
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (5): 1351-1363.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2025-0116
王庆彪1, 王艳萍1, 吴翔宇1, 陈宁杰1, 池婷1, 化定珠1, 葛艾伶1, 郭宇1, 魏蕾2,*( ), 张丽1,*(
), 张丽1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-12
修回日期:2025-05-12
出版日期:2025-05-25
发布日期:2025-05-21
通讯作者:
基金资助:
WANG Qingbiao1, WANG Yanping1, WU Xiangyu1, CHEN Ningjie1, CHI Ting1, HUA Dingzhu1, GE Ailing1, GUO Yu1, WEI Lei2,*( ), ZHANG Li1,*(
), ZHANG Li1,*( )
)
Received:2025-02-12
Revised:2025-05-12
Published:2025-05-25
Online:2025-05-21
摘要:
萝卜(Raphanus sativus L.)NWB细胞质雄性不育NWB-CMS是一种不同于Ogura-CMS的不育源,目前已经广泛应用于萝卜杂交育种。以10份东亚大长萝卜(R. sativus var. hortensis L.)和6份欧洲小萝卜(R. sativus var. sativus L.)为父本,对NWB-CMS进行遗传测试,解析NWB-CMS育性恢复的遗传规律,并在此基础上对育性恢复基因进行初步定位。结果表明,欧洲小萝卜普遍能够恢复NWB-CMS的育性,且不同品种包含的育性恢复基因数量不同,至少存在3个育性恢复基因。其中恢复系“KP”的育性恢复受两对显性上位性主基因加微效基因控制。利用混合群体分离分析,将育性恢复基因定位在Chr1:32.5 ~ 33.7 Mb(Rfn1.1)、Chr 9:12.2 ~ 13.3 Mb(Rfn9.1)和Chr4:16.7 ~ 18.6 Mb(Rfn4.1)、31.9 ~ 33.1 Mb(Rfn4.2)、34.3 ~ 37.9 Mb(Rfn4.3)范围内。对Rfn4位点进一步定位和分析发现,3个定位区间之间可能存在染色体大片段重复和倒位等结构变异。针对该位点开发的Rf-118等分子标记可用于雄性不育系的辅助选育和辅助追踪Rfn4位点,便于筛选和定位其他育性恢复基因位点。
王庆彪, 王艳萍, 吴翔宇, 陈宁杰, 池婷, 化定珠, 葛艾伶, 郭宇, 魏蕾, 张丽. 萝卜NWB-CMS育性恢复基因的遗传分析及初步定位[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1351-1363.
WANG Qingbiao, WANG Yanping, WU Xiangyu, CHEN Ningjie, CHI Ting, HUA Dingzhu, GE Ailing, GUO Yu, WEI Lei, ZHANG Li. Genetic Analysis and Preliminary Mapping of the Fertility Restoration Gene for NWB-CMS in Radish(Raphanus sativus)[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1351-1363.
| 标记 Marker | 位置 Position | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf-117 | 16109162 | TCTCGCGGATGTAGTAAGCT | TTACGTGCCAATTATGTAGGAGAA |
| Rf-6 | 17270936 | GCCACTATCACAATACTAGCATGA | ACTTGATTCTTGCAGAGTGATTGA |
| Rf-8 | 18574289 | ACGCATTTTCGATGTGTGTACA | TGAGGGATATGATCTGCATTGTCA |
| Rf-113 | 19086196 | TCTGGTCCAAGTCAGGAGGA | GGGGAGTGACAAGAACCTGA |
| Rf-1 | 31297167 | CCACCTGTCTCGTTGAAGGA | TCTCAAGTCTGATTCCCCGC |
| Rf-120 | 33851811 | CCACATACAGATTAACAGTGCCC | AGATTTCACTTTTGGGTTTTGGTTT |
| Rf-119 | 34029651 | CCCGAGAAAGCCTAACTGCT | AAGGAACAAAGGCCAAGGGT |
| Rf-122 | 37683242 | GGCATAGGTAGCAGGAGGC | TCCGTAAAACCCTAAACCGCA |
| Rf-118 | 38202091 | AGTGACGTGGCACTCTCAAA | TTTATCGTCGGCAAAATTTGATGA |
| Rf-10 | 38864737 | CTTTGCGCGGGTCTTTCAAA | ACACCTTGTGACTGAAGAGGA |
| Rf-11 | 39147363 | TCCAATATATAATGGCTTTTGTGCAAA | TGAGATCGGCGGAAGACTTG |
| Rf-14 | 40214027 | AAACTTACTTGTGTCGGAGATCC | CCTTCTAGAACATTTACTCTCCAGGT |
| Rf-16 | 42080242 | GCCAAGACACAGTACGGTCA | CGAGTCAGGAAGCTGGTCAT |
| Rf-128 | 42368813 | ACATCTCTGGGGAAAAAGCTTT | GCTATAGTCCCCGCATCAAGT |
| Rf-131 | 40586659 | TGTTTTACCGTTACATTCAGTTTCAGT | CCAAAAGCCTATTCAACACTCGT |
表1 本研究中使用的多态性InDel引物
Table 1 The polymorphic InDel primers used in this study
| 标记 Marker | 位置 Position | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rf-117 | 16109162 | TCTCGCGGATGTAGTAAGCT | TTACGTGCCAATTATGTAGGAGAA |
| Rf-6 | 17270936 | GCCACTATCACAATACTAGCATGA | ACTTGATTCTTGCAGAGTGATTGA |
| Rf-8 | 18574289 | ACGCATTTTCGATGTGTGTACA | TGAGGGATATGATCTGCATTGTCA |
| Rf-113 | 19086196 | TCTGGTCCAAGTCAGGAGGA | GGGGAGTGACAAGAACCTGA |
| Rf-1 | 31297167 | CCACCTGTCTCGTTGAAGGA | TCTCAAGTCTGATTCCCCGC |
| Rf-120 | 33851811 | CCACATACAGATTAACAGTGCCC | AGATTTCACTTTTGGGTTTTGGTTT |
| Rf-119 | 34029651 | CCCGAGAAAGCCTAACTGCT | AAGGAACAAAGGCCAAGGGT |
| Rf-122 | 37683242 | GGCATAGGTAGCAGGAGGC | TCCGTAAAACCCTAAACCGCA |
| Rf-118 | 38202091 | AGTGACGTGGCACTCTCAAA | TTTATCGTCGGCAAAATTTGATGA |
| Rf-10 | 38864737 | CTTTGCGCGGGTCTTTCAAA | ACACCTTGTGACTGAAGAGGA |
| Rf-11 | 39147363 | TCCAATATATAATGGCTTTTGTGCAAA | TGAGATCGGCGGAAGACTTG |
| Rf-14 | 40214027 | AAACTTACTTGTGTCGGAGATCC | CCTTCTAGAACATTTACTCTCCAGGT |
| Rf-16 | 42080242 | GCCAAGACACAGTACGGTCA | CGAGTCAGGAAGCTGGTCAT |
| Rf-128 | 42368813 | ACATCTCTGGGGAAAAAGCTTT | GCTATAGTCCCCGCATCAAGT |
| Rf-131 | 40586659 | TGTTTTACCGTTACATTCAGTTTCAGT | CCAAAAGCCTATTCAACACTCGT |
| 父本种类 Male subspecies | 亲本来源 Parental origin | 世代 Generation | F:MF:S | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 观测值Observed | 期望值Expected | ||||||
| 东亚大长萝卜 | YB-A × 短叶13 Duanye 13 | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| East Asia big long | YB-A × 象牙白 Xiangyabai | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| radish | YB-A × 潍县青 Weixianqing | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| YB-A × YR Tengu | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × YR Kurama | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 西星5号 Xixing 5 | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 卫青萝卜 Weiqing | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 锦州五斤红 Jinzhou Wujinhong | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 北京花叶心里美 Beijing Huaye Xinlimei | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 板叶心里美 Banye Xinlimei | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 欧洲小萝卜 | YB-A × KP | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| European small | F2-1 | 114:24:10 | 12:3:1 | 0.65 | 0.72 | ||
| radish | F2-2 | 238:68:29 | 12:3:1 | 4.23 | 0.12 | ||
| BC1 | 136:74:84 | 2:1:1 | 2.33 | 0.31 | |||
| YB-A × лΑТΑ | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 288:0:16 | 15:0:1 | 0.51 | 0.48 | |||
| YB-A × NST601 | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 275:0:6 | 63:0:1 | 0.60 | 0.44 | |||
| YB-A × DQG | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 282:0:1 | 63:1 | 2.69 | 0.10 | |||
| YB-A × 红樱桃 Hongyingtao | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 266:0:4 | 63:0:1 | 0.01 | 0.91 | |||
| YB-A × GiSi | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 287:0:19 | 15:0:1 | < 0.001 | 0.98 | |||
表2 NWB-CMS育性恢复性状的遗传模式
Table 2 Inheritance patterns of fertility restoration of NWB-CMS
| 父本种类 Male subspecies | 亲本来源 Parental origin | 世代 Generation | F:MF:S | χ2 | P | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 观测值Observed | 期望值Expected | ||||||
| 东亚大长萝卜 | YB-A × 短叶13 Duanye 13 | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| East Asia big long | YB-A × 象牙白 Xiangyabai | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| radish | YB-A × 潍县青 Weixianqing | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| YB-A × YR Tengu | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × YR Kurama | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 西星5号 Xixing 5 | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 卫青萝卜 Weiqing | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 锦州五斤红 Jinzhou Wujinhong | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 北京花叶心里美 Beijing Huaye Xinlimei | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| YB-A × 板叶心里美 Banye Xinlimei | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 欧洲小萝卜 | YB-A × KP | F1 | 0:0:15 | 0:0:1 | 0 | 1 | |
| European small | F2-1 | 114:24:10 | 12:3:1 | 0.65 | 0.72 | ||
| radish | F2-2 | 238:68:29 | 12:3:1 | 4.23 | 0.12 | ||
| BC1 | 136:74:84 | 2:1:1 | 2.33 | 0.31 | |||
| YB-A × лΑТΑ | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 288:0:16 | 15:0:1 | 0.51 | 0.48 | |||
| YB-A × NST601 | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 275:0:6 | 63:0:1 | 0.60 | 0.44 | |||
| YB-A × DQG | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 282:0:1 | 63:1 | 2.69 | 0.10 | |||
| YB-A × 红樱桃 Hongyingtao | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 266:0:4 | 63:0:1 | 0.01 | 0.91 | |||
| YB-A × GiSi | F1 | 15:0:0 | 1:0:0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| F2 | 287:0:19 | 15:0:1 | < 0.001 | 0.98 | |||

图1 YB-A × KP的F2群体中不同育性单株成熟花粉粒阶段的花药细胞学结构 A:可育株;B和C:微量花粉株;D:不育株。PS:花粉囊;PG:花粉粒。红色箭头表示有活力的花粉粒被染成深色
Fig. 1 Microscopical structure of anthers at mature pollen grain stages of F2 individuals(YB-A × KP) A:Fertile plant;B and C:Micro- fertile plant;D:Sterile plant. PS:Pollen sac;PG:Pollen grain. The red arrows indicate viable pollen grains stained darkly

图2 ΔSNP/Indel -index分布图 A:可育池和不育池间的比较;B:微量花粉池和不育池间的比较;C:可育池和微量花粉池间的比较。散点图为原始值,黑色曲线为窗口拟合值。随机进行1 000次置换检验,红色线表示99%置信水平,蓝色线表示95%置信水平
Fig. 2 Distribution of ΔSNP/Indel index A:F_pool vs. S_pool;B:MF_pool vs. S_poll;C:F_pool vs. MF_pool. The scatter plot represents the raw values,and the black curve is the fitted value based on the sliding-window. A random permutation test was performed 1 000 times,with the red line indicating the 99% confidence level and the blue line indicating the 95% confidence level
| 极端池 Extreme pool | 位点 QTL | 起始 ~ 终止/Mb Start-End | 区间大小/Mb Region length | SNP和InDel数量 No. of SNPs and InDels | 基因数 No. of genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F_pool vs. S_pool | Chr1:Rfn1.1 | 32.5 ~ 33.7 | 1.2 | 5 517 | 5 |
| MF_pool vs. S_pool | Chr1:Rfn1.1 | 32.5 ~ 33.7 | 1.2 | 5 469 | 5 |
| Chr9:Rfn9.1 | 12.2 ~ 13.3 | 1.1 | 34 167 | 128 | |
| F_pool vs. MF_pool | Chr4:Rfn4.1 | 16.7 ~ 18.6 | 1.9 | 60 301 | 167 |
| Chr4:Rfn4.2 | 31.9 ~ 33.1 | 1.2 | 28 059 | 55 | |
| Chr4:Rfn4.3 | 34.3 ~ 37.9 | 3.6 | 54 362 | 106 |
表3 NWB-CMS育性恢复基因初定位区间及区间内基因统计
Table 3 Preliminary mapping intervals for NWB-CMS fertility restoration genes and statistics within these intervals
| 极端池 Extreme pool | 位点 QTL | 起始 ~ 终止/Mb Start-End | 区间大小/Mb Region length | SNP和InDel数量 No. of SNPs and InDels | 基因数 No. of genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F_pool vs. S_pool | Chr1:Rfn1.1 | 32.5 ~ 33.7 | 1.2 | 5 517 | 5 |
| MF_pool vs. S_pool | Chr1:Rfn1.1 | 32.5 ~ 33.7 | 1.2 | 5 469 | 5 |
| Chr9:Rfn9.1 | 12.2 ~ 13.3 | 1.1 | 34 167 | 128 | |
| F_pool vs. MF_pool | Chr4:Rfn4.1 | 16.7 ~ 18.6 | 1.9 | 60 301 | 167 |
| Chr4:Rfn4.2 | 31.9 ~ 33.1 | 1.2 | 28 059 | 55 | |
| Chr4:Rfn4.3 | 34.3 ~ 37.9 | 3.6 | 54 362 | 106 |
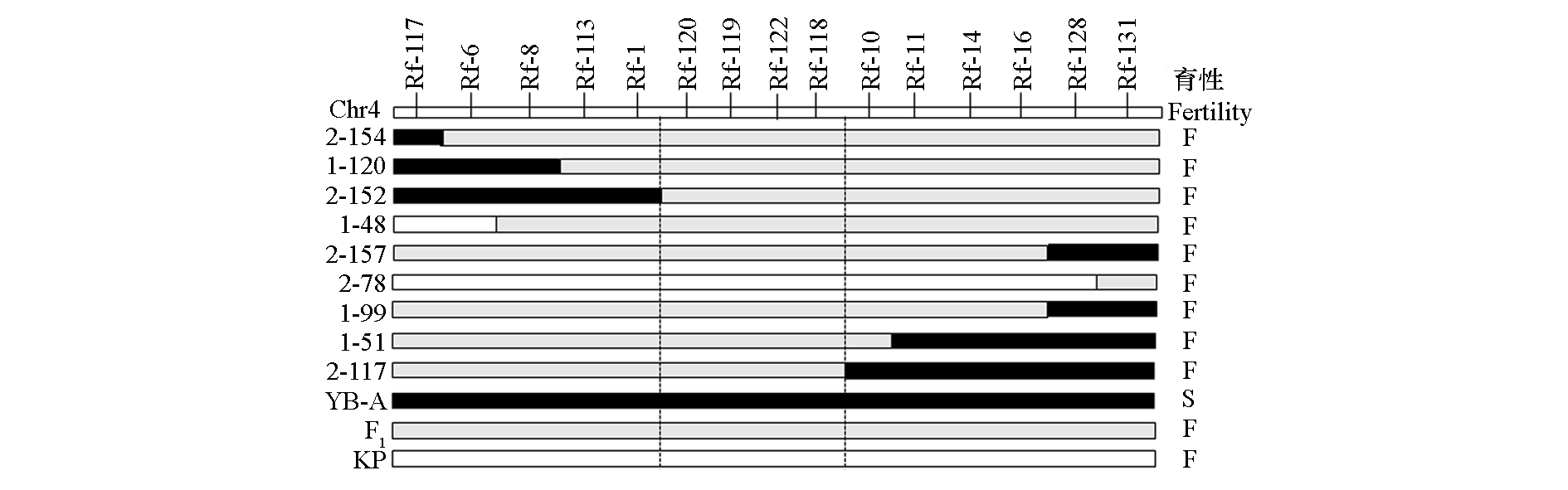
图3 Rfn4定位区间内YB-A × KP的F2群体中重组单株的InDel标记基因型 虚线条间为基因定位区间。F:可育;S:不育黑框表示和不育系YB-A基因型一致;白框表示和恢复系KP基因型一致;灰框表示杂合基因型
Fig. 3 Genotypes of recombinant plants in the F2 population(YB-A×KP)using InDel markers within the Rfn4 localization interval The region between dashed lines indicates the refined interval for further gene mapping. F:Fertility;S:Sterility. Black boxes represent genotypes identical to the sterile line YB-A,white boxes correspond to the restorer line KP,and gray boxes indicate heterozygous genotypes
| 基因组 Genome | 位点/Mb Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rfn4.1 | Rfn4.2 | Rfn4.3 | |
| ROD | 15.4 ~ 18.7 | 31.9 ~ 33.1 | 34.2 ~ 37.9 |
| RS03 | 15.9 ~ 19.0 | 35.6 ~ 36.5 | 33.2 ~ 34.5 |
| RS04 | 16.0 ~ 19.4 | 35.2 ~ 36.1 | 32.7 ~ 33.7 |
| RS05 | 16.4 ~ 19.8 | 36.3 ~ 37.2 | 33.4 ~ 35.2 |
| RS06 | 16.0 ~ 19.2 | 35.9 ~ 36.4 | 33.4 ~ 34.4 |
| WK10039 | 18.7 ~ 23.7 | 29.0 ~ 29.2 | 19.1 ~ 23.7 |
| XYB36-2 | 16.0 ~ 21.1 | 25.2 ~ 27.6 | 25.4 ~ 26.5 |
表4 NWB-CMS育性恢复基因QTL区域在不同基因组中的线性比对
Table 4 Linear alignment of QTL regions for fertility restoration genes of NWB-CMS across genomes
| 基因组 Genome | 位点/Mb Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rfn4.1 | Rfn4.2 | Rfn4.3 | |
| ROD | 15.4 ~ 18.7 | 31.9 ~ 33.1 | 34.2 ~ 37.9 |
| RS03 | 15.9 ~ 19.0 | 35.6 ~ 36.5 | 33.2 ~ 34.5 |
| RS04 | 16.0 ~ 19.4 | 35.2 ~ 36.1 | 32.7 ~ 33.7 |
| RS05 | 16.4 ~ 19.8 | 36.3 ~ 37.2 | 33.4 ~ 35.2 |
| RS06 | 16.0 ~ 19.2 | 35.9 ~ 36.4 | 33.4 ~ 34.4 |
| WK10039 | 18.7 ~ 23.7 | 29.0 ~ 29.2 | 19.1 ~ 23.7 |
| XYB36-2 | 16.0 ~ 21.1 | 25.2 ~ 27.6 | 25.4 ~ 26.5 |

图4 Rfn4定位区间内共线性和结构变异分析 黄色和蓝色线条分别表示倒位和重复。横坐标表示Rfn4定位区间片段的相对位置
Fig. 4 Collinearity and structural variation analysis within the Rfn4 mapped interval Yellow and blue lines represent inversions and duplications,respectively. The horizontal axis indicates the relative position of fragments in the Rfn4 mapped interval

图5 NWB-CMS育性恢复Rfn4位点内Rf-118、Rf-119、Rf-120和Rf-122标记在F2-2群体中的基因分型 上带表示YB-A相同等位基因“aa”,下带表示恢复系KP相同等位基因“AA”,双带表示杂合类型“Aa”
Fig. 5 Genotyping of the Rf-118,Rf-119,Rf-120,Rf-122 marker within the Rfn4 fertility restoration locus of NWB-CMS in the F2-2 population The upper band represents the“aa”allele identical to YB-A,the lower band represents the“AA”allele identical to the restorer line KP,and the double band represents the heterozygous type“Aa”
| [1] |
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.384 pmid: 17406474 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.05.009 pmid: 15979231 |
| [5] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9461-6 pmid: 19199092 |
| [6] |
|
|
傅廷栋, 杨光圣, 杨小牛. 1990. 甘蓝型油菜波里马细胞质雄性不育的研究与利用. 作物研究, 4 (3):9-12.
|
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
|
胡天华, 包崇来, 胡海娇, 王五宏, 魏庆镇, 汪精磊. 2021. 心里美萝卜雄性不育系XM221-131A的选育. 浙江农业科学, 62 (1):57-60.
doi: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20210125 |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00222982 pmid: 24169844 |
| [15] |
doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04398-8 pmid: 37330934 |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r12 pmid: 14759262 |
| [18] |
|
|
郎丰庆, 王施慧, 刘淑梅, 苏晓梅, 吕宏君, 侯丽霞. 2021. 心里美萝卜雄性不育系XA选育. 长江蔬菜,(22):49-51.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191800 |
|
李晓梅, 杨峰, 雍晓平, 陈琳, 冉科, 冉茂林. 2021. 萝卜NWB CMS败育特征及其育性恢复基因的遗传规律. 华北农学报, 36 (3):90-95.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.20191800 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21225-0 pmid: 33589621 |
| [23] |
|
|
闵炳桓, 南奭铉, 李熙正, 李时雨, 梁承均. 2003. 一种萝卜系胼胝体和用它培育植物体及杂交种子的方法:中国,ZL03055556.X.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
doi: 10.1007/BF02172406 pmid: 8914521 |
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00232384 pmid: 24212876 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
|
于海龙, 李志远, 杨丽梅, 刘玉梅, 庄木, 吕红豪, 李占省, 方智远, 张扬勇. 2018. 芥蓝Ogura CMS恢复系BC3代创制及Rfo基因传递与遗传背景分析. 中国农业科学, 51 (9):1746-1757.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2018.09.012 |
|
| [39] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0795 |
|
于海龙, 任文静, 方智远, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 吕红豪, 王勇, 季佳磊, 张扬勇. 2021. 蔬菜细胞质雄性不育的育性恢复研究进展. 园艺学报, 48 (5):1031-1046.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0795 |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2014.05.021 |
|
张丽, 王庆彪, 郑鹏婧. 2014. 萝卜雄性不育细胞质的鉴定与分类. 华北农学报, 29 (5):125-129.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2014.05.021 |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [1] | 崔 磊, 严承欢, 甘彩霞, 於校青, 袁伟玲, 邱正明, 邓晓辉. 萝卜抗根肿病新品种‘CR楚玉2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 77-78. |
| [2] | 文正华, 张 伟, 孙德岭, 张小丽, 江汉民. 青花菜新品种‘领秀5号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S1): 99-100. |
| [3] | 褚文龙, 张晓莉, 徐良, 王燕, 柳李旺. 萝卜基因组学与分子育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(5): 1251-1270. |
| [4] | 付琪, 王丹, 景维坤, 张颢, 王慧纯, 蹇洪英, 邱显钦, 王其刚, 唐开学, 晏慧君. 月季类胡萝卜素裂解双加氧酶基因RcCCD4在花香合成中的功能[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 623-634. |
| [5] | 夏志磊, 俞冰昕, 杨梦, 连子林, 官利兰, 何艺超, 颜爽爽, 曹必好, 邱正坤. 茄子绿果基因的精细定位及其KASP标记开发[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2008-2018. |
| [6] | 赵佳莹, 曾周婷, 岑欣颖, 施姣淇, 李效贤, 沈晓霞, 俞振明. 铁皮石斛CCO基因家族鉴定及其在花发育中的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2075-2088. |
| [7] | 段敏杰, 李怡斐, 王春萍, 杨小苗, 黄任中, 黄启中, 张世才. 辣椒果实类胡萝卜素调控因子转录组和靶向代谢组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(8): 1773-1791. |
| [8] | 李肯, 张伟, 武云鹏, 彭冬秀, 张若纬. 甜瓜果肉硬度KASP标记的开发与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 773-786. |
| [9] | 张正海, 王永富, 吴华茂, 于海龙, 曹亚从, 冯锡刚, 王立浩. 辣椒重要性状遗传定位与候选基因研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 669-696. |
| [10] | 杨亮, 刘欢, 马燕勤, 李菊, 王海娥, 周玉洁, 龙海成, 苗明军, 李志, 常伟. 利用CRISPR/Cas9技术创制高番茄红素番茄新材料[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [11] | 汪书杰, 栾雨婷, 徐昌杰. 植物叶黄素酯化研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1830-1840. |
| [12] | 田密霞, 周福慧, 姜爱丽, 祝朋芳, 陈晨, 刘程惠, 原畅. 芸薹属植物呈色机理研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1971-1986. |
| [13] | 肖翔, 周储江, 金舒婉, 施丽愉, 杨震峰, 曹士锋, 陈伟. PpMADS2与PpMADS3协同调控黄肉桃果实类胡萝卜素积累机制的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1173-1186. |
| [14] | 杜艳霞, 王艺光, 肖政, 董彬, 方遒, 钟诗蔚, 杨丽媛, 赵宏波. 桂花OfNCED3调控转基因烟草叶片类胡萝卜素和叶绿素的合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(6): 1284-1294. |
| [15] | 张鲁刚, 卢倩倩, 何琼, 薛一花, 马晓敏, 马帅, 聂姗姗, 杨文静. 紫橙色大白菜新种质的创制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司