
园艺学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 574-584.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-1059
收稿日期:2025-10-30
修回日期:2026-01-27
出版日期:2026-02-25
发布日期:2026-02-12
基金资助:
XU Yong, YANG Yang, WANG Ruotong, MAO Yiru, FENG Liguo( )
)
Received:2025-10-30
Revised:2026-01-27
Published:2026-02-25
Online:2026-02-12
摘要:
以二年生‘丰花’玫瑰(Rosa rugosa‘Fenghua’)为材料,通过叶面喷施0.1、0.3和0.5 mmol · L-1的褪黑素,研究其对玫瑰挥发性有机化合物的影响。结果表明,0.3和0.5 mmol · L-1褪黑素处理花朵直径分别显著增加21.3%和22.2%。0.3 mmol · L-1处理后,花蕾期香叶醇、香茅醇和甲基丁香酚的含量显著提升,分别提高100.0%、39.1%和52.2%;盛花期香茅醇及单萜衍生物乙酸香茅酯和乙酸香叶酯的含量显著提升,分别提高50.7%、102.2%和108.2%;同时,2-苯乙醇及其衍生物乙酸苯乙酯分别显著提升71.9%和164.8%。以上结果表明,两个花期主要香气成分的含量均随褪黑素浓度增加呈先升后降趋势,在0.3 mmol · L-1下达到峰值。qRT-PCR分析表明,0.3 mmol · L-1处理4个萜类以及1个2-苯乙醇合成关键基因RrAADC(芳香族氨基酸脱羧酶)显著上调。病毒诱导基因沉默(VIGS)实验进一步表明,在沉默RrAADC的花瓣中,褪黑素处理可使其表达量以及2-苯乙醇的含量恢复至对照水平,证实RrAADC是褪黑素调控2-苯乙醇积累的关键靶基因。
徐勇, 杨阳, 王若彤, 毛一茹, 冯立国. 外源褪黑素对玫瑰花香的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 574-584.
XU Yong, YANG Yang, WANG Ruotong, MAO Yiru, FENG Liguo. Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Rose Fragrance[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2026, 53(2): 574-584.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因Gene | 编码的酶Encoded enzyme | 引物序列Primer sequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rru04G032370.1 | RrDXS | 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合酶1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase | F:CAAGTTGTTTCCGGTACCCAA |
| R:ATCCATAGCCCAAGAGTGCAA | |||
| Rru07G014880.1 | RrDXR | 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸还原异构酶1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase | F:ATTTGTTCTTCCTCTTGCACAC |
| R:GCTGTCAAAATGATACGCCGAA | |||
| Rru07G036650.1 | RrMCT | 2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇-4-磷酸胞苷转移酶2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase | F:TTTTAAGCCAGCCTATTGCAT |
| R:GCAACGTGAATTTAAGTTCCG | |||
| Rru06G031540.1 | RrGPPS | 香叶基焦磷酸合酶 Geranyl diphosphate synthase | F:GCCTTCAGATCTTGTGCCAG |
| R:TTCAACCGCATTAGGCCCTC | |||
| Rru02G052860.1 | RrNUDX | 核苷酸二磷酸水解酶 Nucleoside diphosphate hydrolase | F:GCGCACCTATCCGAACGCGA |
| R:GCGCACCTATCCGAACGCGA | |||
| Rru05G045820.1 | RrPAR | 苯乙醛还原酶 Phenylacetaldehyde reductase | F:AGCTGTACCCTGATTTGCAACTTCC |
| R:ACCCAAGCTCTTTGCCTTTTCTTTGG | |||
| Rru01G008380.1 | RrAADC | 芳香族氨基酸脱羧酶 Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase | F:ACGCCGAATTGGTAGCGAGA |
| R:GGCCCGGAAGTTCTCCATGT | |||
| * F:ATGGGTAGCCTCCCATTCCAC | |||
| * R:TGAGAGTTCGGGTATCAAATTGACC | |||
| Rru03G012520.1 | RrPPDC | 苯丙酮酸脱羧酶 Phenylpyruvate decarboxylase | F:GCAACTTGGCCGGGATTCCT |
| R:TGCCTCCACTGCAGCCTCTA | |||
| 5.8S (内参基因 Reference) | 5.8S 核糖体 RNA 5.8S rDNA | F:CGGCAACGGATATCTCGG | |
| R:TGTGACGCCCAGGCAGACG |
表1 用于qRT-PCR分析及基因克隆的特异性引物
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR analysis or gene cloning
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因Gene | 编码的酶Encoded enzyme | 引物序列Primer sequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rru04G032370.1 | RrDXS | 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸合酶1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase | F:CAAGTTGTTTCCGGTACCCAA |
| R:ATCCATAGCCCAAGAGTGCAA | |||
| Rru07G014880.1 | RrDXR | 1-脱氧-D-木酮糖-5-磷酸还原异构酶1-Deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase | F:ATTTGTTCTTCCTCTTGCACAC |
| R:GCTGTCAAAATGATACGCCGAA | |||
| Rru07G036650.1 | RrMCT | 2-C-甲基-D-赤藓糖醇-4-磷酸胞苷转移酶2-C-Methyl-D-erythritol-4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase | F:TTTTAAGCCAGCCTATTGCAT |
| R:GCAACGTGAATTTAAGTTCCG | |||
| Rru06G031540.1 | RrGPPS | 香叶基焦磷酸合酶 Geranyl diphosphate synthase | F:GCCTTCAGATCTTGTGCCAG |
| R:TTCAACCGCATTAGGCCCTC | |||
| Rru02G052860.1 | RrNUDX | 核苷酸二磷酸水解酶 Nucleoside diphosphate hydrolase | F:GCGCACCTATCCGAACGCGA |
| R:GCGCACCTATCCGAACGCGA | |||
| Rru05G045820.1 | RrPAR | 苯乙醛还原酶 Phenylacetaldehyde reductase | F:AGCTGTACCCTGATTTGCAACTTCC |
| R:ACCCAAGCTCTTTGCCTTTTCTTTGG | |||
| Rru01G008380.1 | RrAADC | 芳香族氨基酸脱羧酶 Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase | F:ACGCCGAATTGGTAGCGAGA |
| R:GGCCCGGAAGTTCTCCATGT | |||
| * F:ATGGGTAGCCTCCCATTCCAC | |||
| * R:TGAGAGTTCGGGTATCAAATTGACC | |||
| Rru03G012520.1 | RrPPDC | 苯丙酮酸脱羧酶 Phenylpyruvate decarboxylase | F:GCAACTTGGCCGGGATTCCT |
| R:TGCCTCCACTGCAGCCTCTA | |||
| 5.8S (内参基因 Reference) | 5.8S 核糖体 RNA 5.8S rDNA | F:CGGCAACGGATATCTCGG | |
| R:TGTGACGCCCAGGCAGACG |
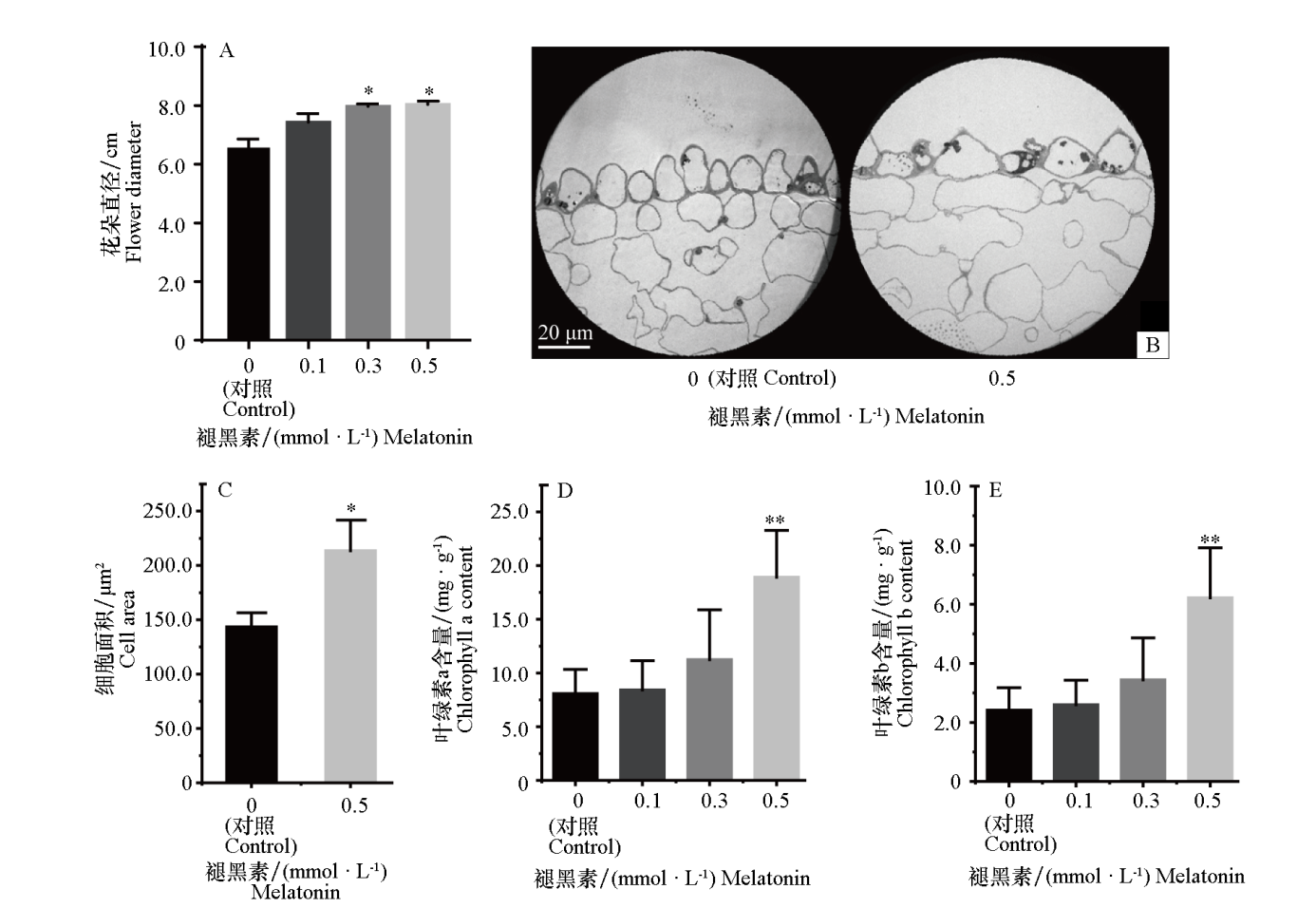
图1 不同浓度褪黑素处理对玫瑰花朵大小(A)、花瓣表皮细胞形态及大小(B、C)和叶片叶绿素a、b含量(D、E)的影响 采用单因素方差分析差异显著性,* P < 0.05、** P < 0.01、*** P < 0.001。下同
Fig. 1 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin treatment on rose flower size(A),petal epidermal cell morphology and area(B,C),and chlorophyll a and b content(D,E) Analysis of variance was used to assess the significance of differences. * P < 0.05,** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001. The same below
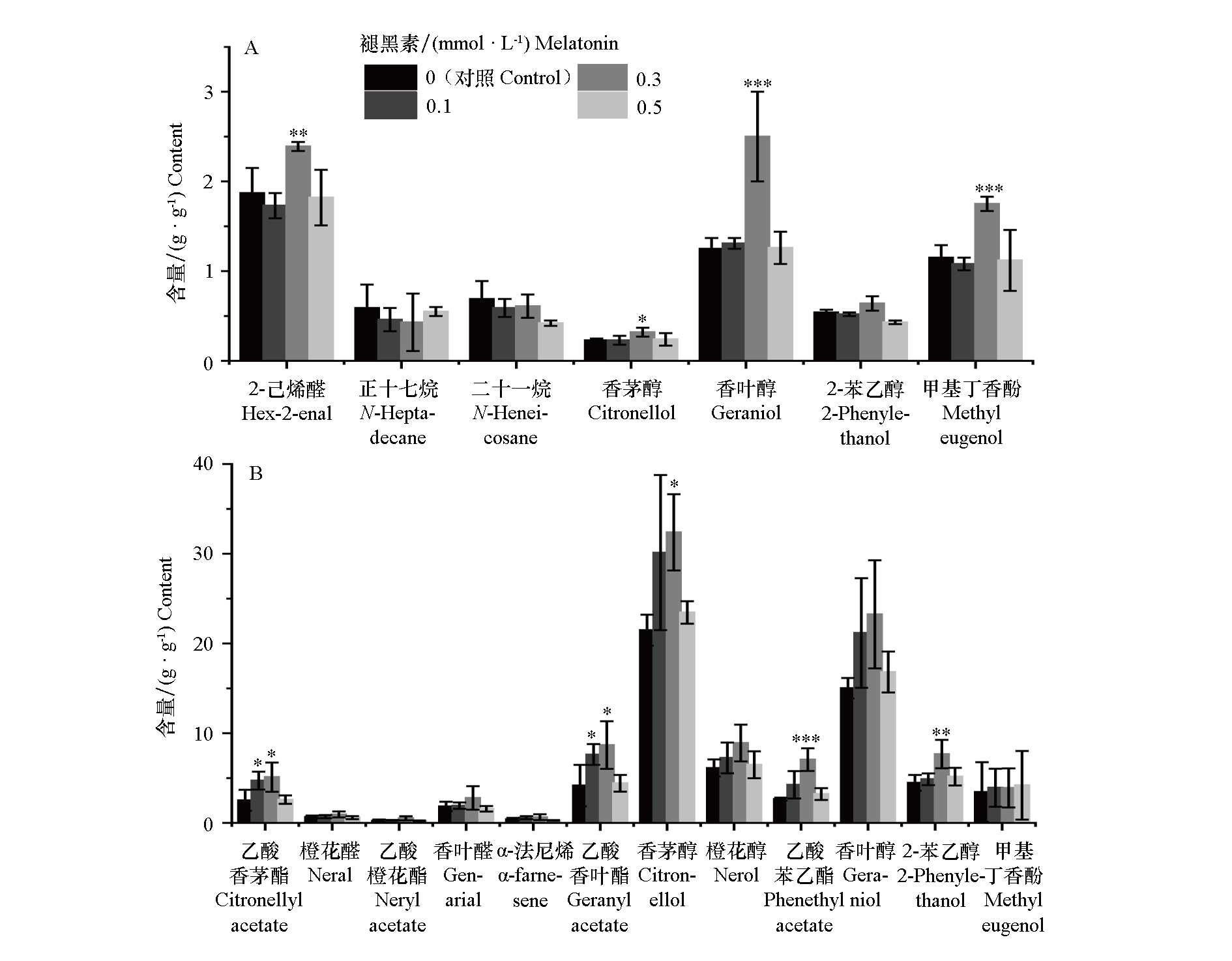
图2 不同浓度褪黑素处理对玫瑰花蕾期(A)和盛花期(B)主要香气成分含量(FW)的影响
Fig. 2 Effects of different concentrations of melatonin on the content of major aroma components(FW)in rose buds(A)and full-blooming stage(B)
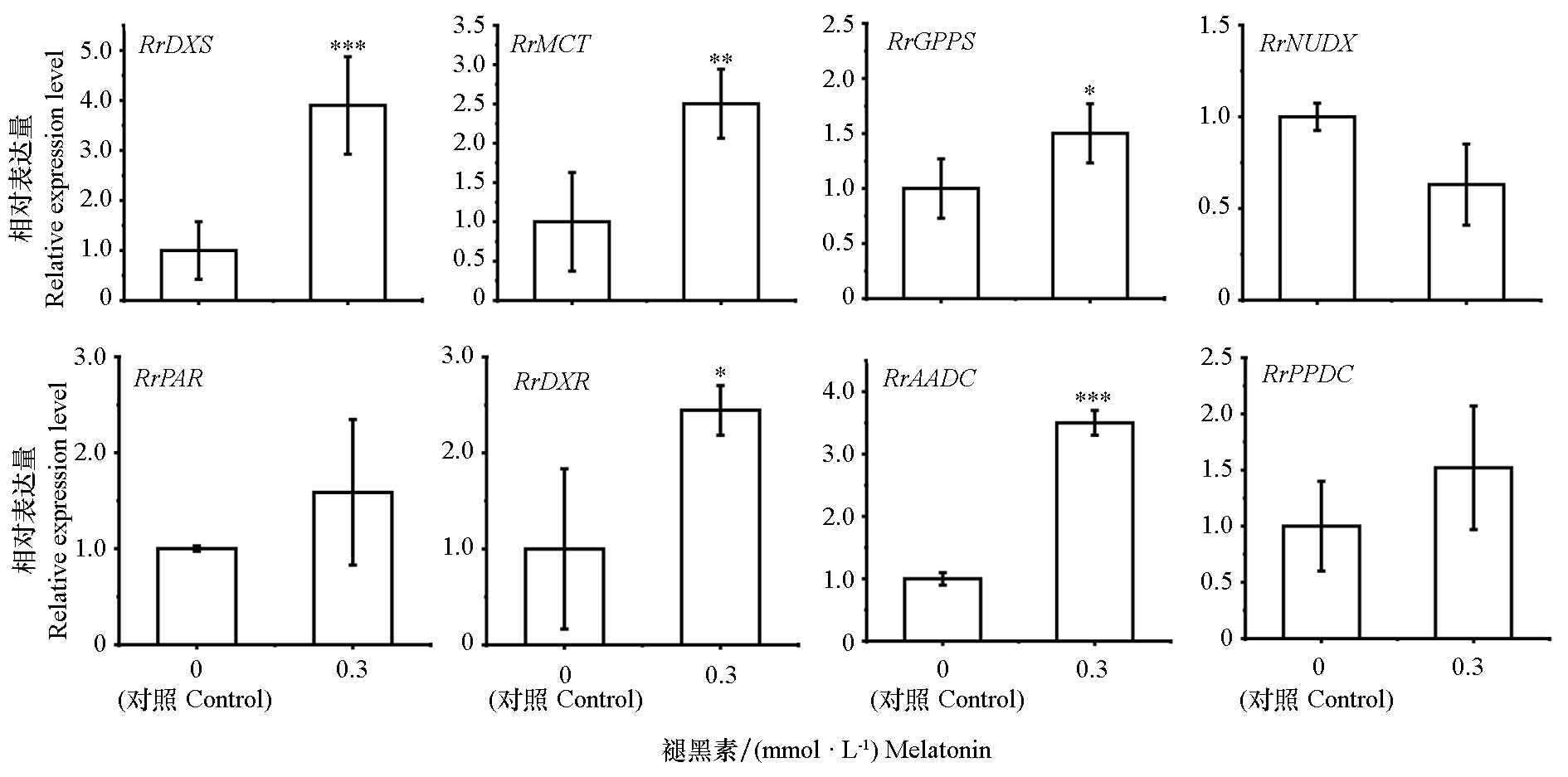
图3 外源褪黑素处理对玫瑰萜类和2-苯乙醇合成途径关键基因表达量的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of exogenous melatonin on expression of key genes in rose terpenoid and 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis
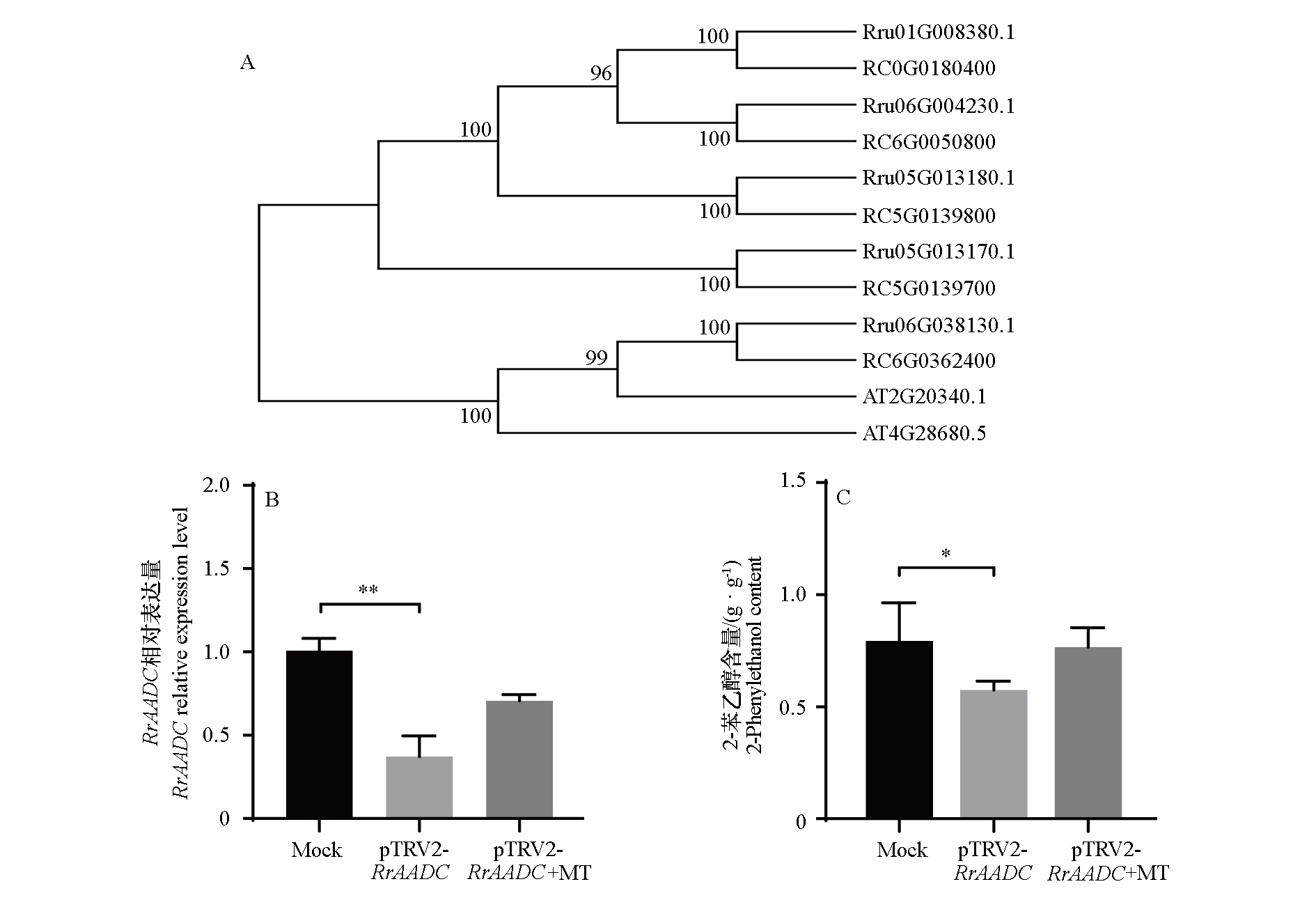
图4 玫瑰(Rr)、月季(RC)与拟南芥(At)AADC基因家族系统进化树(A)及基于VIGS的褪黑素响应验证(B和C)
Fig. 4 Phylogenetic tree(A)of the AADC gene family in Rosa rugosa(Rr),R. chinensis(RC),and Arabidopsis thaliana(At),and melatonin response validation based on VIGS(B and C)
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
李恭峰, 高亚新, 马万成, 张振兴, 刘益克, 李宁, 李青云. 2022. 叶喷褪黑素对草莓生长、光合及果实品质的影响. 中国蔬菜,(12):80-85.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
李园子, 高靖怡, 王凤寰, 廖永红. 2024. 2-苯乙醇合成研究进展. 生物工程学报, 40 (6):1694-1710.
|
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
|
徐勇, 马远潇, 梁悦, 董桂芝, 白梦娟, 冯立国. 2024. 玫瑰花瓣表皮分泌细胞的显微观察及其与精油含量的关系. 江苏农业科学, 52 (24):148-155.
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
|
张磊, 寇亚平, 段铭奥, 王晓飞, 贾瑞冬, 赵鑫, 李秋香, 葛红, 杨树华. 2024. 油用玫瑰研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报, 25 (5):777-789.
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
张诗瑶, 王力, 张颖, 刘秋艳, 毛一茹, 徐梓怿, 龚琴, 王萱. 2023. 食用玫瑰产业发展现状与对策. 黑龙江农业科学,(7):86-91.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
|
赵雨晴, 陈涛, 袁明. 2021. 褪黑素在果实发育和采后保鲜中的作用综述. 园艺学报, 48 (6):1233-1249.
|
| [1] | 王芳, 范燕萍. 观赏植物花香性状形成及调控机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 359-385. |
| [2] | 牛童非, 杨迪, 马慧丽, 郭丽丽, 侯小改. 牡丹花香的生物合成及调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 447-466. |
| [3] | 张鹏, 叶新茹, 栗华隆, 陈昱媛, 孙明, 唐玉超. ‘梨香’菊花香成分鉴定及香气特征分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 496-512. |
| [4] | 沈言, 夏子轶, 冷平生, 马波, 胡增辉. ‘西伯利亚’百合LiMYB4的克隆及在萜烯合成中的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 525-537. |
| [5] | 李崇晖, 洪小雨, 陆顺教, 廖易, 尹俊梅. 基于代谢组与转录组联合分析解析秋石斛花香形成机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2026, 53(2): 557-573. |
| [6] | 冯玲佳, 刘毓婕, 何林彤, 王新超, 叶萌. 芳樟醇合成调控机制及其生态功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2270-2290. |
| [7] | 李雯, 李绍朋, 李东海, 吴福川, 田波. 瓷玫瑰切花瓶插期间观赏品质和生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(6): 1633-1643. |
| [8] | 段青青, 韩梅梅, 王友平, 常培培, 谭月强, 张自坤. 外源褪黑素影响盐碱复合胁迫下西瓜种子萌发的综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 1020-1036. |
| [9] | 许桐, 王越, 吴丽娜, 张航, 尹立来, 徐柯宇, 郑小林. 褪黑素处理对‘桃形李’采后果实品质及花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 395-405. |
| [10] | 覃艮红, 袁洪波, 王卓妮, 史冰柯, 范洋洋, 王丽, 张猛, 涂洪涛, 徐超, 侯珲. 蜡样芽孢杆菌挥发物对苹果轮纹病菌的拮抗活性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1403-1412. |
| [11] | 郝金倩, 王宝驹, 佟静, 刘明池, 武占会, 王素娜, 刘宁. 外源褪黑素对水培韭菜生长和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 847-858. |
| [12] | 关思慧, 刘晨旭, 姚祝平, 万红建, 刁明, 程远. 腐植酸处理对樱桃番茄挥发性有机化合物成分和含量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 346-360. |
| [13] | 王雅楠, 刘绪涛, 景桐彤, 柴亚婷, 张晓伟, 艾希珍, 毕焕改. 褪黑素对番茄衰老叶片抗氧化系统的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2594-2606. |
| [14] | 冯一清, 仇胜囡, 吴月, 解阳, 张晓伟, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 褪黑素对日光温室黄瓜耐冷性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2633-2644. |
| [15] | 梁宇卿, 孙春辉, 邓丛良, 史喜菊, 种焱, 李永强. 蚕豆萎蔫病毒2号北京玫瑰分离物的鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(10): 2320-2328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司