
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 62-72.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1058
王荣花, 王树彬, 刘栓桃, 李巧云, 张志刚, 王立华, 赵智中( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-01
修回日期:2021-08-19
出版日期:2022-01-25
发布日期:2022-01-24
基金资助:
WANG Ronghua, WANG Shubin, LIU Shuantao, LI Qiaoyun, ZHANG Zhigang, WANG Lihua, ZHAO Zhizhong( )
)
Received:2021-03-01
Revised:2021-08-19
Online:2022-01-25
Published:2022-01-24
摘要:
为研究大白菜花茎蜡粉分子调控机制,针对大白菜一对花茎蜡粉差异的近等基因系进行了转录组比较分析。在有蜡粉材料RHL065_1和无蜡粉材料RHL065_2之间总共鉴定到7 237个基因存在显著差异表达,主要富集在碳水化合物生物过程、原生质膜的组成成分和四吡咯结合分子功能。结合基因功能注释,筛选到17个蜡粉相关基因,包括蜡粉合成基因MAH1、CYTB5-B(Bra022898,Bra021809)、KCS6/CER6/CUT1、KCS9、FAR3/CER4、KCS1、CER2、KCD/PAS2、CYTB5-C(Bra039268,Bra004518)、CER2-LIKE,蜡粉转运基因LTPG1(Bra010912,Bra030067)和转录因子基因WIN1/SHINE1、MYB30、DEWAX在两自交系间存在显著差异表达,其可能参与了大白菜花茎表皮蜡粉形成。利用qRT-PCR验证了转录组分析的可靠性以及差异表达基因在不同组织的表达模式。研究结果有助于进一步克隆大白菜蜡粉调控基因和开发相关功能分子标记。
中图分类号:
王荣花, 王树彬, 刘栓桃, 李巧云, 张志刚, 王立华, 赵智中. 大白菜花茎蜡粉近等基因系转录组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 62-72.
WANG Ronghua, WANG Shubin, LIU Shuantao, LI Qiaoyun, ZHANG Zhigang, WANG Lihua, ZHAO Zhizhong. Transcriptome Analysis of Waxy Near-isogenic Lines in Chinese Cabbage Floral Axis[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 62-72.
| 基因 | 基因号 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| CER2* | Bra013809 | TGAATATAGTGTGAACGCATTAGC | GCCCTAGTGATAACCCACCA |
| MAH1 | Bra027904 | AGGTTCATGAGGCCAACGAT | CGGAAATTTTGAGCTGAGCAT |
| KCS9 | Bra001974 | TAAGAAGGCGATGCTGATCC | ACGCCTTCTCATCAGCTCCT |
| KCS1 | Bra033283 | CTCTATCGGCGATGATCGTG | GTTGGCGAGTTCGATTGAGA |
| CER2 | Bra013809 | GCTCGACCTCCAGTGTTATGA | ACTGTCGTTGCAGCGAATGT |
| CYTB5-B | Bra021809 | GCACAATCACGCTCATGACTG | TCATCCGTTGCATCCTTACC |
| CYTB5-C | Bra039268 | GCGGTGACAATGTTCTCCTC | TGGAATATACTTCGCCGTCAC |
| MYB30 | Bra033067 | TGCCGTAGCACCGATCAAT | TCGCTATGTTCTCGGTGTTTG |
| LTPG1 | Bra030067 | AACGCTAGCATCTCCAACTGTC | TTGGAGTTGCCGGAGACTTC |
| G6PD | GGGTATGCCAGGACTAAGCTC | GAATCATAAGGGCCACTCACAT |
表1 所有引物序列
Table 1 All the primer sequences
| 基因 | 基因号 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| CER2* | Bra013809 | TGAATATAGTGTGAACGCATTAGC | GCCCTAGTGATAACCCACCA |
| MAH1 | Bra027904 | AGGTTCATGAGGCCAACGAT | CGGAAATTTTGAGCTGAGCAT |
| KCS9 | Bra001974 | TAAGAAGGCGATGCTGATCC | ACGCCTTCTCATCAGCTCCT |
| KCS1 | Bra033283 | CTCTATCGGCGATGATCGTG | GTTGGCGAGTTCGATTGAGA |
| CER2 | Bra013809 | GCTCGACCTCCAGTGTTATGA | ACTGTCGTTGCAGCGAATGT |
| CYTB5-B | Bra021809 | GCACAATCACGCTCATGACTG | TCATCCGTTGCATCCTTACC |
| CYTB5-C | Bra039268 | GCGGTGACAATGTTCTCCTC | TGGAATATACTTCGCCGTCAC |
| MYB30 | Bra033067 | TGCCGTAGCACCGATCAAT | TCGCTATGTTCTCGGTGTTTG |
| LTPG1 | Bra030067 | AACGCTAGCATCTCCAACTGTC | TTGGAGTTGCCGGAGACTTC |
| G6PD | GGGTATGCCAGGACTAAGCTC | GAATCATAAGGGCCACTCACAT |
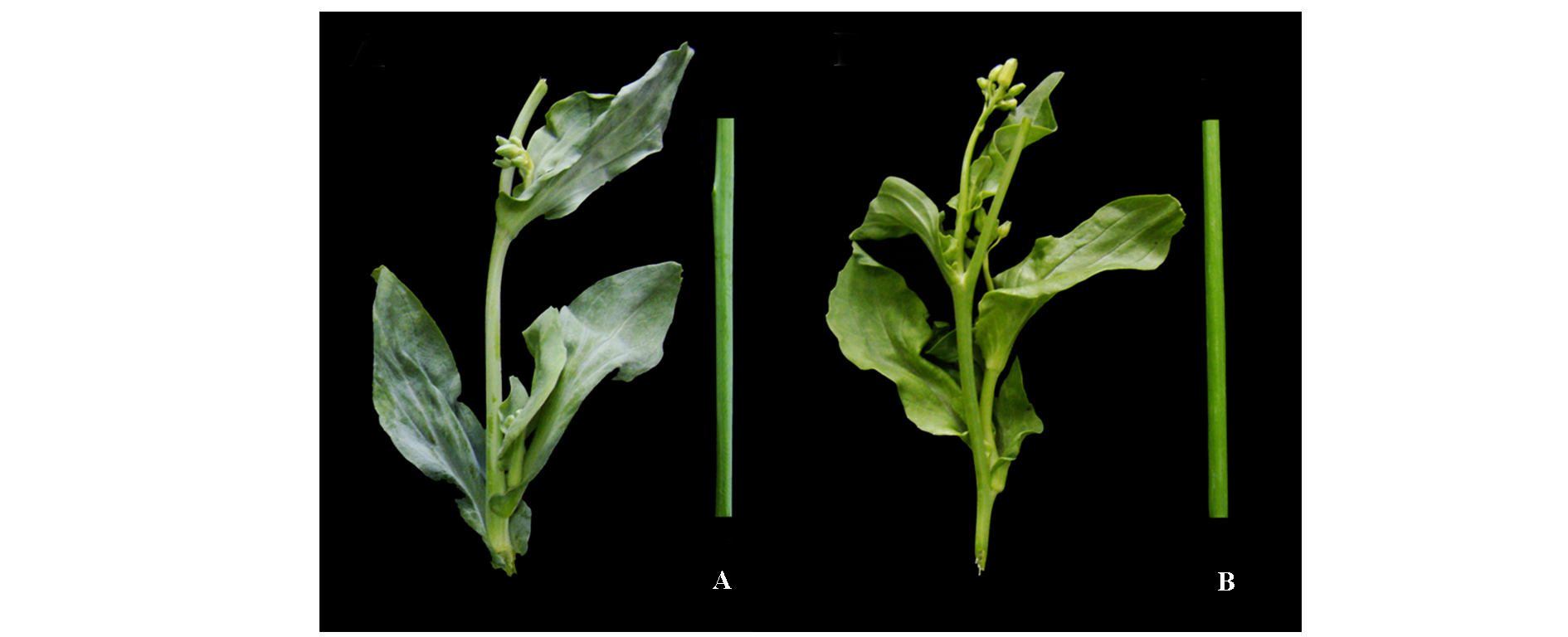

图1 大白菜有蜡粉RHL065_1(A)和无蜡粉RHL065_2(B)叶片和花茎表型
Fig. 1 Chinese cabbage germplasm with waxy RHL065_1(A)and non-waxy RHL065_2(B)phenotypes on leaf and floral axis
| 样品名称 | 原始序列 | 高质量序列 | 高质量碱基数/Gb | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Clean base | Error rate | GC content | ||
| RHL065_1_T1 | 42628776 | 41061052 | 6.16 | 0.02 | 98.53 | 95.36 | 47.34 |
| RHL065_1_T2 | 59538100 | 56577062 | 8.49 | 0.02 | 98.22 | 94.59 | 47.28 |
| RHL065_1_T3 | 45954482 | 43800974 | 6.57 | 0.02 | 98.36 | 94.96 | 47.24 |
| RHL065_2_T1 | 61069026 | 57685276 | 8.65 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 47.15 |
| RHL065_2_T2 | 59286084 | 56360648 | 8.45 | 0.02 | 98.26 | 94.74 | 47.11 |
| RHL065_2_T3 | 61847196 | 58688916 | 8.80 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 46.79 |
表2 大白菜有蜡粉RHL065_1和无蜡粉RHL065_2材料花茎转录组测序结果
Table 2 Statistical analysis of transcriptome sequencing in waxy RHL065_1 and non-waxy RHL065_2 material of Chinese cabbage floral axis
| 样品名称 | 原始序列 | 高质量序列 | 高质量碱基数/Gb | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Clean base | Error rate | GC content | ||
| RHL065_1_T1 | 42628776 | 41061052 | 6.16 | 0.02 | 98.53 | 95.36 | 47.34 |
| RHL065_1_T2 | 59538100 | 56577062 | 8.49 | 0.02 | 98.22 | 94.59 | 47.28 |
| RHL065_1_T3 | 45954482 | 43800974 | 6.57 | 0.02 | 98.36 | 94.96 | 47.24 |
| RHL065_2_T1 | 61069026 | 57685276 | 8.65 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 47.15 |
| RHL065_2_T2 | 59286084 | 56360648 | 8.45 | 0.02 | 98.26 | 94.74 | 47.11 |
| RHL065_2_T3 | 61847196 | 58688916 | 8.80 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 46.79 |
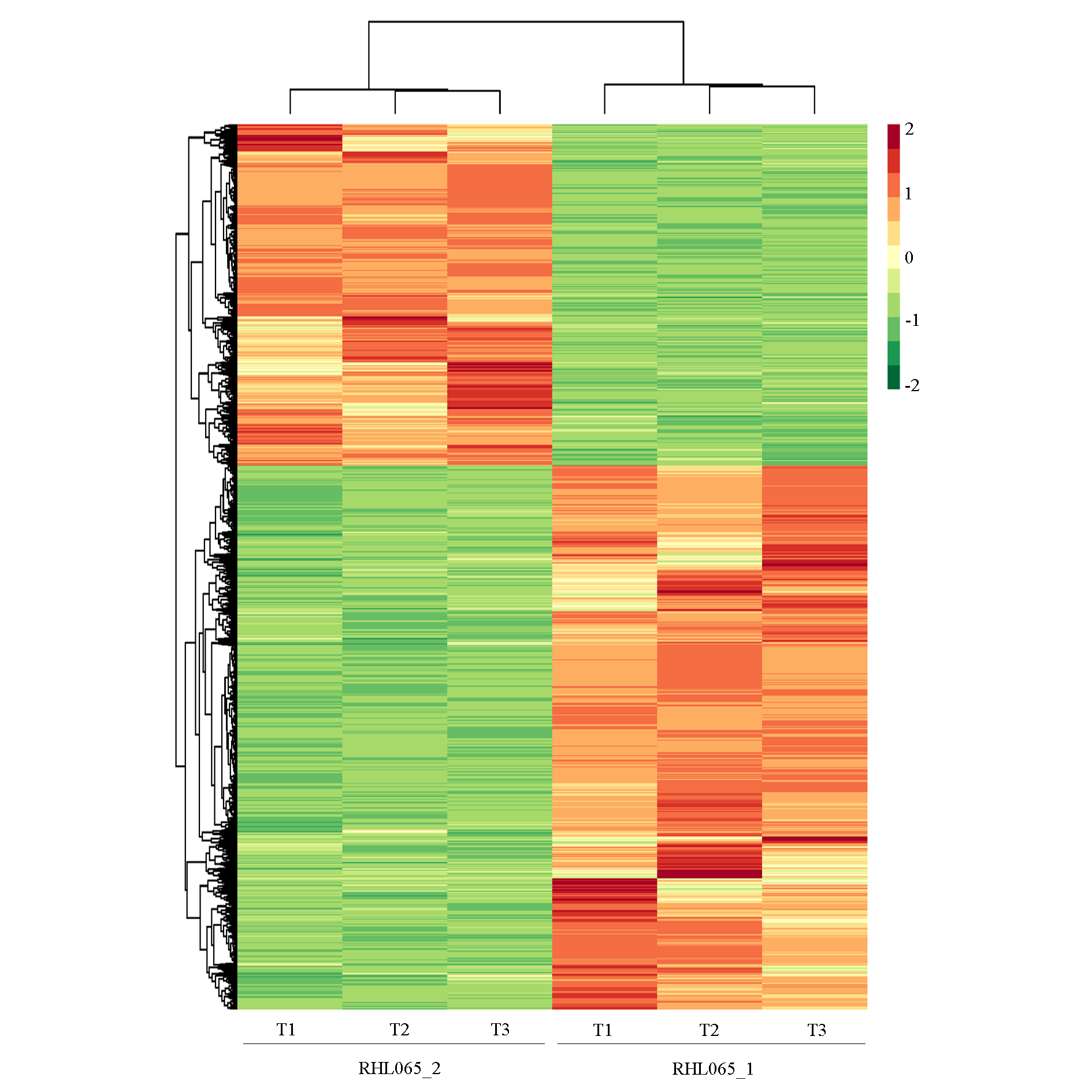
图3 大白菜有蜡粉RHL065_1与无蜡粉RHL065_2材料中差异基因表达聚类热图
Fig. 3 Heatmap of differential gene expression related to waxy RHL065_1 and non-waxy RHL065_2 pools in Chinese cabbage
| 通路 | 基因号 | 基因名称 | 差异倍数 | 显著性 | 调控模式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Gene ID | Gene name | log2 Fold Change | P value | Regulated mode |
| 表皮蜡粉生物合成 Cuticular wax biosynthesis | Bra027904 | MAH1 | 3.342 | 1.1326E-07 | 上调 Up |
| Bra022898 | CYTB5-B | 2.732 | 4.7382E-17 | 上调 Up | |
| Bra004034 | KCS6/CER6/CUT1 | -1.193 | 1.2047E-38 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra001974 | KCS9 | -1.250 | 7.6776E-63 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra034583 | FAR3/CER4 | -1.372 | 7.6944E-35 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra033283 | KCS1 | -1.399 | 8.2146E-66 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra013809 | CER2 | -1.691 | 7.229E-73 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra021809 | CYTB5-B | -1.715 | 5.039E-135 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra006062 | KCD/PAS2 | -2.222 | 5.411E-240 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra039268 | CYTB5-C | -2.239 | 4.6399E-50 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra004518 | CYTB5-C | -5.226 | 4.6843E-12 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra014988 | CER2-LIKE | -6.478 | 1.1694E-05 | 下调 Down | |
| 转录调控 Transcriptional regulation | Bra026140 | WIN1/SHINE1 | 1.451 | 0.0011061 | 上调 Up |
| Bra033067 | MYB30 | -1.063 | 0.00044649 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra029319 | DEWAX | -2.482 | 2.287E-15 | 下调 Down | |
| 表皮蜡粉转运 Cuticular wax transport | Bra010912 | LTPG1 | -1.024 | 3.5614E-13 | 下调 Down |
| Bra030067 | LTPG1 | 2.232 | 9.9446E-09 | 上调 Up |
表3 大白菜蜡粉合成、调控及转运关键基因的差异表达模式
Table 3 Differential expression patterns of key genes involved in wax synthesis, transportation and regulation in Chinese cabbage
| 通路 | 基因号 | 基因名称 | 差异倍数 | 显著性 | 调控模式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Gene ID | Gene name | log2 Fold Change | P value | Regulated mode |
| 表皮蜡粉生物合成 Cuticular wax biosynthesis | Bra027904 | MAH1 | 3.342 | 1.1326E-07 | 上调 Up |
| Bra022898 | CYTB5-B | 2.732 | 4.7382E-17 | 上调 Up | |
| Bra004034 | KCS6/CER6/CUT1 | -1.193 | 1.2047E-38 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra001974 | KCS9 | -1.250 | 7.6776E-63 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra034583 | FAR3/CER4 | -1.372 | 7.6944E-35 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra033283 | KCS1 | -1.399 | 8.2146E-66 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra013809 | CER2 | -1.691 | 7.229E-73 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra021809 | CYTB5-B | -1.715 | 5.039E-135 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra006062 | KCD/PAS2 | -2.222 | 5.411E-240 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra039268 | CYTB5-C | -2.239 | 4.6399E-50 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra004518 | CYTB5-C | -5.226 | 4.6843E-12 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra014988 | CER2-LIKE | -6.478 | 1.1694E-05 | 下调 Down | |
| 转录调控 Transcriptional regulation | Bra026140 | WIN1/SHINE1 | 1.451 | 0.0011061 | 上调 Up |
| Bra033067 | MYB30 | -1.063 | 0.00044649 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra029319 | DEWAX | -2.482 | 2.287E-15 | 下调 Down | |
| 表皮蜡粉转运 Cuticular wax transport | Bra010912 | LTPG1 | -1.024 | 3.5614E-13 | 下调 Down |
| Bra030067 | LTPG1 | 2.232 | 9.9446E-09 | 上调 Up |
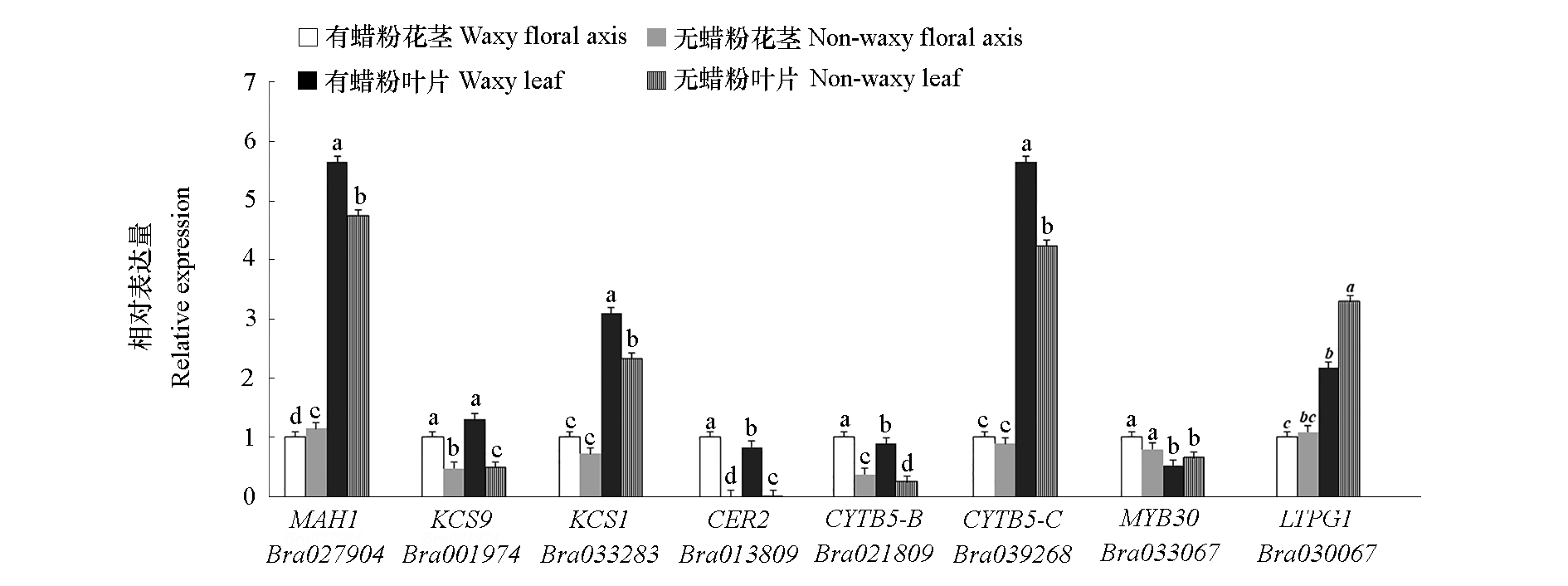
图4 大白菜蜡粉关键基因在花茎和叶片中的相对表达量 小写字母表示在P < 0.05水平下差异显著。
Fig. 4 Relative expression of key genes in wax synthesis,transportation and regulation on floral axis and leaf in Chinese cabbage Different lowercase letters indicate significantly different at P < 0.05.
| [1] |
Aharoni A, Dixit S, Jetter R, Thoenes E, Pereira A A. 2004. The SHINE clade of AP2 domain transcription factors activates wax biosynthesis,alters cuticle properties,and confers drought tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 16:2463-2480.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.022897 URL |
| [2] |
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C, Cutler D, Ditsch F, Meusel I, Theisen I, Wilhelmi H. 1998. Classification and terminology of plant epicuticular waxes. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 126 (3):237-260.
doi: 10.1111/boj.1998.126.issue-3 URL |
| [3] |
Bernard A, Domergue F, Pascal S, Jetter R, Renne C, Faure J D, Haslam R P, Napier J A, Lessire, Joubes J. 2012. Reconstitution of plant alkane biosynthesis in yeast demonstrates that Arabidopsis ECERIFERUM1 and ECERIFERUM3 are core components of a very-long-chain alkane synthesis complex. The Plant Cell, 24:3106-3118.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.099796 pmid: 22773744 |
| [4] | Bourdenx B, Bernard A, Domergue F, Pascal S, Leger A. 2011. Overexpression of Arabidopsis ECERIFERUM1 promotes wax very-long-chain alkane biosynthesis and influences plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiolgy, 156:29-45. |
| [5] |
Busta L, Hegebarth D, Kroc E, Jetter R. 2017. Changes in cuticular wax coverage and composition on developing Arabidopsis leaves are influenced by wax biosynthesis gene expression levels and trichome density. Planta, 245:297-311.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2603-6 URL |
| [6] |
Debono A, Yeats T H, Rose J K, Bird D, Jetter R, Kunst L, Samuels L. 2009. Arabidopsis LTPG is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein required for export of lipids to the plant surface. Plant Cell, 21 (4):1230-1238.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.064451 pmid: 19366900 |
| [7] |
Go Y S, Kim H, Kim H J, Suh M C. 2014. Arabidopsis cuticular wax biosynthesis is negatively regulated by the DEWAX gene encoding an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor. The Plant Cell, 26 (4):1666-1680.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.123307 URL |
| [8] |
Kannangara R, Branigan C, Liu Y, Penfield T, Rao V, Mouille G, Hofte H, Pauly M, Riechmann J L, Broun P. 2007. The transcription factor WIN1/SHN1 regulates cutin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell, 19 (4):1278-1294.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047076 URL |
| [9] |
Kim H. 2012. Characterization of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein 2(LTPG2) and overlapping function between LTPG/LTPG1 and LTPG 2 in cuticular wax export or accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology, 53:1391-1403.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs083 URL |
| [10] |
Kim H, Choi D, Suh M C. 2017. Cuticle ultrastructure,cuticular lipid composition,and gene expression in hypoxia-stressed Arabidopsis stems and leaves. Plant Cell Reports, 36 (6):815-827.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2112-5 URL |
| [11] |
Kim J, Jung J H, Lee S B, Go Y S, Kim H J, Cahoon R, Markham J E, Cahoon E B, Suh M C. 2013. Arabidopsis 3-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase 9 is involved in the synthesis of tetracosanoic acids as precursors of cuticular waxes,suberins,sphingolipids,and phospholipids. Plant Physiology, 162:567-580.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.210450 URL |
| [12] | Lam P, Zhao L, Eveleigh N, Yu X, Chen L. 2015. The exosome and trans-acting small interfering RNAs regulate cuticular wax biosynthesis during Arabidopsis inflorescence stem development. Plant Physiolgy, 167:323-336. |
| [13] |
Lee S, Go Y, Bae H, Park J, Cho S, Cho H, Lee D, Park O, Hwang I, Suh M. 2009. Disruption of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein gene altered cuticular lipid composition,increased plastoglobules,and enhanced susceptibility to infection by the fungal pathogen Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Physiology, 150:42-54.
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.137745 URL |
| [14] |
Lee S B, Kim H U, Suh M C. 2016. MYB94 and MYB96 additively activate cuticular wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 57:2300-2311.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw147 URL |
| [15] |
Lee S B, Suh M C. 2015. Advances in the understanding of cuticular waxes in Arabidopsis thaliana and crop species. Plant Cell Reports, 34:557-572.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1772-2 URL |
| [16] |
Liu S, Wang R, Zhang Z, Li Q, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhao Z. 2019. High-resolution mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling main floral stalk length in Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genomics, 20:437.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5810-2 URL |
| [17] | Liu Z, Fang Z, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Liu Y, Li Z, Sun P, Tang J, Liu D, Zhang Z, Yang L. 2017. Fine-mapping and analysis of Cgl1,a gene conferring glossy trait in cabbage(Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Frontiers in Plant Science, 8 (14024):239. |
| [18] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25:402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [19] |
McFarlane H E, Shin J J H, Bird D A, Samuels A L. 2010. Arabidopsis ABCG transporters,which are required for export of diverse cuticular lipids,dimerize in different combinations. The Plant Cell, 22:3066-3075.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.077974 pmid: 20870961 |
| [20] | McFarlane H E, Watanabe Y, Yang W, Huang Y, Ohlrogge J, Samuels A L. 2014. Golgi- and trans-Golgi network-mediated vesicle trafficking is required for wax secretion from epidermal cells. Plant Physiolgy, 164:1250-1260. |
| [21] | Mu Xiangli, Wang Chao, Wang Shuai. 2013. Observation of ultra microstructure of wax-less mutant epicuticular wax on Cabbage. Chinese Vegetable,(4):32. (in Chinese) |
| 牟香丽, 王超, 王帅. 2013. 甘蓝无蜡质突变体叶表皮蜡质超微结构观察. 中国蔬菜,(4):32. | |
| [22] |
Ni Z, Xin M, Hu Z, Yao Y, Wang T, Liu X, Xing J, Peng H, Zhang Y, Zhou D. 2018. GCN5 contributes to stem cuticular wax biosynthesis by histone acetylation of CER3 in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69 (12):2911-2922.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery077 URL |
| [23] |
Oshima Y, Shikata M, Koyama T, Ohtsubo N, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. 2013. MIXTA-like transcription factors and WAX INDUCER1/SHINE1 coordinately regulate cuticle development in Arabidopsis and Torenia fournieri. The Plant Cell, 25:1609-1624.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.110783 URL |
| [24] |
Park C S, Go Y S, Suh M C. 2016. Cuticular wax biosynthesis is positively regulated by WRINKLED4,an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor,in Arabidopsis stems. The Plant Journal, 88:257-270.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2016.88.issue-2 URL |
| [25] |
Pu Y, Gao J, Guo Y, Liu T, Zhu L, Xu P, Yi B, Wen J, Tu J, Ma C, Fu T, Zou J, Shen J. 2013. A novel dominant glossy mutation causes suppression of wax biosynthesis pathway and deficiency of cuticular wax in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biology, 13:215.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-215 URL |
| [26] |
Raffaele S, Vailleau F, Léger A, Joubes J, Miersch O, Huard C, Blee E, Mongrand S, Domergue F, Roby D. 2008. A MYB transcription factor regulates very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis for activation of the hypersensitive cell death response in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 20:752-767.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054858 URL |
| [27] |
Rowland O, Domergue F. 2012. Plant fatty acyl reductases:enzymes generating fatty alcohols for protective layers with potential for industrial applications. Plant Science, 193-194:28-38.
doi: S0168-9452(12)00095-7 pmid: 22794916 |
| [28] | Shao Meini, Hao Xin, Cui Na, Qu Bo, Guan Ping, Jia Weikang, Xu Yufeng. 2020. Effects of epicuticular waxes on the physiological characteristics of blue-leaf Hosta. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (7):1401-1411. (in Chinese) |
| 邵美妮, 郝鑫, 崔娜, 曲波, 关萍, 贾伟康, 许玉凤. 2020. 蓝叶类型玉簪叶片表皮蜡质对光合生理的影响. 园艺学报, 47 (7):1401-1411. | |
| [29] |
Todd J, Post-Beittenmiller D, Jaworski J G. 1999. KCS1 encodes a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase affecting wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 17:119-130.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00352.x URL |
| [30] |
Xue Y, Xiao S, Kim J, Lung S, Chen L, Tanner J A, Suh M C, Chye M L. 2014. Arabidopsis membrane-associated acyl-CoA-binding protein ACBP1 is involved in stem cuticle formation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65:5473-5483.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru304 URL |
| [31] |
Yeats T H, Rose J K. 2008. The biochemistry and biology of extracellular plant lipid-transfer proteins(LTPs). Protein Science, 17 (2):191-198.
doi: 10.1110/ps.073300108 URL |
| [32] |
Zhang X, Liu Z, Wang P, Wang Q, Yang S, Feng H. 2013. Fine mapping of BrWax1,a gene controlling cuticular wax biosynthesis in Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Molecular Breeding, 32 (4):867-874.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9914-0 URL |
| [33] | Zhao L, Kunst L. 2016. SUPERKILLER complex components are required for the RNA exosome-mediated control of cuticular wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant Physiology, 171:960-973. |
| [1] | 蒋 彧, 涂勋良, 何俊蓉. 国兰叶色突变体叶片差异表达基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [2] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [4] | 韩书辉, 韩彩锋, 韩书荣, 韩彩梅, 韩 旭. 秋大白菜新品种‘胶研秋宝’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 83-84. |
| [5] | 汪维红, 张凤兰, 余阳俊, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 苏同兵, 李佩荣, 辛晓云. 秋大白菜新品种‘京秋1518’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 85-86. |
| [6] | 余阳俊, 汪维红, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣. 抗根肿病耐抽薹大白菜新品种‘京春CR3’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [7] | 王丽丽, 王 鑫, 吴海东, 温 蔷, 杨晓飞. 抗根肿病大白菜新品种‘辽白28’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [8] | 余阳俊, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 汪维红, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣, 武长见. 紫色苗用型大白菜新品种‘京研紫快菜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 91-92. |
| [9] | 徐立功, 韩太利, 孙继峰, 杨晓东, 谭金霞. 苗用大白菜新品种‘锦绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 67-68. |
| [10] | 王钰, 张雪, 张学颖, 张思雨, 闻婷婷, 王迎君, 甘彩霞, 庞文星. 抗毒素Camalexin对大白菜抗根肿病的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [11] | 张鲁刚, 卢倩倩, 何琼, 薛一花, 马晓敏, 马帅, 聂姗姗, 杨文静. 紫橙色大白菜新种质的创制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [12] | 周徐子鑫, 杨威, 毛美琴, 薛彦斌, 马均. 金边红苞凤梨叶色突变体色素鉴定及类胡萝卜素合成限速基因筛选[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1081-1091. |
| [13] | 沈楠, 张荆城, 王成晨, 边银丙, 肖扬. 香菇子实体发育过程中的转录组研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 801-815. |
| [14] | 夏铭, 李经纬, 罗章瑞, 祖贵东, 王娅, 张万萍. 外源褪黑素影响萝卜生长及对链格孢菌抗性的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 548-560. |
| [15] | 张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司