258 | ||||
表6 差异基因表达水平与心皮特征相关性分析
Table 6 Correlation analysis between the expression level of genes and the carpel feature
| 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | 基因 Gene | 相关系数 Correlation coefficient | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | 现瓣期 Petals emerging stage | 即将开放期 Pre-anthesis stage | |||
| SEP1 | -0.358 | 0.086 | YABBY4 | 0.501 | 0.258 | |
| SEP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | YABBY5A | 0.645 | 0.430 | |
| SEP4 | 0.788* | -0.430 | CRC | 0.358 | 0.775 | |
| SHP1 | -0.072 | -0.775* | WOX1 | 0.788* | -0.775* | |
| SHP2 | -0.645 | -0.775* | PRS | 0.620 | 0.430 | |
| SPL6 | -0.358 | 0.775* | LUG | -0.072 | -0.775* | |
| SPL8 | -0.501 | -0.430 | AGL66 | -0.358 | 0.086 | |
| SPL9 | 0.501 | 0.258 | AP2 | -0.501 | -0.602 | |
| YABBY1A | 0.358 | 0.258 | TIR1 | 0.501 | 0.775* | |
| YABBY1B | 0.501 | 0.258 | ||||

图6 差异基因在即将开放期的佛手、香橼及F1代雌蕊中的表达分析
Fig. 6 Expression analysis of differential expressed genes in fingered citron, citron and F1 generation hybrid in the pre-anthesis stage LSD,P < 0.05.
| 基因 Gene | AGL66 | AP2 | CRC | LUG | PRS | SEP1 | SEP2 | SEP4 | SHP1 | SHP2 | SPL6 | SPL9 | WOX1 | YABBY1A | YABBY1B | YABBY4 | YABBY5A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGL66 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| AP2 | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CRC | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| LUG | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| PRS | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SEP1 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1 | |||||||||||
| SEP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||||
| SEP4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||
| SHP1 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||
| SHP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | |||||||
| SPL6 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | 1 | ||||||
| SPL9 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1.000** | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.333 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||
| WOX1 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||
| YABBY1A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1 | |||
| YABBY1B | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||
| YABBY4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |
| YABBY5A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 1 |
表7 差异基因在F1代杂交后代及父母本的表达相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis of differential genes expression between F1 generation hybrid and parent
| 基因 Gene | AGL66 | AP2 | CRC | LUG | PRS | SEP1 | SEP2 | SEP4 | SHP1 | SHP2 | SPL6 | SPL9 | WOX1 | YABBY1A | YABBY1B | YABBY4 | YABBY5A |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGL66 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| AP2 | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| CRC | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| LUG | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| PRS | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| SEP1 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1 | |||||||||||
| SEP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||||
| SEP4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |||||||||
| SHP1 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||||||||
| SHP2 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1 | |||||||
| SPL6 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | -0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.333 | 1.000** | 1 | ||||||
| SPL9 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | 1.000** | 0.000 | 0.000 | -0.333 | 0.000 | 0.333 | -0.333 | -0.333 | 1 | |||||
| WOX1 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 1 | ||||
| YABBY1A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1 | |||
| YABBY1B | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.333 | 0.667 | 1 | ||
| YABBY4 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1 | |
| YABBY5A | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 1.000** | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 1.000** | 0.667 | 1.000** | 1 |
| [1] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.126.11.2387 pmid: 10225998 |
| [2] |
|
|
陈民管. 2014. 佛手坐果及果形发育的初步研究[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.126.12.2715 pmid: 10331982 |
| [4] |
|
|
陈小灵, 王念, 朱延林. 2012. 植物返祖现象研究. 上海农业学报, 28 (1):102-105.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00331 URL |
| [7] |
|
|
董清华, 王西成, 赵密珍, 宋长年, 葛安静, 王静. 2011. 草莓EST-SSR标记开发及在品种遗传多样性分析中的应用. 中国农业科学, 44 (17):3603-3612.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.17.013 |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90551-9 pmid: 1675158 |
| [9] |
Editorial Committee of flora of China,Chinese Academy of Sciences. 1997. Flora of China. 43 (2). Beijing:Science Press:184. (in Chinese)
|
|
中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会. 1997. 中国植物志. 43 (2). 北京:科学出版社:184.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
房经贵, 章镇, 马正强, 刘大钧, 王三红, Lavi U. 2000. AFLP标记在两个芒果品种间杂交Fl代的多态性及分离方式. 中国农业科学, 33 (3):19-24.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2000-33-3-22-27 |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0675 |
|
方茜, 张园园, 杨钰婷, 黄苗苗, 符巧丽, 周慧莎, 陈文荣, 宗宇, 郭卫东. 2018. 越橘叶片转录组SSR发掘及其多态性研究. 园艺学报, 45 (7):1359-1370.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0675 |
|
| [12] |
|
|
方治伟, 李论. 2018. SSR分型技术研究进展. 生物化工, 4 (1):118-121.
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.01600 URL |
| [14] |
|
|
郭吉春, 叶乃兴, 何孝延. 2004. 茶树杂交一代展叶期的遗传变异. 茶叶科学,(4):255-259.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
韩国辉, 向素琼, 汪卫星, 魏旭, 何波, 李晓林, 梁国鲁. 2010. 沙田柚杂交后代群体的 SSR 鉴定与遗传多样性分析. 中国农业科学, 43 (22):4678-4686.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
韩晓霞. 2017. YABBY5和CRC基因在佛手果实发育中的功能初探[硕士论文]. 金华: 浙江师范大学.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1242/dev.124.19.3845 pmid: 9367440 |
| [18] |
|
|
胡文舜, 黄爱萍, 姜帆, 蒋际, 陈秀萍, 郑少泉. 2015. 龙眼正反交后代的SSR鉴定及遗传多样性分析. 园艺学报, 42 (10):1899-1908.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0131 |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 16625833 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02778.x pmid: 21564987 |
| [21] |
pmid: 16391668 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.026666 URL |
| [23] |
|
|
李会勇, 王天宇, 黎裕, 石云素, 宋艳春, 陆平. 2005. TP-M13自动荧光检测法在高粱SSR基因型鉴定中的应用. 物遗传资源学报, 6 (1):68-70.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
李响, 杨楠, 赵凯歌, 陈玉星, 唐锐君, 陈龙清. 2013. 蜡梅转录组EST-SSR标记开发与引物筛选. 北京林业大学学报, 35 (1):25-32.
|
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-35 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/s11032-017-0693-x URL |
| [27] |
|
|
廖芳蕾, 陈民管, 桑丹, 陈文荣, 郭卫东. 2013. 佛手种质资源遗传多样性的ISSR 分析. 园艺学报, 40 (11):2222-2228.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0502 |
|
廖芳蕾, 陈泽宇, 徐启越, 杨莉, 陈文荣, 郭卫东. 2018. 果形建成基因研究进展及其对佛手果形发育研究的启示. 园艺学报, 45 (9):1701-1714.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0502 |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0358 |
|
廖芳蕾, 韩晓霞, 陈文荣, 郭艳, 张晨晓, 陈泽宇, 周亚艳, 郭卫东. 2016. 佛手果形发育观察及果形相关基因表达分析. 园艺学报, 43 (11):2141-2150.
|
|
| [30] |
doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211012.102 pmid: 34951256 |
|
刘航秀, 冯迪, 龙春瑞, 周先艳, 刘红明, 杨虹霞, 杜玉霞, 郭丽娜, 付小猛, 马兆成, 岳建强. 2021. 枸橼药用植物果实变异及地理分布研究. 中国中药杂志, 46 (23):6289-6293.
pmid: 34951256 |
|
| [31] |
|
|
刘升锐. 2016. 柑橘高密度遗传连锁图谱的构建及落叶性状的QTL定位[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
罗球, 张庆祥. 2020. SSR技术在果树上的应用. 江西农业,(10):36-38.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.113209 pmid: 23821642 |
| [34] |
doi: 10.1038/72708 pmid: 10657137 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1086/337805 URL |
| [36] |
|
|
王彬, 刘丽丽, 吴效芳. 2019. 孟德尔遗传定律中2种分离比的2个认识误区. 生物学通报, 54 (12):40-41.
|
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa574 URL |
| [38] |
|
|
王静毅, 陈业渊, 刘伟良, 武耀廷. 2008. 香蕉EST-SSRs标记的开发与应用. 遗传, 30 (7):933-940.
|
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0519-2 URL |
| [40] |
|
|
伍涵宇. 2019. 光周期响应基因StYABBY1调控光合作用功能研究[硕士论文]. 银川: 宁夏大学.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
鄢秀芹, 鲁敏, 安华明. 2015. 刺梨转录组SSR信息分析及其分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 42 (2):341-349.
|
|
| [42] |
|
|
杨梦婷, 黄洲, 干建平, 徐君驰, 庞基良. 2019. SSR分子标记的研究进展. 杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 18 (4):429-436.
|
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-253 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1300240 URL |
| [45] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0659 |
|
张庆田, 李晓艳, 杨义明, 范书田, 艾军. 2016. 蓝靛果忍冬转录组SSR信息分析及其分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 43 (3):557-563.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2015-0659 |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060277 URL |
|
张田, 李作洲, 刘亚令, 姜正旺, 黄宏文. 2007. 猕猴桃属植物的cpSSR遗传多样性及其同域分布物种的杂交渐渗与同塑. 生物多样性, 15 (1):1-22.
doi: 10.1360/biodiv.060277 |
|
| [47] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0377 |
|
赵玉洁, 刘翠玉, 招雪晴, 汪钰莹, 闫明, 苑兆和. 2021. 石榴花器官发育相关基因PgWUS和PgBEL1克隆及其时空表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (2):355-366.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0377 |
|
| [48] |
|
|
宗宇, 王月, 朱友银, 邵姁, 李永强, 郭卫东. 2016. 基于中国樱桃转录组的SSR分子标记开发与鉴定. 园艺学报, 43 (8):1566-1576.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2016-0005 |
| [1] | 聂兴华, 张 煜, 刘 松, 杨佳宾, 郝雅琼, 刘 阳, 秦 岭, 邢 宇. 基于基因组重测序的野生板栗遗传特征和分类地位研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(8): 1622-1636. |
| [2] | 孙泽硕, 蒋冬月, 柳新红, 沈鑫, 李因刚, 屈雨飞, 李永华. 基于SSR标记的42份樱花品种的聚类分析及DNA指纹图谱构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 657-668. |
| [3] | 王瑞, 洪文娟, 罗华, 赵丽娜, 陈颖, 王君. 石榴品种SSR指纹图谱构建及杂种父本鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 265-278. |
| [4] | 刘艺平, 倪梦辉, 吴芳芳, 刘红利, 贺丹, 孔德政. 荷花花器官性状与SSR标记的关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 103-115. |
| [5] | 李超, 杨英, 陈伟, 郑贺云, 廖新福, 孙玉萍. 西州密系列甜瓜SSR指纹图谱构建及聚类分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 622-632. |
| [6] | 聂兴华, 李伊然, 田寿乐, 王雪峰, 苏淑钗, 曹庆芹, 邢宇, 秦岭. 中国板栗品种(系)DNA指纹图谱构建及其遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2313-2324. |
| [7] | 陈明堃, 陈璐, 孙维红, 马山虎, 兰思仁, 彭东辉, 刘仲健, 艾叶. 建兰种质资源遗传多样性分析及核心种质构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 175-186. |
| [8] | 宋芸, 贾孟君, 曹亚萍, 李政, 贺嘉欣, 王勇飞, 张鑫瑞, 乔永刚. 连翘叶绿体基因组特征分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 187-199. |
| [9] | 王鑫, 李明阳, 田琳, 刘冬云. 利用ISSR标记及rDNA-ITS序列分析河北省野生铁线莲的亲缘关系[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1755-1767. |
| [10] | 王小青, 梅煜琳, 刘金莲, 徐劲剑, 李永强, 陈文荣, 宗宇, 邵文科, 廖芳蕾, 郭卫东. 佛手新品种‘翠指’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1639-1640. |
| [11] | 丁云花, Budahn Holger, 赵泓, 赵岫云. 白菜与甘蓝型油菜—萝卜F染色体附加系回交BC1中萝卜F染色体的精准鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1295-1303. |
| [12] | 赵青, 都真真, 李锡香, 宋江萍, 张晓辉, 阳文龙, 贾会霞, 王海平. 利用SSRseq分子标记的大蒜种质资源遗传多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1397-1408. |
| [13] | 江锡兵, 章平生, 徐阳, 吴聪连, 张东北, 龚榜初, 吴开云, 赖俊声. 栗杂交F1代SSR标记遗传多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 897-907. |
| [14] | 董艺, 冯羽飞, 许忠民, 王世民, 唐鸿吕, 黄炜. SSR标记遗传距离与结球甘蓝杂种优势的关系分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 934-946. |
| [15] | 蒋爽, 张学英, 安海山, 徐芳杰, 章加应. 枇杷全基因组SSR标记开发及其多态性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 1013-1022. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司