
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 758-768.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0202
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Jianrong1, YANG Yuan1,2, QIN Gaihua2,*( ), LIU Chunyan2, YU Qing2,3, JIA Botao2, SU Ying2,3, CAO Zhen2, LI Jiyu2,*(
), LIU Chunyan2, YU Qing2,3, JIA Botao2, SU Ying2,3, CAO Zhen2, LI Jiyu2,*( )
)
Received:2021-11-23
Revised:2022-01-12
Online:2022-04-25
Published:2022-04-24
Contact:
QIN Gaihua,LI Jiyu
E-mail:qghahstu@163.com;lijiyugx@163.com
CLC Number:
ZHAO Jianrong, YANG Yuan, QIN Gaihua, LIU Chunyan, YU Qing, JIA Botao, SU Ying, CAO Zhen, LI Jiyu. Identification and Functional Analysis of HAK/KUP/KT Family Genes in Pomegranate[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 758-768.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0202
| 名称 Name | 基因号 ID | 染色体号 Chr. | 氨基酸 aa | 蛋白质分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数II Coefficient of instability | 跨膜区 Transmem- brane domain | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PgrHAK1 | Pgr022478.1 | Chr02 | 788 | 88.31 | 7.58 | 40.47 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK2 | Pgr025731.1 | Chr09 | 798 | 88.95 | 7.87 | 40.61 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK3 | Pgr028419.1 | Chr03 | 786 | 87.46 | 8.84 | 44.52 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK4 | Pgr017987.1 | Chr05 | 745 | 83.65 | 9.15 | 40.44 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK5 | Pgr009913.1 | scaffold21 | 810 | 90.23 | 8.63 | 34.14 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK6 | Pgr024378.1 | Chr01 | 783 | 87.91 | 8.49 | 41.77 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK7 | Pgr016451.1 | Chr06 | 757 | 84.37 | 5.12 | 41.43 | 10 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK8 | Pgr014342.1 | Chr07 | 779 | 87.06 | 8.00 | 37.49 | 10 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK9 | Pgr008140.1 | Chr09 | 808 | 90.09 | 5.66 | 41.94 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK10 | Pgr027044.1 | Chr03 | 794 | 89.00 | 7.31 | 42.90 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK11 | Pgr029120.1 | Chr07 | 800 | 89.40 | 8.62 | 35.17 | 13 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK12 | Pgr009693.1 | scaffold21 | 837 | 92.45 | 5.46 | 43.09 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK13 | Pgr009692.3 | scaffold21 | 697 | 78.48 | 8.56 | 41.39 | 10 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK14 | Pgr018572.1 | Chr08 | 772 | 87.36 | 6.55 | 36.03 | 11 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK15 | Pgr023110.1 | Chr03 | 689 | 77.41 | 8.75 | 32.10 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK16 | Pgr011385.2 | Chr05 | 757 | 84.26 | 8.86 | 34.05 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK17 | Pgr011384.1 | Chr05 | 799 | 89.40 | 8.92 | 38.17 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK18 | Pgr026837.2 | Chr01 | 695 | 77.11 | 8.12 | 41.49 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
Table 1 Members of HAK/KUP/KT gene family in pomegranate
| 名称 Name | 基因号 ID | 染色体号 Chr. | 氨基酸 aa | 蛋白质分子量/kD MW | 等电点 pI | 不稳定系数II Coefficient of instability | 跨膜区 Transmem- brane domain | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PgrHAK1 | Pgr022478.1 | Chr02 | 788 | 88.31 | 7.58 | 40.47 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK2 | Pgr025731.1 | Chr09 | 798 | 88.95 | 7.87 | 40.61 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK3 | Pgr028419.1 | Chr03 | 786 | 87.46 | 8.84 | 44.52 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK4 | Pgr017987.1 | Chr05 | 745 | 83.65 | 9.15 | 40.44 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK5 | Pgr009913.1 | scaffold21 | 810 | 90.23 | 8.63 | 34.14 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK6 | Pgr024378.1 | Chr01 | 783 | 87.91 | 8.49 | 41.77 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK7 | Pgr016451.1 | Chr06 | 757 | 84.37 | 5.12 | 41.43 | 10 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK8 | Pgr014342.1 | Chr07 | 779 | 87.06 | 8.00 | 37.49 | 10 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK9 | Pgr008140.1 | Chr09 | 808 | 90.09 | 5.66 | 41.94 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK10 | Pgr027044.1 | Chr03 | 794 | 89.00 | 7.31 | 42.90 | 13 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK11 | Pgr029120.1 | Chr07 | 800 | 89.40 | 8.62 | 35.17 | 13 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK12 | Pgr009693.1 | scaffold21 | 837 | 92.45 | 5.46 | 43.09 | 12 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK13 | Pgr009692.3 | scaffold21 | 697 | 78.48 | 8.56 | 41.39 | 10 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK14 | Pgr018572.1 | Chr08 | 772 | 87.36 | 6.55 | 36.03 | 11 | 液泡膜 Vacuolar |
| PgrHAK15 | Pgr023110.1 | Chr03 | 689 | 77.41 | 8.75 | 32.10 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK16 | Pgr011385.2 | Chr05 | 757 | 84.26 | 8.86 | 34.05 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK17 | Pgr011384.1 | Chr05 | 799 | 89.40 | 8.92 | 38.17 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
| PgrHAK18 | Pgr026837.2 | Chr01 | 695 | 77.11 | 8.12 | 41.49 | 12 | 质膜 Plasma membrane |
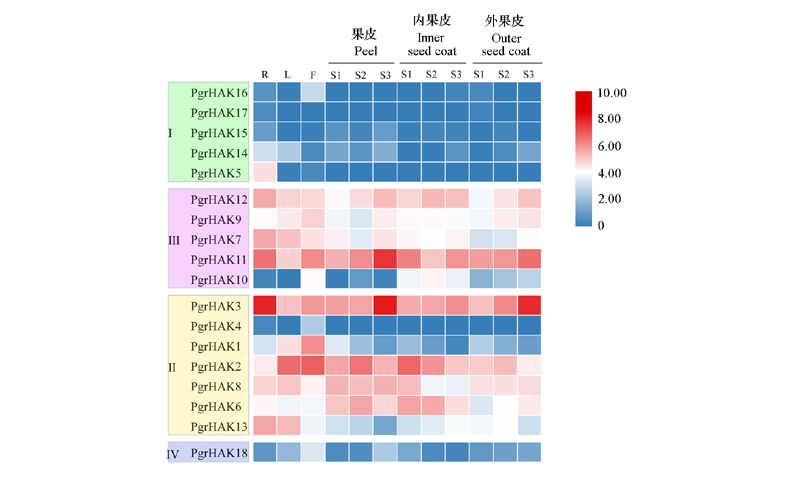
Fig. 2 Expression pattern analysis of HAK/KUP/KT family members in pomegranate R:Root;L:Leaf;F:Flower. S1,S2,and S3 represent 50,95,and 140 d after pollination,respectively.
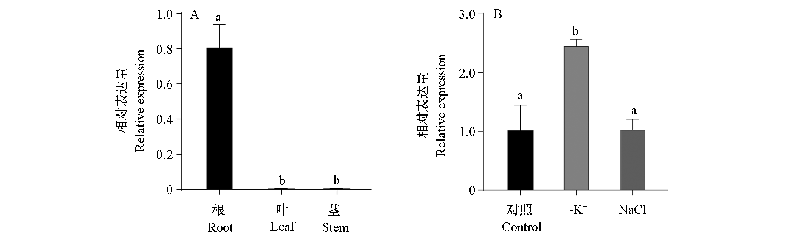
Fig. 3 Expression of PgrHAK5 in different tissues and different stresses -K+:1/2 Hogland-3 mmol · L-1 KNO3+0.2 mmol · L-1 NaH2PO4,NaCl:1/2 Hogland+50 mmol · L-1 NaCl.
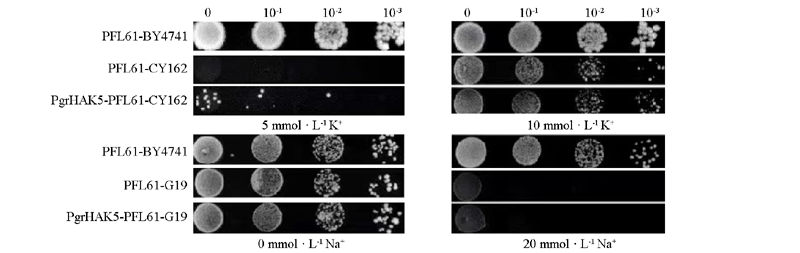
Fig. 5 Yeast complementation assay CY162:Potassium uptake deficient yeast mutant;G19:Salt tolerance yeast mutant,wild type BY4741 and yeast mutants transformed with the empty vector(PFL61)were used as positive and negative controls.
| [1] |
Ahn S J, Shin R, Schachtman D P. 1992. 2004. Expression of KT/KUP genes in Arabidopsis and the role of root hairs in K+uptake. Plant Physiology, 134 (3):1135-1145.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.034660 URL |
| [2] |
Alexander G. 2007. Plant KT/KUP/HAK potassium transporter:single family-multiple functions. Annals of Botany,(6):1035-1041.
pmid: 17495982 |
| [3] |
Anderson J A, Huprikar S S, Kochian L V, Lucas W J, Gaber R F. 1992. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 89 (9):3736-3740.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3736 URL |
| [4] |
Bañuelos M A, Garciadeblas B, Cubero B. 2002. Inventory and functional characterization of the HAK potassium transporters of rice. Plant Physiology, 130 (2):784-795.
pmid: 12376644 |
| [5] | Chai W W, Wang W Y, Cui Y N, Wang S M. 2019. Research progress of function on KUP/HAK/KT family in plants. Plant Physiology Journal, 55 (12):1747-1761. |
| [6] | Chen G, Hu Q D, Luo L, Yang T Y, Zhang S. 2015. Rice potassium transporter OsHAK 1 is essential for maintaining potassium-mediated growth and functions in salt tolerance over low and high potassium concentration ranges. Plant,Cell & Environment, 38 (12):2747-2765. |
| [7] |
Chen G, Liu C, Gao Z Y, Yu Z, Jiang H, Zhu J, Ren D, Yu L, Xu G, Qian Q. 2017. OsHAK1,a high-affinity potassium transporter,positively regulates responses to drought stress in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:1885.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01885 URL |
| [8] |
Chen X Y, Liu X D, Mao W W, Zhang X R, Chen S L, Zhan K H, Bi H H, Xu H X. 2018. Genome-wide identification and analysis of HAK/KUP/KT potassium transporters gene family in wheat(Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19:12.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19010012 URL |
| [9] |
Davies C, Shin R, Liu W, Thomas M R, Schachtman, 2006. Transporters expressed during grape berry(Vitis vinifera L.)development are associated with an increase in berry size and berry potassium accumulation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57 (12):3209-3216.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erl091 URL |
| [10] |
Elumalai R P, Nagpal P, Reed J W. 2002. A mutation in the Arabidopsis KT2/KUP 2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. The Plant Cell Online, 14 (1):119-131.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.010322 URL |
| [11] | Epstein E, Rains D W, Elzam O E. 1963. Resolution of dual mechanisms of potassium absorption by barley roots. Proc Natl Acad USA, 499 (5):684-692. |
| [12] |
Gierth M, Schroeder P M I. 2005. The potassium transporter AtHAK5 functions in K+ deprivation-induced high-affinity K+ uptake and AKT1 K+ channel con to K+ uptake kontributiinetics in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiology, 137 (3):1105-1114.
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.057216 URL |
| [13] |
Gomez-Porras J L, Riaño-Pachón Diego Mauricio, Benito Begoña, Haro Rosario, Sklodowski Kamil, Rodríguez-Navarro Alonso, Dreyer Ingo. 2012. Phylogenetic analysis of K+ transporters in bryophytes,lycophytes,and flowering plants indicates a specialization of vascular plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 3:167.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00167 pmid: 22876252 |
| [14] | Gupta M, Qiu X, Wang L, Xie W, Zhang C, Xiong L, Lian X, Zhang Q. 2008. KT/HAK/KUP potassium transporters gene family and their whole-life cycle expression profile in rice(Oryza sativa). Molecular Genetics & Genomics, 280 (5):437-452. |
| [15] |
Hasanuzzaman M, Bhuyan M H M B, Nahar K, Hossain M S, Fujita M. 2018. Potassium:a vital regulator of plant responses and tolerance to abiotic stresses. Agronomy, 8:31.
doi: 10.3390/agronomy8030031 URL |
| [16] |
Hu B, Jin J, Guo A Y, He Z, Ge G. 2014. GSDS 2.0:an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics, 31(8):1296.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817 URL |
| [17] | Lacombe B. 2000. A shaker-like K+ channel with weak rectification is expressed in both source and sink phloem tissues of Arabidopsis. The Plant Call Online, 12 (6):837-851. |
| [18] | Li W, Xu G, Alli A, Abdel L. 2018. Plant HAK/KUP/KT K+ transporters:function and regulation. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 74:133-141. |
| [19] | Ling Qiuping, Zeng Qiaoying, Hu Fei, Wu Jiayun, Fan Lina, Li Qiwei, Qi Yongwen. 2017. Cloning and expression analysis of potassium transporter SsHAK2 in sugarcane(Saccharum species hybrid). Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 25 (3):378-385. (in Chinese) |
| 凌秋平, 曾巧英, 胡斐, 吴嘉云, 樊丽娜, 李奇伟, 齐永文. 2017. 甘蔗钾转运蛋白基因SsHAK2的克隆及表达特性分析. 农业生物技术学报, 25 (3):378-385. | |
| [20] | Ma Li-juan, Ma Yu, He Hong-hong, Liang Guo-ping, Wang Peng, Chen Bai-hong, Mao Juan. 2019. Identification and expression analysis of grape HAK gene family. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 28 (6):922-934. (in Chinese) |
| 马丽娟, 马钰, 何红红, 梁国平, 万鹏, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 2019. 葡萄HAK基因家族的鉴定与表达分析. 西北农业学报, 28 (6):922-934. | |
| [21] | Ma Li-ying. 2011. Comparative analysis of HAK/KUP/KT gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana and PaHAK1 in Phytolacca acinosa[M. D. Dissertation]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 马立英. 2011. 商陆高亲和性K+转运体基因PaHAK1的克隆及其功能的初步分析[博士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学. | |
| [22] |
Maathuis F J M. 2006. The role of monovalent cation transporters in plant responses to salinity. Journal of Experimental Botany, 57 (5):1137-1147.
pmid: 16263900 |
| [23] | Magali L. 2002. PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 30 (1):325-327. |
| [24] |
Mäser P, Thomine S, Schroeder J I, Ward J M, Guerinot M L. 2001. Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of arabidopsis1. Plant Physiology, 126 (4):1646-1667.
pmid: 11500563 |
| [25] |
Nieves-Cordones M, Alemán F, Martínez V, Rubio F. 2010. The arabidopsis thaliana HAK 5 K+ transporter is required for plant growth and K+ acquisition from low K+ solutions under saline conditions. Molecular Plant, 3 (2):326-333.
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssp102 pmid: 20028724 |
| [26] |
Osakabe Y, Arinaga N, Umezawa T, KatsuraS, Nagamachi K, Tanaka H, Ohiraki H, Yamada K, Seo SU, Abo M. 2013. Osmotic stress responses and plant growth controlled by potassium transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 25 (2):609-624.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.105700 URL |
| [27] |
Qi J G, Sun S M, Yang L, Li M J, Ma F W, Zou Y J. 2019. Potassium uptake and transport in apple roots under drought stress. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5 (1):10-16.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2018.10.001 URL |
| [28] |
Qi Z, Hampton C R, Ryoung S, Barkla B J, White P J, Schachtman D P. 2008. The high affinity K+ transporter AtHAK 5 plays a physiological role in planta at very low K+ concentrations and provides a caesium uptake pathway in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59 (3):595-607.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm330 URL |
| [29] |
Qin G H, Ming C Y, Tang H B, Guyot, 2017. The pomegranate(Punica granatum L.)genome and the genomics of punicalagin biosynthesis. Plant Journal, 91 (6):1108-1128.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13625 URL |
| [30] |
Quintero F J, Garciadeblás B, Rodríguez-Navarro A. 1996. The SAL 1 gene of Arabidopsis,encoding an enzyme with 3'(2'),5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase and inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase activities,increases salt tolerance in yeast. Plant Cell, 8 (3):529-537.
pmid: 8721754 |
| [31] |
Rodríguez-Navarro A. 2000. Potassium transport in fungi and plants. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1469 (1):1-30.
pmid: 10692635 |
| [32] |
Rubio F, Guillermo E Santa-aría, Alonso Rodríguez-Navarro. 2010. Cloning of Arabidopsis and barley cDNAs encoding HAK potassium transporters in root and shoot cells. Physiologia Plantarum, 109 (1):34-43.
doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2000.100106.x URL |
| [33] | Santa-Maria G E, Rubio F, Dubcovsky J, Rodriguez-Navarro A. 1998. The HAK 1 gene of barley is a member of a large gene family and encodes a high-affinity potassium transporter. The Plant Cell, 9 (12):2281-2289. |
| [34] | Shen Y, Shen L, Shen Z, Jing W, Ge H, Zhao J, Zhang W. 2015. The potassium transporter OsHAK 21 functions in the maintenance of ion homeostasis and tolerance to salt stress in rice. Plant Cell & Environment, 38 (12):2766-2799. |
| [35] | Shen Yue. 2015. Functional analyses ofpotassium transporter OsHAK21 and channel OsKs in response to salt stress in rice[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 沈悦. 2015. 水稻钾转运蛋白OsHAK21和通道蛋白OsKx响应盐胁迫的功能研究[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学. | |
| [36] |
Rigas S, Ditengou F A, Ljung K, Daras G, Tietz O, Palme K, Hatzopoulos P. 2012. Root gravitropism and root hair development constitute coupled developmental responses regulated by auxin homeostasis in the Arabidopsis root apex. New Phytologist, 197 (4):1130-1141.
doi: 10.1111/nph.12092 URL |
| [37] | Véry A-A, Nieves-Cordones M, Daly M, Khan I, Fizames C, Sentenac H. 2014. Molecular biology of K+ transport across the plant cell membrane:what do we learn from comparison between plant species? Journal of Plant Physiology, 171 (9):748-769. |
| [38] | Vicente-Agullo F, Rigas S, Desbrosses G, Dolan L, Grabov A. 2004. Potassium carrier TRH 1 is required for auxin transport in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 40 (4):523-535. |
| [39] |
Wang Y, Wu W H. 2013. Potassium transport and signaling in higher plants. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 64 (1):451-476.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050312-120153 URL |
| [40] | Wang Y Z, Lv J H, Chen D, Zhang J, Qi K J, Cheng R, Zhang H P, Zhang S L. 2018. Genome-wide identification,evolution,and expression analysis of the KT/HAK/KUP family in pear. Genome,61: gen-2017-0254. |
| [41] |
Yang T, Zhang S, Hu Y, Wu F, Hu Q, Chen G, Cai J, Wu T, Moran N, Yu L. 2014. The role of a potassium transporter OsHAK 5 in potassium acquisition and transport from roots to shoots in rice at low potassium supply levels. Plant Physiology, 166 (2):945-959.
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.246520 URL |
| [42] |
Youn-Jeong N, Phan L S, Mikiko K, Hitoshi S, Rie N, Ryoung S, Ivan B. 2012. Regulatory roles of cytokinins and cytokinin signaling in response to potassium deficiency in Arabidopsis. PLoS One, 7 (10):e47797.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047797 URL |
| [43] |
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Chen Y, Li R, Wei J. 2012. Genome-wide analysis and identification of HAK potassium transporter gene family in maize(Zea mays L.). Molecular Biology Reports, 39 (8):8465-8473.
doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1700-2 URL |
| [1] | QIN Gaihua, LIU Chunyan, LI Jiyu, and XU Yiliu, . A New Pomegranate Cultivar‘Feihong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 37-38. |
| [2] | QIN Gaihua, LIU Chunyan, LI Jiyu, and XU Yiliu, . A New Pomegranate Cultivar‘Suzi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 39-40. |
| [3] | WANG Sha, ZHANG Xinhui, ZHAO Yujie, LI Bianbian, ZHAO Xueqing, SHEN Yu, DONG Jianmei, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PgMYB111 Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pomegranate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [4] | LIN Yuanmi, ZHU Wenjiao, CHEN Min, XUE Chunmei, JIN Fangyu, ZHU Yuping, JIANG Xinyue, YE Lingfeng, NI Shunanling, YANG Qing. Mir396b Negatively Regulates Eggplant Defense Response to Verticillium Wilt [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1713-1722. |
| [5] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [6] | ZHOU Lin, ZOU Hongzhu, HAN Lulu, JIA Yinghua, WANG Yan. Research Progress on the Role of Glycosyltransferases in Color Formation of Petals [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 687-700. |
| [7] | LI Na, SHANG Jianli, LI Nannan, ZHOU Dan, KONG Shengnan, WANG Jiming, MA Shuangwu. Accurate Molecular Identification for Fruit Shape in Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1386-1396. |
| [8] | MA Junjie, SONG Lina, LI Le, MA Xiaochun, JIN Lei, XU Weirong. VaCBL6 from Vitis amurensis Involved in Abiotic Stress Response and ABA-mediated Pathway [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(6): 1079-1093. |
| [9] | ZHAO Yujie, LIU Cuiyu, ZHAO Xueqing, WANG Yuying, YAN Ming, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Spatiotemporal Expression Analysis of PgWUS and PgBEL1 in Punica granatum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 355-366. |
| [10] | JI Miaomiao, WAN Ye, ZHANG Yiping, MA Hai, WANG Xiping, GAO Hua. Studies on the Resistance of Apple MdMYB116 to Powdery Mildew [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(11): 2133-2145. |
| [11] | ZHANG Qian, YANG Nan, SANG Haiyu, ZHAO Rong, SONG Xiaoxi, CHEN Longqing, XIANG Lin, ZHAO Kaige. Cloning and Functional Analysis of CpTT8 Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Wintersweet(Chimonanthus praecox) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(10): 1945-1955. |
| [12] | LI Yuzhuo, LIU Ke, YUAN Lu, CAO Liwen, WANG Tingjin, GAN Susheng, CHEN Liping. Cloning and Functional Analyses of BrNAP in Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Chinese Flowering Cabbage [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 60-72. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zhongxing, CHENG Li, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG De, LIU Bing, WANG Yanxiu. Cloning of MhMYB114-Like from Malus halliana and Its Functional Identification of Iron Deficiency Tolerance in Apple Callus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 127-136. |
| [14] | XU Longxiao,XUN Mi,SONG Jianfei,TIAN Xiaozhi,YIN Fangpeng,HUANG Weinan,ZHANG Weiwei,and YANG Hongqiang*. Effect of Soil Textures and Rootstock on Rhizosphere Microorganism and Carbon Source Utilization of Apple Roots [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(8): 1530-1540. |
| [15] | ZHANG Shaowei1,*,YUAN Chao1,*,NIU Yi1,*,TANG Qinglin1,WEI Dayong1,WANG Yongqing2,TIAN Shibing2,YANG Yang2,**,and WANG Zhimin1,**. Cloning and Functional Analysis of SmDAD1 Promoter in Solanum melongena [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(4): 643-652. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd