
园艺学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 346-360.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0811
关思慧1,2, 刘晨旭2, 姚祝平2, 万红建2, 刁明1,*( ), 程远2,*(
), 程远2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-12-05
修回日期:2024-01-04
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-02-26
通讯作者:
基金资助:
GUAN Sihui1,2, LIU Chenxu2, YAO Zhuping2, WAN Hongjian2, DIAO Ming1,*( ), CHENG Yuan2,*(
), CHENG Yuan2,*( )
)
Received:2023-12-05
Revised:2024-01-04
Published:2024-02-25
Online:2024-02-26
摘要:
以果实香气浓郁的樱桃番茄(Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme)品种‘浙樱粉1号’为研究对象,采用顶空固相微萃取—气相色谱—质谱联用技术,对腐殖酸不同处理(对照:根部和叶面均施清水;根和叶施:根部和叶面均施腐植酸;根施:根部施腐植酸,叶面施清水;叶施:根部施清水,叶面施腐植酸)下果实挥发性有机化合物(volatile organic compounds,VOC)组成、含量及差异进行比较分析,共检测到15类340种VOC。与清水对照相比,根和叶施、根施、叶施腐殖酸处理后,果实中的VOC相对含量分别提升了49.3%、25.6%、14.4%,其中根和叶施、叶施处理显著提高了果实中醛类的相对含量,而根施处理显著提高了萜类的相对含量。差异VOC统计结果表明,与对照相比,根和叶施、根施、叶施腐植酸处理VOC积累上调数量分别为153、147和13个,占总差异积累VOC数量的97.5%、97.4%和81.3%,根和叶施、根施处理的差异VOC数量显著多于叶施处理。感官风味特征分析表明,根和叶施腐植酸能够增加番茄果实的甜香型香味特征,而单独根施和叶施处理则能够增加果香型香味特征。主成分分析结果表明:腐植酸处理后番茄果实香气特征不是被其中1或2种相对含量高或相对气味活度值较高的VOC主导,而是被多种VOC相互作用影响,使其呈现出不一样的香气类型。综上,腐殖酸处理,尤其是根和叶施处理,可显著影响番茄果实中VOC的组成和相对含量,提升风味品质。
关思慧, 刘晨旭, 姚祝平, 万红建, 刁明, 程远. 腐植酸处理对樱桃番茄挥发性有机化合物成分和含量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 346-360.
GUAN Sihui, LIU Chenxu, YAO Zhuping, WAN Hongjian, DIAO Ming, CHENG Yuan. Effects of Humic Acid Treatment on the Composition and Content of Volatile Organic Compounds in Cherry Tomato[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 346-360.

图1 腐植酸处理对番茄果实挥发性有机化合物的统计分析 A:主成分分析(PCA);B:正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA);C:聚类分析(HCA);D:不同样本皮尔逊乘积相关系数。所有收集到的数据都在95%置信区间内。
Fig. 1 Statistical analysis of VOCs in tomato fruit treated with humic acid A:Principal component analysis (PCA). B:Orthogonal partial least square discriminant analysis(OPLS-DA). C:Cluster analysis(HCA).D:Pearson product correlation coefficients. All the data collected are within the 95% confidence interval.
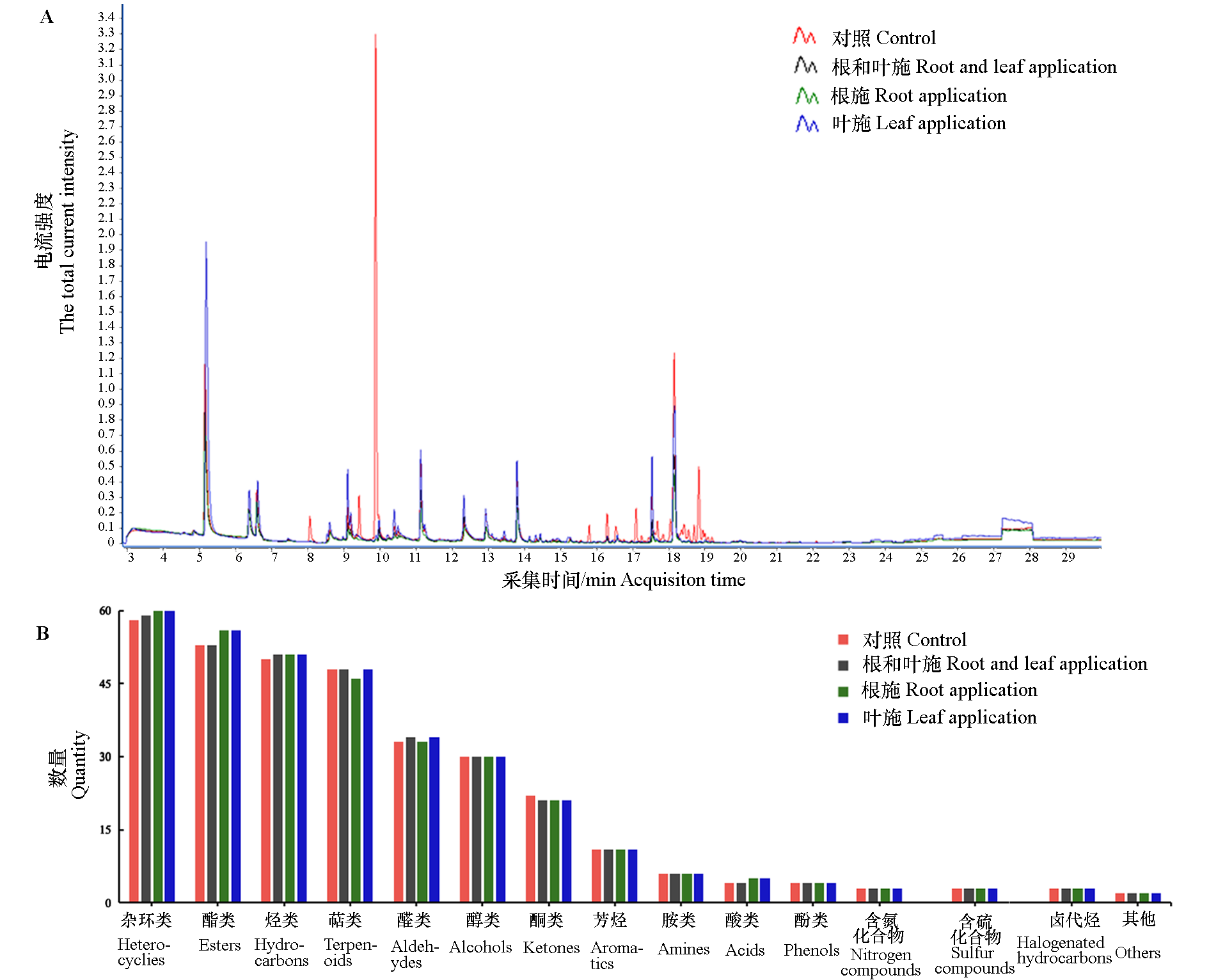
图2 腐植酸处理下番茄果实挥发性有机化合物的检测 A:顶空固相微萃取与气相色谱—质谱联用检测总离子流图;B:不同类型挥发性有机化合物数量。
Fig. 2 Detection effect of humic acid treatment on VOCs of tomato fruit A:Total ion flow diagram of VOCs for each treatment detected by HS-SPME-GC-MS;B:Bar chart of different types of VOCs for each processing.
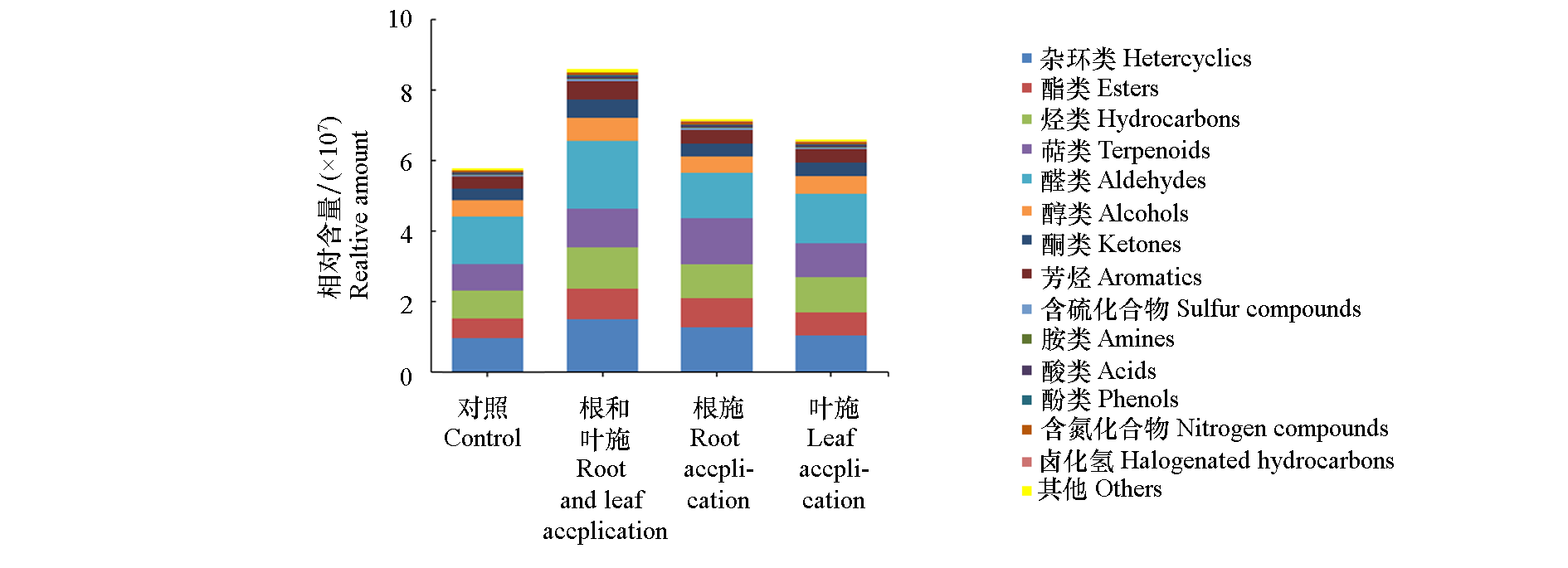
图3 腐殖酸不同施用方式对不同类型挥发性有机化合物相对含量的影响
Fig. 3 Effects of different humic acid application methods on the relative contents of different types of volatile organic compounds
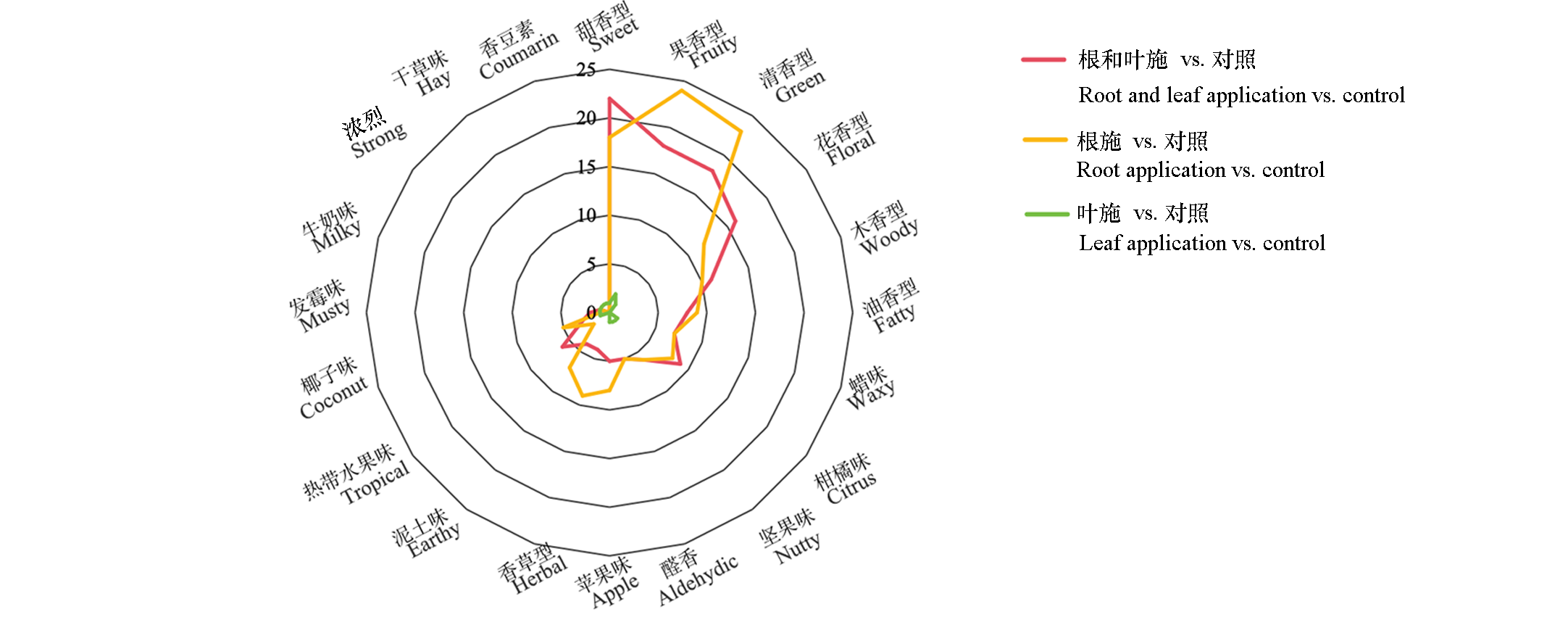
图5 腐殖酸处理对番茄果实感官风味特征变化的影响 刻度为出现频次。
Fig. 5 Effects of humic acid treatments on sensory flavor characteristics of tomato fruits The scale indicates the frequency of occurrence.
| 处理 Treatment | 化合物名称 Name | 种类 Type | CAS | 上调差异倍数 Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根和叶施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Root | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| and | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| leaf | 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline,6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — |
| application | 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 99-86-5 | 3.95 |
| 己酸丙酯 Hexanoic acid,propyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 626-77-7 | 3.27 | |
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 醇类 Alcohols | 628-99-9 | 2.86 | |
| 4-异丙基甲苯 p-Cymene | 芳烃 Aromatics | 99-87-6 | 2.65 | |
| 异丁酸异丁酯 Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-methylpropyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 97-85-8 | 2.40 | |
| 2,4-己二醛 2,4-Hexadienal, (E, E)- | 醛类 Aldehydes | 142-83-6 | 2.34 | |
| 1,3,3-三甲基-二环[2.2.1]庚-2-酮 Fenchone | 萜类 Terpenoids | 1195-79-5 | 2.33 | |
| 2-甲基-壬烷 Nonane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 871-83-0 | 2.31 | |
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 芳烃 Aromatics | 5279-14-1 | 2.27 | |
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-89-0 | 2.10 | |
| α-松油醇 L-α-Terpineol | 萜类 Terpenoids | 10482-56-1 | 2.08 | |
| 根施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Root | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| application | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline, 6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — | |
| 2-丁基四氢呋喃 Furan, 2-butyltetrahydro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1004-29-1 | — | |
| 2-甲基-戊酸 Pentanoic acid, 2-methyl- | 酸类 Acids | 97-61-0 | — | |
| 顺-3-己烯基丁酸酯Butanoic acid, 3-hexenyl ester, (Z)- | 酯类 Esters | 16491-36-4 | — | |
| 2-乙酰基吡咯烷 2-Acetylpyrrolidine | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 60026-20-2 | — | |
| 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 99-86-5 | 3.54 | |
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-89-0 | 2.54 | |
| 1-十二碳烯 1-Dodecene | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 112-41-4 | 2.40 | |
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 芳烃 Aromatics | 5279-14-1 | 2.25 | |
| 1-甲基-4-(1-甲基亚乙基)-环己醇 1-Cyclohexanol, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethylidene)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 586-81-2 | 2.17 | |
| 4-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 4-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 2801-87-8 | 2.14 | |
| 2-呋喃丙酸乙酯 2-Furanpropanoic acid, ethyl ester | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 10031-90-0 | 2.13 | |
| 顺式对甲酚 p-Menth-2-en-7-ol, cis- | 酚类 Phenols | 19898-86-3 | 2.08 | |
| 2-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-93-6 | 2.08 | |
| (1S-顺式)-2,3,5,7a-四氢-1-羟基-1H-吡咯嗪7-甲醇 1H-Pyrrolizine-7-methanol, 2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-, (1S-cis)- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 520-63-8 | 2.07 | |
| 4- (1-甲基乙烯基)-1-环己烯-1-羧酸 1-Cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, 4-(1-methylethenyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 7694-45-3 | 2.04 | |
| (Z)-3,3-二甲基环亚己基乙醇 Ethanol, 2-(3,3-dimethylcyclohexylidene)-,(Z)- | 醇类 Alcohols | 26532-23-0 | 2.01 | |
| 二甲基丁酸叶醇酯 cis-3-Hexenyl-α-methylbutyrate | 酯类 Esters | 53398-85-9 | 2.01 | |
| 7-羟基-6-甲基-呋喃[3,4-c]吡啶-1(3H)-酮 Furo[3,4-c]pyridin-1(3H)-one, 7-hydroxy-6-methyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 4753-19-9 | 2.00 | |
| 叶施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Leaf | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| application | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline, 6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — | |
| 2-丁基四氢呋喃 Furan, 2-butyltetrahydro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1004-29-1 | — | |
| 2-甲基-戊酸 Pentanoic acid, 2-methyl- | 酸类 Acids | 97-61-0 | — | |
| 顺-3-己烯基丁酸酯 Butanoic acid, 3-hexenyl ester, (Z)- | 酯类 Esters | 16491-36-4 | — | |
| 4-(1-甲基乙基)-1,5-环己二烯-1-甲醇 1,5-Cyclohexadiene-1-methanol, 4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 19876-45-0 | 2.65 | |
| 四甲基十四烷 Tetradecane, 4-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 25117-24-2 | 2.09 |
表1 番茄腐植酸处理与对照相比果实显著差异的挥发性有机化合物
Table 1 VOCs of tomato fruit treated with humic acids were significantly different compared with the control
| 处理 Treatment | 化合物名称 Name | 种类 Type | CAS | 上调差异倍数 Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根和叶施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Root | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| and | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| leaf | 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline,6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — |
| application | 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 99-86-5 | 3.95 |
| 己酸丙酯 Hexanoic acid,propyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 626-77-7 | 3.27 | |
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 醇类 Alcohols | 628-99-9 | 2.86 | |
| 4-异丙基甲苯 p-Cymene | 芳烃 Aromatics | 99-87-6 | 2.65 | |
| 异丁酸异丁酯 Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-methylpropyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 97-85-8 | 2.40 | |
| 2,4-己二醛 2,4-Hexadienal, (E, E)- | 醛类 Aldehydes | 142-83-6 | 2.34 | |
| 1,3,3-三甲基-二环[2.2.1]庚-2-酮 Fenchone | 萜类 Terpenoids | 1195-79-5 | 2.33 | |
| 2-甲基-壬烷 Nonane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 871-83-0 | 2.31 | |
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 芳烃 Aromatics | 5279-14-1 | 2.27 | |
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-89-0 | 2.10 | |
| α-松油醇 L-α-Terpineol | 萜类 Terpenoids | 10482-56-1 | 2.08 | |
| 根施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Root | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| application | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline, 6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — | |
| 2-丁基四氢呋喃 Furan, 2-butyltetrahydro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1004-29-1 | — | |
| 2-甲基-戊酸 Pentanoic acid, 2-methyl- | 酸类 Acids | 97-61-0 | — | |
| 顺-3-己烯基丁酸酯Butanoic acid, 3-hexenyl ester, (Z)- | 酯类 Esters | 16491-36-4 | — | |
| 2-乙酰基吡咯烷 2-Acetylpyrrolidine | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 60026-20-2 | — | |
| 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 99-86-5 | 3.54 | |
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-89-0 | 2.54 | |
| 1-十二碳烯 1-Dodecene | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 112-41-4 | 2.40 | |
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 芳烃 Aromatics | 5279-14-1 | 2.25 | |
| 1-甲基-4-(1-甲基亚乙基)-环己醇 1-Cyclohexanol, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethylidene)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 586-81-2 | 2.17 | |
| 4-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 4-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 2801-87-8 | 2.14 | |
| 2-呋喃丙酸乙酯 2-Furanpropanoic acid, ethyl ester | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 10031-90-0 | 2.13 | |
| 顺式对甲酚 p-Menth-2-en-7-ol, cis- | 酚类 Phenols | 19898-86-3 | 2.08 | |
| 2-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 2-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 1560-93-6 | 2.08 | |
| (1S-顺式)-2,3,5,7a-四氢-1-羟基-1H-吡咯嗪7-甲醇 1H-Pyrrolizine-7-methanol, 2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-, (1S-cis)- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 520-63-8 | 2.07 | |
| 4- (1-甲基乙烯基)-1-环己烯-1-羧酸 1-Cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, 4-(1-methylethenyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 7694-45-3 | 2.04 | |
| (Z)-3,3-二甲基环亚己基乙醇 Ethanol, 2-(3,3-dimethylcyclohexylidene)-,(Z)- | 醇类 Alcohols | 26532-23-0 | 2.01 | |
| 二甲基丁酸叶醇酯 cis-3-Hexenyl-α-methylbutyrate | 酯类 Esters | 53398-85-9 | 2.01 | |
| 7-羟基-6-甲基-呋喃[3,4-c]吡啶-1(3H)-酮 Furo[3,4-c]pyridin-1(3H)-one, 7-hydroxy-6-methyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 4753-19-9 | 2.00 | |
| 叶施 | 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid, cyclopentyl ester | 酯类 Esters | 6290-13-7 | — |
| Leaf | 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 醛类 Aldehydes | 21661-97-2 | — |
| application | 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 25115-69-9 | — |
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline, 6-nitro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 18368-61-1 | — | |
| 2-丁基四氢呋喃 Furan, 2-butyltetrahydro- | 杂环类 Heterocyclics | 1004-29-1 | — | |
| 2-甲基-戊酸 Pentanoic acid, 2-methyl- | 酸类 Acids | 97-61-0 | — | |
| 顺-3-己烯基丁酸酯 Butanoic acid, 3-hexenyl ester, (Z)- | 酯类 Esters | 16491-36-4 | — | |
| 4-(1-甲基乙基)-1,5-环己二烯-1-甲醇 1,5-Cyclohexadiene-1-methanol, 4-(1-methylethyl)- | 萜类 Terpenoids | 19876-45-0 | 2.65 | |
| 四甲基十四烷 Tetradecane, 4-methyl- | 烃类 Hydrocarbons | 25117-24-2 | 2.09 |
| 化合物 Compound | PC1 | PC2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | |||||
| 顺-4-庚烯醛 4-Heptenal, (Z)- | 0.878 | 0.033 | -0.479 | -0.031 | ||||
| 5-甲基-2-呋喃甲硫醇 2-Furanmethanethiol, 5-methyl- | 0.748 | 0.028 | -0.664 | -0.042 | ||||
| 2-噻吩甲基硫醇 2-Thiophenemethanethiol | 0.974 | 0.037 | 0.224 | 0.014 | ||||
| 二甲基三硫 Dimethyl triSulfur compounds | 0.998 | 0.038 | 0.058 | 0.004 | ||||
| 苯甲硫醇 Benzenemethanethiol | 0.344 | 0.013 | -0.939 | -0.060 | ||||
| 5-乙基-3-羟基-4-甲基-2(5H)-呋喃酮 2(5H)-Furanone, 5-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-methyl- | 0.971 | 0.037 | 0.240 | 0.015 | ||||
| 己醛 Hexanal | 0.542 | 0.021 | -0.841 | -0.054 | ||||
| (E)-2-壬烯醛 2-Nonenal, (E)- | -1.000 | -0.038 | 0.026 | 0.002 | ||||
| 1-辛烯-3-酮 1-Octen-3-one | 0.950 | 0.036 | -0.313 | -0.020 | ||||
| 甲酸-3-巯基-3-甲基丁酯 3-Mercapto-3-methylbutyl formate (ester) | -0.307 | -0.012 | 0.952 | 0.061 | ||||
| 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid,cyclopentyl ester | 0.963 | 0.037 | -0.269 | -0.017 | ||||
| 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 0.639 | 0.024 | 0.770 | 0.049 | ||||
| 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 0.682 | 0.026 | 0.731 | 0.047 | ||||
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline,6-nitro- | -0.961 | -0.036 | 0.278 | 0.018 | ||||
| 异丁酸异丁酯 Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-methylpropyl ester | 0.837 | 0.032 | -0.548 | -0.035 | ||||
| 1,3,3-三甲基-二环[2.2.1]庚-2-酮 Fenchone | 0.450 | 0.017 | -0.893 | -0.057 | ||||
| 2,4-己二醛 2,4-Hexadienal, (E, E)- | 0.738 | 0.028 | -0.675 | -0.043 | ||||
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 0.509 | 0.019 | 0.861 | 0.055 | ||||
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 0.782 | 0.030 | -0.623 | -0.040 | ||||
| 己酸丙酯 Hexanoic acid, propyl ester | 0.912 | 0.035 | -0.411 | -0.026 | ||||
| 2-甲基-壬烷 Nonane, 2-methyl- | 0.987 | 0.037 | -0.162 | -0.010 | ||||
| 4-异丙基甲苯 p-Cymene | 0.809 | 0.031 | 0.587 | 0.037 | ||||
| α-松油醇 L-α-Terpineol | 0.003 | 0.000 | -1.000 | -0.064 | ||||
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 0.974 | 0.037 | 0.227 | 0.014 | ||||
| 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 0.990 | 0.038 | -0.141 | -0.009 | ||||
| (Z)-3, 3-二甲基环亚己基乙醇 Ethanol, 2-(3,3-dimethylcyclohexylidene)-, (Z)- | 0.773 | 0.029 | 0.635 | 0.041 | ||||
| 1-十二碳烯 1-Dodecene | 0.208 | 0.008 | 0.978 | 0.062 | ||||
| 2-呋喃丙酸乙酯 2-Furanpropanoic acid,ethyl ester | -0.911 | -0.035 | -0.412 | -0.026 | ||||
| 1-甲基-4-(1-甲基亚乙基)-环己醇 Cyclohexanol, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethylidene)- | -1.000 | -0.038 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| 顺式对甲酚 p-Menth-2-en-7-ol, cis- | -0.957 | -0.036 | -0.291 | -0.019 | ||||
| 4- (1-甲基乙烯基)-1-环己烯-1-羧酸 1-Cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, 4-(1-methylethenyl)- | 0.661 | 0.025 | 0.751 | 0.048 | ||||
| (1S-顺式)-2,3,5,7a-四氢-1-羟基-1H-吡咯嗪7-甲醇 1H-Pyrrolizine-7-methanol, 2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-,(1S-cis)- | 0.685 | 0.026 | 0.728 | 0.046 | ||||
| 2-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 2-methyl- | 0.899 | 0.034 | 0.438 | 0.028 | ||||
| 4-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 4-methyl- | 0.741 | 0.028 | 0.671 | 0.043 | ||||
表2 番茄腐植酸处理对果实关键挥发性有机化合物的前2个主要成分的特征向量和载荷量
Table 2 The eigenvectors and loads of the first two main components of key VOCs in tomato fruit treated with humic acid
| 化合物 Compound | PC1 | PC2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | 载荷量 Load capacity | 特征向量 Feature vector | |||||
| 顺-4-庚烯醛 4-Heptenal, (Z)- | 0.878 | 0.033 | -0.479 | -0.031 | ||||
| 5-甲基-2-呋喃甲硫醇 2-Furanmethanethiol, 5-methyl- | 0.748 | 0.028 | -0.664 | -0.042 | ||||
| 2-噻吩甲基硫醇 2-Thiophenemethanethiol | 0.974 | 0.037 | 0.224 | 0.014 | ||||
| 二甲基三硫 Dimethyl triSulfur compounds | 0.998 | 0.038 | 0.058 | 0.004 | ||||
| 苯甲硫醇 Benzenemethanethiol | 0.344 | 0.013 | -0.939 | -0.060 | ||||
| 5-乙基-3-羟基-4-甲基-2(5H)-呋喃酮 2(5H)-Furanone, 5-ethyl-3-hydroxy-4-methyl- | 0.971 | 0.037 | 0.240 | 0.015 | ||||
| 己醛 Hexanal | 0.542 | 0.021 | -0.841 | -0.054 | ||||
| (E)-2-壬烯醛 2-Nonenal, (E)- | -1.000 | -0.038 | 0.026 | 0.002 | ||||
| 1-辛烯-3-酮 1-Octen-3-one | 0.950 | 0.036 | -0.313 | -0.020 | ||||
| 甲酸-3-巯基-3-甲基丁酯 3-Mercapto-3-methylbutyl formate (ester) | -0.307 | -0.012 | 0.952 | 0.061 | ||||
| 丁酸环戊酯 Butanoic acid,cyclopentyl ester | 0.963 | 0.037 | -0.269 | -0.017 | ||||
| 顺-7-癸烯醛 cis-7-Decen-1-al | 0.639 | 0.024 | 0.770 | 0.049 | ||||
| 3-乙基-2,6-哌啶二酮 2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-ethyl- | 0.682 | 0.026 | 0.731 | 0.047 | ||||
| 6-硝基-2-吡啶啉 2-Picoline,6-nitro- | -0.961 | -0.036 | 0.278 | 0.018 | ||||
| 异丁酸异丁酯 Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-methylpropyl ester | 0.837 | 0.032 | -0.548 | -0.035 | ||||
| 1,3,3-三甲基-二环[2.2.1]庚-2-酮 Fenchone | 0.450 | 0.017 | -0.893 | -0.057 | ||||
| 2,4-己二醛 2,4-Hexadienal, (E, E)- | 0.738 | 0.028 | -0.675 | -0.043 | ||||
| 2-甲基-十七烷 Heptadecane, 2-methyl- | 0.509 | 0.019 | 0.861 | 0.055 | ||||
| 2-壬醇 2-Nonanol | 0.782 | 0.030 | -0.623 | -0.040 | ||||
| 己酸丙酯 Hexanoic acid, propyl ester | 0.912 | 0.035 | -0.411 | -0.026 | ||||
| 2-甲基-壬烷 Nonane, 2-methyl- | 0.987 | 0.037 | -0.162 | -0.010 | ||||
| 4-异丙基甲苯 p-Cymene | 0.809 | 0.031 | 0.587 | 0.037 | ||||
| α-松油醇 L-α-Terpineol | 0.003 | 0.000 | -1.000 | -0.064 | ||||
| (1-硝基丙基)-苯 Benzene, (1-nitropropyl)- | 0.974 | 0.037 | 0.227 | 0.014 | ||||
| 松油烯 1,3-Cyclohexadiene, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethyl)- | 0.990 | 0.038 | -0.141 | -0.009 | ||||
| (Z)-3, 3-二甲基环亚己基乙醇 Ethanol, 2-(3,3-dimethylcyclohexylidene)-, (Z)- | 0.773 | 0.029 | 0.635 | 0.041 | ||||
| 1-十二碳烯 1-Dodecene | 0.208 | 0.008 | 0.978 | 0.062 | ||||
| 2-呋喃丙酸乙酯 2-Furanpropanoic acid,ethyl ester | -0.911 | -0.035 | -0.412 | -0.026 | ||||
| 1-甲基-4-(1-甲基亚乙基)-环己醇 Cyclohexanol, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethylidene)- | -1.000 | -0.038 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| 顺式对甲酚 p-Menth-2-en-7-ol, cis- | -0.957 | -0.036 | -0.291 | -0.019 | ||||
| 4- (1-甲基乙烯基)-1-环己烯-1-羧酸 1-Cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, 4-(1-methylethenyl)- | 0.661 | 0.025 | 0.751 | 0.048 | ||||
| (1S-顺式)-2,3,5,7a-四氢-1-羟基-1H-吡咯嗪7-甲醇 1H-Pyrrolizine-7-methanol, 2,3,5,7a-tetrahydro-1-hydroxy-,(1S-cis)- | 0.685 | 0.026 | 0.728 | 0.046 | ||||
| 2-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 2-methyl- | 0.899 | 0.034 | 0.438 | 0.028 | ||||
| 4-甲基-十五烷 Pentadecane, 4-methyl- | 0.741 | 0.028 | 0.671 | 0.043 | ||||
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈臻, 曾翠云, 张永合. 2023. 腐植酸在土壤污染防治修复技术中的应用. 腐植酸,(4):1-6,57.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
程国亭, 娄茜棋, 栗现芳, 孙会茹, 徐成楠, 李爽, 赵继荣, 乔宏喜, 王延峰, 梁燕. 2022. 番茄果实风味物质组成及其影响因素研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(7):23-33.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
丁守鹏, 张国新, 姚玉涛, 孙叶烁, 丁冯洁. 2021. 腐植酸肥料对滨海盐碱地土壤性状及番茄生长和品质的影响. 河北农业科学, 25 (6):65-70.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
豆建华, 张洋, 袁鸿, 王光正, 王俊文, 汪洁, 武玥, 唐中祺, 郁继华. 2023. 外源褪黑素对番茄果实品质和挥发性物质的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 41 (4):83-95,117.
|
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.3390/molecules18078200 pmid: 23852166 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
郭精桐, 赵圆, 孙玉敬. 2023. 番茄果实风味及其影响因素的研究进展. 食品科学: 44 ( 17):169-177.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
郝晓莉, 卜庆状, 张馨予, 陈芳. 2023. 腐植酸基肥对日光温室番茄农艺性状、产量、品质的影响. 园艺与种苗, 43 (4):5-6,50.
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.10.010 pmid: 36302334 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00472 pmid: 32477378 |
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
李道岭, 杜光补, 刘景凯, 黄祥川. 2021. 含腐植酸水溶肥施用方式对大棚西红柿产量和经济效益的影响. 腐植酸,(6):41-44.
|
|
| [24] |
|
|
刘晓奇, 肖雪梅, 王俊文, 唐中祺, 武玥, 刘泽慈, 张丹, 郁继华. 2021. 水分亏缺对日光温室基质栽培番茄果实营养和风味品质的影响. 江苏农业学报, 37 (2):443-453.
|
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
|
罗华, 李敏, 胡大刚, 宋红日, 郝玉金, 张连忠. 2012. 不同有机肥对肥城桃果实产量及品质的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 18 (4):955-964.
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
马宗桓, 贺雅娟, 李蔚, 李文芳, 左存武, 郭艳兰, 毛娟, 陈佰鸿. 2022. 施氮量对‘马瑟兰’葡萄果实挥发物质组分与含量的影响. 干旱地区农业研究, 40 (5):201-211.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: S0045-6535(18)30609-X pmid: 29621679 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru128 pmid: 24692651 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msz297 pmid: 31912142 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02663 pmid: 36061675 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
|
田甜, 封碧红, 宁明岸, 史君彦, 高丽朴, 左进华, 王清. 2023. 两种樱桃番茄冷藏后风味品质分析. 食品工业科技, 44 (22):294-302.
|
|
| [41] |
|
|
田永强, 高丽红. 2021. 设施番茄高品质栽培理论与技术. 中国蔬菜,(2):30-40.
|
|
| [42] |
doi: 10.1126/science.aal1556 pmid: 28126817 |
| [43] |
|
|
王俊文, 武玥, 郁继华, 张婧, 颉建明, 冯致, 唐中祺, 刘晓奇, 李晶, 钟源. 2021. 外源ALA促进番茄糖酸品质及挥发性物质含量的作用研究. 园艺学报, 48 (5):973-986.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0586 |
|
| [44] |
|
|
王同林, 叶红霞, 郑积荣, 李明. 2020. 番茄果实中主要风味物质研究进展. 浙江农业学报, 32 (8):1513-1522.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2020.08.22 |
|
| [45] |
|
|
王雅婷, 陈子平, 陈世金, 祖艳红, 张富源, 黄顺启, 谈恩培. 2023. 腐植酸肥料增产作物与改良土壤研究新进展. 腐植酸,(4):21-26.
|
|
| [46] |
|
|
王准, 程红颂, 张梦君, 王亮亮, 郭景丽. 2022. 腐植酸叶面肥复配聚合氨基酸对番茄生长及品质的影响. 腐植酸,(3):93-98.
|
|
| [47] |
|
|
肖雪梅, 高程斐, 武玥, 唐中祺, 钟源, 张丹, 魏晋梅, 郁继华. 2023. 不同类型叶面肥对日光温室越冬番茄风味品质的影响. 农业工程学报, 39 (10):218-226.
|
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01042 pmid: 26640472 |
| [50] |
|
|
张水勤, 袁亮, 林治安, 李燕婷, 胡树文, 赵秉强. 2017. 腐植酸促进植物生长的机理研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23 (4):1065-1076.
|
|
| [51] |
|
|
张天皓, 陶茹, 靳元凯, 李凤龙, 樊淼淼, 高华. 2022. 水肥一体化减量施肥对苹果果实挥发性物质的影响. 中国果树,(2):25-31.
|
|
| [52] |
|
|
赵银平, 赵增寿, 孙利萍, 高敏丽, 史亮. 2022. 叶面肥对设施番茄产量、品质及经济效益的影响. 中国瓜菜, 35 (1):60-64.
|
|
| [53] |
|
|
朱小洁, 周翔宇, 范航, 高喜凤, 杨蕾. 2020. 9种唇形科芳香植物挥发性萜类成分的比较分析. 植物研究, 40 (5):696-705.
doi: 10.7525/j.issn.1673-5102.2020.05.008 |
|
| [54] |
|
|
邹庆圆, 刘会丽, 赵佳宗, 黄泽双, 陈晨. 2021. 腐植酸钾复合肥在番茄上的应用效果研究. 腐植酸,(6):32-35.
|
| [1] | 覃艮红, 袁洪波, 王卓妮, 史冰柯, 范洋洋, 王丽, 张猛, 涂洪涛, 徐超, 侯珲. 蜡样芽孢杆菌挥发物对苹果轮纹病菌的拮抗活性[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1403-1412. |
| [2] | 何洁, 邓军均, 高敏, 朱宏华, 王炳琳, 孙红波, 杨源, 严寒. 樱桃番茄新品种‘粉宝2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(11): 2729-2730. |
| [3] | 李素平, 李微, 韩冷, 黄建国. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HY19挥发物对采后柑橘的防腐效果[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(1): 162-174. |
| [4] | 郑锦荣, 聂俊, 李艳红, 谭德龙, 谢玉明, 张长远. 樱桃番茄新品种‘粤科达101’[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(4): 909-910. |
| [5] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 番茄新品种‘杭杂601’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 105-106. |
| [6] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂503’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 107-108. |
| [7] | 李艳红, 聂俊, 郑锦荣, 谭德龙, 张长远, 史亮亮, 谢玉明. 华南地区樱桃番茄表型性状遗传多样性分析及综合评价[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1717-1730. |
| [8] | 严从生,贾 利,方 凌*,张其安,江海坤,王 艳,王明霞,田红梅,张 建,王朋成. 樱桃番茄新品种‘红珍珠’[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(7): 1421-1422. |
| [9] | 曹 霞1,武春成1,孙中峰1,叶景学2,王 帅1,毛秀杰1,*. 樱桃番茄 保护地专用新品种‘吉农番茄5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2017, 44(3): 603-604. |
| [10] | 刘淑芹,黄婷婷*,佘 红,张永志,李 平. 樱桃番茄新品种‘樱莎红3号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(S2): 2747-2748. |
| [11] | 郑积荣1,*,王慧俐2. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(2): 403-404. |
| [12] | 王梦晗1,2,王凯晨2,马 丽1,2,唐 坚2,乔勇进2,*,张 敏3. 酵母多糖处理对樱桃番茄抗冷性及品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(10): 2068-2074. |
| [13] | 赵统敏, 杨玛丽, 余文贵, 赵丽萍, 王银磊. 樱桃番茄新品种‘金陵美玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(12): 2535-2536. |
| [14] | 赵统敏;余文贵;杨玛丽;赵丽萍. 抗番茄黄化曲叶病毒病樱桃番茄新品种‘金陵甜玉’[J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(09): 1825-1826. |
| [15] | 姚方杰;苏桂娟;叶景学. 樱桃番茄新品种‘吉农2号小番茄’[J]. 园艺学报, 2004, 31(3): 423-423. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司