
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (1): 62-72.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1058
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Ronghua, WANG Shubin, LIU Shuantao, LI Qiaoyun, ZHANG Zhigang, WANG Lihua, ZHAO Zhizhong( )
)
Received:2021-03-01
Revised:2021-08-19
Online:2022-01-25
Published:2022-01-24
CLC Number:
WANG Ronghua, WANG Shubin, LIU Shuantao, LI Qiaoyun, ZHANG Zhigang, WANG Lihua, ZHAO Zhizhong. Transcriptome Analysis of Waxy Near-isogenic Lines in Chinese Cabbage Floral Axis[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 62-72.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1058
| 基因 | 基因号 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| CER2* | Bra013809 | TGAATATAGTGTGAACGCATTAGC | GCCCTAGTGATAACCCACCA |
| MAH1 | Bra027904 | AGGTTCATGAGGCCAACGAT | CGGAAATTTTGAGCTGAGCAT |
| KCS9 | Bra001974 | TAAGAAGGCGATGCTGATCC | ACGCCTTCTCATCAGCTCCT |
| KCS1 | Bra033283 | CTCTATCGGCGATGATCGTG | GTTGGCGAGTTCGATTGAGA |
| CER2 | Bra013809 | GCTCGACCTCCAGTGTTATGA | ACTGTCGTTGCAGCGAATGT |
| CYTB5-B | Bra021809 | GCACAATCACGCTCATGACTG | TCATCCGTTGCATCCTTACC |
| CYTB5-C | Bra039268 | GCGGTGACAATGTTCTCCTC | TGGAATATACTTCGCCGTCAC |
| MYB30 | Bra033067 | TGCCGTAGCACCGATCAAT | TCGCTATGTTCTCGGTGTTTG |
| LTPG1 | Bra030067 | AACGCTAGCATCTCCAACTGTC | TTGGAGTTGCCGGAGACTTC |
| G6PD | GGGTATGCCAGGACTAAGCTC | GAATCATAAGGGCCACTCACAT |
Table 1 All the primer sequences
| 基因 | 基因号 | 正向引物(5′-3′) | 反向引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| CER2* | Bra013809 | TGAATATAGTGTGAACGCATTAGC | GCCCTAGTGATAACCCACCA |
| MAH1 | Bra027904 | AGGTTCATGAGGCCAACGAT | CGGAAATTTTGAGCTGAGCAT |
| KCS9 | Bra001974 | TAAGAAGGCGATGCTGATCC | ACGCCTTCTCATCAGCTCCT |
| KCS1 | Bra033283 | CTCTATCGGCGATGATCGTG | GTTGGCGAGTTCGATTGAGA |
| CER2 | Bra013809 | GCTCGACCTCCAGTGTTATGA | ACTGTCGTTGCAGCGAATGT |
| CYTB5-B | Bra021809 | GCACAATCACGCTCATGACTG | TCATCCGTTGCATCCTTACC |
| CYTB5-C | Bra039268 | GCGGTGACAATGTTCTCCTC | TGGAATATACTTCGCCGTCAC |
| MYB30 | Bra033067 | TGCCGTAGCACCGATCAAT | TCGCTATGTTCTCGGTGTTTG |
| LTPG1 | Bra030067 | AACGCTAGCATCTCCAACTGTC | TTGGAGTTGCCGGAGACTTC |
| G6PD | GGGTATGCCAGGACTAAGCTC | GAATCATAAGGGCCACTCACAT |
| 样品名称 | 原始序列 | 高质量序列 | 高质量碱基数/Gb | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Clean base | Error rate | GC content | ||
| RHL065_1_T1 | 42628776 | 41061052 | 6.16 | 0.02 | 98.53 | 95.36 | 47.34 |
| RHL065_1_T2 | 59538100 | 56577062 | 8.49 | 0.02 | 98.22 | 94.59 | 47.28 |
| RHL065_1_T3 | 45954482 | 43800974 | 6.57 | 0.02 | 98.36 | 94.96 | 47.24 |
| RHL065_2_T1 | 61069026 | 57685276 | 8.65 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 47.15 |
| RHL065_2_T2 | 59286084 | 56360648 | 8.45 | 0.02 | 98.26 | 94.74 | 47.11 |
| RHL065_2_T3 | 61847196 | 58688916 | 8.80 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 46.79 |
Table 2 Statistical analysis of transcriptome sequencing in waxy RHL065_1 and non-waxy RHL065_2 material of Chinese cabbage floral axis
| 样品名称 | 原始序列 | 高质量序列 | 高质量碱基数/Gb | 错误率/% | Q20/% | Q30/% | GC含量/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Clean base | Error rate | GC content | ||
| RHL065_1_T1 | 42628776 | 41061052 | 6.16 | 0.02 | 98.53 | 95.36 | 47.34 |
| RHL065_1_T2 | 59538100 | 56577062 | 8.49 | 0.02 | 98.22 | 94.59 | 47.28 |
| RHL065_1_T3 | 45954482 | 43800974 | 6.57 | 0.02 | 98.36 | 94.96 | 47.24 |
| RHL065_2_T1 | 61069026 | 57685276 | 8.65 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 47.15 |
| RHL065_2_T2 | 59286084 | 56360648 | 8.45 | 0.02 | 98.26 | 94.74 | 47.11 |
| RHL065_2_T3 | 61847196 | 58688916 | 8.80 | 0.02 | 98.42 | 95.12 | 46.79 |
| 通路 | 基因号 | 基因名称 | 差异倍数 | 显著性 | 调控模式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Gene ID | Gene name | log2 Fold Change | P value | Regulated mode |
| 表皮蜡粉生物合成 Cuticular wax biosynthesis | Bra027904 | MAH1 | 3.342 | 1.1326E-07 | 上调 Up |
| Bra022898 | CYTB5-B | 2.732 | 4.7382E-17 | 上调 Up | |
| Bra004034 | KCS6/CER6/CUT1 | -1.193 | 1.2047E-38 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra001974 | KCS9 | -1.250 | 7.6776E-63 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra034583 | FAR3/CER4 | -1.372 | 7.6944E-35 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra033283 | KCS1 | -1.399 | 8.2146E-66 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra013809 | CER2 | -1.691 | 7.229E-73 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra021809 | CYTB5-B | -1.715 | 5.039E-135 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra006062 | KCD/PAS2 | -2.222 | 5.411E-240 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra039268 | CYTB5-C | -2.239 | 4.6399E-50 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra004518 | CYTB5-C | -5.226 | 4.6843E-12 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra014988 | CER2-LIKE | -6.478 | 1.1694E-05 | 下调 Down | |
| 转录调控 Transcriptional regulation | Bra026140 | WIN1/SHINE1 | 1.451 | 0.0011061 | 上调 Up |
| Bra033067 | MYB30 | -1.063 | 0.00044649 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra029319 | DEWAX | -2.482 | 2.287E-15 | 下调 Down | |
| 表皮蜡粉转运 Cuticular wax transport | Bra010912 | LTPG1 | -1.024 | 3.5614E-13 | 下调 Down |
| Bra030067 | LTPG1 | 2.232 | 9.9446E-09 | 上调 Up |
Table 3 Differential expression patterns of key genes involved in wax synthesis, transportation and regulation in Chinese cabbage
| 通路 | 基因号 | 基因名称 | 差异倍数 | 显著性 | 调控模式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathway | Gene ID | Gene name | log2 Fold Change | P value | Regulated mode |
| 表皮蜡粉生物合成 Cuticular wax biosynthesis | Bra027904 | MAH1 | 3.342 | 1.1326E-07 | 上调 Up |
| Bra022898 | CYTB5-B | 2.732 | 4.7382E-17 | 上调 Up | |
| Bra004034 | KCS6/CER6/CUT1 | -1.193 | 1.2047E-38 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra001974 | KCS9 | -1.250 | 7.6776E-63 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra034583 | FAR3/CER4 | -1.372 | 7.6944E-35 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra033283 | KCS1 | -1.399 | 8.2146E-66 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra013809 | CER2 | -1.691 | 7.229E-73 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra021809 | CYTB5-B | -1.715 | 5.039E-135 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra006062 | KCD/PAS2 | -2.222 | 5.411E-240 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra039268 | CYTB5-C | -2.239 | 4.6399E-50 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra004518 | CYTB5-C | -5.226 | 4.6843E-12 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra014988 | CER2-LIKE | -6.478 | 1.1694E-05 | 下调 Down | |
| 转录调控 Transcriptional regulation | Bra026140 | WIN1/SHINE1 | 1.451 | 0.0011061 | 上调 Up |
| Bra033067 | MYB30 | -1.063 | 0.00044649 | 下调 Down | |
| Bra029319 | DEWAX | -2.482 | 2.287E-15 | 下调 Down | |
| 表皮蜡粉转运 Cuticular wax transport | Bra010912 | LTPG1 | -1.024 | 3.5614E-13 | 下调 Down |
| Bra030067 | LTPG1 | 2.232 | 9.9446E-09 | 上调 Up |
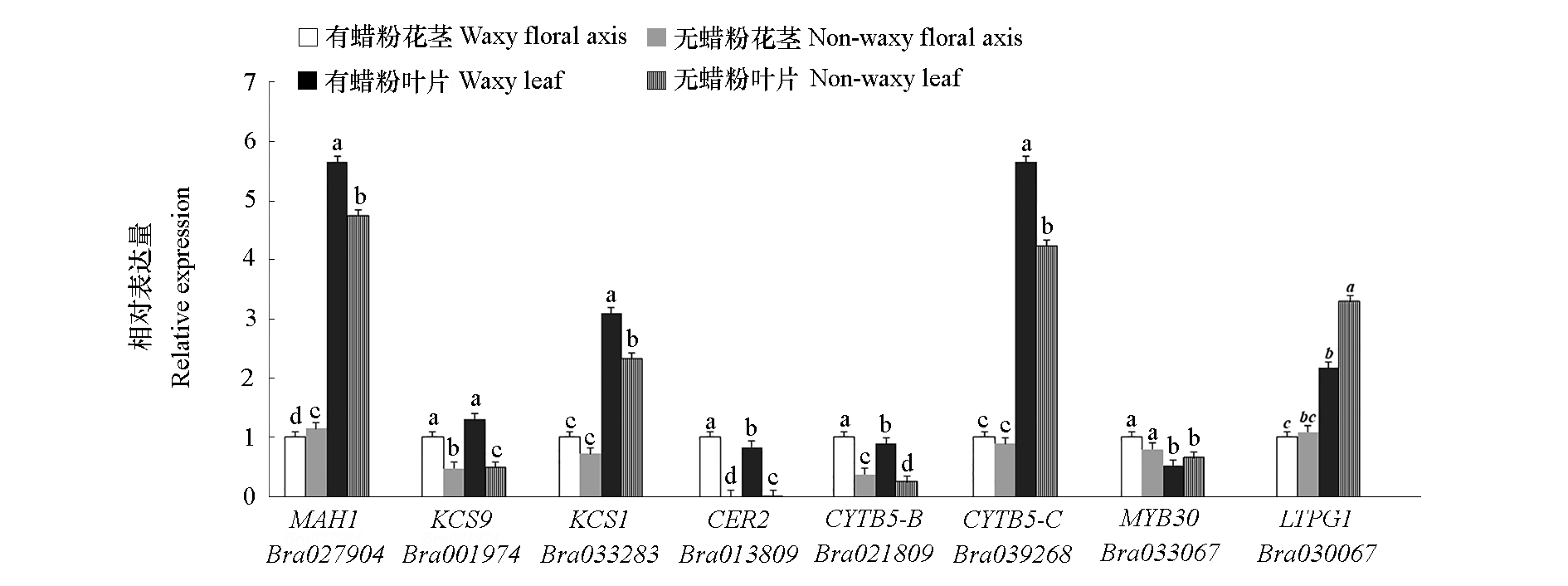
Fig. 4 Relative expression of key genes in wax synthesis,transportation and regulation on floral axis and leaf in Chinese cabbage Different lowercase letters indicate significantly different at P < 0.05.
| [1] |
Aharoni A, Dixit S, Jetter R, Thoenes E, Pereira A A. 2004. The SHINE clade of AP2 domain transcription factors activates wax biosynthesis,alters cuticle properties,and confers drought tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 16:2463-2480.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.022897 URL |
| [2] |
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C, Cutler D, Ditsch F, Meusel I, Theisen I, Wilhelmi H. 1998. Classification and terminology of plant epicuticular waxes. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 126 (3):237-260.
doi: 10.1111/boj.1998.126.issue-3 URL |
| [3] |
Bernard A, Domergue F, Pascal S, Jetter R, Renne C, Faure J D, Haslam R P, Napier J A, Lessire, Joubes J. 2012. Reconstitution of plant alkane biosynthesis in yeast demonstrates that Arabidopsis ECERIFERUM1 and ECERIFERUM3 are core components of a very-long-chain alkane synthesis complex. The Plant Cell, 24:3106-3118.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.099796 pmid: 22773744 |
| [4] | Bourdenx B, Bernard A, Domergue F, Pascal S, Leger A. 2011. Overexpression of Arabidopsis ECERIFERUM1 promotes wax very-long-chain alkane biosynthesis and influences plant response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Physiolgy, 156:29-45. |
| [5] |
Busta L, Hegebarth D, Kroc E, Jetter R. 2017. Changes in cuticular wax coverage and composition on developing Arabidopsis leaves are influenced by wax biosynthesis gene expression levels and trichome density. Planta, 245:297-311.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2603-6 URL |
| [6] |
Debono A, Yeats T H, Rose J K, Bird D, Jetter R, Kunst L, Samuels L. 2009. Arabidopsis LTPG is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein required for export of lipids to the plant surface. Plant Cell, 21 (4):1230-1238.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.064451 pmid: 19366900 |
| [7] |
Go Y S, Kim H, Kim H J, Suh M C. 2014. Arabidopsis cuticular wax biosynthesis is negatively regulated by the DEWAX gene encoding an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor. The Plant Cell, 26 (4):1666-1680.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.123307 URL |
| [8] |
Kannangara R, Branigan C, Liu Y, Penfield T, Rao V, Mouille G, Hofte H, Pauly M, Riechmann J L, Broun P. 2007. The transcription factor WIN1/SHN1 regulates cutin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell, 19 (4):1278-1294.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.047076 URL |
| [9] |
Kim H. 2012. Characterization of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein 2(LTPG2) and overlapping function between LTPG/LTPG1 and LTPG 2 in cuticular wax export or accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology, 53:1391-1403.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs083 URL |
| [10] |
Kim H, Choi D, Suh M C. 2017. Cuticle ultrastructure,cuticular lipid composition,and gene expression in hypoxia-stressed Arabidopsis stems and leaves. Plant Cell Reports, 36 (6):815-827.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2112-5 URL |
| [11] |
Kim J, Jung J H, Lee S B, Go Y S, Kim H J, Cahoon R, Markham J E, Cahoon E B, Suh M C. 2013. Arabidopsis 3-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase 9 is involved in the synthesis of tetracosanoic acids as precursors of cuticular waxes,suberins,sphingolipids,and phospholipids. Plant Physiology, 162:567-580.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.210450 URL |
| [12] | Lam P, Zhao L, Eveleigh N, Yu X, Chen L. 2015. The exosome and trans-acting small interfering RNAs regulate cuticular wax biosynthesis during Arabidopsis inflorescence stem development. Plant Physiolgy, 167:323-336. |
| [13] |
Lee S, Go Y, Bae H, Park J, Cho S, Cho H, Lee D, Park O, Hwang I, Suh M. 2009. Disruption of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored lipid transfer protein gene altered cuticular lipid composition,increased plastoglobules,and enhanced susceptibility to infection by the fungal pathogen Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Physiology, 150:42-54.
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.137745 URL |
| [14] |
Lee S B, Kim H U, Suh M C. 2016. MYB94 and MYB96 additively activate cuticular wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 57:2300-2311.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw147 URL |
| [15] |
Lee S B, Suh M C. 2015. Advances in the understanding of cuticular waxes in Arabidopsis thaliana and crop species. Plant Cell Reports, 34:557-572.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1772-2 URL |
| [16] |
Liu S, Wang R, Zhang Z, Li Q, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhao Z. 2019. High-resolution mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling main floral stalk length in Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genomics, 20:437.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5810-2 URL |
| [17] | Liu Z, Fang Z, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Liu Y, Li Z, Sun P, Tang J, Liu D, Zhang Z, Yang L. 2017. Fine-mapping and analysis of Cgl1,a gene conferring glossy trait in cabbage(Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Frontiers in Plant Science, 8 (14024):239. |
| [18] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25:402-408.
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [19] |
McFarlane H E, Shin J J H, Bird D A, Samuels A L. 2010. Arabidopsis ABCG transporters,which are required for export of diverse cuticular lipids,dimerize in different combinations. The Plant Cell, 22:3066-3075.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.077974 pmid: 20870961 |
| [20] | McFarlane H E, Watanabe Y, Yang W, Huang Y, Ohlrogge J, Samuels A L. 2014. Golgi- and trans-Golgi network-mediated vesicle trafficking is required for wax secretion from epidermal cells. Plant Physiolgy, 164:1250-1260. |
| [21] | Mu Xiangli, Wang Chao, Wang Shuai. 2013. Observation of ultra microstructure of wax-less mutant epicuticular wax on Cabbage. Chinese Vegetable,(4):32. (in Chinese) |
| 牟香丽, 王超, 王帅. 2013. 甘蓝无蜡质突变体叶表皮蜡质超微结构观察. 中国蔬菜,(4):32. | |
| [22] |
Ni Z, Xin M, Hu Z, Yao Y, Wang T, Liu X, Xing J, Peng H, Zhang Y, Zhou D. 2018. GCN5 contributes to stem cuticular wax biosynthesis by histone acetylation of CER3 in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69 (12):2911-2922.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery077 URL |
| [23] |
Oshima Y, Shikata M, Koyama T, Ohtsubo N, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. 2013. MIXTA-like transcription factors and WAX INDUCER1/SHINE1 coordinately regulate cuticle development in Arabidopsis and Torenia fournieri. The Plant Cell, 25:1609-1624.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.110783 URL |
| [24] |
Park C S, Go Y S, Suh M C. 2016. Cuticular wax biosynthesis is positively regulated by WRINKLED4,an AP2/ERF-type transcription factor,in Arabidopsis stems. The Plant Journal, 88:257-270.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2016.88.issue-2 URL |
| [25] |
Pu Y, Gao J, Guo Y, Liu T, Zhu L, Xu P, Yi B, Wen J, Tu J, Ma C, Fu T, Zou J, Shen J. 2013. A novel dominant glossy mutation causes suppression of wax biosynthesis pathway and deficiency of cuticular wax in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biology, 13:215.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-215 URL |
| [26] |
Raffaele S, Vailleau F, Léger A, Joubes J, Miersch O, Huard C, Blee E, Mongrand S, Domergue F, Roby D. 2008. A MYB transcription factor regulates very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis for activation of the hypersensitive cell death response in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 20:752-767.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054858 URL |
| [27] |
Rowland O, Domergue F. 2012. Plant fatty acyl reductases:enzymes generating fatty alcohols for protective layers with potential for industrial applications. Plant Science, 193-194:28-38.
doi: S0168-9452(12)00095-7 pmid: 22794916 |
| [28] | Shao Meini, Hao Xin, Cui Na, Qu Bo, Guan Ping, Jia Weikang, Xu Yufeng. 2020. Effects of epicuticular waxes on the physiological characteristics of blue-leaf Hosta. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (7):1401-1411. (in Chinese) |
| 邵美妮, 郝鑫, 崔娜, 曲波, 关萍, 贾伟康, 许玉凤. 2020. 蓝叶类型玉簪叶片表皮蜡质对光合生理的影响. 园艺学报, 47 (7):1401-1411. | |
| [29] |
Todd J, Post-Beittenmiller D, Jaworski J G. 1999. KCS1 encodes a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase affecting wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 17:119-130.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00352.x URL |
| [30] |
Xue Y, Xiao S, Kim J, Lung S, Chen L, Tanner J A, Suh M C, Chye M L. 2014. Arabidopsis membrane-associated acyl-CoA-binding protein ACBP1 is involved in stem cuticle formation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65:5473-5483.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru304 URL |
| [31] |
Yeats T H, Rose J K. 2008. The biochemistry and biology of extracellular plant lipid-transfer proteins(LTPs). Protein Science, 17 (2):191-198.
doi: 10.1110/ps.073300108 URL |
| [32] |
Zhang X, Liu Z, Wang P, Wang Q, Yang S, Feng H. 2013. Fine mapping of BrWax1,a gene controlling cuticular wax biosynthesis in Chinese cabbage(Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Molecular Breeding, 32 (4):867-874.
doi: 10.1007/s11032-013-9914-0 URL |
| [33] | Zhao L, Kunst L. 2016. SUPERKILLER complex components are required for the RNA exosome-mediated control of cuticular wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis inflorescence stems. Plant Physiology, 171:960-973. |
| [1] | JIANG Yu, TU Xunliang, and HE Junrong. Analysis of Differential Expression Genes in Leaves of Leaf Color Mutant of Chinese Orchid [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 371-381. |
| [2] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [3] | HAN Shuhui, HAN Caifeng, HAN Shurong, HAN Caimei, and HAN Xu. A New Autumn Chinese Cabbage Hybrid‘Jiaoyan Qiubao’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 83-84. |
| [4] | WANG Weihong, ZHANG Fenglan, YU Yangjun, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, SU Tongbing, LI Peirong, and XIN Xiaoyun. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jingqiu 1518’for Autumn Cultivation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 85-86. |
| [5] | YU Yangjun, WANG Weihong, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Fenglan, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun, and WANG Jiao. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jingchun CR3’with Clubroot Resistance and Bolting Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [6] | WANG Lili, WANG Xin, WU Haidong, WEN Qiang, and Yang Xiaofei. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Liaobai 28’with Resistance to Clubroot Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [7] | YU Yangjun, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Fenglan, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, WANG Weihong, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun, WANG Jiao, and WU Changjian. A New Purple Seedling-Edible Chinese Cabbage F1 Hybrid‘Jingyan Zikuaicai’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 91-92. |
| [8] | HUANG Li, CHEN Caizhi, YU Xiaolin, YAO Xiangtan, and CAO Jiashu, . A New Early-mid Maturing Chinese Cabbage Pak-choi Cultivar‘Zhedaqing’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 93-94. |
| [9] | LI Zhongjian, WANG Shaoxin, WANG Baobao, XU Luo, and FENG Jianying. A New Waxy Corn Cultivar‘Shibainuo 3’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 153-154. |
| [10] | WANG Shaoxin, LI Zhongjian, XU Luo, FENG Jianying, WANG Baobao, and CHEN Li. A New Waxy Corn Cultivar‘Shibainuo 5’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 155-156. |
| [11] | ZHANG Caibo, ZHANG Shuya, CHEN Xiangying, YU Tingyue, CHEN Lei, ZHANG Wei, and WEN Shouyun, . A New Waxy Corn Cultivar‘Jinnuo 6’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 157-158. |
| [12] | TANG Gui, SUI Donghua, WU Liren, WU Xinjuan, ZHANG Dongxue, GAO Jiayuan, ZHANG Lei, WANG Teng, ZHANG Zhe, ZHOU Chunwei, WANG Lin, and LI Dongming. A New Waxy Maize Cultivar‘Suinuo 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 159-160. |
| [13] | SUI Donghua, TANG Gui, NING Lipeng, WU Xinjuan, ZHANG Dongxue, GAO Jiayuan, ZHANG Lei, WANG Teng, ZHANG Lili, HOU Shuai, SONG Penghui, ZHANG Kun, and WU Liren. A New Waxy Maize Cultivar‘Suinuo 3’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 161-162. |
| [14] | XU Ligong, HAN Taili, SUN Jifeng, YANG Xiaodong, and TAN Jinxia. A New Seedling-edible Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jinlü 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 67-68. |
| [15] | WANG Yu, ZHANG Xue, ZHANG Xueying, ZHANG Siyu, WEN Tingting, WANG Yingjun, GAN Caixia, PANG Wenxing. The Effect of Camalexin on Chinese Cabbage Resistance to Clubroot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd