
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1803-1816.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0650
• Genetic & Breeding·Germplasm Resources·Molecular Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YU Cannan1, GUO Anfang1, LU Chun2, MIAO Hongjun2, HOU Xiaoyu1, YUAN Tianyi1, LIU Guoyuan1, WEI Hui1, ZHANG Jian1, and YU Chunmei1,*( )
)
Received:2024-10-15
Revised:2025-04-18
Online:2025-07-23
Published:2025-07-23
Contact:
and YU Chunmei
YU Cannan, GUO Anfang, LU Chun, MIAO Hongjun, HOU Xiaoyu, YUAN Tianyi, LIU Guoyuan, WEI Hui, ZHANG Jian, and YU Chunmei. Identification and Development of SNP Markers for Lagerstroemia indica Leaf Color Based on Transcriptome and Genome Analysis[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(7): 1803-1816.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0650
| 母本 Female | 父本 Male | F1群体数量 Plants of F1 population | 靶向测序材料数量/个 Plants for target sequencing | 靶向测序材料编号 Code number of plants for target sequencing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blush | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 50 | 5 | Z26 ~ Z30 |
| Best red | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 101 | 3 | Z1 ~ Z3 |
| Crimson Red | 10-6 | 42 | 1 | Z51 |
| Crimson Red | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 92 | 17 | Z43 ~ Z50,Z52 ~ Z60 |
| Crimson Red | 10-16 | 51 | 12 | Z31 ~ Z42 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 紫玉 Ziyu | 35 | 3 | Z23 ~ Z25 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 10-6 | 45 | 6 | Z17 ~ Z22 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 191 | 13 | Z4 ~ Z16 |
Table 1 Source of F1 progenies
| 母本 Female | 父本 Male | F1群体数量 Plants of F1 population | 靶向测序材料数量/个 Plants for target sequencing | 靶向测序材料编号 Code number of plants for target sequencing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blush | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 50 | 5 | Z26 ~ Z30 |
| Best red | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 101 | 3 | Z1 ~ Z3 |
| Crimson Red | 10-6 | 42 | 1 | Z51 |
| Crimson Red | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 92 | 17 | Z43 ~ Z50,Z52 ~ Z60 |
| Crimson Red | 10-16 | 51 | 12 | Z31 ~ Z42 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 紫玉 Ziyu | 35 | 3 | Z23 ~ Z25 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 10-6 | 45 | 6 | Z17 ~ Z22 |
| 红火球 Dynamite | 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 191 | 13 | Z4 ~ Z16 |
| 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA01 | TTTCGGATGTTAGAATAAGTCAATAGAGCAAG | CTTATTCCCAACACAAATGACACTAATAGAAA | 61 |
| PA02 | ACACAGTTTTCAGCATCCTCTCATAATAAAAT | GTGCACATAATTGTCATTAGATTCATTTGGTG | 62 |
| PA03 | CTCCACCTCCACCTTACTACTACTCATC | CATCTGTAGCAATAAACCTTCCCAACTAC | 62 |
| PA04 | GTCTCCTCCTGGCTCTCTTCCTTG | AGTAGTTTTATAGAATCCAGCTCATGCATTTC | 62 |
| PA05 | AAAAATATTTAAGGAAAGAAGCAGACAAAGCC | ACACTTCACCAATTCAATCTCCATATATGTCT | 62 |
| PA06 | ATGGAGGGAGTGGTAATTTTGGAATAAGTAAT | GGATTTTTCTTTTCATGTTATTTTGCAGGGAT | 62 |
| PA07 | AATTCTCTGTTTTCCCTAAAGAAAGAGGCTAA | TAAAACTTCTGATAAATCCACCAGAGAAACGA | 62 |
| PA08 | CCGTGTAGTTTATCCACAACATTATTCAGT | TTAGTTAAAACAAGAGAGAGAGACAGAGAGAG | 62 |
| PA09 | AGCTGATCTGTATCAATAAATAGCAACAACTT | TTGATAGAATTTTCAGAATTACCCTTCCCATC | 62 |
| PA10 | TCTTCTAACTTGTTTGGTTGATTTCTTGTTTG | GAATCATTTCGACACACACAATCATCATACTT | 62 |
| PA11 | CTATCTTGAAGCCCCCAGTGACG | CTACAGGATCTCCCAGTCCGATGTG | 63 |
| PA12 | TTAAAATTGTTCAATGCTAAAGTGCCTTATCG | CAATGAGAAGCTGAGTGTTTTCGATCTTAATG | 62 |
| PA13 | CTTGCTTTACAGCAGCTAACATAAACTTCTAC | ATTATGGTAACATTCTCATGTTCGTACAGTTC | 62 |
| PA14 | CTCCGAAAAGGTAAAGAAAGAAACAGTACGAT | ATTGTAAGCTTAGAGCTGCTTCACAATC | 62 |
| PA15 | ATTAAATGAAAATGAGACGAAAGACATACCGT | CTGAAGAAGATCATCTACGCCGTCC | 62 |
| PA16 | CCCCTCTATATATCTATCTCTCTGACTCATCA | GTAAAGGTTGTGTCAGTGTTGTTTCTGATTTG | 62 |
| PA17 | CCACATTCCACATTACAAAATCAACCATTTTA | TTTTTCTTGTTCTTCAGTGTTCTTCAGTCG | 62 |
| PA18 | GAAGGTGAGATCAATGAAATGTAGGGATAAAA | ATATTTTCATTTGGTGCAAATACATCACTTGT | 62 |
| PA19 | ACTTGCCTGCTCTTTTTGTTTATTTTATCAAT | GTGTACTAATCAACTAATACCCAGAATGGTTC | 62 |
| PA20 | ACTTGACGTTAGTAAACTACTTCTATCCATTG | AGCTTTTCAAGCTTAAATATGAGCATTAGTTG | 62 |
| PA21 | AGAACCACTAAGTAATCATCGCAGTACTATAA | TGGGTGATATTGTTTCTACTTATTTTCCAGTT | 62 |
| PA22 | TGTGTACAAGTTCTTAGGATACGTCAAAAA | TTCATAAACTGAGACGGATATTATGATTGGAG | 62 |
| PA23 | ATGTCTTCCTGTGAATTTATTGGTTGTATTCT | GTATTGGCATTCAAGGACTGAATTTTGTAACT | 62 |
| PA24 | TTTATCGGATATTATTCAAGCTTTACACTGCT | CTATAAGATGCTTTACTGTGGTCAAAAGACTG | 62 |
| PA25 | TATCAAGTTCAAAATTATGCAAGCAGATGGTA | AATTACCGTCAATTGGATAGAGCCTACAGTTA | 62 |
| PA26 | GGTATCACAGGAGAATATTACTGCACATCT | AGGATGATCTTAAAATTTCTCGTCTTCTTCTG | 62 |
| PA27 | AGAATCATCCCTTTTTATAATTTTCTGGGCTT | TAATTGCATGGTTCAGATCAATTTCCATTAAC | 62 |
| PA28 | CAGCAAGAGTGCCTTCCCATATATGTTT | CATAAAACCAAGCATTCTTCAACTCCCTTTTG | 63 |
| PA29 | AGGATCATACCAACGTTCAAGATATTCAAAAA | GAATGGAGGGACAGGGATCTAGAAATAGAAAA | 62 |
| PA30 | AAGAATCATCTAAAGGAGGGAATAGTATTGGG | ATGAAGAAGTGTTTCTTGATCTTGTGCG | 62 |
| PA31 | GATGATATAGTTGATCAAATGAGGTTCGTGAT | TAGGAAATAGGGTTTTGGTACATTCAAACATT | 62 |
| PA32 | CCCTTTGACAGGAGACAAGACTAAGAAAG | GATCCCTTTCTGCAAAGAAGGTTCCTG | 62 |
| PA33 | AAATTTGTACTTTGAACTTCTTAGATTGTGCC | CACATGGATCAAAAGAATGATTCAAGATGGTC | 63 |
| PA34 | GATAGAAACTCTATTTCCACTCAAAACCATGT | GCAAGTTAACGTTTATTTTGGGAAATTCTACT | 62 |
| PA35 | AACCCATCTGATAAAGAAAACAATAGATGGAC | CTGTGTGTATATAAATACGTAAGGAGCTCAAG | 62 |
| PA36 | CTAAGCATCTAGGCATGCATTTGAGATTT | AATTTGCATGACTCAAGAGATACCATAAAAGT | 62 |
| PA37 | CTATTACCATTTGACCGTTGGTAAGGAGAG | TTTGATTCTGTTTAATTGGGTGATATGGAACT | 63 |
| PA38 | CTGCGCCTTCTCAGAGGTTAAGAG | GATATGCAATTGCTAGAAAGTGAGGAAATCG | 63 |
| PA39 | GGAACCATATATGTTGCACTCGATCTTTTATT | GAAGTGAAGGGATCGAACATCAATCAAACT | 63 |
| PA40 | GATGGAAGATTTGGAGTAGGAGATGGAAGA | ACACTCTAAAAGGAAGAGCTATATTAGGAGTT | 62 |
| PA41 | AATTAAAACCAGATTGGCTCATTACACATAGT | TTAGTGATGGGTTTTCTTTCCTTTTCAATTTC | 62 |
| PA42 | AAAAAGATGTTCCATGAGAGAAAGTGATTCG | TGAGAGAGAAAGGAATTAGCAGTAAACTATGA | 62 |
| PA43 | GATCGACAGAAAAGCTTCATGGTATTACTTAT | AACAAAATTGACTTGGTATTGCTATTTAAGCG | 62 |
| PA44 | AAGAACTCGACATTCTCCAAGGAAAACAG | GAACACCAAATTCAACCCGAACAGATTC | 63 |
| PA45 | TATCTCCTGTCCTAGGAATCAACTGAAATAAG | AGAAAAAGACAAATCCAACGGCTACATAAC | 63 |
| PA46 | CTTTGCGCCTAACCTTAACTAGCATC | GTCCGTTGTCCAGTAGGATATAAACAAAATAG | 62 |
| PA47 | CTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCAC | TAATTCTCCGTCTAGCTCCTTCGACATTT | 62 |
| PA48 | CATGTTTTTCCAACCACCTTTTTGTTTTTG | CCATCTGTCTCTCTCATTCTTAGTTTCAATTC | 62 |
| PA49 | TTATTCTTGCCAGATCTAGTGACTATCTCATC | TTTTCTGTGTATCTATATATTGTTCAGCTCGG | 62 |
| PA50 | CATGTAGTAATTAACTTAACTCGGTGGGGATG | GATTGCTGATCTGCCGGGTCATT | 63 |
| PA51 | GAGTTACCATCCAGTCCTAGCTCAC | GATTATCTTCGAGACGGACTGGACC | 63 |
| PA52 | AAGAAGAAGCAGCCGAGGTAGAG | CCTTTCGTTAGTTCTTCTCCTCTCTGATTTAG | 61 |
| PA53 | TCAATACAAAATCACATCTACCCAATGAAGAG | GTTGTGGTCATTGTGAGGGGATTGAG | 63 |
Table 2 Fifty-three primers for construct library of target sequencing
| 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA01 | TTTCGGATGTTAGAATAAGTCAATAGAGCAAG | CTTATTCCCAACACAAATGACACTAATAGAAA | 61 |
| PA02 | ACACAGTTTTCAGCATCCTCTCATAATAAAAT | GTGCACATAATTGTCATTAGATTCATTTGGTG | 62 |
| PA03 | CTCCACCTCCACCTTACTACTACTCATC | CATCTGTAGCAATAAACCTTCCCAACTAC | 62 |
| PA04 | GTCTCCTCCTGGCTCTCTTCCTTG | AGTAGTTTTATAGAATCCAGCTCATGCATTTC | 62 |
| PA05 | AAAAATATTTAAGGAAAGAAGCAGACAAAGCC | ACACTTCACCAATTCAATCTCCATATATGTCT | 62 |
| PA06 | ATGGAGGGAGTGGTAATTTTGGAATAAGTAAT | GGATTTTTCTTTTCATGTTATTTTGCAGGGAT | 62 |
| PA07 | AATTCTCTGTTTTCCCTAAAGAAAGAGGCTAA | TAAAACTTCTGATAAATCCACCAGAGAAACGA | 62 |
| PA08 | CCGTGTAGTTTATCCACAACATTATTCAGT | TTAGTTAAAACAAGAGAGAGAGACAGAGAGAG | 62 |
| PA09 | AGCTGATCTGTATCAATAAATAGCAACAACTT | TTGATAGAATTTTCAGAATTACCCTTCCCATC | 62 |
| PA10 | TCTTCTAACTTGTTTGGTTGATTTCTTGTTTG | GAATCATTTCGACACACACAATCATCATACTT | 62 |
| PA11 | CTATCTTGAAGCCCCCAGTGACG | CTACAGGATCTCCCAGTCCGATGTG | 63 |
| PA12 | TTAAAATTGTTCAATGCTAAAGTGCCTTATCG | CAATGAGAAGCTGAGTGTTTTCGATCTTAATG | 62 |
| PA13 | CTTGCTTTACAGCAGCTAACATAAACTTCTAC | ATTATGGTAACATTCTCATGTTCGTACAGTTC | 62 |
| PA14 | CTCCGAAAAGGTAAAGAAAGAAACAGTACGAT | ATTGTAAGCTTAGAGCTGCTTCACAATC | 62 |
| PA15 | ATTAAATGAAAATGAGACGAAAGACATACCGT | CTGAAGAAGATCATCTACGCCGTCC | 62 |
| PA16 | CCCCTCTATATATCTATCTCTCTGACTCATCA | GTAAAGGTTGTGTCAGTGTTGTTTCTGATTTG | 62 |
| PA17 | CCACATTCCACATTACAAAATCAACCATTTTA | TTTTTCTTGTTCTTCAGTGTTCTTCAGTCG | 62 |
| PA18 | GAAGGTGAGATCAATGAAATGTAGGGATAAAA | ATATTTTCATTTGGTGCAAATACATCACTTGT | 62 |
| PA19 | ACTTGCCTGCTCTTTTTGTTTATTTTATCAAT | GTGTACTAATCAACTAATACCCAGAATGGTTC | 62 |
| PA20 | ACTTGACGTTAGTAAACTACTTCTATCCATTG | AGCTTTTCAAGCTTAAATATGAGCATTAGTTG | 62 |
| PA21 | AGAACCACTAAGTAATCATCGCAGTACTATAA | TGGGTGATATTGTTTCTACTTATTTTCCAGTT | 62 |
| PA22 | TGTGTACAAGTTCTTAGGATACGTCAAAAA | TTCATAAACTGAGACGGATATTATGATTGGAG | 62 |
| PA23 | ATGTCTTCCTGTGAATTTATTGGTTGTATTCT | GTATTGGCATTCAAGGACTGAATTTTGTAACT | 62 |
| PA24 | TTTATCGGATATTATTCAAGCTTTACACTGCT | CTATAAGATGCTTTACTGTGGTCAAAAGACTG | 62 |
| PA25 | TATCAAGTTCAAAATTATGCAAGCAGATGGTA | AATTACCGTCAATTGGATAGAGCCTACAGTTA | 62 |
| PA26 | GGTATCACAGGAGAATATTACTGCACATCT | AGGATGATCTTAAAATTTCTCGTCTTCTTCTG | 62 |
| PA27 | AGAATCATCCCTTTTTATAATTTTCTGGGCTT | TAATTGCATGGTTCAGATCAATTTCCATTAAC | 62 |
| PA28 | CAGCAAGAGTGCCTTCCCATATATGTTT | CATAAAACCAAGCATTCTTCAACTCCCTTTTG | 63 |
| PA29 | AGGATCATACCAACGTTCAAGATATTCAAAAA | GAATGGAGGGACAGGGATCTAGAAATAGAAAA | 62 |
| PA30 | AAGAATCATCTAAAGGAGGGAATAGTATTGGG | ATGAAGAAGTGTTTCTTGATCTTGTGCG | 62 |
| PA31 | GATGATATAGTTGATCAAATGAGGTTCGTGAT | TAGGAAATAGGGTTTTGGTACATTCAAACATT | 62 |
| PA32 | CCCTTTGACAGGAGACAAGACTAAGAAAG | GATCCCTTTCTGCAAAGAAGGTTCCTG | 62 |
| PA33 | AAATTTGTACTTTGAACTTCTTAGATTGTGCC | CACATGGATCAAAAGAATGATTCAAGATGGTC | 63 |
| PA34 | GATAGAAACTCTATTTCCACTCAAAACCATGT | GCAAGTTAACGTTTATTTTGGGAAATTCTACT | 62 |
| PA35 | AACCCATCTGATAAAGAAAACAATAGATGGAC | CTGTGTGTATATAAATACGTAAGGAGCTCAAG | 62 |
| PA36 | CTAAGCATCTAGGCATGCATTTGAGATTT | AATTTGCATGACTCAAGAGATACCATAAAAGT | 62 |
| PA37 | CTATTACCATTTGACCGTTGGTAAGGAGAG | TTTGATTCTGTTTAATTGGGTGATATGGAACT | 63 |
| PA38 | CTGCGCCTTCTCAGAGGTTAAGAG | GATATGCAATTGCTAGAAAGTGAGGAAATCG | 63 |
| PA39 | GGAACCATATATGTTGCACTCGATCTTTTATT | GAAGTGAAGGGATCGAACATCAATCAAACT | 63 |
| PA40 | GATGGAAGATTTGGAGTAGGAGATGGAAGA | ACACTCTAAAAGGAAGAGCTATATTAGGAGTT | 62 |
| PA41 | AATTAAAACCAGATTGGCTCATTACACATAGT | TTAGTGATGGGTTTTCTTTCCTTTTCAATTTC | 62 |
| PA42 | AAAAAGATGTTCCATGAGAGAAAGTGATTCG | TGAGAGAGAAAGGAATTAGCAGTAAACTATGA | 62 |
| PA43 | GATCGACAGAAAAGCTTCATGGTATTACTTAT | AACAAAATTGACTTGGTATTGCTATTTAAGCG | 62 |
| PA44 | AAGAACTCGACATTCTCCAAGGAAAACAG | GAACACCAAATTCAACCCGAACAGATTC | 63 |
| PA45 | TATCTCCTGTCCTAGGAATCAACTGAAATAAG | AGAAAAAGACAAATCCAACGGCTACATAAC | 63 |
| PA46 | CTTTGCGCCTAACCTTAACTAGCATC | GTCCGTTGTCCAGTAGGATATAAACAAAATAG | 62 |
| PA47 | CTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCTTCAC | TAATTCTCCGTCTAGCTCCTTCGACATTT | 62 |
| PA48 | CATGTTTTTCCAACCACCTTTTTGTTTTTG | CCATCTGTCTCTCTCATTCTTAGTTTCAATTC | 62 |
| PA49 | TTATTCTTGCCAGATCTAGTGACTATCTCATC | TTTTCTGTGTATCTATATATTGTTCAGCTCGG | 62 |
| PA50 | CATGTAGTAATTAACTTAACTCGGTGGGGATG | GATTGCTGATCTGCCGGGTCATT | 63 |
| PA51 | GAGTTACCATCCAGTCCTAGCTCAC | GATTATCTTCGAGACGGACTGGACC | 63 |
| PA52 | AAGAAGAAGCAGCCGAGGTAGAG | CCTTTCGTTAGTTCTTCTCCTCTCTGATTTAG | 61 |
| PA53 | TCAATACAAAATCACATCTACCCAATGAAGAG | GTTGTGGTCATTGTGAGGGGATTGAG | 63 |
| 品种 Cultivars | 幼叶期 Young leaf stage | 完全展叶期 Full leaf stage | 盛花期 Full bloom stage | 落叶期 Deciduous stage | 季相分类 Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垂枝粉Chuizhifen | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 紫锦Zijin | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 紫玉Ziyu | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 10-6 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 10-16 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色 Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| NTU-1 | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春季彩叶Red purple leaves in spring |
| Blush V2 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| Red Hot | 红绿色 Red green | 紫红色 Red purple | 暗红色 Dark red | 暗红色 Dark red | 生长季彩叶Colored leaves during the growth season |
| Blush | 紫色Purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Best Red | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Crimson Red | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫绿色 Purple green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Pure White | 绿色Green | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 红色Red | 夏秋两季相彩叶Colored leaves in summer and autumn |
| 澧浦2号 Lipu No. 2 | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 生长季彩叶Colored leaves during the growth season |
| 国旗红Guoqihong | 紫红色 Red purple | 亮红色 Britght red | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红火球Dynamite | 橙红色 Red orange | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红火箭Red rocket | 橙红色 Red orange | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
| 天鹅绒 Pink Velour | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红叶乔木 Hongye Qiaomu | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫绿色 Purple green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
Table 3 Leaves color of 19 cultivars of four developmental stages
| 品种 Cultivars | 幼叶期 Young leaf stage | 完全展叶期 Full leaf stage | 盛花期 Full bloom stage | 落叶期 Deciduous stage | 季相分类 Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 垂枝粉Chuizhifen | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 紫锦Zijin | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 紫玉Ziyu | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 10-6 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 白云映霞 Baiyun Yingxia | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| 10-16 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色 Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| NTU-1 | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春季彩叶Red purple leaves in spring |
| Blush V2 | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 生长季绿色叶Green leaves during the growth season |
| Red Hot | 红绿色 Red green | 紫红色 Red purple | 暗红色 Dark red | 暗红色 Dark red | 生长季彩叶Colored leaves during the growth season |
| Blush | 紫色Purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Best Red | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Crimson Red | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫绿色 Purple green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple leaves in spring and summer |
| Pure White | 绿色Green | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 红色Red | 夏秋两季相彩叶Colored leaves in summer and autumn |
| 澧浦2号 Lipu No. 2 | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 黑紫色 Dark purple | 生长季彩叶Colored leaves during the growth season |
| 国旗红Guoqihong | 紫红色 Red purple | 亮红色 Britght red | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红火球Dynamite | 橙红色 Red orange | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红火箭Red rocket | 橙红色 Red orange | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
| 天鹅绒 Pink Velour | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫红色 Red purple | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
| 红叶乔木 Hongye Qiaomu | 紫红色 Red purple | 紫绿色 Purple green | 绿色Green | 绿色Green | 春夏两季相紫红叶 Red purple in spring and summer |
| 编号 | 幼叶期 Young leaf stage | 完全展叶期 Full leaf stage | 色系分类 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | Classes |
| Z-4 | 34.41 ± 2.18 | 13.24 ± 1.22 | 8.48 ± 0.62 | 42.71 ± 2.97 | -5.31 ± 1.35 | 24.53 ± 2.83 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-7 | 45.21 ± 2.26 | 8.56 ± 0.32 | 14.93 ± 0.21 | 43.99 ± 1.87 | -1.65 ± 1.05 | 27.32 ± 2.69 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-8 | 34.90 ± 2.44 | 10.68 ± 1.30 | 9.37 ± 0.52 | 42.96 ± 2.48 | -8.14 ± 0.79 | 26.73 ± 2.11 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-10 | 30.24 ± 2.84 | 10.85 ± 0.68 | 7.61 ± 1.10 | 42.98 ± 1.96 | -6.93 ± 1.00 | 23.53 ± 0.61 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-18 | 35.30 ± 1.19 | 11.77 ± 1.13 | 12.50 ± 1.21 | 39.08 ± 1.60 | -6.34 ± 1.58 | 21.49 ± 2.71 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-25 | 33.37 ± 2.38 | 9.72 ± 0.69 | 5.25 ± 1.27 | 43.82 ± 2.87 | -3.61 ± 1.01 | 21.74 ± 2.61 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-31 | 34.26 ± 2.74 | 6.68 ± 0.42 | 8.44 ± 1.22 | 38.49 ± 3.52 | -10.98 ± 1.80 | 21.35 ± 0.63 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-32 | 37.58 ± 2.66 | 10.47 ± 0.82 | 14.11 ± 0.97 | 39.80 ± 3.17 | -8.89 ± 1.94 | 20.54 ± 1.01 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-33 | 37.42 ± 2.41 | 15.51 ± 1.43 | 9.65 ± 1.21 | 42.88 ± 2.88 | -9.62 ± 1.46 | 24.51 ± 2.77 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-34 | 32.59 ± 2.66 | 14.00 ± 1.08 | 7.77 ± 1.01 | 37.09 ± 0.67 | -9.11 ± 1.71 | 18.25 ± 2.06 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-35 | 36.95 ± 2.69 | 9.40 ± 0.83 | 13.41 ± 0.96 | 39.91 ± 2.23 | -9.69 ± 1.89 | 24.30 ± 1.03 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-36 | 35.80 ± 2.53 | 12.58 ± 0.40 | 9.40 ± 0.86 | 41.50 ± 3.44 | -11.23 ± 1.11 | 26.79 ± 2.37 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-37 | 34.29 ± 2.20 | 14.02 ± 1.05 | 6.31 ± 1.40 | 42.20 ± 1.74 | -9.11 ± 1.43 | 24.19 ± 1.32 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-38 | 33.28 ± 2.07 | 13.14 ± 0.54 | 3.90 ± 0.43 | 41.60 ± 3.57 | -8.07 ± 1.04 | 25.36 ± 0.59 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-39 | 31.97 ± 2.64 | 8.80 ± 0.82 | 4.28 ± 1.19 | 39.17 ± 3.43 | -8.14 ± 1.22 | 16.31 ± 2.64 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-40 | 34.84 ± 2.20 | 9.49 ± 0.67 | 6.30 ± 0.77 | 38.85 ± 3.10 | -8.87 ± 1.55 | 18.94 ± 0.68 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-41 | 41.04 ± 2.58 | 2.11 ± 0.54 | 19.15 ± 0.90 | 42.05 ± 2.77 | -10.84 ± 0.7 | 26.76 ± 1.17 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-42 | 36.33 ± 3.24 | 8.89 ± 0.99 | 7.11 ± 0.53 | 36.95 ± 3.20 | -8.46 ± 1.51 | 17.14 ± 2.97 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-44 | 37.99 ± 2.41 | 8.70 ± 1.08 | 10.21 ± 0.50 | 38.12 ± 1.78 | -10.99 ± 1.42 | 15.30 ± 1.73 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-45 | 30.72 ± 2.68 | 10.17 ± 1.11 | 3.40 ± 0.83 | 39.09 ± 1.39 | -7.18 ± 1.83 | 19.28 ± 2.27 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-46 | 34.60 ± 2.06 | 15.33 ± 0.40 | 10.91 ± 0.44 | 43.06 ± 1.60 | -9.25 ± 0.48 | 26.70 ± 2.94 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-47 | 31.77 ± 2.66 | 10.54 ± 0.60 | 6.29 ± 1.14 | 38.03 ± 1.35 | -8.43 ± 0.17 | 19.76 ± 2.97 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-48 | 32.56 ± 2.67 | 12.41 ± 1.38 | 5.19 ± 1.49 | 35.33 ± 2.66 | -8.62 ± 0.35 | 16.89 ± 1.05 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-49 | 45.31 ± 2.84 | 2.41 ± 0.98 | 16.09 ± 0.64 | 38.53 ± 1.71 | -9.64 ± 0.88 | 19.81 ± 1.14 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-50 | 32.36 ± 2.59 | 7.46 ± 0.58 | 9.20 ± 1.10 | 37.79 ± 3.11 | -7.05 ± 1.41 | 14.86 ± 2.98 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-51 | 32.06 ± 2.44 | 11.63 ± 0.61 | 7.77 ± 0.82 | 36.94 ± 3.41 | -7.14 ± 0.65 | 14.88 ± 2.17 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-52 | 27.96 ± 2.19 | 9.72 ± 0.68 | 3.52 ± 0.52 | 38.39 ± 1.02 | -8.48 ± 1.48 | 18.14 ± 1.11 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-53 | 30.32 ± 2.68 | 7.42 ± 1.21 | 5.28 ± 1.47 | 37.69 ± 0.81 | -6.46 ± 1.41 | 19.85 ± 2.02 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-54 | 33.91 ±2.13 | 12.00 ± 0.63 | 7.49 ± 1.30 | 43.06 ± 1.75 | -4.97 ± 0.85 | 21.87 ± 1.93 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-55 | 32.50 ± 2.02 | 9.37 ± 1.23 | 7.51 ± 1.42 | 40.37 ± 1.16 | -7.68 ± 0.49 | 21.23 ± 0.54 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-56 | 35.72 ± 2.40 | 12.06 ± 0.35 | 8.06 ± 0.86 | 47.22 ± 2.81 | -11.49 ± 0.24 | 28.94 ± 2.88 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-57 | 31.87 ± 2.89 | 6.01 ± 0.81 | 6.57 ± 1.28 | 40.07 ± 3.88 | -9.49 ± 1.31 | 22.61 ± 1.19 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-58 | 37.00 ± 2.25 | 6.93 ± 0.91 | 12.19 ± 0.53 | 41.51 ± 3.07 | -10.55 ± 1.96 | 24.35 ± 1.90 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-59 | 39.88 ± 1 81 | 6.18 ± 0.63 | 16.45 ± 0.81 | 34.94 ± 1.69 | -7.72 ± 0.35 | 16.26 ± 1.13 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-60 | 39.81 ± 2.02 | 9.99 ± 1.04 | 7.72 ± 0.46 | 45.10 ± 1.88 | -9.76 ± 0.95 | 28.02 ± 2.94 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-2 | 33.35 ± 2.14 | 9.20 ± 0.59 | 13.78 ± 0.29 | 40.86 ± 1.90 | 2.02 ± 0.62 | 21.56 ± 2.88 | 红色 Red |
| Z-5 | 39.26 ± 1.77 | 14.14 ± 0.79 | 8.23 ± 1.48 | 35.41 ± 3.72 | 6.96 ± 0.62 | 11.60 ± 0.82 | 红色 Red |
| Z-6 | 36.06 ± 1.15 | 10.15 ± 0.85 | 8.38 ± 1.17 | 38.81 ± 2.81 | 3.89 ± 1.73 | 21.25 ± 2.94 | 红色 Red |
| Z-11 | 41.15 ± 1.97 | 11.95 ± 1.44 | 11.09 ± 0.82 | 35.45 ± 1.86 | 6.36 ± 1.94 | 14.58 ± 0.90 | 红色 Red |
| Z-12 | 43.73 ± 1.20 | 11.82 ± 0.74 | 13.07 ± 0.95 | 41.95 ± 2.88 | 6.47 ± 1.98 | 23.91 ± 1.15 | 红色 Red |
| Z-13 | 33.26 ± 1.18 | 13.33 ± 1.09 | 1.16 ± 0.36 | 38.23 ± 2.07 | 5.40 ± 1.27 | 15.24 ± 0.62 | 红色 Red |
| Z-14 | 44.59 ± 2.86 | 8.97 ± 1.01 | 10.24 ± 0.49 | 36.74 ± 2.22 | 4.67 ± 0.20 | 16.48 ± 2.25 | 红色 Red |
| Z-15 | 39.60 ± 2.92 | 14.15 ± 0.78 | 8.87 ± 0.23 | 37.47 ± 2.60 | 8.12 ± 1.91 | 18.86 ± 2.14 | 红色 Red |
| Z-16 | 40.50 ± 1.24 | 10.06 ± 0.82 | 6.69 ± 1.40 | 35.42 ± 2.75 | 8.56 ± 1.60 | 12.66 ± 1.61 | 红色 Red |
| Z-17 | 40.38 ± 1.86 | 15.19 ± 0.98 | 8.56 ± 1.47 | 38.00 ± 3.46 | 6.39 ± 0.21 | 15.78 ± 2.93 | 红色 Red |
| Z-24 | 44.55 ± 1.34 | 8.43 ± 0.88 | 10.36 ± 1.15 | 38.39 ± 2.99 | 8.70 ± 0.46 | 11.17 ± 2.22 | 红色 Red |
| Z-26 | 36.10 ± 2.92 | 4.37 ± 1.34 | 15.01 ± 1.4 | 42.20 ± 0.51 | 9.18 ± 1.10 | 11.68 ± 0.59 | 红色 Red |
| Z-1 | 28.20 ± 2.13 | 10.33 ± 0.91 | 6.81 ± 1.47 | 33.42 ± 1.49 | 12.98 ± 0.87 | 10.76 ± 1.77 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-3 | 28.82 ± 2.43 | 7.70 ± 0.81 | -0.03 ± 1.21 | 31.63 ± 0.93 | 5.91 ± 1.50 | 7.56 ± 2.50 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-9 | 43.53 ± 2.71 | 8.41 ± 1.44 | 13.73 ± 0.72 | 32.12 ± 3.09 | 11.10 ± 0.76 | 10.20 ± 2.83 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-19 | 32.32 ± 2.06 | 12.68 ± 1.22 | 5.33 ± 1.27 | 32.49 ± 3.08 | 10.89 ± 1.06 | 7.38 ± 2.84 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-20 | 35.86 ± 2.20 | 7.90 ± 1.14 | 11.82 ± 0.53 | 33.56 ± 1.11 | 9.69 ± 1.22 | 7.68 ± 2.44 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-21 | 33.74 ± 1.48 | 11.93 ± 0.73 | 3.07 ± 1.42 | 32.51 ± 1.42 | 10.57 ± 0.79 | 8.58 ± 2.85 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-22 | 30.57 ± 2.31 | 9.92 ± 1.00 | 3.08 ± 1.47 | 32.02 ± 3.31 | 11.90 ± 1.30 | 10.15 ± 2.13 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-23 | 27.93 ± 1.78 | 12.85 ± 0.70 | 1.71 ± 1.48 | 29.17 ± 3.81 | 6.10 ± 0.27 | 4.96 ± 0.59 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-27 | 34.72 ± 2.92 | 4.15 ± 1.16 | 10.95 ± 1.35 | 34.15 ± 1.45 | 3.93 ± 0.21 | 2.42 ± 1.71 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-28 | 30.89 ± 2.42 | 10.92 ± 1.35 | 4.26 ± 1.42 | 35.55 ± 1.38 | 2.71 ± 1.63 | 2.70 ± 1.89 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-29 | 34.15 ± 1.04 | 15.12 ± 1.47 | 2.44 ± 0.67 | 34.34 ± 1.34 | 4.90 ± 0.51 | 1.12 ± 1.49 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-30 | 38.11 ± 2.00 | 11.06 ± 1.44 | 5.93 ± 0.23 | 36.76 ± 1.93 | 8.80 ± 1.43 | 5.23 ± 2.63 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-43 | 32.71 ± 1.22 | 2.79 ± 0.47 | 6.45 ± 1.39 | 30.29 ± 3.25 | 2.82 ± 0.92 | 5.04 ± 1.79 | 紫红色 Red purple |
Table 4 CIE L*a* b* value and classification of 60 F1 individual plants during the young and vigorous leaf stages
| 编号 | 幼叶期 Young leaf stage | 完全展叶期 Full leaf stage | 色系分类 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | Classes |
| Z-4 | 34.41 ± 2.18 | 13.24 ± 1.22 | 8.48 ± 0.62 | 42.71 ± 2.97 | -5.31 ± 1.35 | 24.53 ± 2.83 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-7 | 45.21 ± 2.26 | 8.56 ± 0.32 | 14.93 ± 0.21 | 43.99 ± 1.87 | -1.65 ± 1.05 | 27.32 ± 2.69 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-8 | 34.90 ± 2.44 | 10.68 ± 1.30 | 9.37 ± 0.52 | 42.96 ± 2.48 | -8.14 ± 0.79 | 26.73 ± 2.11 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-10 | 30.24 ± 2.84 | 10.85 ± 0.68 | 7.61 ± 1.10 | 42.98 ± 1.96 | -6.93 ± 1.00 | 23.53 ± 0.61 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-18 | 35.30 ± 1.19 | 11.77 ± 1.13 | 12.50 ± 1.21 | 39.08 ± 1.60 | -6.34 ± 1.58 | 21.49 ± 2.71 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-25 | 33.37 ± 2.38 | 9.72 ± 0.69 | 5.25 ± 1.27 | 43.82 ± 2.87 | -3.61 ± 1.01 | 21.74 ± 2.61 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-31 | 34.26 ± 2.74 | 6.68 ± 0.42 | 8.44 ± 1.22 | 38.49 ± 3.52 | -10.98 ± 1.80 | 21.35 ± 0.63 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-32 | 37.58 ± 2.66 | 10.47 ± 0.82 | 14.11 ± 0.97 | 39.80 ± 3.17 | -8.89 ± 1.94 | 20.54 ± 1.01 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-33 | 37.42 ± 2.41 | 15.51 ± 1.43 | 9.65 ± 1.21 | 42.88 ± 2.88 | -9.62 ± 1.46 | 24.51 ± 2.77 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-34 | 32.59 ± 2.66 | 14.00 ± 1.08 | 7.77 ± 1.01 | 37.09 ± 0.67 | -9.11 ± 1.71 | 18.25 ± 2.06 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-35 | 36.95 ± 2.69 | 9.40 ± 0.83 | 13.41 ± 0.96 | 39.91 ± 2.23 | -9.69 ± 1.89 | 24.30 ± 1.03 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-36 | 35.80 ± 2.53 | 12.58 ± 0.40 | 9.40 ± 0.86 | 41.50 ± 3.44 | -11.23 ± 1.11 | 26.79 ± 2.37 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-37 | 34.29 ± 2.20 | 14.02 ± 1.05 | 6.31 ± 1.40 | 42.20 ± 1.74 | -9.11 ± 1.43 | 24.19 ± 1.32 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-38 | 33.28 ± 2.07 | 13.14 ± 0.54 | 3.90 ± 0.43 | 41.60 ± 3.57 | -8.07 ± 1.04 | 25.36 ± 0.59 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-39 | 31.97 ± 2.64 | 8.80 ± 0.82 | 4.28 ± 1.19 | 39.17 ± 3.43 | -8.14 ± 1.22 | 16.31 ± 2.64 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-40 | 34.84 ± 2.20 | 9.49 ± 0.67 | 6.30 ± 0.77 | 38.85 ± 3.10 | -8.87 ± 1.55 | 18.94 ± 0.68 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-41 | 41.04 ± 2.58 | 2.11 ± 0.54 | 19.15 ± 0.90 | 42.05 ± 2.77 | -10.84 ± 0.7 | 26.76 ± 1.17 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-42 | 36.33 ± 3.24 | 8.89 ± 0.99 | 7.11 ± 0.53 | 36.95 ± 3.20 | -8.46 ± 1.51 | 17.14 ± 2.97 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-44 | 37.99 ± 2.41 | 8.70 ± 1.08 | 10.21 ± 0.50 | 38.12 ± 1.78 | -10.99 ± 1.42 | 15.30 ± 1.73 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-45 | 30.72 ± 2.68 | 10.17 ± 1.11 | 3.40 ± 0.83 | 39.09 ± 1.39 | -7.18 ± 1.83 | 19.28 ± 2.27 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-46 | 34.60 ± 2.06 | 15.33 ± 0.40 | 10.91 ± 0.44 | 43.06 ± 1.60 | -9.25 ± 0.48 | 26.70 ± 2.94 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-47 | 31.77 ± 2.66 | 10.54 ± 0.60 | 6.29 ± 1.14 | 38.03 ± 1.35 | -8.43 ± 0.17 | 19.76 ± 2.97 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-48 | 32.56 ± 2.67 | 12.41 ± 1.38 | 5.19 ± 1.49 | 35.33 ± 2.66 | -8.62 ± 0.35 | 16.89 ± 1.05 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-49 | 45.31 ± 2.84 | 2.41 ± 0.98 | 16.09 ± 0.64 | 38.53 ± 1.71 | -9.64 ± 0.88 | 19.81 ± 1.14 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-50 | 32.36 ± 2.59 | 7.46 ± 0.58 | 9.20 ± 1.10 | 37.79 ± 3.11 | -7.05 ± 1.41 | 14.86 ± 2.98 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-51 | 32.06 ± 2.44 | 11.63 ± 0.61 | 7.77 ± 0.82 | 36.94 ± 3.41 | -7.14 ± 0.65 | 14.88 ± 2.17 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-52 | 27.96 ± 2.19 | 9.72 ± 0.68 | 3.52 ± 0.52 | 38.39 ± 1.02 | -8.48 ± 1.48 | 18.14 ± 1.11 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-53 | 30.32 ± 2.68 | 7.42 ± 1.21 | 5.28 ± 1.47 | 37.69 ± 0.81 | -6.46 ± 1.41 | 19.85 ± 2.02 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-54 | 33.91 ±2.13 | 12.00 ± 0.63 | 7.49 ± 1.30 | 43.06 ± 1.75 | -4.97 ± 0.85 | 21.87 ± 1.93 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-55 | 32.50 ± 2.02 | 9.37 ± 1.23 | 7.51 ± 1.42 | 40.37 ± 1.16 | -7.68 ± 0.49 | 21.23 ± 0.54 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-56 | 35.72 ± 2.40 | 12.06 ± 0.35 | 8.06 ± 0.86 | 47.22 ± 2.81 | -11.49 ± 0.24 | 28.94 ± 2.88 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-57 | 31.87 ± 2.89 | 6.01 ± 0.81 | 6.57 ± 1.28 | 40.07 ± 3.88 | -9.49 ± 1.31 | 22.61 ± 1.19 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-58 | 37.00 ± 2.25 | 6.93 ± 0.91 | 12.19 ± 0.53 | 41.51 ± 3.07 | -10.55 ± 1.96 | 24.35 ± 1.90 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-59 | 39.88 ± 1 81 | 6.18 ± 0.63 | 16.45 ± 0.81 | 34.94 ± 1.69 | -7.72 ± 0.35 | 16.26 ± 1.13 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-60 | 39.81 ± 2.02 | 9.99 ± 1.04 | 7.72 ± 0.46 | 45.10 ± 1.88 | -9.76 ± 0.95 | 28.02 ± 2.94 | 绿色 Green |
| Z-2 | 33.35 ± 2.14 | 9.20 ± 0.59 | 13.78 ± 0.29 | 40.86 ± 1.90 | 2.02 ± 0.62 | 21.56 ± 2.88 | 红色 Red |
| Z-5 | 39.26 ± 1.77 | 14.14 ± 0.79 | 8.23 ± 1.48 | 35.41 ± 3.72 | 6.96 ± 0.62 | 11.60 ± 0.82 | 红色 Red |
| Z-6 | 36.06 ± 1.15 | 10.15 ± 0.85 | 8.38 ± 1.17 | 38.81 ± 2.81 | 3.89 ± 1.73 | 21.25 ± 2.94 | 红色 Red |
| Z-11 | 41.15 ± 1.97 | 11.95 ± 1.44 | 11.09 ± 0.82 | 35.45 ± 1.86 | 6.36 ± 1.94 | 14.58 ± 0.90 | 红色 Red |
| Z-12 | 43.73 ± 1.20 | 11.82 ± 0.74 | 13.07 ± 0.95 | 41.95 ± 2.88 | 6.47 ± 1.98 | 23.91 ± 1.15 | 红色 Red |
| Z-13 | 33.26 ± 1.18 | 13.33 ± 1.09 | 1.16 ± 0.36 | 38.23 ± 2.07 | 5.40 ± 1.27 | 15.24 ± 0.62 | 红色 Red |
| Z-14 | 44.59 ± 2.86 | 8.97 ± 1.01 | 10.24 ± 0.49 | 36.74 ± 2.22 | 4.67 ± 0.20 | 16.48 ± 2.25 | 红色 Red |
| Z-15 | 39.60 ± 2.92 | 14.15 ± 0.78 | 8.87 ± 0.23 | 37.47 ± 2.60 | 8.12 ± 1.91 | 18.86 ± 2.14 | 红色 Red |
| Z-16 | 40.50 ± 1.24 | 10.06 ± 0.82 | 6.69 ± 1.40 | 35.42 ± 2.75 | 8.56 ± 1.60 | 12.66 ± 1.61 | 红色 Red |
| Z-17 | 40.38 ± 1.86 | 15.19 ± 0.98 | 8.56 ± 1.47 | 38.00 ± 3.46 | 6.39 ± 0.21 | 15.78 ± 2.93 | 红色 Red |
| Z-24 | 44.55 ± 1.34 | 8.43 ± 0.88 | 10.36 ± 1.15 | 38.39 ± 2.99 | 8.70 ± 0.46 | 11.17 ± 2.22 | 红色 Red |
| Z-26 | 36.10 ± 2.92 | 4.37 ± 1.34 | 15.01 ± 1.4 | 42.20 ± 0.51 | 9.18 ± 1.10 | 11.68 ± 0.59 | 红色 Red |
| Z-1 | 28.20 ± 2.13 | 10.33 ± 0.91 | 6.81 ± 1.47 | 33.42 ± 1.49 | 12.98 ± 0.87 | 10.76 ± 1.77 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-3 | 28.82 ± 2.43 | 7.70 ± 0.81 | -0.03 ± 1.21 | 31.63 ± 0.93 | 5.91 ± 1.50 | 7.56 ± 2.50 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-9 | 43.53 ± 2.71 | 8.41 ± 1.44 | 13.73 ± 0.72 | 32.12 ± 3.09 | 11.10 ± 0.76 | 10.20 ± 2.83 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-19 | 32.32 ± 2.06 | 12.68 ± 1.22 | 5.33 ± 1.27 | 32.49 ± 3.08 | 10.89 ± 1.06 | 7.38 ± 2.84 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-20 | 35.86 ± 2.20 | 7.90 ± 1.14 | 11.82 ± 0.53 | 33.56 ± 1.11 | 9.69 ± 1.22 | 7.68 ± 2.44 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-21 | 33.74 ± 1.48 | 11.93 ± 0.73 | 3.07 ± 1.42 | 32.51 ± 1.42 | 10.57 ± 0.79 | 8.58 ± 2.85 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-22 | 30.57 ± 2.31 | 9.92 ± 1.00 | 3.08 ± 1.47 | 32.02 ± 3.31 | 11.90 ± 1.30 | 10.15 ± 2.13 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-23 | 27.93 ± 1.78 | 12.85 ± 0.70 | 1.71 ± 1.48 | 29.17 ± 3.81 | 6.10 ± 0.27 | 4.96 ± 0.59 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-27 | 34.72 ± 2.92 | 4.15 ± 1.16 | 10.95 ± 1.35 | 34.15 ± 1.45 | 3.93 ± 0.21 | 2.42 ± 1.71 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-28 | 30.89 ± 2.42 | 10.92 ± 1.35 | 4.26 ± 1.42 | 35.55 ± 1.38 | 2.71 ± 1.63 | 2.70 ± 1.89 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-29 | 34.15 ± 1.04 | 15.12 ± 1.47 | 2.44 ± 0.67 | 34.34 ± 1.34 | 4.90 ± 0.51 | 1.12 ± 1.49 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-30 | 38.11 ± 2.00 | 11.06 ± 1.44 | 5.93 ± 0.23 | 36.76 ± 1.93 | 8.80 ± 1.43 | 5.23 ± 2.63 | 紫红色 Red purple |
| Z-43 | 32.71 ± 1.22 | 2.79 ± 0.47 | 6.45 ± 1.39 | 30.29 ± 3.25 | 2.82 ± 0.92 | 5.04 ± 1.79 | 紫红色 Red purple |
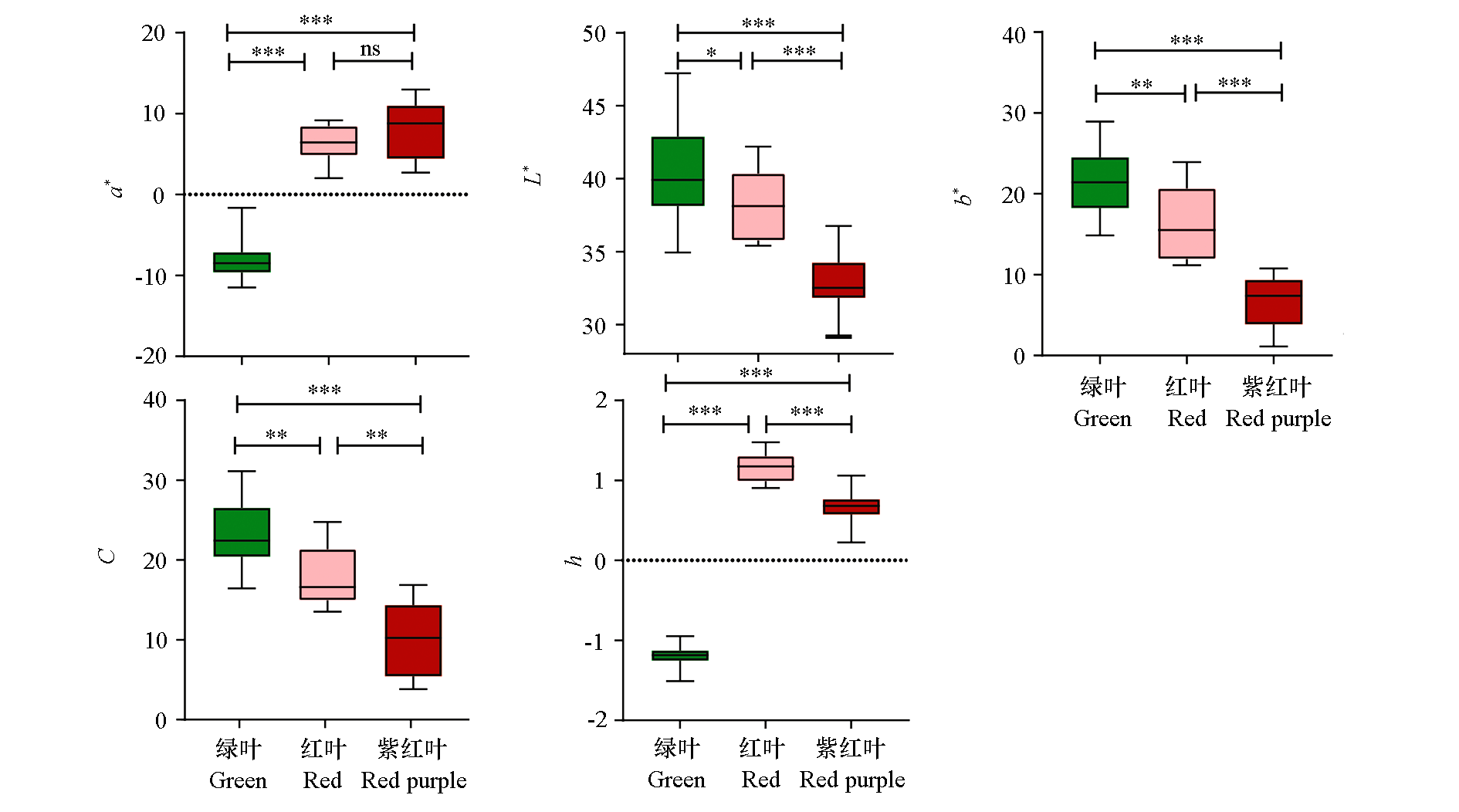
Fig. 2 Boxplots of leaf L*,a*,b*,C,h value of 60 progenies at full leaf stage n ≥ 5,ns:No statistical difference in the data t-test,* P < 0.05,** P < 0.01,*** P < 0.001
| SNP标记 SNP markers | 彩叶池SNP-index SNP-index of colored leaf pool | 绿叶池SNP-index SNP-index of green leaf pool | ∆SNP |
|---|---|---|---|
| V16 | 1.000 | 0.714 | 0.286 |
| V18 | 0.875 | 0.500 | 0.375 |
| V34 | 0.934 | 0.652 | 0.282 |
| V35 | 0.656 | 0.429 | 0.227 |
| V38 | 0.531 | 0.280 | 0.251 |
| V40 | 0.969 | 0.714 | 0.255 |
Table 5 SNP and ΔSNP-index of colored leaf pool and green leaf pool
| SNP标记 SNP markers | 彩叶池SNP-index SNP-index of colored leaf pool | 绿叶池SNP-index SNP-index of green leaf pool | ∆SNP |
|---|---|---|---|
| V16 | 1.000 | 0.714 | 0.286 |
| V18 | 0.875 | 0.500 | 0.375 |
| V34 | 0.934 | 0.652 | 0.282 |
| V35 | 0.656 | 0.429 | 0.227 |
| V38 | 0.531 | 0.280 | 0.251 |
| V40 | 0.969 | 0.714 | 0.255 |
| 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| V16 | ATCTTGAAGCCCCCAGTGAC | TGGCTTGGTGATGATGGGTG |
| V18 | TTTTTGGTGTAAGCTCCCACT | CTCATGTTCGTACAGTTCAAC |
| V34 | GCTGGCCAAGAATTGTTC | CGGAGGAGTAAAGTAACCAG |
| V35 | CCCATCTTGTCACATGTGAG | CCGTAAGCCGATGAAAGA |
| V38 | ATTGACTGGCGGACAACTGAG | CCATTGACAAGTAGATCCTTT |
Table 6 Primers of five SNPs marker
| 名称 Name | 正向引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 反向引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| V16 | ATCTTGAAGCCCCCAGTGAC | TGGCTTGGTGATGATGGGTG |
| V18 | TTTTTGGTGTAAGCTCCCACT | CTCATGTTCGTACAGTTCAAC |
| V34 | GCTGGCCAAGAATTGTTC | CGGAGGAGTAAAGTAACCAG |
| V35 | CCCATCTTGTCACATGTGAG | CCGTAAGCCGATGAAAGA |
| V38 | ATTGACTGGCGGACAACTGAG | CCATTGACAAGTAGATCCTTT |
| SNP名称 SNP name | PR型(红色) Purple type(red) (P) | Green型 Green type (G) | G型检测数 G type number | 杂合基因检测数 Heterozygous number | P型检测数 P type number | r | 显著水平 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V16 | C | CTG | 37 | 12 | 41 | 0.623 | ** |
| V18 | - | + | 29 | - | - | nd | - |
| V34 | AT | A | 25 | 20 | 45 | 0.184 | * |
| V35 | TCC | T | 42 | 20 | 28 | 0.255 | ** |
| V38 | G | GAC | 32 | 26 | 32 | 0.618 | ** |
Table 7 Genotype and phenotypic association analysis of 90 F1 plants
| SNP名称 SNP name | PR型(红色) Purple type(red) (P) | Green型 Green type (G) | G型检测数 G type number | 杂合基因检测数 Heterozygous number | P型检测数 P type number | r | 显著水平 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V16 | C | CTG | 37 | 12 | 41 | 0.623 | ** |
| V18 | - | + | 29 | - | - | nd | - |
| V34 | AT | A | 25 | 20 | 45 | 0.184 | * |
| V35 | TCC | T | 42 | 20 | 28 | 0.255 | ** |
| V38 | G | GAC | 32 | 26 | 32 | 0.618 | ** |
| [1] |
|
|
陈可欣, 乔中全, 曾慧杰, 李永欣, 蔡能, 陈艺, 王晓明, 何钢. 2021a. 紫薇F3H基因的克隆与生物信息学分析. 湖南林业科技, 48 (2):55-60.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈可欣, 王晓明, 曾慧杰, 李永欣, 何钢, 乔中全. 2021b. 紫薇LiA NS基因的克隆和表达及与花青素含量的关系. 分子植物育种, 19 (12):3915-3922.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
邓涪元, 乔中全, 王晓明, 李春霞, 陆柳淑, 李雪露, 何钢. 2022. 紫薇LiHY5基因的克隆、亚细胞定位与不同光质下的表达分析. 江西农业大学学报, 44 (6):1546-1554.
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
|
姜聖姬, 王淑安, 张恩亮, 李林芳, 高露璐, 杨如同, 王鹏. 2023. 紫薇遗传图谱构建及株型性状的QTL定位. 江苏农业学报, 39 (9):1818-1826.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
冷嘉文, 乔中全, 唐丽, 王晓明, 陈前欣, 邵雯雯. 2021. 基于SSR分子标记的紫薇遗传多样性分析. 湖南生态科学学报, 8 (4):1-7.
|
|
| [7] |
|
|
李春霞, 乔中全, 邓涪元, 陆柳淑, 李雪露, 何钢. 2023. 紫薇LiUFGT基因的克隆与生物信息学分析. 湖南林业科技, 50 (1):24-30.
|
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
|
李金璐, 王硕, 于婧, 王玲, 周世良. 2013. 一种改良的植物DNA提取方法. 植物学报, 48 (1):72-78.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1259.2013.00072 |
|
| [10] |
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0782 |
|
廖婷, 付琳, 郭丽琴, 刘国彬, 王烨, 姚砚武, 曹均. 2021. 洒金柏色素变化及光合作用响应特征. 中国农学通报, 37 (29):56-63.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2020-0782 |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
乔东亚, 王鹏, 王淑安, 张恩亮, 高露璐, 李亚, 杨如同. 2020. 紫薇金叶品种金幌叶色变化响应高光照的生理特性. 江苏农业学报, 36 (1):180-186.
|
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
|
邵雯雯, 何钢, 乔中全, 曾慧杰, 蔡能, 石炳霖. 2022. 6个紫薇品种叶片色彩变化及其与色素含量的相关性. 西北林学院学报, 37 (5):104-110,123.
|
|
| [15] |
|
|
[ 田苗. 2008. 我国紫薇新品种DUS测试指南及已知品种数据库的研究[硕士论文]. 北京:北京林业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
王文雅, 庞尔丽. 2021. 利用人类全基因组二代测序数据比较BWA-MEM和NovoAlign. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 57 (3):337-344.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
王晓明, 李永欣, 曾慧杰, 蔡能, 乔中全, 王湘莹, 刘思思. 2018. ‘红叶’等美国紫薇新品种品比试验. 湖南林业科技, 45 (6):9-13.
|
|
| [19] |
|
|
王莹, 李玉娟, 李敏, 马祥建, 谈峰, 郭聪, 张健. 2018. 紫叶紫薇新品系叶色变化转录组分析. 江苏农业学报, 34 (5):1128-1137.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
王芝懿, 李振芳, 彭婵, 陈英, 张新月. 2024. 基于SSR标记的紫薇核心种质构建及取样策略对比. 分子植物育种, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220916.1035.008.html.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0084 |
|
吴际洋, 焦垚, 叶远俊, 鞠易倩, 刘婷婷, 梁晓涵, 程堂仁, 王佳, 张启翔, 潘会堂. 2018. 大花紫薇与紫薇杂交F1群体表型评价及分子标记连锁分析. 园艺学报, 45 (11):2153-2163.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0084 |
|
| [24] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.03.014 |
|
吴霞, 毛行简, 凡莉莉, 陈凌艳, 何天友, 荣俊冬, 郑郁善. 2022. 花叶鹅掌柴不同颜色叶片光合特性. 热带作物学报, 43 (3):556-564.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.03.014 |
|
| [25] |
|
|
杨姝琦, 杨彦伶, 彭婵, 张新叶, 李振芳. 2024. 基于SSR标记的紫薇分子鉴定及遗传分析. 安徽农业大学学报, 51 (3):397-403.
|
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [1] | ZHANG Yiying, ZHANG Yu, CHU Yunxia, CHEN Hairong, DENG Shan, LI Aiai, ZHAO Hong, LIU Kun, HAN Ruixi, REN Li. Color Characteristics of Broccoli and Cauliflower Leaves Based on the Colorimeter Parameters [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(4): 872-882. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jie, WEN Haoyu, MA Lixin, ZHU Qingchao, LIU Long, JIANG Jing, and LIU Guifeng. Preliminary Analysis and Selection of Parental Combining Ability of Hybrid Progenies of Betula pendula‘Purple Rain’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(11): 2565-2574. |
| [3] | LÜ Yunzhou, DONG Xiaoyun, SUN Hainan, LIANG Zhenhai, and HUANG Libin. A New Koelreuteria paniculata Cultivar‘Caihong’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 187-188. |
| [4] | PAN Keyu , MENG Gang , SHAO Weiqian , HUANG Cheng , YANG Fan , WU Mengmeng , and FU Songling, . A New Cotinus coggygria Cultivar‘Wanlu 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(S1): 189-190. |
| [5] | JIANG Yu, TU Xunliang, HE Junrong. Analysis of Differential Expression Genes in Leaves of Leaf Color Mutant of Chinese Orchid [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [6] | BI Sisheng, ZHANG Lanying, WANG Hongyong, WANG Zhenmeng, MA Bingyao, GAO Wei, and LIU Guimin, . A New Northern Red Oak Cultivar‘Golden Prince' [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 179-180. |
| [7] | JIANG Jing, CHEN Kun, LI Yidi, CHEN Su, and LIU Guifeng. A New Poplar Cultivar‘Huihuang 1’with Yellower Green Leaves [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(S2): 3011-3012. |
| [8] | CHEN Qianru, CAI Wenqi, ZHANG Xia, ZHANG Damao, LI Weidong, XU Lu, YU Xiaoying, LI Yanlin. The Comparative Studies on Phytochemicals of Leaf Coloration of Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(10): 1969-1982. |
| [9] | JIANG Jing, ZHENG Yu, LI Huiyu, GANG Huixin, CHEN Su, and LIU Guifeng. A New Birch Cultivar‘Zhaoxia 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(S2): 3125-3126. |
| [10] | LIU Fuzhong, ZHANG Ying, YANG Jinkun, CHEN Yuhui, SHU Jinshuai, LI shupei, and CHEN Lulu. Characterization and Genetic Analysis of a Yellowing Mutant of Eggplant Leaf Color [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2020, 47(12): 2340-2348. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lulu1,MAO Yunfei1,ZHANG Canhong2,ZHANG Duojiao2,and SHEN Xiang1,*. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar‘Duojiao’ [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(S2): 2907-2908. |
| [12] | LI Weixing1,2,YANG Shunbo1,HE Zhichong1,and JIN Biao1,*. Research Advances in the Regulatory Mechanisms of Leaf Coloration [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(9): 1811-1824. |
| [13] | JIANG Wenlong1,FAN Junjun1,ZHANG Dandan1,LI Qianhui1,WU Qifei1,SHEN Xingcheng1,and ZHANG Wangxiang1,2,*. Research on the Characteristics of Different Leaf Positions of Crabapple’s Leaf Color and Elite Germplasm Excavation [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(6): 1135-1145. |
| [14] | SHAN Youxia1,DENG Chaojun2,3,HU Wenshun2,3,CHEN Junwei4,CHEN Xiuping2,3,QIN Qiaoping1,*,and ZHENG Shaoquan2,3,*. Diversity Analysis of Loquat(Eriobotrya)Defoliation Color [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(4): 755-767. |
| [15] | LI Binbin,YANG Junfeng,GAO Yuan,PAN Meina,and HOU Zhixia*. Variations of Anthocyanin and Chlorophyll Contents and Composition in ‘Northland’Blueberry Leaf Throughout the Color Changing Process in Autumn [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(12): 2361-2371. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd