
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (12): 2701-2712.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1208
• Plant Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Qi1( ), LI Ting1, CHEN Jialin1, CHEN Ou1, WANG Wenjun1,2, YAO Shixiang1,2, ZENG Kaifang1,2,3,*(
), LI Ting1, CHEN Jialin1, CHEN Ou1, WANG Wenjun1,2, YAO Shixiang1,2, ZENG Kaifang1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2023-01-18
Revised:2023-05-08
Online:2023-12-25
Published:2023-12-29
Contact:
ZENG Kaifang
CHEN Qi, LI Ting, CHEN Jialin, CHEN Ou, WANG Wenjun, YAO Shixiang, ZENG Kaifang. Studies on Function and Mechanism of CsNAC2 Transcription Factor in Resistance to Green Mold in Citrus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(12): 2701-2712.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-1208
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|
| CsNAC2-For | ATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-Rev | TTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-For | AGGCCGAATTCCCGGGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-Rev | CTAGTTATGCGGCCGCTGCAGTTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-For | CAAATTCGCGACCGGTATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-Rev | AGTTAAAGGCCTCGAGAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-GST-For | GGTTCCGCGTGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-GST-Rev | AGTCACGATGCGGCCGCAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsLAC7-probe-For | AATTTTTCACGGCACTGCTTCAATTGTAATGCGTGTGTCAGTAG |
| CsLAC7-probe-Rev | TGCTGACAAGCTACTGACACACGCATTACAATTGAAGCAGTG |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-For | AATTTTTAAAAGCACTAAAACAATTGTAATGAAAATGTCAGTAAAAAGTCAGCA |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-Rev | TGCTGACTTTTTACTGACATTTTCATTACAATTGTTTTAGTGCTTTTAAAAATT |
| CsEP3-probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCCGTAGTCAACACGGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCCGTGTTGACTACGGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCAAAAGTCAAAAAAGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCTTTTTTGACTTTTGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsLAC7-For | CCTGCAAAACACAGCGTTGA |
| CsLAC7-Rev | GTAGGGATCCCGTCCTGAAA |
| CsEP3-For | TGTGTCAAAACTCCGTTGCC |
| CsEP3-Rev | AGCACAATGAGACGGAGAACT |
| Action-For | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Action-Rev | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA |
Table 1 Specific primer sequences used in experiments
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|
| CsNAC2-For | ATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-Rev | TTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-For | AGGCCGAATTCCCGGGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pGBKT7-Rev | CTAGTTATGCGGCCGCTGCAGTTAAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-For | CAAATTCGCGACCGGTATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-pEAQ-Rev | AGTTAAAGGCCTCGAGAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsNAC2-GST-For | GGTTCCGCGTGGATCCATGACGGCTGAGTTACAGTTACCA |
| CsNAC2-GST-Rev | AGTCACGATGCGGCCGCAAAGGGTTTCGGAAGGTACATGAA |
| CsLAC7-probe-For | AATTTTTCACGGCACTGCTTCAATTGTAATGCGTGTGTCAGTAG |
| CsLAC7-probe-Rev | TGCTGACAAGCTACTGACACACGCATTACAATTGAAGCAGTG |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-For | AATTTTTAAAAGCACTAAAACAATTGTAATGAAAATGTCAGTAAAAAGTCAGCA |
| CsLAC7-mutant probe-Rev | TGCTGACTTTTTACTGACATTTTCATTACAATTGTTTTAGTGCTTTTAAAAATT |
| CsEP3-probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCCGTAGTCAACACGGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCCGTGTTGACTACGGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-For | TACTCGCTCGACAATAGATCAAAAGTCAAAAAAGAGGACAAGAA |
| CsEP3-mutant probe-Rev | TTCTTGTCCTCTTTTTTGACTTTTGATCTATTGTCGAGCGAGTA |
| CsLAC7-For | CCTGCAAAACACAGCGTTGA |
| CsLAC7-Rev | GTAGGGATCCCGTCCTGAAA |
| CsEP3-For | TGTGTCAAAACTCCGTTGCC |
| CsEP3-Rev | AGCACAATGAGACGGAGAACT |
| Action-For | ATCTGCTGGAAGGTGCTGAG |
| Action-Rev | CCAAGCAGCATGAAGATCAA |

Fig. 1 Comparison of amino acid sequences between CsNAC2 and NAC transcription factors in other species Mi:Mangifera indica;Cc:Citrus clementina;Me:Manihot esculenta;Cp:Carica papaya.
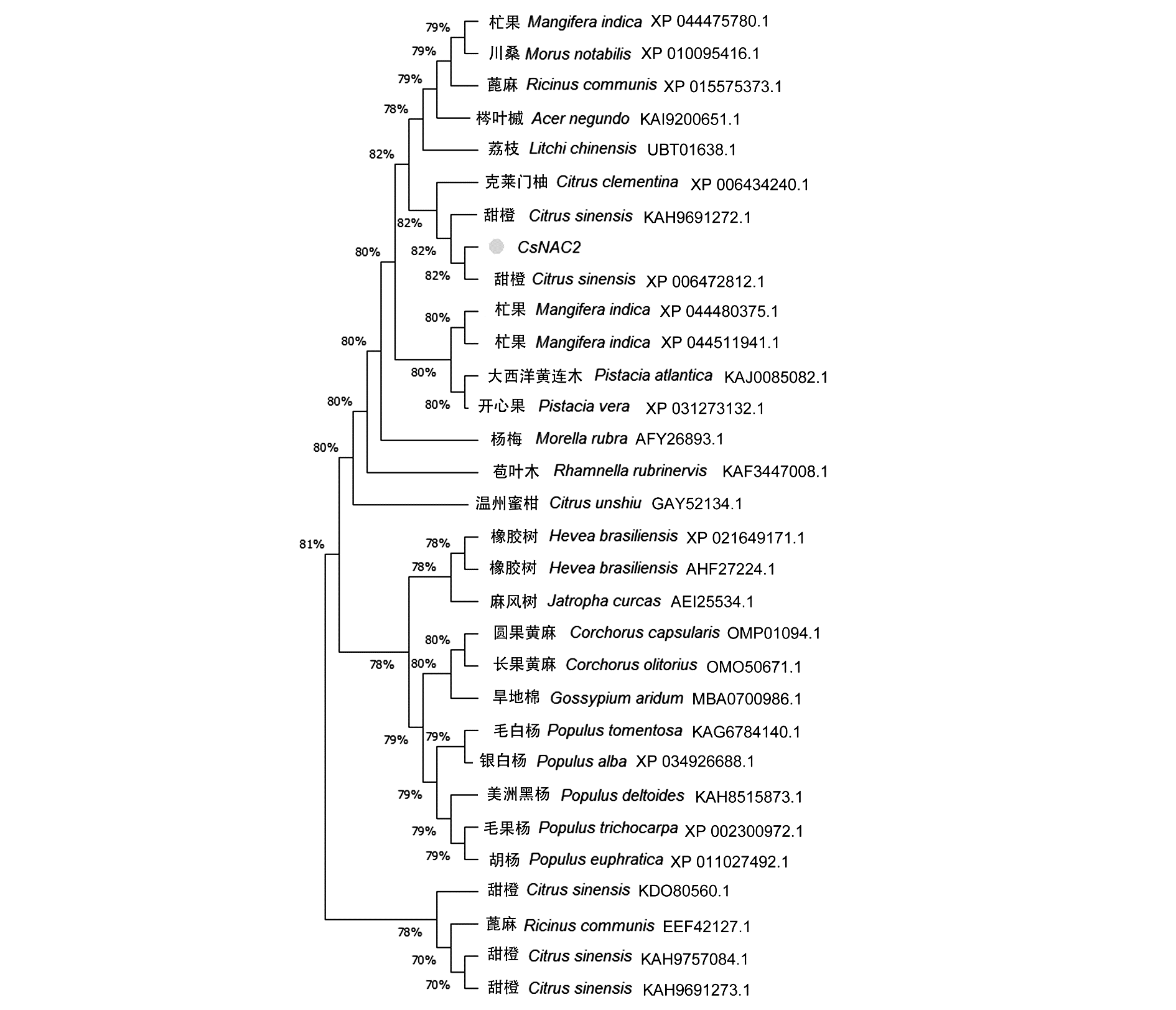
Fig. 2 The evolutionary relationship between CsNAC2 and NAC transcription factors in other species The value at the node represents the bootstrap value,and the larger the value,the higher the confidence of the node.
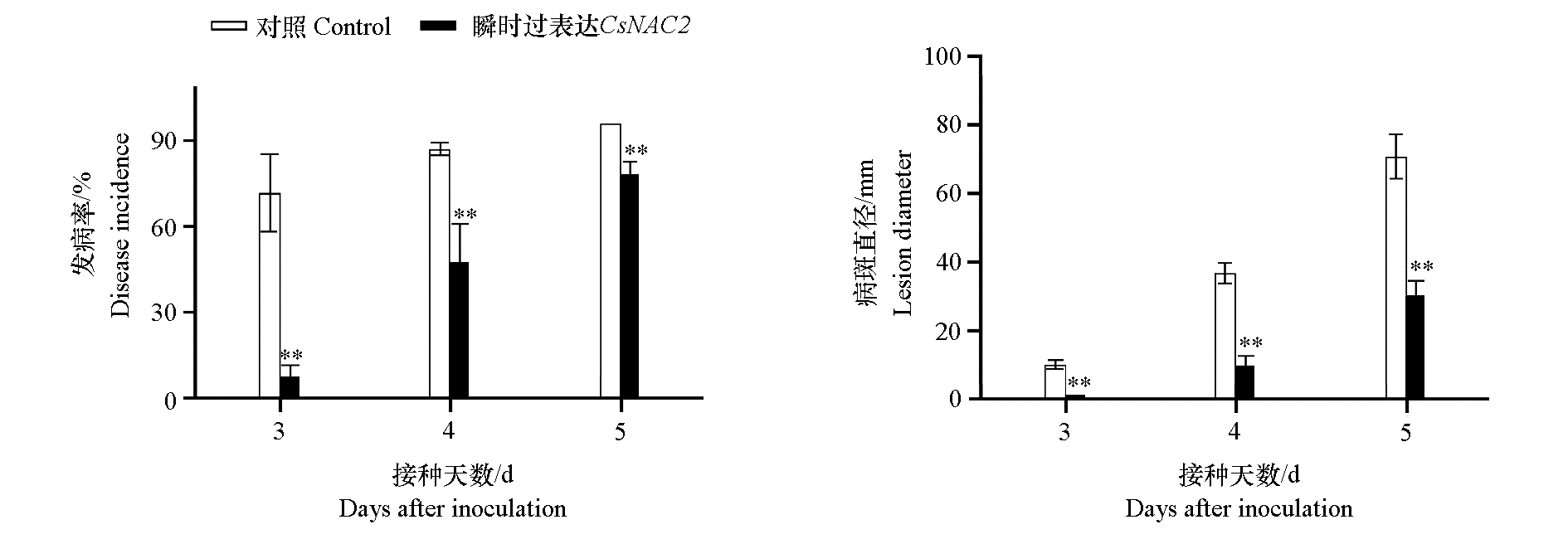
Fig. 4 Effect of transient overexpression of CsNAC2 on the disease incidence and lesion diameter of citrus green mold caused by inoculation of Penicillium digitalum in citrus fruits
| 途径Pathway | 基因 Gene symbol | log2(FC) | 功能注释 Description | 基因编号 Citrus sinensis ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙烷生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | COMT1 | 1.07 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g13580 |
| COMT | 1.29 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g18050 | |
| LAC7 | 1.18 | 漆酶 Laccase-7-like | Cs6g07400 | |
| 类胡萝卜素生物合成 Carotenoid biosynthesis | NCED1 | 1.18 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs2g03270 |
| NCED3 | 1.42 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs5g14370 | |
| 氨基酸和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | EP3 | 1.38 | 几丁质酶 Chitinase | Cs5g21870 |
| 角质素、软木脂和蜡质生物合成 Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | CER1 | 1.22 | 乙醛脱羧酶 Aldehyde decarbonylase | Cs1g02750 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | CAS2 | 1.29 | 半胱胺酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | orange1.1t00386 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | HSP26-A | 1.06 | 谷胱甘肽S转移酶 Glutathione S-transferase | Cs7g15760 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | IAA29 | 1.25 | 植物激素响应蛋白IAA Auxin-responsive protein IAA | Cs4g18240 |
Table 2 Possible downstream target genes of CsNAC2 associated with disease resistance
| 途径Pathway | 基因 Gene symbol | log2(FC) | 功能注释 Description | 基因编号 Citrus sinensis ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苯丙烷生物合成 Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | COMT1 | 1.07 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g13580 |
| COMT | 1.29 | 咖啡酸3甲基转移酶 Caffeic acid 3-O-Methyltransferase-like | Cs5g18050 | |
| LAC7 | 1.18 | 漆酶 Laccase-7-like | Cs6g07400 | |
| 类胡萝卜素生物合成 Carotenoid biosynthesis | NCED1 | 1.18 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs2g03270 |
| NCED3 | 1.42 | 9-顺式环氧类胡萝卜素双加氧酶 9-cis-Epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase | Cs5g14370 | |
| 氨基酸和核苷酸糖代谢 Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | EP3 | 1.38 | 几丁质酶 Chitinase | Cs5g21870 |
| 角质素、软木脂和蜡质生物合成 Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | CER1 | 1.22 | 乙醛脱羧酶 Aldehyde decarbonylase | Cs1g02750 |
| 半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸代谢 Cysteine and methionine metabolism | CAS2 | 1.29 | 半胱胺酸合成酶 Cysteine synthase | orange1.1t00386 |
| 谷胱甘肽代谢 Glutathione metabolism | HSP26-A | 1.06 | 谷胱甘肽S转移酶 Glutathione S-transferase | Cs7g15760 |
| 植物激素信号转导 Plant hormone signal transduction | IAA29 | 1.25 | 植物激素响应蛋白IAA Auxin-responsive protein IAA | Cs4g18240 |
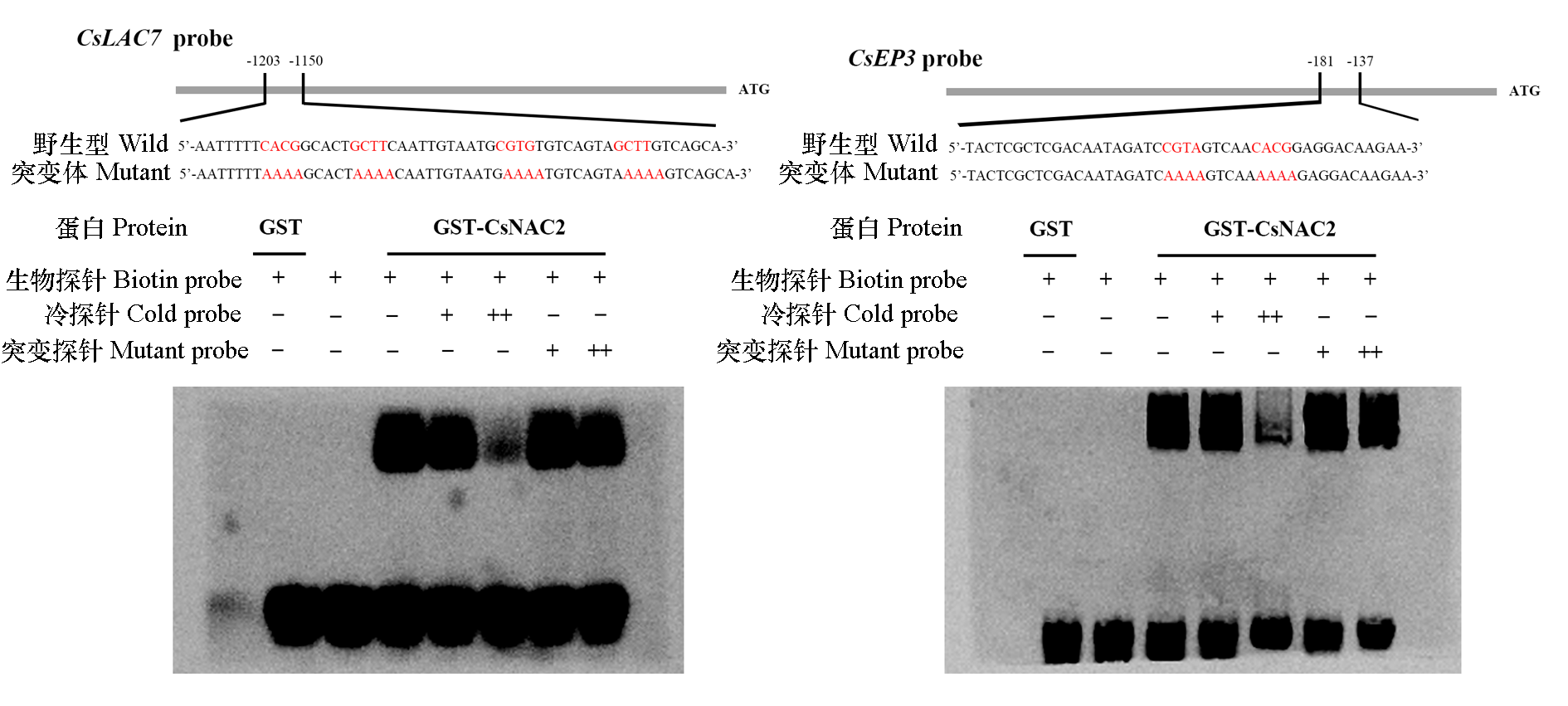
Fig. 5 The binding ability of CsNAC2 to promoters of downstream target genes CsLAC7 and CsEP3 GST protein and no protein were used as negative controls,respectively,and all experimental groups were added with GST-CsNAC2 protein. The marked red part represents the cis-acting elements NACRS in the promoter of downstream target genes of NAC,and the mutant probe replaced the core motif of NACRS with the“AAAA”base sequence. The symbols“+”and“−”represent presence or absence of the probe and the symbol“++”represent high concentration probe.
| [1] |
doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab383 pmid: 34618056 |
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1111/tpj.v106.3 URL |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1071/FP19331 pmid: 32454004 |
| [5] |
|
|
陈江华, 崔雪婧, 程家森, 林杨, 谢甲涛, 付艳苹. 2019. 我国主要产区柑橘采后病害发生动态. 华中农业大学学报, 38 (6):92-97.
|
|
| [6] |
|
|
陈娜, 蒋晶, 曹必好, 雷建军, 陈长明. 2015. 植物NAC转录因子功能研究新进展. 分子植物育种, 13 (6):1407-1414.
|
|
| [7] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.08.012 URL |
| [8] |
doi: 10.1111/nph.v232.1 URL |
| [9] |
|
|
韩立涛. 2022. 玉米NAC类转录因子ZmNAC19的功能研究[硕士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学.
|
|
| [10] |
|
|
胡嘉祺. 2020. 融合基因4CL1-CCR对烟草细胞壁影响的研究[博士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [11] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.03.018 URL |
| [12] |
doi: 10.1007/s11105-017-1043-1 URL |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.008 URL |
| [15] |
|
|
梁珂豪. 2020. 青杄NAC转录因子PwNAC30/PwNAC31的功能研究与验证[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京林业大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
梁攀, 李悦妍, 黄少云, 陈良哲, 易庆平. 2021. 柑橘类水果贮藏保鲜技术研究进展. 包装工程, 42 (13):57-66.
|
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0768-z pmid: 30387038 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0710-4 |
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.057 URL |
| [20] |
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1273 |
|
秦娟, 余凡, 刘璐, 朱婷婷, 陈伟, 曹士锋, 杨震峰, 施丽愉. 2021. 桃PpNAC19的克隆及其对PpCCD4启动子活性的调节分析. 核农学报, 35 (6):1273-1280.
doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.06.1273 |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12281 pmid: 26033522 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.3390/ijms21031120 URL |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1111/mpp.v20.12 URL |
| [24] |
|
|
王芳, 孙立娇, 赵晓宇, 王婕婉, 宋兴舜. 2019. 植物NAC转录因子的研究进展. 生物技术通报, 35 (4):88-93.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0905 |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.02.002 URL |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2022.10.009 URL |
| [27] |
|
|
张晓孟. 2017. 黄瓜番茄NAC转录因子鉴定及在逆境应答和果实发育中的功能初步分析[博士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
郑林, 王帅, 刘语诺, 杜美霞, 彭爱红, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 2022. 柑橘响应黄龙病菌侵染的NAC基因的克隆及表达分析. 园艺学报, 49 (7):1441-1457.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0553 URL |
|
| [29] |
|
|
周雅涵. 2017. 水杨酸、膜醭毕赤酵母、壳寡糖诱导柑橘果实抗病性及其生物学机制研究[博士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [30] |
|
|
周杨开. 2019. 转录因子NbNAC1调控植物系统性抗性防御病毒入侵的机制及其蛋白抗体制备[硕士论文]. 扬州: 扬州大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
|
朱自果, 阴启忠, 张庆田, 韩真, 张倩, 李勃. 2020. 欧洲葡萄‘粉红亚都蜜'NAC基因DRL1负向调节植物抗旱性. 园艺学报, 47 (12):2290-2300.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
朱凤鹃. 2005. 谈谈植物中的几丁质酶. 中国野生植物资源,(5):46-47,61.
|
| [1] | JIN Tian, XU Yuemei, KUANG Guanling, and LIU Guidong, . Effect of Boron Deficiency on the Root Growth and Mitochondrial Function of Trifoliate Orange Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 121-132. |
| [2] | LI Suping, LI Wei, HAN Leng, and HUANG Jianguo, . Bacillus velezensis HY19 Volatile Organic Compounds as a Preservative in Postharvest Citrus Fruit Management [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(1): 162-174. |
| [3] | CHEN Min, WU Tianli, Lü Yuanda, JIANG Bo, YAN Huaxue, LI Juan, ZHONG Yun. Analysis on Growth,Physiology and Fruit Quality of‘Hongjiang’Orange Grafted with Different Rootstocks Under Container Culture [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1547-1562. |
| [4] | DENG Chengfeng, LI Suping, ZHANG Ruixuan, HAN Leng, LI Yong. Control Effect of Lysobacter enzymogenes LE16 on Rot Disease in Post-harvest Citrus Fruit Caused by Penicillium digitatum and P. italicum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(7): 1574-1586. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lehuan, ZOU Changyu, WANG Zhaohao, YANG Wen, ZOU Xiuping, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, LONG Qin. Cloning and Expression Analysis of CsAOS1-2 in Responding to Citrus Canker Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(6): 1355-1367. |
| [6] | GUO Jing, LIAO Manyu, JIN Yan, MA Xiaochuan, ZHANG Fen, LU Xiaopeng, DENG Ziniu, SHENG Ling. Functional Analysis of Transcription Factor CsbHLH3 in Regulating Citric Acid Metabolism of Citrus Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 947-958. |
| [7] | ZHOU Ping, GUO Rui, YAN Shaobin, JIN Guang. Molecular Mechanism Study of Exogenous Sorbitol Effects on Sugar Metabolism in Peach Leaves and Fruits [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 959-971. |
| [8] | LÜ Ruoya, LI Yun, ZHENG Yongqin, DENG Xiaoling, ZHENG Zheng. The Distribution Pattern of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus in Fruit Pith [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1110-1117. |
| [9] | WANG Ping, SHENG Ling, YANG Jinpeng, ZHOU Linglei, JIN Yan, LUO Xuzhao, MA Xianfeng, DENG Ziniu. Evaluation of Resistance to Citrus Canker Disease in Hybrid Progeny of Red Pomelo and American Citron [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 765-777. |
| [10] | ZOU Yunqian, LUO Qujuan, ZHANG Jin, XU Rangwei, CHENG Yunjiang. Coating Containing Shellac,Rosin Significantly Improves Commercial Value of Satsuma Mandarins and Lane Late Navel Orange During Shelf Life [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(4): 853-863. |
| [11] | LAI Hengxin, LI Wenguang, PENG Liangzhi, HE Yizhong, ZHU Panpan, YANG Wanyun, LING Lili, FU Xingzheng, CHUN Changpin, CAO Li. Quality Changes of On-tree Storage Fruit of Orah Mandarin(Citrus reticulata Blanco)During Spring and Summer Seasons [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 485-494. |
| [12] | LIU Yunuo, CAO Ya, WANG Shuai, DU Meixia, ZHENG Lin, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Expression Analysis of CsMYB41 and CsMYB63 Genes in Response to Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 495-507. |
| [13] | LEI Jianjun, ZHU Zhangsheng, CHEN Changming, CHEN Guoju, CAO Bihao, ZHENG Jie, WU Hao, XIAO Yanhui, QIU Zhengkun, YAN Shuangshuang. Research Progress on Pepper Main Red Pigments and Their Molecular Mechanisms of Biosynthesis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(3): 669-684. |
| [14] | YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, ZHAO Xiaochun. Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [15] | LIANG Shengmin, ZHANG Fei, WU Qiangsheng. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Improve Drought Tolerance of Trifoliate Orange Seedlings by Regulating Root Polyamines [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(12): 2680-2688. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd