
园艺学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 2270-2290.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2024-0845
• 综述 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-11-02
修回日期:2025-06-18
出版日期:2025-08-19
发布日期:2025-08-19
通讯作者:
基金资助:
FENG Lingjia, LIU Yujie, HE Lintong, WANG Xinchao, and YE Meng*( )
)
Received:2024-11-02
Revised:2025-06-18
Published:2025-08-19
Online:2025-08-19
摘要:
芳樟醇是一种重要的单萜类植物次生代谢物,广泛分布于植物的花、果、叶、茎和根中。其生物合成主要在质体内通过MEP途径完成,受到转录、表观遗传及转录后等多层次的分子调控。作为植物香气的关键成分,芳樟醇在植物与传粉昆虫、植食性昆虫及其天敌之间的生态相互作用中发挥着重要作用。此外,芳樟醇还参与植物对病原体和非生物胁迫的防御响应。本文中综述了芳樟醇的合成路径与调控机制,系统总结了其在吸引传粉者、抗病虫害及应对非生物胁迫等方面的研究进展,探讨其在植物适应复杂环境中的重要意义。同时,对芳樟醇在田间生态环境中的调控效应、单一对映体及衍生物的功能特异性、以及多重胁迫中的协同作用机制研究提出了展望,以期为园艺作物绿色农业应用提供理论支撑和技术指导。
冯玲佳, 刘毓婕, 何林彤, 王新超, 叶萌. 芳樟醇合成调控机制及其生态功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 2270-2290.
FENG Lingjia, LIU Yujie, HE Lintong, WANG Xinchao, and YE Meng. Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Linalool Synthesis and Its Ecological Functions[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2025, 52(8): 2270-2290.
| 科Family | 物种Species | 基因Gene | 合成产物Synthetic product | 参考文献Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 毛果杨 Populus trichocarpa | PtTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and (S)-nerolidol | Danner et al., | |
| PtTPS4 | 主要产物:(R)-(−)-芳樟醇和(R)-橙花叔醇; 次要产物:(S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool and(R)-nerolidol; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool and(S)-nerolidol | ||||
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 水稻 Oryza sativa | OsTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Yuan et al., | |
| 玉米 Zea mays | ZmTPS1 | 芳樟醇和β-月桂烯 Linalool and β-myrcene | Yactayo-Chang et al., | ||
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 铁线莲 Clematis florida | CfTPS1、CfTPS2 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Jiang et al., | |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 苹果 Malus domestica | MdLIS-RG1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nieuwenhuizen et al., | |
| 桃 Prunus persica | PpTPS1、PpTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., Wei et al., | ||
| 草莓 Fragaria × ananassa | FaNES1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | Aharoni et al., | ||
| 月季花 Rosa chinensis | RcLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(−)-linalool | Magnard et al., Ibdah et al., | ||
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | AjTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |
| 芸香科 Rutaceae | 柑橘 Citrus unshiu | CuSTS3-1、CuSTS3-2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shimada et al., | |
| CuSTS4 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 罗勒 Ocimum basilicum | ObLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Iijima et al., | |
| 柠檬薄荷 Mentha citrata | McLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Sugiura et al., | ||
| 薰衣草 Lavandula augustifolia | LaLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Landmann et al., | ||
| LIS1、LIS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 龚林涛 等, | |||
| 紫苏 Perilla hirtella Perilla setoyensis | PhTps-5042L、 PhTps-5073L、 PsTps-5031L | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Masumoto et al., | ||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 黄花蒿 Artemisia annua | AaQH1、AaQH5 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Jia et al., | |
| 茄科 Solanaceae | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | TPS5、TPS39 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Cao et al., | |
| TPS37、TPS39 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Falara et al., | |||
| LeMTS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | van Schie et al., | |||
| 烟草 Nicotiana attenuata | NaLIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | He et al., | ||
| 伞形科 Apiaceae | 芫荽 Coriandrum sativum | CsLINS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Galata et al., | |
| 葡萄科 Vitaceae | 葡萄 Vitis vinifera | VvPNRLin | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| VvPNLinNer1、 VvPNLinNer2、 VvCSLinNer | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | ||||
| 山茶科 Theaceae | 茶 Camellia sinensis | CsLIS1、CsLIS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Mei et al., | |
| CsRLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Zhou et al., | |||
| CsLIS/NES-1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |||
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | GhTPS12、GhTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Huang et al., | |
| GhTPS4 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| GhTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | ||||
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | AtTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Ginglinger et al., | |
| AtTPS10 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 木樨 Osmanthus fragrans | OfTPS1、 OfTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Zeng et al., | |
| OfTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 刘偲 等, | |||
| 素馨 Jasminum grandiflorum | LIS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Pragadheesh et al., | ||
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 土肉桂 Cinnamomum osmophloeum | CoLIS-D4、CoLIS-HS、 CoLIS-LL、CoLIS-T1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Lin et al., | |
| 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | CcTPS54 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yang et al., | ||
| CcTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 马青 等, | |||
| CcTPS6 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 鸢尾科 Iridaceae | 香雪兰 Fressia × hybrida | FhTPS1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Gao et al., | |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 百合 Lilium brownii | LiTPS2 | 芳樟醇和其他单萜、橙花叔醇和其他倍半萜 Linalool and other monoterpenes,nerolidol and other sesquiterpenes | Zhang et al., | |
| LoTPS1 | 芳樟醇和(Z)-β-罗勒烯 Linalool and (Z)-β-ocimene | Abbas et al., | |||
| LoTPS3 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 姜科 Zingiberaceae | 姜花 Hedychium coronarium | HcTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yue et al., Ke et al., | |
| HcTPS8 | 芳樟醇和倍半萜 Linalool and sesquiterpenes | Yue et al., | |||
| 海南砂仁 Amomum longiligulare | AlTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Zhao et al., | ||
| 阳春砂仁 Amomum villosum | AvTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | |||
| 桑科 Moraceae | 无花果 Ficus carica | FcTPS7 FcTPS8 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Nawade et al., | |
| 车前科 Plantaginaceae | 金鱼草 Antirrhinum majus | AmNES/LIS-2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nagegowda et al., | |
| 柳叶菜科 Onagraceae | 仙女扇 Clarkia breweri | LIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Dudareva et al., | |
| 腊梅科 Calycanthaceae | 腊梅 Chimonanthus praecox | CpTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shang et al., | |
| 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃 Actinidia chinensis Actinidia arguta Actinidia polygama | AcLIS/NES | 主要产物芳樟醇,次要产物橙花叔醇 Major products:linalool,minor products:nerolidol | Wang et al., | |
| AaLS1、ApLS1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Chen et al., Günther et al., | |||
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 柠檬香桃 Backhousia citriodora | BcLS | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Sugiura et al., | |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜 Carica papaya | CpTPS18 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yao et al., | |
| 檀香科 Santalaceae | 檀香 Santalum album | SaNES/LIS | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Zhang et al., | |
| 菖蒲科 Acoraceae | 菖蒲 Acorus calamus | AcTPS3、AcTPS4、 AcTPS5 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Ibdah et al., | |
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 铁皮石斛 Dendrobium officinale | DoTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yu et al., | |
| 蝴蝶兰 Phalaenopsis bellina | PbTPS4、PbTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Huang et al., | ||
| PbTPS3 | 芳樟醇、β-罗勒烯 Linalool and β-ocimene | ||||
| PbTPS5 | 芳樟醇、香叶醇 Linalool and geraniol | ||||
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 牡丹 Paeonia delavayi Paeonia suffruticosa | PdTPS1、PdTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Li et al., | |
| PsTPS14 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 王佩云 等, | |||
| 松科 Pinaceae | 欧洲云杉 Picea abies | PaLIN | 主要产物(R)-(-)-芳樟醇;次要产物(S)-(+)-芳樟醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 乳香 Boswellia serrata | BsTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Bhargav et al., | |
表1 各物种中已鉴定的芳樟醇合酶基因
Table 1 The identified LIS in several plant species
| 科Family | 物种Species | 基因Gene | 合成产物Synthetic product | 参考文献Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杨柳科 Salicaceae | 毛果杨 Populus trichocarpa | PtTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and (S)-nerolidol | Danner et al., | |
| PtTPS4 | 主要产物:(R)-(−)-芳樟醇和(R)-橙花叔醇; 次要产物:(S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(S)-橙花叔醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool and(R)-nerolidol; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool and(S)-nerolidol | ||||
| 禾本科 Poaceae | 水稻 Oryza sativa | OsTPS3 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Yuan et al., | |
| 玉米 Zea mays | ZmTPS1 | 芳樟醇和β-月桂烯 Linalool and β-myrcene | Yactayo-Chang et al., | ||
| 毛茛科 Ranunculaceae | 铁线莲 Clematis florida | CfTPS1、CfTPS2 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Jiang et al., | |
| 蔷薇科 Rosaceae | 苹果 Malus domestica | MdLIS-RG1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nieuwenhuizen et al., | |
| 桃 Prunus persica | PpTPS1、PpTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., Wei et al., | ||
| 草莓 Fragaria × ananassa | FaNES1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | Aharoni et al., | ||
| 月季花 Rosa chinensis | RcLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(−)-linalool | Magnard et al., Ibdah et al., | ||
| 豆科 Fabaceae | 合欢 Albizia julibrissin | AjTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |
| 芸香科 Rutaceae | 柑橘 Citrus unshiu | CuSTS3-1、CuSTS3-2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shimada et al., | |
| CuSTS4 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 唇形科 Lamiaceae | 罗勒 Ocimum basilicum | ObLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Iijima et al., | |
| 柠檬薄荷 Mentha citrata | McLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Sugiura et al., | ||
| 薰衣草 Lavandula augustifolia | LaLINS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Landmann et al., | ||
| LIS1、LIS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 龚林涛 等, | |||
| 紫苏 Perilla hirtella Perilla setoyensis | PhTps-5042L、 PhTps-5073L、 PsTps-5031L | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Masumoto et al., | ||
| 菊科 Asteraceae | 黄花蒿 Artemisia annua | AaQH1、AaQH5 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Jia et al., | |
| 茄科 Solanaceae | 番茄 Solanum lycopersicum | TPS5、TPS39 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Cao et al., | |
| TPS37、TPS39 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Falara et al., | |||
| LeMTS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | van Schie et al., | |||
| 烟草 Nicotiana attenuata | NaLIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | He et al., | ||
| 伞形科 Apiaceae | 芫荽 Coriandrum sativum | CsLINS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Galata et al., | |
| 葡萄科 Vitaceae | 葡萄 Vitis vinifera | VvPNRLin | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| VvPNLinNer1、 VvPNLinNer2、 VvCSLinNer | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇和(E)-橙花叔醇 (S)-(+)-linalool and(E)-nerolidol | ||||
| 山茶科 Theaceae | 茶 Camellia sinensis | CsLIS1、CsLIS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Mei et al., | |
| CsRLIS | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Zhou et al., | |||
| CsLIS/NES-1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Liu et al., | |||
| 锦葵科 Malvaceae | 陆地棉 Gossypium hirsutum | GhTPS12、GhTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Huang et al., | |
| GhTPS4 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| GhTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | ||||
| 十字花科 Brassicaceae | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana | AtTPS14 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Ginglinger et al., | |
| AtTPS10 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | ||||
| 木樨科 Oleaceae | 木樨 Osmanthus fragrans | OfTPS1、 OfTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Zeng et al., | |
| OfTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 刘偲 等, | |||
| 素馨 Jasminum grandiflorum | LIS1 | (R)-(-)-芳樟醇 (R)-(-)-linalool | Pragadheesh et al., | ||
| 樟科 Lauraceae | 土肉桂 Cinnamomum osmophloeum | CoLIS-D4、CoLIS-HS、 CoLIS-LL、CoLIS-T1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Lin et al., | |
| 香樟 Cinnamomum camphora | CcTPS54 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yang et al., | ||
| CcTPS3 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 马青 等, | |||
| CcTPS6 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 鸢尾科 Iridaceae | 香雪兰 Fressia × hybrida | FhTPS1 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Gao et al., | |
| 百合科 Liliaceae | 百合 Lilium brownii | LiTPS2 | 芳樟醇和其他单萜、橙花叔醇和其他倍半萜 Linalool and other monoterpenes,nerolidol and other sesquiterpenes | Zhang et al., | |
| LoTPS1 | 芳樟醇和(Z)-β-罗勒烯 Linalool and (Z)-β-ocimene | Abbas et al., | |||
| LoTPS3 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | ||||
| 姜科 Zingiberaceae | 姜花 Hedychium coronarium | HcTPS5 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yue et al., Ke et al., | |
| HcTPS8 | 芳樟醇和倍半萜 Linalool and sesquiterpenes | Yue et al., | |||
| 海南砂仁 Amomum longiligulare | AlTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Zhao et al., | ||
| 阳春砂仁 Amomum villosum | AvTPS2 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | |||
| 桑科 Moraceae | 无花果 Ficus carica | FcTPS7 FcTPS8 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Nawade et al., | |
| 车前科 Plantaginaceae | 金鱼草 Antirrhinum majus | AmNES/LIS-2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Nagegowda et al., | |
| 柳叶菜科 Onagraceae | 仙女扇 Clarkia breweri | LIS | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Dudareva et al., | |
| 腊梅科 Calycanthaceae | 腊梅 Chimonanthus praecox | CpTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Shang et al., | |
| 猕猴桃科 Actinidiaceae | 猕猴桃 Actinidia chinensis Actinidia arguta Actinidia polygama | AcLIS/NES | 主要产物芳樟醇,次要产物橙花叔醇 Major products:linalool,minor products:nerolidol | Wang et al., | |
| AaLS1、ApLS1 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Chen et al., Günther et al., | |||
| 桃金娘科 Myrtaceae | 柠檬香桃 Backhousia citriodora | BcLS | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Sugiura et al., | |
| 番木瓜科 Caricaceae | 番木瓜 Carica papaya | CpTPS18 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yao et al., | |
| 檀香科 Santalaceae | 檀香 Santalum album | SaNES/LIS | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Zhang et al., | |
| 菖蒲科 Acoraceae | 菖蒲 Acorus calamus | AcTPS3、AcTPS4、 AcTPS5 | 芳樟醇和橙花叔醇 Linalool and nerolidol | Ibdah et al., | |
| 兰科 Orchidaceae | 铁皮石斛 Dendrobium officinale | DoTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Yu et al., | |
| 蝴蝶兰 Phalaenopsis bellina | PbTPS4、PbTPS10 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Huang et al., | ||
| PbTPS3 | 芳樟醇、β-罗勒烯 Linalool and β-ocimene | ||||
| PbTPS5 | 芳樟醇、香叶醇 Linalool and geraniol | ||||
| 芍药科 Paeoniaceae | 牡丹 Paeonia delavayi Paeonia suffruticosa | PdTPS1、PdTPS4 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | Li et al., | |
| PsTPS14 | 芳樟醇 Linalool | 王佩云 等, | |||
| 松科 Pinaceae | 欧洲云杉 Picea abies | PaLIN | 主要产物(R)-(-)-芳樟醇;次要产物(S)-(+)-芳樟醇 Major products:(R)-(-)-linalool; minor products:(S)-(+)-linalool | Martin et al., | |
| 橄榄科 Burseraceae | 乳香 Boswellia serrata | BsTPS2 | (S)-(+)-芳樟醇 (S)-(+)-linalool | Bhargav et al., | |
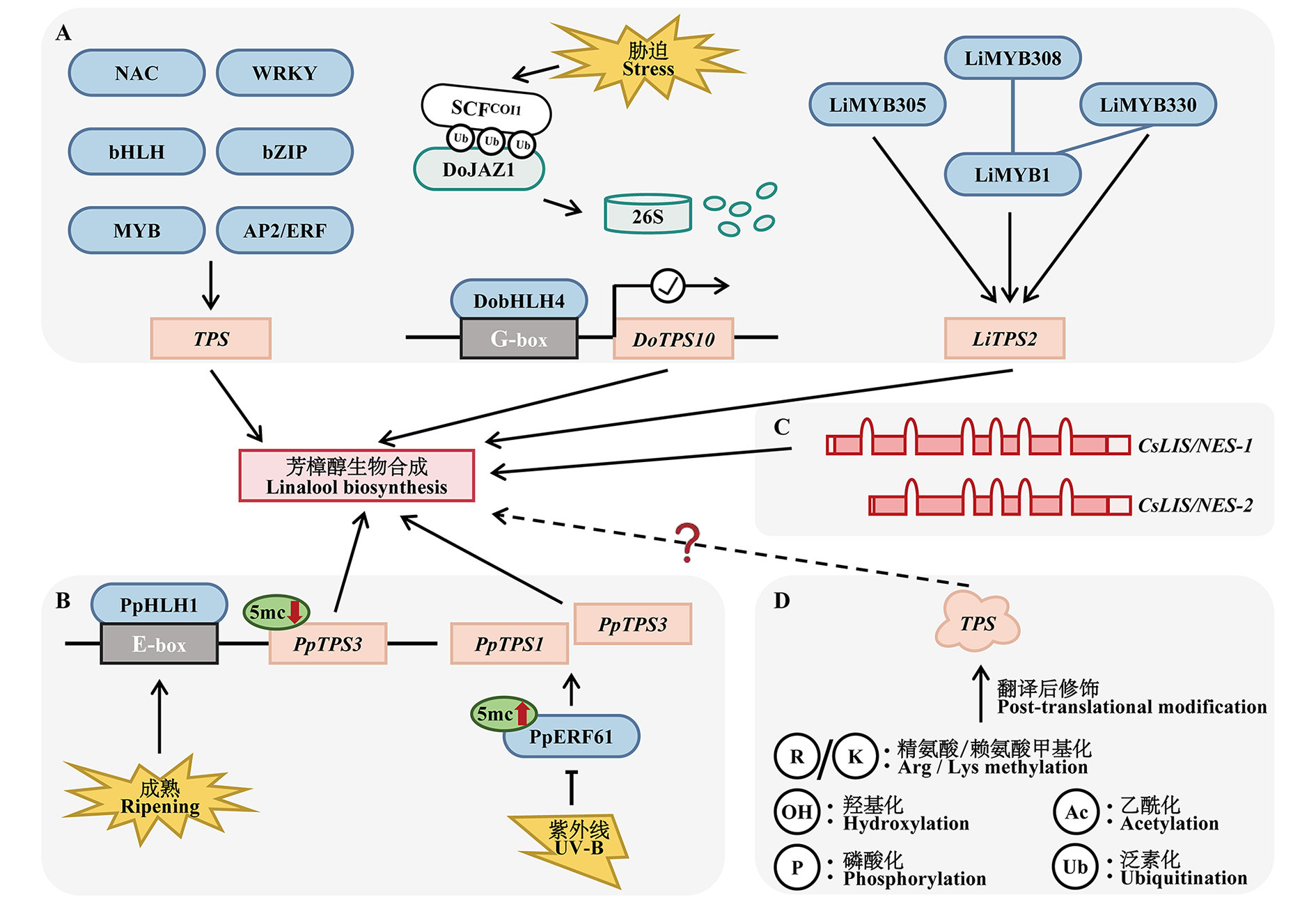
图2 芳樟醇合成调控的分子机制 A:转录调控;B:表观遗传调控;C:转录后调控;D:蛋白翻译后修饰调控。符号“?”代表尚未阐明的分子机制
Fig. 2 Molecular mechanisms of linalool synthesis regulation A:Transcriptional regulation;B:Epigenetic regulation;C:Post-transcriptional regulation;D:Regulation of protein post-translational modification. Symbol“?”represents knowledge gaps in molecular mechanisms

图3 芳樟醇的生态功能 符号“?”代表尚未阐明的具体生态功能和/或其分子机制
Fig. 3 Ecological function of linalool Symbol“?”identifies knowledge gaps in ecological functions and/or their molecular mechanisms
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.016253 pmid: 14630967 |
| [4] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.023895 pmid: 15522848 |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1007/s00606-019-01605-2 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1007/s10886-006-9117-9 pmid: 16902828 |
| [18] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.4.1337 pmid: 12228673 |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450 |
|
陈祖民, 校诺娅, 张艳霞, 史晓敏, 郭帅奇, 高虎, 王振平. 2021. 水分胁迫对‘玫瑰香’葡萄果实挥发性化合物及相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 48 (5):883-896.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0450 |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
doi: 10.1007/BF01021772 pmid: 24263497 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
pmid: 16441752 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1105/tpc.8.7.1137 pmid: 8768373 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179648 pmid: 21813655 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
|
龚林涛, 苏秀娟, 廖燕, 克热木汗·吾斯曼, 周迪, 尹松松. 2021. 薰衣草芳樟醇合酶基因的克隆、表达及酶活性检测. 作物杂志,(6):78-87.
|
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1093/jxb/err393 pmid: 22162874 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2011.02.026 pmid: 21450321 |
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2011.12.001 pmid: 22197147 |
| [44] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.114.244814 pmid: 25082892 |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.032946 pmid: 14657409 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
doi: 10.1126/science.291.5511.2141 pmid: 11251117 |
| [55] |
doi: 10.1016/j.aspen.2020.02.008 |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
|
刘偲, 席婉, 袁金梅, 朱琳琳, 陈洪国, 邹晶晶, 郑日如, 王彩云. 2020. 桂花‘莲籽丹桂’芳樟醇合酶基因OfTPS5的克隆及功能鉴定. 园艺学报, 47 (2):310-320.
|
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
|
卢凯, 李欣, 周嘉良, 解晓军, 戚舒, 周强. 2010. 虫害诱导的水稻挥发物抑制水稻病原菌的生长. 科学通报, 55 (30):2927-2932.
|
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
|
罗宇婕, 汪洋, 周琼, 何杰, 李幸. 2023. 玉带凤蝶成虫对柑橘枝叶挥发物的嗅觉和行为反应. 昆虫学报, 66 (12):1612-1625.
|
|
| [73] |
doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230213.103 pmid: 37282859 |
|
马青, 马蕊, 苏平, 申业, 陈美兰, 靳保龙, 欧阳少林, 郭娟, 崔光红, 黄璐琦. 2023. 樟树化学型形成关键萜类合酶的系统鉴定. 中国中药杂志, 48 (9):2307-2315.
pmid: 37282859 |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
pmid: 17576427 |
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
pmid: 16222807 |
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.042028 pmid: 15310829 |
| [81] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021196 pmid: 12857838 |
| [82] |
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.04.006 pmid: 20447664 |
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208249 pmid: 23256150 |
| [92] |
pmid: 12012103 |
| [93] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00403 pmid: 25922059 |
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3240 pmid: 24686413 |
| [96] |
doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01027-w pmid: 34366594 |
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
doi: 10.1104/pp.106.4.1533 pmid: 12232428 |
| [99] |
doi: S0031-9422(17)30167-X pmid: 28463687 |
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
doi: 10.1039/a709175c pmid: 10584331 |
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
doi: 10.1007/s10886-013-0259-2 pmid: 23420175 |
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
pmid: 16739013 |
| [116] |
pmid: 16495438 |
| [117] |
doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9149-8 pmid: 17440821 |
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
doi: 10.1093/mp/sss015 pmid: 22442388 |
| [120] |
|
|
王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. 2024. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证. 园艺学报, 51 (6):1273-1283.
|
|
| [121] |
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202301.011 |
|
王启方, 王晓云, 李浩森, 杨晓玉, 张锐敏, 巩彪, 李秀明, 史庆华. 2023. 芳樟醇对灰葡萄孢生长的影响及对番茄灰霉病的防控效果. 应用生态学报, 34 (1):213-220.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202301.011 |
|
| [122] |
doi: 10.1186/s43897-023-00057-0 pmid: 37789478 |
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
doi: 10.1007/BF00982309 pmid: 24249242 |
| [126] |
doi: 10.1038/nbt1251 pmid: 17057703 |
| [127] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2012.01835.x pmid: 22804824 |
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.01.039 pmid: 36696798 |
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
|
张献英, 霍治国, 犹昌艳, 胡飞. 2014. 20种非寄主植物挥发物对褐飞虱拒避与引诱行为的影响. 华南农业大学学报, 35 (3):63-68.
|
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12937 |
| [149] |
|
|
周丽荣, 张玲玲, 熊诗洁, 马佳伟, 朱永兴, 孙冲, 朱学栋, 刘奕清. 2024. 芳樟醇对生姜枯萎病菌的抑制作用. 食品科学, 45 (6):72-79.
|
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [1] | 谭筱玉, 牛军鹏, 王全智, 张丽, 朱丽娟, 王国栋, 郑贺云, 郁志芳, 段玉权, 姜丽, 孙秀秀, 杨瑛, 罗伟奇, 李雪晖, 管乐, 赵艳岭, 李国晓, 殷从飞, 葛成, 马敏, 贾璐婷, 张旭, 赵垚垚, 耿新丽, 王利斌, 张绍铃. 茉莉酸及其衍生物提高园艺作物采后低温抗性的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2025, 52(8): 1987-2020. |
| [2] | 王佩云, 李子昂, 白杨, 杨萍, 尹承芃, 李传荣, 张馨文, 宋秀华. ‘海黄’牡丹芳樟醇合酶基因PsTPS14的克隆及功能验证[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1273-1283. |
| [3] | 王稳, 张鹏, 王志敏, 刘根忠, 包志龙, 马方放. 菊花脑管状花响应蔗糖饲喂的差异基因分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1297-1310. |
| [4] | 田歌, 刘建廷, 高传彩, 赵雪惠, 樊永信, 李森, 张寒啸, 陈修德, 李玲, 李冬梅. UV-B对设施油桃叶片叶绿素生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(6): 1332-1344. |
| [5] | 陈佳悦, 段英明, 周雁, 肖扬, 边银丙, 龚钰华. 香菇ALDH家族基因鉴定、表达及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(5): 1033-1046. |
| [6] | 沈衡, 王琳, 李骞, 袁守娟, 郑伟, 王涛涛, 叶志彪, 杨长宪. 番茄风味和功能性成分研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2024, 51(2): 423-438. |
| [7] | 何义仲, 庞尧, 孙浩谦, 李欣宇, 王振豪, 钱卫, 张印, 何发, 尹杭, 赖恒鑫, 淳长品, 付行政, 彭良志. 果实抗坏血酸生物合成、代谢循环及其调控的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 1899-1915. |
| [8] | 张巧丽, 陈笛, 宋艳萍, 朱鸿亮, 罗云波, 曲桂芹. 番茄果实叶绿素代谢转录调控网络研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(9): 2031-2047. |
| [9] | 雷建军, 朱张生, 陈长明, 陈国菊, 曹必好, 郑婕, 吴昊, 肖艳辉, 邱正坤, 颜爽爽. 辣椒红色素及其生物合成的分子机理研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(3): 669-684. |
| [10] | 郑天一, 胡玉杰, 张学昊, 李婉平, 房玉林, 张克坤, 陈可钦. 激素信号调控果树果实花色苷合成机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(11): 2516-2536. |
| [11] | 葛诗蓓, 张学宁, 韩文炎, 李青云, 李鑫. 植物类黄酮的生物合成及其抗逆作用机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 209-224. |
| [12] | 沈植国, 张琳, 袁德义, 程建明. 蜡梅花色及其红花新资源研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 924-934. |
| [13] | 赵晖, 耿兴敏, 王露露, 许世达. 乙烯在杜鹃花耐热机制中的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 561-570. |
| [14] | 王福生, 刘晓纳, 徐媛媛, 刘小丰, 朱世平, 赵晓春. 柑橘SQS基因的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1641-1652. |
| [15] | 谯正林, 胡慧贞, 鄢波, 陈龙清. 花香挥发性苯/苯丙素类化合物的生物合成及基因调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1815-1826. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司