
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 103-115.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0919
刘艺平1,2, 倪梦辉1, 吴芳芳1, 刘红利1,2, 贺丹1,2, 孔德政1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-14
修回日期:2022-11-01
出版日期:2023-01-25
发布日期:2023-01-18
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:基金资助:
LIU Yiping1,2, NI Menghui1, WU Fangfang1, LIU Hongli1,2, HE Dan1,2, KONG Dezheng1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-09-14
Revised:2022-11-01
Online:2023-01-25
Published:2023-01-18
Contact:
*(E-mail:摘要:
为了挖掘与荷花花器官性状显著相关的分子标记,对60份荷花种质资源的18个花器官性状进行鉴定描述,用筛选得到的16个具有多态性的SSR标记进行遗传多样性分析,并使用TASSEL5.0软件的广义线性模型(general linear mode,GLM)和混合线性模型(mixed linear mode,MLM)对18个花器官性状进行关联分析。研究结果显示,16个SSR标记以二核苷酸重复和三核苷酸重复类型为主,两者占比均为43.75%;在60份荷花种质中扩增出105个多态性位点,平均多态性位点为6.5625;引物多态性含量(PIC)为0.2898 ~ 0.7029,平均值为0.5242;Shannon’s信息指数(I)平均值为1.1548;观测杂合度(Ho)和期望杂合度(He)平均值分别为0.4308和0.5819。60份荷花品种的遗传相似系数(GS)为0.38 ~ 0.92,平均值为0.67;在GS为0.60处将60份荷花种质分为3大种群。GLM模型分析共检测到31个SSR位点,表型解释率为15.72% ~ 76.76%;MLM模型分析共检测到13个SSR位点,表型解释率为20.25% ~ 78.40%;其中有10个位点被二者同时检测到。此外有9个SSR标记的位点在2 ~ 5个花器官性状中被检测到,表现出显著的“一因多效”现象。
中图分类号:
刘艺平, 倪梦辉, 吴芳芳, 刘红利, 贺丹, 孔德政. 荷花花器官性状与SSR标记的关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 103-115.
LIU Yiping, NI Menghui, WU Fangfang, LIU Hongli, HE Dan, KONG Dezheng. Association Analysis of Organ Traits with SSR Markers in Lotus(Nelumbo nucifera)[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 103-115.
| 来源 Origin | 编号 Code | 品种/品系名称 Cultivar/Line name | 来源 Origin | 编号 Code | 品种/品系名称 Cultivar/Line name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国莲 | 1 | 矮牡丹 Aimudan | 中国莲 | 31 | 雪翠 Xuecui | |
| Nelumbo nucifera | 2 | 粉龙莲 Fenlonglian | N. nucifera Gaertn. | 32 | 瑰丽Guili | |
| Gaertn. | 3 | 红思莲 Hongsilian | 33 | 小红荷Xiaohonghe | ||
| 4 | 中山红台Zhongshan Hongtai | 34 | 淡黄红光Danhuang Hongguang | |||
| 5 | 彩云莲 Caiyunlian | 35 | 翡翠10号 Feicui 10 | |||
| 6 | 红重中型Hongchongzhongxing | 36 | 艳阳天Yanyangtian | |||
| 7 | 天地红 Tiandihong | 37 | 鸳鸯出水Yuanyangchushui | |||
| 8 | 高风亮节Gaofengliangjie | 38 | 杏黄Xinghuang | |||
| 9 | 披针粉Pizhenfen | 39 | 太空娇容Taikong Jiaorong | |||
| 10 | 玉翠莲 Yucuilian | 40 | 大紫玉 Daziyu | |||
| 11 | 晚霞 Wanxia | 41 | 娇红 Jiaohong | |||
| 12 | 新披针红Xinpizhenhong | 42 | 山东红牡丹Shandong Hongmudan | |||
| 13 | 粉红重瓣Fenhong Chongban | 43 | 泰泊白玉 Taibo Baiyu | |||
| 14 | 素雅 Suya | 44 | 红云 Hongyun | |||
| 15 | 紫光阁 Ziguang’ge | 45 | 紫重阳 Zichongyang | |||
| 16 | 新深情 Xinshenqing | 46 | 红彩云 Hongcaiyun | |||
| 17 | 乳燕欢 Ruyanhuan | 47 | 桌上珍Zhuoshangzhen | |||
| 18 | 光辉 Guanghui | 48 | 墨红1号 Mohong 1 | |||
| 19 | 芙蓉秋色Furong Qiuse | 49 | 南阳黄Nanyanghuang | |||
| 20 | 惊艳 Jingyan | 中国莲与美洲黄莲 | 50 | 金苹果 Jinpinghuo | ||
| 21 | 红裙 Hongqun | 杂交种 | 51 | 红莺 Hongying | ||
| 22 | 红飞菊 Hongfeiju | N. nucifera Gaertn. × | 52 | 莺莺 Yingying | ||
| 23 | 粉团儿 Fentuan’er | N. lutea Pear. | 53 | 黄鹂 Huangli | ||
| 24 | 月华 Yuehua | 54 | 冰娇 Bingjiao | |||
| 25 | 粉霞 Fenxia | 55 | 白兰媚 Bailanmei | |||
| 26 | 露华浓 Luhuanong | 56 | 雪涛 Xuetao | |||
| 27 | 玛瑙红 Ma’naohong | 57 | 友谊牡丹 Youyi Mudan | |||
| 28 | 红牡丹 Hongmudan | 58 | 新云锦 Xinyunjin | |||
| 29 | 红绸 Hongchou | 59 | 雨花情 Yuhuaqing | |||
| 30 | 海南 Hainan | 60 | 黄帅 Huangshuai |
表1 荷花材料的名称和来源
Table 1 The name and origin of lotus materials
| 来源 Origin | 编号 Code | 品种/品系名称 Cultivar/Line name | 来源 Origin | 编号 Code | 品种/品系名称 Cultivar/Line name | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中国莲 | 1 | 矮牡丹 Aimudan | 中国莲 | 31 | 雪翠 Xuecui | |
| Nelumbo nucifera | 2 | 粉龙莲 Fenlonglian | N. nucifera Gaertn. | 32 | 瑰丽Guili | |
| Gaertn. | 3 | 红思莲 Hongsilian | 33 | 小红荷Xiaohonghe | ||
| 4 | 中山红台Zhongshan Hongtai | 34 | 淡黄红光Danhuang Hongguang | |||
| 5 | 彩云莲 Caiyunlian | 35 | 翡翠10号 Feicui 10 | |||
| 6 | 红重中型Hongchongzhongxing | 36 | 艳阳天Yanyangtian | |||
| 7 | 天地红 Tiandihong | 37 | 鸳鸯出水Yuanyangchushui | |||
| 8 | 高风亮节Gaofengliangjie | 38 | 杏黄Xinghuang | |||
| 9 | 披针粉Pizhenfen | 39 | 太空娇容Taikong Jiaorong | |||
| 10 | 玉翠莲 Yucuilian | 40 | 大紫玉 Daziyu | |||
| 11 | 晚霞 Wanxia | 41 | 娇红 Jiaohong | |||
| 12 | 新披针红Xinpizhenhong | 42 | 山东红牡丹Shandong Hongmudan | |||
| 13 | 粉红重瓣Fenhong Chongban | 43 | 泰泊白玉 Taibo Baiyu | |||
| 14 | 素雅 Suya | 44 | 红云 Hongyun | |||
| 15 | 紫光阁 Ziguang’ge | 45 | 紫重阳 Zichongyang | |||
| 16 | 新深情 Xinshenqing | 46 | 红彩云 Hongcaiyun | |||
| 17 | 乳燕欢 Ruyanhuan | 47 | 桌上珍Zhuoshangzhen | |||
| 18 | 光辉 Guanghui | 48 | 墨红1号 Mohong 1 | |||
| 19 | 芙蓉秋色Furong Qiuse | 49 | 南阳黄Nanyanghuang | |||
| 20 | 惊艳 Jingyan | 中国莲与美洲黄莲 | 50 | 金苹果 Jinpinghuo | ||
| 21 | 红裙 Hongqun | 杂交种 | 51 | 红莺 Hongying | ||
| 22 | 红飞菊 Hongfeiju | N. nucifera Gaertn. × | 52 | 莺莺 Yingying | ||
| 23 | 粉团儿 Fentuan’er | N. lutea Pear. | 53 | 黄鹂 Huangli | ||
| 24 | 月华 Yuehua | 54 | 冰娇 Bingjiao | |||
| 25 | 粉霞 Fenxia | 55 | 白兰媚 Bailanmei | |||
| 26 | 露华浓 Luhuanong | 56 | 雪涛 Xuetao | |||
| 27 | 玛瑙红 Ma’naohong | 57 | 友谊牡丹 Youyi Mudan | |||
| 28 | 红牡丹 Hongmudan | 58 | 新云锦 Xinyunjin | |||
| 29 | 红绸 Hongchou | 59 | 雨花情 Yuhuaqing | |||
| 30 | 海南 Hainan | 60 | 黄帅 Huangshuai |
| 性状 Trait | 遗传多样性指数 H’ | 性状描述级别 Character description level | 资源数 Accessions | 分布频率/% Distribution frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花色 Flower color | 2.19 | 白色 Black 黄色 Yellow 粉红 Pink 红色 Red 复色 Recolor | 12 5 18 17 8 | 20.00 8.33 30.00 28.33 13.33 |
| 花型 Flower type | 1.41 | 单瓣 Single flower 半重瓣 Semidouble flower 重瓣 Double flower 重台 Proliferation Flower | 2 7 39 13 | 3.33 11.67 65.00 21.67 |
| 花态 Flower form | 1.73 | 杯状 Cup-shape 碗状 Bowl shape 飞舞状 Flying shape 碟状 Disc shape 叠球状 Stacked sphere shape | 9 31 1 16 3 | 15.00 51.67 1.67 26.67 5.00 |
| 花蕾色 Bud color | 1.40 | 绿色 Green 红绿 Red green 红色 Red | 15 35 11 | 25.00 58.33 18.33 |
| 花蕾形状 Bud shape | 1.04 | 长卵圆锥形 Long cone shape 卵圆锥形 Cone shape 卵球形 Egg ball shape | 5 45 10 | 8.33 25.00 26.67 |
| 雌蕊泡化程度 Degree of pistil vesiculation | 1.55 | 正常 Normal 部分泡化 Partial bubbling 全泡化 Full bubbling 全瓣化 Total petalization | 32 15 12 1 | 53.33 25.00 20.00 1.67 |
| 成熟花托形状 Mature receptacle shape | 1.76 | 喇叭形 Trumpet shape 倒圆锥形 Inverted cone shape 伞形 Umbrella shape 扁球形 Oblate shape 碗形 Bowl shape | 7 31 1 5 16 | 11.00 51.67 1.67 8.33 26.67 |
表2 荷花花器官7个质量性状分类及资源分布
Table 2 Grades and distribution of 7 quality characters of lotus flower organs
| 性状 Trait | 遗传多样性指数 H’ | 性状描述级别 Character description level | 资源数 Accessions | 分布频率/% Distribution frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花色 Flower color | 2.19 | 白色 Black 黄色 Yellow 粉红 Pink 红色 Red 复色 Recolor | 12 5 18 17 8 | 20.00 8.33 30.00 28.33 13.33 |
| 花型 Flower type | 1.41 | 单瓣 Single flower 半重瓣 Semidouble flower 重瓣 Double flower 重台 Proliferation Flower | 2 7 39 13 | 3.33 11.67 65.00 21.67 |
| 花态 Flower form | 1.73 | 杯状 Cup-shape 碗状 Bowl shape 飞舞状 Flying shape 碟状 Disc shape 叠球状 Stacked sphere shape | 9 31 1 16 3 | 15.00 51.67 1.67 26.67 5.00 |
| 花蕾色 Bud color | 1.40 | 绿色 Green 红绿 Red green 红色 Red | 15 35 11 | 25.00 58.33 18.33 |
| 花蕾形状 Bud shape | 1.04 | 长卵圆锥形 Long cone shape 卵圆锥形 Cone shape 卵球形 Egg ball shape | 5 45 10 | 8.33 25.00 26.67 |
| 雌蕊泡化程度 Degree of pistil vesiculation | 1.55 | 正常 Normal 部分泡化 Partial bubbling 全泡化 Full bubbling 全瓣化 Total petalization | 32 15 12 1 | 53.33 25.00 20.00 1.67 |
| 成熟花托形状 Mature receptacle shape | 1.76 | 喇叭形 Trumpet shape 倒圆锥形 Inverted cone shape 伞形 Umbrella shape 扁球形 Oblate shape 碗形 Bowl shape | 7 31 1 5 16 | 11.00 51.67 1.67 8.33 26.67 |
| 性状 Trait | 最小值 Max | 最大值 Min | 平均值 Mean | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | 变异系数/% CV | 遗传多样性指数 H’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花期/d Flowering period | 29.00 | 58.00 | 49.16 ± 10.32 | -1.17 | 0.22 | 20.98 | 5.87 |
| 着花密度Flowering density | 3.00 | 12.00 | 6.86 ± 1.42 | -0.86 | 0.25 | 35.34 | 5.82 |
| 花高/cm Flower height | 39.70 | 119.40 | 64.74 ± 17.69 | 0.94 | 1.11 | 27.33 | 5.85 |
| 花冠直径/cm Corolla diameter | 5.00 | 18.50 | 11.09 ± 3.23 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 29.13 | 5.85 |
| 花被片数量Number of tepals | 19.00 | 264.00 | 106.42 ± 36.35 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 43.56 | 5.77 |
| 雄蕊数Number of stamens | 5.00 | 140.00 | 54.56 ± 24.49 | -0.21 | 0.74 | 63.22 | 13.44 |
| 雌蕊心皮数Number of pistil carpel | 5.00 | 20.00 | 8.58 ± 3.12 | 0.79 | 1.47 | 36.40 | 5.83 |
| 花丝长/mm Filament length | 4.00 | 14.00 | 7.66 ± 2.15 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 28.11 | 5.85 |
| 花药长/mm Anthers length | 6.00 | 29.00 | 10.04 ± 3.41 | 0.91 | 1.63 | 34.03 | 5.85 |
| 花托大小/cm Receptacle size | 1.27 | 3.80 | 2.28 ± 0.55 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 24.49 | 5.86 |
| 花托直径/cm Torus diameter | 1.30 | 5.30 | 3.02 ± 1.04 | -0.65 | 0.39 | 34.52 | 5.82 |
| 均值Average | 34.28 | 6.53 |
表3 荷花花器官11个数量性状的变异
Table 3 Basic statistic information for 11 traits of garlic germplasm
| 性状 Trait | 最小值 Max | 最大值 Min | 平均值 Mean | 峰度 Kurtosis | 偏度 Skewness | 变异系数/% CV | 遗传多样性指数 H’ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花期/d Flowering period | 29.00 | 58.00 | 49.16 ± 10.32 | -1.17 | 0.22 | 20.98 | 5.87 |
| 着花密度Flowering density | 3.00 | 12.00 | 6.86 ± 1.42 | -0.86 | 0.25 | 35.34 | 5.82 |
| 花高/cm Flower height | 39.70 | 119.40 | 64.74 ± 17.69 | 0.94 | 1.11 | 27.33 | 5.85 |
| 花冠直径/cm Corolla diameter | 5.00 | 18.50 | 11.09 ± 3.23 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 29.13 | 5.85 |
| 花被片数量Number of tepals | 19.00 | 264.00 | 106.42 ± 36.35 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 43.56 | 5.77 |
| 雄蕊数Number of stamens | 5.00 | 140.00 | 54.56 ± 24.49 | -0.21 | 0.74 | 63.22 | 13.44 |
| 雌蕊心皮数Number of pistil carpel | 5.00 | 20.00 | 8.58 ± 3.12 | 0.79 | 1.47 | 36.40 | 5.83 |
| 花丝长/mm Filament length | 4.00 | 14.00 | 7.66 ± 2.15 | 0.10 | 0.40 | 28.11 | 5.85 |
| 花药长/mm Anthers length | 6.00 | 29.00 | 10.04 ± 3.41 | 0.91 | 1.63 | 34.03 | 5.85 |
| 花托大小/cm Receptacle size | 1.27 | 3.80 | 2.28 ± 0.55 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 24.49 | 5.86 |
| 花托直径/cm Torus diameter | 1.30 | 5.30 | 3.02 ± 1.04 | -0.65 | 0.39 | 34.52 | 5.82 |
| 均值Average | 34.28 | 6.53 |
| SSR位点 SSR locus | 等位基因数 Na | 有效等位基因数 Ne | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 香农多样性指数 I | 多态性信息含量 PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR1 | 5 | 2.4599 | 0.5833 | 0.5985 | 1.0479 | 0.5066 |
| SSR2 | 5 | 2.2025 | 0.4667 | 0.5506 | 0.9431 | 0.4417 |
| SSR3 | 4 | 2.3990 | 0.3889 | 0.5886 | 1.0397 | 0.5092 |
| SSR4 | 5 | 1.5602 | 0.1579 | 0.3639 | 0.7470 | 0.3039 |
| SSR5 | 5 | 3.2008 | 0.6552 | 0.6936 | 1.3166 | 0.6203 |
| SSR6 | 6 | 1.5632 | 0.2667 | 0.3633 | 0.7234 | 0.3047 |
| SSR7 | 10 | 3.1887 | 0.2667 | 0.6922 | 1.5752 | 0.6595 |
| SSR8 | 7 | 2.6012 | 0.5833 | 0.6207 | 1.2745 | 0.5896 |
| SSR9 | 10 | 4.0268 | 0.5500 | 0.7580 | 1.6393 | 0.6988 |
| SSR10 | 5 | 3.1304 | 0.2667 | 0.6863 | 1.2005 | 0.6054 |
| SSR11 | 7 | 3.2393 | 0.5088 | 0.6974 | 1.4004 | 0.6100 |
| SSR12 | 9 | 1.5094 | 0.3167 | 0.3403 | 0.8078 | 0.3327 |
| SSR13 | 10 | 3.7336 | 0.5000 | 0.7385 | 1.6748 | 0.7029 |
| SSR14 | 5 | 1.4496 | 0.3000 | 0.3127 | 0.5980 | 0.2898 |
| SSR15 | 7 | 2.4271 | 0.4828 | 0.5931 | 1.1267 | 0.5299 |
| SSR16 | 5 | 3.4156 | 0.6000 | 0.7132 | 1.3628 | 0.6820 |
| 平均值Average | 6.5625 | 2.6317 | 0.4308 | 0.5819 | 1.1548 | 0.5242 |
表4 SSR多态性引物多样性分析
Table 4 Diversity of polymorphic primers
| SSR位点 SSR locus | 等位基因数 Na | 有效等位基因数 Ne | 观测杂合度 Ho | 期望杂合度 He | 香农多样性指数 I | 多态性信息含量 PIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR1 | 5 | 2.4599 | 0.5833 | 0.5985 | 1.0479 | 0.5066 |
| SSR2 | 5 | 2.2025 | 0.4667 | 0.5506 | 0.9431 | 0.4417 |
| SSR3 | 4 | 2.3990 | 0.3889 | 0.5886 | 1.0397 | 0.5092 |
| SSR4 | 5 | 1.5602 | 0.1579 | 0.3639 | 0.7470 | 0.3039 |
| SSR5 | 5 | 3.2008 | 0.6552 | 0.6936 | 1.3166 | 0.6203 |
| SSR6 | 6 | 1.5632 | 0.2667 | 0.3633 | 0.7234 | 0.3047 |
| SSR7 | 10 | 3.1887 | 0.2667 | 0.6922 | 1.5752 | 0.6595 |
| SSR8 | 7 | 2.6012 | 0.5833 | 0.6207 | 1.2745 | 0.5896 |
| SSR9 | 10 | 4.0268 | 0.5500 | 0.7580 | 1.6393 | 0.6988 |
| SSR10 | 5 | 3.1304 | 0.2667 | 0.6863 | 1.2005 | 0.6054 |
| SSR11 | 7 | 3.2393 | 0.5088 | 0.6974 | 1.4004 | 0.6100 |
| SSR12 | 9 | 1.5094 | 0.3167 | 0.3403 | 0.8078 | 0.3327 |
| SSR13 | 10 | 3.7336 | 0.5000 | 0.7385 | 1.6748 | 0.7029 |
| SSR14 | 5 | 1.4496 | 0.3000 | 0.3127 | 0.5980 | 0.2898 |
| SSR15 | 7 | 2.4271 | 0.4828 | 0.5931 | 1.1267 | 0.5299 |
| SSR16 | 5 | 3.4156 | 0.6000 | 0.7132 | 1.3628 | 0.6820 |
| 平均值Average | 6.5625 | 2.6317 | 0.4308 | 0.5819 | 1.1548 | 0.5242 |
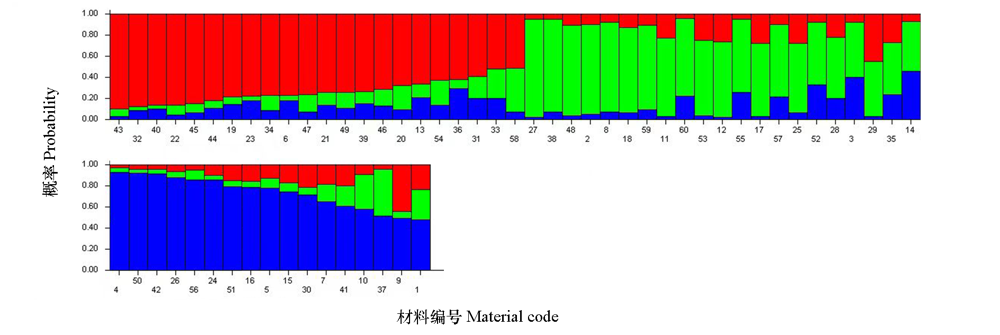
图6 60份荷花材料群体结构分析 红、绿、蓝分别代表不同基因型个体占亚群1(POP1)、亚群2(POP2)、亚群3(POP3)的比例。图中不同的色块代表着不同的群体。
Fig. 6 Analysis of population structure of 60 lotus germplasms Red,blue and green represent the individual’s estimated membership fractions of POP1,POP2 and POP3. The different colour blocks in the plot represent different populations.
| 性状 Trait | 标记 Marker | GLM | MLM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P值 P value | 表型解释率/% Phenotypic interpretation rate | P值 P value | 表型解释率/% Phenotypic interpretation rate | ||
| 花色 Flower color | S2 | 0.0980 | 18.05 | — | — |
| S7 | 0.0968 | 26.77 | — | — | |
| S8 | 0.0091 | 34.27 | 0.0560 | 32.70 | |
| S15 | 0.0571 | 23.66 | — | — | |
| 花型Flower type | S11 | 0.0059 | 42.15 | 0.0522 | 44.92 |
| S13 | 0.0198 | 46.39 | — | — | |
| S14 | 0.0673 | 15.72 | — | — | |
| 花态Flower form | S12 | 0.0306 | 19.60 | 0.0725 | 20.75 |
| 花蕾形状Bud shape | S2 | 0.0163 | 24.19 | — | — |
| 雌蕊泡化程度 Degree of pistil vesiculation | S9 | 0.0687 | 37.40 | — | — |
| S11 | 0.0865 | 34.02 | — | — | |
| S13 | 0.0559 | 45.17 | — | — | |
| 花期 Flowering period | S1 | 0.0132 | 30.45 | 0.0726 | 30.43 |
| S7 | 0.0242 | 32.60 | 0.0822 | 32.51 | |
| 着花密度 Flowering density | S1 | 0.0580 | 24.67 | — | — |
| S9 | 0.0873 | 37.06 | — | — | |
| S10 | — | — | 0.0587 | 25.56 | |
| 花被片数量 Number of Tepals | S9 | 0.0961 | 32.89 | — | — |
| S15 | 0.0851 | 19.29 | — | — | |
| 雄蕊数 Number of stamens | S2 | — | — | 0.0862 | 20.25 |
| S4 | 0.0803 | 29.88 | — | — | |
| 雌蕊心皮数 Number of pistil carpel | S13 | 0.0680 | 41.28 | — | — |
| 花丝长 Filament length | S4 | 0.0501 | 31.33 | — | — |
| S8 | 0.0882 | 25.18 | — | — | |
| S11 | 0.0208 | 41.98 | — | — | |
| 花药长 Anthers length | S5 | 0.0197 | 33.54 | 0.0931 | 34.20 |
| S6 | 0.0006 | 36.38 | 0.0147 | 37.37 | |
| S9 | 0.0000 | 70.95 | 0.0081 | 74.34 | |
| S11 | 0.0000 | 76.76 | 0.0033 | 78.40 | |
| 花托大小 Receptacle size | S1 | 0.0263 | 23.21 | — | — |
| S7 | 0.0253 | 27.00 | 0.0501 | 31.89 | |
| S8 | 0.0614 | 22.13 | — | — | |
| 花托直径 Torus diameter | S2 | — | — | 0.0436 | 22.16 |
| S11 | 0.0884 | 32.12 | — | — |
表5 SSR标记性状关联分析结果
Table 5 Results of trait association analysis by SSR
| 性状 Trait | 标记 Marker | GLM | MLM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P值 P value | 表型解释率/% Phenotypic interpretation rate | P值 P value | 表型解释率/% Phenotypic interpretation rate | ||
| 花色 Flower color | S2 | 0.0980 | 18.05 | — | — |
| S7 | 0.0968 | 26.77 | — | — | |
| S8 | 0.0091 | 34.27 | 0.0560 | 32.70 | |
| S15 | 0.0571 | 23.66 | — | — | |
| 花型Flower type | S11 | 0.0059 | 42.15 | 0.0522 | 44.92 |
| S13 | 0.0198 | 46.39 | — | — | |
| S14 | 0.0673 | 15.72 | — | — | |
| 花态Flower form | S12 | 0.0306 | 19.60 | 0.0725 | 20.75 |
| 花蕾形状Bud shape | S2 | 0.0163 | 24.19 | — | — |
| 雌蕊泡化程度 Degree of pistil vesiculation | S9 | 0.0687 | 37.40 | — | — |
| S11 | 0.0865 | 34.02 | — | — | |
| S13 | 0.0559 | 45.17 | — | — | |
| 花期 Flowering period | S1 | 0.0132 | 30.45 | 0.0726 | 30.43 |
| S7 | 0.0242 | 32.60 | 0.0822 | 32.51 | |
| 着花密度 Flowering density | S1 | 0.0580 | 24.67 | — | — |
| S9 | 0.0873 | 37.06 | — | — | |
| S10 | — | — | 0.0587 | 25.56 | |
| 花被片数量 Number of Tepals | S9 | 0.0961 | 32.89 | — | — |
| S15 | 0.0851 | 19.29 | — | — | |
| 雄蕊数 Number of stamens | S2 | — | — | 0.0862 | 20.25 |
| S4 | 0.0803 | 29.88 | — | — | |
| 雌蕊心皮数 Number of pistil carpel | S13 | 0.0680 | 41.28 | — | — |
| 花丝长 Filament length | S4 | 0.0501 | 31.33 | — | — |
| S8 | 0.0882 | 25.18 | — | — | |
| S11 | 0.0208 | 41.98 | — | — | |
| 花药长 Anthers length | S5 | 0.0197 | 33.54 | 0.0931 | 34.20 |
| S6 | 0.0006 | 36.38 | 0.0147 | 37.37 | |
| S9 | 0.0000 | 70.95 | 0.0081 | 74.34 | |
| S11 | 0.0000 | 76.76 | 0.0033 | 78.40 | |
| 花托大小 Receptacle size | S1 | 0.0263 | 23.21 | — | — |
| S7 | 0.0253 | 27.00 | 0.0501 | 31.89 | |
| S8 | 0.0614 | 22.13 | — | — | |
| 花托直径 Torus diameter | S2 | — | — | 0.0436 | 22.16 |
| S11 | 0.0884 | 32.12 | — | — |
| [1] |
Aslam M Q, Akhtar K P, Akram M, Saleem M Y, Yousaf S. 2017. Association of chili leaf curl betasatellite with tomato leaf curl disease. Journal of General Plant Pathology, 83 (6):402-405.
doi: 10.1007/s10327-017-0743-6 URL |
| [2] |
Botstein D, White R L, Skolnick M, Davis R W. 1980. Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisom. American Journal of Human Genetics, 32 (3):314-331.
pmid: 6247908 |
| [3] | Cao Hui. 2016. Analysis of genetic diversity of lotus varieties based on morphological markers and SSR markers[M. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 曹辉. 2016. 基于形态学标记和SSR标记的荷花品种遗传多样性分析[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. | |
| [4] | Chen H, Wang L, Wang S, Liu C, Cheng X. 2015. Transcriptome sequencing of mung bean(Vigna radiata L.)genes and the identification of EST-SSR markers. PLoS ONE, 10:1-15. |
| [5] |
Chen J F, Li R H, Xia Y S, Bai G, Guo P, Wang Z. 2017. Development of EST-SSR markers in flowering Chinese cabbage(Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis Tsen et Lee)based on de novo transcriptomic assemblies. PLoS ONE, 12 (9):e0184736.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184736 URL |
| [6] | Chen Li, Xue Liangjiao, Li Shuxian. 2021. Genome-wide association study of flower color trait in Prunus persica f. versicolor. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (3):553-565. (in Chinese) |
| 陈丽, 薛良交, 李淑娴. 2021. 跳枝碧桃花色性状的全基因组关联分析. 园艺学报, 48 (3):553-565. | |
| [7] |
Dias P, Julier B, Sampoux J P, Barre P, M Dall’Agnol. 2008. Genetic diversity in red clover(Trifolium pratense L.)revealed by morphological and microsatellite(SSR)markers. Euphytica, 160 (2):189-205.
doi: 10.1007/s10681-007-9534-z URL |
| [8] |
Ding J, Ali F, Chen G, Li H, Mahuku G, Yang N, Narro L, Magorokosho C, Makumbi D, Yan J. 2015. Genome-wide association mapping reveals novel sources of resistance to northern corn leaf blight in maize. BMC Plant Biol, 15 (1):206.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0589-z URL |
| [9] | Du Feng-feng, Liu Xiao-jing, Chang Ya-jun, Li Nai-wei, Li Pi-rui, Yao Dong-rui. 2016. Analysis of genetic diversity and population structure of lotus varieties based on SSR markers. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 25 (1):9-16. (in Chinese) |
| 杜凤凤, 刘晓静, 常雅军, 李乃伟, 李丕睿, 姚东瑞. 2016. 基于SSR标记的荷花品种遗传多样性及群体结构分析. 植物资源与环境学报, 25 (1):9-16. | |
| [10] | Du Li. 2017. Study on the genetic diversity and morphological variation of 28 Hosta germplasm resources by SSR[M. D. Dissertation]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 杜丽. 2017. 28份玉簪种质资源SSR遗传多样性及形态变异研究[硕士论文]. 郑州: 河南农业大学. | |
| [11] |
Evanno G S, Regnaut S J, Goudet J. 2005. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE:a simulation study. Molecular Ecology, 14 (8):2611-2620.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x pmid: 15969739 |
| [12] |
Flint-Garcia S A, Thornsberry J M. 2003. Structure of 1inkage disequilibrium in plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 54 (4):357-374.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.031902.134907 URL |
| [13] |
Fu Y R, Liu F L, Li S, Tian D K, Dong L, Chen Y C, Su Y. 2021. Genetic diversity of the wild Asian lotus(Nelumbo nucifera)from Northern China. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (5):488-500.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.04.005 URL |
| [14] | Guan Zhi-tao, Hao Gai-lian, Kong De-zheng. 2013. Classification of henan lotus variety resources based on cluster analysis. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,(9):123-126. (in Chinese) |
| 管志涛, 郝改莲, 孔德政. 2013. 基于聚类分析的河南荷花品种资源分类. 东北林业大学学报,(9):123-126. | |
| [15] |
Han Z, Ma X, Wei M, Zhao T, Zhan R, Chen W. 2018. SSR marker development and intraspecific genetic divergence exploration of Chrysanthemum indicum based on transcriptome analysis. BMC Genomics, 19:291.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4702-1 URL |
| [16] | He Dan, Tang Wan, Liu Yang, Cai Ming, Pan Hui-tang, Zhang Qi-xiang. 2012. Linkage analysis of main phenotypic traits and SSR markers in F1 populations of Lagerstroemia urophylla and Lagerstroemia indica. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 34 (6):121-125. (in Chinese) |
| 贺丹, 唐婉, 刘阳, 蔡明, 潘会堂, 张启翔. 2012. 尾叶紫薇与紫薇F1代群体主要表型性状与SSR标记的连锁分析. 北京林业大学学报, 34 (6):121-125. | |
| [17] | Ke Wei-dong. 2005. Description and data standards of lotus germplasm resources. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese) |
| 柯卫东. 2005. 莲种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社. | |
| [18] | Li Zuo. 2010. Using molecular markers and pollen morphology markers to study the genetic diversity of lotus germplasm[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 李佐. 2010. 用分子标记和花粉形态学标记研究莲种质的遗传多样性[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. | |
| [19] |
Lin Z, Zhang C, Cao D, Damaris R N, Yang P. 2019. The latest studies on lotus(Nelumbo nucifera)-an emerging horticultural model plant. Int J Mol Sci, 20 (15):3680.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20153680 URL |
| [20] | Liu Qingqing, Zhang Dasheng, Liu Fengluan, Cai Dong, Wang Xiaohan, Liang Lu, Tian Daike, Wang Liangsheng. 2021. Advances in flower color research on lotus (Nelumbo). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (10):2100-2112. (in Chinese) |
| 刘青青, 张大生, 刘凤栾, 蔡栋, 王晓晗, 梁露, 田代科, 王亮生. 2021. 荷花花色研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (10):2100-2112. | |
| [21] |
Ming C, Pan H T, Wang X F, He D, Wang X Y, Wang X J, Zhang Q X. 2011. Development of novel microsatellites in Lagerstroemia indica and DNA fingerprinting in Chinese Lagerstroemia cultivars. Scientia Horticulturae, 131:88-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2011.09.031 URL |
| [22] | Saha M C, Cooper J D, Mian M A, Chekhovskiy K, May G D. 2006. Tall fescue genomic SSR markers: development and transferability across multiple grass species. Theoretical & Applied Genetics, 113 (8):1449-1458. |
| [23] | Wang Qi-chao, Zhang Xing-yan. 2005. Chinese lotus varieties pictorial notes(Fine). Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House. (in Chinese) |
| 王其超, 张行言. 2005. 中国荷花品种图志(精). 北京: 中国林业出版社. | |
| [24] |
Wang X, Jia M H, Ghai P, Lee F N, Jia Y. 2015. Genome-wide association of rice blast disease resistance and yield-related components of rice. Molecular plant-microbe interactions:MPMI, 28(12):1383-1392.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-15-0131-R URL |
| [25] |
Wang Z, Yan H, Fu X, Gao H. 2013. Development of simple sequence repeat markers and diversity analysis in alfalfa(Medicago sativa L.). Molecular Biology Reports, 40 (4):3291-3298.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2404-3 pmid: 23275197 |
| [26] | Wu Fang-fang, Yuan Xin, Su Shao-wen, He Dan, Liu Yi-ping, Kong De-zheng. 2020. Analysis of phenotypic traits and flower color of flower organs of lotus plants. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,(1):24-29. (in Chinese) |
| 吴芳芳, 原鑫, 苏少文, 贺丹, 刘艺平, 孔德政. 2020. 荷花品种的花器官表型性状及花色多样性分析. 河南农业大学学报,(1):24-29. | |
| [27] | Wu Jing, Cheng Fang-yun, Pang Li-zheng, Zhong Yuan, Cai Chang-fu. 2016. Association analysis of phenotypic traits of purple spotted tree peony and SSR molecular markers. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 38 (8):80-87. (in Chinese) |
| 吴静, 成仿云, 庞利铮, 钟原, 蔡长福. 2016. 紫斑牡丹表型性状与SSR分子标记的关联分析. 北京林业大学学报, 38 (8):80-87. | |
| [28] | Wu Qian, Zhang Huijin, Wang Xiaohan, Zhao Wen, Zhou Xian, Wang Liangsheng. 2021. Research progress on flower color of waterlil (Nymphaea). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (10):2087-2099. (in Chinese) |
| 吴倩, 张会金, 王晓晗, 赵文, 周娴, 王亮生. 2021. 睡莲花色研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (10):2087-2099. | |
| [29] | Xu Yu-xian, Zhang Wei-wei, Mo Hai-bo, Li Chun, Cao Jian-Guo. 2015. Genetic diversity analysis of lotus germplasm resources based on EST-SSR markers. Journal of Plant Taxonomy and Resources, 37 (5):595-604. (in Chinese) |
| 徐玉仙, 张微微, 莫海波, 李春, 曹建国. 2015. 基于EST-SSR标记的莲属种质资源遗传多样性分析. 植物分类与资源学报, 37 (5):595-604. | |
| [30] | Yang Dan, Du Feng-feng, Chang Ya-jun, Cui Jian, Sun Lin-he. 2020. Association analysis of lotus plant type related traits and SSR molecular markers. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 41 (11):2149-2155. (in Chinese) |
| 杨丹, 杜凤凤, 常雅军, 崔键, 孙林鹤. 2020. 荷花株型相关性状与SSR分子标记的关联分析. 热带作物学报, 41 (11):2149-2155. | |
| [31] | Yang Guo-yang. 2018. Construction of lotus genetic linkage map and QTLs analysis of plant type related traits [M. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 杨郭阳. 2018. 荷花遗传连锁图谱的构建及株型相关性状QTLs分析[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. | |
| [32] |
Yang M, Zhu L P, Xu L M, Liu Y L. 2014. Population structure and association mapping of flower-related traits in lotus(Nelumbo adans.) accessions. Scientia Horticulturae, 175:214-222.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.06.017 URL |
| [33] |
Yang Y, He R, Zheng J, Hu Z, Wu J, Leng P. 2020. Development of EST-SSR markers and association mapping with floral traits in Syringa oblata. BMC Plant Biology, 20 (1):436-436.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02652-5 URL |
| [34] | Yuan Xin, Li Wen-ling, Liu Zhao-qiang, Wu Fang-fang, Liu Yi-ping. 2020. Genetic diversity analysis of phenotypic traits of lotus cultivars. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 48 (16):194-199. (in Chinese) |
| 原鑫, 李文玲, 刘召强, 吴芳芳, 刘艺平. 2020. 荷花品种表型性状遗传多样性分析. 江苏农业科学, 48 (16):194-199. | |
| [35] | Yuan Xin-jie, Fang Rong, Zhou Kun-hua, Lei Gang, Huang Yue-qin. 2020. Association analysis of important agronomic traits and discovery of excellent allelic variation in pepper. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 34 (12):2658-2672. (in Chinese) |
|
袁欣捷, 方荣, 周坤华, 雷刚, 黄月琴. 2020. 辣椒重要农艺性状关联分析与优异等位变异发掘. 核农学报, 34 (12):2658-2672.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.12.2658 |
|
| [36] | Zhang Lin, Wang Pei-pei, Han Ya-zhen, Xu Long-wei, Wang Rui-bo. 2019. Association analysis of main related traits of oil tree peony and SSR molecular markers. Journal of Northeast Forestry, 47 (3):31-37. (in Chinese) |
| 张琳, 王佩佩, 韩雅祯, 许龙伟, 王瑞博. 2019. 油用牡丹主要相关性状与SSR分子标记的关联分析. 东北林业大学学报, 47 (3):31-37. | |
| [37] | Zhao Mei. 2019. Association analysis of lotus ornamental traits and fine positioning of plant type traits [Ph. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 赵玫. 2019. 莲观赏性状的关联分析及株型性状的精细定位[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. | |
| [38] | Zheng X, Pan C, Diao Y, You Y, Yang C, Hu Z. 2013. Development of microsatellite markers by transcriptome sequencing in two species of Amorphophallus(Araceae). Bio Med Central, 14 (1):490. |
| [39] | Zhou Yiwei, Xu Guoyu, Wang Qin, Yan Fulong, Yu Yunyi, Yu Rangcai, Fan Yanping. 2021. Genetic analysis and development of associated SSR markers of the flower color in F1population of Hedychium coronarium‘COR01’× H.‘Jin’. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (10):1921-1933. (in Chinese) |
| 周熠玮, 许国宇, 王琴, 严福龙, 玉云祎, 余让才, 范燕萍. 2021. ‘白姜花’ב金姜花’杂交F1代花色遗传分析及其相关SSR分子标记开发. 园艺学报, 48 (10):1921-1933. |
| [1] | 王梦梦, 孙德岭, 陈 锐, 杨迎霞, 张 冠, 吕明杰, 王 倩, 谢添羽, 牛国保, 单晓政, 谭 津, 姚星伟, . 花椰菜核心种质的构建与评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 421-431. |
| [2] | 杨植, 张川疆, 杨芯芳, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 枣与酸枣杂交后代果实遗传倾向及混合遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 36-52. |
| [3] | 李清清, 赵广胜, 吉建斌, 崔建平. 观赏荷花新品种‘燕赵牡丹’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 211-212. |
| [4] | 吉建斌, 李清清, 赵广胜, 崔建平. 观赏荷花新品种‘隆福之光’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 213-214. |
| [5] | 王晶晶, 郁琳洁, 柳 斌, 杨丽娟, 杨欣宇, 唐 菲, . 观赏荷花新品种‘玉堂春’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 215-216. |
| [6] | 章志远, 姜海翠, 张玲玲, 万金丹, 胡骏婷, 顾 琪, . 观赏荷花新品种‘钟山暖阳’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 159-160. |
| [7] | 王燕, 刘针杉, 张静, 杨鹏飞, 马蓝, 王旨意, 涂红霞, 杨绍凤, 王浩, 陈涛, 王小蓉. 中国樱桃杂交F1代花和果实若干性状遗传倾向分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1853-1865. |
| [8] | 杨兴玉, 许林兵, 吴元立, 邱迪洋, 范琳琳, 黄秉智. 香蕉杂交种‘粉杂1号’ABBB基因组鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1991-1997. |
| [9] | 郭燕, 张树航, 李颖, 张馨方, 王英杰, 王广鹏. 燕山板栗种质资源叶片表型性状多样性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1673-1688. |
| [10] | 张悦, 索玉静, 孙鹏, 韩卫娟, 刁松锋, 李华威, 张嘉嘉, 傅建敏, 李芳东. 柿种质资源果实形态多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1473-1490. |
| [11] | 刘瑶瑶, 吴严严, 石岩, 毛天宇, 包满珠, 张俊卫, 张杰. 垂枝与直枝梅花PmTAC1启动子序列差异与垂枝性状的关系初探[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1327-1338. |
| [12] | 卢甜甜, 刘志远, 徐兆生, 张合龙, 李国亮, 折红兵, 钱伟. 菜豆花色全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 332-340. |
| [13] | 武红霞, 李星, 许文天, 郑斌, 马小卫, 苏穆清, 梁清志, 姚全胜, 王松标. 杧果‘金煌’ב热农1号’后代果实性状遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 416-426. |
| [14] | 徐婉, 林雅君, 赵荘, 周庄. 兰属植物资源与育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2722-2742. |
| [15] | 肖军, 陈珣, 肇莹, 马晓颖, 龚娜, 刘国丽. 野生蛹虫草分化株子实体表型性状的分离[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2449-2454. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司