
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 439-452.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0728
毛欣1,*, 元文飞1,*, 郭雨润1, 徐欣欣1, 李艺1, 张毅1, 苗妍秀1, 白龙强1,**( ), 李衍素2,**(
), 李衍素2,**( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-18
修回日期:2024-12-03
出版日期:2025-02-25
发布日期:2025-02-23
通讯作者:
作者简介:*共同第一作者
基金资助:
MAO Xin1, YUAN Wenfei1, GUO Yurun1, XU Xinxin1, LI Yi1, ZHANG Yi1, MIAO Yanxiu1, BAI Longqiang1,**( ), LI Yansu2,**(
), LI Yansu2,**( )
)
Received:2024-09-18
Revised:2024-12-03
Published:2025-02-25
Online:2025-02-23
摘要:
有机物料种植板(organic substrate planting board)栽培可实现设施蔬菜有机肥施用自动化作业。为了探究该栽培模式对有机物料腐解、养分释放和作物生长与养分吸收等的影响,以‘中农46号’黄瓜(Cucumis sativus L.)为试材,进行了有机物料种植板栽培和有机物料撒施后深翻起垄的常规土壤栽培对比试验。结果表明:有机物料种植板处理在0 ~ 30 d腐解较快,常规撒施深翻处理在0 ~ 60 d腐解较快,之后均变慢。30 d时有机物料种植板处理的有机物料腐解率较常规撒施深翻处理高3.7个百分点,但120 d时低7.8个百分点。两种施肥模式下有机物料的全N含量在试验期间迅速降低,而全P和全K含量变化较小。2021年秋冬茬试验,根区深度0 ~ 5 cm土层有机物料种植板处理的碱解氮含量,及根区0 ~ 5 cm和5 ~ 15 cm土层速效磷和速效钾含量均显著高于常规撒施深翻处理;有机物料种植板处理根区养分含量变异系数较常规撒施深翻处理高;2023年秋冬茬两处理根区碱解氮含量变化趋势与2021年基本一致,但速效磷含量和变异系数在两处理间差异不大。与常规撒施深翻处理相比,有机物料种植板处理黄瓜叶片全N、P和K含量在2021年秋冬茬未降低,而2023年秋冬茬120 d时全K含量降低了9.6%;光合速率(Pn)和地上部干物质量显著高升高;黄瓜产量在2021年秋冬茬无差异,2023年秋冬茬提高了10.9%。以上表明有机物料种植板栽培下的有机物料腐解率较常规撒施深翻栽培低,养分在根区表层集中分布,使得黄瓜对养分吸收较为充分,满足了黄瓜对养分的需求。
毛欣, 元文飞, 郭雨润, 徐欣欣, 李艺, 张毅, 苗妍秀, 白龙强, 李衍素. 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培中有机物料腐解及根区和叶片养分含量的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 439-452.
MAO Xin, YUAN Wenfei, GUO Yurun, XU Xinxin, LI Yi, ZHANG Yi, MIAO Yanxiu, BAI Longqiang, LI Yansu. Analysis of the Decomposition of Organic Materials and Nutrients Contents in Root Zone and Leaves of Cucumber Under Organic Substrate Planting Board Cultivation in Solar Greenhouse[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(2): 439-452.
| 试验材料 Material | 容重/(g · cm-3) Bulk density | 全氮含量/(g · kg-1) Total N content | 全磷含量/(g · kg-1) Total P content | 全钾/(g · kg-1) Total K content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 Soil | 1.19 | 1.40 | 0.74 | 8.25 |
| 玉米秸秆 Maize straw | 0.19 | 18.06 | 1.69 | 20.00 |
| 羊粪 Sheep manure | 0.39 | 28.95 | 5.33 | 13.81 |
| 育苗基质 Seedling medium | 0.29 | 4.93 | 0.95 | 0.59 |
表1 土壤和有机物料的理化性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical characteristics of soil and organic waste substrates
| 试验材料 Material | 容重/(g · cm-3) Bulk density | 全氮含量/(g · kg-1) Total N content | 全磷含量/(g · kg-1) Total P content | 全钾/(g · kg-1) Total K content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤 Soil | 1.19 | 1.40 | 0.74 | 8.25 |
| 玉米秸秆 Maize straw | 0.19 | 18.06 | 1.69 | 20.00 |
| 羊粪 Sheep manure | 0.39 | 28.95 | 5.33 | 13.81 |
| 育苗基质 Seedling medium | 0.29 | 4.93 | 0.95 | 0.59 |
图1 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻起垄栽培(S)示意图
Fig. 1 Sketch map of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse
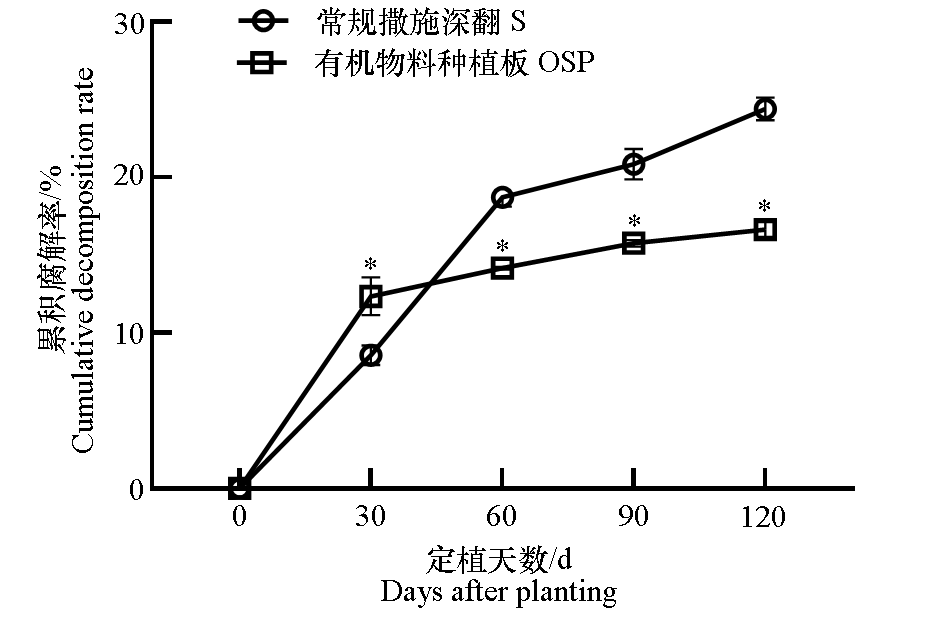
图2 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中有机物料的累积腐解率 使用t检验。*表示同一天两处理间存在显著差异(P < 0.05)。 下同
Fig. 2 Cumulative decomposition rates of organic materials under organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse t-Test. * indicates significant difference(P < 0.05)between two treatments on the same day. The same below
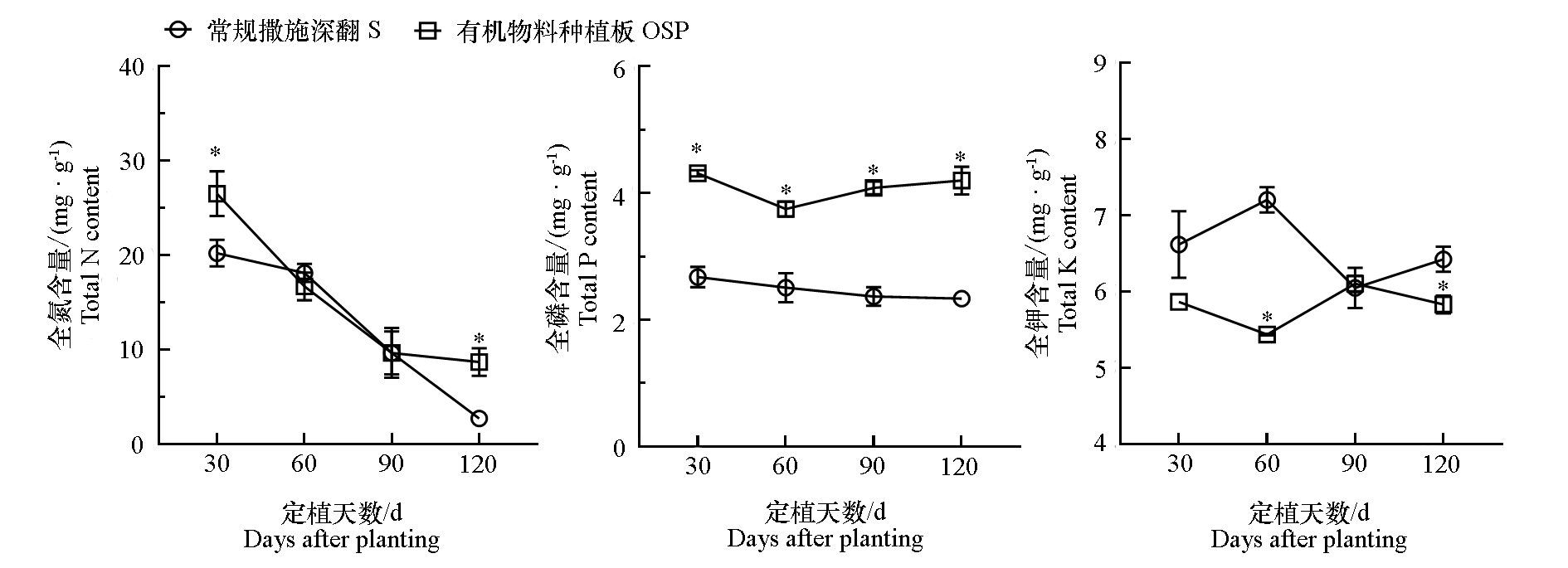
图3 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中有机物料元素含量变化
Fig. 3 Changes of nutrients contents in the organic materials under organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse

图4 2021年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中根区土壤的碱解氮含量 单因素方差分析,LSD法进行多重比较。不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同
Fig. 4 The contents of alkaline N in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2021 Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by LSD method test for multiple comparisons. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. The same below

图5 2023年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板照片(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中根区土壤的碱解氮含量
Fig. 5 The contents of alkaline N in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2023
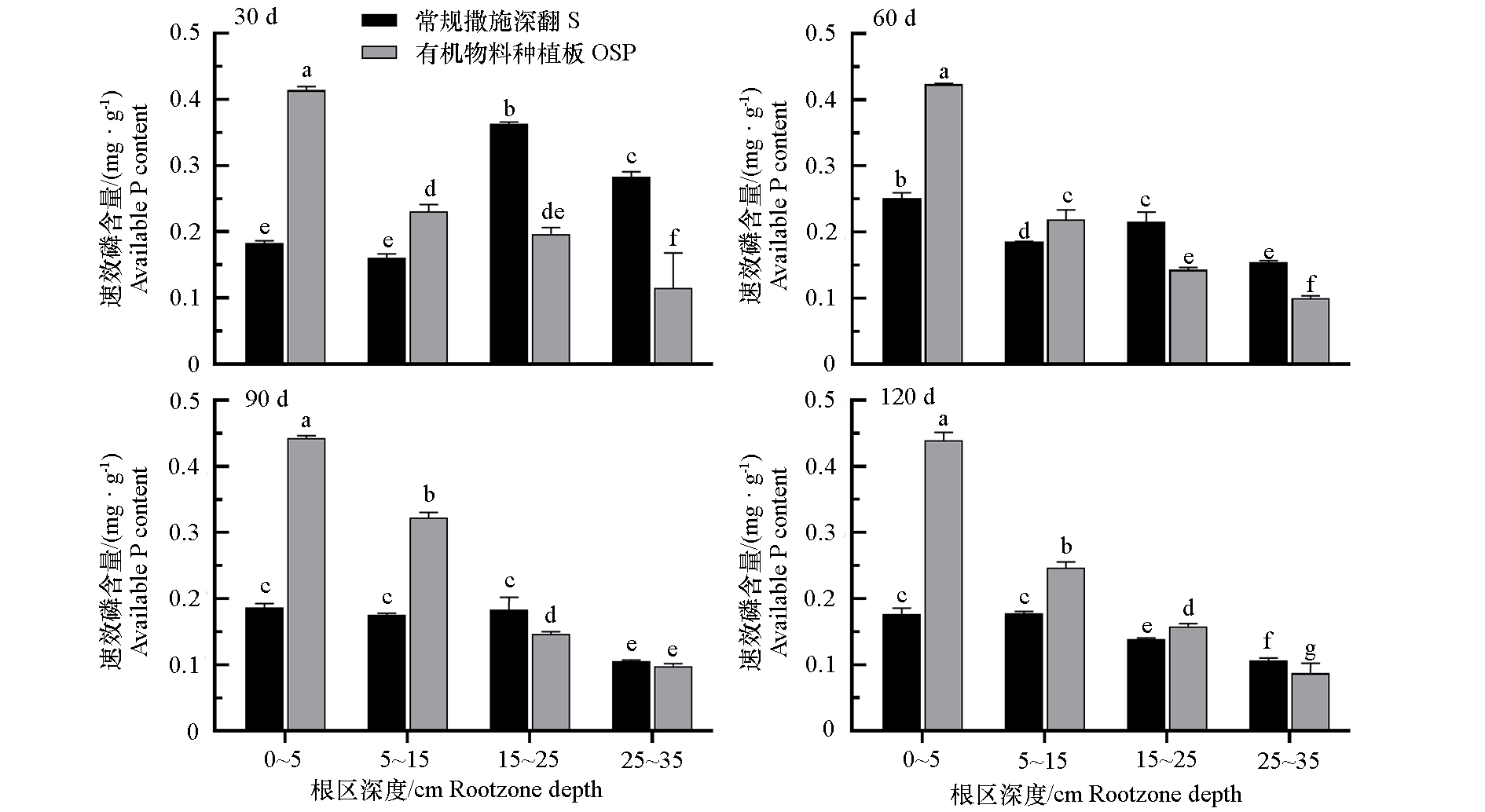
图6 2021年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中根区土壤的速效磷含量
Fig. 6 The contents of available P in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2021

图7 2023年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中根区土壤的速效磷含量
Fig. 7 The contents of available P in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2023

图8 2021年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)中根区土壤的速效钾含量
Fig. 8 The contents of available K in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2021
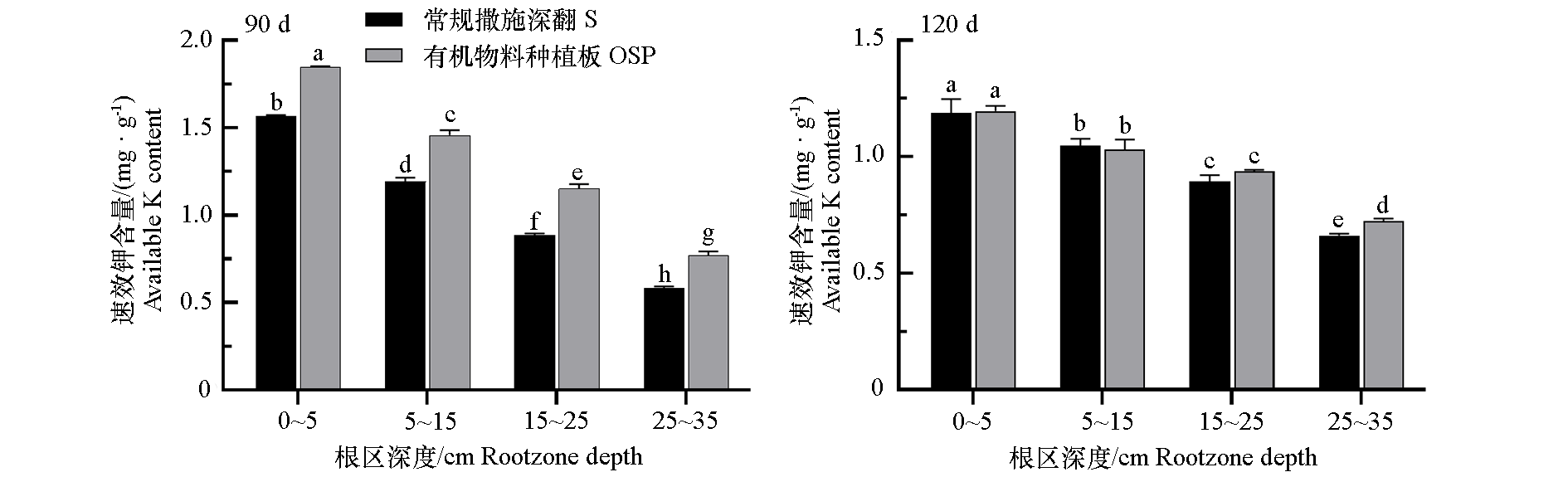
图9 2023年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施栽培(S)中根区土壤的速效钾含量
Fig. 9 The contents of available K in root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2023
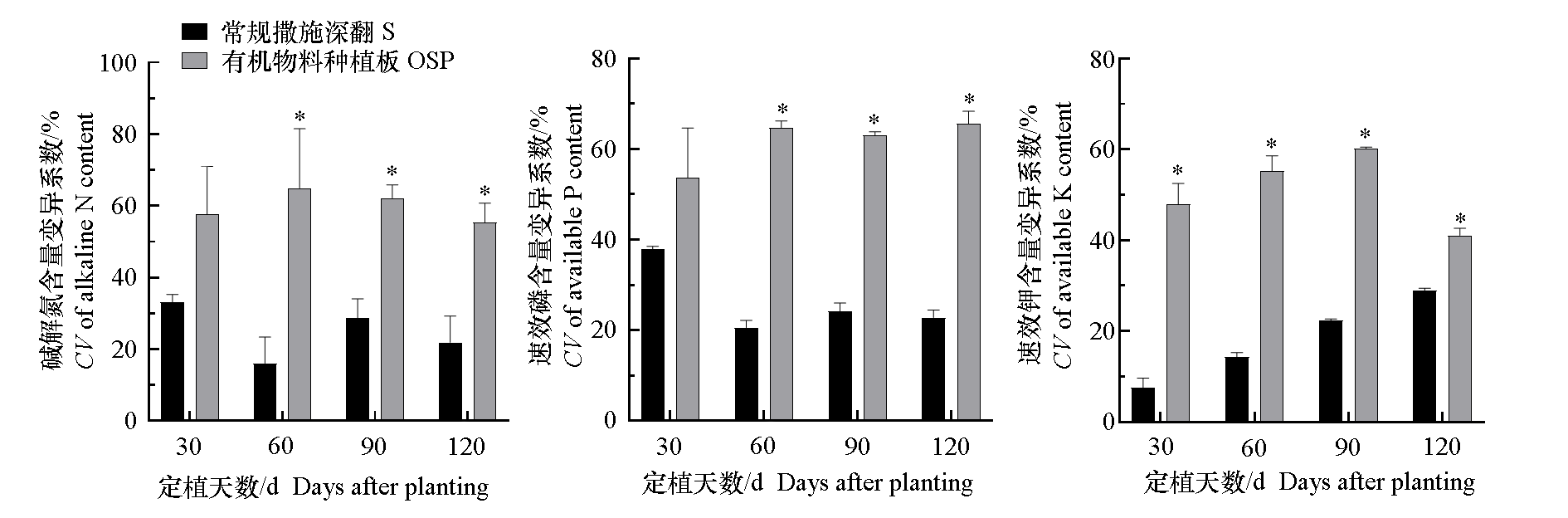
图10 2021年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施栽培(S)中根区0 ~ 35 cm土层养分含量的变异系数(CV)
Fig. 10 Analysis of coefficient of varation(CV)of nutrients in 0-35 cm layer in the root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2021

图11 2023年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施栽培(S)中根区0 ~ 35 cm土层养分含量的变异系数(CV)
Fig. 11 Analysis of coefficient of varation(CV)of nutrients in 0-35 cm layer in the root zone of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S)cultivation of cucumber in solar greenhouse in 2023
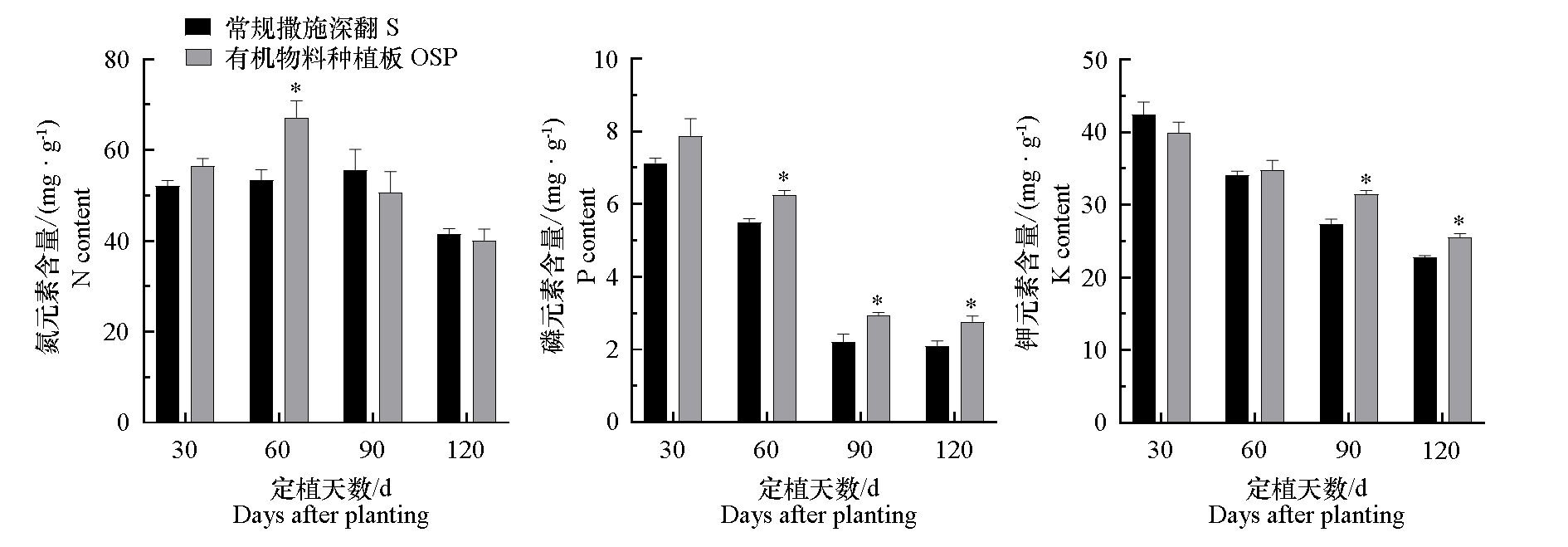
图12 2021年秋冬茬日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)对叶片N、P、K含量的影响
Fig. 12 The elements content in cucumber leaves of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation in solar greenhouse in 2021
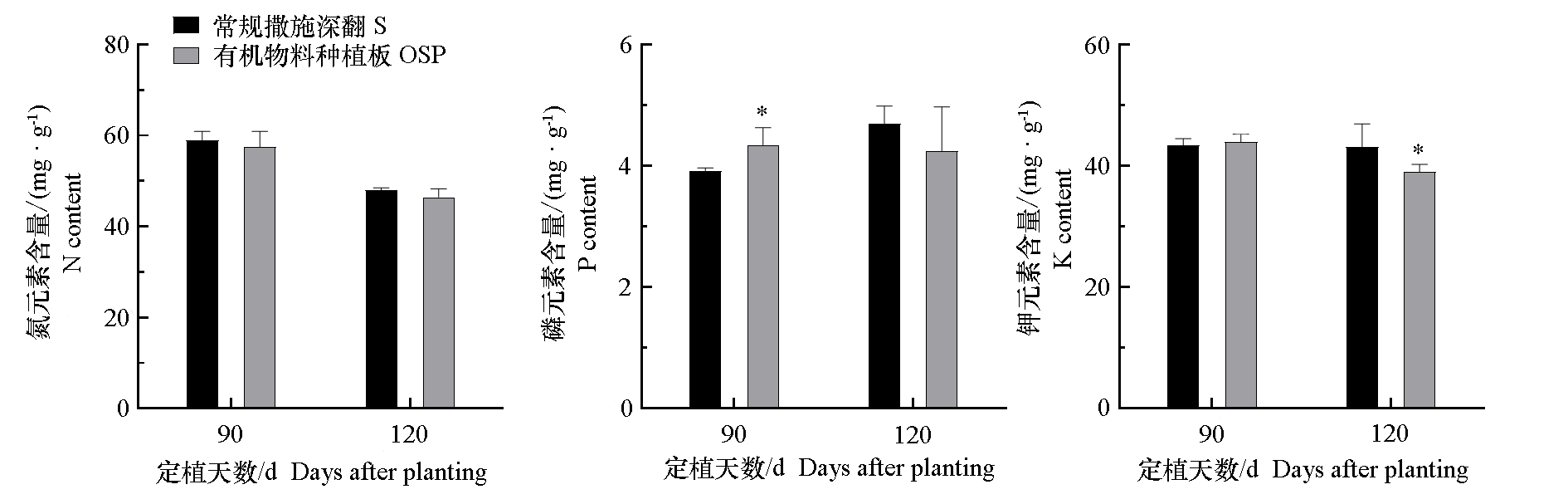
图13 2023年秋冬茬光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)对叶片N、P、K含量的影响
Fig. 13 The elements content in cucumber leaves of organic substrate planting board(OSP)and conventional soil(S) cultivation in solar greenhouse in 2023
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率/(μmol · m-2 · s-1) Pn | 干物质量/(g · plant-1)Dry weight | 产量/(kg · m-2) Yield | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 d | 60 d | 90 d | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Above ground part | |||
| 2021 | 常规撒施深翻 S | 14.98 ± 2.58 | 10.20 ± 1.41 | 11.23 ± 1.75 | 28.84 ± 4.69 | 6.90 ± 0.65 | 35.19 ± 8.10 | 4.56 ± 0.73 |
| 有机物料种植板 OSP | 17.92 ± 1.73* | 15.80 ± 1.71* | 13.36 ± 3.36* | 38.16 ± 6.18* | 8.31 ± 0.92* | 46.34 ± 7.25* | 4.43 ± 0.18 | |
| 2023 | 常规撒施深翻 S | 15.01 ± 2.66 | 14.70 ± 2.11 | 12.72 ± 0.56 | 32.05 ± 5.54 | 14.24 ± 1.24 | 46.15 ± 6.77 | 5.69 ± 0.28 |
| 有机物料种植板 OSP | 16.70 ± 1.07 | 16.47 ± 1.26* | 14.60 ± 0.42* | 37.04 ± 2.39 | 14.44 ± 1.03 | 51.66 ± 2.24 | 6.31 ± 0.15* | |
表2 日光温室黄瓜有机物料种植板栽培(OSP)和常规撒施深翻栽培(S)对叶片光合速率、植株生物量和产量的影响
Table 2 The effects of organic substrate planting board(OSP)cultivation and conventional soil(S)cultivation on the photosynthetic rate,biomass and yield of cucumber
| 年份 Year | 处理 Treatment | 净光合速率/(μmol · m-2 · s-1) Pn | 干物质量/(g · plant-1)Dry weight | 产量/(kg · m-2) Yield | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 d | 60 d | 90 d | 叶 Leaf | 茎 Stem | 地上部 Above ground part | |||
| 2021 | 常规撒施深翻 S | 14.98 ± 2.58 | 10.20 ± 1.41 | 11.23 ± 1.75 | 28.84 ± 4.69 | 6.90 ± 0.65 | 35.19 ± 8.10 | 4.56 ± 0.73 |
| 有机物料种植板 OSP | 17.92 ± 1.73* | 15.80 ± 1.71* | 13.36 ± 3.36* | 38.16 ± 6.18* | 8.31 ± 0.92* | 46.34 ± 7.25* | 4.43 ± 0.18 | |
| 2023 | 常规撒施深翻 S | 15.01 ± 2.66 | 14.70 ± 2.11 | 12.72 ± 0.56 | 32.05 ± 5.54 | 14.24 ± 1.24 | 46.15 ± 6.77 | 5.69 ± 0.28 |
| 有机物料种植板 OSP | 16.70 ± 1.07 | 16.47 ± 1.26* | 14.60 ± 0.42* | 37.04 ± 2.39 | 14.44 ± 1.03 | 51.66 ± 2.24 | 6.31 ± 0.15* | |
| [1] |
|
|
鲍士旦. 2000. 土壤农化分析. 3版. 北京:中国农业出版社:56-188.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈淑芳, 窦锟贤. 2007. 不同营养液浓度对黄瓜幼苗生长的影响. 安徽农业科学, 35 (34):11056-11057,11064.
|
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
代文才, 高明, 兰木羚, 黄容, 王金柱, 王子芳, 韩晓飞. 2017. 不同作物秸秆在旱地和水田中的腐解特性及养分释放规律. 中国生态农业学报, 25 (2):188-199.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
高丽红, 郭世荣, 李式军. 2012. 绿色环保高效的设施蔬菜土壤滴灌施肥体系. 长江蔬菜,(12):5-10.
|
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas20190600084 |
|
郭娅, 尹焕丽, 常凤, 李岚涛, 赵丽芳, 张倩, 王宜伦. 2020. 株间穴施对夏玉米产量和养分吸收的影响. 农学学报, 10 (3):43-48.
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas20190600084 |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0348 URL |
|
韩鲁杰, 冯一清, 杨秀华, 张宁, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 2022. 有机肥化肥配施对大棚黄瓜根区土壤与根系特征的影响. 园艺学报, 49 (5):1047-1059.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0348 URL |
|
| [9] |
|
|
黄绍文, 唐继伟, 李春花, 张怀志, 袁硕. 2017. 我国蔬菜化肥减施潜力与科学施用对策. 植物营养与肥料学报, 23 (6):1480-1493.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
姜超强, 王火焰, 卢殿君, 周健民, 王世济, 祖朝龙. 2018. 一次性根区穴施尿素提高夏玉米产量和养分吸收利用效率. 农业工程学报, 34 (12):146-153.
|
|
| [11] |
|
|
焦晓燕, 王立革, 张东玲, 张京社, 董二伟. 2010. 山西省日光节能温室蔬菜施肥现状、存在问题及建议. 山西农业科学, 38 (4):37-41.
|
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.06.014 |
|
李亚林, 张旭博, 任凤玲, 孙楠, 徐梦, 徐明岗. 2020. 长期施肥对中国农田土壤溶解性有机碳氮含量影响的整合分析. 中国农业科学, 53 (6):1224-1233.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2020.06.014 |
|
| [13] |
|
|
梁金凤, 贾小红, 金强, 文方芳, 于跃跃. 2013. 北京市设施蔬菜施肥状况变化分析. 中国蔬菜,(19):18-22.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘成良, 贡亮, 苑进, 李彦明. 2022. 农业机器人关键技术研究现状与发展趋势. 农业机械学报, 53 (7):1-22,55.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1002/jobm.201300744 pmid: 24652702 |
| [17] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.09.008 |
|
马想, 徐明岗, 赵惠丽, 段英华. 2019. 我国典型农田土壤中有机物料腐解特征及驱动因子. 中国农业科学, 52 (9):1564-1573.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.09.008 |
|
| [18] |
|
|
毛欣, 元文飞, 张毅, 李亚灵, 温祥珍, 侯雷平, 白龙强, 李衍素. 2022. 成型有机基质种植板在设施叶用莴苣栽培中的应用效果. 中国蔬菜,(6):44-49.
|
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
|
钱瑞雪, 刘岩, 陈智文, 何红波, 张清. 2020. 玉米秸秆添加对土壤碳氮周转相关酶活性动态的影响. 土壤通报, 51 (5):1109-1117.
|
|
| [21] |
|
|
荣勤雷, 李若楠, 黄绍文, 周春火, 唐继伟, 王丽英, 张彦才. 2019. 不同施肥模式下设施菜田土壤团聚体养分和微生物量特征. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (7):1084-1096.
|
|
| [22] |
|
|
史央, 蒋爱芹, 戴传超, 陆玲. 2002. 秸秆降解的微生物学机理研究及应用进展. 微生物学杂志, 22 (1):47-50.
|
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0481 URL |
|
疏再发, 吉庆勇, 邵静娜, 郑生宏, 周慧娟, 何卫中. 2023. 茶园有机肥替代化肥对土壤养分和茶叶产量与品质的影响. 园艺学报, 50 (10):2207-2219.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0481 URL |
|
| [24] |
|
|
孙艳, 洪婉婷, 韩阳, 徐梓楷, 程凌云. 2021. 植物内部磷循环利用提高磷效率的研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报, 27 (12):2216-2228.
|
|
| [25] |
|
|
唐继伟, 徐久凯, 温延臣, 田昌玉, 林治安, 赵秉强. 2019. 长期单施有机肥和化肥对土壤养分和小麦产量的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 25 (11):1827-1834.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
王火焰, 周健民. 2013. 根区施肥——提高肥料养分利用率和减少面源污染的关键和必需措施. 土壤, 45 (5):785-790.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
王文锋, 李春花, 黄绍文, 高伟, 唐继伟. 2016. 不同施肥模式对设施菜田土壤微生物量碳、氮的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报, 22 (5):1286-1297.
|
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.16.007 |
|
武际, 郭熙盛, 王允青, 许征宇, 鲁剑巍. 2011. 不同水稻栽培模式和秸秆还田方式下的油菜、小麦秸秆腐解特征. 中国农业科学, 44 (16):3351-3360.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2011.16.007 |
|
| [29] |
|
|
杨冬艳, 桑婷, 冯海萍, 赵云霞, 王丹, 王蓉. 2022. 灌溉频率对日光温室早春茬黄瓜果实发育及根系分布的影响. 节水灌溉,(4):31-36.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
张福锁. 2017. 科学认识化肥的作用及合理利用. 农机科技推广,(1):38-40,43.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
张云鹤, 温靖, 林森, 沈剑波, 师翊. 2023. 北京市设施农业机器人发展现状及策略. 农业工程技术, 43 (2):27-28,91.
|
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.01.037 |
|
赵征宇, 孙永红, 赵明, 蔡葵, 王文娇, 陈建美. 2013. 有机无机肥配施对土壤氮素转化和番茄产量品质的影响. 华北农学报, 28 (1):208-212.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7091.2013.01.037 |
|
| [34] |
pmid: 12222046 |
|
朱世东, 徐文娟, 赵国荣. 2002. 多功能营养型蔬菜无土栽培基质的特性研究. 应用生态学报, 13 (4):425-428.
pmid: 12222046 |
| [1] | 温正阳, 孙靖博, 张梦夏, 张锋, 董春娟. 黄瓜CsCuAO家族基因鉴定及其在不定根形成中的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 309-321. |
| [2] | 李敖, 郑旭, 吴承勖, 聂瑞宁, 姬新颖, 唐佳莉, 张俊佩. 丛枝菌根真菌对盐胁迫下核桃幼苗生长及生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(2): 423-438. |
| [3] | 杨艳, 刘军, 周晓慧, 刘松瑜, 庄勇. 茄子SmWRKY4的克隆及耐冷性功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(1): 101-110. |
| [4] | 刘新月, 翟昭慈, 陶佳淋, 冯坤, 蔡晓腾, 刘志国, 刘孟军. 不同落叶剂对冬枣落叶效果及养分回流的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2120-2130. |
| [5] | 张松彦, 迭鹏翔, 宋梦婷, 李志坚, 周建. 烟草过表达刺槐RpACBP3对光合生理的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [6] | 袁泉, 卢威, 王君, 陈茹, 李衍素, 于贤昌, 贺超兴, 孙敏涛, 闫妍. 日光温室不同土质灌水下限对早春黄瓜生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1377-1385. |
| [7] | 王文娇, 邢军杰, 申成丞, 李斌. 黄瓜蜡质基因CsCER1调控因子CsCOL5的筛选及其功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| [8] | 伍少福, 韩科峰, 吴良欢. 生物有机肥加专用肥对葡萄园土壤养分、微生物和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1099-1112. |
| [9] | 张丛莹, 顾兴芳, 苗晗, 董邵云, 刘小萍, 官健涛, 张圣平. 黄瓜新品种‘中农脆玉1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1173-1174. |
| [10] | 于静, 冯向君, 金英学, 丁国华. 焦脱镁叶绿酸a对黄瓜枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 859-874. |
| [11] | 张丛莹, 顾兴芳, 苗晗, 董邵云, 刘小萍, 官健涛, 张圣平. 黄瓜新品种‘中农脆绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(4): 919-920. |
| [12] | 夏宏义, 刘巧, 彭家清, 吴伟, 龚林忠. ‘阳光玫瑰’葡萄避雨栽培f式树形对光合及果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 560-570. |
| [13] | 高永臣, 苏新建, 余城, 刘铸, 毛柯, 邹养军, 龚小庆. 苹果树盘地布和药渣覆盖对土壤理化性质和细菌群落的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 587-600. |
| [14] | 刘梦, 贾惠婷, 周新刚. 黄瓜枯萎病菌共生细菌的分离鉴定及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 643-655. |
| [15] | 孙挺, 蒋茹佳, 施政, Menachem Moshelion, 孙玉东, 程瑞, 徐沛. 菜豆“水分利用效率黄金时段”量化解析方法的建立及应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(3): 656-668. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司