
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2761-2773.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0876
周小林, 林俊轩, 李彩霞, 孙美华, 白龙强, 侯雷平, 苗妍秀*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-14
修回日期:2025-07-28
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-10-28
通讯作者:
基金资助:
ZHOU Xiaolin, LIN Junxuan, LI Caixia, SUN Meihua, BAI Longqiang, HOU Leiping, MIAO Yanxiu*( )
)
Received:2025-04-14
Revised:2025-07-28
Published:2025-10-25
Online:2025-10-28
摘要:
以叶用莴苣‘玻璃生菜’为试材,分析不同温度和不同浓度外源谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)对叶片气体交换参数、叶绿素荧光参数和光合相关基因表达量的影响,探究高温胁迫下外源GSH对叶用莴苣光合特性的影响。结果表明,高温胁迫(36 ℃/30 ℃)显著降低生长量、光合速率(Pn)、最大光化学效率(Fv/Fm)、实际光化学效率(ΦPSII)、叶片色素含量,显著提升非光化学猝灭系数(ΦNPQ)、可溶性蛋白质和游离氨基酸含量,即高温胁迫显著抑制生长,降低叶片光合效率和光合电子传递链性能。高温胁迫下,叶面施用0.5和1.0 mmol · L-1 GSH均显著增加全株鲜质量、Pn、ΦPSII,显著上调叶片PSⅡ反应中心蛋白关键基因psbA、psbB、psbD、psbH、psbK、psbN的表达量,且0.5 mmol · L-1 GSH处理还显著提高叶片色素和可溶性糖含量。可见外源GSH能有效缓解高温胁迫对叶用莴苣光合特性带来的不良影响。
周小林, 林俊轩, 李彩霞, 孙美华, 白龙强, 侯雷平, 苗妍秀. 外源谷胱甘肽对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣光合特性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(10): 2761-2773.
ZHOU Xiaolin, LIN Junxuan, LI Caixia, SUN Meihua, BAI Longqiang, HOU Leiping, MIAO Yanxiu. Effects of Exogenous Glutathione on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Leaf Lettuce Under High Temperature Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(10): 2761-2773.
| 基因名 Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Actin | F:GTGAGTGAAGAAGGGCAATG;R:CACTTTCAACCCGATTCACC |
| psbA | F:GCGAAAGCGAAAGCCTATGGG;R:ATACAGAAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTAG |
| psbB | F:GTGCCCGAACCTTGTTTAGAGATG;R:TCAGCCTATTTGTCTTCTTGTAGTTGG |
| psbD | F:AGTTTCTACTCCTGCGAATAGTTTAGC;R:CCACAGACCGCCTAATTGACAC |
| psbH | F:TGGTCCAAGACGAACTACTGTAGG;R:GAGCCATTGCGACACCCATC |
| psbK | F:ATCTGTCTTAATTCTGCCCTTTATCCG;R:ATGACTGGCATAACATCTACGATTGG |
| psbN | F:AGCAACCCTAGTCGCTATCTTTATATC;R:CGTGTTCCTCGAATGGATCTCTTAG |
表1 莴苣叶片PSⅡ反应中心蛋白基因的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences of genes coding PSⅡ reaction center protein in lettuce leaves
| 基因名 Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Actin | F:GTGAGTGAAGAAGGGCAATG;R:CACTTTCAACCCGATTCACC |
| psbA | F:GCGAAAGCGAAAGCCTATGGG;R:ATACAGAAGTTGCGGTCAATAAGGTAG |
| psbB | F:GTGCCCGAACCTTGTTTAGAGATG;R:TCAGCCTATTTGTCTTCTTGTAGTTGG |
| psbD | F:AGTTTCTACTCCTGCGAATAGTTTAGC;R:CCACAGACCGCCTAATTGACAC |
| psbH | F:TGGTCCAAGACGAACTACTGTAGG;R:GAGCCATTGCGACACCCATC |
| psbK | F:ATCTGTCTTAATTCTGCCCTTTATCCG;R:ATGACTGGCATAACATCTACGATTGG |
| psbN | F:AGCAACCCTAGTCGCTATCTTTATATC;R:CGTGTTCCTCGAATGGATCTCTTAG |
| 昼夜温度/℃ Temperature of day/night | GSH/(mmol · L-1) | 叶片数 Leaf number | 叶面积/cm2 Lef area | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22/16 | 0 | 12.50 ± 0.29 c | 277.72 ± 19.44 ab | 19.39 ± 0.56 b | 1.57 ± 0.06 b | |
| 22/16 | 0.5 | 14.75 ± 0.48 a | 324.96 ± 19.66 a | 24.91 ± 3.33 a | 2.02 ± 0.22 a | |
| 22/16 | 1.0 | 14.00 ± 0.41 ab | 291.39 ± 16.90 ab | 23.86 ± 1.20 ab | 1.78 ± 0.12 ab | |
| 36/30 | 0 | 10.25 ± 0.48 d | 229.83 ± 17.85 b | 7.77 ± 0.47 d | 1.11 ± 0.05 c | |
| 36/30 | 0.5 | 14.00 ± 0.41 ab | 316.27 ± 18.50 a | 13.28 ± 0.81 c | 1.60 ± 0.10 b | |
| 36/30 | 1.0 | 13.00 ± 0.41 bc | 271.71 ± 22.70 ab | 12.76 ± 1.51 c | 1.48 ± 0.07 b | |
| L | ** | ns | *** | *** | ||
| N | *** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| L × N | ns | ns | ns | ns |
表2 外源GSH对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣生长指标的影响
Table 2 Effect of exogenous GSH on leaf lettuce growth indexes under high temperature stress
| 昼夜温度/℃ Temperature of day/night | GSH/(mmol · L-1) | 叶片数 Leaf number | 叶面积/cm2 Lef area | 鲜质量/g Fresh weight | 干质量/g Dry weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22/16 | 0 | 12.50 ± 0.29 c | 277.72 ± 19.44 ab | 19.39 ± 0.56 b | 1.57 ± 0.06 b | |
| 22/16 | 0.5 | 14.75 ± 0.48 a | 324.96 ± 19.66 a | 24.91 ± 3.33 a | 2.02 ± 0.22 a | |
| 22/16 | 1.0 | 14.00 ± 0.41 ab | 291.39 ± 16.90 ab | 23.86 ± 1.20 ab | 1.78 ± 0.12 ab | |
| 36/30 | 0 | 10.25 ± 0.48 d | 229.83 ± 17.85 b | 7.77 ± 0.47 d | 1.11 ± 0.05 c | |
| 36/30 | 0.5 | 14.00 ± 0.41 ab | 316.27 ± 18.50 a | 13.28 ± 0.81 c | 1.60 ± 0.10 b | |
| 36/30 | 1.0 | 13.00 ± 0.41 bc | 271.71 ± 22.70 ab | 12.76 ± 1.51 c | 1.48 ± 0.07 b | |
| L | ** | ns | *** | *** | ||
| N | *** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| L × N | ns | ns | ns | ns |
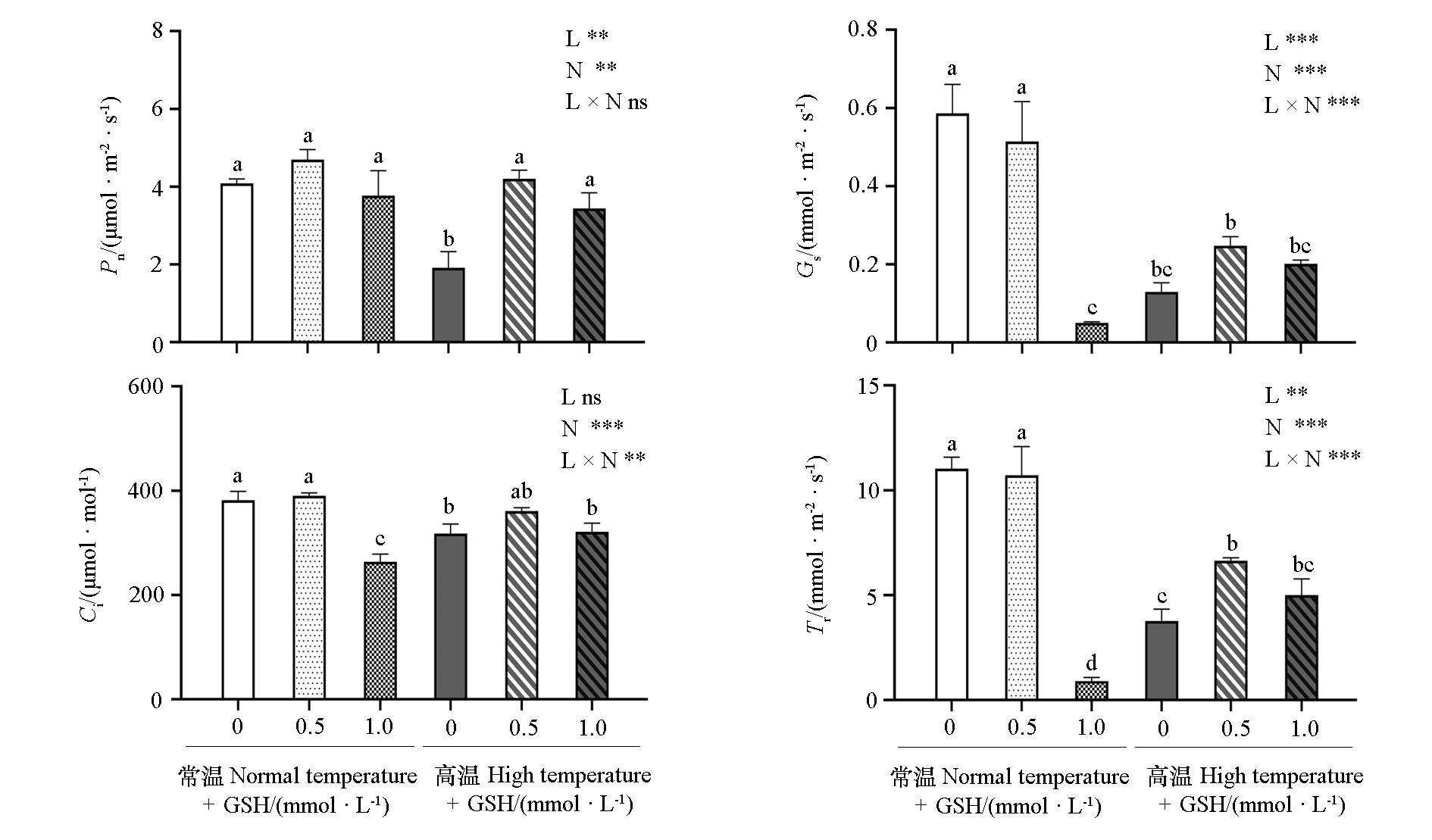
图2 外源GSH对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣叶片气体交换参数 不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P < 0.05)。L:温度;N:GSH浓度;L × N:温度和GSH浓度的互作效应。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;ns:差异不显著。下同
Fig. 2 Gas exchange parameters of exogenous GSH on leaf lettuce leaves under high temperature stress Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments at 0.05 level. L:Temperature;N:GSH concentration;L × N:Interaction between temperature and GSH concentration. * P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;ns:not significant. The same below
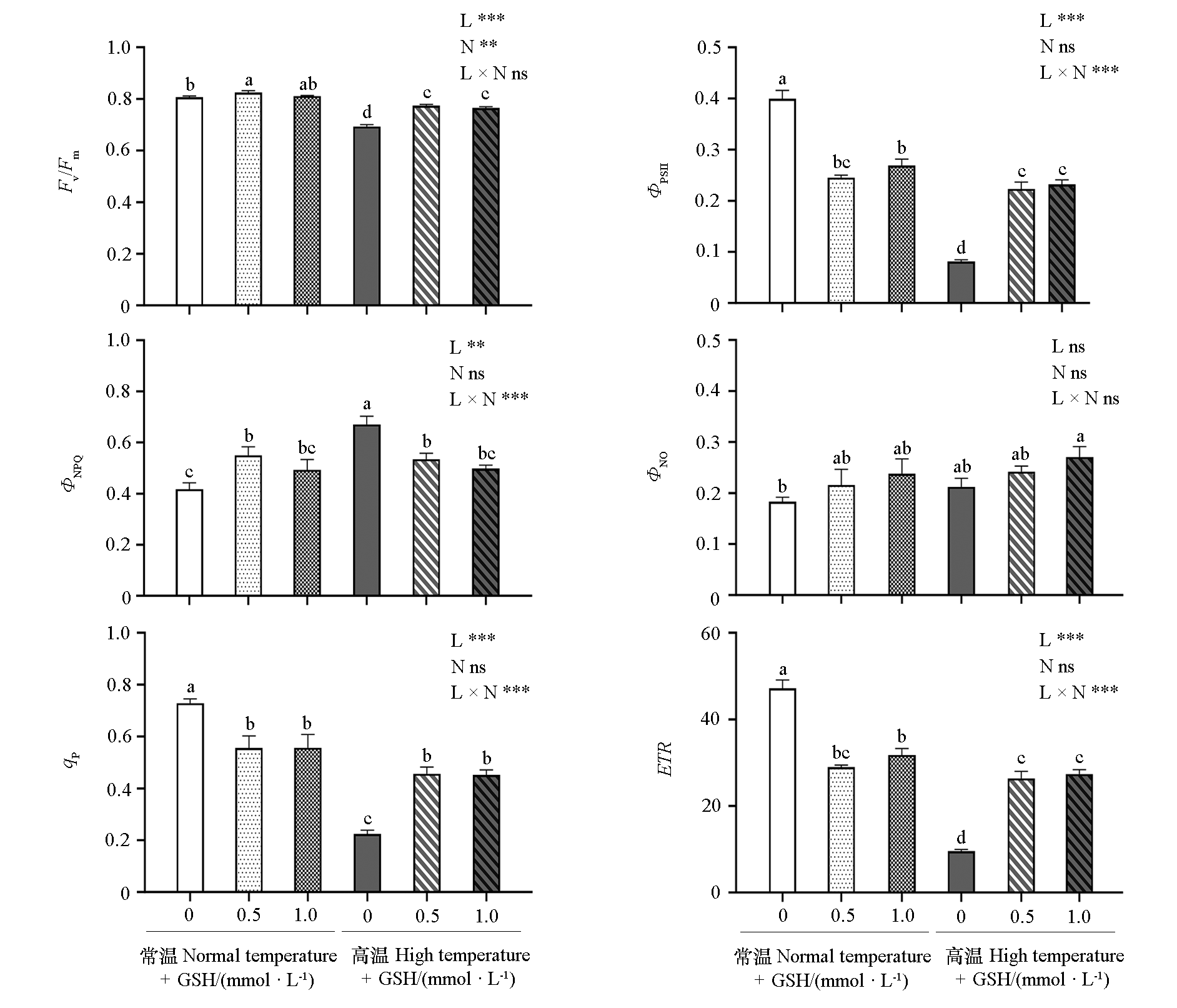
图4 外源GSH对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣叶片叶绿素荧光参数的影响
Fig. 4 Effect of exogenous GSH on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaf lettuce leaves under high temperature stress
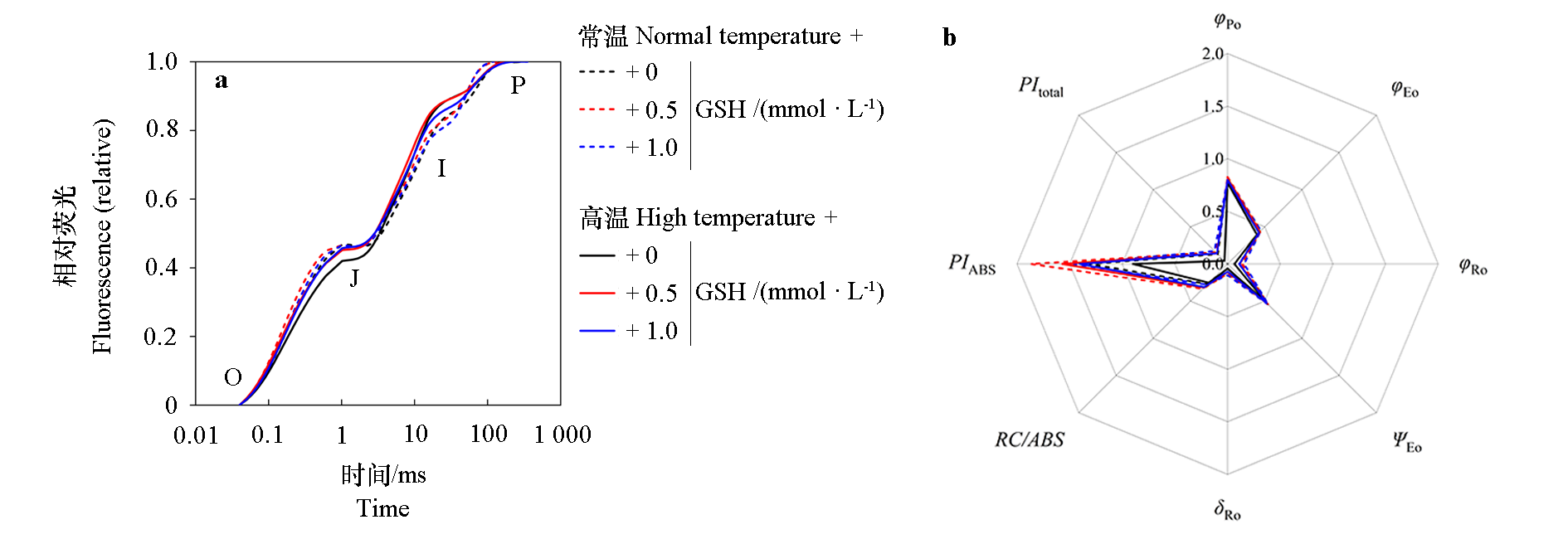
图5 外源GSH对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣叶片OJIP曲线(a)和JIP-test参数(b)的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of exogenous GSH on OJIP curve(a)and JIP-test parameters(b)of leaf lettuce leaves under high temperature stress
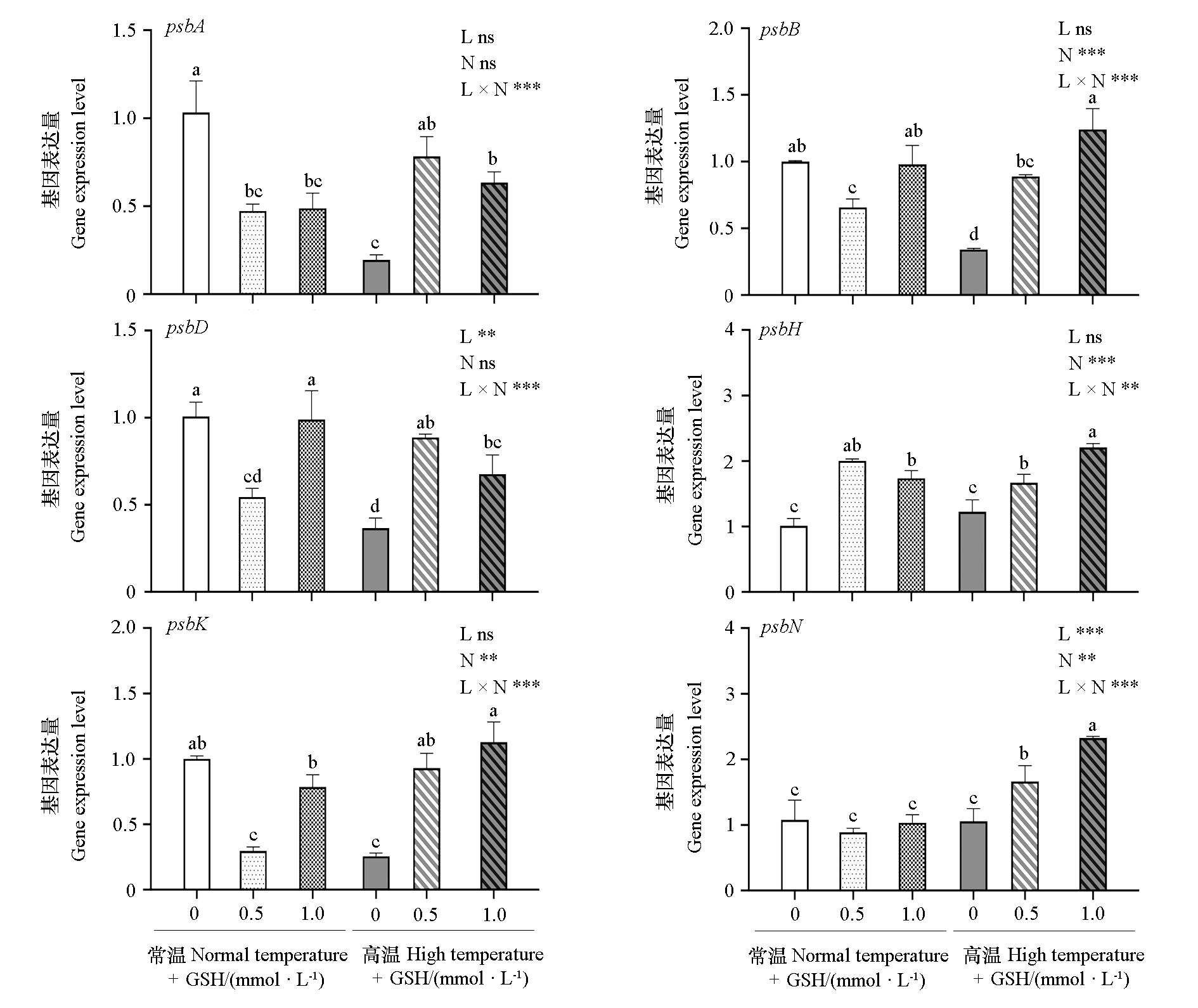
图7 外源GSH对高温胁迫下叶用莴苣叶片光系统Ⅱ反应中心蛋白基因转录水平的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of exogenous GSH on the transcription levels of photosystemⅡreaction center gene in leaf lettuce leaves under high temperature stress
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
|
曹健康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 2020. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2009-2354 |
|
段九菊, 王云山, 康黎芳, 张超, 王曼, 杜少敏, 曹冬梅. 2010. 高温胁迫对观赏凤梨叶片抗氧化系统和渗透调节物质积累的影响. 中国农学通报, 26 (8):164-169.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
高俊凤. 2006. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
高晓萍, 张婧, 牛天航, 刘阳, 常有麟, 刘思恬, 颉建明. 2023. 甜菜碱对高温胁迫下茄子幼苗生理特性的影响. 浙江农业学报, 35 (9):2097-2108.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.20221258 |
|
| [11] |
|
|
高星星. 2022. 红光与远红光比值对盐胁迫下黄瓜叶片光合作用的影响[硕士论文]. 太谷: 山西农业大学.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s12298-017-0422-2 pmid: 28461715 |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
李合生, 孙群, 赵世杰. 2000. 植物生理生化试验原理和技术. 北京: 高等教育出版社.
|
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0110 URL |
|
刘尚佳, 吕尧, 曹逼力, 陈子敬, 高松, 徐坤. 2022. 高温渍涝胁迫对姜叶片光合作用和氮代谢的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1073-1080.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0110 URL |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
pmid: 18088327 |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
庞克坚, 魏沣, 唐萍, 唐辉, 杨新洲. 2021. 莴苣化学成分及药理作用研究进展. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 40 (4):361-369.
|
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201705.009 |
|
孙胜楠, 王强, 孙晨晨, 刘丰娇, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 2017. 黄瓜幼苗光合作用对高温胁迫的响应与适应. 应用生态学报, 28 (5):1603-1610.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.201705.009 |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
|
王博伟, 陈艳丽, 朱国鹏, 王旭, 杨雨, 刘金伟. 2021. 叶面喷施氯化钙对海南高温季节水培生菜生长生理的影响. 中国瓜菜, 34 (4):94-98.
|
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0589 |
|
汪宽鸿, 祝彪, 朱祝军. 2021. GSH/GSSG 在植物应对非生物胁迫中的作用综述. 园艺学报, 48 (4):647-660.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0589 |
|
| [30] |
|
|
王延书, 王学义, 郁松林, 孟凤, 肖年湘, 王春飞. 2007. 水杨酸与热锻炼对葡萄幼苗可溶性糖、游离氨基酸和叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 西北农业学报, 16 (4):29-33.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
向丽霞, 胡立盼, 孟森, 邹志荣. 2020. 叶面喷施亚精胺对高温胁迫下番茄叶绿素合成代谢的影响. 西北植物学报, 40 (5):846-851.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.028 |
|
徐超, 王明田, 杨再强, 韩玮, 郑盛华. 2021. 高温对温室草莓光合生理特性的影响及胁迫等级构建. 应用生态学报, 32 (1):231-240.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202101.028 |
|
| [34] |
|
|
薛思嘉, 杨再强, 李军. 2017. 黄瓜花期高温热害对叶片光合特性和果实品质的影响. 北方园艺,(6):1-7.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
杨立, 杨再强, 陆思宇, 张源达, 郑涵. 2022. 高温高湿胁迫对黄瓜产量形成的影响机理. 中国农业气象, 43 (5):392-407.
|
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.07.011 |
|
余琦隆, 韩莹琰, 郝敬虹, 秦晓晓, 刘超杰, 范双喜. 2022. 外源亚精胺对高温胁迫下生菜氮代谢的影响. 中国农业科学, 55 (7):1399-1410.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2022.07.011 |
|
| [38] |
|
|
查倩, 奚晓军, 蒋爱丽, 田益华, 黄健. 2016. 高温胁迫对葡萄幼树叶绿素荧光特性和抗氧化酶活性的影响. 植物生理学报, 52 (4):525-532.
|
|
| [39] |
|
|
钟敏, 张文标, 邹梁峰, 黄清, 陈璐, 黄春辉, 陶俊杰, 徐小彪. 2018. 高温下猕猴桃光合作用和叶绿素荧光特性的日变化. 江西农业大学学报, 40 (3):472-478.
|
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
|
朱长志, 张志仙, 檀国印, 高旭, 何道根. 2017. 蔬菜作物高温胁迫研究进展. 江西农业学报, 29 (2):53-57.
|
| [1] | 黄涛, 张丽, 蒋慧, 宋波, 彭洁, 杨其长, 李跃建, 杨晓. 叶用莴苣新品种‘中生4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(S2): 111-112. |
| [2] | 唐嘉怡, 缪绸雨, 尹豪杰, 吴明月, 曹向敏, 张惠敏, 金燕, 卢晓鹏, 朱亦赤, 李大志, 盛玲. 外源草酸对采后血橙果实品质和花色苷代谢的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(9): 2425-2438. |
| [3] | 周天, 吕帅丽, 韩晗, 李雨佳, 刘海强, 刘永忠. 外源独脚金内酯对枳幼苗茎增粗生长的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(7): 1843-1854. |
| [4] | 王毅, 梁振昌. 基于群体转录组的葡萄远缘杂交遗传机制分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 835-845. |
| [5] | 唐伶俐, 贺玉花, 王庆涛, 安璐璐, 徐永阳, 张健, 孔维虎, 户克云, 赵光伟. 非呼吸跃变和呼吸跃变型甜瓜成熟果实的激素与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(4): 883-896. |
| [6] | 程小改, 万源, 林琭, 谢鹏, 李志强, 李谧, 王鹏鹏, 牛自勉. 苹果开心树形树干高度对不同冠层部位叶片光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(3): 671-692. |
| [7] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [8] | 李慧, 阚家亮, 李晓刚, 王中华, 蔺经, 杨青松. 赤霉素对‘苏翠1号’梨花芽松散的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(10): 2713-2726. |
| [9] | 史兴秀, 冯贝贝, 闫鹏, 耿文娟, 朱玛孜拉·沙尔山木汗. ‘王林’苹果早期水心病发生过程中的相关生理变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 171-184. |
| [10] | 任思源, 陈森, 龙治坚, 王博雅, 唐登国, 王正前, 杨斌, 胡尚连, 曹颖. 花魔芋球茎发育期氮分配变化和相关基因表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2019-2030. |
| [11] | 张松彦, 迭鹏翔, 宋梦婷, 李志坚, 周建. 烟草过表达刺槐RpACBP3对光合生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [12] | 周平, 颜少宾, 郭瑞, 金光. 桃镁离子转运蛋白MGT基因家族鉴定与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 463-478. |
| [13] | 夏宏义, 刘巧, 彭家清, 吴伟, 龚林忠. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄避雨栽培f式树形对光合及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [14] | 卜文轩, 姚奕平, 黄宇, 杨星宇, 罗小宁, 张旻桓, 雷维群, 王政, 田珈宁, 陈露洁, 秦莉萍. ‘呼红’牡丹高温胁迫响应生理与转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2800-2816. |
| [15] | 杨江山, 陈亚娟, 戴子博, 李斗, 邵璋, 金鑫, 王宇航, 王春恒. 黄腐酸钾对‘蛇龙珠’葡萄光合特性及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(12): 2843-2856. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司