
园艺学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (3): 569-582.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1056
王泉城, 武军, 李磊, 石延霞, 谢学文, 李宝聚*( ), 柴阿丽*(
), 柴阿丽*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-23
修回日期:2022-10-19
出版日期:2023-03-25
发布日期:2023-04-03
通讯作者:
*(E-mail:chaiali@caas.cn,libaojuivf@163.com)
基金资助:
WANG Quancheng, WU Jun, LI Lei, SHI Yanxia, XIE Xuewen, LI Baoju*( ), CHAI Ali*(
), CHAI Ali*( )
)
Received:2022-08-23
Revised:2022-10-19
Online:2023-03-25
Published:2023-04-03
Contact:
*(E-mail:chaiali@caas.cn,libaojuivf@163.com)
摘要:
为了解多主棒孢菌CcTLS1基因对黄瓜棒孢叶斑病的致病机理,以多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104为研究对象,通过对CcTLS1在强致病力菌株中敲除、回补以及在弱致病力菌株中异源表达等方法,研究CcTLS1在多主棒孢菌对黄瓜致病过程中的作用。CcTLS1全长为1 222 bp,与GenBank中已注释的基因无序列相似性。与野生型菌株相比,CcTLS1基因敲除菌株对黄瓜的致病力明显下降,产孢量和产孢梗数量显著减少,菌丝变细易卷曲,隔膜减少,纤维二糖水解酶分泌显著降低;而CcTLS1回补菌株致病力、产孢量以及纤维二糖水解酶分泌得到恢复;与野生型菌株相比,CcTLS1异源表达菌株对黄瓜的致病力提升,菌丝粗壮且隔膜增多,纤维素酶及纤维二糖分解酶分泌显著增加。影响多主棒孢菌致病的蛋白激酶基因CCK1、产孢相关基因(Ccflbc、CcstuA)以及黑色素合成相关基因CcSCD1,在CcTLS1基因敲除菌株中的相对表达量显著下调。结果表明,CcTLS1的表达影响菌株产孢机制、菌丝生长、蛋白激酶表达以及黑色素合成,在多主棒孢菌致病中起重要作用。
中图分类号:
王泉城, 武军, 李磊, 石延霞, 谢学文, 李宝聚, 柴阿丽. 多主棒孢菌CcTLS1对黄瓜的致病机理分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 569-582.
WANG Quancheng, WU Jun, LI Lei, SHI Yanxia, XIE Xuewen, LI Baoju, CHAI Ali. Exploration on the Function of Pathogenicity-related Gene CcTLS1 in Corynespora cassiicola From Cucumber[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 569-582.
| 基因、载体 Gene,vector | 引物 Primer | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CcTLS1 | CcTLS1 | F:ATGCGTTCCTCAATCATCATCGC | |
| R:TTACAATGGCTGTCGTACTGGG | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-ΔCcTLS1 | CcTLS1-51 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCATCCGGTCTGTTGGGTCG | |
| R:AACCGCCTCTCCCCGGTACCGTTGTCAGTTGTGAGGAGTATT | |||
| CcTLS1-31 | F:AACAGCTCCCTCTAGAAGACCAAAAGAGCATTAGTTCATC | ||
| R:CCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGAGATCTCATTGGCAGCGTAAAAAC | |||
| CcTLS1-h | F:GGGGTACCGGGGAGAGGCGGTTTGC | ||
| R:GCTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGC | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-cΔCcTLS1 | CcTLS1-52 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCGCTCGGGATTTGGCACACG | |
| R:CTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCTTACAATGGCTGTCGTACTGGG | |||
| CcTLS1-32 | F:GTTCTTCTGAAGACCAAAAGAGCATTAGTTCATCA | ||
| R:CAGTGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGAGCTTACTGGGGTCCGGG | |||
| CcTLS1-g | F:GGTACCCGGGGATCCTCTAGAGTCGACAGAAGATGATATTGAAGG | ||
| R:CTTTTGGTCTTCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAGGC | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-h, pCAMBIA1300-heΔCcTLS1 | CcITS-5 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCCTTAGATGTTCTGGGCCGCAC | |
| R:CTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCTACTTCCTCTAAATGACCGAGTTTG | |||
| CcITS-3 | F:AACAGCTCCCTCTAGAAAAGAAACCAACAGGGATTGCC | ||
| R:GCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGCTGG | |||
| CcITS-h | F:ATTTAGAGGAAGTAGGTACCGGGGAGAGGCGGTTTGCG | ||
| R:GCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGCTGG | |||
| CcTLS1-I | F:ATTTAGAGGAAGTAGGGCAGGTACTGGTTCGGATGT | ||
| R:AACCGCCTCTCCCCGACAGCCTTTCGGCGGTTAGA | |||
| 突变株验证 Mutant validation | FhphU | TGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | Fu et al., |
| FhphL | TTGTTGGAGCCGAAATCC | ||
| FrbU | CCTCTTCGCTATTACGCC | ||
| FrbUC | GGCGTAATAGCGAAGAGG | ||
| M13R | CAGGAAACAGCTATGACC | 通用引物 Universal primer | |
| FhphLL | GGATTTCGGCTCCAACAA | ||
| F5F | TTGTTGGAGCCGAAATCC | ||
| F3F | AATTGCGATAACGAACGAGACC | ||
| F4F2 | GAATTAGCTGCGCTCATGCAC | ||
| Neo-G418 | F:GTCGACAGAAGATGATATTG | 张晓珂,2015 | |
| R:TCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAGGCG | |||
| qSdhB | F:GGCGAAGTTGCCGTGAG | ||
| R:CTTGGTGGTATCGGTGGG | |||
| qCcTLS1 | F:GACGAGGATGCTGATGAGGA | ||
| R:TGTCGTACTGGGATGCTGTT |
表1 载体构建及突变菌株验证所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for vector construction and mutant validation
| 基因、载体 Gene,vector | 引物 Primer | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CcTLS1 | CcTLS1 | F:ATGCGTTCCTCAATCATCATCGC | |
| R:TTACAATGGCTGTCGTACTGGG | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-ΔCcTLS1 | CcTLS1-51 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCATCCGGTCTGTTGGGTCG | |
| R:AACCGCCTCTCCCCGGTACCGTTGTCAGTTGTGAGGAGTATT | |||
| CcTLS1-31 | F:AACAGCTCCCTCTAGAAGACCAAAAGAGCATTAGTTCATC | ||
| R:CCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGAGATCTCATTGGCAGCGTAAAAAC | |||
| CcTLS1-h | F:GGGGTACCGGGGAGAGGCGGTTTGC | ||
| R:GCTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGC | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-cΔCcTLS1 | CcTLS1-52 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCGCTCGGGATTTGGCACACG | |
| R:CTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCTTACAATGGCTGTCGTACTGGG | |||
| CcTLS1-32 | F:GTTCTTCTGAAGACCAAAAGAGCATTAGTTCATCA | ||
| R:CAGTGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGAGCTTACTGGGGTCCGGG | |||
| CcTLS1-g | F:GGTACCCGGGGATCCTCTAGAGTCGACAGAAGATGATATTGAAGG | ||
| R:CTTTTGGTCTTCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAGGC | |||
| pCAMBIA1300-h, pCAMBIA1300-heΔCcTLS1 | CcITS-5 | F:CCATGATTACGAATTCCTTAGATGTTCTGGGCCGCAC | |
| R:CTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCTACTTCCTCTAAATGACCGAGTTTG | |||
| CcITS-3 | F:AACAGCTCCCTCTAGAAAAGAAACCAACAGGGATTGCC | ||
| R:GCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGCTGG | |||
| CcITS-h | F:ATTTAGAGGAAGTAGGTACCGGGGAGAGGCGGTTTGCG | ||
| R:GCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGGGAGCTGTTGGCTGGCTGG | |||
| CcTLS1-I | F:ATTTAGAGGAAGTAGGGCAGGTACTGGTTCGGATGT | ||
| R:AACCGCCTCTCCCCGACAGCCTTTCGGCGGTTAGA | |||
| 突变株验证 Mutant validation | FhphU | TGTCCTGCGGGTAAATAGC | Fu et al., |
| FhphL | TTGTTGGAGCCGAAATCC | ||
| FrbU | CCTCTTCGCTATTACGCC | ||
| FrbUC | GGCGTAATAGCGAAGAGG | ||
| M13R | CAGGAAACAGCTATGACC | 通用引物 Universal primer | |
| FhphLL | GGATTTCGGCTCCAACAA | ||
| F5F | TTGTTGGAGCCGAAATCC | ||
| F3F | AATTGCGATAACGAACGAGACC | ||
| F4F2 | GAATTAGCTGCGCTCATGCAC | ||
| Neo-G418 | F:GTCGACAGAAGATGATATTG | 张晓珂,2015 | |
| R:TCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAGGCG | |||
| qSdhB | F:GGCGAAGTTGCCGTGAG | ||
| R:CTTGGTGGTATCGGTGGG | |||
| qCcTLS1 | F:GACGAGGATGCTGATGAGGA | ||
| R:TGTCGTACTGGGATGCTGTT |
| 基因 Gene | 引物 Primer | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CcstuA | qstuA | F:GATCCATACCGCCCAGACAG | |
| R:CGAGTACGCTGGCTTATCGT | |||
| CcHog1 | qHog1 | F:TGTCGACCCGATACTACCGT | |
| R:GCGTAATGTGTTCTCGCTGC | |||
| CcSCD1 | qSCD1 | F:TGTAATGGGCTGCCAGAGTG | |
| R:CCAGCTCTTGTCCAGGAAGG | |||
| CCK1 | qCCK1 | F:AAAGGACTACCACCACCAGC | |
| R:TCTTGGGGAACATGGCCTTC | |||
| Ccflbc | qflbc | F:GATCAGGTATTGCCCTCCCG | |
| R:TCGGGTGCTGTTGCCATATT | |||
| Cas2 | qCas2 | F:TCTGCTTTTGTAGCAGCCGT | |
| R:TAACAACCCGAACAAGCCCA | |||
| EF4α | qEF4α | F:TCACCGTCATTGACGCCC | Shi et al., |
| R:CGGCAGCGATAATGAGGATAG |
表2 基因相对表达量测定所用引物
Table 2 Primers for relative expression determination
| 基因 Gene | 引物 Primer | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CcstuA | qstuA | F:GATCCATACCGCCCAGACAG | |
| R:CGAGTACGCTGGCTTATCGT | |||
| CcHog1 | qHog1 | F:TGTCGACCCGATACTACCGT | |
| R:GCGTAATGTGTTCTCGCTGC | |||
| CcSCD1 | qSCD1 | F:TGTAATGGGCTGCCAGAGTG | |
| R:CCAGCTCTTGTCCAGGAAGG | |||
| CCK1 | qCCK1 | F:AAAGGACTACCACCACCAGC | |
| R:TCTTGGGGAACATGGCCTTC | |||
| Ccflbc | qflbc | F:GATCAGGTATTGCCCTCCCG | |
| R:TCGGGTGCTGTTGCCATATT | |||
| Cas2 | qCas2 | F:TCTGCTTTTGTAGCAGCCGT | |
| R:TAACAACCCGAACAAGCCCA | |||
| EF4α | qEF4α | F:TCACCGTCATTGACGCCC | Shi et al., |
| R:CGGCAGCGATAATGAGGATAG |
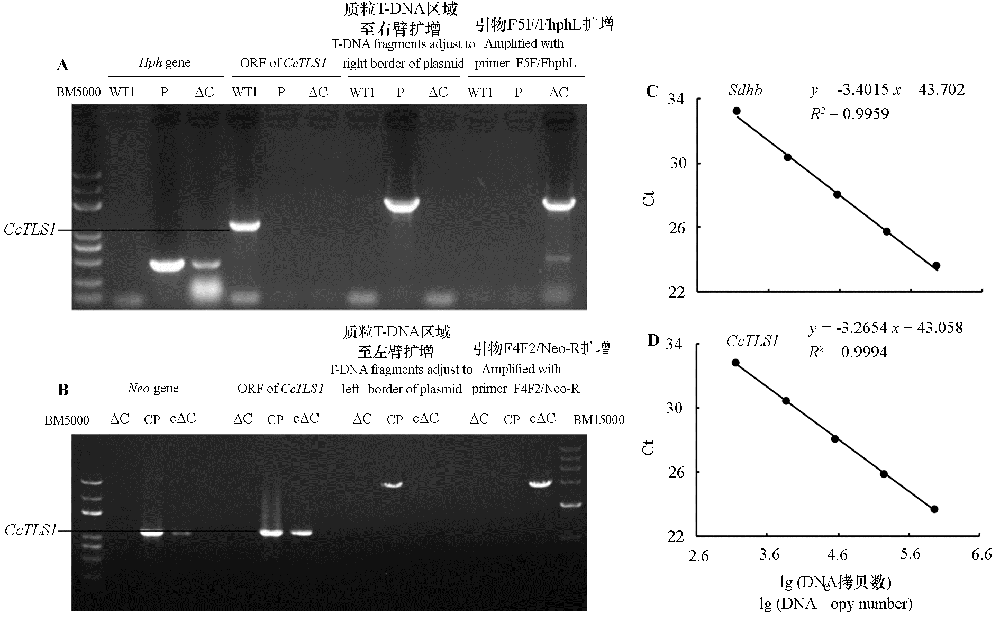
图1 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524 CcTLS1敲除(A)和回补(B)菌株PCR及SdhB、CcTLS1(C、D)标准曲线 WT1:HG14102524野生型;P:敲除载体质粒;ΔC:敲除菌株;CP:回补载体质粒;cΔC:回补菌株。下同。
Fig. 1 PCR of virulent Corynespora cassiicola HG14102524 CcTLS1 knockout(A)and complementary(B)strains and standard curves of SdhB,CcTLS1(C,D) WT1:HG14102524 Wild-type;P:Knockout vector plasmid;ΔC:Knockout strain;CP:Complementary vector plasmid;cΔC:Complementary strain. The same below.
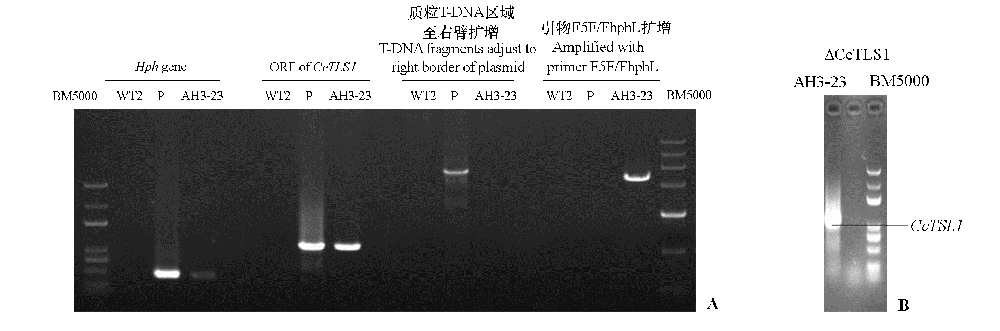
图2 多主棒孢菌弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1异源表达菌株的PCR(A)及其CcTLS1表达的qRT-PCR(B) WT2:HG15052104野生型;P:异源表达载体质粒;AH3-23:异源表达菌株;ΔCcTLS1:敲除菌株。下同。
Fig. 2 PCR of low virulent Corynespora cassiicola HG15052104 CcTLS1 heterologous expression strains(A)and qRT-PCRof CcTLS1 expression(B) WT2:HG15052104 Wild-type:P:Heterologous expression vector plasmid;AH3-23:Heterologous expression strain;ΔCcTLS1:Knockout strain. The same below.

图3 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1突变菌株在活体黄瓜植株的致病力 H1-2:潮霉素表达菌株。下同。
Fig. 3 Pathogenicity of CcTLS1 mutants of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulent strain HG15052104 in vivo cucumber plants H1-2:Hygromycin expressing strain. The same below.
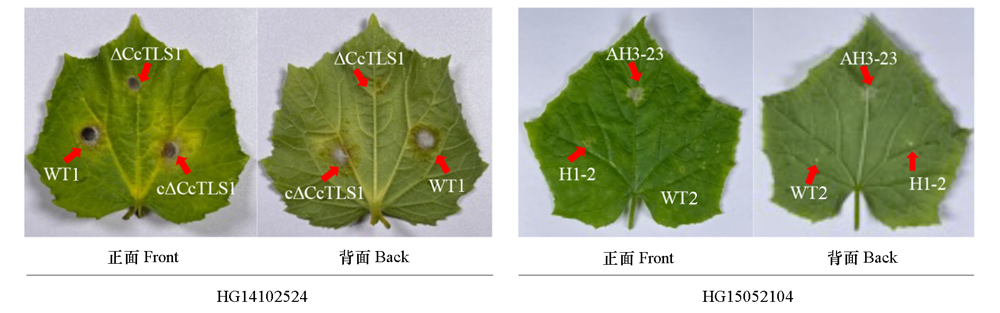
图4 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1突变菌株在离体黄瓜叶片的致病力
Fig. 4 Pathogenicity of CcTLS1 mutants of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulent strain HG15052104 in vitro cucumber plants
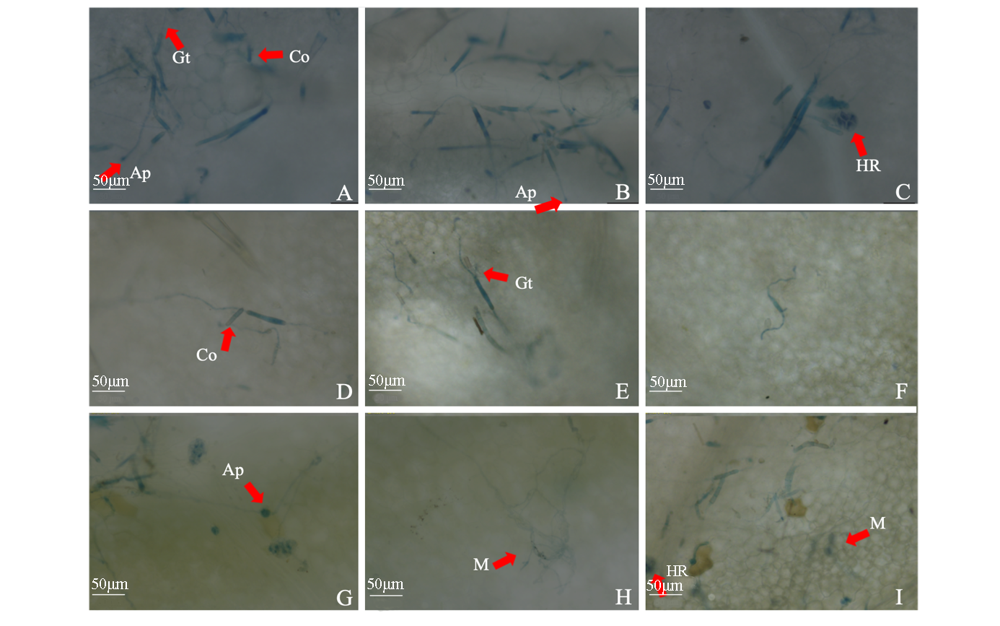
图5 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524分生孢子接种黄瓜叶片侵染过程显微形态观察 A ~ C:野生型菌株接种12 h;D ~ F:敲除菌株ΔCcTLS1接种12 h;G、H:野生型菌株接种24 h;I:敲除菌株ΔCcTLS1接种24 h。Co:分生孢子;Gt:芽管;Ap:类似附着孢结构;M:菌丝体;HR:过敏反应。
Fig. 5 Observation on micromorphology of cucumber leaves infected by conidia of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 A-C:Inoculation with HG14102524 wild-type for 12 h;D-F:Inoculation with knockout strain ΔCcTLS1 for 12 h;G,H:Inoculation with HG14102524 Wild-type for 24 h;I:Inoculation with knockout strain ΔCcTLS1 for 24 h;Co:Conidia;Gt:Germ tube;Ap:Similar to appressorium structure;M:Mycelium;HR:Hypersensitive response.
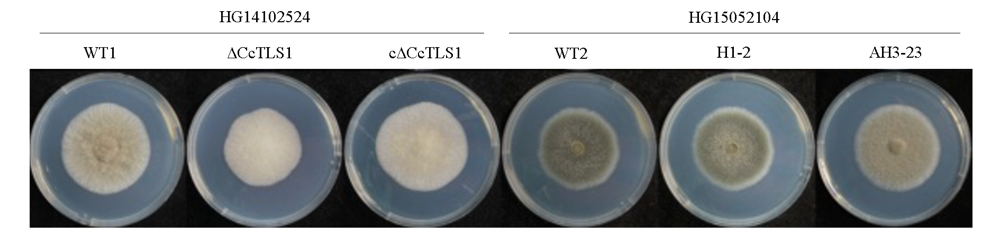
图6 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1突变菌株在PDA上的菌落形态
Fig. 6 Colonial morphology of CcTLS1 mutant of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulents train HG15052104 on PDA
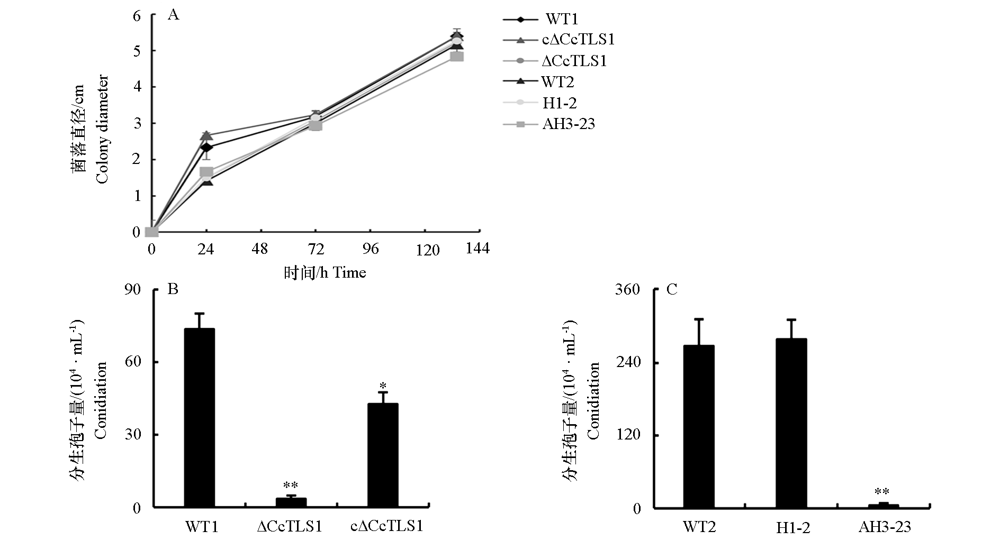
图7 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1突变菌株菌落直径和产孢量 在PDA培养基上生长5 d。* P < 0.05,** P < 0.01。下同。
Fig. 7 Colony diameter and conidiation of CcTLS1 mutant of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulent strain HG15052104 on PDA On PDA medium for 5 days. * P < 0.05,** P < 0.01. The same below.
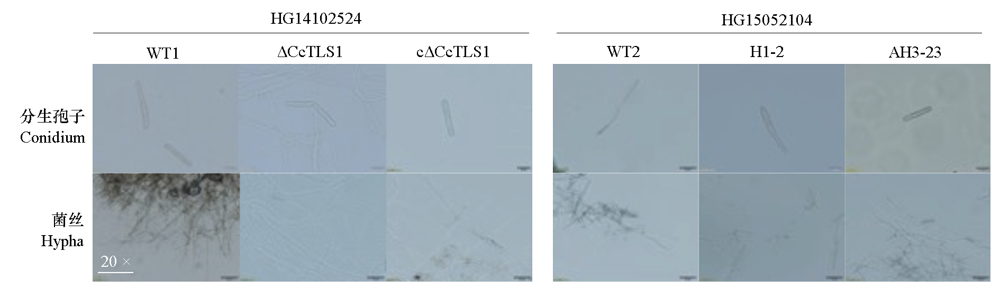
图8 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1突变菌株的菌丝形态特征
Fig. 8 Morphology of hyphae under microscope of CcTLS1 mutant of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulent strain HG15052104 on PDA
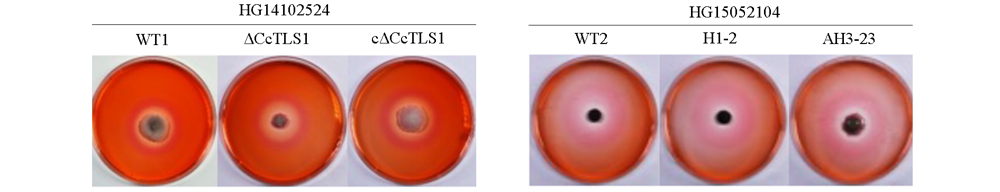
图9 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524和弱致病力菌株HG15052104的CcTLS1的突变菌株纤维素酶分泌测定
Fig. 9 Determination of mutant to cellulase secretion of CcTLS1 mutant of Corynespora cassiicola virulent strain HG14102524 and low virulent strain HG15052104

图10 多主棒孢菌强致病力菌株HG14102524的CcTLS1的突变菌株中致病相关基因的相对表达量 A:产孢相关基因;B:蛋白激酶基因;C:黑色素合成关键基因。
Fig. 10 Relative expression levels of disease-related genes in CcTLS1 knockout mutants A:Sporulation-related genes;B:Protein kinase gene;C:Key genes for melanin synthesis.
| [1] | Cao Shen-wen. 2015. Functional complementation of a MAPK homologous gene(CCK1)-deficient mutants in Corynespora cassiicola[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Haikou: Hainan University. (in Chinese) |
| 曹申文. 2015. 巴西橡胶树棒孢霉落叶病菌蛋白激酶基因(CCK1)突变体功能互补分析[博士论文]. 海口: 海南大学. | |
| [2] |
Chen L L, Zhao J Y, Xia H Q, Ma Y M, Liu Y K, Peng M Y, Xing X P, Sun B J, Shi Y, Li H L. 2020. FpCzf14 is a putative C2H 2 transcription factor regulating conidiation in Fusarium pseudograminearum. Phytopathology Research, 2 (1):33.
doi: 10.1186/s42483-020-00074-7 |
| [3] |
Déon M, Scomparin A, Tixier A, Mattos C R R, Leroy T, Seguin M, Roeckel-Drevet P, Pujade-Renaud V. 2012a. First characterization of endophytic Corynespora cassiicola isolates with variant cassiicolin genes recovered from rubber trees in Brazil. Fungal Diversity, 54 (1):87-99.
doi: 10.1007/s13225-012-0169-6 URL |
| [4] | Déon M, Bourré Y, Gimenez S, Berger A, Bieysse D, De L F, Poncet J, Roussel V, Bonnot F, Oliver G, Franchel J, Seguin M, Leroy T, Roeckel-Drevet P, Pujade-Renaud V. 2012b. Characterization of a cassiicolin-encoding gene from Corynespora cassiicola,pathogen of rubber tree(Hevea brasiliensis). Plant Science, 185:227-237. |
| [5] |
Déon M, Fumanal B, Gimenez S, Bieysse D, Oliveira R R, Shuib S S, Breton F, Elumalai S, Vida J B, Seguin M, Leroy T, Roeckel-Drevet P, Pujade-Renaud V. 2014. Diversity of the Cassiicolin gene in Corynespora cassiicola and relation with the pathogenicity in Hevea brasiliensis. Fungal Biology, 118 (1):32-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2013.10.011 URL |
| [6] |
Fortunato A A, Araujo L, Rodrigues F Á. 2017. Association of the production of phenylpropanoid compounds at the infection sites of Corynespora cassiicola with soybean resistance against target spot. Journal of Phytopathology, 165 (2):131-142.
doi: 10.1111/jph.2017.165.issue-2 URL |
| [7] |
Fu K, Fan L L, Li Y Y, Gao S G, Chen J. 2012. Tmac1,a transcription factor which regulated high affinity copper transport in Trichoderma reesei. Microbiological Research, 167 (9):536-543.
doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2012.02.002 URL |
| [8] |
Gao S, Zeng R, Xu L, Song Z, Gao P, Dai F. 2020. Genome sequence and spore germination-associated transcriptome analysis of Corynespora cassiicola from cucumber. BMC Microbiology, 20 (1):199.
doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01873-w |
| [9] | Gao Wei, Li Bao-ju, Shi Yan-xia, Xie Xue-wen. 2011. Studies on pathogenicity differentiation of Corynespora cassiicola isolates,against cucumber,tomato and eggplant. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 38 (3):465-470. (in Chinese) |
| 高苇, 李宝聚, 石延霞, 谢学文. 2011. 多主棒孢菌在黄瓜、番茄和茄子寄主上致病力的分化. 园艺学报, 38 (3):465-470. | |
| [10] | Hohmann S, Krantz M, Nordlander B. 2007. Yeast Osmoregulation. Methods in Enzymology, 428 (2):29-45. |
| [11] | Li Bao-ju, Gao Wei, Shi Yan-xia, Xie Xue-wen. 2012. Progress in researches on Corynespora leaf spot. Journal of Plant Protection, 39 (2):171-176. (in Chinese) |
| 李宝聚, 高苇, 石延霞, 谢学文. 2012. 多主棒孢和棒孢叶斑病的研究进展. 植物保护学报, 39 (2):171-176. | |
| [12] |
Li J X, Ni H, Peng B, Wu H J, Gu Q S. 2019. Transformation of Corynespora cassiicola by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Fungal Biology, 123 (9):669-675.
doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2019.05.011 URL |
| [13] | Li Xin-yu, Li Lei, Shi Yan-xia, Chai A-li, Xie Xue-wen, Li Bao-ju. 2020. Screening,identification and control effects of antagonistic bacteria against cucumber Corynespora leaf spot. Journal of Plant Protection,(3):620-627. (in Chinese) |
| 李新宇, 李磊, 石延霞, 柴阿丽, 谢学文, 李宝聚. 2020. 黄瓜棒孢叶斑病拮抗细菌的筛选、鉴定及防治效果. 植物保护学报,(3):620-627. | |
| [14] |
Liu D, Qin Z W, Zhang Y J, Zhou X Y, Xin M. 2017. Histological observation of cucumber infected with Corynespora cassiicola. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 149 (2):455-466.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-017-1195-8 URL |
| [15] | Liu Peng, Jiang Hong-xia, Bao Zheng-zhou, Zhou Bao-qiang, Sui Jun-kang, Zhao Xu, Wang Xiao-hui, Liu Xun-li. 2014. Identification of a cellulose degrading fungal strain and determination of cellulase activity. Science of Sericulture, 40 (1):97-102. (in Chinese) |
| 刘鹏, 姜红霞, 鲍正宗, 周保强, 隋君康, 赵旭, 王晓辉, 刘训理. 2014. 一株纤维素降解菌的鉴定及产酶活力测定. 蚕业科学, 40 (1):97-102. | |
| [16] | Liu X M, Qi Y X, Zhang X, Xie Y Y, Zhang H, Wei Y X, Cao S W, Pu J J. 2014. Infection process of Corynespora cassiicola tagged with GFP on Hevea brasiliensis. Australasian Plant Pahtologyogy, 43 (5):523-525. |
| [17] | Liu Xian-bao, Li Bo-xun, Chen Shan, Huang Gui-xiu. 2016. Diversity and pathogenicity of the cassiicolin gene in Corynespora cassiicola of rubber tree in China. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 37 (10):1969-1973. (in Chinese) |
| 刘先宝, 李博勋, 陈珊, 黄贵修. 2016. 国内橡胶树多主棒孢菌Cassiicolin毒素多样性及致病性分析. 热带作物学报, 37 (10):1969-1973. | |
| [18] | Liu Xiao-mei. 2012. Coloning and functional identification of a mitogen-activated protein kinase gene(CCK1)and toxin ecoding gene(ct)of Corynespora cassiicola the pathogen of Corynespora leaf fall disease of Hevea brasiliensis[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Haikou: Hainan University. (in Chinese) |
| 刘晓妹. 2012. 巴西橡胶树棒孢霉落叶病病菌 MAPK 基因(CCK1)和毒素基因(ct)克隆与功能鉴定[博士论文]. 海口: 海南大学. | |
| [19] | Liu Xiao-mei, Zhang He, Zhang Xin, Xie Yi-xian, Wei Yun-xie, Cao Shen-wen, Pu Jin-ji. 2015. GFP as a marker in Corynespora cassiicola from Hevea brasiliensis using ITS sequence. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 36 (3):575-580. (in Chinese) |
| 刘晓妹, 张贺, 张欣, 谢艺贤, 韦运谢, 曹申文, 蒲金基. 2015. 借助ITS序列用GFP标记巴西橡胶树棒孢霉落叶病病原菌. 热带作物学报, 36 (3):575-580. | |
| [20] |
Livark K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆Ct method. Methods, 25:402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 URL |
| [21] |
Maeda T, Wurgler-Murphy S M, Saito H. 1994. A two-component system that regulates an osmosensing MAP kinase cascade. Nature, 369:242-245.
doi: 10.1038/369242a0 |
| [22] | Qi Yan-xiang, Zhang Xin, Pu Jin-ji, Lu Ying, Zhang He, Zhang Hui-qiang, Xie Yi-xian. 2010. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Slt2-type MAPK homologous gene CMP1 from Corynespora cassiicola of Hevea brasiliensis. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 31 (11):1951-1958. (in Chinese) |
| 漆艳香, 张欣, 蒲金基, 陆英, 张贺, 张辉强, 谢艺贤. 2010. 巴西橡胶树棒孢霉落叶病菌Slt2类MAPK同源基因CMP1的克隆与序列分析. 热带作物学报, 31 (11):1951-1958. | |
| [23] |
Ribeiro S, Label P, Garcia D, Montoro P, Pujade R V. 2021. Transcriptome profiling in susceptible and tolerant rubber tree clones in response to cassiicolin Cas1,a necrotrophic effector from Corynespora cassiicola. PLoS ONE, 16 (7):e0254541.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254541 URL |
| [24] |
Sheppard D C. 2006. The Aspergillus fumigatus StuA protein governs the up-regulation of a discrete transcriptional program during the acquisition of developmental competence. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 16 (12):5866-5879.
doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-07-0617 URL |
| [25] |
Shi Y X, Sun B X, Xie X W, Chai A L, Li L, Li B J. 2021a. Site-directed mutagenesis of the succinate dehydrogenase subunits B and D from Corynespora cassiicola reveals different fitness costs and sensitivities to succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors. Environmental Microbiology, 23 (10):5769-5783.
doi: 10.1111/emi.v23.10 URL |
| [26] |
Shi Y X, Zhu F D, Sun B X, Xie X W, Chai A L, Li B J. 2021b. Two adjacent mutations in the conserved domain of SdhB confer various resistance phenotypes to fluopyram in Corynespora cassiicola. Pest Management Science, 77 (9):3980-3989.
doi: 10.1002/ps.v77.9 URL |
| [27] |
Tanaka M, Yoshimura M, Ogawa M, Koyama Y, Shintani T, Gomi K. 2016. The C2H2-type transcription factor,FlbC,is involved in the transcriptional regulation of Aspergillus oryzae glucoamylase and protease genes specifically expressed in solid-state culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 100 (13):5859-5868.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7419-6 URL |
| [28] | Wang Yan-li, Lin Chun-hua, Shi Tao, Li Bo-xun, Huang Gui-xiu. 2013. Cloning and sequence analysis of Hog1 gene from Corynespora cassiicola of Hevea brasiliensis. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 34 (3):424-428. (in Chinese) |
| 王延丽, 林春花, 时涛, 李博勋, 黄贵修. 2013. 巴西橡胶树棒孢霉落叶病菌Hog1同源基因的克隆和序列分析. 热带作物学报, 34 (3):424-428. | |
| [29] |
Wu J, Xie X W, Shi Y, Chai A L, Li B J. 2018a. Analysis of pathogenic and genetic variability of Corynespora cassiicola based on iPBS retrotransposons. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology, 41 (1):329-338.
doi: 10.1080/07060661.2019.1584588 URL |
| [30] |
Wu J, Xie X W, Shi Y, Chai A L, Wang Q, Li B J. 2018b. Variation of cassiicolin genes among Chinese isolates of Corynespora cassiicola. Journal of Microbiology, 56:634-647.
doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7497-5 |
| [31] | Xue Cai-ying, Wu Hai-yan, Hou Meng-yuan, Ma Qing-zhou, Guo Ya-shuang, Geng Yue-hua, Zang Rui, Zhang Meng, Xu Chao. 2021. Functional analysis of the scytalone dehydratase gene CcSCD1 in Corynespora cassiicola from strawberry. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 52 (1):25-36. (in Chinese) |
| 薛彩英, 武海燕, 侯梦圆, 马庆周, 郭雅双, 耿月华, 臧睿, 张猛, 徐超. 2021. 草莓多主棒孢霉小柱孢酮脱水酶基因CcSCD1的功能研究. 植物病理学报, 52 (1):25-36. | |
| [32] |
Zhang Zi-xin, Xie Xue-wen, Fu Jun-fan, Li Bao-ju. 2016. Status on pathogenic and resistance gene of cucumber target leaf spot. Current Biotechnology, 6 (3):169-173. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2016.03.03 |
|
张自心, 谢学文, 傅俊范, 李宝聚. 2016. 黄瓜棒孢叶斑病病原学和抗性基因研究进展. 生物技术进展, 6 (3):169-173.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2016.03.03 |
| [1] | 张欣, 漆艳香, 曾凡云, 王艳玮, 谢培兰, 谢艺贤, 彭军. 香蕉枯萎病菌Dicer-like基因的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 279-294. |
| [2] | 罗天宽, 吴海涛, 张圣美, 黄宗安, 孙 继, 水德聚, 陈先知. 黄瓜新品种‘瓯翠1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 125-126. |
| [3] | 王鹤冰, 向华丰, 陈新中, 张 生, 张洪成. 华南型黄瓜新品种‘新燕095’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 79-80. |
| [4] | 许春梅, 张作标, 柳景兰, 王 昕, 杨 龙, 赵 丹, 刘思宇, 贾云鹤, 孟雪娇, 崔嵩岑. 黄瓜新品种‘绿春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 81-82. |
| [5] | 张利东, 黄洪宇, 孔维良, 李加旺, 李愚鹤, . 华北型黄瓜新品种‘津优355’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 83-84. |
| [6] | 王惠哲, 杨瑞环, 邓 强, 曹明明, 李淑菊, . 抗黑星病黄瓜新品种‘津冬369’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 85-86. |
| [7] | 聂鑫淼, 栾恒, 冯改利, 王超, 李岩, 魏珉. 硅营养和嫁接砧木对黄瓜幼苗耐冷性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804. |
| [8] | 韩鲁杰, 冯一清, 杨秀华, 张宁, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 有机肥化肥配施对大棚黄瓜根区土壤与根系特征的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1047-1059. |
| [9] | 权建华, 段誉, 罗天, 袁强, 齐鑫, 王勤礼. 黄瓜新品种‘裕研9号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 703-704. |
| [10] | 宋蒙飞, 查高辉, 陈劲枫, 娄群峰. 黄瓜株型性状分子基础研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2683-2702. |
| [11] | 王团团, 缑晨星, 夏磊, 朱拼玉, 李季, 陈劲枫. 黄瓜10个基因型材料外植体内源激素水平及比例对其离体再生的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1731-1742. |
| [12] | 赵昌博, 郑世伟, 边婷, 王爽, 张小兰, 富宏丹, 孙周平, 李天来. 日光温室黄瓜不同连作茬次土壤的中量与微量元素含量变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1805-1814. |
| [13] | 胡伟, 刘昱希, 赵勤政, 陈劲枫, 娄群峰. 黄瓜—酸黄瓜异附加系的创制与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1349-1358. |
| [14] | 程凤, 宋蒙飞, 曹蕾, 张孟茹, 杨志歌, 陈劲枫, 娄群峰. 黄瓜的一个中短果突变体基因的初步定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1359-1370. |
| [15] | 贾会霞, 李锡香, 宋江萍, 林毓娥, 张晓辉, 邱杨, 阳文龙, 娄群峰, 王海平. 黄瓜核心种质白粉病抗性的全基因组关联分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1371-1385. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司