
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 2270-2290.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0845
• Reviews • Previous Articles
FENG Lingjia, LIU Yujie, HE Lintong, WANG Xinchao, and YE Meng*( )
)
Received:2024-11-02
Revised:2025-06-18
Online:2025-08-19
Published:2025-08-19
Contact:
and YE Meng
FENG Lingjia, LIU Yujie, HE Lintong, WANG Xinchao, and YE Meng. Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Linalool Synthesis and Its Ecological Functions[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(8): 2270-2290.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0845
| 科Family | 物种Species | 基因Gene | 合成产物Synthetic product | 参考文献Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 毛果杨 Populus trichocarpa | PtTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and (S)-nerolidol | Danner et al., | |
| PtTPS4 | 主要产物:(R)-(−)-芳樟醇和(R)-橙花叔醇; 次要产物:(S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool and(R)-nerolidol; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool and(S)-nerolidol | ||||
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 水稻 Oryza sativa | OsTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Yuan et al., | |
| 玉米 Zea mays | ZmTPS1 | 芳樟醇和β-月桂烯 Linalool and β-myrcene | Yactayo-Chang et al., | ||
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 铁线莲 Clematis florida | CfTPS1、CfTPS2 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Jiang et al., | |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 苹果 Malus domestica | MdLIS-RG1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nieuwenhuizen et al., | |
| 桃 Prunus persica | PpTPS1、PpTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., Wei et al., | ||
| 草莓 Fragaria × ananassa | FaNES1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | Aharoni et al., | ||
| 月季花 Rosa chinensis | RcLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(−)-linalool | Magnard et al., Ibdah et al., | ||
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | AjTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |
| 芸香科 Rutaceae | 柑橘 Citrus unshiu | CuSTS3-1、CuSTS3-2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shimada et al., | |
| CuSTS4 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 罗勒 Ocimum basilicum | ObLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Iijima et al., | |
| 柠檬薄荷 Mentha citrata | McLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Sugiura et al., | ||
| 薰衣草 Lavandula augustifolia | LaLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Landmann et al., | ||
| LIS1、LIS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 龚林涛 等, | |||
| 紫苏 Perilla hirtella Perilla setoyensis | PhTps-5042L、 PhTps-5073L、 PsTps-5031L | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Masumoto et al., | ||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 黄花蒿 Artemisia annua | AaQH1、AaQH5 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Jia et al., | |
| 茄科 Solanaceae | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | TPS5、TPS39 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Cao et al., | |
| TPS37、TPS39 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Falara et al., | |||
| LeMTS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | van Schie et al., | |||
| 烟草 Nicotiana attenuata | NaLIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | He et al., | ||
| 伞形科 Apiaceae | 芫荽 Coriandrum sativum | CsLINS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Galata et al., | |
| 葡萄科 Vitaceae | 葡萄 Vitis vinifera | VvPNRLin | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| VvPNLinNer1、 VvPNLinNer2、 VvCSLinNer | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | ||||
| 山茶科 Theaceae | 茶 Camellia sinensis | CsLIS1、CsLIS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Mei et al., | |
| CsRLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Zhou et al., | |||
| CsLIS/NES-1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |||
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | GhTPS12、GhTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Huang et al., | |
| GhTPS4 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| GhTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | ||||
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | AtTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Ginglinger et al., | |
| AtTPS10 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 木樨 Osmanthus fragrans | OfTPS1、 OfTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Zeng et al., | |
| OfTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 刘偲 等, | |||
| 素馨 Jasminum grandiflorum | LIS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Pragadheesh et al., | ||
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 土肉桂 Cinnamomum osmophloeum | CoLIS-D4、CoLIS-HS、 CoLIS-LL、CoLIS-T1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Lin et al., | |
| 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | CcTPS54 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yang et al., | ||
| CcTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 马青 等, | |||
| CcTPS6 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 鸢尾科 Iridaceae | 香雪兰 Fressia × hybrida | FhTPS1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Gao et al., | |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 百合 Lilium brownii | LiTPS2 | 芳樟醇和其他单萜、橙花叔醇和其他倍半萜 Linalool and other monoterpenes,nerolidol and other sesquiterpenes | Zhang et al., | |
| LoTPS1 | 芳樟醇和(Z)-β-罗勒烯 Linalool and (Z)-β-ocimene | Abbas et al., | |||
| LoTPS3 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 姜科 Zingiberaceae | 姜花 Hedychium coronarium | HcTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yue et al., Ke et al., | |
| HcTPS8 | 芳樟醇和倍半萜 Linalool and sesquiterpenes | Yue et al., | |||
| 海南砂仁 Amomum longiligulare | AlTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Zhao et al., | ||
| 阳春砂仁 Amomum villosum | AvTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | |||
| 桑科 Moraceae | 无花果 Ficus carica | FcTPS7 FcTPS8 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Nawade et al., | |
| 车前科 Plantaginaceae | 金鱼草 Antirrhinum majus | AmNES/LIS-2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nagegowda et al., | |
| 柳叶菜科 Onagraceae | 仙女扇 Clarkia breweri | LIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Dudareva et al., | |
| 腊梅科 Calycanthaceae | 腊梅 Chimonanthus praecox | CpTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shang et al., | |
| 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃 Actinidia chinensis Actinidia arguta Actinidia polygama | AcLIS/NES | 主要产物芳樟醇,次要产物橙花叔醇 Major products:linalool,minor products:nerolidol | Wang et al., | |
| AaLS1、ApLS1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Chen et al., Günther et al., | |||
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 柠檬香桃 Backhousia citriodora | BcLS | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Sugiura et al., | |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜 Carica papaya | CpTPS18 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yao et al., | |
| 檀香科 Santalaceae | 檀香 Santalum album | SaNES/LIS | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Zhang et al., | |
| 菖蒲科 Acoraceae | 菖蒲 Acorus calamus | AcTPS3、AcTPS4、 AcTPS5 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Ibdah et al., | |
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 铁皮石斛 Dendrobium officinale | DoTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yu et al., | |
| 蝴蝶兰 Phalaenopsis bellina | PbTPS4、PbTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Huang et al., | ||
| PbTPS3 | 芳樟醇、β-罗勒烯 Linalool and β-ocimene | ||||
| PbTPS5 | 芳樟醇、香叶醇 Linalool and geraniol | ||||
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 牡丹 Paeonia delavayi Paeonia suffruticosa | PdTPS1、PdTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Li et al., | |
| PsTPS14 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 王佩云 等, | |||
| 松科 Pinaceae | 欧洲云杉 Picea abies | PaLIN | 主要产物(R)-(-)-芳樟醇;次要产物(S)-(+)-芳樟醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 乳香 Boswellia serrata | BsTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Bhargav et al., | |
Table 1 The identified LIS in several plant species
| 科Family | 物种Species | 基因Gene | 合成产物Synthetic product | 参考文献Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 毛果杨 Populus trichocarpa | PtTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and (S)-nerolidol | Danner et al., | |
| PtTPS4 | 主要产物:(R)-(−)-芳樟醇和(R)-橙花叔醇; 次要产物:(S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool and(R)-nerolidol; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool and(S)-nerolidol | ||||
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 水稻 Oryza sativa | OsTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Yuan et al., | |
| 玉米 Zea mays | ZmTPS1 | 芳樟醇和β-月桂烯 Linalool and β-myrcene | Yactayo-Chang et al., | ||
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 铁线莲 Clematis florida | CfTPS1、CfTPS2 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Jiang et al., | |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 苹果 Malus domestica | MdLIS-RG1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nieuwenhuizen et al., | |
| 桃 Prunus persica | PpTPS1、PpTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., Wei et al., | ||
| 草莓 Fragaria × ananassa | FaNES1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | Aharoni et al., | ||
| 月季花 Rosa chinensis | RcLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(−)-linalool | Magnard et al., Ibdah et al., | ||
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | AjTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |
| 芸香科 Rutaceae | 柑橘 Citrus unshiu | CuSTS3-1、CuSTS3-2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shimada et al., | |
| CuSTS4 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 罗勒 Ocimum basilicum | ObLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Iijima et al., | |
| 柠檬薄荷 Mentha citrata | McLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Sugiura et al., | ||
| 薰衣草 Lavandula augustifolia | LaLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Landmann et al., | ||
| LIS1、LIS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 龚林涛 等, | |||
| 紫苏 Perilla hirtella Perilla setoyensis | PhTps-5042L、 PhTps-5073L、 PsTps-5031L | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Masumoto et al., | ||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 黄花蒿 Artemisia annua | AaQH1、AaQH5 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Jia et al., | |
| 茄科 Solanaceae | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | TPS5、TPS39 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Cao et al., | |
| TPS37、TPS39 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Falara et al., | |||
| LeMTS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | van Schie et al., | |||
| 烟草 Nicotiana attenuata | NaLIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | He et al., | ||
| 伞形科 Apiaceae | 芫荽 Coriandrum sativum | CsLINS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Galata et al., | |
| 葡萄科 Vitaceae | 葡萄 Vitis vinifera | VvPNRLin | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| VvPNLinNer1、 VvPNLinNer2、 VvCSLinNer | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | ||||
| 山茶科 Theaceae | 茶 Camellia sinensis | CsLIS1、CsLIS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Mei et al., | |
| CsRLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Zhou et al., | |||
| CsLIS/NES-1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |||
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | GhTPS12、GhTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Huang et al., | |
| GhTPS4 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| GhTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | ||||
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | AtTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Ginglinger et al., | |
| AtTPS10 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 木樨 Osmanthus fragrans | OfTPS1、 OfTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Zeng et al., | |
| OfTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 刘偲 等, | |||
| 素馨 Jasminum grandiflorum | LIS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Pragadheesh et al., | ||
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 土肉桂 Cinnamomum osmophloeum | CoLIS-D4、CoLIS-HS、 CoLIS-LL、CoLIS-T1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Lin et al., | |
| 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | CcTPS54 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yang et al., | ||
| CcTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 马青 等, | |||
| CcTPS6 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 鸢尾科 Iridaceae | 香雪兰 Fressia × hybrida | FhTPS1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Gao et al., | |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 百合 Lilium brownii | LiTPS2 | 芳樟醇和其他单萜、橙花叔醇和其他倍半萜 Linalool and other monoterpenes,nerolidol and other sesquiterpenes | Zhang et al., | |
| LoTPS1 | 芳樟醇和(Z)-β-罗勒烯 Linalool and (Z)-β-ocimene | Abbas et al., | |||
| LoTPS3 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 姜科 Zingiberaceae | 姜花 Hedychium coronarium | HcTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yue et al., Ke et al., | |
| HcTPS8 | 芳樟醇和倍半萜 Linalool and sesquiterpenes | Yue et al., | |||
| 海南砂仁 Amomum longiligulare | AlTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Zhao et al., | ||
| 阳春砂仁 Amomum villosum | AvTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | |||
| 桑科 Moraceae | 无花果 Ficus carica | FcTPS7 FcTPS8 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Nawade et al., | |
| 车前科 Plantaginaceae | 金鱼草 Antirrhinum majus | AmNES/LIS-2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nagegowda et al., | |
| 柳叶菜科 Onagraceae | 仙女扇 Clarkia breweri | LIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Dudareva et al., | |
| 腊梅科 Calycanthaceae | 腊梅 Chimonanthus praecox | CpTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shang et al., | |
| 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃 Actinidia chinensis Actinidia arguta Actinidia polygama | AcLIS/NES | 主要产物芳樟醇,次要产物橙花叔醇 Major products:linalool,minor products:nerolidol | Wang et al., | |
| AaLS1、ApLS1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Chen et al., Günther et al., | |||
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 柠檬香桃 Backhousia citriodora | BcLS | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Sugiura et al., | |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜 Carica papaya | CpTPS18 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yao et al., | |
| 檀香科 Santalaceae | 檀香 Santalum album | SaNES/LIS | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Zhang et al., | |
| 菖蒲科 Acoraceae | 菖蒲 Acorus calamus | AcTPS3、AcTPS4、 AcTPS5 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Ibdah et al., | |
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 铁皮石斛 Dendrobium officinale | DoTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yu et al., | |
| 蝴蝶兰 Phalaenopsis bellina | PbTPS4、PbTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Huang et al., | ||
| PbTPS3 | 芳樟醇、β-罗勒烯 Linalool and β-ocimene | ||||
| PbTPS5 | 芳樟醇、香叶醇 Linalool and geraniol | ||||
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 牡丹 Paeonia delavayi Paeonia suffruticosa | PdTPS1、PdTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Li et al., | |
| PsTPS14 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 王佩云 等, | |||
| 松科 Pinaceae | 欧洲云杉 Picea abies | PaLIN | 主要产物(R)-(-)-芳樟醇;次要产物(S)-(+)-芳樟醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 乳香 Boswellia serrata | BsTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Bhargav et al., | |
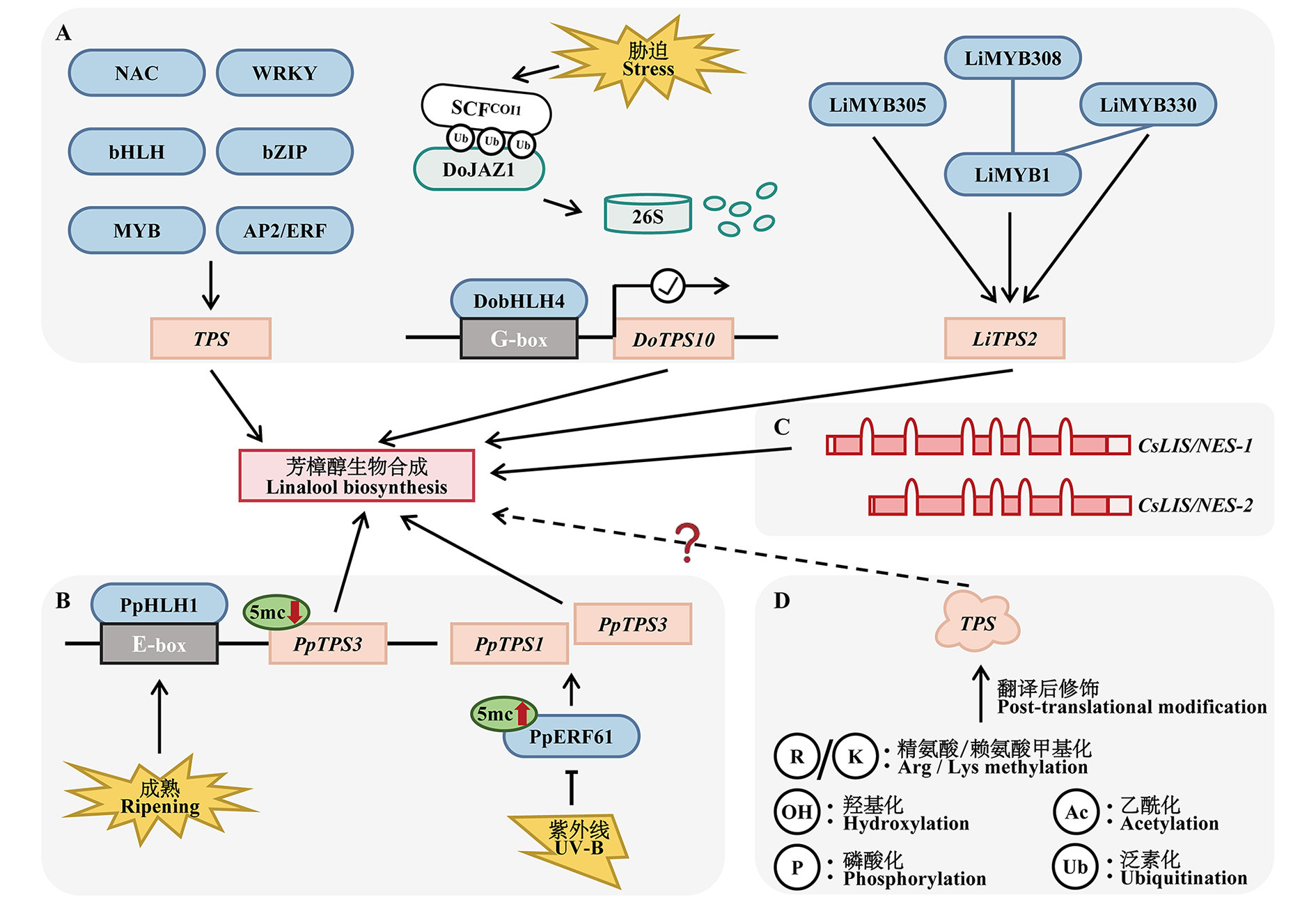
Fig. 2 Molecular mechanisms of linalool synthesis regulation A:Transcriptional regulation;B:Epigenetic regulation;C:Post-transcriptional regulation;D:Regulation of protein post-translational modification. Symbol“?”represents knowledge gaps in molecular mechanisms
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.016253 pmid: 14630967 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.023895 pmid: 15522848 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1007/s00606-019-01605-2 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1007/s10886-006-9117-9 pmid: 16902828 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.4.1337 pmid: 12228673 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450 |
|
陈祖民, 校诺娅, 张艳霞, 史晓敏, 郭帅奇, 高虎, 王振平. 2021. 水分胁迫对‘玫瑰香’葡萄果实挥发性化合物及相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 48 (5):883-896.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1007/BF01021772 pmid: 24263497 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
pmid: 16441752 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.7.1137 pmid: 8768373 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179648 pmid: 21813655 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
龚林涛, 苏秀娟, 廖燕, 克热木汗·吾斯曼, 周迪, 尹松松. 2021. 薰衣草芳樟醇合酶基因的克隆、表达及酶活性检测. 作物杂志,(6):78-87.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/err393 pmid: 22162874 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.02.026 pmid: 21450321 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.12.001 pmid: 22197147 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.244814 pmid: 25082892 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.032946 pmid: 14657409 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
doi: 10.1126/science.291.5511.2141 pmid: 11251117 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2020.02.008 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
|
刘偲, 席婉, 袁金梅, 朱琳琳, 陈洪国, 邹晶晶, 郑日如, 王彩云. 2020. 桂花‘莲籽丹桂’芳樟醇合酶基因OfTPS5的克隆及功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 47 (2):310-320.
|
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
|
卢凯, 李欣, 周嘉良, 解晓军, 戚舒, 周强. 2010. 虫害诱导的水稻挥发物抑制水稻病原菌的生长. 科学通报, 55 (30):2927-2932.
|
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
|
罗宇婕, 汪洋, 周琼, 何杰, 李幸. 2023. 玉带凤蝶成虫对柑橘枝叶挥发物的嗅觉和行为反应. 昆虫学报, 66 (12):1612-1625.
|
|
| [73] |
doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230213.103 pmid: 37282859 |
|
马青, 马蕊, 苏平, 申业, 陈美兰, 靳保龙, 欧阳少林, 郭娟, 崔光红, 黄璐琦. 2023. 樟树化学型形成关键萜类合酶的系统鉴定. 中国中药杂志, 48 (9):2307-2315.
pmid: 37282859 |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
pmid: 17576427 |
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
pmid: 16222807 |
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.042028 pmid: 15310829 |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021196 pmid: 12857838 |
| [82] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.04.006 pmid: 20447664 |
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208249 pmid: 23256150 |
| [92] |
pmid: 12012103 |
| [93] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00403 pmid: 25922059 |
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3240 pmid: 24686413 |
| [96] |
doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01027-w pmid: 34366594 |
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.106.4.1533 pmid: 12232428 |
| [99] |
doi: S0031-9422(17)30167-X pmid: 28463687 |
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
doi: 10.1039/a709175c pmid: 10584331 |
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0259-2 pmid: 23420175 |
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
pmid: 16739013 |
| [116] |
pmid: 16495438 |
| [117] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9149-8 pmid: 17440821 |
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
doi: 10.1093/mp/sss015 pmid: 22442388 |
| [120] |
|
|
王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. 2024. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1273-1283.
|
|
| [121] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202301.011 |
|
王启方, 王晓云, 李浩森, 杨晓玉, 张锐敏, 巩彪, 李秀明, 史庆华. 2023. 芳樟醇对灰葡萄孢生长的影响及对番茄灰霉病的防控效果. 应用生态学报, 34 (1):213-220.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202301.011 |
|
| [122] |
doi: 10.1186/s43897-023-00057-0 pmid: 37789478 |
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00982309 pmid: 24249242 |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1038/nbt1251 pmid: 17057703 |
| [127] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01835.x pmid: 22804824 |
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.01.039 pmid: 36696798 |
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
|
张献英, 霍治国, 犹昌艳, 胡飞. 2014. 20种非寄主植物挥发物对褐飞虱拒避与引诱行为的影响. 华南农业大学学报, 35 (3):63-68.
|
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12937 |
| [149] |
|
|
周丽荣, 张玲玲, 熊诗洁, 马佳伟, 朱永兴, 孙冲, 朱学栋, 刘奕清. 2024. 芳樟醇对生姜枯萎病菌的抑制作用. 食品科学, 45 (6):72-79.
|
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [1] | LI Meiyu, WANG Benqi, HUANG Shuping, CHEN Xia, TAN Jie, ZHANG Hongyuan, WANG Junliang, CHEN Rong, ZHANG Junhong, and ZHANG Min. The Research Progress of Inflorescence Structure Regulation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(8): 2249-2269. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yiman, LI Jingfei, TANG Zhuoran, GE Jiaxing, WEI Dayong, WANG Zhimin, ZOU Jiaqi, TANG Qinglin. Functional Identification and Expression Analysis of BjuSPL10 in Regulating Brassica juncea Bolting and Flowering [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(5): 1341-1350. |
| [3] | WANG Rui, WU Hongfei, ZHANG Changyuan, CAO Haishun, TAN Delong, GUO Jinju, WANG Yunlong, WANG Rufang, YUAN Yu, WU Tingquan. CsPUB54 Negatively Regulates Cucumber Resistance to Phytophthora Melonis by Interacting with PmRXLR1 Effector [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(3): 591-602. |
| [4] | LIU Yuxiang, HAN Fengqing, ZHAO Xinyu, LIU Yumei, LI Zhansheng, $\boxed{\hbox{FANG Zhiyuan}}$. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Lateral Branching Regulatory Gene BoBRC1 in Broccoli [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 1997-2007. |
| [5] | ZHAO Jingyi, WU Xiaoxu, HU Yunjie, GAI Shuting, ZHU Zhihao, QIN Lei, WANG Yong. Molecular Cloning and Functional Analysis of AcGAI in Onion Flowering Regulation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1792-1802. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lihua, XU Yu, Zheng Litong, Wang Changzhi, ZHU Lingcheng, MA Baiquan, LI Mingjun. The Relevance Research Between Acid Transporters and Fruit Acidity [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1474-1488. |
| [7] | WANG Peiyun, LI Ziang, BAI Yang, YANG Ping, YIN Chengpeng, LI Chuanrong, ZHANG Xinwen, SONG Xiuhua. Cloning and Functional Verification of Linalool Synthase Gene PsTPS14 in Tree Peony‘High Noon’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [8] | TIAN Ge, LIU Jianting, GAO Chuancai, ZHAO Xuehui, FAN Yongxin, LI Sen, ZHANG Hanxiao, CHEN Xiude, LI Ling, LI Dongmei. Effects of UV-B on Chlorophyll Biosynthesis in Greenhouse Nectarine Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1332-1344. |
| [9] | WANG Wenjiao, XING Junjie, SHEN Chengcheng, LI Bin. Screening and Functional Analysis of CsCOL5,the Upstream Regulator of CsCER1,in Cucumber Pericarp Wax Synthesis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1005-1016. |
| [10] | CHEN Jiayue, DUAN Yingming, ZHOU Yan, XIAO Yang, BIAN Yinbing, GONG Yuhua. Identification,Expression and Function Analysis of ALDH Gene Family in Lentinula edodes [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1033-1046. |
| [11] | LIN Lu, YU Lu, XIE Peng, LI Zhiqiang, WANG Hongning, ZHAO Guoping, NIU Zimian. Influences of Dwarfing Intermediate Stock SC1 on Apple Photosynthetic Characteristics and Fruit Quality [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2871-2885. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yin, HU Luyan, WANG Shuming, JING Danlong, GUO Qigao, LIANG Guolu. Research Advances in ABA-mediated Fruit Ripening [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1889-1898. |
| [13] | HE Yizhong, PANG Yao, SUN Haoqian, LI Xinyu, WANG Zhenhao, QIAN Wei, ZHANG Yin, HE Fa, YIN Hang, LAI Hengxin, CHUN Changpin, FU Xingzheng, PENG Liangzhi. Recent Advances in the Biosynthesis,Recycling and Regulation of Ascorbic Acid in Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915. |
| [14] | ZHANG Yue, ZHANG Yunchun, DANG Jiangbo, LIN Shoukai, WU Di, JING Danlong, GUO Qigao, LIANG Guolu, XIANG Suqiong. A Review of Inflorescence Development and Formation Mechanism of Loquat [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1929-1943. |
| [15] | JI Yajing, LI Jinyan, ZHANG Peiyu, MA Liqun, ZHU Hongliang. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of Shape Formation in Tomato Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 2015-2030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd