
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (12): 2669-2682.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0913
王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-26
修回日期:2022-07-15
出版日期:2022-12-25
发布日期:2023-01-02
通讯作者:
梁燕
E-mail:liangyan@nwsuaf.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Jin, WANG Xinyu, SHEN Yuanbo, ZHANG Qinghua, Lou Qianqi, ZHANG Shijie, ZHAO Pan, LIANG Yan( )
)
Received:2022-04-26
Revised:2022-07-15
Online:2022-12-25
Published:2023-01-02
Contact:
LIANG Yan
E-mail:liangyan@nwsuaf.edu.cn
摘要:
果实叶绿体的丰度和功能直接影响着果实品质。在果实成熟前,叶绿体作为同化器官合成大量同化物用于果实发育和品质相关代谢物的合成,在果实成熟期,叶绿体转化为有色体,存储前期在光合作用驱动下不同代谢途径合成的营养和风味物质。因此,通过调控果实叶绿体发育来提高果实品质成为研究热点,在果实叶绿体发育调控研究方面取得了显著进展。本文从影响果实叶绿体发育的转录因子、光信号、激素信号、氧化应激信号等几个方面对番茄果实叶绿体发育调控的研究进展综合论述,并提出了面临的挑战和今后研究的方向,旨在明晰番茄果实叶绿体发育的特异性调控机制,为番茄及其他作物果实的品质改良提供新思路。
中图分类号:
王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕. 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控及其应用的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2669-2682.
WANG Jin, WANG Xinyu, SHEN Yuanbo, ZHANG Qinghua, Lou Qianqi, ZHANG Shijie, ZHAO Pan, LIANG Yan. Regulation of Chloroplast Development in Tomato Fruit and Its Application[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(12): 2669-2682.
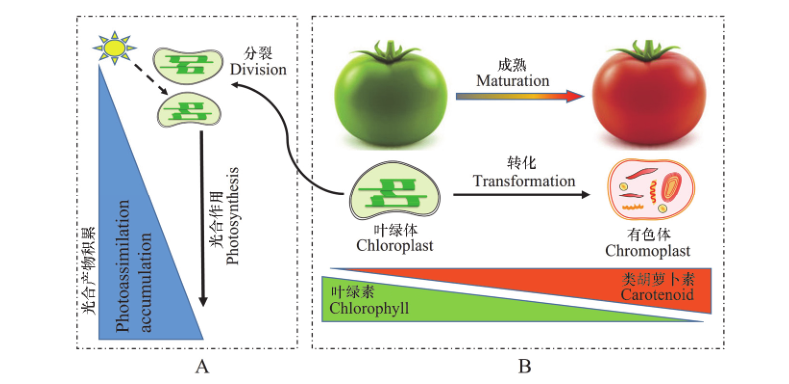
图1 番茄果实叶绿体的光合作用及成熟时向有色体转化 A:成熟前叶绿体可分裂增殖,合成叶绿素,进行光合作用并积累大量光合产物;B:成熟时叶绿体向有色体转化,叶绿素降解,有色体中合成并积累类胡萝卜素,细胞中积累糖类、有机酸和挥发性香气化合物。
Fig. 1 Photosynthesis in tomato fruit chloroplasts and the transformation of chloroplasts to chromoplasts during ripening A:Before ripening,the chloroplasts can proliferate by division,synthesize chlorophyll,and accumulate amounts of photosynthetic products through photosynthesis;B:During ripening,the chloroplasts transform into chromoplasts,with chlorophyll degradation,carotenoids synthesis and accumulation in chromoplasts,and sugars,organic acids and volatile aroma compounds are accumulated in fruit cells.
| 名称 Name | 番茄材料 Material | 功能与性状 Function and characteristic | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLK2 | uniform ripening (u)mutant | 调控绿果肩形成;u果实均匀浅绿,叶绿素含量降低,叶绿体的数量和体积及基粒类囊体数量减少 Regulation of green fruit shoulder formation;u fruit were uniformly light green with reduced chloroplast number and volume,granum thylakoids number and chlorophyll content | Powell et al., |
| APRR2-Like | APRR2-Like overexpression | 果实呈均匀深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量和体积略增 Fruit were uniformly dark green,with increased chlorophyll content and slightly increased chloroplast number and volume | Pan et al., |
| TKN2 | Curl(Cu)mutant | 果实深绿且较小,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量和体积略增,基粒类囊体数量增多 Fruit were dark green and smaller,with increased chlorophyll content,slightly increased chloroplast number and volume,and increased granum thylakoid number | Nadakuduti et al., |
| TKN4 | uniform gray-green(ug)mutant | 调控绿果肩形成;ug果实叶绿素含量、叶绿体体积及基粒类囊体数量下降 Regulation of green fruit shoulder formation;with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast volume and granum thylakoid number in ug fruit | Nadakuduti et al., |
| BEL4 | Micro-Tom BEL4-RNAi | 果实略呈深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加、体积增大 Fruit were slightly dark green,with increased chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Yan et al., |
| BEL11 | Micro-Tom BEL11-RNAi | 果实呈深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加、体积增大 Fruits were light green with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Meng et al., |
| LOL1 | LOL1 knock out | 果实呈浅绿色,叶绿素含量降低,叶绿体数量减少、体积减小 Fruit were light green with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Borovsky et al., |
| TAGL1 | green stripe(gs)mutant | 调控果实深绿条纹形成,深绿条纹区叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加 Regulation of dark green stripe formation on the fruit,with increased chlorophyll content and chloroplast number in the dark green stripe region | Liu et al., |
表1 调控番茄果实叶绿体发育的转录因子
Table 1 Transcription factors regulating chloroplast development in tomato fruit
| 名称 Name | 番茄材料 Material | 功能与性状 Function and characteristic | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLK2 | uniform ripening (u)mutant | 调控绿果肩形成;u果实均匀浅绿,叶绿素含量降低,叶绿体的数量和体积及基粒类囊体数量减少 Regulation of green fruit shoulder formation;u fruit were uniformly light green with reduced chloroplast number and volume,granum thylakoids number and chlorophyll content | Powell et al., |
| APRR2-Like | APRR2-Like overexpression | 果实呈均匀深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量和体积略增 Fruit were uniformly dark green,with increased chlorophyll content and slightly increased chloroplast number and volume | Pan et al., |
| TKN2 | Curl(Cu)mutant | 果实深绿且较小,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量和体积略增,基粒类囊体数量增多 Fruit were dark green and smaller,with increased chlorophyll content,slightly increased chloroplast number and volume,and increased granum thylakoid number | Nadakuduti et al., |
| TKN4 | uniform gray-green(ug)mutant | 调控绿果肩形成;ug果实叶绿素含量、叶绿体体积及基粒类囊体数量下降 Regulation of green fruit shoulder formation;with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast volume and granum thylakoid number in ug fruit | Nadakuduti et al., |
| BEL4 | Micro-Tom BEL4-RNAi | 果实略呈深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加、体积增大 Fruit were slightly dark green,with increased chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Yan et al., |
| BEL11 | Micro-Tom BEL11-RNAi | 果实呈深绿色,叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加、体积增大 Fruits were light green with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Meng et al., |
| LOL1 | LOL1 knock out | 果实呈浅绿色,叶绿素含量降低,叶绿体数量减少、体积减小 Fruit were light green with reduced chlorophyll content,chloroplast number and volume | Borovsky et al., |
| TAGL1 | green stripe(gs)mutant | 调控果实深绿条纹形成,深绿条纹区叶绿素含量升高,叶绿体数量增加 Regulation of dark green stripe formation on the fruit,with increased chlorophyll content and chloroplast number in the dark green stripe region | Liu et al., |

图2 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控网络 A:以GLK2、APRR2-Like基因为核心的转录水平调控;B:以GLK2、HY5蛋白为核心的转录后调控。蓝线表示正调控,红线表示负调控,黑色箭头表示基因转录和翻译,实线表示直接调控,虚线表示间接调控或调控机制不确定。
Fig. 2 Regulatory network of chloroplast development in tomato fruit A:Regulation at the transcriptional level centered on GLK2 and APRR2-Like genes;B:Post-transcriptional regulation centered on GLK2 and HY5 proteins. Blue lines indicate positive regulation,red lines indicate negative regulation,black arrows indicate gene transcription and translation,solid lines indicate direct regulation,and dashed lines indicate indirect regulation or uncertain regulatory mechanisms.
| [1] |
Barry C S, Aldridge G M, Herzog G, Ma Q, McQuinn R P, Hirschberg J, Giovannoni J J. 2012. Altered chloroplast development and delayed fruit ripening caused by mutations in a zinc metalloprotease at the lutescent2 locus of tomato. Plant Physiology, 159 (3):1086-1098.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.197483 URL |
| [2] |
Bernhardt A, Lechner E, Hano P, Schade V, Dieterle M, Anders M, Dubin M J, Benvenuto G, Bowler C, Genschik P, Hellmann H. 2006. CUL 4 associates with DDB1 and DET1 and its downregulation affects diverse aspects of development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 47 (4):591-603.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02810.x pmid: 16792691 |
| [3] |
Bhatt A M, Etchells J P, Canales C, Lagodienko A, Dickinson H. 2004. VAAMANA-A BEL1-like homeodomain protein,interacts with KNOX proteins BP and STM and regulates inflorescence stem growth in Arabidopsis. Gene, 328:103-111.
pmid: 15019989 |
| [4] |
Bohk G W, Scott D H. 1945. A second gene for uniform unripe fruit color in the tomato. Journal of Heredity, 36 (6):169-172.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a105489 URL |
| [5] |
Borovsky Y, Monsonego N, Mohan V, Shabtai S, Kamara I, Faigenboim A, Hill T, Chen S, Stoffel K, van Deynze A, Paran I. 2019. The zinc-finger transcription factor CcLOL1 controls chloroplast development and immature pepper fruit color in Capsicum chinense and its function is conserved in tomato. Plant Journal, 99 (1):41-55.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.14305 |
| [6] |
Brand A, Borovsky Y, Hill T, Rahman K A A, Bellalou A, van Deynze A, Paran I. 2014. CaGLK2 regulates natural variation of chlorophyll content and fruit color in pepper fruit. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 127 (10):2139-2148.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2367-y URL |
| [7] |
Büker M, Schünemann D, Borchert S. 1998. Enzymic properties and capacities of developing tomato(Lycopersicon esculentum L.)fruit plastids. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49 (321):681-691.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/49.321.681 URL |
| [8] |
Bürglin T R, Affolter M. 2016. Homeodomain proteins:an update. Chromosoma, 125 (3):497-521.
doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0543-8 pmid: 26464018 |
| [9] |
Carrara S, Pardossi A, Soldatini G F, Tognoni F, Guidi L. 2001. Photosynthetic activity of ripening tomato fruit. Photosynthetica, 39 (1):75-78.
doi: 10.1023/A:1012495903093 URL |
| [10] |
Carrasco P, Manzara T, Gruissem W. 1993. Developmental and organ-specific changes in DNA-protein interactions in the tomato rbcS3B and rbcS3C promoter regions. Plant Molecular Biology, 21 (1):1-15.
pmid: 8425041 |
| [11] |
Carvalho R F, Campos M L, Pino L E, Crestana S L, Zsögön A, Lima J E, Benedito V A, Peres L E. 2011. Convergence of developmental mutants into a single tomato model system:'Micro-Tom' as an effective toolkit for plant development research. Plant Methods, 7 (1):18.
doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-7-18 pmid: 21714900 |
| [12] |
Causse M, Friguet C, Coiret C, Lépicier M, Navez B, Lee M, Holthuysen N, Sinesio F, Moneta E, Grandillo S. 2010. Consumer preferences for fresh tomato at the european scale: A common segmentation on taste and firmness. Journal of Food Science, 75 (9):S531-S541.
doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01841.x URL |
| [13] |
Chan K, Phua S, Crisp P A, McQuinn R P, Pogson B J. 2016. Learning the languages of the chloroplast: retrograde signaling and beyond. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 67 (1):25-53.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111854 URL |
| [14] |
Chandler J W. 2016. Auxin response factors. Plant Cell and Environment, 39 (5):1014-1028.
doi: 10.1111/pce.12662 URL |
| [15] |
Chen H, Shen Y, Tang X, Yu L, Wang J, Guo L, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Feng S, Strickland E, Zheng N, Deng X W. 2006. Arabidopsis CULLIN4 forms an E 3 ubiquitin ligase with RBX1 and the CDD complex in mediating light control of development. The Plant Cell, 18 (8):1991-2004.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.043224 URL |
| [16] |
Cocaliadis M F, Fernández-Muñoz R, Pons C, Orzaez D, Granell A. 2013. Increasing tomato fruit quality by enhancing fruit chloroplast function. A double-edged sword? Journal of Experimental Botany, 65 (16):4589-4598.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru165 URL |
| [17] |
Cole M, Nolte C, Werr W. 2006. Nuclear import of the transcription factor SHOOT MERISTEMLESS depends on heterodimerization with BLH proteins expressed in discrete sub-domains of the shoot apical meristem of Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Research, 34 (4):1281-1292.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl016 URL |
| [18] |
Davuluri G R, van Tuinen A, Fraser P D, Manfredonia A, Newman R, Burgess D, Brummell D A, King S R, Palys J, Uhlig J, Bramley P M, Pennings H M J, Bowler C. 2005. Fruit-specific RNAi-mediated suppression of DET1 enhances carotenoid and flavonoid content in tomatoes. Nature Biotechnology, 23 (7):890-895.
doi: 10.1038/nbt1108 pmid: 15951803 |
| [19] | Epple P, Mack A A, Morris V R F, Dangl J L. 2003. Antagonistic control of oxidative stress-induced cell death in Arabidopsis by two related,plant-specific zinc finger proteins. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100 (11):6831-6836. |
| [20] |
Fitter D W, Martin D J, Copley M J, Scotland R W, Langdale J A. 2002. GLK gene pairs regulate chloroplast development in diverse plant species. Plant Journal, 31(6):713-727.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01390.x pmid: 12220263 |
| [21] |
Francis D M, Barringer S A, Whitmoyer R E. 2000. Ultrastructural characterization of yellow shoulder disorder in a uniform ripening tomato genotype. Hortscience, 35 (6):1114-1117.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.35.6.1114 URL |
| [22] |
Galpaz N, Wang Q, Menda N, Zamir D, Hirschberg J. 2008. Abscisic acid deficiency in the tomato mutant high-pigment 3 leading to increased plastid number and higher fruit lycopene content. Plant Journal, 53 (5):717-730.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03362.x URL |
| [23] |
Gillaspy G, Ben-David H, Gruissem W. 1993. Fruits:A developmental perspective. The Plant Cell, 5 (10):1439-1451.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.10.1439 pmid: 12271039 |
| [24] |
Giménez E, Dominguez E, Pineda B, Heredia A, Moreno V, Lozano R, Angosto T. 2015. Transcriptional activity of the MADS box ARLEQUIN/TOMATO AGAMOUS-LIKE1 gene is required for cuticle development of tomato fruit. Plant Physiology, 168 (3):1036-1048.
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00469 pmid: 26019301 |
| [25] |
Giménez E, Pineda B, Capel J, Antón M T, Atarés A, Pérez-Martín F, García-Sogo B, Angosto T, Moreno V, Lozano R. 2010. Functional analysis of the Arlequin mutant corroborates the essential role of the Arlequin/TAGL1 gene during reproductive development of tomato. PLoS ONE, 5 (12):e14427.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014427 URL |
| [26] |
Hay A, Tsiantis M. 2010. KNOX genes: versatile regulators of plant development and diversity. Development, 137 (19):3153-3165.
doi: 10.1242/dev.030049 pmid: 20823061 |
| [27] |
Hetherington S E, Smillie R M, Davies W J. 1998. Photosynthetic activities of vegetative and fruiting tissues of tomato. Journal of Experimental Botany, 49 (324):1173-1181.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/49.324.1173 URL |
| [28] | Huang X, Ouyang X, Yang P, Lau O S, Chen L, Wei N, Deng X W. 2013. Conversion from CUL4-based COP1-SPA E3 apparatus to UVR8-COP1-SPA complexes underlies a distinct biochemical function of COP1 under UV-B. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110 (41):16669-16674. |
| [29] |
Jarvis P, López-Juez E. 2013. Biogenesis and homeostasis of chloroplasts and other plastids. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 14 (12):787-802.
doi: 10.1038/nrm3702 pmid: 24263360 |
| [30] |
Jia T, Cheng Y, Khan I, Zhao X, Gu T, Hu X. 2020. Progress on understanding transcriptional regulation of chloroplast development in fleshy fruit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21 (18):6951.
doi: 10.3390/ijms21186951 URL |
| [31] |
Jimenez A, Creissen G, Kular B, Firmin J, Robinson S, Verhoeyen M, Mullineaux P. 2002. Changes in oxidative processes and components of the antioxidant system during tomato fruit ripening. Planta, 214 (5):751-758.
doi: 10.1007/s004250100667 pmid: 11882944 |
| [32] |
Jones B, Frasse P, Olmos E, Zegzouti H, Li Z G, Latché A, Pech J C, Bouzayen M. 2002. Down-regulation of DR12,an auxin-response-factor homolog,in the tomato results in a pleiotropic phenotype including dark green and blotchy ripening fruit. Plant Journal, 32 (4):603-613.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01450.x URL |
| [33] |
Kawata E E, Cheung A Y. 1990. Molecular analysis of an aurea photosynthetic mutant(Su/Su)in tobacco:LHCP depletion leads to pleiotropic mutant phenotypes. The EMBO Journal, 9 (12):4197-4203.
doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07644.x URL |
| [34] |
Kerckhoffs L H J, de Groot N A M A, van Tuinen A, Schreuder M E L, Nagatani A, Koornneef M, Kendrick R E. 1997. Physiological characterization of exaggerated-photoresponse mutants of tomato. Journal of Plant Physiology, 150 (5):578-587.
doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(97)80322-7 URL |
| [35] |
Kim E J, Russinova E. 2020. Brassinosteroid signalling. Current Biology, 30 (7):R294-R298.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.02.011 URL |
| [36] |
Klee H J, Giovannoni J J. 2011. Genetics and control of tomato fruit ripening and quality attributes. Annual Review of Genetics, 45 (1):41-59.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132507 URL |
| [37] |
Kobayashi K, Baba S, Obayashi T, Sato M, Toyooka K, Keränen M, Aro E, Fukaki H, Ohta H, Sugimoto K, Masuda T. 2012. Regulation of root greening by light and auxin/cytokinin signaling in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 24 (3):1081-1095.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.092254 pmid: 22415275 |
| [38] |
Kobayashi K, Ohnishi A, Sasaki D, Fujii S, Iwase A, Sugimoto K, Masuda T, Wada H. 2017. Shoot removal induces chloroplast development in roots via cytokinin signaling. Plant Physiology, 173 (4):2340-2355.
doi: 10.1104/pp.16.01368 pmid: 28193764 |
| [39] |
Kolotilin I, Koltai H, Tadmor Y, Bar-Or C, Reuveni M, Meir A, Nahon S, Shlomo H, Chen L, Levin I. 2007. Transcriptional profiling of high pigment-2dg tomato mutant links early fruit plastid biogenesis with its overproduction of phytonutrients. Plant Physiology, 145 (2):389-401.
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.102962 pmid: 17704236 |
| [40] |
Krupinska K, Braun S, Nia M S, Schäfer A, Hensel G, Bilger W. 2019. The nucleoid-associated protein WHIRLY 1 is required for the coordinate assembly of plastid and nucleus-encoded proteins during chloroplast development. Planta, 249 (5):1337-1347.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-03085-z pmid: 30631956 |
| [41] |
Kurup S, Jones H D, Holdsworth M J. 2000. Interactions of the developmental regulator ABI 3 with proteins identified from developing Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Journal, 21 (2):143-155.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00663.x pmid: 10743655 |
| [42] |
Lee J, He K, Stolc V, Lee H, Figueroa P, Gao Y, Tongprasit W, Zhao H, Lee I, Deng X W. 2007. Analysis of transcription factor HY 5 genomic binding sites revealed its hierarchical role in light regulation of development. The Plant Cell, 19 (3):731-749.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047688 URL |
| [43] |
Levin I, Frankel P, Gilboa N, Tanny S, Lalazar A. 2003. The tomato dark green mutation is a novel allele of the tomato homolog of the DEETIOLATED1 gene. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 106 (3):454-460.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-002-1080-4 pmid: 12589545 |
| [44] |
Li G, Chen D, Tang X, Liu Y. 2018a. Heterologous expression of kiwifruit(Actinidia chinensis)GOLDEN2-LIKE homolog elevates chloroplast level and nutritional quality in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum). Planta, 247 (6):1351-1362.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2853-6 URL |
| [45] |
Li G, Wang J, Zhang C, Ai G, Zhang D, Wei J, Cai L, Li C, Zhu W, Larkin R M, Zhang J. 2021. L2,a chloroplast metalloproteinase,regulates fruit ripening by participating in ethylene autocatalysis under the control of ERFs. Journal of Experimental Botany, 72 (20):7035-7048.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab325 URL |
| [46] |
Li H, Li Y, Deng H, Sun X, Wang A, Tang X, Gao Y, Zhang N, Wang L, Yang S, Liu Y, Wang S. 2018b. Tomato UV-B receptor SlUVR8 mediates plant acclimation to UV-B radiation and enhances fruit chloroplast development via regulating SlGLK2. Scientific Reports, 8 (1):6097.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24309-y URL |
| [47] |
Li Y, Deng H, Miao M, Li H, Huang S, Wang S, Liu Y. 2016. Tomato MBD5,a methyl CpG binding domain protein,physically interacting with UV-damaged DNA binding protein-1,functions in multiple processes. New Phytologist, 210 (1):208-226.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13745 URL |
| [48] |
Lieberman M, Segev O, Gilboa N, Lalazar A, Levin I. 2004. The tomato homolog of the gene encoding UV-damaged DNA binding protein 1 (DDB1) underlined as the gene that causes the high pigment-1 mutant phenotype. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 108 (8):1574-1581.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-004-1584-1 pmid: 14968305 |
| [49] |
Ling Q, Sadali N M, Soufi Z, Zhou Y, Huang B, Zeng Y, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Jarvis R P. 2021. The chloroplast-associated protein degradation pathway controls chromoplast development and fruit ripening in tomato. Nature plants, 7 (5):655-666.
doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00916-y pmid: 34007040 |
| [50] |
Liu G, Li C, Yu H, Tao P, Yuan L, Ye J, Chen W, Wang Y, Ge P, Zhang J, Zhou G, Zheng W, Ye Z, Zhang Y. 2020. GREEN STRIPE,encoding methylated TOMATO AGAMOUS‐LIKE 1,regulates chloroplast development and Chl synthesis in fruit. New Phytologist, 228 (1):302-317.
doi: 10.1111/nph.16705 URL |
| [51] |
Liu G, Yu H, Yuan L, Li C, Ye J, Chen W, Wang Y, Ge P, Zhang J, Ye Z, Zhang Y. 2021. SlRCM1,which encodes tomato Lutescent1,is required for chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development in fruits. Horticulture research, 8 (1):128.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00563-6 URL |
| [52] |
Liu H, Jiao J, Liang X, Liu J, Meng H, Chen S, Li Y, Cheng Z. 2016. Map-based cloning,identification and characterization of the w gene controlling white immature fruit color in cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 129 (7):1247-1256.
doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2700-8 URL |
| [53] |
Liu L, Jia C, Zhang M, Chen D, Chen S, Guo R, Guo D, Wang Q. 2014. Ectopic expression of a BZR1-1D transcription factor in brassinosteroid signalling enhances carotenoid accumulation and fruit quality attributes in tomato. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 12 (1):105-115.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12121 URL |
| [54] | Liu Xin, Chen Yunzhu, Kim Pyol, Kim Min-Jun, Song Hyondok, Li Yuhua, Wang Yu. 2020. Progress on molecular mechanism and regulation of tomato fruit color formation. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (9):1689-1704. (in Chinese) |
| 刘昕, 陈韵竹, Kim Pyol, Kim Min-Jun, Song Hyondok, 李玉花, 王宇. 2020. 番茄果实颜色形成的分子机制及调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1689-1704. | |
| [55] | Liu Y, Roof S, Ye Z, Barry C, van Tuinen A, Vrebalov J, Bowler C, Giovannoni J. 2004. Manipulation of light signal transduction as a means of modifying fruit nutritional quality in tomato. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101 (26):9897-9902. |
| [56] |
Livne A, Gepstein S. 1988. Abundance of the major chloroplast polypeptides during development and ripening of tomato fruits:an immunological study. Plant Physiology, 87 (1):239-243.
doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.239 pmid: 16666110 |
| [57] | Llorente B, Torres-Montilla S, Morelli L, Florez-Sarasa I, Matus J T, Ezquerro M, D'Andrea L, Houhou F, Majer E, Picó B, Cebolla J, Troncoso A, Fernie A R, Daròs J A, Rodriguez-Concepcion M. 2020. Synthetic conversion of leaf chloroplasts into carotenoid-rich plastids reveals mechanistic basis of natural chromoplast development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117 (35):21796-21803. |
| [58] |
Lupi A C D, Lira B S, Gramegna G, Trench B, Alves F R R, Demarco D, Peres L E P, Purgatto E, Freschi L, Rossi M. 2019. Solanum lycopersicum GOLDEN 2-LIKE 2 transcription factor affects fruit quality in a light- and auxin-dependent manner. PLoS ONE, 14 (2):e0212224.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212224 URL |
| [59] |
Meng L, Fan Z, Zhang Q, Wang C, Gao Y, Deng Y, Zhu B, Zhu H, Chen J, Shan W, Yin X, Zhong S, Grierson D, Jiang C, Luo Y, Fu D. 2018. BEL1-LIKE HOMEODOMAIN 11 regulates chloroplast development and chlorophyll synthesis in tomato fruit. Plant Journal, 94 (6):1126-1140.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13924 URL |
| [60] |
Miyagishima S, Suzuki K, Okazaki K, Kabeya Y. 2012. Expression of the nucleus-encoded chloroplast division genes and proteins regulated by the algal cell cycle. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29 (10):2957-2970.
pmid: 22490821 |
| [61] |
Mondal K, Sharma N S, Malhotra S P, Dhawan K, Singh R. 2004. Antioxidant systems in ripening tomato fruits. Biologia Plantarum, 48 (1):49-53.
doi: 10.1023/B:BIOP.0000024274.43874.5b URL |
| [62] |
Mustilli A C, Fenzi F, Ciliento R, Alfano F, Bowler C. 1999. Phenotype of the tomato high pigment-2 mutant is caused by a mutation in the tomato homolog of DEETIOLATED1. The Plant Cell, 11 (2):145-157.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.2.145 URL |
| [63] |
Nadakuduti S S, Holdsworth W L, Klein C L, Barry C S. 2014. KNOX genes influence a gradient of fruit chloroplast development through regulation of GOLDEN2-LIKE expression in tomato. Plant Journal, 78 (6):1022-1033.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12529 URL |
| [64] |
Nguyen C V, Vrebalov J T, Gapper N E, Zheng Y, Zhong S, Fei Z, Giovannoni J J. 2014. Tomato GOLDEN2-LIKE transcription factors reveal molecular gradients that function during fruit development and ripening. The Plant Cell, 26 (2):585-601.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.118794 pmid: 24510723 |
| [65] |
Oh E, Zhu J Y, Bai M Y, Arenhart R A, Sun Y, Wang Z Y. 2014. Cell elongation is regulated through a central circuit of interacting transcription factors in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl. eLIFE, 3 (3):e03031.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.03031 URL |
| [66] |
Oren E, Tzuri G, Vexler L, Dafna A, Meir A, Faigenboim A, Kenigswald M, Portnoy V, Schaffer A A, Levi A, Buckler E S, Katzir N, Burger J, Tadmor Y, Gur A. 2019. The multi-allelic APRR2 gene is associated with fruit pigment accumulation in melon and watermelon. Journal of Experimental Botany, 70 (15):3781-3794.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz182 URL |
| [67] |
Osterlund M T, Hardtke C S, Wei N, Deng X W. 2000. Targeted destabilization of HY 5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature, 405 (6785):462-466.
doi: 10.1038/35013076 URL |
| [68] |
Pan Y, Bradley G, Pyke K, Ball G, Lu C, Fray R, Marshall A, Jayasuta S, Baxter C, van Wijk R, Boyden L, Cade R, Chapman N H, Fraser P D, Hodgman C, Seymour G B. 2013. Network inference analysis identifies an APRR2-like gene linked to pigment accumulation in tomato and pepper fruits. Plant Physiology, 161 (3):1476-1485.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.212654 pmid: 23292788 |
| [69] |
Piechulla B, Glick R E, Bahl H, Melis A, Gruissem W. 1987. Changes in photosynthetic capacity and photosynthetic protein pattern during tomato fruit ripening. Plant Physiology, 84 (3):911-917.
doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.911 pmid: 16665543 |
| [70] |
Pogson B J, Ganguly D, Albrecht-Borth V. 2015. Insights into chloroplast biogenesis and development. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1847 (9):1017-1024.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.02.003 pmid: 25667967 |
| [71] |
Powell A L T, Nguyen C V, Hill T, Cheng K L, Figueroa-Balderas R, Aktas H, Ashrafi H, Pons C, Fernández-Muñoz R, Vicente A, Lopez-Baltazar J, Barry C S, Liu Y, Chetelat R, Granell A, van Deynze A, Giovannoni J J, Bennett A B. 2012. Uniform ripening encodes a Golden 2-like transcription factor regulating tomato fruit chloroplast development. Science, 336 (6089):1711-1715.
doi: 10.1126/science.1222218 pmid: 22745430 |
| [72] | Reynard G B. 1956. Origin of the Webb Special(Black Queen)tomato. Rep Tomato Genet Coop, 6:22. |
| [73] |
Ribelles C, García-Sogo B, Yuste-Lisbona F J, Atarés A, Castañeda L, Capel C, Lozano R, Moreno V, Pineda B. 2019. Alq mutation increases fruit set rate and allows the maintenance of fruit yield under moderate saline conditions. Journal of Experimental Botany, 70 (20):5731-5744.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz342 pmid: 31328220 |
| [74] |
Rohrmann J, Tohge T, Alba R, Osorio S, Caldana C, McQuinn R, Arvidsson S, van der Merwe M J, Riaño-Pachón D M, Mueller-Roeber B, Fei Z, Nesi A N, Giovannoni J J, Fernie A R. 2011. Combined transcription factor profiling,microarray analysis and metabolite profiling reveals the transcriptional control of metabolic shifts occurring during tomato fruit development. Plant Journal, 68 (6):999-1013.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04750.x URL |
| [75] |
Sagar M, Chervin C, Mila I, Hao Y, Roustan J, Benichou M, Gibon Y, Biais B, Maury P, Latché A, Pech J, Bouzayen M, Zouine M. 2013. SlARF4,an auxin response factor involved in the control of sugar metabolism during tomato fruit development. Plant Physiology, 161 (3):1362-1374.
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.213843 pmid: 23341361 |
| [76] |
Schroeder D F, Gahrtz M, Maxwell B B, Cook R K, Kan J M, Alonso J M, Ecker J R, Chory J. 2002. De-etiolated 1 and damaged DNA binding protein 1 interact to regulate Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis. Current Biology, 12 (17):1462-1472.
pmid: 12225661 |
| [77] | Sugita M, Gruissem W. 1987. Developmental,organ-specific,and light-dependent expression of the tomato ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit gene family. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 84 (20):7104-7108. |
| [78] |
Tang X, Miao M, Niu X, Zhang D, Cao X, Jin X, Zhu Y, Fan Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Sui Y, Wang W, Wang A, Xiao F, Giovannoni J, Liu Y. 2016. Ubiquitin-conjugated degradation of golden 2-like transcription factor is mediated by CUL4-DDB1-based E 3 ligase complex in tomato. New Phytologist, 209 (3):1028-1039.
doi: 10.1111/nph.13635 URL |
| [79] |
Tang X, Tang Z, Huang S, Liu J, Liu J, Shi W, Tian X, Li Y, Zhang D, Yang J, Gao Y, Zeng D, Hou P, Niu X, Cao Y, Li G, Li X, Xiao F, Liu Y. 2013. Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals genes involved in plastid/chloroplast division and development are regulated by the HP1/DDB1 at an early stage of tomato fruit development. Planta, 238 (5):923-936.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1942-9 URL |
| [80] |
van Tuinen A, Koornneef M, Cordonnier-Pratt M M, Pratt L H, Verkerk R, Zabel P. 1997. The mapping of phytochrome genes and photomorphogenic mutants of tomato. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 94 (1):115-122.
doi: 10.1007/s001220050389 pmid: 19352753 |
| [81] |
Wang L, Pei Z, Tian Y, He C. 2005. OsLSD1,a rice zinc finger protein,regulates programmed cell death and callus differentiation. Molecular Plant-microbe Interactions, 18 (5):375-384.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-18-0375 URL |
| [82] |
Wang S, Liu J, Feng Y, Niu X, Giovannoni J, Liu Y. 2008. Altered plastid levels and potential for improved fruit nutrient content by downregulation of the tomato DDB1-interacting protein CUL4. Plant Journal, 55 (1):89-103.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03489.x URL |
| [83] | Wanner L A, Gruissem W. 1991. Expression dynamics of the tomato rbcS gene family during development. The Plant Cell, 3 (12):1289-1303. |
| [84] |
Waters M T, Wang P, Korkaric M, Capper R G, Saunders N J, Langdale J A. 2009. GLK transcription factors coordinate expression of the photosynthetic apparatus in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 21 (4):1109-1128.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.065250 URL |
| [85] |
Wurtzel E T. 2019. Changing Form and Function through Carotenoids and Synthetic Biology. Plant Physiology, 179 (3):830-843.
doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01122 pmid: 30361256 |
| [86] |
Yan F, Gao Y, Pang X, Xu X, Zhu N, Chan H, Hu G, Wu M, Yuan Y, Li H, Zhong S, Hada W, Deng W, Li Z. 2020. BEL1-LIKE HOMEODOMAIN4 regulates chlorophyll accumulation,chloroplast development,and cell wall metabolism in tomato fruit. Journal of Experimental Botany, 71 (18):5549-5561.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa272 URL |
| [87] |
Yen H C, Shelton B A, Howard L R, Lee S, Vrebalov J, Giovannoni J J. 1997. The tomato high-pigment(hp)locus maps to chromosome 2 and influences plastome copy number and fruit quality. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 95 (7):1069-1079.
doi: 10.1007/s001220050664 URL |
| [88] |
Yin R, Arongaus A B, Binkert M, Ulm R. 2015. Two Distinct Domains of the UVR8 Photoreceptor Interact with COP 1 to Initiate UV-B Signaling in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 27 (1):202-213.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.133868 URL |
| [89] | Yuan Y, Mei L, Wu M, Wei W, Shan W, Gong Z, Zhang Q, Yang F, Yan F, Zhang Q, Luo Y, Xu X, Zhang W, Miao M, Lu W, Li Z, Deng W. 2018. SlARF10,an auxin response factor,is involved in chlorophyll and sugar accumulation during tomato fruit development. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69 (22):5507-5518. |
| [90] |
Yuan Y, Xu X, Gong Z, Tang Y, Wu M, Yan F, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Yang F, Hu X, Yang Q, Luo Y, Mei L, Zhang W, Jiang C, Lu W, Li Z, Deng W. 2019. Auxin response factor 6A regulates photosynthesis,sugar accumulation,and fruit development in tomato. Horticulture Research, 6 (1):85.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-019-0167-x URL |
| [91] |
Zhu J Y, Sae-Seaw J, Wang Z Y. 2013. Brassinosteroid signalling. Development, 140 (8):1615-1620.
doi: 10.1242/dev.060590 URL |
| [1] | 杨植, 张川疆, 杨芯芳, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 枣与酸枣杂交后代果实遗传倾向及混合遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 36-52. |
| [2] | 史洪丽, 李腊, 郭翠梅, 余婷婷, 简伟, 杨星勇. 番茄灰霉病生防菌株TL1的分离、鉴定及其生防能力分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 79-90. |
| [3] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [4] | 邵凤清, 罗秀荣, 王奇, 张宪智, 王文彩. 果实成熟过程中的DNA甲基化调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 197-208. |
| [5] | 郑积荣, 王同林, 胡松申. 高品质番茄新品种‘杭杂603’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 103-104. |
| [6] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 番茄新品种‘杭杂601’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 105-106. |
| [7] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂503’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 107-108. |
| [8] | 黄婷婷, 刘淑芹, 张永志, 李 平, 张志焕, 宋立波. 樱桃番茄新品种‘樱莎红4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 109-110. |
| [9] | 张前荣, 李大忠, 裘波音, 林 珲, 马慧斐, 叶新如, 刘建汀, 朱海生, 温庆放. 设施番茄新品种‘闽农科2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 73-74. |
| [10] | 王燕, 刘针杉, 张静, 杨鹏飞, 马蓝, 王旨意, 涂红霞, 杨绍凤, 王浩, 陈涛, 王小蓉. 中国樱桃杂交F1代花和果实若干性状遗传倾向分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1853-1865. |
| [11] | 蒙小玉, 穆悦, 胡杨, 吴潇, 朱辰, 王慧敏, 陶书田, 张绍铃, 殷豪. 几种果实表面积的三维激光扫描测定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1998-2006. |
| [12] | 韩帅, 吴婕, 张河庆, 席亚东. 四川莴笋上番茄斑萎病毒的电镜观察与小RNA测序鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 2007-2016. |
| [13] | 陈礼浪, 杨天章, 蔡儒平, 林小漫, 邓南康, 车海彦, 林雅婷, 孔祥义. 海南西番莲主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1785-1794. |
| [14] | 张悦, 索玉静, 孙鹏, 韩卫娟, 刁松锋, 李华威, 张嘉嘉, 傅建敏, 李芳东. 柿种质资源果实形态多样性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1473-1490. |
| [15] | 魏晓羽, 王跃进. 中国野生葡萄果皮解剖结构与白粉病抗性的相关性研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1200-1212. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司