
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 2791-2799.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0934
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
FENG Zhijuan, LIU Na, ZHANG Guwen, BU Yuanpeng, WANG Bin, GONG Yaming( )
)
Received:2024-10-08
Revised:2024-11-13
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2024-12-13
Contact:
GONG Yaming
FENG Zhijuan, LIU Na, ZHANG Guwen, BU Yuanpeng, WANG Bin, GONG Yaming. Promoter of Vegetable Soybean GmDi19-3 Responds to Salt Stress and Exogenous ABA and MeJA[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2791-2799.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0934
| 元件名称 Element name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 数量 Number | 位置/bp Location | 功能 Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+)链 (+)Strand | (-)链 (-)Strand | ||||
| ABRE | ACGTG | 2 | 452 757 | 脱落酸响应ABA responsiveness | |
| ARE | AAACCA | 2 | 498 958 | 厌氧诱导 Anaerobic induction | |
| CGTCA基序 GTCA-motif | CGTCA | 1 | 755 | 茉莉酸响应MeJA responsiveness | |
| ERE | ATTTTAAA | 1 | 236 | 乙烯响应ET responsiveness | |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 1 | 947 | 低温响应Low temperature responsiveness | |
| MYB | CAACCA | 2 | 502 | 312 | 激素信号诱导和非生物胁迫响应 Hormone signal induction andabiotic stress responsiveness |
| MYB识别位点 MYB recognition site | CCGTTG | 1 | 605 | ||
| MYC | GTTTAC | 1 | 133 | 植物生长和防御响应Plant growth and defense responsiveness | |
| TCA元件 TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 831 | 水杨酸响应SA responsiveness | |
| TGA元件 TGA-element | AACGAC | 1 | 485 | 生长素响应Auxin responsiveness | |
| TGACG基序 TGACG-motif | TGACG | 1 | 191 | 茉莉酸响应MeJA responsiveness | |
Table 1 Distribution of cis-acting elements in the GmDi19-3 promoter of vegetable soybean
| 元件名称 Element name | 核心序列 Core sequence | 数量 Number | 位置/bp Location | 功能 Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+)链 (+)Strand | (-)链 (-)Strand | ||||
| ABRE | ACGTG | 2 | 452 757 | 脱落酸响应ABA responsiveness | |
| ARE | AAACCA | 2 | 498 958 | 厌氧诱导 Anaerobic induction | |
| CGTCA基序 GTCA-motif | CGTCA | 1 | 755 | 茉莉酸响应MeJA responsiveness | |
| ERE | ATTTTAAA | 1 | 236 | 乙烯响应ET responsiveness | |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 1 | 947 | 低温响应Low temperature responsiveness | |
| MYB | CAACCA | 2 | 502 | 312 | 激素信号诱导和非生物胁迫响应 Hormone signal induction andabiotic stress responsiveness |
| MYB识别位点 MYB recognition site | CCGTTG | 1 | 605 | ||
| MYC | GTTTAC | 1 | 133 | 植物生长和防御响应Plant growth and defense responsiveness | |
| TCA元件 TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 831 | 水杨酸响应SA responsiveness | |
| TGA元件 TGA-element | AACGAC | 1 | 485 | 生长素响应Auxin responsiveness | |
| TGACG基序 TGACG-motif | TGACG | 1 | 191 | 茉莉酸响应MeJA responsiveness | |
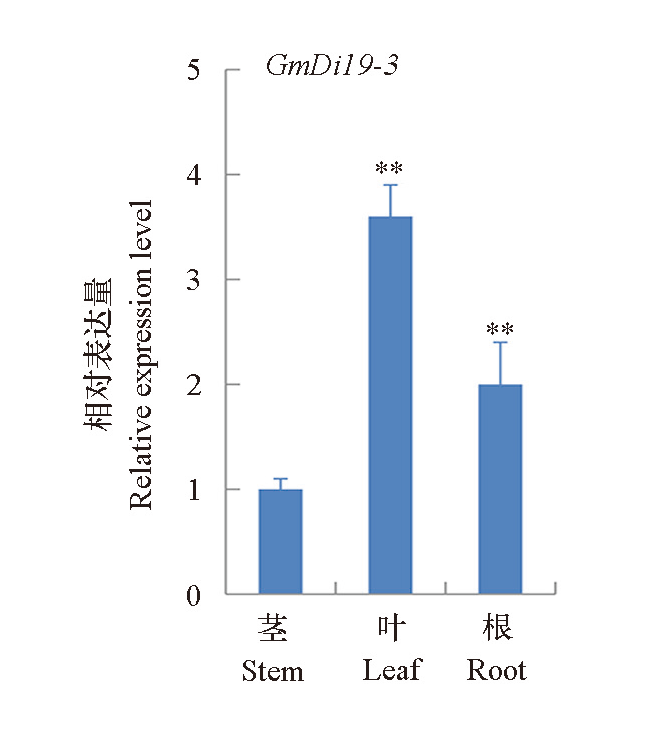
Fig. 1 Expression patterns of GmDi19-3 in different tissues of vegetable soybean **:Significant differences in comparison between the leaf and stem,root and stem(t-test,P < 0.01).
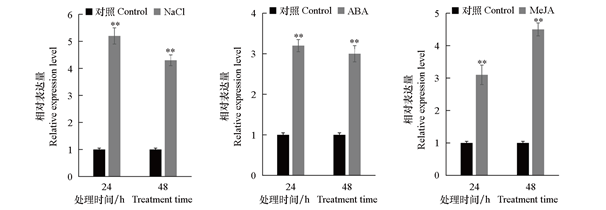
Fig. 3 Expression patterns of GmDi19-3 in vegetable soybean after salt,exogenous ABA and MeJA treatments **:Significant differences in comparison between the treatment and control seedlings(t-test,P < 0.01). The same below.
| [1] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2023.06.08 |
|
卜远鹏, 刘娜, 张古文, 冯志娟, 王斌, 龚亚明, 许林英. 2023. 菜用大豆种质资源的农艺性状多样性评价及核心种质与食味品质评价体系的构建. 浙江农业学报, 35 (6):1307-1314.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2023.06.08 |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
|
李松琦, 李旭飞, 李敏, 刘海楠, 裴茂松, 韦同路, 郭大龙, 余义和. 2023. 葡萄细胞分裂素响应调节因子VlRRA1的克隆、表达及启动子活性分析. 园艺学报, 50 (8):1609-1621.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0007 URL |
|
刘筱玮, 夏斌, 李子葳, 杨宇佳, 陈斌, 周蕴薇, 何淼. 2022. 拟南芥中过表达野菊miR396a基因增强其耐盐性. 园艺学报, 49 (4):816-826.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0007 URL |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
|
王萌, 刘文君, 鲁雪莉, 陈庆山, 杨明亮, 吕波, 徐宗昌. 2023. 大豆种质资源萌发期耐盐性评价和耐盐机理解析. 中国农学通报, 39 (26):8-16.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2022-0834 |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
|
张古文, 沈立, 郑华章, 刘娜, 冯志娟, 龚亚明. 2020. 锌指蛋白转录因子Di19参与调控大豆干旱响应的研究进展. 浙江农业学报, 32 (2):373-382.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2020.02.22 |
|
| [22] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.12.25 |
|
张伟梅, 张古文, 冯志娟, 刘娜, 王斌, 卜远鹏. 2021. 菜用大豆籽粒中蔗糖的遗传与调控机制研究进展. 浙江农业学报, 33 (12):2446-2456.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.12.25 |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
赵娟莹, 刘佳明, 冯志娟, 陈明, 周永斌, 陈隽, 徐兆师, 郭长虹. 2017. 大豆锌指转录因子GmDi19-5对高温的响应及互作蛋白的筛选. 中国农业科学, 50 (12):2389-2398.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2017.12.019 |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [1] | WANG Shanshan, GUO Rui, HE Ling, WU Chunhong, CHEN Chanyou, WAN Heping, and ZHAO Huixia. Identification of Long Cowpea Lhc Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Salt Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 111-122. |
| [2] | ZHANG Shiqi, HUANG Lu, CHENG Xi, ZHANG Xiaoyan, YUAN Yuting, HOU Yichen, DAI Dongqing, XIA Xiudong, YUAN Xingxing, CHEN Xin, ZHU Yuelin, and XUE Chenchen, . Influence of Different Sowing Dates on the Quality of Vegetable Soybeans [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(1): 213-228. |
| [3] | ZHANG Songyan, DIE Pengxiang, SONG Mengting, LI Zhijian, ZHOU Jian. Effect of Overexpression of Robinia pseudoacacia RpACBP3 Gene on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics of Nicotiana tabacum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2155-2167. |
| [4] | JIA Linguang, ZHANG He, ZHANG Xueying, SUN Jianshe, GAO Yi, LI Guofang, TAN Ming, SHAO Jianzhu. A New Edible Crabapple Cultivar‘Jinxing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2227-2228. |
| [5] | LI Qinqin, DONG Shanrong, LUO Jianrang, ZHANG Yanlong. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PqDFR and PqANS Genes and Its Promoters from Paeonia qiui [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1256-1272. |
| [6] | ZHU Jie, LU Dingyihui, ZHANG Deyong, ZHANG Zhanhong, ZHANG Zhuo, SHI Xiaobin, LIU Yong. Effect of ToCV and TYLCV Infection on Detoxification Enzymes of Bemisia tabaci [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 411-422. |
| [7] | SUN Huiru, DANG Fengfeng, REN Min, ZHANG Jianing, FAN Bei, CHEN Guoliang, CHENG Guoting, WANG Yanfeng. Function Analysis of SlWRKY46 in Regulating Tomato Response to Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2758-2774. |
| [8] | YUAN Qingyun, HAN Yu, HE Wei, SU Hui, BAN Qiuyan, WU Chunlai, ZHOU Qiongqiong, XU Wenjing, WANG Liyuan, ZHANG Fen. Cloning and ABA Transport Function Analysis of CsNPF6.1/6.3 in Tea Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2817-2828. |
| [9] | YANG Xue, HU Jinhong, LI Jingjing, ZHANG Yingcai, WANG Lingxia, LIANG Wenyu. Genetic Transformation of Lycium Barbarum TGA2 Gene in Arabidopsis Enhances Its Salt Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(12): 2829-2842. |
| [10] | YANG Juanbo, GUO Lili, LU Shixiong, GOU Huimin, WANG Shuaiting, ZENG Baozhen, MAO Juan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of FaGH3.17 Gene in Strawberry [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2483-2494. |
| [11] | YE Yufan, WANG Yujie, FU Qianyuan, WANG Lu, HAO Xinyuan, DING Changqing, WANG Xinchao, CAO Hongli, LI Nana. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Mg-Chelatase H Subunit Gene CsChlH in Tea Plant(Camellia sinensis) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 91-102. |
| [12] | LI Songqi, LI Xufei, LI Min, LIU Hainan, PEI Maosong, WEI Tonglu, GUO Dalong, YU Yihe. Cloning,Expression and Promoter Activity Analysis of VlRRA1 Gene in Grape [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(8): 1609-1621. |
| [13] | LIU Hui, YIN Xiangjing, FANG Jinghao, GAO Min, LI Zhi, WANG Xiping. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the CDS and Promoter of Synthase Gene STS19 in Chinese Wild Grapevine [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1389-1401. |
| [14] | DU Yanxia, WANG Yiguang, XIAO Zheng, DONG Bin, FANG Qiu, ZHONG Shiwei, YANG Liyuan, ZHAO Hongbo. Ectopic Overexpression of OfNCED3 Regulates the Synthesis of Carotenoids and Chlorophylls in Transgenic Tobacco Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1284-1294. |
| [15] | LIU Jiaqi, GONG Feifei, ZHANG Hao, JING Weikun, QU Suping, MA Nan, GAO Junping, SUN Xiaoming. Jasmonic Acid Carboxy Methyltransferase Gene RhJMT Regulates Petal Senescence in Rosa hybrida [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1025-1036. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd